Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
- Brianne Shepherd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin, TB Ng, YC Chen * K e y M e s s a g e s 1. mir-21 overexpression is critical to promote early carcinogenesis of hepatocytes upon hepatitis B virus infection. 2. HBx-induced IL-6-STAT3 pathway upregulates mir-21 expression. 3. The high dependency of mir-21 expression on HBx is a unique viral oncogenic pathway aberrantly affecting gene expression network. 4. Inhibition of mir-21 attenuates the anchorageindependent colony formation and subcutaneous tumour growth of non-tumour hepatocytes. Hong Kong Med J 2016;22(Suppl 4):S37-42 RFCID project number: CH Li, 1 SC Chow, 2 DL Yin, 1 TB Ng, 1 YC Chen 1 School of Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong 2 Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN, USA * Principal applicant and corresponding author: frankch@cuhk.edu.hk Introduction Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) associated with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection exhibits a higher degree of aggressiveness than non-infected tumours. HBV X protein (HBx) is encoded from the HBV genome 1 and is involved in the pathogenic mechanism of HBV-associated HCC. It has multiple molecular functions in human hepatocytes via interactions with various transcription factors and modulates numerous cellular signalling pathways of the host. 2 The role of HBx protein in HCC biology has been studied, but the gene expression network affected by the viral protein is not fully understood. HBx protein induces differential expression of micrornas (mirnas). Aberrant expression of mirnas has been implicated in numerous cancer types including HCC. Nonetheless, HBV-associated mirnas that drive the transformation of normal hepatocytes and HCC carcinogenesis are poorly studied. In addition, the mechanism by which HBx alters the expression of mirnas is largely unexplored. In this project, we demonstrated that induction of mir-21 was dependent on HBx-activation of the IL- 6-STAT3 pathway. Expression of mir-21 is essential in transforming non-tumour hepatocytes to gain the ability to form anchorage-independent colonies and in vivo tumours, and implies a critical role during early HCC development. Methods This study was conducted from December 2011 to December Cell culture and drug treatment A human hepatoma cell line, Hep3B, immortalised non-tumourigenic hepatocyte cells, MIHA, and 293T, were maintained under standard procedures. Cells were treated with STAT3 inhibitor, cucurbitacin (Tocris, Bristol, UK), at a dose of 0.5 µm for 72 hours, or with recombinant human IL-6 (Invitrogen) at designated doses and durations. Cancer-associated mirna profiling in HBxexpressing stable cell line MIHA cells were transfected with pcdna3.1/ myc containing COOH-terminal truncated HBx cdna (HBx- 35). After transfection, the cells were incubated with G418 (Invitrogen) for ~2 weeks. Differential expression of cancer-associated mirna in HBx protein expressing MIHA cells was measured by Cancer MicroRNA qpcr Array with QuantiMir (System Biosciences). As an internal control, U6 primers were used for RNA template normalisation. Lentivirus packaging and transduction Myc-tagged full-length human HBx (HBx-FL) and HBx- 35 were cloned into a lentiviral vector coexpressing EGFP (plig). Lentiviral vector carrying transgene of small hairpin RNA targeting STAT3 (shstat3) (BLOCK-iT RNAi system) (Invitrogen) or mirzip-21 (MZIP21-PA-1) (System Biosciences) was purchased. Lentiviruses containing either myctagged HBx, HBx- 35, shstat3 or mirzip-21 were packaged and transduced into MIHA cells with the presence of 8 µg/ml polybrene (Sigma). Cells were Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 3 (Supplement 4) June
