Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition
|
|
|
- Magdalene Russell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells in 10% FCS were exposed to 25 mm sodium lactate for 24 hours. Cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated antibodies. (b) HT29 cells growing in 10% FCS/normoxia or 10% FCS/hypoxia were treated with increasing concentrations of Chk1i for 72 hours. Cell viability was determined using SRB (n=3, mean ± SD). 1
2 Supplementary Figure S2. Related to Fig. 2. (a) The percentage changes in growth of cells treated with 0.3 or 1.0 µm Chk1i for 96 hours compared to DMSO control were calculated from Figure 2A. Negative growth indicates a reduction in cell number at 96 hours compared to time 0. Statistical significance was determined using a 2-tailed t- test. ns, not significant; ***, P < (b) Tumour cell lines growing in 10% or 0.5% FCS were treated with 0 1 µm Chk1i for 96 hours. Cell mass was determined by SRB staining (n=6, mean ± SD). (c) Tumour cell lines were grown in 10% or 0.5% FCS for 48 hours then treated with 0 or 1 µm Chk1i (in the same FCS percentage) for a further 72 hours. Cell number or confluency was determined using repeated live cell imaging (n=6, mean). 2
3 Supplementary Figure S3. Related to Fig. 3. Protein expression data in figure 3A was quantified by densitometry and the ratios of pchk1 (S296) / Chk1, pchk1 (S317) / Chk1, pchk2 (T68) / Chk2, prpa32 (S4/S8) / RPA32 and γh2ax / GAPDH calculated. From these, the fold change relative to 2D for cells grown as spheroids or on the mimetix scaffold calculated. Supplementary Figure S4. Related to Fig. 4. (a) Cell lysates prepared from HT29 or Colo205 cell line derived tumour xenografts (CDX) or anchorage-dependent cell culture (2D) were immunoblotted using the indicated antibodies. (b) Protein expression levels of pchk1 (S296), pchk1 (S317) and total Chk1 were determined by densitometry from Figure 4 western blots of cell lysates derived from cell lines growing as tumour xenografts (CDX) or anchorage-dependently (2D). 3
4 Supplementary Figure S5. Related to Fig. 4, 5 and 6. Composite images of pchk1 (S296), pchk1 (S317), Chk1 and Cdc6 expression data from (a) Fig. 4a and 5a, (b) Fig. 4b and 6a and (c) Fig. 3a and 6b. Protein expression levels in (b) were determined by densitometry. Supplementary Figure S6. Related to Fig. 6. Expression levels of Cdc6 and Chk1 determined in figure 6A were correlated with the 72 hour Chk1i GI 50. 4
5 Supplementary Figure S7. Related to Fig. 7. (a) CDC6 or CHEK1 mrna expression in human tumours and normal tissue controls was determined using the Firehose analysis tool from the Broad Institute TCGA Genome Data Analysis Center. (b) The correlation between CHEK1 (Chk1) and CDC6 mrna expression levels was determined from publicly available datasets in breast tumours. (c) The correlation between CHEK1 (Chk1) and CDC6 mrna expression levels in breast, CNS, colon, liver, lung, oesophageal, ovarian or pancreatic cancer derived cell lines was determined using publically available data from the Broad Institute Cancer Cell Line Encyclopaedia. 5
6 Supplementary Table S1. Summary of proteins used in experiments. Abbrv Protein Name Notes ATM Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated STK, mol. sensor of DNA damage predominantly DSB ATR Cdc6 ATM- and RAD3-related Cell division control protein 6 homolog CDK1 Cyclin dependent kinase 1 CDK2 CDT1 Cyclin dependent kinase DNA replication factor Cdt1 Chk1 Checkpoint kinase 1 STK, mol. sensor of DNA damage predominantly ssdna Role in initiation of DNA replication and preventing re-replication before mitosis completed STK, regulates G2-M transition, P on Y15 by Wee1 (negative regulator of CDK activity) STK, regulates G1-S and S-phase transition, P on Y15 by Wee1 (negative regulator of CDK activity) Co-operates with Cdc6 to load MCM onto replication origins STK, effector kinase of DRR, cis-autop on S296, P on S317 and S345 by ATR Chk2 Checkpoint kinase 2 STK, effector kinase of