THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
|
|
|
- Antony Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
2 ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated in the viral genome (viruses as carriers of host genes)
3 Retroviruses can cause cancer by picking up mutated versions of normal cellular genes
4 ONCOGENES
5 COMMON PROTO-ONCOGENE ALTERATIONS
6 FUNCTIONAL CLASSES OF ONCOGENES 1. Growth factors: PDGF, EGF 2. Growth factor receptors: EGFR, FLT3 3. Signal transduction proteins: SRC, RAS, PI3K 4. Proteins that control cell cycle: cyclins, CDK 5. Proteins that control cell survival and/or apoptosis: Bcl-2 6. Transcription factors: myc, NF-kB
7 1. ONCOGENES: GROWTH FACTORS NGF (1952 Rita Levi Montalcini): secreted by murine cancer cells that promoted neurite outgrowth EGF (1962 Cohen): first proliferation factor for epithelial cells thta induced precocius eyelid opening and tooth eruption when injected in newborn mice 1986 Nobel prize to Cohen to Levi-Montalcini Others PDGF, Ins, IGF, FGF etc
8 2. ONCOGENES: RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASES (RTK) Hubbard & Till 2001
9 EGFR FAMILY Extracellular domain, leucin rich - EGFR (HER1 or ErbB1) - HER2 (neu or ErbB2): no ligands, heterodimers with ErbB1 - HER3 (ErbB3): no intrinsic enzymatic activity - HER4 (ErbB4) Functional domains of interaction: SH2 (100 aa): binds tyrosine phosphorylated sequences SH3 (100 aa): binds proline-rich sequences PH: binds phospholipids (es. PIP3 in Akt, PDK1)
10 RECRUITMENT OF PROTEINS THROUGH THE SH2 DOMAINS
11 EGFR SIGNALLING Grb2-SOS: activates RAS/Raf/ERK pathway > Elk1 (c-fos) and c-myc PLC: hydrolysis of PIP2 in IP3 (Ca2+) and DAG (PKC) > NF-kB Vav1 and Nck: Rac1 GTPase (actin cytoskeleton reorganization) PAK1/MEEK/JNK > c-jun that together with c-fos forms AP-1 STAT1/STAT3 nuclear translocation transcriptional activation PI3K/Akt/mTOR: survival, metabolism and protein synthesis
12 PI3K
13 DEREGULATION OF EGFR IN HUMAN CANCERS 1980: Overexpression of EGFR in several epithelial tumors and autocrine stimulation Point Mutation and deletions resulted in increased catalytic activity Deletion of exons 2-7 (EGFRvIII): induced by rearrangement or alternative mrna splicing > constitutive active EGFR without an extracellular domain.
14 v-erbb: EGFR without an extracellular domain, constitutive activity v-erb: avian erythroblastosis virus
15 HER2 (1985) HER2 is the preferred heterodimerization partner for EGFR, HER3 and HER4, - Controls cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and remodelling of mammary gland Alteration of HER2 receptor in mammary and ovarian tumors (HER2 gene is amplified in 30% of invasive breast cancers) - Most common mutation Val- Gln664 substitution > tyrosine kinase (TK) with a constitutive activity
16 INCREASED EXPRESSION OF HER2 - Induces high survival and cell proliferation - Increases the metastatic potential of tumour cells > synthesis and secretion of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) - Overexpression of HER2 is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with mammary carcinoma - HER2 as a target of novel therapeutic approaches
17 Specific therapy for RTK
18
19 Second generation of EGFR mabs
20 NSCLC, non small cell lung cancer; mcrc, metastatic colorectal carcinoma HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
21 FLT3 (FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3) FLT3 is a RTK regulating proliferation, differentiation and survival of staminal haemopoietic cells FLT3 Expressed by early myeloid and lymphoid progenitors FLT3L is produced by different haemopoietic cell types of spleen, thymus, bone marrow and peripheral blood. FLT3L in prostate, ovary, lung, gut, testis, kidney, placenta. NO BRAIN
22 STRUCTURE AND SIGNALLING RTK of 993 amino acids with an extracellular domain of five Ig-like domains, a transmembrane domain, and two intracellular tyrosine kinase domains (TKDs) linked by a kinase-insert domain FLT3 receptors reside as inactive monomers in the plasma membrane Ligand-mediated dimerization induces a conformational changes with activation of the TKD
23 FLT3 FUNCTIONS IN NORMAL CELLS Activation of FLT3 promotes the in vitro growth of early progenitor cells Promotes the monocytic differentiation of early haematopoietic progenitor cell without proliferation if stimulated in the absence of other factors FLT3 stimulation in combination with other growth factors (IL-3, GM- CSF ) produced a more vigorous proliferative response Stimulation of FLT3 promotes dendritic-cell development and expansion in the bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes and peripheral blood Stimulation of FLT3 in combination with IL-7 and IL-11 is also important in T and B lymphoctye development.
