Molecular Hematopathology
|
|
|
- Sybil Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Molecular Hematopathology Charles E. Hill, MD, PhD Emory University School of Medicine April 2013 The Association for Molecular Pathology Education. Innovation and Improved Patient Care. Advocacy.
2 Disclosure(s) In accordance with ACCME guidelines, any individual in a position to influence and/or control the content of this ASCP CME activity has disclosed all relevant financial relationships within the past 12 months with commercial interests that provide products and/or services related to the content of this CME activity. The individual below has responded that he/she has no relevant financial relationship(s) with commercial interest(s) to disclose: Charles E. Hill, MD, PhD 2
3 Outline Molecular alterations in hematopathology Methods Lymphomas Leukemias Summary 3
4 Molecular Alterations in Hematopathology Rearrangements Physiologic (antigen receptors) Pathologic (translocations) Mutations Gains/Losses 4
5 Physiologic Rearrangements Normal part of immune system Occur as both B and T cells mature Determine antigen specificity May be used to determine clonality in B and T cells 5
6 Pathologic Rearrangements Dysregulated normal protein Chimeric protein with novel protein function Enhancer/promoter Oncogene Chimeric product 6
7 Mutations Point mutations (e.g. JAK2 V617F) Larger mutations (e.g. FLT3 ITD) Activating vs. Inactivating Helpful in some situations to assess drug resistance 7
8 Gains/Losses May affect prognosis Gene doasge Loss of heterozygosity 8
9 Indications for Molecular Testing Diagnosis Classification Prognosis Response to therapy/detection of relapse Minimal residual disease testing Drug selection? 9
10 Major Methods Southern blot (mostly historical for hematopathology) Karyotyping FISH PCR Various detection methods Q-PCR (Q-RT-PCR) Arrays (CGH/SNP, Expression) Next Generation Sequencing/Whole Genome Analysis 10
11 Southern Blot Usually separate nucleic acids by gel elctrophoresis Immobilization of nucleic acids on nylon Target specific probe Typically chemiluminescent detection Requires large amounts of nucleic acid 11
12 Karyotyping Whole Genome Analysis Gross structural abnormalities Requires viable cells (metaphase spreads) Low sensitivity (~5%) 12
13 FISH Specific targets Very good for balanced translocations Copy number variation Localizes abnormality to cells of interest Moderate sensitivity (~1-2%) Can select cells for analysis (e.g. CD138 selection for plasma cells) 13
14 Karyotyping 14
15 FISH Can be performed on multiple specimen types Tissue does not need to be viable Can detect cryptic translocations Large probe size can detect multiple breakpoints More sensitive than cytogenetics Less sensitive than PCR Easier to run single samples 15
16 PCR (and variants) Very sensitive (1% and much less) May be quantitative Multiple possible detection methods DNA or RNA Most commonly used technique for molecular hematopathology 16
17 HRM, DGGE, dhplc, etc. 17
18 Arrays CGH/SNP arrays Whole Genome Analysis Good for copy number variation Not useful for balanced translocation Expression arrays Very uncommon for clinical use Can classify some processes into multiple categories 18
19 NGS Not commonly used clinically Very expensive True whole genome analysis Depth of coverage issues Analysis algorithms still have trouble with balanced translocations 19
20 Clonality Testing Target Immunoglobulin Locus Heavy Chain Kappa Light Chain Lambda Light Chain T-cell Receptor Locus Gamma Beta Delta Alpha 20
21 Antigen Receptors Antigen Immunoglobulin T-cell receptor B-cell T-cell 21
22 Rearrangement V H segments D H segments J H segments C H segments DJ rearrangement V-DJ rearrangement High power view V H 2 N D H 3 N J H 5 L FR I CDR I FR II CDR II FR III CDR III FR IV CDRs, FRs and primers Diagram courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg 22
23 gene rearrangement and PCR gel-based PCR product detection Size Poly Mono Mono Mono Poly Neg Slide courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg
24 Polyclonal B cells 24
25 Rearrangement V segments J segments C J segments C P1 P 1 1 P2 2 2 VJ rearrangement 6 P High power view V 6 N J P2 Multiplex PCR V 1-8 V 9 V 10 V 11 J P1 J P J 1 J P2 J 2 Diagram courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg 25
26 Polyclonal T cells 26
27 Indications for Clonality Testing Atypical lymphoid proliferations Equivocal immunophenotype Assistance in establishing lineage? Monitoring disease (MRD?) Multifocal disease 27
28 Flow Cytometry Sensitive Can determine lineage and/or type of lymphoma Able to distinguish clonality for B cells (based on immunoglobulin light chain distribution (kappa vs lambda) Difficult to distinguish clonality for T cells Need intact cells Cannot be done on formalin fixed tissue 28
29 Limitations of Clonality Analysis Tests only determine clonality and must be interpreted in the clinical and pathologic context Clonality does not imply malignancy Clonal but not malignant: Lymphomatoid papulosis MGUS Multicentic Castleman Disease 29
30 Limitations of Clonality (cont.) Not all clones are detectable using PCR based assays Sensitivity of 1:1000 cells to 1:100 cells Clonal TCR or IgH locus does not define lineage Some lymphomas rearrange both Lineage infidelity in ALL and immunodeficiency states 30
31 Interpretation Clonality does not equal malignancy Lack of detectable clone does not rule out clonality Tiered testing - diminishing returns
32 Better Basis to Behold B- (and T-) cell clones: BIOMED 2 5 IGH 3 VJ 2 DJ hierarchy of IG GR 100% IG-lambda+ 97 primers 8 IG 2 IGK 1 VJ 1 Kde will be IGK+ but 14 tubes 418 reactions 6 TCR 1 IGL 3 TRB 2 TRG 1 TRD 1 VJ 2 VJ 1 DJ TRB analysis - 38 primers reactions ~5-10% IG-kappa+ will be IGL+ IGK and IGL also subjected to SHM, but? less so Kde reaction not affected by SHM Side courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg
33 Lymphoma Follicular lymphoma Mantle Cell Lymphoma MALT lymphoma CLL/SLL Cutaneous T cell Lymphoma Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Others 33
34 Histology 34
35 Follicular Lymphoma 2nd most common lymphoma (~35%) Germinal center B cell origin Can be nodal or disseminated Follicular pattern on morphology CD10+, BCL6+, CD43- Usually indolent, may transform (~30%) Somatic hypermutation can decrease detection of clonal population using IGH@ 35
36 Follicular Lymphoma t(14;18) testing used to aid diagnosis Only about 85% positive Positive t(14;18) does not establish a diagnosis IGH@ positive in about 80% IGK@ somewhat better for follicular In t(14;18) negative cases, extra copies of chromosome 18/BCL2 or translocation involving BCL6
37 BCL2 gene rearrangements BCL2 on 18q21 on 14q J H VCR MBR ICR MCR PCR [~75%] Southern blot FISH Slide courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg Classical cytogenetics