DDR, P on T68 by ATM Cyclin A2 Cyclin E1 DNA-PKcs E2F1 GAPDH Geminin Cyclin-A2 Cyclin-E1 DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit Transcription factor E2F1 Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase Geminin Regulates cell cycle transitions. Complex with CDK2 in S-phase and CDK1 in G2/M Regulates cell cycle transitions. Complex with CDK2 in G1 phase, regulates G1-S transition STK, mol. sensor of DNA damage, involved in NHEJ of DSB TF of genes whose products are involved in cell cycle regulation or DNA replication Loading control Inhibits MCM incorporation into pre-rc. Degraded during mitosis, re-expressed in S-phase HH3 Histone H3 P on S10 by Aurora B, marker of mitosis Ki-67 Antigen KI-67 Expressed in all phases of the cell cycle except G0 MCM2 DNA replication licensing Subunit of mini-chromosome maintenance complex factor MCM2 (MCM 2-7) PCNA Proliferating cell nuclear Auxiliary protein of DNA pol δ; involved in the control antigen of eukaryotic DNA replication Rb Retinoblastoma-associated Key regulator of entry into G1, transcription protein repressor of E2F1 genes, P on S807 / S811 by CDKs RPA32 Replication protein A, 32kDa Subunit of trimeric ssdna RPA binding protein, P on Subunit S4/S8 by DNA-PKcs RRM2 Ribonucleoside-diphosphate Catalyses biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from reductase subunit M2 ribonucleotides, predominantly S-phase expressed γh2ax Histone H2AX Variant of Histone H2A, P on S139 by DNA-PKcs (also ATR and ATM) P, phosphorylated; STK, serine / threonine protein kinase; DDR, DNA damage response; mol., molecular; NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; DSB, DNA double strand break; ssdna, single stranded DNA; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; TF, transcription factor Protein function summarised from UniProt ( 6
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Cell cycle control (mammalian)
 Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2)
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Control of Cell Cycle. Unit 2 Part f III
 Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest)
 Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest) Carsten Herskind Dept. of Radiation Oncology. Universitätsmedizin Mannheim Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg
Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest) Carsten Herskind Dept. of Radiation Oncology. Universitätsmedizin Mannheim Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Chapter 2. Aims & Objectives
 2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Genomic instability. Amin Mahpour
 Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology
 Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology Epithelial Ovarian Cancer - Standard Current Treatment: Surgery with De-bulking + Platinum-Taxane based Chemotherapy - No
Brian T Burgess, DO, PhD, GYN Oncology Fellow Rachel W. Miller, MD, GYN Oncology Epithelial Ovarian Cancer - Standard Current Treatment: Surgery with De-bulking + Platinum-Taxane based Chemotherapy - No
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0494 TITLE: Tumor Suppression by BRCA-1: A Critical Role at DNA Replication Forks PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jean Gautier, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0494 TITLE: Tumor Suppression by BRCA-1: A Critical Role at DNA Replication Forks PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jean Gautier, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
Prognostic value of DNA repair based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma
 Prognostic value of DNA repair based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma Zhuo Lin 1, 2 #, Shi-Hao Xu 3 #, Hai-Qing Wang 4, Yi-Jing Cai 1, 2, Li Ying 3, Mei Song 1, 2, Yu-Qun Wang 1, 2, Shan-Jie
Prognostic value of DNA repair based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma Zhuo Lin 1, 2 #, Shi-Hao Xu 3 #, Hai-Qing Wang 4, Yi-Jing Cai 1, 2, Li Ying 3, Mei Song 1, 2, Yu-Qun Wang 1, 2, Shan-Jie
