Ovarian, Peritoneal, and Fallopian Tube Epithelial Cancer (OPT)
|
|
|
- Agatha Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ovarian, Peritoneal, and Fallopian Tube Epithelial Cancer (OPT) ACOG District II 2 Learning Objectives At the end of this clinical presentation, obstetrician gynecologists and other women s health care providers will be able to: 1. Interpret updated clinical guidance on the etiology, risk assessment and mitigation, and management of ovarian, fallopian tube and peritoneal cancer* 2. Outline the assessment and comprehensive management of adnexal masses as set forth in current clinical guidelines 3. Recommend guidance on appropriate timing for when to refer to a gynecologic oncologist We will refer to epithelial ovarian cancer as EOC from this point forward. 1
2 Background Disease Burden Disease Classification Risk Factors U.S. Disease Burden American Cancer Society annual statistics 22,000 25,000 incidence 14,000 mortality rate 1 in 70 lifetime incidence of US women 5 year survival rate for localized ovarian cancer 92% 5 year survival rate for advanced ovarian cancer 30% 2
3 Disease Classification Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type Accounts for approximately 90% of ovarian cancers 3 5% 2 6% % Six main histological subtypes of epithelial ovarian cancer 10 26% 7 24% 70 74% 1 7% NOTE: Other* refers to mixed or transitional carcinomas where it is not possible to categorize to a single subtype. Source(s): Alvarez RD, Karlan BY, Strauss JF. Ovarian Cancer: Evolving Paradigms in Research and Care: Report from the Institute of Medicine, Gynecologic Oncology, 141: , Risk Factors Established Age Hereditary predisposition Family history Nulliparity Suspected/Possible Early age at menarche Endometriosis Hormone replacement therapy Infertility Late age at menopause Obesity Sedentary lifestyle Tobacco use Source: Permuth Wey J, Sellers TA. Epidemiology of ovarian cancers. Methods of Molecular Biology, Cancer Epidemiology. 2009; 472:
4 Risk Status Average risk: Risk reported for the general population High risk: Women with a genetic predisposition Deleterious mutation associated with ovarian, peritoneal, and fallopian tube (OPT) cancers Women with a significant family history but no known deleterious mutation, are also considered high risk. Assessment of Hereditary Predisposition Assess risk based on both paternal and maternal family history and personal history of cancers, particularly those related to deleterious mutations Consider performing genetic testing Refer to a genetics professional (geneticist or genetic counselor) when appropriate If a deleterious mutation is found, a patient is considered high risk If patient declines testing or counseling, history dictates risk level 4
5 Primary Protective Factors Oral contraceptive use >5 years of OCP use reduces risk by ~50% in both low and high risk women Pregnancy Risk reducing bilateral salpingo oophorectomy (RRSO) RRSO reduces incidence in high risk women by ~90% Not recommended for women at average risk Other factors that are associated with a decreased risk of developing ovarian cancer: Tubal ligation Hysterectomy Breastfeeding Asymptomatic Women Cancer Screening 5
6 Performance Metrics for Screening Tests: Four Key Measures Sensitivity % of people who are affected that the test correctly identifies as positive Specificity % of people who are not affected that correctly test negative Positive predictive value (PPV) % of people with positive test who are affected Negative predictive value (NPV) % of people with negative test who are not affected The higher the sensitivity, the fewer false negative tests The higher the specificity, the fewer false positive tests 6
7 Principles of Screening: Types of Testing Screening Tests do not provide a definitive answer; provide only odds of a given condition Offered to a much wider population to define the level of risk, starting with the a priori baseline risk modified by screening parameters Based on adjusted level of risk, appropriate patients will be offered diagnostic testing Diagnostic Developed to provide definitive answer May be invasive, expensive, and potentially risky Typically reserved for at risk patients based on screening, symptoms, or physical findings Only 1 in 5 ovarian cancer cases are localized when diagnosed OPT Cancer Screening: Challenges Low prevalence of disease causes even a poor test to have high NPV, thus limiting meaning of the result High numbers of false positive results of current screening tests in average risk women may result in an unacceptable number undergoing invasive procedures Screening has not been shown to reduce mortality from ovarian cancer even in high risk patients No tests currently available have adequate sensitivity, specificity, or positive predictive value (PPV) to effectively screen for ovarian cancer 7
8 FDA Statement on Ovarian Cancer Screening FDA Statement, September 7, 2016: There are no ovarian cancer screening tests that have been cleared or approved by the FDA and information in the medical literature, including published clinical trial data, do not demonstrate that currently available ovarian cancer screening tests are accurate and reliable, particularly for asymptomatic women. ACOG and the USPSTF recommend AGAINST routine screening for ovarian cancer Current methods are not adequately effective Screening Strategies Currently recommended screening tests (for high risk individuals) include CA125 and transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) A multimodal approach is more effective, but does not achieve adequate sensitivity, specificity, or positive predictive value (PPV) CA125: Not sensitive for early disease Elevated in a number of benign conditions, even in older women TVS: Not reliable in distinguishing benign from malignant tumors Its use in the asymptomatic patient leads to unnecessary surgery 8
9 Risk Reducing Strategies Medical Surgical 9
10 Risk Reducing Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy High Risk Population Timing: Age when childbearing completed for women with BRCA1 mutation Age for women with BRCA2 Preventive benefit: risk of gynecologic malignancy (85 90%) risk of breast cancer when performed prior to menopause Surgeon s responsibility: Peritoneal cytology, inspection of the abdomen, adequate margin, and 2 3mm sectioning by a pathologist Awareness of rising risk of occult malignancy with increase in woman s age (4 10%) Patient counseling on potential extent of surgery Surgical preparation to treat malignancy if identified Source(s): Rebbeck et al. Prophylactic Oophorectomy in Carriers of BRCA1 or BRCA2 Mutations. NEJM, 2002: 346, Kauff et al. Risk Reducing Salpingo oophorectomy in Women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 Mutation. NEJM, 2002: 346: Estimated Benefits of Risk Reducing Surgeries in BRCA Carriers 2,482 women in Europe and North America from 1974 to 2008 with median follow up of 3.65 years Approximately half of the women had risk reducing surgery Breast cancer mortality reduced by 56% (2% vs. 6%) and ovarian cancer mortality by 79% (0.4% vs. 3%) Mastectomy 0 breast cancers vs. 7% in those without risk reducing mastectomy RRSO 86% reduction in ovarian cancer (1% v. 6%) 37% reduction in breast cancer in BRCA1 (14% v. 20% ) 64% reduction in breast cancer in BRCA2 (7% v. 23%) Source(s): Domcheck SM et al. Association of risk reducing surgery in BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation carriers with cancer risk and mortality. JAMA 2010;304(9):
