IN VIVO. bleomycin interacts with radiation in our. tumour system as it appears to do in vitro. WHT/Ht were used as tumour hosts in the
|
|
|
- Alan James
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Br. J. Cancer (1974) 3, 463 THE EFFECT OF BLEOMYCIN AND ITS COMBINED EFFECT WITH RADIATION ON MURINE SQUAMOUS CARCINOMA TREATED IN VIVO K. SAKAMOTO* AND M. SAKKA Fromn the Departm,ent of Radiation Research, Tohoku University School of Medicine, 2-1 Seiryocho, Sendai, Japan Received 13 June Accepted 1 July 1974 Summary.-Many previous reports testify to the effectiveness of bleomycin as a drug for the clinical treatment of squamous carcinomata, and some radiotherapists have considered the possibility that an improved therapeutic ratio might be obtained by combined treatment with bleomycin and radiation. This consideration has been stimulated by recent reports of the effects of combined treatment with bleomycin using mammalian cells in vitro. Experiments are described here in which a murine squamous carcinoma has been used to obtain a survival curve for cells of tumours treated in vivo with single doses of bleomycin alone or in combination with radiation given before or after the drug. The survival curve for drug alone was a multicomponent curve with Do values of.1, -75 and2-7mg/kg. However,theresultsof the experiments with combined treatment showed no evidence of potentiation. BLEOMYCIN is an anti-tumour drug discovered by Umezawa et al. (1966a, b). Investigations have been made of its actions on mammalian cells (Kunimoto, Hori and Umezawa, 1967; Terasima, Yasukawa and Umezawa, 197; Terasima and Umezawa, 197). The drug has been used clinically and has shown strong antitumour activities against human tumours, being specifically remarkably effective against squamous carcinoma (Ichikawa, 1969; Miyake and Inuyama, 1971; Blum, Carter and Agre, 1973). However, there are no experimental data demonstrating its effect on squamous carcinoma. Recently, Matsuzawa et al. (1972) suggested that bleomycin had a potentiating effect when used in combination with radiation. The purpose of the present work was to determine the dose survival relationship with a murine epithelioma, whose response to bleomycin has not yet been studied, and to ascertain whether or not bleomycin interacts with radiation in our tumour system as it appears to do in vitro. MATERIALS AND METHODS Mlice.-Male or female mice of strain WHT/Ht were used as tumour hosts in the TD5 experiments. Tumour.-This was a transplantable keratinizing squamous carcinoma which arose spontaneously in a WHT/Ht mouse and has since been maintained by serial passage subcutaneously. A full description of the tumour has been reported by Hewitt, Chan and Blake (1967) and Hewitt and Sakamoto (1971). Treatment with bleomycin.-the stock solution of bleomycin was prepared at a concentration of 5 mg/ml in saline from powder as is used clinically. For use, the stock solution was diluted with saline to give a range of concentration of the drug from 3 mg/ml to 2- mg/ml, in order to keep the volume of 3 ml as a constant volume, to be injected intraperitoneally with changes in drug dose. * Present address: Department of Radiation Biophysics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113, Japan.
2 464 K. SAKAMOTO AND M. SAKKA Irradiation. X-rays were geneiated by a therapy machine operated at 18 kvp and 2 ma and were filtered through 7 mm Cu and -5 mm A]. The exposure rate, measured with a Victoreen condenser chamber (Model 57) without any additional absorber, using the calibration factor supplied by the Electro Technical Laboratories, Tokyo, was 78 rad/min; the FSD w%as 35 cm. Single unanaesthetized tumour bearing mite were exposed to whole body irradiation while confined in a perforated Perspex cylinder, immediately before or at 1 h after bleomycin treatment. Survival of tumour cells. Tumour bearing mice were prepared by the subcutaneous injection of 8, tumour cells into each axilla 1-11 days before treatment; the tumour at this stage weighed g. The mice were treated intraperitoneally with a range of doses of bleomycin 1 h before killing. Single-cell suspensions of tumours cells were prepared from the tumours by a method described previously (Hewitt, 1966). Transplantation assays of counted suspensions were performed by the technique described by Hewitt et al. (1967). The TD5 (number of cells required for successful transplantation to half a group of injected sites) and its 95% confidence limits were calculated from the results of an assay by the method of Litchfield and Wilcoxon (1949). A series of assays of cells from untreated tumours yielded a mean TD5 of 9-6 cells. The surviving fraction of cells from treated tumours was therefore obtained from the expression 9.6/TD5 for treated cells. RESULTS Survival of tumour cells treated by bleomycin The single-dose survival curves of the squamous carcinoma cells exposed to bleomycin are shown in Fig. 1 and 2. The curve in Fig. 1 has 2 components, the first part bending at a dose level of approximately -2 mg/kg. The Do of the first component is 41 mg/kg and that of the second part is 75 mg/kg. The single-dose survival curve of the tumour cells treated at higher dose levels of bleomycin, shown in Fig. 2, demonstrates a third component. (The first component in Fig. 2 corresponds to the second component in Fig. 1.) In Fig. 2 the second component shifts to the third ' {5 c I- c C- ur j BIeomycin (mg/ kg ) FIG. 1. Survival of clonogenic squamous carcinoma cells 1 h after treatment with mg/kg bleomycin.
3 EFFECT OF BLEOMYCIN AND ITS COMBINED EFFECT WITH RADIATION C V.S- to C.c > n) I Bleomycin ( mg/kg) FIG. 2.-Survival of clonogenic squamous carcinoma cells 1 h after treatment with 15-l1 mg/kg bleomycin. I component at a dose level of 2-5 mg/kg, the Do of the third component being 2-7 mg/kg. The explanation for the trimodal response to the drug, indicated by the shape of the survival curve, is not clear but will be considered further in the Discussion. Survival of tumour cells treated by combined bleomycin and radiation Figures 3 and 4 show the survival of squamous carcinoma cells given combined treatment with bleomycin and x-rays. In Fig. 3 the open circles indicate the survival of tumour cells exposed to graded doses of x-rays 1 h after treatment with 3 mg/kg of bleomycin; the closed circles show the survival of tumour cells treated with 3 mg/kg of bleomycin for 1 h immediately after exposure to graded doses of x-rays. Figure 4 shows the results of similar experiments to those in Fig. 3, except that 1 mg/kg of bleomycin was given instead of 3 mg/kg (as in the experiments shown in Fig. 3). In Fig. 3 and 4 the solid lines are superimposed from previously published data (Sakamoto and Sakka, 1973a), these being the survival curve for squamous carcinoma cells irradiated in air under the same irradiation conditions as used in this paper. The interrupted lines show the expected tumour cell survivals if bleomycin has only an additive cell killing effect when combined with x-rays. It is clear from the results shown that bleomycin has no potentiating effect with radiation in the killing of squamous carcinoma cells.