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
CYCLINS ON THE MOVE: A TIME AND A PLACE FOR CYCLIN A2 AND CYCLIN B1 IN THE HUMAN CELL CYCLE
 From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CYCLINS ON THE MOVE: A TIME AND A PLACE FOR CYCLIN A2 AND CYCLIN B1 IN THE HUMAN CELL CYCLE Helena Silva Cascales
From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CYCLINS ON THE MOVE: A TIME AND A PLACE FOR CYCLIN A2 AND CYCLIN B1 IN THE HUMAN CELL CYCLE Helena Silva Cascales
Role of genetic testing in familial breast cancer outside of BRCA1 and BRCA2
 Role of genetic testing in familial breast cancer outside of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Introduction Most commonly diagnosed cancer in South African women and the second most commonly diagnosed cancer in Black women
Role of genetic testing in familial breast cancer outside of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Introduction Most commonly diagnosed cancer in South African women and the second most commonly diagnosed cancer in Black women
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I. Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017
 Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Jessica Whitney Luzwick. Dissertation. Submitted to the Faculty of the. Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
 Regulation of the ATR Pathway in the Replication Stress Response By Jessica Whitney Luzwick Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment
Regulation of the ATR Pathway in the Replication Stress Response By Jessica Whitney Luzwick Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci METODI DDR foci formation in irradiated (2 Gy) cells fixed 2 h later IRIF IRradiation Induced Focus Laser micro-irradiation DDR
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci METODI DDR foci formation in irradiated (2 Gy) cells fixed 2 h later IRIF IRradiation Induced Focus Laser micro-irradiation DDR
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available
 Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Oncolytic virus strategy
 Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage
 1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
Supplementary Figure 1
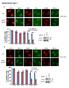 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
Human Papillomaviruses Activate the ATM DNA Damage Pathway for Viral Genome Amplification upon Differentiation
 Human Papillomaviruses Activate the ATM DNA Damage Pathway for Viral Genome Amplification upon Differentiation Cary A. Moody, Laimonis A. Laimins* Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Feinberg School
Human Papillomaviruses Activate the ATM DNA Damage Pathway for Viral Genome Amplification upon Differentiation Cary A. Moody, Laimonis A. Laimins* Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Feinberg School
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Dox Cis Cam Pac 0 15 1 15 1 15 1 15 1 15 µmole/l Ub p53 Cytotoxic anticancer agents increase p53 levels but do not generally promote the accumulation of ubiquitinated. Western blots
Supplementary Figure 1 Dox Cis Cam Pac 0 15 1 15 1 15 1 15 1 15 µmole/l Ub p53 Cytotoxic anticancer agents increase p53 levels but do not generally promote the accumulation of ubiquitinated. Western blots
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
The interaction between Rad9 and Tousled-like kinase 1 in the cell cycle and the DNA damage response
 The interaction between Rad9 and Tousled-like kinase 1 in the cell cycle and the DNA damage response By Ryan Patrick Kelly A thesis submitted to the Graduate Program in Biochemistry in conformity with
The interaction between Rad9 and Tousled-like kinase 1 in the cell cycle and the DNA damage response By Ryan Patrick Kelly A thesis submitted to the Graduate Program in Biochemistry in conformity with
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Breast Cancer Susceptibility and HLA Complex: Source of Missing Heritability?