11 Serous Tubal Intraepithelial Carcinoma (STIC): Ovarian Cancer Precursor Type II Tumors: 70% of sporadic (non hereditary) ovarian and peritoneal high grade serous carcinomas demonstrated mucosal tubal involvement including STIC Nearly all STICs overexpress p53 similar to high grade serous carcinoma. Source(s): Kindelberger DW, Lee Y, Miron A, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31: RRSO Controversies Balancing increased risk of cardiac disease, bone loss, adverse affect on cognitive function, and other quality of life issues with the timing of RRSO Performing a hysterectomy at the time of RRSO Will risk reducing salpingectomy provide similar benefit as RRSO? STIC (serous tubal in situ carcinoma) tumors fallopian tube in situ lesions that may predispose to ovarian cancer Evidence suggests that a majority of serous ovarian tumors arise in fallopian tube 11
12 Opportunistic Salpingectomy ACOG Committee Opinion #620 Surgeon should discuss the following with women at population risk of ovarian cancer: Benefits of removal of the fallopian tubes during a hysterectomy with ovarian preservation Bilateral salpingectomy can be considered a method that provides effective contraception Summary of Recommendations for High Risk Women Medical Oral contraceptive use Surgical RRSO when childbearing completed All cause mortality increased if hormone replacement not provided Risks of breast, ovarian, and fallopian tube cancer decreased; greatest impact in younger women Screening Has not been shown to be effective TVS every 6 months CA125 every 6 months Cancer mortality not reduced 12
13 Symptomatic Women Symptoms or Presence of Suspicious Physical Findings 13
14 Evaluation: Symptomatic Patient/Suspicious Physical Findings Personal and/or family history of: Breast, ovarian, endometrial, and/or colorectal cancer Known hereditary cancer syndrome, and/or Ashkenazi (Eastern European) Jewish ancestry Complete physical examination, including an abdominal/pelvic exam with a rectovaginal exam TVS as the imaging modality of choice for initial evaluation If no gynecologic pathology is identified, consider referral to gastroenterologist Evaluation of an Ovarian Mass: Symptomatic Patient/Suspicious Physical Findings Key TVS findings: Size Consistency (cystic, solid, mixed) Presence of septations, mural nodules or papillary projections Presence of ascites Abnormal vascularity The majority of simple cysts <10 cm are benign. May be treated conservatively with serial TVS if asymptomatic and not increasing in size Complex lesions, abnormal vascularity, or ascites are highly concerning for malignancy 14
15 Evaluation: Symptomatic Patient/Suspicious Physical Findings Biomarkers CA125 Elevated in 80% of women with ovarian cancer but only 50% of women with stage I disease Normal CA125 does not rule out cancer and is of limited value in pre menopausal women OVA 1, ROMA Combined testing associated with higher sensitivity CT Scan Evaluate if symptoms are persistent when initial work up is negative Evaluate the extent of abdominal spread when pelvic malignancy is suspected MRI May distinguish lesions indeterminate on TVS Additional Tests Available for Symptomatic Patients Single marker assay (CA125, HE4) Combination of markers & algorithms: Multivariate Index Assay (MIA) Risk of Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) Risk of Malignancy Index (RMI) 15
16 Assessment of Women with Adnexal Masses Malignant or Not? Test Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV ROMA 74 96% 75 95% 34 74% 95%+ Clinical Assessment 75% 86% 65% 91%* MIA** + Clinical Assessment 95% 44% 36% 97%* + Algorithm utilizing single marker assay, range of results based on menopausal status. * Source: Li AJ, New biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Contemporary OB/GYN, April 2012 ** MIA = Ova 1 Source(s): Langoria TC, et al. Clinical performance of a multivariate index assay for detecting early stage ovarian cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2014, Jan: 210(1): 78. Consulting with a Gynecologic Oncologist Organizations that support gynecologic oncologist involvement: Meta analysis of 18 studies confirmed survival benefit with a gynecologic oncologist: Complete surgical staging with early disease Optimal cytoreductive surgery with advanced disease Improved median and overall survival Performance of comprehensive and appropriate surgery is significantly more likely in a teaching hospital The rate of comprehensive surgery is significantly higher in hospitals in urban settings <50% of patients received comprehensive surgery at small rural hospitals Adjuvant chemotherapy/follow up and supportive care may often be administered locally Source(s): Giede K, et al. Gynecologic Oncology, 99:447 61, Cress RD, Bauer K, O'Malley CD, et al. Gynecologic Oncology, 121: 94 99,
17 Laparoscopy for Benign Adnexal Masses Preferred surgical approach Unexpected ovarian cancer discovered in adnexal masses Must be considered preoperatively and discussed with the patient Effort should be made to avoid cyst leakage to prevent seeding of the peritoneal cavity with potentially malignant cells Consultation and potential expeditious referral to gynecologic oncologist 17
18 Evaluation: When to Refer ACOG/SGO Referral Guidelines for a Newly Diagnosed Pelvic Mass Refer if one or more of the following indicators:* Very elevated CA125 level Ultrasound findings suggestive of malignancy Ascites A nodular or fixed pelvic mass Evidence of abdominal or distant metastasis (by exam or imaging study) Elevated score on a formal risk assessment test such as the multivariate index assay or the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm or one of the ultrasound based scoring systems from the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis group Significant family history of breast or ovarian cancer (in a first degree relative) * For additional information, please refer to the ACOG District II website at acogny.org Source(s): The American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists. Evaluation and Management of Adnexal Masses, Practice Bulletin #174. November Management of an Unsuspected Malignancy Staging is essential to: Define the extent of disease Determine subsequent treatment recommendation Complete surgical staging is performed by: Gynecologic oncologists: 97% of the time Ob gyns: 52% of the time General surgeons: 36% of the time Removal of uterus and adnexa is one step in the staging process Exceptions include fertility preservation, particularly for early stage disease and non epithelial subtypes Source(s): Goff B, et al. Predictors of comprehensive surgical treatment in patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer, Volume 109, Issue May 2007;
19 Management of Malignancy Surgical Staging Cytoreductive Surgery Adjuvant or Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy 19
20 Complete Surgical Staging Steps Evaluation of any free fluid for cytology; peritoneal washings Intact removal of the adnexal mass, if possible Systematic inspection of all intra abdominal surfaces, biopsy or removal of any suspicious areas or adhesions Biopsies of peritoneum of the posterior and anterior cul desac, both paracolic gutters, and the intestinal mesenteries and diaphragm (or scraping) if no suspicious areas seen Omentectomy Bilateral pelvic and para aortic lymphadenectomy Removal of the uterus and the adnexa Fertility Sparing Surgery Women with apparent early stage disease (clinical stage IA, grade 1 or 2), may be considered for conservative surgical staging which includes: Desire for fertility sparing Unilateral salpingo oophorectomy Biopsy assessment of the contralateral ovary Pelvic washings Pelvic and para aortic lymphadenectomy, omentectomy, peritoneal and diaphragmatic biopsies Genetic risk assessment is warranted 20