4 466 K. SAKAMOTO AND M. SAKKA _ - -2 c. _.C 3 tni 4; Dose( rad) FiG. 3.-Survival of tumour cells after combined treatment with bleomycin and x-rays., survival of cells exposed to x-rays I h after treatment with 3 mg/kg bleomycin., survival of cells treated for 1 h with 3 mg/kg bleomycin immediately after exposure to graded doses of x-rays. Solid line is superimposed from previously published data (Sakamoto and Sakka, 1973a). Iinterrupted line shows the expected tumour cell survivals if bleomycin has only an additive cell killing effect with x-rays. DISCUTSSION The compound survival curve obtained for bleomycin shows some resemblance to that commonly obtained for cells of solid tumours irradiated in vivo (Powers and Tolmach, 1963; Clifton, Briggs and Stone, 1966; Reinhold, 1966), in which the cell population exposed consists of a mixture of oxygenated and hypoxic cells of widely different radiosensitivities. The bleomycin dose survival curve also resembles the survival curve for epithelioma cells exposed to neocarzinostatin (Sakamoto and Sakka, 1973b), except for the third component in the survival curve for bleomycin. In the case of the survival curve for bleomycin, its shape is open to several possible interpretations: (1) hypoxic cells may be more resistant to the drug, as they are to irradiation; (2) the cell population may consist of 3 components differing in sensitivity to the drug on account of some feature other than their oxygenation; (3) the more resistant cells
5 EFFECT OF BLEOMYCIN AND ITS COMBINED EFFECT WITH RADIATION 467 _ 1- c 2 U 1- C. > Ln 9- L s~~~~~ Dose ( rad ) Fie-. 4. Survival of tumour cells after combine(d treat,ment with bleomycin an(l x-rays., survival of cells of tumours exposed to x-rays I h after treatment with 1- mg/kg bleomycin., survival of cells treated for 1 h with 1- mg/kg bleomycin imme(liately after exposure to gradedl doses of x-rays. Solid line and interrupted line are the same as in Fig. 3. niay be those less accessible to the drug because of vascular deficiency; (4) there may be a limiting concentration of drug, above which there is no enhancement of cytolethality, additional drug being wasted ". Matsuzawa et al. (1972) suggest that bleomycin potentiates the effect of x-rays using mouse cancer cells in vitro; Bienkowska, Dawson and Peacock (1973) showed no interaction between bleomycin and x-rays using HeLa cells. In ouir experimental system, bleomycin shows no potentiating effect with x-rays. In the experiment using combined treatment, we administered x-ray doses over 1 rad, but recently it has become clear that there is no potentiating effect even with a dose of less than 1 rad. Bleomycin has been reported to have a remarkable effect on clinical squamous carcinomata; it was also found to be as effective in the present experimental system as neocarzinostatin given in doses 1 times as large (Sakamoto and Sakka, 1 973b). However, the results reported
6 468 K. SAKAMOTO AND M. SAKKA here do not suggest that a potentiating effect between bleomycin and radiation can be expected. This investigation was supported in part by the Wacksman's Foundation of Japan. REFERENCES BIENKOWSKA, Z. Al., DAWSON, K. B. & PEACOCK, J. H. (1973) Action of Actinomycin D, Bleomycin and X-rays on HeLa Cells. Br. J. Radiol., 46, 619. BLUMA, R. H., CARTER, S. K. & AGRE, K (1973) A Clinical Review of Bleomycin-A New Antineoplastic Agent. Cacnncer, N. Y., 31, 93. CLIFTON, K. H., BRIGGS, R. C. & STONE, H. B. (1966) Quantitative Radiosensitivity Studies of Solid Carcinoma in vivo: Metho(lology and Effect of Anoxia. J. natn. Cancer Inst., 36, 965. HEWITT, H. B. (1966) The Effect on Cell Survival of Inhalation of Oxygen under High Pressure during Irradiation in vivo of a Solid Mouse Sarcoma. Br. J. Radiol., 39, 19. HEWITT, H. B., CHAN, D. P. & BLAKE, E. R. (1967) Survival Curves of Colonogenic Cells of a Murine Keratinizing Squamous Carcinoma Irradiated int vsivo or under Hypoxic Conditions. Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 12, 535. HEWITT, H. B. & SAKAMOTO, K. ( 1971 ) The Comparative Survival of Clonogenic Cells of a Murine Epithelioma after Irradiation in Mice breathing Air, Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide, or Hyperbaric Oxygen. Br. J. Radiol., 44, 457. ICHIKAWA, T. (1969) The Clinical Effect of Bleomycin against Squamous Carcinoma and Further Development. Proc. 6th Int. Cong. Chemother. (Tokyo), Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press., 2, 288. KUNIMOTO, T., HORI, M. & UMEZAWA, H. (1967) Modes of Action of Phleomycin, Bleomycin and Formycin on HeLa S3 Cells in Synchronous Culture. J. Anztibiot., Ser. A, (Tokyo), 2, 277. LITCHFIELD, J. T. & WILCOXON, F. (1949) A Simplified Method of Evaluating Dose-effect ExperimeInts. J. Pharm. exp. Ther., 96, 99. MATSITZAWA, T., ONOZAWA, M., MORITA, K. & KAKEHI, M. (1972) Radiosensitization of Bleomycin on Lethal Effect of AMouse Cancer Cell int vitro. Strahlentherapy, 144, 614. MIYAKE, H. & INUYAMA, Y. (1971) Bleomycin in Malignant Tumours of the Head and Neck. Proc. 7th Int. Cong. C(hernother. (Prague), MIiinchen/ Berlin/Wien: Urban and Schwarzenberg, 2, 633. POWERS, W. E. & TOLMACH, L. J. (1963) A Multicomponent X-ray Survival Curve for Mouse Lymphosarcoma Cells Irradiated in vivo. Nature, Lond., 197, 71. REINHOLD, H. S. (1966) Quantitative Evaluation of the Radiosensitivity of Cells of a Transplantable Rhabdomyosarcoma in the Rat. Eur. J. Cancer, 2, 33. SAKAMOTO, K. & SAKKA, MI. (1973a) Reduced Effect of Irradiation on Normal and AMalignant Cells Irradiated in vivo in Mice Pretreated with Vitamin E. Br. J. Radiol., 46, 538. SAKAMOTO, K. & SAKKA, Al. (1973b) Survival of Clonogenic Cells of a Murine Epithelioma Treated with Neocarzinostatin. Eur. J. Cancer, 9, 829. TERASIMA, T. & UMEZAWA, H. (197) Lethal Effect of Bleomycin on Cultured Mammalian Cells. J. Antibiot., 23, 3. TERASIMA, T., YASUKAWA, AM. & UMEZAWA, H. (197) Breaks and Rejoining of DNA in Culturedl Mammalian Cells Treated with Bleomycin. Gann, 61, 513. UMEZAWA, H., AIAEDA, K., TAKEUCHI, T. & OKAMr, Y. (1966a) New antibiotic, Bleomycin A and B. J. Antibiot. Ser A, (Tokyo), 19, 2. UMEZAWA, H., SLJHARA, Y., TAKITA, T. & MAEDA, K. (1966b) Purification of Bleomycin. J. Antibiot., Ser A, (Tokyo), 19, 21.
