Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in vitro
|
|
|
- Scott Doyle
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Radiat Environ Biophys (1986) 25: Radiation and Environmental Biophysics Springer-Verlag 1986 Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in vitro W.-U. Mfiller and C. Streffer Institut fiir Medizinische Strahlenphysik und Strahlenbiologie, Universit/itsklinikum Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, D-4300 Essen 1, Federal Republic of Germany Received April 4, 1986 / Accepted April 24, 1986 Summary. Two-cell mouse embryos were X-irradiated (2 Gy) in vitro. Comparison of the frequency of micronuclei in the early interphase of the four-cell stage with that in the late interphase revealed a small, but significant loss of micronuclei during interphase: 27.9 versus 23.4 micro:. nuclei per 100 cells. Introduction Micronuclei are small DNA-positive particles in the cytoplasm which arise from the main nucleus. They can be formed by various processes. After ionizing radiation, the presumably most important one is by formation of acentric fragments, which cannot be distributed to the daughter nuclei because of a lacking centromere (Heddle and Carrano 1977). Micronuclei are also to be expected, if the centromere is present, but damaged (Brenner 1980), or if the spindle apparatus is not working properly (Yamamoto and Kikuchi 1980). All three mechanisms have in common the requirement of a mitosis between induction and expression of micronuclei. However, there are processes that might result in micronuclei without the necessity of a mitosis: after comparatively high doses of ionizing radiation (about 5 to 10 Gy) the formation of nuclear 'buds' has been reported (Wen.dt 1959), which detach from the nucleus after some time and meet all criteria of a micronucleus. With even higher doses a fragmentation of the interphase nucleus (karyorhexis) can be observed. There are no data which allow a decision whether these are high dose phenomena only, or whether some sort of' limited' fragmentation of a cell nucleus during interphase is possible also after doses in the range of a few Gray. Thus, there is a chance of micronuclei being induced and expressed during the same interphase. On the other hand, micronuclei could get lost during interphase due to, for example, enzymatic degradation. Any excessive loss or formation
2 196 of micronuclei during interphase would have considerable implications for those experiments using micronucleus formation as an indicator of risk exerted by presumed harmful agents. Because in this case the time point of micronucleus determination within interphase would be crucial, in particular for those agents that cause a division delay. Therefore, we studied in which way the frequency of radiation-induced micronuclei changes during interphase. We did this by comparing the number of micronuclei shortly after mitosis with the number shortly before the next mitosis, that is early and late in one and the same interphase. Mouse embryos of the two- and four-cell stage were used as in vitro test system. Mouse embryos develop rather synchronously between the oneand eight-cell stage (Streffer et al. 1980; Molls et al. 1983), so that no manipulations are required for achieving synchronism. Obviously, a synchronous cell population is of great advantage for the type of study outlined above. An additional advantage is the in vitro technique which allows the direct observation of development under a microscope. After induction of micronuclei by X-rays, we found a small, but statistically significant loss of micronuclei during interphase. Materials and methods Details of isolation, culture, and X-irradiation of embryos have been published elsewhere (Mfiller and Streffer 1984). Briefly, two-cell mouse embryos of the G2-phase were isolated about 30 h after conception, irradiated with X-rays (2 Gy) about two hours before mitosis, and checked for development to the four-cell stage every two hours. Four-cell embryos were collected and split up into two groups; one of these groups was analyzed for the number of micronuclei immediately, the other one was allowed to develop close to the mitosis to the eight-cell stage and analyzed then for the number of micronuclei. Micronuclei were determined using the fixation technique of Tarkowski (1966). The embryos were treated with 1% sodium citrate solution for about 1 rain, transferred to a glass slide, and spread by the addition of about 10 gl of fixative solution (acetic acid and ethanol 1 : 3). All particles with the following properties were counted as micronuclei: 1. stainable with ethidium bromide (detected by fluorescence at 530 nm); 2, round-shaped with distinct boundaries; 3. diameter between 5 and 20% that of the main nucleus. Results and discussion An essential point of the experimental design is, that the early group, which is tested for micronuclei, should be separated by an interval as long as possible from the late group; any change in the number of micronuclei should then best be seen. In vitro, the cell cycle of the four-cell stage lasts about twelve hours (Streffer et al. 1980). Taking into account a duration of about two hours for mitosis results in an interval of ten hours for the