21 Primary Cytoreductive Surgery Maximal cytoreduction (debulking) is the most significant predictor of survival Cytoreductive surgery for advanced stage disease Purpose to remove macroscopic disease evident at the time of initial surgery Goal to remove bulky disease as identified at the time of initial surgery Optimal debulking Removal of bulky disease so that largest single residual tumor nodule is 1cm Bulky Stage IIIC disease no residual disease at the completion of surgery Median survival of 106 months The five year survival for this group was over 70% Source: Chi DS, Eisenhauer EL, Lang J, Huh J, Haddad L, Abu Rustum NR, Sonoda Y, Levine DA, Hensley M, Barakat RR. What is the optimal goal of primary cytoreductive surgery for bulky stage IIIC epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC)? Gynecol Oncol Nov;103(2): Epub 2006 May 22. PubMed PMID: Omental Cake 21
22 Diaphragmatic and Liver Capsular Disease Optimal Debulking Surgery Benefits Patients with low volume residual disease ( 1cm) after surgery have: Significantly improved rates of response to adjuvant chemotherapy Lower rates of platinum resistance Improved survival compared to patients with bulky residual disease Improved quality of life by reducing symptoms caused by the increased tumor burden Source: Chi DS, Eisenhauer EL, Lang J, Huh J, Haddad L, Abu Rustum NR, Sonoda Y, Levine DA, Hensley M, Barakat RR. What is the optimal goal of primary cytoreductive surgery for bulky stage IIIC epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC)? Gynecol Oncol Nov;103(2): Epub 2006 May 22. PubMed PMID:
23 Chemotherapy Post operative (adjuvant) chemotherapy is a mainstay in the treatment of patients with a significant risk of recurrence Ovarian cancer is highly chemosensitive 70 80% of women will achieve complete clinical remission with initial chemotherapy following optimal debulking ~20% of women with advanced ovarian cancer will remain free of disease for at least 5 years Source: PMID: Chemotherapy Recommendations Combination of Taxane and Platinum Adjuvant therapy options for Stages IA & IBIII, IC, II and higher Dose dense chemotherapy IV/IP treatment Neoadjuvant chemotherapy recommended for non resectable Stage IIIC and Stage IV SGO and ASCO statement (August 2016) Interval cytoreductive surgery if tumor responds to chemotherapy Best outcomes for advance stage disease to date IV/IP chemotherapy in women who had optimal cytoreduction Source: Wright AA, Bohlke K, Armstrong DK, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed, advanced ovarian cancer: Society of Gynecologic Oncology and American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. Gynecol Oncol Oct; 143(1):
24 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy Median PFS (mo) HR Median OS (mo) HR IV IP IV IP GOG 104 Alberts (p = 0.02) GOG 114 Markman GOG 172 Armstrong (p = 0.01) (p = 0.05) (p = 0.05) (p = 0.03) Survivorship 24
25 Counseling: Quality of Life Issues Cancer diagnosis and subsequent treatment can significantly affect woman s quality of life and may impact the physical, psychosocial, spiritual, and sexual aspects of her life The role of the primary ob gyn is important to: Establish the diagnosis and provide referral based on regional expertise Assist in conveying information about the diagnosis and endorsing treatment plan Provide support during treatment, assist in addressing gynecologic symptoms, and be involved with follow up care, including survivorship 25
26 Genetic Counseling, Testing, and Cascade Screening All women with a pelvic malignancy should be offered genetic counseling and testing Approximately 20% are due to BRCA 1/2 and/or other deleterious mutations Referral to a genetic counselor should be considered Ob gyns are uniquely positioned to promote genetic testing in affected individuals Initiate or encourage cascade screening of 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd degree relatives, including males Assist in mitigating their risk or offering risk reducing services Note: Consult ACOG District II s genetics education/resources for additional information on this subject. Conclusion Future Directions Role of Obstetrician Gynecologists & Women s Health Providers 26
27 Future Directions Identify new methods of effective screening and early detection Promote identification of high risk populations and risk reducing surgical interventions Clarify the role of opportunistic and/or risk reducing salpingectomy Identify potential molecular targets and support development of therapeutic agents Encourage and support increased funding for research and participation in clinical trials Highest quality of clinical care Critical in helping advance knowledge Role of Obstetrician Gynecologists Identifying women at risk Avoid ineffective screening testing and encourage women at high risk to proceed with risk reducing strategies Practice evidence based evaluation of symptomatic women and those with suspicious physical findings Refer to a gynecologic oncologist when appropriate Understand and support patient s treatment options Support enrollment in cancer clinical trials Be involved in cancer survivorship plan Provide or assist with cascade testing of family members 27
SCREENING FOR OVARIAN CANCER DR MACİT ARVAS
 SCREENING FOR OVARIAN CANCER DR MACİT ARVAS Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death from gynecologic malignancy In 2008, ovarian cancer was the seventh common cancer in women worldwide There were
SCREENING FOR OVARIAN CANCER DR MACİT ARVAS Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death from gynecologic malignancy In 2008, ovarian cancer was the seventh common cancer in women worldwide There were
GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer
 GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer KRISTEN STARBUCK, MD ROSWELL PARK CANCER INSTITUTE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY APRIL 19 TH, 2018 Objectives Basic Cancer Statistics Discuss
GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer KRISTEN STARBUCK, MD ROSWELL PARK CANCER INSTITUTE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY APRIL 19 TH, 2018 Objectives Basic Cancer Statistics Discuss
OVARIAN CANCER Updates in Screening, Early Detection and Prevention
 UW MEDICINE SUSAN PATRICIA TECK MEMORIAL LECTURE October 2017 OVARIAN CANCER Updates in Screening, Early Detection and Prevention BARBARA GOFF, MD Seattle Gynecologic Society March 2018 OVARIAN CANCER
UW MEDICINE SUSAN PATRICIA TECK MEMORIAL LECTURE October 2017 OVARIAN CANCER Updates in Screening, Early Detection and Prevention BARBARA GOFF, MD Seattle Gynecologic Society March 2018 OVARIAN CANCER
Partners: Introductions: Dr. Carolyn Johnston Deanna Cosens & Ann Garvin. Ovarian Cancer and Primary Care July 16, :00 9:00am EST 7/16/2014
 Welcome To The Webinar Technical Support Ovarian Cancer and Primary Care July 16, 2014 8:00 9:00am EST In order to hear the presentation please call 1 (626) 544-0058, access code 167-314-644, followed
Welcome To The Webinar Technical Support Ovarian Cancer and Primary Care July 16, 2014 8:00 9:00am EST In order to hear the presentation please call 1 (626) 544-0058, access code 167-314-644, followed
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Optimizing First Line Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer
 Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Optimizing First Line Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer Ira R. Horowitz, MD, SM, FACOG, FACS John D. Thompson Professor and Chairman Department of Gynecology
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Optimizing First Line Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer Ira R. Horowitz, MD, SM, FACOG, FACS John D. Thompson Professor and Chairman Department of Gynecology
LAPAROSCOPY and OVARIAN CANCER
 LAPAROSCOPY and OVARIAN CANCER J. DAUPLAT Clermont-Ferrand France UNIVERSITÉ D'AUVERGNE CLERMONT 1 1 - PROPHYLACTIC OOPHORECTOMY 2 - DIAGNOSIS 3 - EARLY STAGES : STAGING 4 - ADVANCED STAGES - ASSESSMENT
LAPAROSCOPY and OVARIAN CANCER J. DAUPLAT Clermont-Ferrand France UNIVERSITÉ D'AUVERGNE CLERMONT 1 1 - PROPHYLACTIC OOPHORECTOMY 2 - DIAGNOSIS 3 - EARLY STAGES : STAGING 4 - ADVANCED STAGES - ASSESSMENT
BRCA mutation carrier patient: How to manage?