24 FLT3 MUTATIONS - Identified and described for the first time in 1996 by Nakao et al. - Mutated in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL, 1 3%), myelodysplasia (5 10%), acute myeloid leukaemia (AML, 15 35%) - Most frequent mutation: in tandem duplication (ITD) of exons 14 and Mutations within the tyrosine kinase domain (TKD): D835Y most frequent
25 ITD AND POINT MUTATIONS INDUCE THE CONSTITUTIVE ACTIVATION OF FLT3 - ITDs probably promote ligand-independent dimerization and activation of FLT3 through changing the conformation of the expressed receptor - Missense mutations in TKD might also promote ligand independent activation.
26 FLT3 SPECIFIC THERAPY CEP-701: inhibits autophosphorylation of mutated and wt Flt3, highly specific Sugen, MLN518, PKC412: also inhibit other RTK, such as PDGFR and VEGFR
27 3. ONCOGENES: NON-RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASES (SRC)
28 C-SRC VS V-SRC Identified in 1970 within the genome of Rous sarcoma virus
29 REGULATION OF SRC ACTIVITY PTP1B CSK C-terminal Y is phosphorylated by Csk and binds to the SH2 domain of Src In this conformational status the SH3 domain interacts with the kinase domain thus causing the c-src molecule to assume a closed configuration that covers the kinase domain and reduces its potential for substrate interaction Dephosphorylation of C- terminal Y by phosphatases (i.e. PTPa or PTP1B) induces the activation of Src
30 CELLULAR TARGETS OFSRC
31 SRC AND CELL ADHESION - E-cadherin: A cytoplasmic complex consisting of α-catenin, β-catenin and p120 catenin (p120ctn) links E-cadherin homodimers to the actin cytoskeleton. c-src associates with this complex and, when activated, is able to promote the disruption of the adherens junction. - Focal adhesions, heterodimers of α- and β-integrin subunits bind the extracellular matrix through their extracellular domains. Their cytoplasmic domains bind to a complex consisting of a range of proteins, including paxilin, talin, vinculin, tensin and α-actinin, which connect integrins to the actin cytoskeleton. Several signalling molecules also associate with this complex, c-src, which can promote the turnover of the focal adhesion when activated, to promote cellular motility > disruption of focal adhesion
32 -c-src stimulates the ubiquitylation of E- cadherin, leading to its endocytosis. - c-src induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of FAK, which results in the loss of focal adhesions. - c-src phosphorylates RRAS and inhibits integrin function. - Motility and invasiveness - Angiogenesis
33 SRC and TUMORS Increased activity of SRC in colorectal, hepatocellular, pancreatic, gastric, mammary, ovarian and lung tumors Inhibitors of Src (Sugen, SKI-606, AP23464) in clinical trials > effective only in solid tumors with high level of Src activity
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Tyrosine kinases. Cell surface receptors ligand binding. Producer cell RNA. Target cell
 Tyrosine kinases http://msbl.helsinki.fi/tkseminar roducer cell Signaling molecules Receptor binding Signal transduction Target cell Activation of Gene expression RNA Biological responses proliferation,
Tyrosine kinases http://msbl.helsinki.fi/tkseminar roducer cell Signaling molecules Receptor binding Signal transduction Target cell Activation of Gene expression RNA Biological responses proliferation,
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
A RENAISSANCE FOR SRC
 A RENAISSANCE FOR SRC Timothy J. Yeatman The c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and activated in a large number of human malignancies and has been linked to the development of cancer and
A RENAISSANCE FOR SRC Timothy J. Yeatman The c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and activated in a large number of human malignancies and has been linked to the development of cancer and
Signal Transduction I
 Signal Transduction I Prof. Tianhua Zhou Department of Cell Biology Zhejiang University School of Medicine Office hours by appointment tzhou@zju.edu.cn Signal transduction: Key contents for signal transduction:
Signal Transduction I Prof. Tianhua Zhou Department of Cell Biology Zhejiang University School of Medicine Office hours by appointment tzhou@zju.edu.cn Signal transduction: Key contents for signal transduction:
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#10:(November-22-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 1 Micro-Environment Story How does the rest of our body influences the cancer cell?