38 IgH Clonality Analysis 38
39 IgH Bcl-2 Translocation 39
40 IgH Bcl-2 Translocation 40
41 Bone Marrow Biopsy 41
42 Mantle Cell Lymphoma Neoplasm of Mantle B cells Male predominance Nodal, extranodal, disseminated Cyclin D1+, CD5+, CD43+ t(11;14) upregulates Cyclin D1 Image courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg 42
43 Mantle Cell Lymphoma t(11;14) most commonly detected by FISH IHC for Cyclin D1 PCR or RT-PCR (limited availability) 43
44 Marginal Zone Lymphoma Neoplasm of marginal zone B cells Associated with chronic inflammatory processes Infections Autoimmune illness MALT lymphoma Generally indolent, but can tranform 44
45 MALT Lymphoma Most common in the stomach, but can occur in many places Gastric MALT lymphoma associated with H. pylori infection In early disease, treating with antibiotics can be curative 45
46 Extranodal MZLs MALTomas site-dependence MALT1 1p22 ~5% BCL-10 FOXP1 18q21 ~50% 3p14 ~10% API2 - stomach - lung IGH@ - parotid - ocular adnexa - liver IGH IGK IGH@ - thyroid - ocular adnexa - skin t(11;18) t(14;18) t(1;14) t(1;2) t(3;14) Side courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg
47 MALT Lymphoma Gastric - API2-MALT1 translocation associated with lack of response to antibiotics Other translocations probably also associated with independence from inflammatory process May test via FISH, PCR, IHC? 47
48 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Neoplasm of small B cells Male predominance CD5+, CD23+, light chain restricted Level of maturation associated with prognosis Molecular testing not really used for diagnosis 48
49 FISH for CLL/SLL Used for prognosis 17p deletion = poor prognosis (p53) 11q deletion = poor prognosis (ATM) +12 = Intermediate prognosis (CDK4?) Isolated 13q deletion = good prognosis (mirna s 15a and 16-1) 49
50 CLL/SLL and Somatic Hypermutation B cells without SHM are considered less mature than those with SHM Normally pre-germinal center B cells have not undergone SHM and memory B cells have CLL/SLL with SHM has significantly better prognosis Can be tested by molecular methods, but generally use surrogate marker 50
51 CLL/SLL and Somatic Hypermutation ZAP70 Testing usually by IHC for ZAP70 Not a great test SHM- SHM+ Image courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg 51
52 Cutaneous T cell Lymphoma 52
53 Testing 53
54 Mycosis Fungoides Not all have demonstrable clonal T cell receptor gene rearrangement May use TRG@ testing to determine if clone is in peripheral blood (Sezary Syndrome) Indolent, may transform 54
55 Sezary Syndrome T-cell clone present in skin and peripheral blood May detect atypical T-cells not visible on peripheral smear 55
56 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Medium-large, atypical cells in background of smaller lymphocytes CD30+ (Ki-1), need to distinguish from Hodgkin Often CD3 negative ALK+ not required for diagnosis Image courtesy of Dr. Adam Bagg
57 ALCL t(2;5) most common Test via FISH, cytogenetics, RT-PCR ALK+ yields better prognosis
58 Translocation ALCL ALK Partner Frequency ALK Stain t(2;5)(q23;q25) NPM1 75% cytoplasm nucleus t(1;2)(q21;p23) TPM3 15% cytoplasm membrane t(2;3)(p23;q21) TFG 2% cytoplasm inv(2)(p23;q35) ATIC 2% cytoplasm t(2;17)(p23;q23) CLTC 2% cytoplasm t(x;2)(q11;p23) MSN 1% membrane
59 Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma Not a well defined entity, many different categories Really multiple types of lymphoma Current stratification is based on morphology or clinicopathologic features 59
60 DLBCL Morphologic Categories Centroblastic Immunoblastic Anaplastic T cell rich Plasmablastic Lymphomatoid granulomatosis type 60
61 DLBCL Clinical Categories Primary CNS lymphoma Primary effusion lymphoma Cutaneous large B cell lymphoma Intravascular large cell lymphoma Thymic large B cell lymphoma 61
62 Gene Expression and DLBCL Study done by Alizadeh, et al. at Stanford (Nature. 2000; 403 (6769): ) Showed that DLBCL has two distinct gene expression groups Germinal center-like B cell lymphoma (good prognosis) Activated B cell like lymphoma (poor prognosis) 62
63 Gene Expression and DLBCL Not routinely performed clinically Difficult to interpret IHC used most commonly to categorize (CD10, BCL6, MUM1, etc.?) 63
64 Other B Lymphomas Burkitt MYC translocations (t(8;14), etc.) Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma - deletions of 6q23 (50%) and 13q14, gains of 3q13-q28, 6p and 18q Splenic marginal zone lymphoma deletion 7q21-32 (40%) or translocation involving CDK6 64
65 Other T Lymphomas T PLL inv 14(q11;q32) (80%) or t(14;14)(q11;q32) (10%) Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma iso(7q) Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma 70% homozygous for DQB1*02 65
66 Myeloma Typically FISH panel and conventional cytogenetics FISH panels vary (especially for hyperdiploidy) May perform arrays (CNV or expression) 66
67 Myeloma Abnormality del 13q Trisomy (odd # s except 13) Prognosis Poor Good 1q+ Poor Del 17p (TP53) t(11;14) Poor Good? t(4;14), t(14;16) Poor 67
68 Leukemia MPN s CML PV/ET/PMF AML ALL 68
69 Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Chronic myelogenous leukemia Polycythemia vera Essential Thrombocythemia Primary myelofibrosis Myelodysplastic syndromes 69
70 CML 1-2 per 100,000 population 1.75:1 male predominance t(9;22) BCR-ABL1 Nowell and Hungerford Philadelphia Chromosome (der 22) Janet Rowley Molecular monitoring standard of care 70
71 CML BCR Breakpoint Cluster Region ABL1 - V-abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 Translocation produces fusion protein with novel function RT-PCR 71
72 BCR-ABL e1a2 ALL p190 e13a2 e13a3 e14a2 e14a3 e19a2 CML p210 CML p230 72
73 Why test? BCR-ABL1 targeted by small molecules Prognosis Monitoring response Prediction of relapse 73
74 Testing for BCR-ABL1 Karyotype FISH PCR RT-PCR Competitive RT-PCR Nested RT-PCR qrt-pcr 74
75 NCCN Guidelines From NCCN , qpcr should be performed: At diagnosis Every 3 months when responding to therapy. After CCyR, every 3 months for 3 years, then every 3-6 months For rising transcript levels (1 log) with MMR, repeat in 1-3 months 75
76 QRT-PCR 76
77 Harmonizing Results Median measurement of 30 shared baseline samples established as 100% 0.1% is Major Molecular Response For example, if median ratio BCR- ABL/control is 0.75, MMR = International Scale defined by these two points 77
78 What does an IS do? An International Scale helps standardize quantification An IS does not improve pre-analytic issues An IS does not reduce inherent assay variability An IS does improve reporting 78
79 Control Genes and Quantification ABL1 is the most commonly used control gene BCR was used as control gene for IRIS trial labs GUSB used by some EAC found ABL1, GUSB, and B2M suitable (Beillard, Leukemia, 2003, 17:2474) BCR was not reported in study by EAC 79