 BRCA mutation carrier patient: How to manage? Clinical Case Presentation Katarzyna Sosińska-Mielcarek Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy University Clinical Center Gdansk, Poland esmo.org DISCLOSURE
BRCA mutation carrier patient: How to manage? Clinical Case Presentation Katarzyna Sosińska-Mielcarek Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy University Clinical Center Gdansk, Poland esmo.org DISCLOSURE
Is It Time To Implement Ovarian Cancer Screening?
 Is It Time To Implement Ovarian Cancer Screening? Prof Dr Samet Topuz Istanbul Medıcal Faculty Department Of Obstetrics and Gynecology ESGO Prevention in Gynaecological Malignancies September 08 2016 Antalya
Is It Time To Implement Ovarian Cancer Screening? Prof Dr Samet Topuz Istanbul Medıcal Faculty Department Of Obstetrics and Gynecology ESGO Prevention in Gynaecological Malignancies September 08 2016 Antalya
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer 8/2/2013. Tu-be or Not Tu-be: Is the Fallopian Tube the Source of Ovarian Cancer?
 Tu-be or Not Tu-be: Is the Fallopian Tube the Source of Ovarian Cancer? Ann E. Smith Sehdev, MD Director, Center for Gynecologic Pathology Cascade Pathology, Portland, Oregon Ann E. Smith Sehdev has no
Tu-be or Not Tu-be: Is the Fallopian Tube the Source of Ovarian Cancer? Ann E. Smith Sehdev, MD Director, Center for Gynecologic Pathology Cascade Pathology, Portland, Oregon Ann E. Smith Sehdev has no
4:00 into mp3 file Huang_342831_5_v1.mp3
 Support for Yale Cancer Answers comes from AstraZeneca, providing important treatment options for women living with advanced ovarian cancer. Learn more at astrazeneca-us.com. Welcome to Yale Cancer Answers
Support for Yale Cancer Answers comes from AstraZeneca, providing important treatment options for women living with advanced ovarian cancer. Learn more at astrazeneca-us.com. Welcome to Yale Cancer Answers
Screening and prevention of ovarian cancer
 Chapter 2 Screening and prevention of ovarian cancer Prevention of ovarian carcinoma Oral contraceptive pills Use of oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) has been associated with a significant reduction in
Chapter 2 Screening and prevention of ovarian cancer Prevention of ovarian carcinoma Oral contraceptive pills Use of oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) has been associated with a significant reduction in
Inherited Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Prevention
 Inherited Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Prevention Dr. Jacob Korach - Deputy director Gynecologic Oncology (past chair - Israeli Society of Gynecologic Oncology) Prof. Eitan Friedman - Head, Oncogenetics
Inherited Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Prevention Dr. Jacob Korach - Deputy director Gynecologic Oncology (past chair - Israeli Society of Gynecologic Oncology) Prof. Eitan Friedman - Head, Oncogenetics
Practice of Medicine-1 Ovarian Cancer Clinical Correlation
 Practice of Medicine-1 Ovarian Cancer Clinical Correlation Amir A. Jazaeri, M.D. Assistant Professor, Division of Gynecologic Oncology American Cancer Society Female Cancers 2000 Statistics Reprinted by
Practice of Medicine-1 Ovarian Cancer Clinical Correlation Amir A. Jazaeri, M.D. Assistant Professor, Division of Gynecologic Oncology American Cancer Society Female Cancers 2000 Statistics Reprinted by
Case Scenario 1. Pathology report Specimen from mediastinoscopy Final Diagnosis : Metastatic small cell carcinoma with residual lymphatic tissue
 Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Hitting the High Points Gynecologic Oncology Review
 Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125. Learning Outcomes
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
 Epithelial Ovarian Cancer GYNE/ONC Practice Guideline Dr. Alex Hammond Dr. Ian Kerr Dr. Akira Sugimoto Dr. Stephen Welch Kay Faroni Christine Gawlik Kerri Thornton Approval Date: This guideline is a statement
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer GYNE/ONC Practice Guideline Dr. Alex Hammond Dr. Ian Kerr Dr. Akira Sugimoto Dr. Stephen Welch Kay Faroni Christine Gawlik Kerri Thornton Approval Date: This guideline is a statement
Biology Response Controversies and Advances
 Biology Response Controversies and Advances in BRCA related ovarian cancer Lessons learned and future directions Michael Friedlander The Prince of Wales Hospital and Royal Hospital for Women Sydney BREAST-CANCER
Biology Response Controversies and Advances in BRCA related ovarian cancer Lessons learned and future directions Michael Friedlander The Prince of Wales Hospital and Royal Hospital for Women Sydney BREAST-CANCER
Key Recommendations. Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer
 Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program Lead, Kaiser Permanente Northern California
Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program Lead, Kaiser Permanente Northern California
Interpretation of p53 Immunostains. P53 Mutations are Ubiquitous in High Grade Serous Carcinoma. Diffuse strong positive nuclear staining
 Stains for Tumor Classification p53 p16 WT1 HMGA2 P53 Mutations are Ubiquitous in High Grade Serous Carcinoma Source Ahmed et al Australian Ovarian Cancer Study Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Cases
Stains for Tumor Classification p53 p16 WT1 HMGA2 P53 Mutations are Ubiquitous in High Grade Serous Carcinoma Source Ahmed et al Australian Ovarian Cancer Study Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Cases
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Speaker Disclosure: Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine. Controversies in Women s Health
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer
 What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
Key Recommendations. Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer. HBOC related genes. I have nothing to disclose
 Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program I have nothing to disclose Key Recommendations
Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program I have nothing to disclose Key Recommendations
patient education Fact Sheet
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
Disclosure. Objectives
 Charles A. Leath, III, MD, MSPH Associate Professor University of Alabama at Birmingham Disclosure I have no potential financial or other conflicts of interest. The view(s) expressed herein are those of
Charles A. Leath, III, MD, MSPH Associate Professor University of Alabama at Birmingham Disclosure I have no potential financial or other conflicts of interest. The view(s) expressed herein are those of
CA125 in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: the art in medicine
 CA125 in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: the art in medicine Dr Marcia Hall Consultant Medical Oncology Mount Vernon Cancer Centre Hillingdon Hospital Wexham Park Hospital Epidemiology Ovarian cancer
CA125 in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: the art in medicine Dr Marcia Hall Consultant Medical Oncology Mount Vernon Cancer Centre Hillingdon Hospital Wexham Park Hospital Epidemiology Ovarian cancer
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine. Speaker Disclosure:
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
MPH Quiz. 1. How many primaries are present based on this pathology report? 2. What rule is this based on?
 MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
Ovarian Cancer. Disclosure. Ovarian Statistics Educational Objectives. The State of Ovarian Care in the US Why aren t we making more progress?
 Esteemed Physician Humanitarian Distinguished Citizen Disclosure Ovarian Cancer The State of Ovarian Care in the US Why aren t we making more progress? Dr. Goff has indicated that she has no relevant financial
Esteemed Physician Humanitarian Distinguished Citizen Disclosure Ovarian Cancer The State of Ovarian Care in the US Why aren t we making more progress? Dr. Goff has indicated that she has no relevant financial
Updates in Gynecologic Oncology. Todd Boren, MD Gynecologic Oncologist Chattanooga s Program in Women s Oncology Sept 8 th, 2018
 Updates in Gynecologic Oncology Todd Boren, MD Gynecologic Oncologist Chattanooga s Program in Women s Oncology Sept 8 th, 2018 COI I have no conflict of interest to report Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors
Updates in Gynecologic Oncology Todd Boren, MD Gynecologic Oncologist Chattanooga s Program in Women s Oncology Sept 8 th, 2018 COI I have no conflict of interest to report Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors
Ask the Experts Obstetrics & Gynecology
 1 Management of the Adnexal Mass James H. Liu, MD, and Kristine M. Zanotti, MD June 2011 Volume 117 Issue 6 Pages 1413 28 Click Here to Read the Full Article Questions written by: Rini Banerjee Ratan,
1 Management of the Adnexal Mass James H. Liu, MD, and Kristine M. Zanotti, MD June 2011 Volume 117 Issue 6 Pages 1413 28 Click Here to Read the Full Article Questions written by: Rini Banerjee Ratan,
Chapter 2: Initial treatment for endometrial cancer (including histologic variant type)
 Chapter 2: Initial treatment for endometrial cancer (including histologic variant type) CQ01 Which surgical techniques for hysterectomy are recommended for patients considered to be stage I preoperatively?
Chapter 2: Initial treatment for endometrial cancer (including histologic variant type) CQ01 Which surgical techniques for hysterectomy are recommended for patients considered to be stage I preoperatively?
Been Diagnosed with Ovarian Cancer, Now What?
 Been Diagnosed with Ovarian Cancer, Now What? Teresa P. Díaz-Montes, MD, MPH, FACOG Associate Director, Lya Segall Ovarian Cancer Institute Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, MD Ovarian Cancer Statistics:
Been Diagnosed with Ovarian Cancer, Now What? Teresa P. Díaz-Montes, MD, MPH, FACOG Associate Director, Lya Segall Ovarian Cancer Institute Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, MD Ovarian Cancer Statistics:
BSO, HRT, and ERT. No relevant financial disclosures
 BSO, HRT, and ERT Jubilee Brown, MD Professor & Associate Director, Gynecologic Oncology Levine Cancer Institute at the Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, North Carolina No relevant financial disclosures
BSO, HRT, and ERT Jubilee Brown, MD Professor & Associate Director, Gynecologic Oncology Levine Cancer Institute at the Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, North Carolina No relevant financial disclosures
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer 15 Years of Progress
 Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer 15 Years of Progress Bethan Powell, M. D. Kaiser Permanente UCSF Gynecologic Cancer Risk Program Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer Syndromes BRCA 1 and 2: ovarian Lynch: ovarian/endometrial
Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer 15 Years of Progress Bethan Powell, M. D. Kaiser Permanente UCSF Gynecologic Cancer Risk Program Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer Syndromes BRCA 1 and 2: ovarian Lynch: ovarian/endometrial
Tumori eredofamiliari: sorveglianza di donne ad alto rischio
 Tumori eredofamiliari: sorveglianza di donne ad alto rischio 14/01/2018 Dott Matteo Generali AUSL Modena Carpi U.O. Ostetricia e Ginecologia Screening for gynaecologic cancer in genetically predisposed
Tumori eredofamiliari: sorveglianza di donne ad alto rischio 14/01/2018 Dott Matteo Generali AUSL Modena Carpi U.O. Ostetricia e Ginecologia Screening for gynaecologic cancer in genetically predisposed
Adnexal Mass Management: Risk Stratification and Management Practice for Best Patient Outcomes
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Gynecologic Oncologist. Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Hormonal Therapy Immunotherapy. Cervical cancer
 Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment
 Introduction Epithelial ovarian cancer continues to be the leading cause of death from gynecologic malignancies in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 1999, 25,200 new cases
Introduction Epithelial ovarian cancer continues to be the leading cause of death from gynecologic malignancies in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 1999, 25,200 new cases
Triage of Ovarian Masses. Andreas Obermair Brisbane
 Triage of Ovarian Masses Andreas Obermair Brisbane Why Triage? In ovarian cancer, best outcomes for patients can be achieved when patients are treated in tertiary centres by a multidisciplinary team led
Triage of Ovarian Masses Andreas Obermair Brisbane Why Triage? In ovarian cancer, best outcomes for patients can be achieved when patients are treated in tertiary centres by a multidisciplinary team led
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
 Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Endometrial Cancer. Incidence. Types 3/25/2019
 Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives
 Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Current Concept in Ovarian
Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Current Concept in Ovarian
OVARIAN CARCINOMA Immune Therapy. Antibodies to CA-125 (Ovarex) Vaccine therapy
 OVARIAN CARCINOMA Immune Therapy Antibodies to CA-125 (Ovarex) Vaccine therapy OVARIAN CARCINOMA Targeted Therapy Bevacizumab (Avastin): GOG- 218 Anti-VEGF, angiogenesis inhibitor TLK 286 (Telcyta): Glutathione
OVARIAN CARCINOMA Immune Therapy Antibodies to CA-125 (Ovarex) Vaccine therapy OVARIAN CARCINOMA Targeted Therapy Bevacizumab (Avastin): GOG- 218 Anti-VEGF, angiogenesis inhibitor TLK 286 (Telcyta): Glutathione
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): October 1, 2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): May 20, 2014 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT
Original Issue Date (Created): October 1, 2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): May 20, 2014 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT
This policy is applicable to Commercial Products only. For BlueCHiP for Medicare, see Related Policy section.
