BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
|
|
|
- Joshua Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology Multiple Choice BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Questions 1-3 refer to the following stages of mitosis. I. Telophase II. Metaphase III. Anaphase IV. Prophase 1. Spindle fibers are present in A) I and II only B) I, II and III only C) I and III only D) II and IV only E) I, II, III and IV 2. The correct sequence of the stages of mitosis is A) I, II, III, IV B) IV, II, III, I C) IV, III, II, I D) II, I, III, IV E) IV, I, III, II 3. Chromatids would move toward the centrosome during A) I only B) III only C) IV only D) I and II only E) II and III only 1
2 Questions 4-8 refer to the following diagram of a chromosome. 4. Which pair of numbered regions belong to a single chromatid? A) 1 and 3 B) 1 and 4 C) 1 and 5 D) 3 and 4 E) 3 and 5 5. The centromere is located at the area labeled A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 6. Sister chromatids are indicated by the numbers A) 1 and 2 B) 1 and 3 C) 2 and 3 D) 3 and 5 E) 4 and 5 7. The structure shown in the diagram above is present during which phase of the cell cycle? A) Anaphase B) G 1 C) G 0 D) Prophase E) Telophase 2
3 8. If structure 1 exists during G 1, then structure 4 is formed during which stage of the cell cycle? A) S B) M C) G 0 D) G 1 E) G 2 Questions 9-11 Crystal used a microscope to view a variety of prepared slides containing different types of cells undergoing cell division. The results of her analysis are shown below. Slide Label Type of Cell Number of Chromosomes A human sperm (n) 23 B fruit fly (2n) 8 C human cheek (2n) 46 D grasshopper gland (2n) 24 E onion root (2n) 6 9. If a grasshopper gland cell goes through mitosis, how many chromosomes would be found in each daughter cell? A) 6 B) 8 C) 16 D) 24 E) While observing slide B, Crystal noticed one cell that had twice as much DNA as the others. Which of the following best explains this difference? A) endocytosis B) osmosis C) dehydration synthesis D) DNA synthesis E) catalysis 11. Two fruit fly cells are observed. Cell A has 16 chromosomes while Cell B has 8 chromosomes. Which of the following statements are true regarding this pair of cells? A) Cell A is in interphase and Cell B is in prophase B) Cell A is in metaphase and Cell B is in interphase C) Cell A is in prophase and Cell B is in prophase D) Cell A is in anaphase and Cell B is in prophase E) Cell A is mutated and Cell B is normal 3
4 12. The purpose of the mitosis includes all of the following EXCEPT A) reproduction in a single-celled amoeba B) repair of tissue in an injury caused by a burn C) replacement of cells removed by a skinned knee D) lengthening the long bones of a child E) formation of sperm by a frog 13. The period of a normal cell cycle during which a cell would complete anaphase would be A) G 1 B) S C) G 2 D) M E) G All of the following events would occur during the M stage of the cell cycle EXCEPT A) chromosomal DNA is synthesized B) chromosomes move toward the poles of the cell C) chromosomes move toward the equatorial plane D) chromatin condenses into chromosomes E) sister chromatids separate 15. The correct order for the phases of the cell cycle is A) M, G 2, S, G 1 B) G 1, M, S, G 2 C) G 1, S, G 2, M D) M, S, G 2, G 1 E) G 2, S, M, G Shantay is observing onion root tip cells under the microscope. She notices the chromosomes are lined up along the equatorial plane in two of the cells. These two cells are most likely in A) anaphase B) interphase C) metaphase D) prophase E) telophase 4
5 17. Which of the following is a region of the cell that helps to organize the spindle? 18. A) Centriole B) Centromere C) Centrosome D) Chromatid E) Chromosome The diagram above depicts A) an animal cell growing a cell plate B) a plant cell developing a cleavage furrow C) an animal cell undergoing cytokinesis D) a plant cell undergoing cytokinesis E) an plant cell during anaphase of mitosis 19. Which of the following descriptions best matches a cell that is in S phase of the cell cycle? A) The chromosomal DNA is being actively replicated. B) The cytoplasm and nuclei are partitioned into two different cells C) The cell is growing, increasing in size and making new organelles. D) Organelles and molecules required for reproduction are being produced. E) The chromosomes are being moved to opposing areas of the cell. 20. Some chemotherapy interferes with the assembly of microtubules at the cellular level. The effectiveness of the treatment must be related to A) condensation of chromatin B) inhibition of DNA replication C) inhibition of spindle formation D) disassembly of the nuclear envelope E) increase in the amount of cytoplasm 21. The stage of cell division in which chromosomes first condense and become visible is A) anaphase B) cytokinesis C) metaphase D) prophase E) telophase 5