80 Kinase domain mutations P = P loop - ATP-binding site -? worst mutations B = Binding domain - where imatinib binds C = Catalytic domain A = Activation loop - conformation altered - affects imatinib binding > 100 different mutations Slide courtesy of Dr. Ada, Bagg green red 2-10% of patients >10% of patients - closed: inactive - open: active 80
81 MPN BCR-ABL1 V617F of JAK2 (exon 14) Exon 12 of JAK2 MPL (5-10% of ET) 81
82 Signalling Through the Erythropoietin Receptor EPO-R JAK2 STAT5 82
83 V617F JAK2 Disrupts autoinhibitory loop Activating mutation Appears as though EpoR is occupied all the time Somatic in erythro-myeloid precursors 83
84 V617F JAK2 Single base change eliminates a BsaX restriction enzyme site PCR followed by digestion and electrophoresis PCR Q-PCR 84
85 JAK2 Testing Aid in confirming diagnosis Possible future targeted therapies Reclassification of myeloproliferative disorders 85
86 JAK2 Assay Controls 86
87 V617F JAK2 87
88 Translocation AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities Prior Class Genes Prognosis t(8;21) M2 RUNX1-RUNXT1 Good t(15;17) M3 PML-RARA Good inv 16 M4Eo CBFB-MYH11 Good t(11q23) M4/M5 MLL-? Poor t(1;22), t(6;19), t(8;16), inv 3 all poor prognosis 88
89 Acute promyelocytic leukemia Distinguished by Auer rods in cytoplasm of blasts DIC in 85% Anemia, thrombocytopenia due to blast proliferation 89
90 APL t(15;17) PML-RARA ATRA responsive Multiple breakpoints in PML Short, Long, Variant PCR, RT-PCR, QRT-PCR, FISH 90
91 Variant APL t(11;17) PLZF-RARA Not ATRA responsive t(5;17) NPM1-RARA ATRA responsive?
92 AML with Normal Cytogenetics Not genetically stable, no gross chormosomal abnormalities Mutations common Many associated with prognosis
93 FLT3 FLT3 = FMS-like Tyrosine Kinase 3 Over-expressed on AML blasts ~20-30% of AML cases Also on t(15;17) blasts Typical mutation is Internal Tandem Duplication (and D835) Reduced overall survival Controversial in older patients Correlates with poor prognosis in younger patients with normal cytogenetics
94 FLT3 Neg Control Patient 94
95 NPM1 Nucleophosmin Most common mutation in AML with normal cytogenetics (~60%) Good prognosis No effect if FLT3 mutated Common insertion 95
96 ALL vs Age Age Translocation Genes Infants t(4;11) AFF1-MLL Children t(12;21) ETV6-RUNX1 Adults t(9;22) BCR-ABL1
97 t(4;11) ALL Most common leukemia of infants May be present/diagnosed at birth Poor prognosis
98 t(12;21) ALL Most common translocation in ALL of children (~25%) Good prognosis Crytpic Need FISH or molecular studies
99 t(9;22) ALL Poor prognosis Different breakpoints (e1a2 vs other) p190 vs p210 Most common translocation in adult ALL Quantitative testing? 99
100 BCR-ABL e1a2 ALL p190 e13a2 e13a3 e14a2 e14a3 e19a2 CML p210 CML p
101 Other Changes C-KIT mutations in mastocytosis IDH1/2 TET2 Gene amplifications Pharmacogenetics Etc,etc,etc 101
102 Summary Molecular testing integral for hematopathology Hematologic neoplasms often defined by molecular abnormalities Diagnosis, response, MRD, relapse 102
103 Association for Molecular Pathology 9650 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD Association for Molecular Pathology,
GENETIC MARKERS IN LYMPHOMA a practical overview. P. Heimann Dpt of Medical Genetics Erasme Hospital - Bordet Institute
 GENETIC MARKERS IN LYMPHOMA a practical overview P. Heimann Dpt of Medical Genetics Erasme Hospital - Bordet Institute B and T cell monoclonalities Rearrangement of immunoglobin and TCR genes may help
GENETIC MARKERS IN LYMPHOMA a practical overview P. Heimann Dpt of Medical Genetics Erasme Hospital - Bordet Institute B and T cell monoclonalities Rearrangement of immunoglobin and TCR genes may help
2010 Hematopoietic and Lymphoid ICD-O Codes - Alphabetical List THIS TABLE REPLACES ALL ICD-O-3 Codes
 Acute basophilic leukemia 9870/3 Acute biphenotypic leukemia [OBS] 9805/3 Acute erythroid leukemia 9840/3 Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia 9910/3 Acute monoblastic and monocytic leukemia 9891/3 Acute myeloid
Acute basophilic leukemia 9870/3 Acute biphenotypic leukemia [OBS] 9805/3 Acute erythroid leukemia 9840/3 Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia 9910/3 Acute monoblastic and monocytic leukemia 9891/3 Acute myeloid
2012 Hematopoietic and Lymphoid ICD-O Codes - Numerical List THIS TABLE REPLACES ALL ICD-O-3 Codes
 Malignant lymphoma, NOS 9590/3 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, NOS 9591/3 B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma 9596/3 Primary
Malignant lymphoma, NOS 9590/3 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, NOS 9591/3 B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma 9596/3 Primary
Combinations of morphology codes of haematological malignancies (HM) referring to the same tumour or to a potential transformation
 Major subgroups according to the World Health Organisation (WHO) Classification Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) Myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia and abnormalities of PDGFRA, PDGFRB or
Major subgroups according to the World Health Organisation (WHO) Classification Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) Myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia and abnormalities of PDGFRA, PDGFRB or
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Bone Marrow. Procedures Blood Film Aspirate, Cell Block Trephine Biopsy, Touch Imprint
 Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Molecular Diagnosis. Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology
 Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Objectives Describe uses of NAT in Oncology Diagnosis, Prediction, monitoring. Genetics Screening, presymptomatic testing, diagnostic testing,
Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Objectives Describe uses of NAT in Oncology Diagnosis, Prediction, monitoring. Genetics Screening, presymptomatic testing, diagnostic testing,
Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology. Molecular Diagnosis. Gain/Loss of Nucleic Acid. Objectives. MYCN and Neuroblastoma. Molecular Diagnosis
 Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Gross alterations in DNA content of tumors (ploidy) Gain/Loss of nucleic acids Markers of Clonality Oncogene/Tumor
Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Gross alterations in DNA content of tumors (ploidy) Gain/Loss of nucleic acids Markers of Clonality Oncogene/Tumor
Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Lymphoid Neoplasms
 Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Lymphoid Neoplasms (Part II) Rational use of molecular testing in lymphomas Beirut, Lebanon Friday December 2, 2011: Hematopathology Session Adam Bagg University of Pennsylvania
Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Lymphoid Neoplasms (Part II) Rational use of molecular testing in lymphomas Beirut, Lebanon Friday December 2, 2011: Hematopathology Session Adam Bagg University of Pennsylvania
Objectives. Morphology and IHC. Flow and Cyto FISH. Testing for Heme Malignancies 3/20/2013
 Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Cost-Effective Strategies in the Workup of Hematologic Neoplasm. Karl S. Theil, Claudiu V. Cotta Cleveland Clinic
 Cost-Effective Strategies in the Workup of Hematologic Neoplasm Karl S. Theil, Claudiu V. Cotta Cleveland Clinic In the past 12 months, we have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
Cost-Effective Strategies in the Workup of Hematologic Neoplasm Karl S. Theil, Claudiu V. Cotta Cleveland Clinic In the past 12 months, we have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Positive
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091534 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105316AM 2/9/2017 104147AM Ref By Final LEUKEMIA GENETIC ROFILE ANY SIX MARKERS, CR QUALITATIVE AML ETO
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091534 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105316AM 2/9/2017 104147AM Ref By Final LEUKEMIA GENETIC ROFILE ANY SIX MARKERS, CR QUALITATIVE AML ETO
Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Myeloid Neoplasms
 Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Myeloid Neoplasms Beirut, Lebanon Tuesday November 29, 2011: Pre-congress workshop Adam Bagg University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, USA Myeloid neoplasms Myeloproliferative
Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Myeloid Neoplasms Beirut, Lebanon Tuesday November 29, 2011: Pre-congress workshop Adam Bagg University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, USA Myeloid neoplasms Myeloproliferative
Reporting cytogenetics Can it make sense? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota
 Reporting cytogenetics Can it make sense? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Reporting cytogenetics What is it? Terminology Clinical value What details are important Diagnostic Tools for Leukemia
Reporting cytogenetics Can it make sense? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Reporting cytogenetics What is it? Terminology Clinical value What details are important Diagnostic Tools for Leukemia
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Positive
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091533 Age 28 Years Gender Male 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105415AM 4/9/2017 23858M Ref By Final LEUKEMIA DIAGNOSTIC COMREHENSIVE ROFILE, ANY 6 MARKERS t (1;19) (q23
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091533 Age 28 Years Gender Male 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105415AM 4/9/2017 23858M Ref By Final LEUKEMIA DIAGNOSTIC COMREHENSIVE ROFILE, ANY 6 MARKERS t (1;19) (q23
WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms with Defined Molecular Abnormalities
 WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms with Defined Molecular Abnormalities Robert W. McKenna, M.D. 1/2009 WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms (4th Edition)--2008 Incorporates new information that
WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms with Defined Molecular Abnormalities Robert W. McKenna, M.D. 1/2009 WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms (4th Edition)--2008 Incorporates new information that
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach
 Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
Role of FISH in Hematological Cancers
 Role of FISH in Hematological Cancers Thomas S.K. Wan PhD,FRCPath,FFSc(RCPA) Honorary Professor, Department of Pathology & Clinical Biochemistry, Queen Mary Hospital, University of Hong Kong. e-mail: wantsk@hku.hk
Role of FISH in Hematological Cancers Thomas S.K. Wan PhD,FRCPath,FFSc(RCPA) Honorary Professor, Department of Pathology & Clinical Biochemistry, Queen Mary Hospital, University of Hong Kong. e-mail: wantsk@hku.hk
GENETICS OF HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES
 de DUVE INSTITUTE GENETICS OF HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES INTERUNIVERSITY CERTIFICATE IN HUMAN GENETICS Université catholique de Louvain Brussels,19/02/2016 Professor Hélène Antoine-Poirel, MD, PhD Center
de DUVE INSTITUTE GENETICS OF HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES INTERUNIVERSITY CERTIFICATE IN HUMAN GENETICS Université catholique de Louvain Brussels,19/02/2016 Professor Hélène Antoine-Poirel, MD, PhD Center
MPL W515L K mutation
 MPL W515L K mutation BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
MPL W515L K mutation BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
JAK2 V617F analysis. Indication: monitoring of therapy
 JAK2 V617F analysis BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
JAK2 V617F analysis BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU
 Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Immunopathology of Lymphoma
 Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma
 Frequency of Lymphoid Neoplasms Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma Stephen Hamilton-Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus University Hospital B-cell neoplasms 88% Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Frequency of Lymphoid Neoplasms Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma Stephen Hamilton-Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus University Hospital B-cell neoplasms 88% Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Molecular Markers in Acute Leukemia. Dr Muhd Zanapiah Zakaria Hospital Ampang
 Molecular Markers in Acute Leukemia Dr Muhd Zanapiah Zakaria Hospital Ampang Molecular Markers Useful at diagnosis Classify groups and prognosis Development of more specific therapies Application of risk-adjusted
Molecular Markers in Acute Leukemia Dr Muhd Zanapiah Zakaria Hospital Ampang Molecular Markers Useful at diagnosis Classify groups and prognosis Development of more specific therapies Application of risk-adjusted
Molecular Diagnostics of Myeloid and Lymphoid Neoplasms
 Molecular Diagnostics of Myeloid and Lymphoid Neoplasms Molecular Pathology: Principles in Clinical Practice - 2012 John Greg Howe Ph.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale University School of Medicine
Molecular Diagnostics of Myeloid and Lymphoid Neoplasms Molecular Pathology: Principles in Clinical Practice - 2012 John Greg Howe Ph.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale University School of Medicine
Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure
 Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure I am receiving an honorarium from Sysmex for today s presentation. 1 Determining the Etiology for
Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure I am receiving an honorarium from Sysmex for today s presentation. 1 Determining the Etiology for
