Unit IV. Chapter 04. Cellular Function. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
|
|
|
- Adrian Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit IV hapter 04 ellular Function opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
2 Fig. 4.2 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. (a) G G T A A T (b) G A T G T A G Sugar phosphate backbone (c) Hydrogen bond Sugar phosphate backbone
3 Fig. 4.1 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Adenine NH 2 H N N N N H O HO P O H 2 O OH H H H H OH H (a) Phosphate Deoxyribose Purines NH 2 N H N N Adenine (A) H NH O N H HN NH N NH 2 Guanine (G) Pyrimidines H H NH 2 N H 3 H O NH HN O H N H O N H O O N H H ytosine () Thymine (T) Uracil (U) (b)
4 Fig. 4.4 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 2 nm 1 DNA double helix hromatin ore particle Nucleolus Linker DNA Nucleosome 11 nm 2 DNA winds around core particles to form nucleosomes 11 nm in diameter 30 nm 3 Nucleosomes fold accordionlike into zigzag fiber 30 nm in diameter (a) 50 nm In dividing cells only 300 nm 4 30 nm fiber is thrown into irregular loops to form a fiber 300 nm thick hromatids entromere 700 nm 5 In dividing cells, looped chromatin coils further into a 700 nm fiber to form each chromatid (b) a: P. Motta & T. Naguro/SPL/Science Source 700 nm 6 hromosome at the midpoint (metaphase) of cell division
5 Fig. 4.5 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Kinetochore entromere Sister chromatids (a) (b) b: Biophoto Associates/Science Source 700 nm
6 Table 4.1
7 Table 4.2
8 Fig. 4.6 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Gene (DNA) 1 Transcription Pre-mRNA Intron Exon A B D E F 2 Splicing mrna 1 mrna 2 mrna 3 A D B D E A E F 3 Translation Protein 1 Protein 2 Protein 3
9 Fig. 4.7 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Amino acid accepting end A U U A Anticodon
10 Fig mrna cap trna opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Pool of free Ribosomal amino acids subunits ATP ADP + Ribosome 2 trna binds an amino acid P i mrna mrna Polyribosome Protein trna released trna delivers amino acid to ribosome Met Ala Thr Nuclear pore Nucleus mrna GGG A Direction of ribosome movement E P A AUG GA GU odon UG AG GA Large ribosomal subunit Anticodon Small ribosomal subunit 3 Free protein Folding proteins 4 Ribosome assembly mrna Ribosome Direction of translation Protein Growing protein Rough endoplasmic reticulum Transport vesicle
11 Fig. 4.9 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Protein mrna Ribosomes 50 nm Dr. Elena Kiseleva/Science Source
12 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 DNA double helix TA G T TG GTA T AT 2 Seven base triplets on the template strand of DNA AUG Start GG GGA AG AU GAG UGA Stop 3 The corresponding codons of mrna transcribed from the DNA triplets UA G U UG GUA U 4 The anticodons of trna that bind to the mrna codons Met Ala Gly Thr His Glu 5 The amino acids carried by those six trna molecules Met Ala Gly Thr His Glu 6 The amino acids linked into a peptide chain
13 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Protein formed by ribosomes on rough ER. 2 Protein packaged into transport vesicle, which buds from ER. Nucleus 3 Transport vesicles fuse into clusters that unload protein into Golgi complex. 4 Golgi complex modifies protein structure. 5 Golgi vesicle containing finished protein is formed. Ribosomes 6 Secretory vesicles release protein by exocytosis. lathrin-coated transport vesicle Golgi complex Rough ER Lysosome
14 Table 4.3
15 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Prolactin Prolactin receptor 1 7 asein Exocytosis 2 ATP ADP + 6 P i Secretory vesicles Golgi complex Regulatory Protein (transcription activator) Rough endoplasmic reticulum mrna for casein asein gene RNA polymerase
16 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Interstitial cell of testis DNA 1 DNA codes for mrna (transcription). From pituitary Luteinizing hormone 3 When testosterone is needed, luteinizing hormone stimulates production of a second messenger within the cell. Second messenger mrna 2 In the cytoplasm, Translation mrna codes for the synthesis of an enzyme (translation). Enzyme H 3 H 3 H 3 4 The second messenger activates the dormant enzyme. Activated enzyme OH HO holesterol 5 The enzyme converts cholesterol to testosterone. O Testosterone Secreted 6 Testosterone is secreted from the cell and exerts various anatomical, physiological, and behavioral effects.