2 # Li et al # sorted for GFP expression by the BD FACSAria III cell sorter (BD Biosciences, New Jersey, USA) to obtain pure populations of MIHA-HBx and MIHA- 35. Soft agar assay Cells (5x10 3 ) were re-suspended in 1.5 ml 0.35% agar in DMEM, and were layered onto six wells containing solidified 0.5% agar. Colonies were allowed to grow for 4-6 weeks before being stained with crystal violet. Subcutaneous xenograft tumour models All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of the Chinese University of Hong Kong. MIHA cells, MIHA-LIG, MIHA-HBx and MIHA-HBx- 35 ( ) were injected subcutaneously into nude mice (n=5). Tumour volume was calculated by the equation: volume=(length x width 2 )/2. Results mir-21 was upregulated by ectopic HBx expression in MIHA cells We profiled cancer-associated mirnas expression in HBx-Δ35 overexpressing MIHA cells by Cancer MicroRNA qpcr Array with QuantiMir. MiRNAs with fold changes larger than 1.5 were considered biologically significant, and oncomirs including mir-21 and mir-373 were upregulated while tumour suppressor mirnas mir-126 and mir-137 were downregulated after HBx-Δ35 overexpression (Fig 1a). To investigate the association between HBx and the mirnas, we generated lentivirus carrying full length HBx (HBx-FL) or HBx- 35 transgene to transduce MIHA cells. We showed that both HBx-FL and HBx- 35 significantly promoted MIHA cell proliferation (Fig 1b). We hypothesised that HBx proteins could induce differential mirnas expression, contributing to the altered phenotypes of non-tumour hepatocytes. Subsequently, we validated the mirna profiling in both HBx-FL- and HBx- 35-expressing MIHA cells by qrt-pcr. MiR-21 expression was significantly increased upon ectopic HBx expression (Fig 1c), whereas mir-126, mir-137 and mir-373 showed no significant change (data not shown). To prove the presence of HBx-miR-21 pathway in HCC cells, we inhibited HBx by sirnas in Hep3B cells that were positive for HBx expression. MiR-21 expression was significantly inhibited upon knockdown of HBx in Hep3B cells (Fig 1d). The level of other mirnas was also measured, but knockdown of HBx failed to alter their expression (data not shown). Inhibition of mir-21 activity by mirzip-21 in HBx-FL expressing MIHA cells could upregulate a putative mir-21 target programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) [Fig 1e]. Taken together, we illustrated that mir-21 was an important downstream regulator of HBx proteins during HBV-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis. Upregulation of IL-6 by HBx protein induced mir-21 expression We studied the association between the HBx- IL-6 pathway and mir-21 induction during early hepatocyte transformation. Overexpression of HBx-FL and HBx- 35 significantly increased the expression of IL-6 in MIHA cells (Fig 1f). HBx- 35 induced a remarkably higher IL-6 expression in cells compared with HBx-FL, suggesting that such variant could activate the IL-6 pathway more robustly. We further treated MIHA cells with recombinant human IL-6, and the level of mir-21 in cells was increased both time-dependently (Fig 1g) and dose-dependently (Fig 1h). Recombinant IL-6 treatment also increased both pri-mir-21 (Fig 1i) and pre-mir-21 levels (Fig 1j) time-dependently. The concurrent upregulation of primary, precursor and mature mir-21 suggested that IL-6 transcriptionally activated the transcription of the mir-21 gene in non-tumour hepatocytes, and subsequently elevated mature mir-21 level. Furthermore, knockdown of IL-6 by sirnas significantly reduced the expression of mir-21 in Hep3B cells (Fig 1k), suggesting that IL-6 signalling was pivotal to HBx-mediated induction of mir-21 expression in HCC cells. Role of STAT3 in HBx-induced mir-21 expression We further delineated the molecular pathway of IL- 6-mediated mir-21 upregulation. IL-6 and STAT3 pathway is prevalent in human HCC. Nonetheless, the role of HBx proteins in regulation of the IL-6- STAT3 pathway was not clear. We showed that phosphorylated STAT3 was significantly elevated after overexpression of HBx-FL