Molecular Hematopathology Leukemias I. January 14, 2005
 Molecular Hematopathology Leukemias I January 14, 2005 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Diagnosis requires presence of Philadelphia chromosome t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation BCR-ABL is the result BCR on chr
Molecular Hematopathology Leukemias I January 14, 2005 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Diagnosis requires presence of Philadelphia chromosome t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation BCR-ABL is the result BCR on chr
Molecular Genetic Testing for the Diagnosis of Haematological Malignancies
 Molecular Genetic Testing for the Diagnosis of Haematological Malignancies Dr Anthony Bench Haemto-Oncology Diagnostic Service Cambrıdge Unıversıty Hospitals NHS Foundatıon Trust Cambridge UK Molecular
Molecular Genetic Testing for the Diagnosis of Haematological Malignancies Dr Anthony Bench Haemto-Oncology Diagnostic Service Cambrıdge Unıversıty Hospitals NHS Foundatıon Trust Cambridge UK Molecular
Molecular Markers. Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC
 Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Molecular Advances in Hematopathology
 Molecular Advances in Hematopathology HOW MOLECULAR METHODS HAVE CHANGED MY PRACTICE Objectives Understand the importance of cytogenetic/molecular studies in hematolymphoid diseases Know some of the important
Molecular Advances in Hematopathology HOW MOLECULAR METHODS HAVE CHANGED MY PRACTICE Objectives Understand the importance of cytogenetic/molecular studies in hematolymphoid diseases Know some of the important
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
Molecular Diagnostics in the Workup of Lymphomas for the General Pathologist. Outline. Role of Molecular Testing in Lymphoma Diagnosis
 Molecular Diagnostics in the Workup of Lymphomas for the General Pathologist L. Jeffrey Medeiros, M.D. M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Outline Gene rearrangement studies / Clonality Translocations / mutations
Molecular Diagnostics in the Workup of Lymphomas for the General Pathologist L. Jeffrey Medeiros, M.D. M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Outline Gene rearrangement studies / Clonality Translocations / mutations
Disclosure: Objectives/Outline. Leukemia: Genealogy of Pathology Practice: Old Diseases New Expectations. Nothing to disclose.
 RC1 Leukemia: Genealogy of Pathology Practice: Old Diseases New Expectations RC2 Disclosure: Nothing to disclose Henry Moon Lecture: UCSF Annual Conference Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu May
RC1 Leukemia: Genealogy of Pathology Practice: Old Diseases New Expectations RC2 Disclosure: Nothing to disclose Henry Moon Lecture: UCSF Annual Conference Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu May
The development of clonality testing for lymphomas in the Bristol Genetics Laboratory. Dr Paula Waits Bristol Genetics Laboratory
 The development of clonality testing for lymphomas in the Bristol Genetics Laboratory Dr Paula Waits Bristol Genetics Laboratory Introduction The majority of lymphoid malignancies belong to the B cell
The development of clonality testing for lymphomas in the Bristol Genetics Laboratory Dr Paula Waits Bristol Genetics Laboratory Introduction The majority of lymphoid malignancies belong to the B cell
Initial Diagnostic Workup of Acute Leukemia
 Initial Diagnostic Workup of Acute Leukemia Guideline from the College of American Pathologists (CAP) and the American Society of Hematology (ASH) Publication: Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
Initial Diagnostic Workup of Acute Leukemia Guideline from the College of American Pathologists (CAP) and the American Society of Hematology (ASH) Publication: Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
5/21/2018. Disclosures. Objectives. Normal blood cells production. Bone marrow failure syndromes. Story of DNA
 AML: Understanding your diagnosis and current and emerging treatments Nothing to disclose. Disclosures Mohammad Abu Zaid, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indiana
AML: Understanding your diagnosis and current and emerging treatments Nothing to disclose. Disclosures Mohammad Abu Zaid, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indiana
WBCs Disorders 1. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
Corrigenda. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (revised 4th edition): corrections made in second print run
 Corrigenda WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (revised 4th edition): corrections made in second print run In addition to corrections of minor typographical errors, corrections
Corrigenda WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (revised 4th edition): corrections made in second print run In addition to corrections of minor typographical errors, corrections
HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIAGNOSIS & SUBTYPING. Use of IHC. Use of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Use of Flow Cytometry
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIAGNOSIS & SUBTYPING HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIAGNOSIS & SUBTYPING The 2008 WHO classification system for tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues specifies that various combinations of immunophenotypic
HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIAGNOSIS & SUBTYPING HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIAGNOSIS & SUBTYPING The 2008 WHO classification system for tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues specifies that various combinations of immunophenotypic
Treatments and Current Research in Leukemia. Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago
 Treatments and Current Research in Leukemia Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago 2 Acute (rapid progression) Myeloid Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) Lymphoid Acute
Treatments and Current Research in Leukemia Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago 2 Acute (rapid progression) Myeloid Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) Lymphoid Acute
The Challenges of Precision Medicine: New Advances in Molecular Diagnostic Testing- Impact for Healthcare
 The Challenges of Precision Medicine: New Advances in Molecular Diagnostic Testing- Impact for Healthcare Jessica Wang-Rodriguez, MD Chief, VISN22 Consolidated Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Services
The Challenges of Precision Medicine: New Advances in Molecular Diagnostic Testing- Impact for Healthcare Jessica Wang-Rodriguez, MD Chief, VISN22 Consolidated Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Services
Current Techniques in Molecular Biology Friedel Nollet, Ph.D.