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#10:(November-22-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 1 Micro-Environment Story How does the rest of our body influences the cancer cell?
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Protein tyrosine kinase signaling
 rotein tyrosine kinase signaling Serge ROCHE CRBM CNRS/Montpellier University serge.roche@crbm.cnrs.fr rotein phosphorylation on Tyr A central mechanism to control cell communication in a multicellular
rotein tyrosine kinase signaling Serge ROCHE CRBM CNRS/Montpellier University serge.roche@crbm.cnrs.fr rotein phosphorylation on Tyr A central mechanism to control cell communication in a multicellular
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
Effects of Second Messengers
 Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Origin of oncogenes? Oncogenes and Proto-oncogenes. Jekyll and Hyde. Oncogene hypothesis. Retroviral oncogenes and cell proto-oncogenes
 Oncogenes and Proto-oncogenes Jekyll and Hyde A double edged sword Origin of oncogenes? Oncogene hypothesis Retroviral oncogenes and cell proto-oncogenes (v-onc) (c-onc) The role of c-onc in cancer How
Oncogenes and Proto-oncogenes Jekyll and Hyde A double edged sword Origin of oncogenes? Oncogene hypothesis Retroviral oncogenes and cell proto-oncogenes (v-onc) (c-onc) The role of c-onc in cancer How
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch
 EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch Guido Lammering MAASTRO Clinic Maastricht, NL What is EGFR?? The EGFR some facts 1186 amino acids 170 kda Expressed by all cells of epithelial origin Increased activation
EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch Guido Lammering MAASTRO Clinic Maastricht, NL What is EGFR?? The EGFR some facts 1186 amino acids 170 kda Expressed by all cells of epithelial origin Increased activation
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
BL 424 Chapter 15: Cell Signaling; Signal Transduction
 BL 424 Chapter 15: Cell Signaling; Signal Transduction All cells receive and respond to signals from their environments. The behavior of each individual cell in multicellular plants and animals must be
BL 424 Chapter 15: Cell Signaling; Signal Transduction All cells receive and respond to signals from their environments. The behavior of each individual cell in multicellular plants and animals must be
Chapter 20. Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors. Three general types of extracellular signaling. endocrine signaling. paracrine signaling
 Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Oncology for Scientists RPN 530
 Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall 2013 Gokul Das, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) Room 4-304 Tel: 845-8542 Email: gokul.das@roswellpark.org Cell,
Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall 2013 Gokul Das, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) Room 4-304 Tel: 845-8542 Email: gokul.das@roswellpark.org Cell,
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Signal transduction and protein kinase inhibitors. Feng Qian ( 钱峰 )
 Signal transduction and protein kinase inhibitors Feng Qian ( 钱峰 ) fengqian@sjtu.edu.cn Protein Kinases in the Human Genome 518 kinases 1.7 % of human genome Lipid kinases Nucleotide kinases Cell Signaling
Signal transduction and protein kinase inhibitors Feng Qian ( 钱峰 ) fengqian@sjtu.edu.cn Protein Kinases in the Human Genome 518 kinases 1.7 % of human genome Lipid kinases Nucleotide kinases Cell Signaling
Concise Reference. HER2 Testing in Breast Cancer. Mary Falzon, Angelica Fasolo, Michael Gandy, Luca Gianni & Stefania Zambelli
 Concise Reference Testing in Breast Cancer Mary Falzon, Angelica Fasolo, Michael Gandy, Luca Gianni & Stefania Zambelli Extracted from Handbook of -Targeted Agents in Breast Cancer ublished by Springer
Concise Reference Testing in Breast Cancer Mary Falzon, Angelica Fasolo, Michael Gandy, Luca Gianni & Stefania Zambelli Extracted from Handbook of -Targeted Agents in Breast Cancer ublished by Springer
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
BL 424 Test pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points.
 BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
Howard Temin. Predicted RSV converted its genome into DNA to become part of host chromosome; later discovered reverse transciptase.
 Howard Temin Predicted RSV converted its genome into DNA to become part of host chromosome; later discovered reverse transciptase Nobel prize 1975 Figure 3.6 The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
Howard Temin Predicted RSV converted its genome into DNA to become part of host chromosome; later discovered reverse transciptase Nobel prize 1975 Figure 3.6 The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit
 The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Cell signaling. How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings?
 Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
 Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
The mutations that drive cancer. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
Cell, Volume 141. Supplemental Information Cell Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Mark A. Lemmon and Joseph Schlessinger
 Cell, Volume 141 Supplemental Information Cell Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Mark A. Lemmon and Joseph Schlessinger Figure S1. RTK Mutations in Diseases Locations of gain-of-function (green arrows)
Cell, Volume 141 Supplemental Information Cell Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Mark A. Lemmon and Joseph Schlessinger Figure S1. RTK Mutations in Diseases Locations of gain-of-function (green arrows)
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II. Prof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department
 Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents:
 Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test
 Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Oncogenes and Tumor. supressors
 Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008
 MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008 Name: ID: Instructions: Answer all 4 questions. The number of marks for each question indicates how many points you need to provide. Write your answers in point form,
MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008 Name: ID: Instructions: Answer all 4 questions. The number of marks for each question indicates how many points you need to provide. Write your answers in point form,
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7)
 Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall Growth Factors/Signal Transduction
 Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall 2015 Growth Factors/Signal Transduction Gokul Das, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) Room 4-304 Tel: 845-8542
Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall 2015 Growth Factors/Signal Transduction Gokul Das, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) Room 4-304 Tel: 845-8542
Cell Motility. Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD
 Cell Motility Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD Professor Laboratory of Somatic Reprogramming and Stem Cell Aging Center for Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering School of Medicine Zhejiang University Email: jijunfeng@zju.edu.cnedu
Cell Motility Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD Professor Laboratory of Somatic Reprogramming and Stem Cell Aging Center for Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering School of Medicine Zhejiang University Email: jijunfeng@zju.edu.cnedu
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS To understand the concept of the hallmarks of cancer and that they are phenotypic changes needed in all cancer cells. To list the tumor enablers
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS To understand the concept of the hallmarks of cancer and that they are phenotypic changes needed in all cancer cells. To list the tumor enablers
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall 2017 Growth Factors/Signal Transduction
 Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall 2017 Growth Factors/Signal Transduction Gokul Das, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) Room 4-304 Tel: 845-8542
Oncology for Scientists RPN 530 Fall 2017 Growth Factors/Signal Transduction Gokul Das, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) Room 4-304 Tel: 845-8542
Phospholipase C γ Prof. Graham Carpenter
 Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Major Principles (cont d) 4. Principle targets of genetic damage: 4 classes
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Major Principles (cont d) 4. Principle targets of genetic damage: 4 classes
Propagation of the Signal
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Supplementary Material. Part I: Sample Information. Part II: Pathway Information
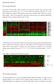 Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
7/6/2015. Cancer Related Deaths: United States. Management of NSCLC TODAY. Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview
 Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
The Role and Mechanism of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 in Cellular Transformation
 The Role and Mechanism of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 in Cellular Transformation By Jiyoung Cha A dissertation submitted to the faculty of University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial
The Role and Mechanism of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 in Cellular Transformation By Jiyoung Cha A dissertation submitted to the faculty of University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial
ONCOGENES. Michael Lea
 ONCOGENES 2011 Michael Lea ONCOGENES - Lecture Outline I. Introduction 2. Identification of oncogenic genes in retroviruses 3. Homologous sequences in transformed and untransformed cells 4. Methods of
ONCOGENES 2011 Michael Lea ONCOGENES - Lecture Outline I. Introduction 2. Identification of oncogenic genes in retroviruses 3. Homologous sequences in transformed and untransformed cells 4. Methods of
BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer
 BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer Topics we will cover today Introduction to normal and cancer cells Characteristics of cells in culture Cancerous changes in cells Viruses can harbor transforming
BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer Topics we will cover today Introduction to normal and cancer cells Characteristics of cells in culture Cancerous changes in cells Viruses can harbor transforming
609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits)
 Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors
 Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the author to give readers additional information about his work. Supplement to: Croce CM. Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J Med 2008;358:502-11.