6 Directions: The group of questions below consists of five lettered answers followed by a list of numbered phrases or sentences. For each numbered phrase or sentence select the one answer that is most closely related to it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Each answer may be used once, more than once or not at all in each group. Questions Crystal used a microscope to view a variety of prepared slides containing different types of cells undergoing cell division. The results of her analysis are shown below. Slide Label Type of Cell Number of Chromosomes A human sperm (n) 23 B fruit fly (2n) 8 C human cheek (2n) 46 D grasshopper gland (2n) 24 E onion root (2n) Which slide has cells that do not go through mitosis? 23. Which slide contains cells that would have 12 chromosomes during anaphase? 24. All of the slides contain diploid cells except. Questions refer to the following diagrams of cells in various stages of division. 25. A cell in telophase 26. A cell in metaphase of mitosis 27. A cell in prophase of mitosis 6
7 28. Shows daughter cells 29. Shows a cleavage furrow 30. Shows a cell in anaphase 31. Shows a cell where the DNA exists as chromatin Questions refer to the following mitotic structures. A C B D E 32. A spindle fiber 33. Nuclear envelope 34. A centromere 35. A centrosome 7
8 Biology Multiple Choice BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Questions 1-3 refer to the following stages of mitosis. I. Telophase II. Metaphase III. Anaphase IV. Prophase 1. Chromatids would move toward the centrosome during A) I only B) III only C) IV only D) I and II only E) II and III only 2. The correct sequence of the stages of mitosis is A) I, II, III, IV B) IV, II, III, I C) IV, III, II, I D) II, I, III, IV E) IV, I, III, II 3. Spindle fibers are present in A) I and II only B) I, II and III only C) I and III only D) II and IV only E) I, II, III and IV 1
9 Questions 4-8 refer to the following diagram of a chromosome. 4. Which pair of numbered regions belong to a single chromatid? A) 1 and 3 B) 1 and 4 C) 1 and 5 D) 3 and 4 E) 3 and 5 5. The structure shown in the diagram above is present during which phase of the cell cycle? A) Anaphase B) G 1 C) G 0 D) Prophase E) Telophase 6. Sister chromatids are indicated by the numbers A) 1 and 2 B) 1 and 3 C) 2 and 3 D) 3 and 5 E) 4 and 5 2
10 7. If structure 1 exists during G 1, then structure 4 is formed during which stage of the cell cycle? A) S B) M C) G 0 D) G 1 E) G 2 8. The centromere is located at the area labeled A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Questions 9-11 Crystal used a microscope to view a variety of prepared slides containing different types of cells undergoing cell division. The results of her analysis are shown below. Slide Label Type of Cell Number of Chromosomes A human sperm (n) 23 B fruit fly (2n) 8 C human cheek (2n) 46 D grasshopper gland (2n) 24 E onion root (2n) 6 9. While observing slide B, Crystal noticed one cell that had twice as much DNA as the others. Which of the following best explains this difference? A) endocytosis B) osmosis C) dehydration synthesis D) DNA synthesis E) catalysis 10. Two fruit fly cells are observed. Cell A has 16 chromosomes while Cell B has 8 chromosomes. Which of the following statements are true regarding this pair of cells? A) Cell A is in interphase and Cell B is in prophase B) Cell A is in metaphase and Cell B is in interphase C) Cell A is in prophase and Cell B is in prophase D) Cell A is in anaphase and Cell B is in prophase E) Cell A is mutated and Cell B is normal 3
11 11. If a grasshopper gland cell goes through mitosis, how many chromosomes would be found in each daughter cell? A) 6 B) 8 C) 16 D) 24 E) The stage of cell division in which chromosomes first condense and become visible is A) anaphase B) cytokinesis C) metaphase D) prophase E) telophase 13. The purpose of the mitosis includes all of the following EXCEPT 14. A) reproduction in a single-celled amoeba B) repair of tissue in an injury caused by a burn C) replacement of cells removed by a skinned knee D) lengthening the long bones of a child E) formation of sperm by a frog The diagram above depicts A) an animal cell growing a cell plate B) a plant cell developing a cleavage furrow C) an animal cell undergoing cytokinesis D) a plant cell undergoing cytokinesis E) an plant cell during anaphase of mitosis 15. Shantay is observing onion root tip cells under the microscope. She notices the chromosomes are lined up along the equatorial plane in two of the cells. These two cells are most likely in A) anaphase B) interphase C) metaphase D) prophase E) telophase 4