 Current Techniques in Molecular Biology Friedel Nollet, Ph.D. Molecular Biology and Cytometry course May 16-17, 2013 Mol, SCK-CEN, Belgium Sanger DNA sequencing Kary Mullis received a Nobel Prize in chemistry
Current Techniques in Molecular Biology Friedel Nollet, Ph.D. Molecular Biology and Cytometry course May 16-17, 2013 Mol, SCK-CEN, Belgium Sanger DNA sequencing Kary Mullis received a Nobel Prize in chemistry
Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification
 Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno Bellinzona, January 29-31, 2016 Evolution of lymphoma classification Rappaport Lukes
Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno Bellinzona, January 29-31, 2016 Evolution of lymphoma classification Rappaport Lukes
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Positive
 Lab No 135091548 Age 35 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 103420AM 4/9/2017 23753M Ref By Dr UNKNWON Final Test Results Units Bio Ref Interval LEUKEMIA DIAGNOSTIC COMREHENSIVE ROFILE 3 t (1;19)
Lab No 135091548 Age 35 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 103420AM 4/9/2017 23753M Ref By Dr UNKNWON Final Test Results Units Bio Ref Interval LEUKEMIA DIAGNOSTIC COMREHENSIVE ROFILE 3 t (1;19)
Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities Acute Myeloid Leukemia with recurrent cytogenetic Abnormalities -t(8;21)(q22;q22)(aml/eto) -inv(16) or t(16;16) -t(15;17) -11q23 Acute Myeloid
Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities Acute Myeloid Leukemia with recurrent cytogenetic Abnormalities -t(8;21)(q22;q22)(aml/eto) -inv(16) or t(16;16) -t(15;17) -11q23 Acute Myeloid
PhenoPath. Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 PhenoPath Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA C urrent diagnosis of B cell non-hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) is based on the 2008 WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid
PhenoPath Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA C urrent diagnosis of B cell non-hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) is based on the 2008 WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid
Molecular. Oncology & Pathology. Diagnostic, Prognostic, Therapeutic, and Predisposition Tests in Precision Medicine. Liquid Biopsy.
 Molecular Oncology & Pathology Hereditary Cancer Somatic Cancer Liquid Biopsy Next-Gen Sequencing qpcr Sanger Sequencing Diagnostic, Prognostic, Therapeutic, and Predisposition Tests in Precision Medicine
Molecular Oncology & Pathology Hereditary Cancer Somatic Cancer Liquid Biopsy Next-Gen Sequencing qpcr Sanger Sequencing Diagnostic, Prognostic, Therapeutic, and Predisposition Tests in Precision Medicine
Opportunities for Optimal Testing in the Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Curtis A. Hanson, MD
 Opportunities for Optimal Testing in the Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Curtis A. Hanson, MD 2013 MFMER slide-1 DISCLOSURES: Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-2
Opportunities for Optimal Testing in the Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Curtis A. Hanson, MD 2013 MFMER slide-1 DISCLOSURES: Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-2
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow
 The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells. Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital
 Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
The next lymphoma classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno
 Evolution of classification The next classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno The Lymphoma Forum of Excellence, Bellinzona, January 2011 Rappaport Lukes and Collins (immunophenotype)
Evolution of classification The next classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno The Lymphoma Forum of Excellence, Bellinzona, January 2011 Rappaport Lukes and Collins (immunophenotype)
Large cell immunoblastic Diffuse histiocytic (DHL) Lymphoblastic lymphoma Diffuse lymphoblastic Small non cleaved cell Burkitt s Non- Burkitt s
 Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Introduction 6th most common cause of cancer death in United States. Increasing in incidence and mortality. Since 1970, the incidence of has almost doubled. Overview The types of
Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Introduction 6th most common cause of cancer death in United States. Increasing in incidence and mortality. Since 1970, the incidence of has almost doubled. Overview The types of
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Case 1. Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX
 Case 1 Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of all CME
Case 1 Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of all CME
[COMPREHENSIVE GENETIC ASSAY PANEL ON
 2014 SN GENELAB AND RESEARCH CENTER DR. SALIL VANIAWALA, PH.D [COMPREHENSIVE GENETIC ASSAY PANEL ON MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASMS] SN Genelab presents one of the most comprehensive genetic assay panel for
2014 SN GENELAB AND RESEARCH CENTER DR. SALIL VANIAWALA, PH.D [COMPREHENSIVE GENETIC ASSAY PANEL ON MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASMS] SN Genelab presents one of the most comprehensive genetic assay panel for
Addressing the challenges of genomic characterization of hematologic malignancies using microarrays
 Addressing the challenges of genomic characterization of hematologic malignancies using microarrays Sarah South, PhD, FACMG Medical Director, ARUP Laboratories Department of Pediatrics and Pathology University
Addressing the challenges of genomic characterization of hematologic malignancies using microarrays Sarah South, PhD, FACMG Medical Director, ARUP Laboratories Department of Pediatrics and Pathology University
Methods used to diagnose lymphomas
 Institut für Pathologie Institut für Pathologie Methods used to diagnose lymphomas Prof. Dr.Med. Leticia Quintanilla-Fend Molecular techniques NGS histology Cytology AS-PCR Sanger seq. MYC Immunohistochemistry
Institut für Pathologie Institut für Pathologie Methods used to diagnose lymphomas Prof. Dr.Med. Leticia Quintanilla-Fend Molecular techniques NGS histology Cytology AS-PCR Sanger seq. MYC Immunohistochemistry
Myeloid neoplasms. Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories:
 Myeloid neoplasms Note: Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories: 1. AML : Acute myeloid leukemia(stem cell with myeloid
Myeloid neoplasms Note: Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories: 1. AML : Acute myeloid leukemia(stem cell with myeloid
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype. Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital
 Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Lab Guide 2018 Diagnostic Genomic Division(DGD)
 Lab Guide 2018 Diagnostic Genomic Division(DGD) Diagnostic Genomic Division DGD lab Guide Page 1 of 74 Cytogenetics Section Title ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA PANEL BY FISH ITEM Days test is performed Turnaround