 Breast Cancer Susceptibility and HLA Complex: Source of Missing Heritability? M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info
Breast Cancer Susceptibility and HLA Complex: Source of Missing Heritability? M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Afrah A. Khalil, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Seta A. Sarkis, B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D. (2) ABSTRACT Background: Understanding the
Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Afrah A. Khalil, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Seta A. Sarkis, B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D. (2) ABSTRACT Background: Understanding the
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Targeting the ATR Kinase in Cancer Therapy
 Targeting the ATR Kinase in Cancer Therapy 2017 Chabner Colloquium October 30, 2017 Lee Zou MGH Cancer Center Harvard Medical School Disclosure Consultant/advisory role: Loxo Oncology DNA Damage and Replication
Targeting the ATR Kinase in Cancer Therapy 2017 Chabner Colloquium October 30, 2017 Lee Zou MGH Cancer Center Harvard Medical School Disclosure Consultant/advisory role: Loxo Oncology DNA Damage and Replication
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts
 Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Rishabh Kala 1, Harsh N. Shah 1, Samantha L. Martin 1 and Trygve O. Tollefsbol 1,2,3,4,5*
 Kala et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:672 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1693-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Epigenetic-based combinatorial resveratrol and pterostilbene alters DNA damage response by affecting SIRT1
Kala et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:672 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1693-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Epigenetic-based combinatorial resveratrol and pterostilbene alters DNA damage response by affecting SIRT1
Cell Cycle. Trends in Cell Biology
 Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
CHARACTERIZATION OF CHECKPOINT ADAPTATION IN HUMAN FIBROBLASTIC GLIOMA CELLS AND AN ANALYSIS OF PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE INHIBITORS
 CHARACTERIZATION OF CHECKPOINT ADAPTATION IN HUMAN FIBROBLASTIC GLIOMA CELLS AND AN ANALYSIS OF PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE INHIBITORS Brittany Lanser Bachelor of Science Honours, University of Saskatchewan, 2010
CHARACTERIZATION OF CHECKPOINT ADAPTATION IN HUMAN FIBROBLASTIC GLIOMA CELLS AND AN ANALYSIS OF PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE INHIBITORS Brittany Lanser Bachelor of Science Honours, University of Saskatchewan, 2010
Novel DNA targeted therapies for head and neck cancers: clinical potential and biomarkers
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 46), pp: 81662-81678 Novel DNA targeted therapies for head and neck cancers: clinical potential and biomarkers Mary Glorieux 1, Rüveyda Dok 1 and Sandra Nuyts 1,2 1 KU Leuven, University
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 46), pp: 81662-81678 Novel DNA targeted therapies for head and neck cancers: clinical potential and biomarkers Mary Glorieux 1, Rüveyda Dok 1 and Sandra Nuyts 1,2 1 KU Leuven, University
Sierra Oncology (SRRA)
 Initiating Coverage June 8, 2017 Sierra Oncology (SRRA) Initiation Report LifeSci Investment Abstract Sierra Oncology (NasdaqGM: SRRA) is a biotechnology company focused on developing oncology treatments
Initiating Coverage June 8, 2017 Sierra Oncology (SRRA) Initiation Report LifeSci Investment Abstract Sierra Oncology (NasdaqGM: SRRA) is a biotechnology company focused on developing oncology treatments
Selective targeting of cancer cells through inhibition of Checkpoint kinase 1
 Selective targeting of cancer cells through inhibition of Checkpoint kinase 1 Grete Hasvold Department of Radiation Biology Institute for Cancer Research The Norwegian Radium Hospital Oslo University Hospital
Selective targeting of cancer cells through inhibition of Checkpoint kinase 1 Grete Hasvold Department of Radiation Biology Institute for Cancer Research The Norwegian Radium Hospital Oslo University Hospital
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics
 Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics Q1 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking statement
Beyond PARP - Next Generation DDR Therapeutics Q1 2017 Safe Harbor Statement Except for statements of historical fact, any information contained in this presentation may be a forward-looking statement
DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective
 DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective Kavanagh, J. N., Redmond, K. M., Schettino, G., & Prise, K. M. (2013). DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective. Antioxidants & Redox
DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective Kavanagh, J. N., Redmond, K. M., Schettino, G., & Prise, K. M. (2013). DNA double strand break repair: a radiation perspective. Antioxidants & Redox
The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
 O[superscript 6]-Methylguanine DNA lesions induce an intra-s-phase arrest from which cells exit into apoptosis governed by early and late multi-pathway signaling The MIT Faculty has made this article openly
O[superscript 6]-Methylguanine DNA lesions induce an intra-s-phase arrest from which cells exit into apoptosis governed by early and late multi-pathway signaling The MIT Faculty has made this article openly
IDENTIFICATION OF NF-KAPPAB AND DNA-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE (DNA-PK) AS NEW PLAYERS IN THE REGULATION AND SIGNALING OF THE ONCOGENIC PHOSPHATASE
 IDENTIFICATION OF NF-KAPPAB AND DNA-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE (DNA-PK) AS NEW PLAYERS IN THE REGULATION AND SIGNALING OF THE ONCOGENIC PHOSPHATASE WIP1 A Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate
IDENTIFICATION OF NF-KAPPAB AND DNA-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE (DNA-PK) AS NEW PLAYERS IN THE REGULATION AND SIGNALING OF THE ONCOGENIC PHOSPHATASE WIP1 A Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate
Factors determining DNA double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase.
 Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
HLA Complex Genetics & Biology
 HLA Complex Genetics & Biology M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info Mount Sinai Medical Center
HLA Complex Genetics & Biology M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info Mount Sinai Medical Center
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Cell Signaling (III) Cell Cycle (I)
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 22: Cell Signaling (III) Cell Cycle (I) Chapter 15 BME42-620 Lecture 22, December 01, 2011 1 Comments on Reading Assignment 5 (I) I assume that this
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 22: Cell Signaling (III) Cell Cycle (I) Chapter 15 BME42-620 Lecture 22, December 01, 2011 1 Comments on Reading Assignment 5 (I) I assume that this
THE ACTIVATION AND CONSEQUENCES OF THE ATM MEDIATED DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE IN HPV INFECTED CELLS. Bryan Allen Johnson
 THE ACTIVATION AND CONSEQUENCES OF THE ATM MEDIATED DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE IN HPV INFECTED CELLS Bryan Allen Johnson A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
THE ACTIVATION AND CONSEQUENCES OF THE ATM MEDIATED DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE IN HPV INFECTED CELLS Bryan Allen Johnson A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy
 Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy Radiology and Physical Medicine María Trinidad Rueda Cáceres Radiotherapy Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy One of the standard treatment options for various malignant
Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy Radiology and Physical Medicine María Trinidad Rueda Cáceres Radiotherapy Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy One of the standard treatment options for various malignant
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis
 Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: Evidence for a regulatory loop between
Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: Evidence for a regulatory loop between
Chapter 12. living /non-living? growth repair renew. Reproduction. Reproduction. living /non-living. fertilized egg (zygote) next chapter
 Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Human Papillomaviruses Recruit Cellular DNA Repair and Homologous Recombination Factors to Viral Replication Centers
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 June 2012 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00247-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 June 2012 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00247-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS. D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH
 E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer. Dan Fisher. Friday 27th October Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6.
