Chapter 44 10/17/2015. Care of the Patient with a Gastrointestinal Disorder. The Digestive System. Organs of the Digestive System
|
|
|
- Cleopatra Craig
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 44 Care of the Patient with a Gastrointestinal Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. The Digestive System Consists of the digestive tract A muscular tube that extends from the mouth to the anus Consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus Accessory organs aid in digestion All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 2 Organs of the Digestive System Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 3 1
2 Mouth Marks the entrance of the digestive system Contains the tongue Involved in chewing and swallowing Contain taste buds Digestion begins in the mouth The teeth, located in the mouth, are an accessory organ of the digestive system All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 4 Esophagus Muscular, collapsible tube Approximately 25 cm long Moves food from the mouth to the stomach All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 5 Stomach Digestion of protein begins in the stomach The stomach breaks the food down into chyme Chyme passes through the pyloric sphincter into the duodenum for the next phase of digestion All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 6 2
3 Small Intestine Approximately 20 feet long Up to 90% of digestion takes place in the small intestine Contain villi that aid in digestion All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 7 Large Intestine (Colon) Approximately 5-6 feet long Larger in diameter than the small intestine Main function is the reabsorption of water All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 8 Rectum The last 8 inches of the large intestine Where fecal material is expelled The anus is the sphincter through which feces are passed All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 9 3
4 Accessory Organs of the Digestive System Liver Gallbladder Pancreas All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 10 Liver Produces bile, which is necessary to digest fat Manages blood coagulation Metabolizes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates Manufactures cholesterol and albumin Detoxifies poisons (alcohol, nicotine, drugs) Converts ammonia to urea All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 11 Gallbladder Connected to the underside of the liver Stores bile Ejects bile into the duodenum to aid in digestion All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 12 4
5 Pancreas For digestion, the pancreas produces enzymes that aid in digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and protein Secretes sodium bicarbonate that aids in neutralizing stomach acid All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 13 Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations Upper Gastrointestinal Series (Upper GI, UGI) Consists of a series of radiographs of the lower esophagus, stomach, and duodenum using barium sulfate as the contrast medium Nursing interventions Keep patient NPO prior to exam No smoking prior to exam Explain importance of ensuring all barium is expelled rectally following procedure Instruct patient to increase fluid intake following exam All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 14 Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations cont d Tube Gastric Analysis Stomach contents are aspirated to determine the amount of acid produced by the parietal cells in the stomach Nursing interventions Patient should receive no anticholinergic medications for 24 hours before the test NPO prior to procedure No smoking prior to the exam Insert an NG tube All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 15 5
6 Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations cont d Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD, UGI Endoscopy, Gastroscopy) Enables direct visualization of a particular hollow organ or cavity by means of a long, flexible fiberoptic scope Nursing interventions Maintain the patient NPO after midnight Ensure the patient has IV access Following procedure, keep patient NPO until after gag reflex returns Monitor vital signs Monitor for signs and symptoms of complications All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 16 Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations cont d Barium Swallow Allows easy recognition of Swallowing difficulties resulting from conditions such as cerebrovascular accidents Anatomical abnormalities, such as hiatal hernia Nursing interventions Keep patient NPO after midnight Explain the importance of ensuring all barium is expelled rectally All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 17 Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations cont d Examination of Stool for Occult Blood Patient is usually asked to collect stool in an appropriate container Nursing interventions Instruct patient to keep sample free from urine or toilet paper Instruct patient to avoid eating organ meat 48 hours prior to collecting sample All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 18 6