Lab Guide 2018 Diagnostic Genomic Division(DGD) Diagnostic Genomic Division DGD lab Guide Page 1 of 74 Cytogenetics Section Title ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA PANEL BY FISH ITEM Days test is performed Turnaround
HEMATOPATHOLOGY SERVICES
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY SERVICES Know what your patient s future holds, NOW. Driven by patient care, GoPath Laboratories has set a new standard for hematologic cancer testing. thick, 2 slides per probe minimum
HEMATOPATHOLOGY SERVICES Know what your patient s future holds, NOW. Driven by patient care, GoPath Laboratories has set a new standard for hematologic cancer testing. thick, 2 slides per probe minimum
School of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine: Current and New Research Interests
 School of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine: Current and New Research Interests W/Professor Wendy Erber Current Research Interests Viral immunology and immunogenetics Bone pathology and cell signalling
School of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine: Current and New Research Interests W/Professor Wendy Erber Current Research Interests Viral immunology and immunogenetics Bone pathology and cell signalling
Update on the WHO Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Kaaren K. Reichard, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester
 Update on the WHO Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Kaaren K. Reichard, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester reichard.kaaren@mayo.edu Nothing to disclose Conflict of Interest Objectives Present a practical
Update on the WHO Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Kaaren K. Reichard, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester reichard.kaaren@mayo.edu Nothing to disclose Conflict of Interest Objectives Present a practical
Introduction: The Revised (4 th Edition) World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues
 Society for Hematopathology Scientific Symposium USCAP Companion Meeting, Boston, MA March 8, 2009 Boston, MA Steven H. Swerdlow and James Vardiman, Moderators Introduction: The Revised (4 th Edition)
Society for Hematopathology Scientific Symposium USCAP Companion Meeting, Boston, MA March 8, 2009 Boston, MA Steven H. Swerdlow and James Vardiman, Moderators Introduction: The Revised (4 th Edition)
3/23/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Pitfalls in Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: CD20 and CD3 Can Let Me Down?!
 Pitfalls in Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: CD20 and CD3 Can Let Me Down?! Judith A. Ferry Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all
Pitfalls in Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: CD20 and CD3 Can Let Me Down?! Judith A. Ferry Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all
HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY
 HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY Failure of terminal differentiation Failure of differentiated cells to undergo apoptosis Failure to control growth Neoplastic stem cell FAILURE OF TERMINAL DIFFERENTIATION
HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY Failure of terminal differentiation Failure of differentiated cells to undergo apoptosis Failure to control growth Neoplastic stem cell FAILURE OF TERMINAL DIFFERENTIATION
Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas
 Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas Stephen Hamilton Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus Kommunehospital B-lymphoblastic lymphoma Diffuse large cell lymphoma, NOS T-cell / histiocyte-rich;
Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas Stephen Hamilton Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus Kommunehospital B-lymphoblastic lymphoma Diffuse large cell lymphoma, NOS T-cell / histiocyte-rich;
Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms. Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University
 Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University What is an integrated approach? What is an integrated approach? Incorporating all diagnostic
Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University What is an integrated approach? What is an integrated approach? Incorporating all diagnostic
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms
 Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
TEST MENU TEST CPT CODES TAT. Chromosome Analysis Bone Marrow x 2, 88264, x 3, Days
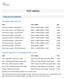 TEST MENU CANCER/LEUKEMIA CHROMOSOME ANALYSIS Chromosome Analysis Bone Marrow 88237 x 2, 88264, 88280 x 3, 88291 4 Days Chromosome Analysis Bone Marrow Core 88237 x 2, 88264, 88280 x 3, 88291 4 Days Chromosome
TEST MENU CANCER/LEUKEMIA CHROMOSOME ANALYSIS Chromosome Analysis Bone Marrow 88237 x 2, 88264, 88280 x 3, 88291 4 Days Chromosome Analysis Bone Marrow Core 88237 x 2, 88264, 88280 x 3, 88291 4 Days Chromosome
Genetic Testing Oncology
 Genetic Testing Oncology Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.010 05/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2014 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Genetic Testing Oncology Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.010 05/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2014 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Oncology Cytogenetics Diagnostic Service - User Guide 2014
 Oncology Cytogenetics Diagnostic Service - User Guide 2014 Contact details Address: Cytogenetics Department 5 th Floor Tower Wing Guy s Hospital Great Maze Pond London SE1 9RT General enquiries 0207 188
Oncology Cytogenetics Diagnostic Service - User Guide 2014 Contact details Address: Cytogenetics Department 5 th Floor Tower Wing Guy s Hospital Great Maze Pond London SE1 9RT General enquiries 0207 188
Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material
 Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+)
 Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
WHO Classification. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small T-cell granular lymphocytic leukemia
 Blood Malignancies-II Prof. Dr. Herman Hariman, a Ph.D, SpPK (KH). Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. of Clinical Pathology, School of Medicine, University of North Sumatra WHO classification
Blood Malignancies-II Prof. Dr. Herman Hariman, a Ph.D, SpPK (KH). Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. of Clinical Pathology, School of Medicine, University of North Sumatra WHO classification
Dr. Anjali Kelkar (DNB Path, IFCAP)
 Acute Leukemias : Morphology and Beyond Dr. Anjali Kelkar (DNB Path, IFCAP) Consultant - Diagnostic Haematology NABL Assessor Senior Associate Professor, Incharge Haematology Labs Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed
Acute Leukemias : Morphology and Beyond Dr. Anjali Kelkar (DNB Path, IFCAP) Consultant - Diagnostic Haematology NABL Assessor Senior Associate Professor, Incharge Haematology Labs Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed
Aggressive B-cell Lymphoma 2013
 Aggressive B-cell Lymphoma 2013 Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Burkitt Lymphoblastic lymphoma Gray zone Intermediate DLBCL/HL Intermediate BL/DLBCL Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma Common morphology: diffuse