 How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS. Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK
 CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK E-Mail:-snsenapati2007@gmail.com IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY TUMOR CELL DEATH CELL DEATH AFTER IRRADIATION OCCURS MOSTLY
CELL CYCLE,CHECK POINTS Prof S.N.Senapati, A.H.REGIONAL CANCER CENTRE, MANGALABAG, CUTTACK E-Mail:-snsenapati2007@gmail.com IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY TUMOR CELL DEATH CELL DEATH AFTER IRRADIATION OCCURS MOSTLY
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Recruitment of HBO1 Histone Acetylase and Blocks
 Molecular Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information JNK1 Phosphorylation of Cdt1 Inhibits Recruitment of HO1 Histone cetylase and locks Replication Licensing in Response to Stress enoit Miotto and Kevin
Molecular Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information JNK1 Phosphorylation of Cdt1 Inhibits Recruitment of HO1 Histone cetylase and locks Replication Licensing in Response to Stress enoit Miotto and Kevin
DNA Replication Stress as a Hallmark of Cancer
 Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2015. 10:425 48 The Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease is online at pathol.annualreviews.org This article s doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012414-040424 Copyright
Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2015. 10:425 48 The Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease is online at pathol.annualreviews.org This article s doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012414-040424 Copyright
Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication
 Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication Shilpa Singh, 1 Catherine A. Vaughan, 1 Rebecca A. Frum, 2 Steven R. Grossman, 2 Sumitra Deb, 1 and Swati Palit Deb
Mutant p53 establishes targetable tumor dependency by promoting unscheduled replication Shilpa Singh, 1 Catherine A. Vaughan, 1 Rebecca A. Frum, 2 Steven R. Grossman, 2 Sumitra Deb, 1 and Swati Palit Deb
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementary Figure S1 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 PF-364422 (µm) U87 (EC 5 = 52.2 ± 8.8 µm) 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-4 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 CMPD1 (µm) Primary GM (EC 5 = 1.55 ±.3 µm) U138 (EC 5 = 1.7
Supplementary Figure S1 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 PF-364422 (µm) U87 (EC 5 = 52.2 ± 8.8 µm) 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-4 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 CMPD1 (µm) Primary GM (EC 5 = 1.55 ±.3 µm) U138 (EC 5 = 1.7
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Assessing the role of Ku70 vwa domain phosphorylation in the inhibition of Aurora B and activation of the DNA damage response
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository April 2017 Assessing the role of Ku70 vwa domain phosphorylation in the inhibition of Aurora B and activation of the
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository April 2017 Assessing the role of Ku70 vwa domain phosphorylation in the inhibition of Aurora B and activation of the
HCMV disrupts both ATM and ATR-mediated. DNA damage responses during lytic infection ACCEPTED
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 December 2006 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01670-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 December 2006 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01670-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
DNA repair and synthetic lethality
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2011 DNA repair and synthetic lethality Gong-she Guo Shandong University Feng-mei Zhang Shandong University Rui-jie
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2011 DNA repair and synthetic lethality Gong-she Guo Shandong University Feng-mei Zhang Shandong University Rui-jie
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada?
 Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada? Alberto Ocana Albacete University Hospital Salamanca May 19th, 2016 WHAT IS PERSONALIZED MEDICINE? Molecular
Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada? Alberto Ocana Albacete University Hospital Salamanca May 19th, 2016 WHAT IS PERSONALIZED MEDICINE? Molecular
Review II: Cell Biology
 Review II: Cell Biology Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2006 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2006 Outline Cell Cycle Signal Transduction 1 Cell Cycle Four
Review II: Cell Biology Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2006 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2006 Outline Cell Cycle Signal Transduction 1 Cell Cycle Four
Post-Translational Regulation of the RSF1 Chromatin Remodeler under DNA Damage
 Molecules and Cells Minireview Post-Translational Regulation of the RSF1 Chromatin Remodeler under DNA Damage Sunwoo Min 1,2,3,5, Yong Won Choi 1,4,5, Hansol Yun 1,2,3, Sujin Jo 3, Jae-Hoon Ji 3, and Hyeseong
Molecules and Cells Minireview Post-Translational Regulation of the RSF1 Chromatin Remodeler under DNA Damage Sunwoo Min 1,2,3,5, Yong Won Choi 1,4,5, Hansol Yun 1,2,3, Sujin Jo 3, Jae-Hoon Ji 3, and Hyeseong
TOUR REPORT. Report on participation of the ICMR International Fellow (ICMR IF) in Training / Research abroad
 TOUR REPORT Report on participation of the ICMR International Fellow (ICMR IF) in Training / Research abroad 1. Name and Designation of ICMR IF : Dr. A. Venkateshwari, Assistant Professor 2. Address: Dr.
TOUR REPORT Report on participation of the ICMR International Fellow (ICMR IF) in Training / Research abroad 1. Name and Designation of ICMR IF : Dr. A. Venkateshwari, Assistant Professor 2. Address: Dr.
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