7 Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations cont d Colonoscopy Can detect lesions in the proximal colon, which would not be found by sigmoidoscopy Nursing interventions Patient should be on a clear liquid diet 1-3 days prior to exam NPO 8 hours prior to procedure Administer bowel cleansers as ordered Assess after procedure for signs of bowel perforation All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 19 Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations cont d Stool Culture Examination of the stool for the presence of bacteria, ova, and parasites Nursing interventions Gloves are worn for sample collection and the specimen is taken to the laboratory within 30 minutes of collection All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 20 Disorders of the Mouth Dental Plaque and Caries Plaque is a film found on the teeth made of mucin and colloidal material Caries are commonly referred to as cavities Treated by removal of decayed portion and replacement with dental material Nursing interventions Stress the importance of, and proper procedure for, brushing and flossing All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 21 7
8 Disorders of the Mouth cont d Candidiasis An infection caused by Candida Also referred to as thrush Presents as milky, curdlike lesions Usually treated with nystatin or Diflucan Nursing interventions Meticulous hand hygiene to prevent the spread of infection Assess regularly Administer meds as prescribed Treat pain All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 22 Disorders of the Mouth cont d Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity May occur on the lips, oral cavity, tongue, and pharynx Higher incidence of cancers of the mouth and throat with a history of heavy drinking, tobacco use, or exposure to HPV Clinical manifestations Leukoplakia Sore in the mouth Assessment Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking Edema, numbness, or loss of feeling in any part of the mouth Earache, facial pain, and toothache Medical management varies greatly and can include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 23 Disorders of the Mouth cont d Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity cont d Nursing interventions Assess oral cavity frequently Monitor saliva output Treat pain Develop methods for communication Provide patient education All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 24 8
9 Disorders of the Esophagus Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Backward flow of stomach acid up into the esophagus Symptoms typically include Burning and pressure behind the sternum Described by patients as heartburn Dry cough Hoarseness Sore throat All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 25 Disorders of the Esophagus cont d GERD Medical Management H 2 receptor antagonist Proton pump inhibitors Antiulcer medications Metoclopramide (Reglan) Nissen fundoplication All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 26 Disorders of the Esophagus cont d GERD Nursing Interventions Provide patient education concerning diet and medications Encourage patient to stop smoking Patient should avoid clothing that is tight over the abdomen Patient should avoid working in a bent-over position Elevate the head of the bed All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 27 9
10 Carcinoma of the Esophagus Malignant epithelial neoplasm that has invaded the esophagus Risk factors Alcohol Tobacco use Acid reflux Obesity Prevention focuses on eliminating risk factors All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 28 Carcinoma of the Esophagus cont d Clinical Manifestations and Assessment Progressive dysphagia over a six-month period Assessment Dysphagia Chronic cough Vomiting Hoarseness All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 29 Carcinoma of the Esophagus cont d Medical Management Radiation Chemotherapy Surgery All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
11 Achalasia Also called cardiospasm Inability of a muscle to relax, particularly the cardiac sphincter of the stomach The primary manifestation is dysphagia Treatment Medications Dilatation All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 31 Disorders of the Stomach Gastritis Peptic ulcer disease Cancer of the stomach All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 32 Gastritis Inflammation of the lining of the stomach Associated with alcoholism, smoking, and stressful physical problems Manifestations Nausea Vomiting Fever Diarrhea Headache Loss of appetite All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
12 Gastritis cont d Assessment Anorexia Nausea Discomfort eating Pain Vomiting Hematemesis Melena All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 34 Gastritis cont d Medical management Medications NG tube Gastric lavage Removal or avoidance of causative factors Nursing interventions Monitor I&O Keep NPO until symptoms subside Administer IV feedings as indicated All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 35 Peptic Ulcer Disease Ulcerations of the mucous membrane or deeper structures of the GI tract Most commonly occur in the stomach and duodenum Pain is the characteristic symptom It is described as dull, burning, boring, or gnawing Pain is located in the epigastric region All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
13 Peptic Ulcer Disease cont d Medical Management Insert an NG tube to monitor gastric content Antacids H 2 receptor blockers Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) Sucralfate Antibiotics for H. pylori All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 37 Peptic Ulcer Disease cont d Nursing Interventions NG or intestinal tube placement Intermittent suction Administer medications Assess frequently Monitor vital signs All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 38 Cancer of the Stomach Men more commonly affected than women Rates are highest in Japan, China, Southern and Eastern Europe, and South and Central America The patient may be asymptomatic in early stages of the disease With more advanced disease, the patient may appear pale and lethargic if anemia is present All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