 Medical Coverage Policy Multimarker Serum Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer EFFECTIVE DATE: 10 01 2015 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 04 17 2018 OVERVIEW This policy documents the coverage determination for Multimarker
Medical Coverage Policy Multimarker Serum Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer EFFECTIVE DATE: 10 01 2015 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 04 17 2018 OVERVIEW This policy documents the coverage determination for Multimarker
Camelia Davtyan, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine Director of Women s Health UCLA Comprehensive Health Program
 Camelia Davtyan, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine Director of Women s Health UCLA Comprehensive Health Program A B C D USPSTF recommends the service. There is high certainty that Offer or provide
Camelia Davtyan, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine Director of Women s Health UCLA Comprehensive Health Program A B C D USPSTF recommends the service. There is high certainty that Offer or provide
THE MODERN GYNECOLOGIC EXAMINATION & SCREENING FOR GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
 THE MODERN GYNECOLOGIC EXAMINATION & SCREENING FOR GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Denise Uyar, MD Associate Professor OB/GYN Chief Gynecologic Oncology Medical College of Wisconsin April 12, 2019 NO DISCLOSURES
THE MODERN GYNECOLOGIC EXAMINATION & SCREENING FOR GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Denise Uyar, MD Associate Professor OB/GYN Chief Gynecologic Oncology Medical College of Wisconsin April 12, 2019 NO DISCLOSURES
Focus on... Ovarian cancer. HE4 & ROMA score
 Focus on... Ovarian cancer HE4 & ROMA score Ovarian cancer in the world* Accounting for around 4% of all cancers diagnosed in women The estimated World age-standardised incidence rate for the more developed
Focus on... Ovarian cancer HE4 & ROMA score Ovarian cancer in the world* Accounting for around 4% of all cancers diagnosed in women The estimated World age-standardised incidence rate for the more developed
Cancer arising from Endometriosis and Its Clinical implications
 Cancer arising from Endometriosis and Its Clinical implications 1) Nezhat F, Cohen C, Rahaman J, Gretz H, Cole P, Kalir T. Comparative immunohistochemical studies of bcl-2 and p53 proteins in benign
Cancer arising from Endometriosis and Its Clinical implications 1) Nezhat F, Cohen C, Rahaman J, Gretz H, Cole P, Kalir T. Comparative immunohistochemical studies of bcl-2 and p53 proteins in benign
Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer: 20 Years of Progress and Future Directions
 Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer: 20 Years of Progress and Future Directions Noah D. Kauff, MD, FACOG Director, Clinical Cancer Genetics Duke Cancer Institute / Duke University Health System Disclosures
Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer: 20 Years of Progress and Future Directions Noah D. Kauff, MD, FACOG Director, Clinical Cancer Genetics Duke Cancer Institute / Duke University Health System Disclosures
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Public Statement: Medical Policy Statement: Limits: Medical Policy Title: OVA1, Detection of Ovarian Cancer. ARBenefits Approval: 10/26/2011
 ARBenefits Approval: 10/26/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: 08/21/2013 Medical Policy Title: OVA1, Detection of Ovarian Cancer Document: ARB0295:02 Administered by: Public Statement: The
ARBenefits Approval: 10/26/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: 08/21/2013 Medical Policy Title: OVA1, Detection of Ovarian Cancer Document: ARB0295:02 Administered by: Public Statement: The
Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN
 Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN Adenocarcinomas of the endometrium Most common gynecologic malignancy in developed countries Second most common in developing countries. Adenocarcinomas, grade 1 and 2 endometrioid
Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN Adenocarcinomas of the endometrium Most common gynecologic malignancy in developed countries Second most common in developing countries. Adenocarcinomas, grade 1 and 2 endometrioid
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer. Information for Women at Increased Risk
 Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
Adnexal Masses in Menopausal Women Surgery or Surveillance?
 Adnexal Masses in Menopausal Women Surgery or Surveillance? FREDTALK IDEASWORTHSPREADING Disclosure I am a member of Vermillion s Speakers Bureau I am NOT a paid consultant for Vermillion Inc. nor do I
Adnexal Masses in Menopausal Women Surgery or Surveillance? FREDTALK IDEASWORTHSPREADING Disclosure I am a member of Vermillion s Speakers Bureau I am NOT a paid consultant for Vermillion Inc. nor do I
Christine Garcia, MD 1, Liisa Lyon, MS 2, Ramey D. Littell, MD 1 and C. Bethan Powell, MD 1
 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Comparison of risk management strategies between women positive for a BRCA variant of unknown significance and women with known BRCA deleterious mutations
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Comparison of risk management strategies between women positive for a BRCA variant of unknown significance and women with known BRCA deleterious mutations
Management of Endometrial Hyperplasia
 Management of Endometrial Hyperplasia I have nothing to disclose. Stefanie M. Ueda, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Division of Gynecologic Oncology Female Malignancies in the United States New
Management of Endometrial Hyperplasia I have nothing to disclose. Stefanie M. Ueda, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Division of Gynecologic Oncology Female Malignancies in the United States New
Clinical guideline Published: 27 April 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg122
 Ovarian cancer: recognition and initial management Clinical guideline Published: 27 April 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg122 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Ovarian cancer: recognition and initial management Clinical guideline Published: 27 April 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg122 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Significance of Ovarian Endometriosis on the Prognosis of Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma
 ORIGINAL STUDY Significance of Ovarian Endometriosis on the Prognosis of Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Jeong-Yeol Park, MD, PhD, Dae-Yeon Kim, MD, PhD, Dae-Shik Suh, MD, PhD, Jong-Hyeok Kim, MD, PhD, Yong-Man
ORIGINAL STUDY Significance of Ovarian Endometriosis on the Prognosis of Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Jeong-Yeol Park, MD, PhD, Dae-Yeon Kim, MD, PhD, Dae-Shik Suh, MD, PhD, Jong-Hyeok Kim, MD, PhD, Yong-Man
--- or not, and do we need to come up with newer strategies for ovarian cancer screening.