3 interphase. However, there were two problems related to synchronism, which prevented a separation of early and late group by ten hours. On the one hand, synchronism between the embryos got worse as a consequence of the radiation event. Whereas more than 80% of the control embryos entered the four-cell stage within two to three hours, it took irradiated embryos more than ten hours. This problem was easily overcome by collecting the four-cell embryos every second hour. However, there was a certain chance that a four-cell embryo was formed immediately after observation. Therefore, the interval between early and late group had to be shortened by two hours to eight hours. On the other hand, and this problem was much more serious, synchronism within one and the same embryo deteriorated. It is well known that one of the earliest indications of differentiation is a slightly faster development of one of the two cells of the two-cell embryo (Kelly et al. 1978), so that also in controls three-cell embryos are observed for a short time (generally less than one hour). This difference in developmental speed was increased by irradiation for a considerable number of embryos. That is, many of the irradiated embryos remained as three-cell embryos for two to three hours. Thus, two of the cells were already for two to three hours in the interphase of the four-cell stage, when the other two cells entered this stage. Consequently, in order to avoid that two of the cells of the four-cell embryo already started mitosis at the time of micronucleus analysis in the late group, the time of the formation of the three-cell embryo was important and not the time of the formation of the four-cell embryo. Or, using a time of two hours for the duration of the three-cell stage, we could separate early and late group by an interval of six hours, without running into risk that some of the cells already had left the interphase of the four-cell stage. Thus, the final experimental approach looked as follows: Two-cell mouse embryos were X-irradiated in vitro (2 Gy; this dose only delays the formation of four-, eight- and sixteen-cell embryos, but does not prevent their formation); four-cell embryos were collected shortly (at most two hours) after mitosis, and partitioned into two groups; one of these groups was analyzed for the number of micronuclei immediately (early interphase), the other one six hours later (late interphase). Table 1 gives the results of six experiments performed in the way just outlined. Five of the six experiments reveal a lower frequency of micronuclei in late interphase compared with early interphase; only one experiment (no. 5) shows just the opposite. (If the totals reflect the true values, then the probability of an outcome like that of experiment 5 is greater than 0.05; thus, statistically there is no reason not to expect such a result in a series of experiments.) The summary of all six experiments points to a small, but significant loss of micronuclei during interphase: 27.9 micronuclei per 100 cells in early and 23.4 micronuclei per 100 cells in late interphase. This result does not completely rule out the possibility that micronuclei are induced and expressed within one and the same interphase, that is with- 197
4 198 Table 1. Micronucleus frequency in early and late interphase of the four-cell stage of mouse embryos after induction by X-rays (2 Gy) during two-cell stage. (95% confidence limits are quoted for the totals (Sachs 1984; p. 148). Figures in parentheses: Number of embryos evaluated. The frequency of micronuclei in controls is about 1 per 100 cells) Experiment Micronuclei per 100 cells Early interphase Late interphase (37) 25.8 (33) (66) 28.8 (53) (56) 17.5 (53) (42) 17.1 (38) (59) 29.5 (50) (57) 21.3 (61) Total 25.1 < 27.9 < 31.0 (317) 20.6 < 23.4 < 26.3 (288) (Difference between early and late interphase significant with P <0.05; (Sachs 1984; p. 152). Test compares two Poisson distributions) out the assistance of a mitosis: it could be that the loss of micronuclei is greater than estimated from the difference mentioned above, so that a potential production of micronuclei only during interphase is masked by this effect. However, preliminary experiments (unpublished) indicate that four-ceu embryos, which were X-irradiated (8 Gy) during Gl-phase, do not show micronuclei when examined in G2-phase of the same stage, that is without a mitosis between irradiation and examination. The experimental approach does not answer the question, whether there is a continuous loss of micronuclei or whether this loss is restricted to a certain time during interphase. This uncertainty prevents an extrapolation of the amount of loss per six hours (= time interval of the experiment) to the loss per ten hours (--actual length of the interphase of the four-cell stage); such an extrapolation requires a continuous loss. Thus, we did find a statistically significant loss of micronuclei during interphase of the four-cell mouse embryo; however, this loss was so small that a major confounding effect cannot be expected from this process in studies counting micronuclei at different times in one and the same interphase. However, care must be taken that counting is not performed in different interphases, because further mitoses may change the number of micronuclei due to premature chromosome condensation (Madle et al. 1976) and formation of additional micronuclei (Miiller and Streffer 1984). Acknowledgement. This work was supported by the Bundesministerium des Innern of the Federal Republic of Germany. References Brenner SL (1980) Laser microirradiation of kinetochores in mitotic PtK2 cells: chromatid separation and micronucleus formation. Cell Biophys 2:
5 Heddle JA, Carrano AV (1977) The DNA content of micronuclei induced in mouse bone marrow by ),-irradiation : Evidence that micronuclei arise from acentric chromosomal fragments. Mutat Res 44: Kelly SJ, Mulnard JG, Graham CF (1978) Cell division and cell allocation in early mouse development. J Embryol Exp Morphol 48:37-51 Madle S, Nowak J, Obe G (1976) Effects of inhibitors of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis on frequencies and types of premature chromosome condensation from X-ray induced micronuclei. Hum Genet 34: Molls M, Zamboglou N, Streffer C (1983) A comparison of the cell kinetics of pre-implantation mouse embryos from two different mouse strains. Cell Tissue Kinet 16: Mfiller W-U, Streffer C (1984) Distribution of micronuclei among single cells of pre-implantation mouse embryos after X-irradiation in vitro. Murat Res 125:65-70 Sachs L (1984) Angewandte Statistik. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, 6th Edn Streffer C, van Beuningen D, Molls M, Zamboglou N, Schulz S (1980) Kinetics of cell proliferation in the preimplanted mouse embryo in vivo and in vitro. Cell Tissue Kinet 13: Tarkowski AK (1966) An air-drying method for chromosome preparations from mouse eggs. Cytogenetics 5: 394~400 Wendt E (1959) Lebendbeobachtungen an bcstrahlten Interphasekernen. Z Zellforsch 49: Yamamoto KI, Kikuchi Y (1980) A comparison of diameters of micronuclei induced by clastogens and by spindle poisons. Murat Res 71 :