14 Cancer of the Stomach cont d Assessment Vague epigastric discomfort Early satiety Weight loss Blood in stools Vomiting after eating or drinking Anemia All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 40 Cancer of the Stomach cont d Medical Management Surgery Dumping syndrome is a possible complication Radiation Chemotherapy All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 41 Cancer of the Stomach cont d Nursing Interventions Improve nutritional status Relieve anxiety Improve understanding of drainage tubes Closely monitor I&O Maintain TPN Remain alert for weight loss All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
15 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ulcerative colitis Crohn s disease All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 43 Ulcerative Colitis Clinical Manifestations Diarrhea that may contain blood, mucus, and pus Abdominal cramps Moderate, up to five stools per day Severe, stools per day Diagnosed with double barium enema All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 44 Ulcerative Colitis cont d Assessment Complaints of rectal bleeding and abdominal cramps Lethargy Frustration Weight loss Fever Tachycardia All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
16 Ulcerative Colitis cont d Medical Management Inflammatory response modifiers Antibiotics Immune response modifiers Antidiarrheals Nutrition therapy Surgical control All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 46 Ulcerative Colitis cont d Nursing Interventions Assess elimination pattern Assess and treat pain Assess nutritional status Assess coping abilities Provide patient education Perform preoperative measures Provide postoperative care All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 47 Crohn s Disease Characterized by inflammation of segments of the GI tract Cause is not known Possible immune link Most commonly occurs during adolescence and early adulthood Mucosa develops a cobblestone appearance Malabsorption is a major issue All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
17 Crohn s Disease cont d Clinical Manifestations Diarrhea Fatigue Abdominal pain Weight loss Fever Malnutrition All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 49 Crohn s Disease cont d Assessment Weakness Loss of appetite Abdominal cramps Pain Frequent BMs Diarrhea Fistulas All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 50 Crohn s Disease cont d Medical Management Antiinflammatory medications Corticosteroids Multivitamins Immunosuppressive therapy Dietary modification Surgery All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
18 Crohn s Disease cont d Nursing Interventions Provide nutritional education Monitor I&O closely Assess and treat pain Provide bedside commode Provide emotional support All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 52 Nursing Interventions for the Patient with a Stoma Assess skin integrity Assess for allergies to powders or adhesive Provide education on changing pouch Assess peristomal area for infection All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 53 Acute Abdominal Inflammations Appendicitis Diverticulitis Peritonitis All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
19 Appendicitis Inflammation of the vermiform appendix Usually acute Characterized by rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen Patient may also experience nausea and anorexia WBC count >10,000/mm 3 Emergency surgical intervention is the treatment of choice All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 55 Diverticulitis Diverticulosis is the presence of pouchlike herniations through the circular smooth muscle of the colon Diverticulitis is the inflammation of one or more of the diverticular sacs Incidence increases after age 40 Inflammation can lead to perforation, abscess, peritonitis, obstruction, and hemorrhage Most common cause of lower GI hemorrhage All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 56 Diverticulitis cont d Characterized by Pain Fever Elevated WBC count Left lower quadrant pain Diarrhea Vomiting Nausea All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
20 Diverticulitis cont d Diagnosed through ultrasound and CT Managed by diet, weight loss, exercise Antibiotics and surgical intervention may be required if complications occur All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 58 Peritonitis Inflammation of the abdominal peritoneum Characterized by severe abdominal pain Assess for severe abdominal pain, nausea, and fever Diagnosed through x-ray and labs CT and MRI may also be used Treatment usually involves pain treatment, antibiotic administration, and surgery All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 59 Hernia External hernia Hiatal hernia All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
21 External Hernia A protrusion of a viscus through an abnormal opening or a weakened area in the wall of the cavity within which it is normally contained Characterized by a visible protruding mass Patient may also experience pain and nausea Hernia may be left untreated, or the patient may wear an abdominal binder Surgical correction may be required All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 61 Hiatal Hernia A protrusion of the stomach and other abdominal viscera through an opening, or hiatus, in the diaphragm Usually corrected with surgery Nursing care similar to that for patients having gastric or thoracic surgery All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 62 Intestinal Obstruction Mechanical obstruction: caused by an occlusion of the lumen of the intestinal tract Nonmechanical obstruction: caused by something that decreases the muscle action of the bowel (may be neurologic or vascular disorders) Early phases of mechanical obstruction: auscultation of the abdomen reveals loud, frequent, high-pitched sounds In later stages, bowel sounds will likely be absent All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