Aggressive B-cell Lymphoma 2013 Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Burkitt Lymphoblastic lymphoma Gray zone Intermediate DLBCL/HL Intermediate BL/DLBCL Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma Common morphology: diffuse
Use of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 FISH for investigations of high grade B cell lymphoma
 Use of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 FISH for investigations of high grade B cell lymphoma Dr Anthony Bench Haematopathology and Oncology Diagnostic Service Cambrıdge Unıversıty Hospitals NHS Foundatıon Trust Cambridge
Use of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 FISH for investigations of high grade B cell lymphoma Dr Anthony Bench Haematopathology and Oncology Diagnostic Service Cambrıdge Unıversıty Hospitals NHS Foundatıon Trust Cambridge
Non-Hodgkin s Lymphomas Version
 NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Non-Hodgkin s Lymphomas Version 2.2015 NCCN.org Continue Use of Immunophenotyping/ Genetic Testing in Differential Diagnosis of Mature B-Cell
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Non-Hodgkin s Lymphomas Version 2.2015 NCCN.org Continue Use of Immunophenotyping/ Genetic Testing in Differential Diagnosis of Mature B-Cell
HIGH GRADE B-CELL LYMPHOMA DAVID NOLTE, MD (PGY-2) HUSSAM AL-KATEB, PHD, FACMG DEBORAH FUCHS, MD
 HIGH GRADE B-CELL LYMPHOMA DAVID NOLTE, MD (PGY-2) HUSSAM AL-KATEB, PHD, FACMG DEBORAH FUCHS, MD OUTLINE High grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements Patient presentation 2008/2016
HIGH GRADE B-CELL LYMPHOMA DAVID NOLTE, MD (PGY-2) HUSSAM AL-KATEB, PHD, FACMG DEBORAH FUCHS, MD OUTLINE High grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements Patient presentation 2008/2016
Integrated Hematopathology. Morphology and FCI with IHC
 Integrated Hematopathology Morphology and FCI with IHC FrontMatter.indd i 9/6/2009 9:30:12 PM FrontMatter.indd ii 9/6/2009 9:30:18 PM Integrated Hematopathology Morphology and FCI with IHC Cherie H Dunphy,
Integrated Hematopathology Morphology and FCI with IHC FrontMatter.indd i 9/6/2009 9:30:12 PM FrontMatter.indd ii 9/6/2009 9:30:18 PM Integrated Hematopathology Morphology and FCI with IHC Cherie H Dunphy,
Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas
 Neoplastic Hematopathology Update 2018 Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center I do not have any disclosures Disclosures Outline New entities and changes in WHO
Neoplastic Hematopathology Update 2018 Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center I do not have any disclosures Disclosures Outline New entities and changes in WHO
Molecular Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma:
 Molecular Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma: Ig translocations hyperdiploid vs non-hyperdiploid CYCLIN D dysregulation other oncogenic events Michael Kuehl MM: post-germinal center tumor of long-lived BM
Molecular Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma: Ig translocations hyperdiploid vs non-hyperdiploid CYCLIN D dysregulation other oncogenic events Michael Kuehl MM: post-germinal center tumor of long-lived BM
Initial Diagnosis and Treatment 81 Male
 Case SH2017-0359 Shiraz Fidai 1, Sandeep Gurbuxani 1, Girish Venkataraman 1, Gordana Raca 2, Madina Sukhanova 3, Michelle M Le Beau 3, Y. Lynn Wang 4, Mir Alikhan 4, Megan M.McNerney 4, Yuri Kobzev 4,
Case SH2017-0359 Shiraz Fidai 1, Sandeep Gurbuxani 1, Girish Venkataraman 1, Gordana Raca 2, Madina Sukhanova 3, Michelle M Le Beau 3, Y. Lynn Wang 4, Mir Alikhan 4, Megan M.McNerney 4, Yuri Kobzev 4,
Recommended Timing for Transplant Consultation
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES Recommended Timing for Transplant Consultation Published jointly by the National Marrow Donor Program /Be The Match and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation BeTheMatchClinical.org
REFERRAL GUIDELINES Recommended Timing for Transplant Consultation Published jointly by the National Marrow Donor Program /Be The Match and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation BeTheMatchClinical.org
Please Silence Your Cell Phones. Thank You
 Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You Utility of NGS and Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Hematopathology Practice Maria E. Arcila M.D. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Disclosure
Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You Utility of NGS and Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Hematopathology Practice Maria E. Arcila M.D. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Disclosure
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1)
 MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
Eosinophilia: A Diagnostic Approach and Test Utilization Strategies for Bone Marrow Evaluation
 Eosinophilia: A Diagnostic Approach and Test Utilization Strategies for Bone Marrow Evaluation American Society for Clinical Pathology 2014 Annual Meeting Presented by: Matthew T. Howard, MD Assistant
Eosinophilia: A Diagnostic Approach and Test Utilization Strategies for Bone Marrow Evaluation American Society for Clinical Pathology 2014 Annual Meeting Presented by: Matthew T. Howard, MD Assistant
Aggressive B-cell lymphomas and gene expression profiling towards individualized therapy?
 Aggressive B-cell lymphomas and gene expression profiling towards individualized therapy? Andreas Rosenwald Institute of Pathology, University of Würzburg, Germany Barcelona, June 18, 2010 NEW WHO CLASSIFICATION
Aggressive B-cell lymphomas and gene expression profiling towards individualized therapy? Andreas Rosenwald Institute of Pathology, University of Würzburg, Germany Barcelona, June 18, 2010 NEW WHO CLASSIFICATION
Malignant lymphomas are neoplasms that arise from B
 Overview of the Role of Molecular Methods in the Diagnosis of Malignant Lymphomas L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD; Jeanne Carr, PhD Objective. To review the role of molecular genetics in the diagnosis of malignant
Overview of the Role of Molecular Methods in the Diagnosis of Malignant Lymphomas L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD; Jeanne Carr, PhD Objective. To review the role of molecular genetics in the diagnosis of malignant
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED
 Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias
 Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
Clinical Policy: Bendamustine (Bendeka, Treanda) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.307
 Clinical Policy: (Bendeka, Treanda) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.307 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 11/17 Coding Implications Revision Log Description The intent of the criteria is to ensure that
Clinical Policy: (Bendeka, Treanda) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.307 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 11/17 Coding Implications Revision Log Description The intent of the criteria is to ensure that
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML
 Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