RADIOSENSITIVITY OF MURINE MALIGNANT CELLS IN VIVO
 323 EFFECT OF INDUCED HOST ANAEMIA ON THE VIABILITY AND RADIOSENSITIVITY OF MURINE MALIGNANT CELLS IN VIVO H. B. HEWITT AND EILEEN R. BLAKE From the Cancer Research Campai'gn, Research Unit in Rabiodiology,
323 EFFECT OF INDUCED HOST ANAEMIA ON THE VIABILITY AND RADIOSENSITIVITY OF MURINE MALIGNANT CELLS IN VIVO H. B. HEWITT AND EILEEN R. BLAKE From the Cancer Research Campai'gn, Research Unit in Rabiodiology,
THE COMBINED EFFECTS OF 60CO GAMMA-RAYS AND CONTINUOUS LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF BLEOMYCIN ON CULTURED MAMMALIAN CELLS
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 46. 27-33. 1984 THE COMBINED EFFECTS OF 6CO GAMMA-RAYS AND CONTINUOUS LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF BLEOMYCIN ON CULTURED MAMMALIAN CELLS HIDETOSHI KOBAYASHI and SADAYUKI SAKUMA Departmem 1'
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 46. 27-33. 1984 THE COMBINED EFFECTS OF 6CO GAMMA-RAYS AND CONTINUOUS LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF BLEOMYCIN ON CULTURED MAMMALIAN CELLS HIDETOSHI KOBAYASHI and SADAYUKI SAKUMA Departmem 1'
(Grey and Michaels, 1972; Halnan et al., (Suzuki, Nagai and Yamaki, (Lundbeck) is composed basically of. (Umezawa et al., 1972; Ichikawa et al.
 Br. J. Cancer (1977) 36, 78 COMBINED EFFECTS OF BLEOMYCIN AND X-RAYS ON DNA SYNTHESIS IN ASYNCHRONOUS EHRLICH ASCITES CELLS IN SUSPENSION F. A. ALALAWI AND I. V. CHAPMAN From the Department of Medical
Br. J. Cancer (1977) 36, 78 COMBINED EFFECTS OF BLEOMYCIN AND X-RAYS ON DNA SYNTHESIS IN ASYNCHRONOUS EHRLICH ASCITES CELLS IN SUSPENSION F. A. ALALAWI AND I. V. CHAPMAN From the Department of Medical
SUBCUTANEOUSLY INOCULATED R-1,M TUMOUR CELLS
 Br. J. Cancer (198) 41, Suppl. IV, 245 INFLUENCES OF THE HOST AND LOCAL CONDITIONS ON THE IN VIVO CLONOGENIC EXPRESSION OF SUBCUTANEOUSLY INOCULATED R-1,M TUMOUR CELLS A. F. HERMENS From the Radiobiological
Br. J. Cancer (198) 41, Suppl. IV, 245 INFLUENCES OF THE HOST AND LOCAL CONDITIONS ON THE IN VIVO CLONOGENIC EXPRESSION OF SUBCUTANEOUSLY INOCULATED R-1,M TUMOUR CELLS A. F. HERMENS From the Radiobiological
American Nuclear Society Annual Meeting Chicago, June 24-28, 2012 President s Special Session
 American Nuclear Society Annual Meeting Chicago, June 24-28, 2012 President s Special Session LOW-LEVEL LEVEL RADIATION AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR FUKUSHIMA RECOVERY Radiation Oncology Kiyohiko Sakamoto
American Nuclear Society Annual Meeting Chicago, June 24-28, 2012 President s Special Session LOW-LEVEL LEVEL RADIATION AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR FUKUSHIMA RECOVERY Radiation Oncology Kiyohiko Sakamoto
Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1
 RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE
 COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
[GANN, 52, ; September, 1961]
![[GANN, 52, ; September, 1961] [GANN, 52, ; September, 1961]](/thumbs/87/97250948.jpg) [GANN, 52, 257-264; September, 1961] CHROMOSOMAL ALTERATION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF TUMORS, VII. KARYOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF SPONTA- NEOUS AND INDUCED LEUKEMIAS IN MICE1)2) YOSHINORI KURITA and TOSIHIDE H.
[GANN, 52, 257-264; September, 1961] CHROMOSOMAL ALTERATION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF TUMORS, VII. KARYOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF SPONTA- NEOUS AND INDUCED LEUKEMIAS IN MICE1)2) YOSHINORI KURITA and TOSIHIDE H.
Radiation-Induced Mitotic Delay in L Cells
 RADIATION RESEARCH 30, 155-171 (1967) Radiation-Induced Mitotic Delay in L Cells G. F. WHITMORE, J. E. TILL, AND S. GULYAS Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, and Ontario Cancer Institute,
RADIATION RESEARCH 30, 155-171 (1967) Radiation-Induced Mitotic Delay in L Cells G. F. WHITMORE, J. E. TILL, AND S. GULYAS Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, and Ontario Cancer Institute,
Combined drug and ionizing radiation: biological basis. Prof. Vincent GREGOIRE Université Catholique de Louvain, Cliniques Universitaires St-Luc
 Combined drug and ionizing radiation: biological basis Prof. Vincent GREGOIRE Université Catholique de Louvain, Cliniques Universitaires St-Luc Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with
Combined drug and ionizing radiation: biological basis Prof. Vincent GREGOIRE Université Catholique de Louvain, Cliniques Universitaires St-Luc Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with
tumors, whose diagnosis had been confirmed
 160 CHEMOTHERAPY JULY, 1955 A CANCER CONTROL WITH SARKOMYCIN SHUNJI ISHIYAM A Director of Surgery, Kanto Teishin Hospital Cancer chemotherapy is nowadays considered as the use of a systematically administered
160 CHEMOTHERAPY JULY, 1955 A CANCER CONTROL WITH SARKOMYCIN SHUNJI ISHIYAM A Director of Surgery, Kanto Teishin Hospital Cancer chemotherapy is nowadays considered as the use of a systematically administered
Assistant Professor Department of Therapeutic Radiology Yale University School of Medicine
 A Mechanism-Based Approach to Predict Relative Biological i Effectiveness and the Effects of Tumor Hypoxia in Charged Particle Radiotherapy David J. Carlson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Therapeutic
A Mechanism-Based Approach to Predict Relative Biological i Effectiveness and the Effects of Tumor Hypoxia in Charged Particle Radiotherapy David J. Carlson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Therapeutic
Stage-dependent changes of chromosomal radiosensitivity in primary oocytes of the Chinese hamster
 Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 30: 174-178 (1981) Stage-dependent changes of chromosomal radiosensitivity in primary oocytes of the Chinese hamster K. M ikamo, Y. Kamiguchi, K. Funaki, S.Sugawara, and H.T ateno
Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 30: 174-178 (1981) Stage-dependent changes of chromosomal radiosensitivity in primary oocytes of the Chinese hamster K. M ikamo, Y. Kamiguchi, K. Funaki, S.Sugawara, and H.T ateno
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs. Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica
 Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Br. J. Cancer (1975) 31, 228
 Br. J. Cancer (1975) 31, 228 RESPONSES OF AN EXPERIMENTAL SOLID TUMOUR TO IRRADIATION: A COMPARISON OF MODES OF FRACTIONATION L. L. SCHENKEN, L. POULAKOS AND R. F. HAGEMIANN Fromt the Clinical Radiation
Br. J. Cancer (1975) 31, 228 RESPONSES OF AN EXPERIMENTAL SOLID TUMOUR TO IRRADIATION: A COMPARISON OF MODES OF FRACTIONATION L. L. SCHENKEN, L. POULAKOS AND R. F. HAGEMIANN Fromt the Clinical Radiation
(From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New Jersey)
 THE YIELD OF RABIES VIRUS IN THE CHICK EMBRYO BY BJORN SIGURDSSON, M.D.* (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New Jersey) (Received
THE YIELD OF RABIES VIRUS IN THE CHICK EMBRYO BY BJORN SIGURDSSON, M.D.* (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New Jersey) (Received
THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION II. HYBRIDS BETWEEN EHRLICH CELLS AND NORMAL DIPLOID CELLS
 J. Cell Sci. 8, 673-68 (97) 673 Printed in Great Britain THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION II. HYBRIDS BETWEEN EHRLICH CELLS AND NORMAL DIPLOID CELLS U. BREGULA,* G. KLEIN Department of Tumor Biology,
J. Cell Sci. 8, 673-68 (97) 673 Printed in Great Britain THE ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANCY BY CELL FUSION II. HYBRIDS BETWEEN EHRLICH CELLS AND NORMAL DIPLOID CELLS U. BREGULA,* G. KLEIN Department of Tumor Biology,
TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK
 Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY Ravi Pachigolla, MD Faculty Advisor: Anna Pou, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2000 HISTORY
PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY Ravi Pachigolla, MD Faculty Advisor: Anna Pou, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2000 HISTORY
Chemo-radiation and targeted agents: biological basis
 Chemoradiation and targeted agents: biological basis Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with pelvic and paraaortic radiation for highrisk cervical cancer. M. Morris et al, NEJM, 3:1137113,
Chemoradiation and targeted agents: biological basis Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with pelvic and paraaortic radiation for highrisk cervical cancer. M. Morris et al, NEJM, 3:1137113,
the Action o f Radium Rays upon the Cells o f Jensen's Rat Sarcoma.