12 16. The correct order for the phases of the cell cycle is A) M, G 2, S, G 1 B) G 1, M, S, G 2 C) G 1, S, G 2, M D) M, S, G 2, G 1 E) G 2, S, M, G Which of the following descriptions best matches a cell that is in S phase of the cell cycle? A) The chromosomal DNA is being actively replicated. B) The cytoplasm and nuclei are partitioned into two different cells C) The cell is growing, increasing in size and making new organelles. D) Organelles and molecules required for reproduction are being produced. E) The chromosomes are being moved to opposing areas of the cell. 18. Which of the following is a region of the cell that helps to organize the spindle? A) Centriole B) Centromere C) Centrosome D) Chromatid E) Chromosome 19. All of the following events would occur during the M stage of the cell cycle EXCEPT A) chromosomal DNA is synthesized B) chromosomes move toward the poles of the cell C) chromosomes move toward the equatorial plane D) chromatin condenses into chromosomes E) sister chromatids separate 20. Some chemotherapy interferes with the assembly of microtubules at the cellular level. The effectiveness of the treatment must be related to A) condensation of chromatin B) inhibition of DNA replication C) inhibition of spindle formation D) disassembly of the nuclear envelope E) increase in the amount of cytoplasm 5
13 21. The period of a normal cell cycle during which a cell would complete anaphase would be A) G 1 B) S C) G 2 D) M E) G 0 Directions: The group of questions below consists of five lettered answers followed by a list of numbered phrases or sentences. For each numbered phrase or sentence select the one answer that is most closely related to it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Each answer may be used once, more than once or not at all in each group. Questions Crystal used a microscope to view a variety of prepared slides containing different types of cells undergoing cell division. The results of her analysis are shown below. Slide Label Type of Cell Number of Chromosomes A human sperm (n) 23 B fruit fly (2n) 8 C human cheek (2n) 46 D grasshopper gland (2n) 24 E onion root (2n) Which slide contains cells that would have 12 chromosomes during anaphase? 23. All of the slides contain diploid cells except. 24. Which slide has cells that do not go through mitosis? 6
14 Questions refer to the following diagrams of cells in various stages of division. 25. A cell in metaphase of mitosis 26. Shows a cleavage furrow 27. Shows daughter cells 28. A cell in prophase of mitosis 29. A cell in anaphase 30. A cell in telophase 31. Shows a cell where the DNA exists as chromatin 7
15 Questions refer to the following mitotic structures. A C B D E 32. A spindle fiber 33. Nuclear envelope 34. A centromere 35. A centrosome 8
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
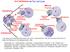 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
Chromosomes & Cell Division
 Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Name: Date: Block: 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet
 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS
 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Growth and Division. Chapter 10
 Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Cell Division Before a cell becomes too large, it undergoes cell division, in which the cell divides and becomes 2 daughter cells. Before cell division occurs, the cell
Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Cell Division Before a cell becomes too large, it undergoes cell division, in which the cell divides and becomes 2 daughter cells. Before cell division occurs, the cell
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION. Cytokinesis. centromere. DNA Replication S-Phase. One Chromosome Two Chromatids. One Chromosome No Chromatids 10.
 MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle
 Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
Section Cell Growth. A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. DNA Overload 2. Exchanging Materials 3. Ratio of Surface Area to Volume 4.
 Getting Through Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all
Getting Through Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. A B C D ... (1) ... (1)
 1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
The Cell Cycle. Materials 2 pipe cleaners of one color and 2 of another color Drawing paper
 The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase
 Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide)
 Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2)
 Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET
 Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET This packet is designed to help you understand several concepts about Cell Division. As you practice the exercises on each handout, you will be able to: Use a model to illustrate
Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET This packet is designed to help you understand several concepts about Cell Division. As you practice the exercises on each handout, you will be able to: Use a model to illustrate
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Cell Division. Introduction. Chromatin, Chromosomes, and Chromatids, Oh My! The Cell Cycle
 Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle
 Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
3.What is the advantage of cells being small? If cells are small, materials can be distributed to all parts of the cell quickly.
 Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all parts of a cell?
Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all parts of a cell?
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages )
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS
 CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
Ploidy and Human Cell Types. Cell Cycle and Mitosis. DNA and Chromosomes. Where It All Began 11/19/2014. Chapter 12 Pg
 Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
CELL DIVISION! Genes, Mitosis and Cytokinesis 12/17/14. G. Podgorski, Biol Mitosis!
 Genes, Mitosis and Cytokinesis 12/17/14 CELL DIVISION! Mitosis! ü Mitotic division results in genetically identical eukaryotic cells or a clone ü Mitosis is the basis of asexual! reproduction G. Podgorski,
Genes, Mitosis and Cytokinesis 12/17/14 CELL DIVISION! Mitosis! ü Mitotic division results in genetically identical eukaryotic cells or a clone ü Mitosis is the basis of asexual! reproduction G. Podgorski,
Name: Cell division and cancer review
 Name: Cell division and cancer review 1. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gamete cells or Somatic cells 2. Define homologous chromosomes. 2 chromosomes with similar structure 3. For each of the following
Name: Cell division and cancer review 1. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gamete cells or Somatic cells 2. Define homologous chromosomes. 2 chromosomes with similar structure 3. For each of the following
Cellular Reproduction
 Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
DR. RAMESH U2 L3. MITOSIS and Cell Cycle
 DR. RAMESH U2 L3 MITOSIS and Cell Cycle Do Now! Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. Describe how bacteria reproduce. Describe how cats reproduce.are there any similarities
DR. RAMESH U2 L3 MITOSIS and Cell Cycle Do Now! Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. Describe how bacteria reproduce. Describe how cats reproduce.are there any similarities
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Genes and Proteins. Key points: The DNA must be copied and then divided exactly so that each cell gets an identical copy.
 Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation
 B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 10-1 & 10-2
 Image from: http://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/models/life/images/grow.jpg CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 10-1 & 10-2 Image by Riedell 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA
Image from: http://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/models/life/images/grow.jpg CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 10-1 & 10-2 Image by Riedell 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA
Cell Growth, Division, & Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, & Reproduction Two main reasons why cells divide rather than continue growing: A larger cell places more demand on the DNA. When a cell s size increases, its DNA does not & the extra
Cell Growth, Division, & Reproduction Two main reasons why cells divide rather than continue growing: A larger cell places more demand on the DNA. When a cell s size increases, its DNA does not & the extra
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION
 CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA genetic library becomes too great Ex: Small town library has 1000 books. As town grows and more people
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA genetic library becomes too great Ex: Small town library has 1000 books. As town grows and more people
Major concepts: Notes: Cell Reproduction: From One Cell to Two. Why do Cells Reproduce?
 Grade 7 Standard: Life Science 1e Students know cells divide to increase their numbers through a process of mitosis, which results in two daughter cells with identical sets of chromosomes. Major concepts:
Grade 7 Standard: Life Science 1e Students know cells divide to increase their numbers through a process of mitosis, which results in two daughter cells with identical sets of chromosomes. Major concepts:
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
Mitosis. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Cell Division
 Mitosis An Introduction to Genetics An Introduction to Cell Division DNA is Packaged in Chromosomes Cell Cycle Mitosis and Cytokinesis Variations in Cell Division Cell Division and Cancer An Introduction
Mitosis An Introduction to Genetics An Introduction to Cell Division DNA is Packaged in Chromosomes Cell Cycle Mitosis and Cytokinesis Variations in Cell Division Cell Division and Cancer An Introduction
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division
 Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
Lesson 1. Quiz (short) Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases
 Lesson 1 Quiz (short) Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases 2 Cell division is needed for Growth (Mitosis) Repair (Mitosis) Reproduction (Meiosis) 3 Mitosis consists of 4 phases (division of the nuclear
Lesson 1 Quiz (short) Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases 2 Cell division is needed for Growth (Mitosis) Repair (Mitosis) Reproduction (Meiosis) 3 Mitosis consists of 4 phases (division of the nuclear
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