and HBx- 35 (Fig 2a). Similar to the upregulation of IL-6 mrna expression, HBx- 35 induced a higher level of phosphorylated STAT3 compared with HBx-FL (Fig 2a). HBx was highly associated with activation of the IL-6-STAT3 pathway in HCC cells, as we further showed that phosphorylation of STAT3 was effectively inhibited when IL-6 was depleted by sirnas in Hep3B cells (Fig 2b). To reveal the importance of STAT3 in HBx-induced mir-21 activation, lentiviral vector containing shstat3 was transduced in MIHA cells with or without HBx-FL and HBx- 35 expression. Western blotting showed that the level of total STAT3 was drastically prohibited in all MIHA cell lines after lentiviral infection (Fig 2c). In turn, we measured the change in mir-21 level in the STAT3- depleted cells. As expected, upregulation of mature mir-21 was significantly attenuated in both HBx-FL and HBx- 35 overexpressed MIHA cells (Fig 2d). In contrast, depletion of STAT3 in parental and control lentivirus infected MIHA cells did not alter mir Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 3 (Supplement 4) June
3 # Hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction # (a) (c) (d) (b) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) FIG 1. Ectopic HBx expression induced mir-21 expression in non-tumour hepatocytes via IL-6 signalling. Differential expression of cancer-associated mirnas was measured in MIHA cells upon overexpression of HBx protein, and (a) upregulated mirnas including mir-21 and mir-373, and downregulated mirnas including mir-126 and mir-137 were identified. (b) Cell proliferation assay showed that ectopic expression of HBx-FL or HBx- 35 significantly increased the cell proliferation rate of MIHA cells compared with parental and lentivirus control cells. (c) Lentiviral overexpression of HBx-FL and HBx-Δ35 upregulated the level of mir-21 in MIHA cells. (d) Knockdown of HBx inhibited the expression of mir-21 in Hep3B cells. (e) Inhibition of mir-21 activity in HBx-expressed MIHA cells through second infection of lentivirus expressing mirzip-21 significantly increased the transcript level of PDCD4. (f) Both HBx-FL and HBx-Δ35 protein induced the expression of IL-6 in MIHA cells, while HBx-Δ35 induced a significantly higher IL-6 level compared with HBx-FL. Recombinant human IL-6 upregulated the expression of mature mir-21 in a (g) time-dependent and (h) dose-dependent manner in parental MIHA cells. (i) Precursor mir-21 and (j) primary mir-21 were upregulated with IL-6 treatment time-dependently. (k) Knockdown of IL-6 by sirnas significantly inhibited the level of endogenous mir-21 in Hep3B cells. (Reproduced with permission from Elsevier) Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 3 (Supplement 4) June
4 # Li et al # (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) FIG 2. Role of STAT3 in HBx-induced mir-21 expression: (a) Phosphorylation of STAT3 was promoted in MIHA cells expressing HBx-FL and HBx-Δ35. (b) Knockdown of IL-6 by sirnas inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT3 in Hep3B cells. (c) shrnas targeting STAT3 were transduced in whole panel of MIHA cell lines, and the protein expression of STAT3 was knocked down. (d) While ectopic expression of HBx induced the expression of mature mir-21, simultaneous inhibition of STAT3 by shrnas prohibited the expression of mir-21. (e) ChIP assay showed that about two-fold of mir-21 promoter was occupied by STAT3 in the presence of HBx-FL or HBx-Δ35 in MIHA cells. (f) STAT3 was activated by IL-6 in parental MIHA cells whereas total STAT3 expression was not influenced. (g) IL-6 treatment was able to induce an eight-fold increase in phosphorylated STAT3 occupancy at mir-21 promoter. (h) Upregulation of mir-21 by HBx-FL and HBx-Δ35 was attenuated when STAT3 was inhibited by STAT3 inhibitor cucurbitacin in MIHA cells. (i) The promotional effect on mir-21 level in MIHA cells by recombinant IL-6 treatment was lost when