The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R
|
|
|
- Edmund Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R
2 Nuclear envelope Transcription DNA RNA Processing Pre-mRNA Translation mrna Nuclear pores Ribosome Polypeptide
3 Transcription RNA is synthesized from DNA in the nucleus mrna (messenger) trna (transfer) rrna (ribosomal)
4 Translation Converts base sequence of nucleic acids into the amino acid sequence of proteins Involves mrna, trna, and rrna Occurs in the cytoplasm
5 Genetic Code Each three-base sequence on DNA is represented by a codon Codon complementary three-base sequence on mrna
6 Figure 3.36 SECOND BASE UUG UUA UUC UUU Phe Leu CUG CUA CUC CUU Leu AUA AUC AUU Ile GUG GUA GUC GUU Val UCG UCA UCC UCU Ser CCG CCA CCC CCU Pro ACG ACA ACC ACU Thr GCG GCA GCC GCU Ala UAC UAU Tyr CAG CAA CAC CAU His Gln AAG AAA AAC AAU Asn Lys GAG GAA GAC GAU Asp Glu UGC UGU Cys Trp CGG CGA CGC CGU Arg AGG AGA AGC AGU Ser Arg GGG GGA GGC GGU Gly UAA Stop UGA Stop AUG Met or Start UAG Stop UGG U C A G G A C U G A C U G A C U G A C U U C A G
7 TRANSCRIPTION DNA 3 5 RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION OF INITIATION COMPLEX Amino acid trna AMINO ACID ACTIVATION A mrna Growing polypeptide Activated amino acid 3 E P Ribosomal subunits 5 TRANSLATION E A Anticodon Codon Ribosome
8 The Cell Cycle An illustration of the life cycle of a cell Consists of four major phases G1 phase S phase G2 phase M phase
9 G 1 checkpoint (restriction point) G 1 Growth S Growth and DNA synthesis G 2 Growth and final preparations for division M G 2 checkpoint Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.31
10 The Cell Cycle Interphase G1 S G2 M phase Mitosis Cytokinesis
11 Cell Division Mitotic (M) phase of the cell cycle Essential for body growth and tissue repair Does not occur in most mature cells of nervous tissue, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle We will come back to cancer
12 Functions of Cell Division Growth Replacement Repair Reproduction
13 The Process of Cell Division Includes two distinct events 1. Mitosis division of chromatin Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 2. Cytokinesis division of cytoplasm by cleavage furrow
14 G 1 checkpoint (restriction point) G 1 Growth S Growth and DNA synthesis G 2 Growth and final preparations for division M G 2 checkpoint Figure 3.31
15 The Process of Cell Division DNA replication Takes place during S (synthesis) phase of cell cycle Occurs in the nucleus
16 Chromosome Free nucleotides DNA polymerase Old strand acts as a template for synthesis of new strand Leading strand Old DNA Helicase unwinds the double helix and exposes the bases Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine Replication fork Two new strands (leading and lagging) synthesized in opposite directions Lagging strand DNA polymerase Old (template) strand Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.32
17 DNA Replication End result is two complete sets of DNA Assures appropriate chromosome number in daughter cells
18 Early Prophase Early mitotic spindle Aster Early Prophase Chromosome consisting of two sister chromatids Centromere Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.33
19 Late Prophase Polar microtubule Spindle pole Fragments of nuclear envelope Late Prophase Kinetochore Kinetochore microtubule Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.33
20 Prophase DNA is condensed centromere Sister chromatids
21 LE µm Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis) Centromere Sister chromatids Separation of sister chromatids Centromeres Sister chromatids
22 Metaphase Spindle Metaphase Metaphase plate Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.33
23 Anaphase Anaphase Daughter chromosomes Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.33
24 Telophase and Cytokinesis Nuclear envelope forming Nucleolus forming Contractile ring at cleavage furrow Telophase Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.33
25 The Process of Cell Division Problems during mitosis May or may not be fatal Examples Non-disjunction Down syndrome X and Y chromosomes
26 Cytokinesis cell movement Cells actually divide Follows nuclear division
27 Cytokinesis Begins during late anaphase Ring of actin microfilaments contract to form a cleavage furrow Two daughter cells are pinched apart Each contains a nucleus identical to the original
28 LE 12-9a Cleavage furrow 100 µm Contractile ring of microfilaments Daughter cells Cleavage of an animal cell (SEM)
29 Cancer Second most common cause of death in U.S. Prostate cancer Estimated 217,730 men will be diagnosed Breast cancer 12.2% women will be diagnosed
30 Cancer Most common types Prostate (men) Breast (women) Lung Colorectal
31 Cancer Normal damage control exists in the cell cycle Control(s) are abnormal in cancer Example: proto-oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes (P53) Uncontrolled cell division Absence of or defective regulatory proteins Cancer cells compete with and crowd out normal cells
32 LE G 1 checkpoint G 1 Control system S M G 2 M checkpoint G 2 checkpoint
