基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
|
|
|
- Albert Walker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1
2 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2
3 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates its contents and then divides in two 3 3
4 The phases of cell cycle 4 4
5 What are the differences between embryonic and somatic cell cycle? 5 5
6 Comparison of the embryonic cell cycle and the somatic cell cycle Early embryonic cell cycle Somatic cell cycle 30 min M S 6h G2 M G1 12h S 6h 6 6
7 Yeast provides a good genetic system for study on cell cycle Mostly proliferating in a haploid state Easy for genetic manipulation Discoveries of Cdc (cell-division-cycle) genes via cdc mutants 7 7
8 How were yeast cdc mutants discovered? What are the major characteristics of the mutants? 8 8
9 Cdc mutants selected by temperature sensitive mutations A mutant that cannot complete the cell cycle, cannot be propagated Temperature-sensitive mutants Functioning in permissive condition (low temp., 23 ) and nonfunctioning in restrictive condition (high temp., 36 ) 9 9
10 Xenopus oocyte: a giant cell for study cell cycle biochemically 1 mm in diameter Carrying 100,000 times more cytoplasm than an average cell in the human body After fertilization occurs, the first division takes about 90 minutes, and the next 11 divisions occur at 30-mim intervals, producing about 4096 cells within 7 hours Each cycle is divided into S and M phase without detectable G1 or G2 phases 10 10
11 Studying the cell cycle in a cell-free system Observation of repeated nuclei decondense and DNA replication and mitosis In vitro Filled with cell-cycle control components 11 11
12 Measurements of cell cycle progression Propidium iodide (PI) staining BrdU staining (bromo deoxyuridine) EMBO 2003, 22:5459 PI staining 12 Oncogene 2001, 20:
13 What are the advantages of using BrdU staining in addition to PI staining? 13 13
14 The cell-cycle control system 14 14
15 The major components of the cell cycle control system Cell, 2008,
16 The evolutionary conserved cell cycle control system Cell 2008,
17 The cell cycle checkpoints G1 checkpoint (start checkpoint) G2 checkpoint Metaphase checkpoint At checkpoints, cell cycle can be arrested if previous events have not been completed At checkpoints, the cell cycle control system can be regulated by extracellular signals from the environment or other cells 17 17
18 What causes the responses of the cell cycle check points? What are the effects? 18 18
19 The regulation of cell cycle 19 19
20 The key regulators of cell cycle Cell, 2008,
21 Regulation of Cdks by reversible phosphorylation Human Cdk1 and also Cdc2 in yeast: Phosphorylation by Wee1 kinase at Tyr15 inhibits CDK activity Cdc25 phosphatase dephosphorylates the p-tyr15 and activates the Cdk 21 21
22 Cyclical proteolysis regulates cyclin-cdk activity Regulated by SCF complex in G1 and S phase SCF complex(ubiquitin ligase) Targets:G1/S cyclins, some CKIs (such as p27kip) 22 22
23 Cyclical proteolysis regulates cyclin-cdk activity Regulated by APC complex in M phase APC: anaphase promoting complex APC complex (Ubiquitin ligase) Target: M cyclin 23 23
24 The evolutionary conserved cell cycle regulators Cell, 2008,
25 E2F promotes cell cycle progression E2F increases the transcription of its own gene Increase in transcription of G1/S cyclin and S-cyclin genes Increases in G1/S cyclin and S-cyclin result in increases in G1/S-Cdk activity and S-Cdk activity Increases in G1/S-Cdk activity and S-Cdk activity result in more Rb phosphorylation and more release of E2F Increases in G1/S-Cdk activity and S-Cdk activity and inactivate p27 (CKI) and Hct-1 by phosphorylation 25 25
26 What triggers E2F synthesis? 26 26
27 Mitogens stimulate activation of Ras and a MAP kinase cascade to trigger cell division 27 27
28 Mechanisms of Myc-promoted cell cycle entry 28 28
29 What is the stage of cells that have influences on another cell to initiate DNA replication after fusion of cells? Can a cell at any stage become responsive and start DNA replication? 29 29
30 Start the DNA replication once per cycle Cell fusion experiments by R.T. Johnson and P. N. Rao, 1970 Only G1 cells are competent to initiate DNA replication S-Cdk triggers the initiation of DNA replication 30 30
31 What controls only one replication per cell cycle in normal cells? 31 31
32 Control of the initiation for DNA replication 32 Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 32
33 Multiple roles of M-Cdk in mitosis Induce the assembly of mitotic spindle Ensure replicated chromosomes attach to the mitotic spindle Chromosome condensation Nuclear envelope breakdown Reorganization of the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum 33 33
34 Mitosis Nocodazole treatment arrested 34 34
35 Mitosis, continued 35 35
36 Centrosome duplication begins at the time entering the S phase Inhibition of DNA replication blocks centrosome duplication Centriole s replication is cell-cycle dependent M-cdk and Aurora A help the centrosome separation and maturation Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 36 36
37 The centrosome duplication cycle reveals asymmetrical characteristics 1: mother centriole 2: daughter centriole cilium Nat Cell Biol Rev 2011, 13:
38 Sister chromatid separation is triggered by proteolysis Separase is required for sister chromatids separation Securin, can inactivate separase; degradation is promoted by APC APC: anaphase-promoting complex, a highly regulated ubiquitin ligase Cdc20 activates APC 38 38
39 The spindle-attachment checkpoint Ensure that all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle before sister-chromatid separation occurs A sensor mechanism monitors the state of the kinetochore, the specialized region of the chromosome that attaches to microtubules of the spindle Improper attachment of kinetochore to the spindle sends out a negative signal to the cell-cycle control system, blocking Cdc20-APC activation and sister chromatid separation Several proteins, including Mad2, are recruited to unattached kinetochores. Mad2 binding results in Inhibition of Cdc20-APC and blocking securin destruction 39 39
40 Exit from mitosis and start of G 1 Complex changes at the end of mitosis The mitotic spindle must be dissembled Chromosomes decondensed The nuclear envelope reformed Inactivation of M-Cdk is required for exit from mitosis Cdc20-APC complex mediated ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of M-cyclin 40 40
41 Suggested readings 1. Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J. et al (eds) (2002, 2008) Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th & 5th ed. Chapter Murray A. and Hunt T. (eds) (1993) The Cell Cycle: an introduction, Bartek J. and Lukas J. (2003) Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell 3:
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Cell cycle control (mammalian)
 Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell Cycle. Trends in Cell Biology
 Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer.