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
Name: Date: Block: 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet
 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
(i) List these events in the correct order, starting with D.... (1)... (1)... (1)
 Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
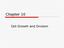 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS
 CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
5.1. KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 68 Reinforcement Unit 2 Resource Book
 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
The Cell Cycle. Materials 2 pipe cleaners of one color and 2 of another color Drawing paper
 The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
NOTES: Cell Growth and Division. centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis
 NOTES: 10.1 10.2 Cell Growth and Division centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg ~8 cm in diameter Average cell
NOTES: 10.1 10.2 Cell Growth and Division centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg ~8 cm in diameter Average cell
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
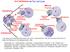 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Ploidy and Human Cell Types. Cell Cycle and Mitosis. DNA and Chromosomes. Where It All Began 11/19/2014. Chapter 12 Pg
 Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division.
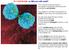 10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division. This relates to cell theory because this is HOW all cells come
10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division. This relates to cell theory because this is HOW all cells come
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Nucleus. centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis
 Nucleus VOCABULARY: chromatid centromere interphase cell cycle mitosis centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg
Nucleus VOCABULARY: chromatid centromere interphase cell cycle mitosis centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. A B C D ... (1) ... (1)
 1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle
 Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Cell Division Questions. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes
 Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Science 9- Mr. Klasz
 Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
A FORMULA TO PREDICT THE TRANSMISSION FREQUENCY OF ACENTRIC FRAGMENTS*
 A FORMULA TO PREDICT THE TRANSMISSION FREQUENCY OF ACENTRIC FRAGMENTS* A. V. CARRANO Laboratory of Radiobiology, University of California, San Francisco, California 94122 Manuscript received August 15,
A FORMULA TO PREDICT THE TRANSMISSION FREQUENCY OF ACENTRIC FRAGMENTS* A. V. CARRANO Laboratory of Radiobiology, University of California, San Francisco, California 94122 Manuscript received August 15,
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Meiosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS
 Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
The Cell Cycle, or Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle, or Cell Division The regular sequence of growth and division that eukaryotic somatic cells undergo is known as the cell cycle. Somatic cells multiply by dividing. This process allows living
The Cell Cycle, or Cell Division The regular sequence of growth and division that eukaryotic somatic cells undergo is known as the cell cycle. Somatic cells multiply by dividing. This process allows living
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother
 Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation
 B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
The Cell Cycle Guided Reading
 Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
Chromosomes & Cell Division
 Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase
 Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Genes and Proteins. Key points: The DNA must be copied and then divided exactly so that each cell gets an identical copy.
 Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1
 Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Connecting
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Overview of the CELL CYCLE
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology Cell Division Quiz
 Word List biphase cell membrane cell wall checkpoint chromosome cytoplasm daughter cell diffusion DNA nuclear membrane nucleus osmosis spindle telomere vacuole Cells reproduce in a process called, which
Word List biphase cell membrane cell wall checkpoint chromosome cytoplasm daughter cell diffusion DNA nuclear membrane nucleus osmosis spindle telomere vacuole Cells reproduce in a process called, which
Cellular Reproduction
 9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
Biology Unit 7. Cell Division
 Biology Unit 7 Cell Division Why would a cell want to divide? Reasons Cells Divide To avoid getting too big (cells not the organism) To help an organism grow and organize To replace old cells Cell Size
Biology Unit 7 Cell Division Why would a cell want to divide? Reasons Cells Divide To avoid getting too big (cells not the organism) To help an organism grow and organize To replace old cells Cell Size
BIOLOGY. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