 Downloaded from http:rspb.royalsocietypublishing.org on May 3, 2018 482 On the Action o f Radium Rays upon the Cells o f Jensen's Rat Sarcoma. By S. Buss, D.Sc.,* and H elen Chambers, M.D. (Communicated
Downloaded from http:rspb.royalsocietypublishing.org on May 3, 2018 482 On the Action o f Radium Rays upon the Cells o f Jensen's Rat Sarcoma. By S. Buss, D.Sc.,* and H elen Chambers, M.D. (Communicated
ENHANCING EFFECT OF COENZYME Q10 ON IMMUNORESTORATION WITH MYCOBACTERIUM BOVIS BCG IN TUMOR-BEARING MICE*1
 ENHANCING EFFECT OF COENZYME Q10 ON IMMUNORESTORATION WITH MYCOBACTERIUM BOVIS BCG IN TUMOR-BEARING MICE*1 Ichiro KAWASE, Hisanobu NIITANI, Nagahiro SAIJO, Haruo SASAKI, and Tatsuhide MORITA National Cancer
ENHANCING EFFECT OF COENZYME Q10 ON IMMUNORESTORATION WITH MYCOBACTERIUM BOVIS BCG IN TUMOR-BEARING MICE*1 Ichiro KAWASE, Hisanobu NIITANI, Nagahiro SAIJO, Haruo SASAKI, and Tatsuhide MORITA National Cancer
CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS
 10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
J. clin. Path.. 30, Suppl. (Ra5y. Coll. Path.), 11, ). It is thus possible that cells do live in the
 Hypoxia and tumours R. H. THOMLINSON J. clin. Path.. 30, Suppl. (Ra5y. Coll. Path.), 11, 105-113 From the Regional Radiotherapy Centre, Mount Vernon Hospital, Northwood, Middlesex Cells in tumours become
Hypoxia and tumours R. H. THOMLINSON J. clin. Path.. 30, Suppl. (Ra5y. Coll. Path.), 11, 105-113 From the Regional Radiotherapy Centre, Mount Vernon Hospital, Northwood, Middlesex Cells in tumours become
SOME ESSENTIAL FACTORS IN THE PATHOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF CANCER OF THE SKIN LOUIS H. JORSTAD, M.D.
 SOME ESSENTIAL FACTORS IN THE PATHOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF CANCER OF THE SKIN LOUIS H. JORSTAD, M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, the Barnard Free Skin and Cancer Hospital, St. Louis, Missouri) The
SOME ESSENTIAL FACTORS IN THE PATHOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF CANCER OF THE SKIN LOUIS H. JORSTAD, M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, the Barnard Free Skin and Cancer Hospital, St. Louis, Missouri) The
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview. Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga
 Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
S Bacg et a1.2 demonstrated the radioprotective
 RADIOPROTECTION OF TUMOR AND NORMAL TISSUES BY THIOPHOSPHATE COMPOUNDS THEODORE L. PHILLIPS, MD,* LAWRENCE KANE, BS,+ JOELLA F. UTLEY, MD* The efficacy of the radioprotective thiophosphate. compounds WR638
RADIOPROTECTION OF TUMOR AND NORMAL TISSUES BY THIOPHOSPHATE COMPOUNDS THEODORE L. PHILLIPS, MD,* LAWRENCE KANE, BS,+ JOELLA F. UTLEY, MD* The efficacy of the radioprotective thiophosphate. compounds WR638
Pathology, the Medical School, Birmingham B15 2TJ
 J. Phygiol. (1973), 228, pp. 279-284 279 Printed in Great Britain BLOOD VOLUME DETERMINATION IN THE MOUSE BY A. C. RICHES, J. G. SHARP, D. BRYNMOR THOMAS AND S. VAUGHAN SMITH From the Department of Anatomy
J. Phygiol. (1973), 228, pp. 279-284 279 Printed in Great Britain BLOOD VOLUME DETERMINATION IN THE MOUSE BY A. C. RICHES, J. G. SHARP, D. BRYNMOR THOMAS AND S. VAUGHAN SMITH From the Department of Anatomy
Appendix Figure S1 A B C D E F G H
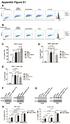 ppendix Figure S1 C D E F G H ppendix Figure S1. RT and chemotherapy alter PD-L1 expression in PDC cells. Flow cytometric analysis of PD-L1 expression in () KPC and () Pan02 cells following treatment with
ppendix Figure S1 C D E F G H ppendix Figure S1. RT and chemotherapy alter PD-L1 expression in PDC cells. Flow cytometric analysis of PD-L1 expression in () KPC and () Pan02 cells following treatment with
Radiotherapy in feline and canine head and neck cancer
 Bettina Kandel Like surgery radiotherapy is usually a localized type of treatment. Today it is more readily available for the treatment of cancer in companion animals and many clients are well informed
Bettina Kandel Like surgery radiotherapy is usually a localized type of treatment. Today it is more readily available for the treatment of cancer in companion animals and many clients are well informed
Radiation Carcinogenesis
 Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons
 Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Residual Late Radiation Damage in Mouse Stromal Tissue Assessed by the Tumor Bed Effect
 J. Radiat. Res., 48, 107 112 (2007) Regular Paper Residual Late Radiation Damage in Mouse Stromal Tissue Assessed by the Tumor Bed Effect Jaap HAVEMAN* 1, Hans RODERMOND 1, Chris van BREE 1, Jan WONDERGEM
J. Radiat. Res., 48, 107 112 (2007) Regular Paper Residual Late Radiation Damage in Mouse Stromal Tissue Assessed by the Tumor Bed Effect Jaap HAVEMAN* 1, Hans RODERMOND 1, Chris van BREE 1, Jan WONDERGEM
THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS
 41 THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS T. J. DEELEY AND V. J. DESMET* From the Radiotherapy Department, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London, IF7.12, and the Department of Pathology, Louvain University,
41 THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS T. J. DEELEY AND V. J. DESMET* From the Radiotherapy Department, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London, IF7.12, and the Department of Pathology, Louvain University,
ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE. (Plates I-V)
 [GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
[GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
A radioprotective effect of vitamin C observed in Chinese hamster ovary cells
 1977, British Journal of Radiology, 50, 587-591 AUGUST 1977 A radioprotective effect of vitamin C observed in Chinese hamster ovary cells By M. K. O'Connor, B.Sc, J. F. Malone, Ph.D., B.Sc, M.lnst.P.,
1977, British Journal of Radiology, 50, 587-591 AUGUST 1977 A radioprotective effect of vitamin C observed in Chinese hamster ovary cells By M. K. O'Connor, B.Sc, J. F. Malone, Ph.D., B.Sc, M.lnst.P.,
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation.
 Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
Klinikleitung: Dr. Kessler Dr. Kosfeld Dr. Tassani-Prell Dr. Bessmann. Radiotherapy in feline and canine head and neck cancer.
 Radiotherapy in feline and canine head and neck cancer Bettina Kandel Like surgery radiotherapy is usually a localized type of treatment. Today it is more readily available for the treatment of cancer
Radiotherapy in feline and canine head and neck cancer Bettina Kandel Like surgery radiotherapy is usually a localized type of treatment. Today it is more readily available for the treatment of cancer
Dosimetry comparison of orthovoltage x-ray and 137 Cs irradiation of the murine bone marrow compartment Matthew Belley
 Dosimetry comparison of orthovoltage x-ray and 137 Cs irradiation of the murine bone marrow compartment Matthew Belley NCHPS Fall Meeting October 9, 2015 Duke Medical Physics Disclaimer Financial support
Dosimetry comparison of orthovoltage x-ray and 137 Cs irradiation of the murine bone marrow compartment Matthew Belley NCHPS Fall Meeting October 9, 2015 Duke Medical Physics Disclaimer Financial support
Hypofractionation in particle therapy. Marco Durante
 Hypofractionation in particle therapy Marco Durante 29.04.2014 Radiosurgery (SBRT): the new frontier in stereotactic imageguided radiotherapy Stage I (T1N0M0) NSCLC Oligometastases Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hypofractionation in particle therapy Marco Durante 29.04.2014 Radiosurgery (SBRT): the new frontier in stereotactic imageguided radiotherapy Stage I (T1N0M0) NSCLC Oligometastases Hepatocellular carcinoma
Different Types of Cancer
 Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
CHMP Oncology Working Party Workshop on: Histology Independent Indications in Oncology. Non-clinical models: Tumour Models - Proof of Concept
 CHMP Oncology Working Party Workshop on: Histology Independent Indications in Oncology Non-clinical models: Tumour Models - Proof of Concept Edward C. Rosfjord Pfizer Worldwide R. & D. 14 December 2017
CHMP Oncology Working Party Workshop on: Histology Independent Indications in Oncology Non-clinical models: Tumour Models - Proof of Concept Edward C. Rosfjord Pfizer Worldwide R. & D. 14 December 2017
66. The Cycle o f Tumor Cells in a Transplant Generation o f the Yoshida Sarcoma.
 No. 6.] 287 66. The Cycle o f Tumor Cells in a Transplant Generation o f the Yoshida Sarcoma. By Sajiro MAKINO. Zoological Institute, Hokkaido University. (Comm. by T. KOMA1, M.J.A., June 12, 1951.) The
No. 6.] 287 66. The Cycle o f Tumor Cells in a Transplant Generation o f the Yoshida Sarcoma. By Sajiro MAKINO. Zoological Institute, Hokkaido University. (Comm. by T. KOMA1, M.J.A., June 12, 1951.) The
Medical physics is beautiful
 Translational research in particle therapy Marco Durante Medical physics is beautiful Pisa, 31.10.2014 Relative dose 1. 2 1. 0 Tumor Durante & Loeffler, Nature Rev Clin Oncol 2010 0. 8 Normal tissue 0.
Translational research in particle therapy Marco Durante Medical physics is beautiful Pisa, 31.10.2014 Relative dose 1. 2 1. 0 Tumor Durante & Loeffler, Nature Rev Clin Oncol 2010 0. 8 Normal tissue 0.
1/31/2014. Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public
 Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Human Biology *P41558A0128* P41558A. Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01. Edexcel International GCSE. Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates
Research Article A Mathematical Model of Tumor Volume Changes during Radiotherapy
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 203, Article ID 8070, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/203/8070 Research Article A Mathematical Model of Tumor Volume Changes during Radiotherapy Ping Wang and Yuanming
The Scientific World Journal Volume 203, Article ID 8070, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/203/8070 Research Article A Mathematical Model of Tumor Volume Changes during Radiotherapy Ping Wang and Yuanming
Tumor hypoxia: its impact on cancer therapy
 Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 5: 313-341, 1987 Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Boston - Printed in the Netherlands. Tumor hypoxia: its impact on cancer therapy John E. Moulder 1, Sara Rockwell 2 1 Department
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 5: 313-341, 1987 Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Boston - Printed in the Netherlands. Tumor hypoxia: its impact on cancer therapy John E. Moulder 1, Sara Rockwell 2 1 Department
THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS RESPONSE TO BLEOMYCIN OF ESCHERICHIA COLI MUTANTS DEFICIENT IN DNA REPAIR
 1181 RESPONSE TO BLEOMYCIN OF ESCHERICHIA COLI MUTANTS DEFICIENT IN DNA REPAIR KAZUO YAMAMOTO and FRANKLIN HUTCHINSON Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
1181 RESPONSE TO BLEOMYCIN OF ESCHERICHIA COLI MUTANTS DEFICIENT IN DNA REPAIR KAZUO YAMAMOTO and FRANKLIN HUTCHINSON Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
Skyscan 1076 in vivo scanning: X-ray dosimetry
 Skyscan 1076 in vivo scanning: X-ray dosimetry DOSIMETRY OF HIGH RESOLUTION IN VIVO RODENT MICRO-CT IMAGING WITH THE SKYSCAN 1076 An important distinction is drawn between local tissue absorbed dose in
Skyscan 1076 in vivo scanning: X-ray dosimetry DOSIMETRY OF HIGH RESOLUTION IN VIVO RODENT MICRO-CT IMAGING WITH THE SKYSCAN 1076 An important distinction is drawn between local tissue absorbed dose in
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
ALTERATIONS OF ASPARTATE- AND ALANINE- TRANSAMINASE IN MICE WITH HEREDITARY MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY
 The Japanese Journal of Physiology 17, pp. 57-64, 1967 ALTERATIONS OF ASPARTATE- AND ALANINE- TRANSAMINASE IN MICE WITH HEREDITARY MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Shigekatsu TSUJI AND Hiroshi MATSUSHITA Department
The Japanese Journal of Physiology 17, pp. 57-64, 1967 ALTERATIONS OF ASPARTATE- AND ALANINE- TRANSAMINASE IN MICE WITH HEREDITARY MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Shigekatsu TSUJI AND Hiroshi MATSUSHITA Department
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION UPON THE REACTION OF THE FLUID OF RAT SARCOMA 10
 THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION UPON THE REACTION OF THE FLUID OF RAT SARCOMA 10 L. C. MAXWELL AND H. J. ULLMANN WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE ELLA MAY OTTERY OF (From the Department oj Cancer Research,
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION UPON THE REACTION OF THE FLUID OF RAT SARCOMA 10 L. C. MAXWELL AND H. J. ULLMANN WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE ELLA MAY OTTERY OF (From the Department oj Cancer Research,
EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS
 EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS INTRACELLULAR GROWTH OF Salmonella enteritidis INGESTED IN MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES OF MICE, AND CELLULAR BASIS OF IMMUNITY SUSUMU MITSUHASHI, ICHIEI SATO, AND TOKUMITSU TANAKA
EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS INTRACELLULAR GROWTH OF Salmonella enteritidis INGESTED IN MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES OF MICE, AND CELLULAR BASIS OF IMMUNITY SUSUMU MITSUHASHI, ICHIEI SATO, AND TOKUMITSU TANAKA
BY F. BROWN, B. CARTWRIGHT AND DOREEN L. STEWART Research Institute (Animal Virus Diseases), Pirbright, Surrey. (Received 22 August 1962) SUMMARY
 J. gen. Microbial. (1963), 31, 179186 Prinied in Great Britain 179 The Effect of Various Inactivating Agents on the Viral and Ribonucleic Acid Infectivities of FootandMouth Disease Virus and on its Attachment
J. gen. Microbial. (1963), 31, 179186 Prinied in Great Britain 179 The Effect of Various Inactivating Agents on the Viral and Ribonucleic Acid Infectivities of FootandMouth Disease Virus and on its Attachment
Introduction to Radiation Biology
 Introduction to Radiation Biology Survey of Clinical Radiation Oncology Outline Ionizing radiation Development of radiobiological damage Cell cycle Cell survival curves Tissue response and fractionation
Introduction to Radiation Biology Survey of Clinical Radiation Oncology Outline Ionizing radiation Development of radiobiological damage Cell cycle Cell survival curves Tissue response and fractionation
(CBA) spontaneous hepatomas of benign character have occurred."2. Boyland and Brues2 have reported work on the carcinogenic
 INDUCTION OF TUMORS BY 3:4:5:6-DIBENZCARBA- ZOLE IN MALE MICE OF THE CBA STRAIN, WHICH DEVELOPS SPONTANEOUS HEPATOMA* L. C. STRONG, G. M. SMITH, AND W. U. GARDNER Boyland and Brues2 have reported work
INDUCTION OF TUMORS BY 3:4:5:6-DIBENZCARBA- ZOLE IN MALE MICE OF THE CBA STRAIN, WHICH DEVELOPS SPONTANEOUS HEPATOMA* L. C. STRONG, G. M. SMITH, AND W. U. GARDNER Boyland and Brues2 have reported work
Nicotinamide, Fluosol DA and Carbogen: A strategy to reoxygenate
 Br. J. Cancer (1991), 63, 19-113 17" Macmillan Press Ltd., 1991 1991 Br. J. Cancer (1991), 63, 19 113 Nicotinamide, Fluosol DA and Carbogen: A strategy to reoxygenate acutely and chronically hypoxic cells
Br. J. Cancer (1991), 63, 19-113 17" Macmillan Press Ltd., 1991 1991 Br. J. Cancer (1991), 63, 19 113 Nicotinamide, Fluosol DA and Carbogen: A strategy to reoxygenate acutely and chronically hypoxic cells
Radiobiological modelling applied to Unsealed Source (radio) Therapy
 Radiobiological modelling applied to Unsealed Source (radio) Therapy Alan E. Nahum Physics Department Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust Bebington, Wirral CH63 4JY UK alan.nahum@clatterbridgecc.nhs.uk
Radiobiological modelling applied to Unsealed Source (radio) Therapy Alan E. Nahum Physics Department Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust Bebington, Wirral CH63 4JY UK alan.nahum@clatterbridgecc.nhs.uk
Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration between LNS INFN and Vinca Institute of Nuclear Sciences
 ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam
 Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
A PROPOSED COMMON MECHANISM OF ACTION FOR GENERAL AND LOCAL ANAESTHETICS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 1-9. A PROPOSED COMMON MECHANISM OF ACTION FOR GENERAL AND LOCAL ANAESTHETICS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BY G. B. FRANK AND H. D. SANDERS From the Department of Pharmacology
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 1-9. A PROPOSED COMMON MECHANISM OF ACTION FOR GENERAL AND LOCAL ANAESTHETICS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BY G. B. FRANK AND H. D. SANDERS From the Department of Pharmacology
IMPURITIES: GUIDELINE FOR RESIDUAL SOLVENTS PDE FOR CUMENE
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE DRAFT CONSENSUS GUIDELINE IMPURITIES: GUIDELINE FOR RESIDUAL SOLVENTS Released for
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE DRAFT CONSENSUS GUIDELINE IMPURITIES: GUIDELINE FOR RESIDUAL SOLVENTS Released for
Cancer. Chapter 31 Lesson 2
 Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Principles of chemotherapy
 Principles of chemotherapy Chemotherapy first coined by Paul Ehrlich Aim to selectively destroy cancer cells whilst relatively sparing tumours cells Growth characteristics of cancer cells allows for selective
Principles of chemotherapy Chemotherapy first coined by Paul Ehrlich Aim to selectively destroy cancer cells whilst relatively sparing tumours cells Growth characteristics of cancer cells allows for selective
Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (7) 264:1387 1391 DOI 1.17/s5-7-374-1 OTOLOGY Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube Yoko Hori Tetsuaki Kawase Takeshi Oshima Shuichi Sakamoto
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (7) 264:1387 1391 DOI 1.17/s5-7-374-1 OTOLOGY Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube Yoko Hori Tetsuaki Kawase Takeshi Oshima Shuichi Sakamoto
Nonparenteral medications
 Nonparenteral medications Capsules and unscored tablets are rounded to the nearest whole tablet. Scored tablets are rounded to the nearest 1/2 tablet. Liquid medications are rounded to one decimal place
Nonparenteral medications Capsules and unscored tablets are rounded to the nearest whole tablet. Scored tablets are rounded to the nearest 1/2 tablet. Liquid medications are rounded to one decimal place
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (2016)
 Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation
 J. RADIAT. RES., 40: SUPPL., 53 59 (1999) Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation RICHARD C. MILLER 1 *, STEPHEN A. MARINO 1, STEWART G. MARTlN 2, KENSHI KOMATSU 3, CHARLES
J. RADIAT. RES., 40: SUPPL., 53 59 (1999) Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation RICHARD C. MILLER 1 *, STEPHEN A. MARINO 1, STEWART G. MARTlN 2, KENSHI KOMATSU 3, CHARLES
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1
 TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
RADIOFREQUENCY DIATHERMY FOR UNIFORM HEATING
 Br. J. Cancer (1982) 45, Suppl. V, 71 RADIOFREQUENCY DIATHERMY FOR UNIFORM HEATING OF MOUSE TUMOURS M. C. JOINER AND B. VOJNOVIC From the Gray Laboratory of the Cancer Research Campaignt, Mount Vernon
Br. J. Cancer (1982) 45, Suppl. V, 71 RADIOFREQUENCY DIATHERMY FOR UNIFORM HEATING OF MOUSE TUMOURS M. C. JOINER AND B. VOJNOVIC From the Gray Laboratory of the Cancer Research Campaignt, Mount Vernon
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI. The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement.
 Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
THE EFFECT OF ADRENAL STEROIDS AND CORTI- COTROPHIN ON THE GROWTH OF A SARCOMA OF HUMAN ORIGIN IN SMALL LABORATORY ANIMALS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 307. THE EFFECT OF ADRENAL STEROIDS AND CORTI- COTROPHIN ON THE GROWTH OF A SARCOMA OF HUMAN ORIGIN IN SMALL LABORATORY ANIMALS BY G. A. H. BUTTLE, P. F. D'ARCY,* E. M.
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 307. THE EFFECT OF ADRENAL STEROIDS AND CORTI- COTROPHIN ON THE GROWTH OF A SARCOMA OF HUMAN ORIGIN IN SMALL LABORATORY ANIMALS BY G. A. H. BUTTLE, P. F. D'ARCY,* E. M.
The Radiobiological Four "R"s of Hypofractionation. Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health Systems
 The Radiobiological Four "R"s of Hypofractionation Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health Systems Overview of the presentation Definition of hypofractionation Radiobiology 4 R s Standard fraction dosing Linear
The Radiobiological Four "R"s of Hypofractionation Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health Systems Overview of the presentation Definition of hypofractionation Radiobiology 4 R s Standard fraction dosing Linear
Cell survival following high dose rate flattening filter free (FFF) and conventional dose rate irradiation
 Cell survival following high dose rate flattening filter free (FFF) and conventional dose rate irradiation Peter Sminia p.sminia@vumc.nl Λαβορατοριυµβεσπρεκινγ 8 νοϖεµβερ 2005 Progress in Radiotherapy:
Cell survival following high dose rate flattening filter free (FFF) and conventional dose rate irradiation Peter Sminia p.sminia@vumc.nl Λαβορατοριυµβεσπρεκινγ 8 νοϖεµβερ 2005 Progress in Radiotherapy:
Trends in cancer incidence in South East England Henrik Møller and all staff at the Thames Cancer Registry, King s College London
 Trends in cancer incidence in South East England 1960-2009 Henrik Møller and all staff at the Thames Cancer Registry, King s College London 1 2 3 Analysts Vicki Coupland Ruth Jack Margreet Lüchtenborg
Trends in cancer incidence in South East England 1960-2009 Henrik Møller and all staff at the Thames Cancer Registry, King s College London 1 2 3 Analysts Vicki Coupland Ruth Jack Margreet Lüchtenborg
Chemical Modification of Radiation Response
 Chemical Modification of Radiation Response Oxygen Oxygen best known and most general radiosensitizer The slopes of survival curves for cells exposed to sparsely ionizing radiation in hypoxia and in well
Chemical Modification of Radiation Response Oxygen Oxygen best known and most general radiosensitizer The slopes of survival curves for cells exposed to sparsely ionizing radiation in hypoxia and in well
nature of Q cells has been extensively examined. However, many aspects of these cells are still unknown (Jackson, 1989).
 British Joumal of Cancer (1997) 76(5), 588-593 1997 Cancer Research Campaign Reduction of hypoxic cells in solid tumours induced by mild hyperthermia: special reference to differences in changes in the
British Joumal of Cancer (1997) 76(5), 588-593 1997 Cancer Research Campaign Reduction of hypoxic cells in solid tumours induced by mild hyperthermia: special reference to differences in changes in the
The Importance of ADME/PK to Inform Human Safety Assessments Based on Animal Studies: Example with Furan. Gregory L. Kedderis, PhD Chapel Hill, NC
 The Importance of ADME/PK to Inform Human Safety Assessments Based on Animal Studies: Example with Furan Gregory L. Kedderis, PhD Chapel Hill, NC Conflict of Interest None This research was conducted at
The Importance of ADME/PK to Inform Human Safety Assessments Based on Animal Studies: Example with Furan Gregory L. Kedderis, PhD Chapel Hill, NC Conflict of Interest None This research was conducted at
TRANSPLANTATION OF EXPERIMENTAL OVARIAN TUMORS AND THEIR SENSITIVITY TO CARCINOSTATICS
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol, 26, No. 2, p.145-151, 1979 TRANSPLANTATION OF EXPERIMENTAL OVARIAN TUMORS AND THEIR SENSITIVITY TO CARCINOSTATICS MICHIAKI YAKUSHIJI, KAIKITSU IDE, HARUO NISHIMURA, TAKASHI
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol, 26, No. 2, p.145-151, 1979 TRANSPLANTATION OF EXPERIMENTAL OVARIAN TUMORS AND THEIR SENSITIVITY TO CARCINOSTATICS MICHIAKI YAKUSHIJI, KAIKITSU IDE, HARUO NISHIMURA, TAKASHI
Colony-forming ability of marrow from patients receiving immunotherapy during chemotherapyinduced
 J. clin. Path., 1977, 3, 7-75 Colony-forming ability of marrow from patients receiving immunotherapy during chemotherapyinduced remission in acute myeloid leukaemia M. Y. GORDON1, R. L. POWLES2, ND I.
J. clin. Path., 1977, 3, 7-75 Colony-forming ability of marrow from patients receiving immunotherapy during chemotherapyinduced remission in acute myeloid leukaemia M. Y. GORDON1, R. L. POWLES2, ND I.