33 Cancer Genes coding for checkpoint proteins Mutation of genes results in uncontrolled cell division Anything that can alter these genes can trigger cancer
34 Cancer Cancer cells form tumors Masses of abnormal cells within otherwise normal tissue Benign tumor Cells are encapsulated and remain at original site Malignant tumor Invades surrounding tissue and may metastasize
35 LE Tumor Lymph vessel Glandular tissue A tumor grows from a single cancer cell. Cancer cells invade neighboring tissue. Cancer cell Cancer cells spread through lymph and blood vessels to other parts of the body. Blood vessel Metastatic tumor A small percentage of cancer cells may survive and establish a new tumor in another part of the body.
36 LE Colon Colon wall Loss of tumorsuppressor gene APC (or other) Activation of ras oncogene Loss of tumorsuppressor gene p53 Normal colon epithelial cells Small benign growth (polyp) Loss of tumorsuppressor gene DCC Larger benign growth (adenoma) Additional mutations Malignant tumor (carcinoma)
37 Cancer Classification 1. Carcinoma Epithelium 2. Sarcoma Connective tissue, bone or muscle 3. Myeloma Plasma cells in bone marrow 4. Lymphoma Lymph tissue 5. Leukemia Abnormal white blood cells
38 Cancer Symptoms vary with type Unusual bleeding or discharge A lump that does not go away A sore that does not heal within two weeks A change in bowel or bladder habits Persistent hoarseness or cough Indigestion or difficulty swallowing Change in a wart or mole
39 Cancer Causes Carcinogens Oncogenic viruses Hereditary factors Early detection is important!
40 Homework Due in Lab HW #5 Page 13 and 14 in the HW section of the Study Guide Pre-Lab 3 Handout
Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423
 Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423 Finding Signals in DNA We just have a long string of A, C, G, Ts. How can we find the signals encoded in it? Suppose you encountered a language you didn t know. How would
Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423 Finding Signals in DNA We just have a long string of A, C, G, Ts. How can we find the signals encoded in it? Suppose you encountered a language you didn t know. How would
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Protein Synthesis - Sentence Activity Summary: Students will simulate transcription and translation by building a sentence/polypeptide from words/amino acids. Goals & Objectives:
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Protein Synthesis - Sentence Activity Summary: Students will simulate transcription and translation by building a sentence/polypeptide from words/amino acids. Goals & Objectives:
The Cell Cycle and Cancer
 The ell ycle and DN Transcription (Nucleus) Transcription DN Nuclear envelope RN Protein Translation (Ribosomes) RN Processing mrn Translation Polypeptide Pre-mRN Nuclear pores Ribosome Transcription Translation
The ell ycle and DN Transcription (Nucleus) Transcription DN Nuclear envelope RN Protein Translation (Ribosomes) RN Processing mrn Translation Polypeptide Pre-mRN Nuclear pores Ribosome Transcription Translation
Protein sequence alignment using binary string
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):220-225 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):220-225 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Biology 12 January 2004 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 January 2004 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
Biology 12 January 2004 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
General aspects of bacteriology, bacterial structure and growth. Che-Hsin Lee, Ph.D. Department of Biological Sciences National Sun Yat-senUniversity
 General aspects of bacteriology, bacterial structure and growth Che-Hsin Lee, Ph.D. Department of Biological Sciences National Sun Yat-senUniversity 1 Human Microbiome Project Providing metabolic function
General aspects of bacteriology, bacterial structure and growth Che-Hsin Lee, Ph.D. Department of Biological Sciences National Sun Yat-senUniversity 1 Human Microbiome Project Providing metabolic function
CASE TEACHING NOTES. Decoding the Flu INTRODUCTION / BACKGROUND CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
 CASE TEACHING NOTES for Decoding the Flu by Norris Armstrong Department of Genetics, University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION / BACKGROUND This case is a clicker case. It is designed to be presented
CASE TEACHING NOTES for Decoding the Flu by Norris Armstrong Department of Genetics, University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION / BACKGROUND This case is a clicker case. It is designed to be presented
The Synthetic Machinery of the Cell
 The Synthetic Machinery of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives State the characteristics of messenger, ribosomal and transfer RNA Distinguish between
The Synthetic Machinery of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives State the characteristics of messenger, ribosomal and transfer RNA Distinguish between
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Protein Synthesis and Mutation Review