22 Intestinal Obstruction cont d Assessment Subjective Pain Flatus Cramping Objective Hernia Abdominal distention Tenderness All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 64 Intestinal Obstruction cont d Diagnosis and Medical Management Diagnosed by X-ray or CT Labs Treatment includes decompression of the bowel and replacement of electrolytes. If less invasive treatment is not effective, surgery may be required. All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 65 Intestinal Obstruction cont d Nursing Interventions Monitor fluid status Monitor electrolytes Assess and treat pain, as indicated If the patient is undergoing surgery Provide emotional support Encourage turning, coughing, and deep breathing Manage pain Ambulate as soon as indicated All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
23 Colorectal Cancer Second leading cause of cancer deaths Most growths found in the sigmoid and rectal regions of the colon Cause remains unknown Risk factors include Adenomatous polyps Ulcerative colitis Diverticulitis Heredity Clinical manifestations are usually nonspecific All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 67 Colorectal Cancer cont d Assessment Constipation or diarrhea Excessive flatus Cramping Vomiting Weight loss All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 68 Colorectal Cancer cont d Diagnostic Exams Fecal occult blood tests Colonoscopy Endorectal ultrasonography CT Routine physical exam with digital rectal exam H&H CEA All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
24 Colorectal Cancer cont d Medical Management Surgery Radiation Chemotherapy All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 70 Colorectal Cancer cont d Nursing Interventions Assess bowel and urinary elimination Monitor fluid and electrolyte balance Assess tissue perfusion Provide adequate nutrition Assess and treat pain Promote gas exchange Prevent infection Maintain peristomal skin integrity All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 71 Fecal Incontinence Has a variety of causes The external sphincter may be relaxed Voluntary control of defecation may be disturbed Distention of the rectum Paralysis All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
25 Fecal Incontinence cont d Medical Management and Nursing Intervention Improve muscle tone of the sphincter Bowel training program Assist patient to toilet without delay when needed Provide patient education All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
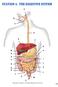
Figure Care of the Patient with a Gastrointestinal Disorder. Location of digestive organs.
 Care of the Patient with a Gastrointestinal Disorder 1 Slide 1 Slide 2 Figure 45-1 (From Thibodeau, G.A., Patton, K.T. [1987]. Anatomy and physiology. St. Louis: Mosby.) Location of digestive organs. Slide
Care of the Patient with a Gastrointestinal Disorder 1 Slide 1 Slide 2 Figure 45-1 (From Thibodeau, G.A., Patton, K.T. [1987]. Anatomy and physiology. St. Louis: Mosby.) Location of digestive organs. Slide
3/22/2011. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Appendicitis. Lemone and Burke Chapter 26
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
F A M N O P R S ! D !
 A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
The Gastrointestinal System
 101 15 The Gastrointestinal System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain key terms related to the body 3. Explain the structure and function of the gastrointestinal system 4. Discuss changes
101 15 The Gastrointestinal System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain key terms related to the body 3. Explain the structure and function of the gastrointestinal system 4. Discuss changes
GI update. Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about
 GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery
 Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
What is Crohn's disease?
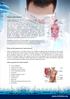 What is Crohn's disease? Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any area of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most
What is Crohn's disease? Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any area of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain
 Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems
 Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Digestive System Digestion is an important process that involves breaking down food and drink into small molecules that can
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 15a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Digestive System Digestion is an important process that involves breaking down food and drink into small molecules that can
Digestion. Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional
 Digestive System 1 Digestion Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional Food behaviors can become just as addictive as any other pleasurable
Digestive System 1 Digestion Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional Food behaviors can become just as addictive as any other pleasurable
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank
 UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
Certain genes passed on from parent to child increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease, if the right trigger occurs.
 Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
64a Pathology: Digestive System!
 64a Pathology: Digestive System! 64a Pathology: Digestive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
64a Pathology: Digestive System! 64a Pathology: Digestive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
PATIENT HISTORY FORM
 PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
Digestion. Absorption and Transport. Digestion. Digestion. (Chapter 3) Your GI tract is like a tube!
 Digestion Absorption and Transport Digestion the process of breaking down food into its basic components so they can be absorbed CHO, fat, pro are hydrolysed Vits, mins, water aren t (Chapter 3) Digestion
Digestion Absorption and Transport Digestion the process of breaking down food into its basic components so they can be absorbed CHO, fat, pro are hydrolysed Vits, mins, water aren t (Chapter 3) Digestion
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
ESSENTIAL QUESTION. What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
Digestive System. Digestion Myths
 Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Nursing Principles & Skills II. Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction
 Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Chapter 14 GASTROINTESTINAL IMPAIRMENT
 Chapter 14 GASTROINTESTINAL IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria for assessing permanent impairment from entitled conditions of the gastrointestinal tract and the accessory organs of
Chapter 14 GASTROINTESTINAL IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria for assessing permanent impairment from entitled conditions of the gastrointestinal tract and the accessory organs of
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels.
 Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
GI -A & P Review PUD. Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) Objectives: Identify different types Gastric Ulcer Duodenal Ulcer Stress Ulcer
 GI -A & P Review Lemone and Burke Chapters 21-26 Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestines Large Intestines Liver and Gallbladder Pancreas Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) Objectives: Identify different
GI -A & P Review Lemone and Burke Chapters 21-26 Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestines Large Intestines Liver and Gallbladder Pancreas Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) Objectives: Identify different
Gastrointestinal. Issues in ElderCare. TCHP Education. Consortium. Part of the ElderCare: Healthcare for the Aging Series
 TCHP Education Consortium Gastrointestinal Issues in ElderCare Part of the ElderCare: Healthcare for the Aging Series TCHP Education Consortium, 2004, 2007 This educational activity expires December 31,
TCHP Education Consortium Gastrointestinal Issues in ElderCare Part of the ElderCare: Healthcare for the Aging Series TCHP Education Consortium, 2004, 2007 This educational activity expires December 31,
Chapter 17. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test
 NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test Applicable CPT Code(s): 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal
NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test Applicable CPT Code(s): 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
X-Plain Sigmoidoscopy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sigmoidoscopy Reference Summary Introduction Colon diseases are common. A sigmoidoscopy is a test that can help detect colon diseases. If your doctor recommends that you have a sigmoidoscopy, the
X-Plain Sigmoidoscopy Reference Summary Introduction Colon diseases are common. A sigmoidoscopy is a test that can help detect colon diseases. If your doctor recommends that you have a sigmoidoscopy, the
Patient Interview Form
 Patient Interview Form Patient Information First Name: Last Name: Date of Birth: Age: Email Personal: Race Select one or more Referring Physician White Black or African Asian American Indian Native Hawaiian
Patient Interview Form Patient Information First Name: Last Name: Date of Birth: Age: Email Personal: Race Select one or more Referring Physician White Black or African Asian American Indian Native Hawaiian
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Why Choose Wudassie Diagnostic Center for GI service? Ease of Use: One Location: Reduced Cross-Infection: Focus on the Patient: Reduced Cost:
 Why Choose Wudassie Diagnostic Center for GI service? In our center, patients find that the process much more convenient, as well as more personal. Our center offers a relaxed environment with medical
Why Choose Wudassie Diagnostic Center for GI service? In our center, patients find that the process much more convenient, as well as more personal. Our center offers a relaxed environment with medical
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
The Aging Digestive System
 The Aging Digestive System shows significant senescence in old age: less saliva food less flavorful, harder swallowing ~half of those over 65 yrs wear dentures gastric mucosa secretes less acid reduces