17 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Metaphase Anaphase G 2 Second gap phase Growth and preparation for mitosis G 1 First gap phase Growth and normal metabolic roles S Synthesis phase DNA replication
18 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Incoming nucleotides Old strand New strand Daughter DNA (e) Parental DNA (b) Replication fork DNA polymerase (a) Key DNA helicase A T G (c) Gap in replication (d) DNA ligase
19 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Prophase hromosomes condense and nuclear envelope breaks down. Spindle fibers grow from centrioles. entrioles migrate to opposite poles of cell. 1 Aster 2 2 Metaphase hromosomes lie along midline of cell. Some spindle fibers attach to kinetochores. Fibers of aster attach to plasma membrane. 3 Spindle fibers entriole hromatids Kinetochore 3 Anaphase entromeres divide in two. Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids to opposite poles of cell. Each pole (future daughter cell) now has an identical set of genes. 4 4 Telophase hromosomes gather at each pole of cell. hromatin decondenses. New nuclear envelope appears at each pole. New nucleoli appear in each nucleus. Mitotic spindle vanishes. Nuclear envelope re-forming Daughter cells in interphase leavage furrow hromatin Nucleolus (1-4): Ed Reschke
20 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Meiosis I (first division) Meiosis II (second division) Early prophase I hromatin condenses to form visible chromosomes; each chromosome has 2 chromatids joined by a centromere. hromosome Nucleus entromere entrioles Prophase II Nuclear envelopes disintegrate again; chromosomes still consist of 2 chromatids. New spindle forms. Mid- to late prophase I Homologous chromosomes form pairs called tetrads. hromatids often break and exchange segments (crossing-over). entrioles produce spindle fibers. Nuclear envelope disintegrates. Metaphase I Tetrads align on equatorial plane of cell with centromeres attached to spindle fibers. Tetrad rossing-over Spindle fibers entromere hromatid Equatorial plane Metaphase II hromosomes align on equatorial plane. Anaphase II entromeres divide; sister chromatids migrate to opposite poles of cell. Each chromatid now constitutes a single-stranded chromosome. Anaphase I Homologous chromosomes separate and migrate to opposite poles of the cell. Telophase II New nuclear envelopes form around chromosomes; chromosomes uncoil and become less visible; cytoplasm divides. Telophase I New nuclear envelopes form around chromosomes; cell undergoes cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis). Each cell is now haploid. leavage furrow Final product is 4 haploid cells with single-stranded chromosomes.
21 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. ross section of seminiferous tubules Lumen of seminiferous tubule Sperm 5 Spermiogenesis Spermatid n n n n 4 Meiosis II Secondary spermatocyte n n 3 Blood testis barrier Primary spermatocyte Nurse cell Meiosis I 2n 2 Type B spermatogonium 2n Tight junction Type A spermatogonium Basement membrane of seminiferous tubule 2n 1
22 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display XX female XY male Science Source
23 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. (a) left chin, c Uncleft chin cc c 15 Homozygous, cleft chin c Heterozygous, cleft chin c c Heterozygous, cc Homozygous, cleft chin uncleft chin XX female (b) a (left): Brad Barket/Getty Images; a (right): Kurt Krieger/orbis; b (top left, top right, bottom left): Brad Barket/Getty Images; b (bottom-right): Kurt Krieger/orbis
24 Fig opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Gene 1 Gene 2 Phenotype (eye color) 13 Gene 3 (top): Getty Images RF; (middle): Anthony Saint James/Getty Images RF; (bottom): JupiterImages/omstock/Getty Images RF
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
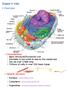 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division 1 The cell cycle Living cells go through a series of stages known as the cell cycle. They undergo a continuous alternation
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division 1 The cell cycle Living cells go through a series of stages known as the cell cycle. They undergo a continuous alternation
HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT
 HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART 1 - BACKGROUND: 1. Heterozygous means. A. Information about heritable traits B. Unique/ different molecular forms of a gene that are possible at a given locus C. Having
HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART 1 - BACKGROUND: 1. Heterozygous means. A. Information about heritable traits B. Unique/ different molecular forms of a gene that are possible at a given locus C. Having
MITOSIS PRESENTATION DR. SUSAN MASKEL (WCSU)
 MITOI REENTATION 1 2 MITOI ackground Information CHROMOOME proteins deoxyribonucleic acid interspersed with stores genetic info controls processes Dr. usan Maskel Western CT tate University 2 strands double
MITOI REENTATION 1 2 MITOI ackground Information CHROMOOME proteins deoxyribonucleic acid interspersed with stores genetic info controls processes Dr. usan Maskel Western CT tate University 2 strands double
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Lesson 1. Quiz (short) Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases
 Lesson 1 Quiz (short) Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases 2 Cell division is needed for Growth (Mitosis) Repair (Mitosis) Reproduction (Meiosis) 3 Mitosis consists of 4 phases (division of the nuclear
Lesson 1 Quiz (short) Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases 2 Cell division is needed for Growth (Mitosis) Repair (Mitosis) Reproduction (Meiosis) 3 Mitosis consists of 4 phases (division of the nuclear
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Chromosomes
 & Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
& Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE Structures in the nucleus that carry genetic information Composed of DNA coiled around proteins called histones Consists of 2 identical parts called sister
CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE Structures in the nucleus that carry genetic information Composed of DNA coiled around proteins called histones Consists of 2 identical parts called sister
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Background Information
 art of Exercise 4 of Human Anatomy & hysiology Laboratory Manual, 8th Edition, by Elaine Marieb lease wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Hit ESCAE
art of Exercise 4 of Human Anatomy & hysiology Laboratory Manual, 8th Edition, by Elaine Marieb lease wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Hit ESCAE
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 122 Cell Cycle and Cell Division 1. Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due to [1988] (a) pairing of homologous chromosomes (b) crossing over (c) separation of chromatids
122 Cell Cycle and Cell Division 1. Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due to [1988] (a) pairing of homologous chromosomes (b) crossing over (c) separation of chromatids
Cell Divisions. The autosomes represent the whole body. * Male Sex Chromosomes: XY * Female Sex Chromosomes: XX
 Cell Divisions Each Cell (including gonads) has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes) which are located in the nucleus). The autosomes represent the
Cell Divisions Each Cell (including gonads) has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes) which are located in the nucleus). The autosomes represent the
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities
 Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells.
 MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
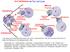 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function. The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Chromosome loci. Organization of the Chromatin. Nucleotide Structure
 Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Week 1 - Introduction
 Genetics Summary 1 Week 1 - Introduction - Polygenic > traits with multiple genes - Gregor Mendel > predictable offspring (didn t work with polygenic) - Friedrich Miescher > discovered DNA in 1869-2 sister
Genetics Summary 1 Week 1 - Introduction - Polygenic > traits with multiple genes - Gregor Mendel > predictable offspring (didn t work with polygenic) - Friedrich Miescher > discovered DNA in 1869-2 sister
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes
 Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide)
 Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis.
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
Goals. Cells. Cells: The Living Units. By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe.
 C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R
 The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R Nuclear envelope Transcription DNA RNA Processing Pre-mRNA Translation mrna Nuclear pores Ribosome Polypeptide Transcription RNA is synthesized from DNA in
The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R Nuclear envelope Transcription DNA RNA Processing Pre-mRNA Translation mrna Nuclear pores Ribosome Polypeptide Transcription RNA is synthesized from DNA in
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division The Links in Life s Chain: Genetics and Cell Division 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics 9.2 An Introduction to Cell Division 9.3
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division The Links in Life s Chain: Genetics and Cell Division 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics 9.2 An Introduction to Cell Division 9.3
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division
 2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
Chromosomes & Cell Division
 Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Cycle. Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase. S phase, synthesis phase
 Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase Cell Cycle interval between cell division and DNA replication accumulates materials needed to replicate
Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase Cell Cycle interval between cell division and DNA replication accumulates materials needed to replicate
Ploidy and Human Cell Types. Cell Cycle and Mitosis. DNA and Chromosomes. Where It All Began 11/19/2014. Chapter 12 Pg
 Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase
 Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle
 Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Connecting
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
 Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION It is within the cell where the functions of the body occur. We are going to look at structure, function and reproduction of cells in this chapter. Cytology
Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION It is within the cell where the functions of the body occur. We are going to look at structure, function and reproduction of cells in this chapter. Cytology
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
Cell. ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange
 Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction
 Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis.
 Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Cytology. Cell Anatomy. Cell Theory - A good place to start! The generalized cell contains: Cell membrane Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytosol Organelles
 Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
How Cells Divide. Chapter 10
 How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction Biology 3201 Introduction One of the important life functions of living things is their ability to reproduce. Reproduction depends on the cell. Cells reproduce in order
Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction Biology 3201 Introduction One of the important life functions of living things is their ability to reproduce. Reproduction depends on the cell. Cells reproduce in order
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