STAT3 was silenced by shrnas. (Reproduced with permission from Elsevier) expression (Fig 2d). This implied that the regulation of mir-21 by STAT3 in non-malignant hepatocytes was dependent on HBx, which proved that aberrant mir-21 expression was driven by HBx-IL-6-STAT3 signalling. Phosphorylation of STAT3 enhanced mir-21 promoter occupancy Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis revealed a significant increase in STAT3 occupancy in the mir-21 promoter upon ectopic expression of HBx-FL or HBx- 35 (Fig 2e). Western blotting analysis revealed an increase in STAT3 phosphorylation after treatment with recombinant IL-6 in MIHA cells (Fig 2f), and ChIP analysis showed that exposure of IL-6 to MIHA cells significantly enriched STAT3 proteins at the promoter of mir-21 gene (Fig 2g). To further demonstrate the importance of STAT3 activity in the HBx-miR-21 pathway, a selective JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway inhibitor, 40 Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 3 (Supplement 4) June
5 # Hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction # (a) (b) HBx-FL HBx- 35 mirzip-21 (c) (d) (e) (f) FIG 3. Role of mir-21 in HBx-induced hepatocarcinogenesis: (a) left panel: soft agar assay demonstrated that MIHA cells expressing HBx-FL or HBx-Δ35 were capable of forming anchorage-independent colonies. (a) right panel: MIHA cells expressing HBx-Δ35 exhibited a higher tendency to form anchorageindependent colonies compared with HBx-FL. (b) Co-expression of mirzip-21 with HBx proteins effectively abrogated the colony forming ability of HBxexpressed MIHA cells. (c) Inhibition of mir-21 significantly reduced the number of colonies formed in both HBx-FL and HBx-Δ35 expressing MIHA cells. (d) Tumour xenografts were extracted from nude mice injected with MIHA cells with or without the expression of HBx or mirzip-21. There were three and four out of five nude mice respectively injected with HBx-FL and HBx- 35 expressing MIHA cells. Coexpression of mirzip-21 was able to inhibit the subcutaneous tumour formation ability of HBx expressing cells. (e) Inhibition of mir-21 by mirzip-21 significantly reduced the tumour weight compared with HBx-FL and HBx- 35. (f) Schematic diagram illustrating the HBx-triggered mir-21 hepatocarcinogenesis pathway. (Reproduced with permission from Elsevier) Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 3 (Supplement 4) June
6 # Li et al # cucurbitacin I, was applied to deactivate STAT3 in HBx-FL and HBx- 35 overexpressed MIHA cells. HBx-induced mir-21 expression in MIHA-HBx and MIHA- 35 was attenuated in the presence of the STAT3 inhibitor at 48 hours of treatment (Fig 2h). In addition, while exposure of recombinant IL-6 significantly increased the level of mir-21 in parental MIHA cells, such treatment failed to activate the expression of mir-21 when STAT3 was constitutively inhibited by shrnas (Fig 2i). Taken together, STAT3 was the key transcriptional factor activated during HBx-induced transformation, which led to the active transcription of mir-21. Role of mir-21 in HBx-induced hepatocarcinogenesis By soft agar assay, overexpression of both full length HBx and HBx- 35 was able to induce anchorage-independent colony formation of MIHA cells, whereas neither parental MIHA cells nor the lentiviral control MIHA-LIG cells could form colonies (Fig 3a). MIHA cells expressing HBx- 35 could generate twice as many colonies as those expressing full length (Fig 3a). HBx- 35 possessed a greater ability to transform non-tumour hepatocytes compared with its full length counterpart. In order to characterise the role of mir-21 in HBx-induced cell proliferation, MIHA cells were co-infected with lentivirus carrying mirzip- 21 transgene. Soft agar assay was conducted after infection of the panel of MIHA cells with lenti-ctrl or lenti-mirzip-21. The colony forming capability of HBx-FL and HBx- 35 expressing MIHA cells was inhibited