The Aging Digestive System shows significant senescence in old age: less saliva food less flavorful, harder swallowing ~half of those over 65 yrs wear dentures gastric mucosa secretes less acid reduces
8/29/2016 DIVERTICULAR DISEASE: WHAT EVERY NURSE PRACTITIONER SHOULD KNOW. LENORE LAMANNA Ed.D, ANP-C LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 DIVERTICULAR DISEASE: WHAT EVERY NURSE PRACTITIONER SHOULD KNOW LENORE LAMANNA Ed.D, ANP-C LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define Diverticular Disease Discuss Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diverticular disease
DIVERTICULAR DISEASE: WHAT EVERY NURSE PRACTITIONER SHOULD KNOW LENORE LAMANNA Ed.D, ANP-C LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define Diverticular Disease Discuss Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diverticular disease
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions
 2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Functions of the gastrointestinal (GI) system: * Process food substances * Absorb the products of digestion into the blood * Excrete unabsorbed materials * Provide an environment
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Functions of the gastrointestinal (GI) system: * Process food substances * Absorb the products of digestion into the blood * Excrete unabsorbed materials * Provide an environment
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Objectives: Disorders of the esophagus and stomach Disorders of the small and large intestine Appendicitis Part 1: Disorders of the esophagus and stomach 1 Dysphagic Disorders
Gastrointestinal Disorders Objectives: Disorders of the esophagus and stomach Disorders of the small and large intestine Appendicitis Part 1: Disorders of the esophagus and stomach 1 Dysphagic Disorders
GI -A & P Review Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestines Large Intestines Liver and Gallbladder Pancreas 8/11/2011
 Lemone and Burke Chapters 21,23-25 ATI M/S Unit 7 Objectives Review A&P Identify diagnostic exams Discuss etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation, and collaborative management of: PUD Hernias
Lemone and Burke Chapters 21,23-25 ATI M/S Unit 7 Objectives Review A&P Identify diagnostic exams Discuss etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation, and collaborative management of: PUD Hernias
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
Bleeding in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
An Approach to Abdominal Pain
 An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD
 GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
How does the form of the digestive system help it with its function?
 Digestive System How does the form of the digestive system help it with its function? Why do you eat? A Calorie (Cal) is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1 C.
Digestive System How does the form of the digestive system help it with its function? Why do you eat? A Calorie (Cal) is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1 C.
HCPCS Codes (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) ICD-9-CM Codes Covered by Medicare Program
 HCPCS s (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal neoplasm screening ICD-9-CM
HCPCS s (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal neoplasm screening ICD-9-CM
The Human Body: Digestive System
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. 1. Digestive System Is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus Carries out digestion which is the process of breaking down food
Directions: Fill in the blanks. 1. Digestive System Is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus Carries out digestion which is the process of breaking down food
INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC ENDOSCOPY
 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC ENDOSCOPY EGD & Colonoscopy Procedure Kolegium Ilmu Bedah Indonesia B. Parish Budiono Sub Bagian Bedah Digestif FK UNDIP/RSUP Dr. Kariadi Semarang GI Endoscopy GI Endoscopy is
INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC ENDOSCOPY EGD & Colonoscopy Procedure Kolegium Ilmu Bedah Indonesia B. Parish Budiono Sub Bagian Bedah Digestif FK UNDIP/RSUP Dr. Kariadi Semarang GI Endoscopy GI Endoscopy is
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Barrett s Oesophagus Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
Chapter 29 Gastrointestinal Intubation
 Chapter 29 Gastrointestinal Intubation Intubation Intubation: placement of a tube into a body structure Types of intubation Orogastric: mouth to stomach Nasogastric: nose to stomach Nasointestinal: nose
Chapter 29 Gastrointestinal Intubation Intubation Intubation: placement of a tube into a body structure Types of intubation Orogastric: mouth to stomach Nasogastric: nose to stomach Nasointestinal: nose
The Digestive System 1
 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