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Division and Mitosis
 Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I. Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017
 Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Meiosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Chapter 12. living /non-living? growth repair renew. Reproduction. Reproduction. living /non-living. fertilized egg (zygote) next chapter
 Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
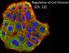 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS. D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH
 E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
Cell cycle and apoptosis
 Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
Why do cells reproduce?
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer. Dan Fisher. Friday 27th October Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6.
 How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
How Cells Divide. Chapter 10
 How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Regulation of Cell Division
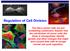 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
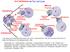 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death
 02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair
 Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Essential Questions. Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase?
 Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Name. A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division. Making new cells. Getting the right stuff. Overview of mitosis 1/5/2015
 Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION
 NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
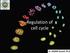 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Key Concepts in Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Video: Sea Urchin Embryonic Development (time-lapse)
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
Cell Signaling (III) Cell Cycle (I)
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 22: Cell Signaling (III) Cell Cycle (I) Chapter 15 BME42-620 Lecture 22, December 01, 2011 1 Comments on Reading Assignment 5 (I) I assume that this
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 22: Cell Signaling (III) Cell Cycle (I) Chapter 15 BME42-620 Lecture 22, December 01, 2011 1 Comments on Reading Assignment 5 (I) I assume that this
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
Chapter 14. Cell Division
 Chapter 14 Cell Division 14.1. The Cell Cycle A eukaryotic cell cannot divide into two, the two into four, etc. unless two processes alternate: doubling of its genome (DNA) in S phase (synthesis phase)
Chapter 14 Cell Division 14.1. The Cell Cycle A eukaryotic cell cannot divide into two, the two into four, etc. unless two processes alternate: doubling of its genome (DNA) in S phase (synthesis phase)
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Mitosis Notes AP Biology Mrs. Laux
 I. Cell Cycle-includes interphase and mitosis (IPPMAT) A. Interphase 1. accounts for 90% of the cycle 2. cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division 3. produces proteins and
I. Cell Cycle-includes interphase and mitosis (IPPMAT) A. Interphase 1. accounts for 90% of the cycle 2. cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division 3. produces proteins and
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION
 AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION CELL CYCLE 2 crucial factors for normal growth: Timing and rate of cell division Cell division frequency depends on cell type: skin cells: frequently Liver cells: can divide when
AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION CELL CYCLE 2 crucial factors for normal growth: Timing and rate of cell division Cell division frequency depends on cell type: skin cells: frequently Liver cells: can divide when
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP
 Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1
Control of Cell Cycle. Unit 2 Part f III
 Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
The larger a cell becomes: 1) the more demands the cell places on its. 2) the more trouble the cell has moving enough and across the cell membrane.
 10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? The larger a cell becomes: 1) the more demands the cell places on its. 2) the more trouble the cell has moving enough and across the cell membrane. The rate at which
10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? The larger a cell becomes: 1) the more demands the cell places on its. 2) the more trouble the cell has moving enough and across the cell membrane. The rate at which
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
Cell Division. During interphase, a cell s DNA is in a loose form called. It condenses into tightly coiled structures called chromosomes during.
 Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Cell Division and Mitosis Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 10 Cell Division and Mitosis A Cell Undergoing Mitosis Why It Matters The zebrafish is a model organism for study of the stages of regeneration at the molecular level If a predator takes a bite
Chapter 10 Cell Division and Mitosis A Cell Undergoing Mitosis Why It Matters The zebrafish is a model organism for study of the stages of regeneration at the molecular level If a predator takes a bite
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS
 Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
 Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Cell Cycle Notes chromatin, somatic cells gametes mitosis sister chromatids, centromere cytokinesis binary fission,
 Cell Cycle Notes 1. Importance of Cell Division a. For single celled organisms, cell division increases the number of individuals. b. In a multicellular organism, cell division functions to repair and
Cell Cycle Notes 1. Importance of Cell Division a. For single celled organisms, cell division increases the number of individuals. b. In a multicellular organism, cell division functions to repair and
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Outline Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to reproduce their kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Outline Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to reproduce their kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from