by mirzip-21 (Figs 3b and 3c). Moreover, MIHA cells expressing HBx and HBx- 35 proteins were injected subcutaneously into nude mice (n=5). Cells expressing HBx-FL developed tumours in three out of five mice, whereas those expressing HBx- 35 developed tumours in four out of five mice (Fig 3d). More importantly, no tumours were found in mice injected with cells coexpressing HBx-FL and mirzip-21. Inhibition of mir-21 also effectively abrogated the effect of HBx- 35 to induce tumour formation, in which only two out of five mice developed tumours with obviously reduced tumour volume and weight (Figs 3d and 3e). Discussion We aimed to identify HBx-induced mirnas that have an important role during early HCC development. Overexpression of mir-21 occurred as soon as the hepatocytes were infected with HBV. Among various upstream pathways that regulate mir-21, the IL-6-STAT3 signalling pathway is closely related to cellular transformation and oncogenesis in HCC. High levels of IL-6 are found in patients with HBV infection and HBV-associated HCC. 3 HBxinduced mir-21 expression was highly dependent on activation of the IL-6-STAT3 pathway, which demonstrated the specificity of mir-21 induction by HBx. Apart from overexpressing HBx in nontumour hepatocytes, silencing IL-6 in HBx protein expressing HCC cell line Hep3B could result in a reduction in mir-21 level, which consolidated the interactions between HBx, IL-6-STAT3 and mir-21. Our results from soft agar assay and xenograft assay suggest that HBx-induced mir-21 is pivotal in the transformation of non-tumour hepatocytes. More importantly, as inhibiting mir-21 with mirzip-21 inhibited tumour xenograft growth, there is high therapeutic value to targeting mir-21 in HBV-associated HCC. Inhibition of mir-21 effectively prohibited MIHA cells from formation of both anchorage-independent colony and in vivo subcutaneous tumour, which suggests abrogation of the transformation of non-tumour hepatocytes. Taken together, mir-21 was a critical downstream effector of HBx that drove the tumourigenesis of non-tumour hepatocytes. Ectopic HBx expression triggered the IL-6 pathway, promoted the phosphorylation and activation of transcriptional factor STAT3, and induced the expression of mir-21. Our in vitro and in vivo studies supported that mir-21 exhibited phenotypical change of the non-tumour cells during HBx-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis. Inhibiting mir-21 or attenuating its activation pathways (ie IL6-STAT3) could be promising when developing novel therapies for HBV-associated HCC. Given the important association between HBx and mir-21 in early HCC development, targeting mir-21 may also provide a novel means to prevent the development of HCC in HBV carriers. Acknowledgement This study was supported by the Research Fund for the Control of Infectious Diseases, Food and Health Bureau, Hong Kong SAR Government (# ). Results of this study have been published in Li CH, Xu F, Chow S, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatocellular carcinoma transformation through interleukin-6 activation of microrna-21 expression. Eur J Cancer 2014;50: References 1. Kremsdorf D, Soussan P, Paterlini-Brechot P, Brechot C. Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: paradigms for viral-related human carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2006;25: Caselmann WH, Koshy R. Transactivators of HBV, signal transduction and tumorigenesis. In: Caselmann WH, Koshy R, editors. Hepatitis B virus: molecular mechanisms in disease and novel strategies for therapy. London: Imperial College Press; 1998: Coskun U, Bukan N, Sancak B, et al. Serum hepatocyte growth factor and interleukin-6 levels can distinguish patients with primary or metastatic liver tumors from those with benign liver lesions. Neoplasma 2004;51: Hong Kong Med J Volume 22 Number 3 (Supplement 4) June
Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p.
 Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
CH Cho *, J Yu, WKK Wu 1,2
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Identification of pathogenic micrornas in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer using a combined approach of animal study and clinical sample
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Identification of pathogenic micrornas in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer using a combined approach of animal study and clinical sample
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Autocrine production of IL-11 mediates tumorigenicity in hypoxic cancer cells
 Research article Autocrine production of IL-11 mediates tumorigenicity in hypoxic cancer cells Barbara Onnis, 1 Nicole Fer, 2 Annamaria Rapisarda, 2 Victor S. Perez, 1 and Giovanni Melillo 2 1 Developmental
Research article Autocrine production of IL-11 mediates tumorigenicity in hypoxic cancer cells Barbara Onnis, 1 Nicole Fer, 2 Annamaria Rapisarda, 2 Victor S. Perez, 1 and Giovanni Melillo 2 1 Developmental
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
Tumor-secreted mir-214 induces regulatory T cells: a major link between immune evasion and tumor growth
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) 24:1164-1180. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg Tumor-secreted mir-214 induces regulatory T cells: a major link between immune
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) 24:1164-1180. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg Tumor-secreted mir-214 induces regulatory T cells: a major link between immune
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Oncogenic Transformation of Human Lung Bronchial Epithelial Cells Induced by Arsenic Involves ROS-Dependent Activation of STAT3-miR-21-PDCD4 Mechanism
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Center for Research on Environmental Disease Faculty Publications Environmental Disease 11-23-2016 Oncogenic Transformation of Human Lung Bronchial Epithelial Cells Induced
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Center for Research on Environmental Disease Faculty Publications Environmental Disease 11-23-2016 Oncogenic Transformation of Human Lung Bronchial Epithelial Cells Induced
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
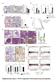 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
~Lentivirus production~
 ~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
Supplementary material. Supplementary Figure legends
 Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development
 Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development Sen-Yung Hsieh, MD, PhD Liver Research Unit Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Taoyuan, Taiwan Aims To identify genes controlling tumor
Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development Sen-Yung Hsieh, MD, PhD Liver Research Unit Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Taoyuan, Taiwan Aims To identify genes controlling tumor
PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype to promote glioblastoma migration and invasion
 Xu et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:158 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0841-0 RESEARCH PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype
Xu et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:158 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0841-0 RESEARCH PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway
 Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0392 TITLE: The Role of Notch Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Annapoorni Rangarajan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indian Institute
AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0392 TITLE: The Role of Notch Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Annapoorni Rangarajan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indian Institute
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 -. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
-. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Cell cycle related kinase is a direct androgen receptor regulated gene that drives β-catenin/ T cell factor dependent hepatocarcinogenesis
 Research article Cell cycle related kinase is a direct androgen receptor regulated gene that drives β-catenin/ T cell factor dependent hepatocarcinogenesis Hai Feng, 1 Alfred S.L. Cheng, 2 Daisy P. Tsang,
Research article Cell cycle related kinase is a direct androgen receptor regulated gene that drives β-catenin/ T cell factor dependent hepatocarcinogenesis Hai Feng, 1 Alfred S.L. Cheng, 2 Daisy P. Tsang,
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells
 let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Fengyan Yu, 1,2 Herui Yao, 1 Pengcheng Zhu, 2 Xiaoqin Zhang, 1 Qiuhui Pan, 1 Chang Gong, 1 Yijun Huang, 3 Xiaoqu Hu, 1 Fengxi Su,
let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Fengyan Yu, 1,2 Herui Yao, 1 Pengcheng Zhu, 2 Xiaoqin Zhang, 1 Qiuhui Pan, 1 Chang Gong, 1 Yijun Huang, 3 Xiaoqu Hu, 1 Fengxi Su,
Silencing Oncogene E6/E7 in HeLa Sphere Forming Cells Inhibits Their Growth. and Decreases Self-renewal Gene TGF-β Expression