 My name is Dr. Karen Lu and I am a Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I also serve as Co-Medical Director for Clinical Cancer Genetics. I m going to
My name is Dr. Karen Lu and I am a Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I also serve as Co-Medical Director for Clinical Cancer Genetics. I m going to
Case Scenario 1. 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain.
 Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Management of BRCA mutation carriers
 Management of BRCA mutation carriers Clinical Case Presentation Shani Paluch-Shimon, MBBS, MSc Head, Breast Cancer Service for Young Women Oncology Institute Sheba Medical Center, Israel esmo.org DISCLOSURES
Management of BRCA mutation carriers Clinical Case Presentation Shani Paluch-Shimon, MBBS, MSc Head, Breast Cancer Service for Young Women Oncology Institute Sheba Medical Center, Israel esmo.org DISCLOSURES
6 Week Course Agenda. Today s Agenda. Ovarian Cancer: Risk Factors. Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention
 6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
General history. Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted: Married status : Married
 General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Cancer of the Ovary
 North of Scotland Cancer Network Cancer of the Ovary Based on WOSCAN CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by NOSCAN Gynaecology Cancer
North of Scotland Cancer Network Cancer of the Ovary Based on WOSCAN CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by NOSCAN Gynaecology Cancer
Opportunistic Risk Reduction Salpingectomy and Ovarian Cancer
 Opportunistic Risk Reduction Salpingectomy and Ovarian Cancer G. Kevin Donovan, MD, MA Kevin FitzGerald, SJ, Ph.D., Ph.D. Daniel Sulmasy, MD, Ph.D. Ovarian cancer has the highest mortality rate of all
Opportunistic Risk Reduction Salpingectomy and Ovarian Cancer G. Kevin Donovan, MD, MA Kevin FitzGerald, SJ, Ph.D., Ph.D. Daniel Sulmasy, MD, Ph.D. Ovarian cancer has the highest mortality rate of all
Serous Tubal Intraepithelial Carcinoma in a Japanese Woman with a Deleterious BRCA1 Mutation
 Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology Advance Access published April 9, 2014 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2014 doi:10.1093/jjco/hyu035 Case Report Serous Tubal Intraepithelial Carcinoma in a Japanese Woman with a
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology Advance Access published April 9, 2014 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2014 doi:10.1093/jjco/hyu035 Case Report Serous Tubal Intraepithelial Carcinoma in a Japanese Woman with a
Case 1. Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno
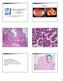 Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes
 Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy. Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine
 Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine Adnexal Mass: Gyn Etiologies Uterine Leiomyomas Pregnancy Malignancy Tubal Pregnancy
Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine Adnexal Mass: Gyn Etiologies Uterine Leiomyomas Pregnancy Malignancy Tubal Pregnancy
Ovarian Cancer. Georgia McCann, MD. Division of Gynecologic Oncology
 Ovarian Cancer Georgia McCann, MD Division of Gynecologic Oncology Myth: Ovarian cancer is a silent killer Non-specific Abdominal pain, discomfort Bloating, back pain Urinary urgency Constipation Tiredness
Ovarian Cancer Georgia McCann, MD Division of Gynecologic Oncology Myth: Ovarian cancer is a silent killer Non-specific Abdominal pain, discomfort Bloating, back pain Urinary urgency Constipation Tiredness
Diagnosi, inquadramento clinico e chirurgia
 Tumori germinali, stromali e forme rare : stato dell arte, novità e prospettive Caravaggio 10-12 giugno 2010 Giorgia Mangili IRCCS San Raffaele Milano Diagnosi, inquadramento clinico e chirurgia SEX-CORD
Tumori germinali, stromali e forme rare : stato dell arte, novità e prospettive Caravaggio 10-12 giugno 2010 Giorgia Mangili IRCCS San Raffaele Milano Diagnosi, inquadramento clinico e chirurgia SEX-CORD
Both type I and type II tumors develop from extraovarian tissue that implants on the ovary. Both for LGSC and HGSC, the fallopian tube appears to be
 Recent studies have led to the development of a new paradigm for the pathogenesis and origin of EOC, based on a dualistic model of carcinogenesis that divides EOC into 2 broad categories designated types
Recent studies have led to the development of a new paradigm for the pathogenesis and origin of EOC, based on a dualistic model of carcinogenesis that divides EOC into 2 broad categories designated types
Case Scenario 1. 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain.
 Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Menopause and Cancer risk; What to do overcome the risks? Fatih DURMUŞOĞLU,M.D
 Menopause and Cancer risk; What to do overcome the risks? Fatih DURMUŞOĞLU,M.D Menopause and Cancer How does menopause affect a woman s cancer risk? Ø Menopause does not cause cancer.but risk of developing
Menopause and Cancer risk; What to do overcome the risks? Fatih DURMUŞOĞLU,M.D Menopause and Cancer How does menopause affect a woman s cancer risk? Ø Menopause does not cause cancer.but risk of developing
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
FAQ-Protocol 3. BRCA mutation carrier guidelines Frequently asked questions
 ULast updated: 09/02/2015 Protocol 3 BRCA mutation carrier guidelines Frequently asked questions UQ: How accurate are the remaining lifetime and 5 year breast cancer risks in the table? These figures are
ULast updated: 09/02/2015 Protocol 3 BRCA mutation carrier guidelines Frequently asked questions UQ: How accurate are the remaining lifetime and 5 year breast cancer risks in the table? These figures are
IMMATURE TERATOMA: SURGICAL TREATMENT
 CARAVAGGIO 10-12 MAGGIO 2010 IMMATURE TERATOMA: SURGICAL TREATMENT G. Mangili, E. Garavaglia, C. Sigismondi R VIGANO Dipartimento Materno Infantile, UF Ginecologia Oncologica IRCCS San Raffaele Milano
CARAVAGGIO 10-12 MAGGIO 2010 IMMATURE TERATOMA: SURGICAL TREATMENT G. Mangili, E. Garavaglia, C. Sigismondi R VIGANO Dipartimento Materno Infantile, UF Ginecologia Oncologica IRCCS San Raffaele Milano
NATIONAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT OVARIAN CYSTS IN POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN
 NATIONAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT OF OVARIAN CYSTS IN POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN Institute of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, Royal College of Physicians of Ireland and the Clinical
NATIONAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT OF OVARIAN CYSTS IN POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN Institute of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, Royal College of Physicians of Ireland and the Clinical
Disclosure. Gynecologic Cancer Genetics. Audience response. Audience response. What was the result? 47%
 Disclosure Cancer Genetics I have served as a moderator for an advisory board to Genentech Lee-may Chen, M.D. Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, & Reproductive Sciences UCSF Obstetrics and
Disclosure Cancer Genetics I have served as a moderator for an advisory board to Genentech Lee-may Chen, M.D. Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, & Reproductive Sciences UCSF Obstetrics and
Uterine Morcellation: Teasing Out the Issues
 Uterine Morcellation: Teasing Out the Issues Stacey A. Scheib, MD, FACOG Director, Minimally Invasive Gynecology Director, Hopkins Multidisciplinary Fibroid Center Johns Hopkins Hospital Disclosures I
Uterine Morcellation: Teasing Out the Issues Stacey A. Scheib, MD, FACOG Director, Minimally Invasive Gynecology Director, Hopkins Multidisciplinary Fibroid Center Johns Hopkins Hospital Disclosures I
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust
 Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
Policy #: 259 Latest Review Date: November 2009
 Name of Policy: Prophylactic Oophorectomy Policy #: 259 Latest Review Date: November 2009 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates.
Name of Policy: Prophylactic Oophorectomy Policy #: 259 Latest Review Date: November 2009 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates.
Newton Wellesley Hospital 2013
 Newton Wellesley Hospital 20 Standard 4.6 Assessment and Evaluation of Treatment Planning Endometrial Cancer Each year a physician member of the cancer committee conducts a study to ensure that diagnostic
Newton Wellesley Hospital 20 Standard 4.6 Assessment and Evaluation of Treatment Planning Endometrial Cancer Each year a physician member of the cancer committee conducts a study to ensure that diagnostic
So, Who are the appropriate individuals that should consider genetic counseling and genetic testing?
 Hello, I m Banu Arun, Professor of Breast Medical Oncology and Co-Director of Clinical Cancer Genetics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Today I will be discussing with you Hereditary
Hello, I m Banu Arun, Professor of Breast Medical Oncology and Co-Director of Clinical Cancer Genetics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Today I will be discussing with you Hereditary
Protocol. Multimarker Serum Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer
 Protocol Multimarker Serum Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer (20462) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 01/11, 01/12, 01/13, 01/14, 01/15,
Protocol Multimarker Serum Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer (20462) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 01/11, 01/12, 01/13, 01/14, 01/15,
Chronic Pelvic Pain. Bridget Kamen, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology, Confluence Health. I have no disclosures
 Chronic Pelvic Pain Bridget Kamen, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology, Confluence Health I have no disclosures Objectives A little epidemiology Understand there are both gynecologic and non-gynecologic causes
Chronic Pelvic Pain Bridget Kamen, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology, Confluence Health I have no disclosures Objectives A little epidemiology Understand there are both gynecologic and non-gynecologic causes
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
 Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Utilization of BRCA Testing. Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Texas
 Utilization of BRCA Testing in Older Ode Women with Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Texas Ana M. Rodriguez, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Texas Medical Branch
Utilization of BRCA Testing in Older Ode Women with Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Texas Ana M. Rodriguez, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Texas Medical Branch
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Proteomics-based Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: proteomics_based_testing_related_to_ovarian_cancer 7/2010
Corporate Medical Policy Proteomics-based Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: proteomics_based_testing_related_to_ovarian_cancer 7/2010
HBOC Syndrome A review of BRCA 1/2 testing, Cancer Risk Assessment, Counseling and Beyond.
 HBOC Syndrome A review of BRCA 1/2 testing, Cancer Risk Assessment, Counseling and Beyond. Conni Murphy, ARNP Cancer Risk Assessment and Genetics Program Jupiter Medical Center Learning Objectives Identify
HBOC Syndrome A review of BRCA 1/2 testing, Cancer Risk Assessment, Counseling and Beyond. Conni Murphy, ARNP Cancer Risk Assessment and Genetics Program Jupiter Medical Center Learning Objectives Identify
What is the gynecologist s role in the care of BRCA previvors?
 What is the gynecologist s role in the care of BRCA previvors? Here, your patient s options for surgery and your best options for her follow-up care and ongoing surveillance OBG Manag. Sept 2013;25(9):10-14.
What is the gynecologist s role in the care of BRCA previvors? Here, your patient s options for surgery and your best options for her follow-up care and ongoing surveillance OBG Manag. Sept 2013;25(9):10-14.
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
FDG-PET/CT in Gynaecologic Cancers
 Friday, August 31, 2012 Session 6, 9:00-9:30 FDG-PET/CT in Gynaecologic Cancers (Uterine) cervical cancer Endometrial cancer & Uterine sarcomas Ovarian cancer Little mermaid (Edvard Eriksen 1913) honoring
Friday, August 31, 2012 Session 6, 9:00-9:30 FDG-PET/CT in Gynaecologic Cancers (Uterine) cervical cancer Endometrial cancer & Uterine sarcomas Ovarian cancer Little mermaid (Edvard Eriksen 1913) honoring
10/24/14. Grand Rounds in Ovarian Cancer: Standards of Care and Novel Treatment Approaches. Disclosure. Learning Objectives
 10/24/14 Grand Rounds in Ovarian Cancer: Standards of Care and Novel Treatment Approaches Jessica Gahres, PA-C Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Don S. Dizon, MD Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer
10/24/14 Grand Rounds in Ovarian Cancer: Standards of Care and Novel Treatment Approaches Jessica Gahres, PA-C Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Don S. Dizon, MD Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer
David Nunns on behalf of the Gynae Guidelines Group Date:
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Borderline tumours of the ovary management and follow-up Author: Contact Name and Job Title Directorate & Speciality
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Borderline tumours of the ovary management and follow-up Author: Contact Name and Job Title Directorate & Speciality
Current state of upfront treatment for newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer
 Current state of upfront treatment for newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer Ursula Matulonis, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine, HMS Program Leader, Medical Gyn Oncology Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Current state of upfront treatment for newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer Ursula Matulonis, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine, HMS Program Leader, Medical Gyn Oncology Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