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the author to give readers additional information about his work. Supplement to: Croce CM. Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J Med 2008;358:502-11.
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling
 Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi. Bayan Abusheikha. Faisal
 24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Part I => CARBS and LIPIDS. 1.7 Signal Transduction 1.7a Endocrine Hormones 1.7b Hormone Receptors
 Part I => CARBS and LIPIDS 1.7 Signal Transduction 1.7a Endocrine Hormones 1.7b Hormone Receptors Section 1.7a: Endocrine Hormones Synopsis 1.7a - Hormones are chemical messengers that play a key role
Part I => CARBS and LIPIDS 1.7 Signal Transduction 1.7a Endocrine Hormones 1.7b Hormone Receptors Section 1.7a: Endocrine Hormones Synopsis 1.7a - Hormones are chemical messengers that play a key role
TRK RECEPTORS: ROLES IN NEURONAL SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION *
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:609 642 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161629 First published online as a Review in Advance on March 27, 2003 TRK RECEPTORS: ROLES IN NEURONAL SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION *
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:609 642 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161629 First published online as a Review in Advance on March 27, 2003 TRK RECEPTORS: ROLES IN NEURONAL SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION *
CXC chemokine (ligand/receptor)
 List of abbreviations -MEM alpha-modified minimal essential AKT protein kinase B (also abbreviated PKB) AMC 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin AP-1 activator protein 1 ARF ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding
List of abbreviations -MEM alpha-modified minimal essential AKT protein kinase B (also abbreviated PKB) AMC 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin AP-1 activator protein 1 ARF ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer
 Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Discovery and Optimization of Inhibitors of STAT3 Activation for the Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
 Discovery and ptimization of Inhibitors of STAT3 Activation for the Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Feng Zhang Wipf Group Research Topic Seminar 02-09-2013 1 Feng Zhang @ Wipf
Discovery and ptimization of Inhibitors of STAT3 Activation for the Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Feng Zhang Wipf Group Research Topic Seminar 02-09-2013 1 Feng Zhang @ Wipf
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes.
 What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2)
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES. Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr.
 BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
Cellular Signaling Pathways. Signaling Overview
 Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: couples therapy
 OPINION Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: couples therapy Niall Tebbutt, Mikkel W. Pedersen and Terrance G. Johns Abstract The ERBB family of receptor tyrosine kinases has a central role in the tumorigenesis
OPINION Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: couples therapy Niall Tebbutt, Mikkel W. Pedersen and Terrance G. Johns Abstract The ERBB family of receptor tyrosine kinases has a central role in the tumorigenesis
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential of Statin-Mediated Inhibition of Tyrosine Kinase Receptors. Tong Tong Zhao
 Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential of Statin-Mediated Inhibition of Tyrosine Kinase Receptors Tong Tong Zhao Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies In partial fulfillment
Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential of Statin-Mediated Inhibition of Tyrosine Kinase Receptors Tong Tong Zhao Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies In partial fulfillment
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