NATURAL CAUSES OF VARIATIONS IN THE WEIGHT
 398 NATURAL CAUSES OF VARIATIONS IN THE WEIGHT OF SARCOMA I8 J. P. AUSTIN* AND E. M. GLASERt From the Riker Laboratories, Welwyn Garden City, Hertfordshire Received for publication November 11, 1969 SUMMARY.-The
398 NATURAL CAUSES OF VARIATIONS IN THE WEIGHT OF SARCOMA I8 J. P. AUSTIN* AND E. M. GLASERt From the Riker Laboratories, Welwyn Garden City, Hertfordshire Received for publication November 11, 1969 SUMMARY.-The
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS
 A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS KANEMATSU SUGIURA AND STANLEY R. BENEDICT (From tha Huntington Fund for Cancer hearch, Memorial Hoepitcrl and the Hamman Raearch Fund, New York) In recent
A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS KANEMATSU SUGIURA AND STANLEY R. BENEDICT (From tha Huntington Fund for Cancer hearch, Memorial Hoepitcrl and the Hamman Raearch Fund, New York) In recent
The Radiation Biology of Dose Fractionation: Determinants of Effect
 The Radiation Biology of Dose Fractionation: Determinants of Effect E. Day Werts, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology West Penn Allegheny Radiation Oncology Network Allegheny General Hospital Historical
The Radiation Biology of Dose Fractionation: Determinants of Effect E. Day Werts, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology West Penn Allegheny Radiation Oncology Network Allegheny General Hospital Historical
Calibration Protocols
 Calibration Protocols (1)OD 600 Reference point LUDOX Protocol Materials: 1ml LUDOX CL-X (provided in kit) ddh20 (provided by team) 96 well plate, black with clear flat bottom preferred (provided by team)
Calibration Protocols (1)OD 600 Reference point LUDOX Protocol Materials: 1ml LUDOX CL-X (provided in kit) ddh20 (provided by team) 96 well plate, black with clear flat bottom preferred (provided by team)
Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, Pamela Myers, Ph.D.
 Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, 2014 Pamela Myers, Ph.D. Introduction o o o o o Outline GRID compensator Purpose of SFRT/GRID therapy Fractionation
Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, 2014 Pamela Myers, Ph.D. Introduction o o o o o Outline GRID compensator Purpose of SFRT/GRID therapy Fractionation
THE TREATMENT OF ADVANCED MALIGNANT DISEASE BY RADIOTHERAPY AND SURGERY
 THE TREATMENT OF ADVANCED MALIGNANT DISEASE BY RADIOTHERAPY AND SURGERY By F. ELLIS, M.D., M.Sc., F.R.C.P., F.F.R., and T. J. S. PATTERSON, M.D., M.Chir., F.R.C.S. From the Departments of Radiotherapy
THE TREATMENT OF ADVANCED MALIGNANT DISEASE BY RADIOTHERAPY AND SURGERY By F. ELLIS, M.D., M.Sc., F.R.C.P., F.F.R., and T. J. S. PATTERSON, M.D., M.Chir., F.R.C.S. From the Departments of Radiotherapy
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Nuclear Extraction Kit NBP2-29447 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 888.506.6887 - technical@novusbio.com Novus kits are
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Nuclear Extraction Kit NBP2-29447 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 888.506.6887 - technical@novusbio.com Novus kits are
EFFECT OF RADIATION ON THYROID PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN RABBIT Murcia, Spain.
 EFFECT OF RADIATION ON THYROID PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN RABBIT. M. Alcaraz 1, F. Solano 2, V. Vicente 3, M.Canteras 4. 1 Radiology and Physical Medicine Department. University of Murcia. 31-Murcia. Spain.
EFFECT OF RADIATION ON THYROID PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN RABBIT. M. Alcaraz 1, F. Solano 2, V. Vicente 3, M.Canteras 4. 1 Radiology and Physical Medicine Department. University of Murcia. 31-Murcia. Spain.
HALF. Who gets radiotherapy? Who gets radiotherapy? Half of all cancer patients get radiotherapy. By 1899 X rays were being used for cancer therapy
 The Physical and Biological Basis of By 1899 X rays were being used for cancer therapy David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Department of Radiation Oncology Columbia University Medical
The Physical and Biological Basis of By 1899 X rays were being used for cancer therapy David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Department of Radiation Oncology Columbia University Medical
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR
 ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
Overview of methodology, tools and reagents for evaluating cell proliferation and invasion using multicellular tumor spheroids.
 The Next Step in the Evolution of 3D Culture: Utilizing Extracellular Matrix to Enhance Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Models for Proliferation and Invasion Overview of methodology, tools and reagents for
The Next Step in the Evolution of 3D Culture: Utilizing Extracellular Matrix to Enhance Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Models for Proliferation and Invasion Overview of methodology, tools and reagents for
INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCE IN THE EFFECT OF DRUGS IN RELATION TO THE TISSUE CONCENTRATION OF DRUGS
 INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCE IN THE EFFECT OF DRUGS IN RELATION TO THE TISSUE CONCENTRATION OF DRUGS RYUICHI KATO, AKIRA TAKANAKA AND KINICHI ONODA Department of Pharmacology, National Institute of Hygienic Sciences,
INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCE IN THE EFFECT OF DRUGS IN RELATION TO THE TISSUE CONCENTRATION OF DRUGS RYUICHI KATO, AKIRA TAKANAKA AND KINICHI ONODA Department of Pharmacology, National Institute of Hygienic Sciences,
What is Cancer? Understanding the basics of
 What is Cancer? Understanding the basics of A process of physical and biological changes that occur when normal healthy cells are transformed into cancer cells What is Cancer? Cancer is an umbrella term
What is Cancer? Understanding the basics of A process of physical and biological changes that occur when normal healthy cells are transformed into cancer cells What is Cancer? Cancer is an umbrella term
CHANGES IN THE MITOTIC INDEX OF THE LANDSCHUTZ INHIBITORY OR NON-INHIBITORY SAMPLES OF GUM- TRAGACANTH OR WITH GUM KARAYA
 528 CHANGES IN THE MITOTIC INDEX OF THE LANDSCHUTZ ASCITES TUAIOUR AFTER TREATMENT WITH TUMOUR- INHIBITORY OR NON-INHIBITORY SAMPLES OF GUM- TRAGACANTH OR WITH GUM KARAYA E. MAYHEW* AND E. M. F. ROE From
528 CHANGES IN THE MITOTIC INDEX OF THE LANDSCHUTZ ASCITES TUAIOUR AFTER TREATMENT WITH TUMOUR- INHIBITORY OR NON-INHIBITORY SAMPLES OF GUM- TRAGACANTH OR WITH GUM KARAYA E. MAYHEW* AND E. M. F. ROE From
THE RELATION BETWEEN SEDATION AND BODY TEMPERATURE IN THE MOUSE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1957), 12, 245. THE RELATION BETWEEN SEDATION AND BODY TEMPERATURE IN THE MOUSE BY A. W. LESSIN AND M. W. PARKES From the Biological Laboratories, Research Department, Roche Products
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1957), 12, 245. THE RELATION BETWEEN SEDATION AND BODY TEMPERATURE IN THE MOUSE BY A. W. LESSIN AND M. W. PARKES From the Biological Laboratories, Research Department, Roche Products
Production of Lung Carcinomas in C57BL Mice Exposed to a Cigarette Smoke and Air Mixture
 16 December 1967 BRITISH MEDICAL JOURNAL 637 Papers and Originals Production of Lung Carcinomas in C57BL Mice Exposed to a Cigarette Smoke and Air Mixture R. J. C. HARRIS,* PH.D., M.C.PATH.; G. NEGRONI,*
16 December 1967 BRITISH MEDICAL JOURNAL 637 Papers and Originals Production of Lung Carcinomas in C57BL Mice Exposed to a Cigarette Smoke and Air Mixture R. J. C. HARRIS,* PH.D., M.C.PATH.; G. NEGRONI,*