 Silencing Oncogene E6/E7 in HeLa Sphere Forming Cells Inhibits Their Growth and Decreases Self-renewal Gene TGF-β Expression Wenyi Gu 1*, Eliza Yeo 2, Fabio Petrocca 3, Nigel McMillan 2, and Chengzhong
Silencing Oncogene E6/E7 in HeLa Sphere Forming Cells Inhibits Their Growth and Decreases Self-renewal Gene TGF-β Expression Wenyi Gu 1*, Eliza Yeo 2, Fabio Petrocca 3, Nigel McMillan 2, and Chengzhong
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1
 Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the
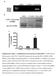 Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
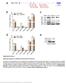 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
MicroRNA-31 initiates lung tumorigenesis and promotes mutant KRAS-driven lung cancer
 The Journal of Clinical Investigation Research article MicroRNA-31 initiates lung tumorigenesis and promotes mutant KRAS-driven lung cancer Mick D. Edmonds, 1 Kelli L. Boyd, 1 Tamara Moyo, 2 Ramkrishna
The Journal of Clinical Investigation Research article MicroRNA-31 initiates lung tumorigenesis and promotes mutant KRAS-driven lung cancer Mick D. Edmonds, 1 Kelli L. Boyd, 1 Tamara Moyo, 2 Ramkrishna
Experimental Therapeutics I
 Experimental Therapeutics I Mary Hitt 5142 Katz Group Centre mhitt@ualberta.ca; or Mary.Hitt@albertahealthservices.ca 1 Specific Topics for Today Preclinical and clinical testing Gene therapy Nonviral
Experimental Therapeutics I Mary Hitt 5142 Katz Group Centre mhitt@ualberta.ca; or Mary.Hitt@albertahealthservices.ca 1 Specific Topics for Today Preclinical and clinical testing Gene therapy Nonviral
LRIG2 promotes the proliferation and cell cycle progression of glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo through enhancing PDGFRβ signaling
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 53: 1069-1082, 2018 LRIG2 promotes the proliferation and cell cycle progression of glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo through enhancing PDGFRβ signaling QUNGEN XIAO,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 53: 1069-1082, 2018 LRIG2 promotes the proliferation and cell cycle progression of glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo through enhancing PDGFRβ signaling QUNGEN XIAO,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifthmost
 Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Modulates Oncogene Yes-Associated Protein by CREB to Promote Growth of Hepatoma Cells Tao Zhang, 1 Junping Zhang, 1 Xiaona You, 1 Qian Liu, 2 Yumei Du, 1 Yuen Gao, 1 Changliang
Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Modulates Oncogene Yes-Associated Protein by CREB to Promote Growth of Hepatoma Cells Tao Zhang, 1 Junping Zhang, 1 Xiaona You, 1 Qian Liu, 2 Yumei Du, 1 Yuen Gao, 1 Changliang
DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors
 ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
Supplemental Information. NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF. in p53-independent Tumor Suppression
 Molecular Cell, Volume 68 Supplemental Information NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF in p53-independent Tumor Suppression Delin Chen, Omid Tavana, Bo Chu, Luke Erber, Yue Chen, Richard Baer, and Wei Gu Figure
Molecular Cell, Volume 68 Supplemental Information NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF in p53-independent Tumor Suppression Delin Chen, Omid Tavana, Bo Chu, Luke Erber, Yue Chen, Richard Baer, and Wei Gu Figure
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication
 Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication Shilpa Singh, 1 Catherine A. Vaughan, 1 Rebecca A. Frum, 2 Steven R. Grossman, 2 Sumitra Deb, 1 and Swati Palit Deb
Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication Shilpa Singh, 1 Catherine A. Vaughan, 1 Rebecca A. Frum, 2 Steven R. Grossman, 2 Sumitra Deb, 1 and Swati Palit Deb
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation
 MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
Supplementary Figure 1. HeliScope CAGE revealed androgen-regulated signaling and differentially regulated promoters in hormone-refractory prostate
 Supplementary Figure 1. HeliScope CAGE revealed androgen-regulated signaling and differentially regulated promoters in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells. (a) Cell proliferation of BicR cells in
Supplementary Figure 1. HeliScope CAGE revealed androgen-regulated signaling and differentially regulated promoters in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells. (a) Cell proliferation of BicR cells in
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Reciprocal regulation by TLR4 and TGF-β in tumor-initiating stem-like cells
 Research article Reciprocal regulation by TLR4 and TGF-β in tumor-initiating stem-like cells Chia-Lin Chen, 1 Hidekazu Tsukamoto, 2,3,4 Jian-Chang Liu, 1 Claudine Kashiwabara, 1 Douglas Feldman, 1,3 Linda
Research article Reciprocal regulation by TLR4 and TGF-β in tumor-initiating stem-like cells Chia-Lin Chen, 1 Hidekazu Tsukamoto, 2,3,4 Jian-Chang Liu, 1 Claudine Kashiwabara, 1 Douglas Feldman, 1,3 Linda
Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery
 Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery Presenter: April 12, 2017 Ed Davis, Ph.D. Senior Application Scientist GeneCopoeia, Inc. Outline Introduction to GeneCopoeia Lentiviral
Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery Presenter: April 12, 2017 Ed Davis, Ph.D. Senior Application Scientist GeneCopoeia, Inc. Outline Introduction to GeneCopoeia Lentiviral
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH CONSIDERATIONS FOR WORK WITH VIRAL VECTORS
 OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH CONSIDERATIONS FOR WORK WITH VIRAL VECTORS GARY R. FUJIMOTO, M.D. PALO ALTO MEDICAL FOUNDATION ADJUNCT ASSOCIATE CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES AND GEOGRAPHIC
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH CONSIDERATIONS FOR WORK WITH VIRAL VECTORS GARY R. FUJIMOTO, M.D. PALO ALTO MEDICAL FOUNDATION ADJUNCT ASSOCIATE CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES AND GEOGRAPHIC
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Exosomes mediate the cell-to-cell transmission of interferon alpha-induced antiviral activity Jianhua Li, Kuancheng Liu, Yang Liu, Yan Xu, Fei Zhang, Huijuan Yang, Jiangxia Liu,
Supplementary information Exosomes mediate the cell-to-cell transmission of interferon alpha-induced antiviral activity Jianhua Li, Kuancheng Liu, Yang Liu, Yan Xu, Fei Zhang, Huijuan Yang, Jiangxia Liu,
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Targeting of the MUC1-C Oncoprotein in Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0322 TITLE: Targeting of the MUC1-C Oncoprotein in Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kufe, Donald W., M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Boston, MA 02215-5450
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0322 TITLE: Targeting of the MUC1-C Oncoprotein in Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kufe, Donald W., M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Boston, MA 02215-5450
Research Article Plasma HULC as a Promising Novel Biomarker for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 BioMed Research International Volume 213, Article ID 13616, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/13616 Research Article Plasma HULC as a Promising Novel Biomarker for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
BioMed Research International Volume 213, Article ID 13616, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/13616 Research Article Plasma HULC as a Promising Novel Biomarker for the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
TITLE: The Role of HOX Proteins in Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-6-1-64 TITLE: The Role of HOX Proteins in Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Sunshine Daddario, B.A. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Colorado Health
AD Award Number: W81XWH-6-1-64 TITLE: The Role of HOX Proteins in Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Sunshine Daddario, B.A. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Colorado Health
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Increased ABHD5 expression in human colon cancer associated macrophages. (a) Murine peritoneal macrophages were treated with regular culture medium (Ctrl) or
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Increased ABHD5 expression in human colon cancer associated macrophages. (a) Murine peritoneal macrophages were treated with regular culture medium (Ctrl) or
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
Prevention and treatment of swine-origin influenza virus with interferon: an in vivo and ex vivo study
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Prevention and treatment of swine-origin influenza virus with interferon: an in vivo and ex vivo study JM Nicholls *, RWY Chan, E Fish K e y M e s s
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Prevention and treatment of swine-origin influenza virus with interferon: an in vivo and ex vivo study JM Nicholls *, RWY Chan, E Fish K e y M e s s
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Temozolomide suppresses MYC via activation of TAp63 to inhibit progression of human glioblastoma Tomohiro Yamaki, Yusuke Suenaga, Toshihiko Iuchi, Jennifer Alagu, Atsushi Takatori,
Supplementary Information Temozolomide suppresses MYC via activation of TAp63 to inhibit progression of human glioblastoma Tomohiro Yamaki, Yusuke Suenaga, Toshihiko Iuchi, Jennifer Alagu, Atsushi Takatori,
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed.
 Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Carboxyl-terminal truncated HBx regulates a distinct microrna transcription program in Hepatocellular carcinoma development. Title
 Title Author(s) Carboxyl-terminal truncated HBx regulates a distinct microrna transcription program in Hepatocellular carcinoma development Yip, WK; Cheng, ASL; Zhu, R; Lung, RWM; Tsang, DPF; Lau, SSK;
Title Author(s) Carboxyl-terminal truncated HBx regulates a distinct microrna transcription program in Hepatocellular carcinoma development Yip, WK; Cheng, ASL; Zhu, R; Lung, RWM; Tsang, DPF; Lau, SSK;
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