 Protein Synthesis and Mutation Review 1. Using the diagram of RNA below, identify at least three things different from a DNA molecule. Additionally, circle a nucleotide. 1) RNA is single stranded; DNA
Protein Synthesis and Mutation Review 1. Using the diagram of RNA below, identify at least three things different from a DNA molecule. Additionally, circle a nucleotide. 1) RNA is single stranded; DNA
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Genomic and evolutionary aspects of chloroplast trna in monocot plants
 Mohanta et al. BMC Plant Biology (2019) 19:39 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1625-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Genomic and evolutionary aspects of chloroplast trna in monocot plants Open Access Tapan Kumar Mohanta
Mohanta et al. BMC Plant Biology (2019) 19:39 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1625-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Genomic and evolutionary aspects of chloroplast trna in monocot plants Open Access Tapan Kumar Mohanta
The transfer RNA genes in Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica
 Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 The transfer RNA genes in Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica WANG Xiyin ( ) 1,2,3*, SHI Xiaoli ( ) 1,2* & HAO Bailin ( ) 2,4 1. College of Life Science,
Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 The transfer RNA genes in Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica WANG Xiyin ( ) 1,2,3*, SHI Xiaoli ( ) 1,2* & HAO Bailin ( ) 2,4 1. College of Life Science,
Biology 12 November 1999 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 November 1999 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G,
Biology 12 November 1999 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G,
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
 INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE AUGUST 1999 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE AUGUST 1999 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Cell Division and Mitosis
 Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
 INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE JUNE 1998 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
INSERT STUDENT I.D. NUMBER (PEN) STICKER IN THIS SPACE JUNE 1998 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION MINISTRY OF EDUCATION BIOLOGY 12 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Insert the stickers with your Student I.D. Number (PEN)
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
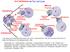 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Cell Cycle. Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase. S phase, synthesis phase
 Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase Cell Cycle interval between cell division and DNA replication accumulates materials needed to replicate
Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase Cell Cycle interval between cell division and DNA replication accumulates materials needed to replicate
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423
 Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423 Is it O.K. to be a Luddite? The New York Times Book Review 28 October 1984, pp. 1, 40-41. As if being 1984 weren't enough, it's also the 25th anniversary this year of C.
Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423 Is it O.K. to be a Luddite? The New York Times Book Review 28 October 1984, pp. 1, 40-41. As if being 1984 weren't enough, it's also the 25th anniversary this year of C.
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Biology 12 JANUARY Course Code = BI. Student Instructions
 MINISTRY USE ONLY MINISTRY USE ONLY Place Personal Education Number (PEN) here. Place Personal Education Number (PEN) here. MINISTRY USE ONLY Biology 12 2004 Ministry of Education JANUARY 2004 Course Code
MINISTRY USE ONLY MINISTRY USE ONLY Place Personal Education Number (PEN) here. Place Personal Education Number (PEN) here. MINISTRY USE ONLY Biology 12 2004 Ministry of Education JANUARY 2004 Course Code
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS SECOND EDITION URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle
 Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
9 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell division plays
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell division plays
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
Unit IV. Chapter 04. Cellular Function. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Unit IV hapter 04 ellular Function opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Fig. 4.2 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Unit IV hapter 04 ellular Function opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Fig. 4.2 opyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks
 Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Key Concepts in Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Video: Sea Urchin Embryonic Development (time-lapse)
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
BIOLOGY 12 NOVEMBER 2000 STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS
 Place Personal Education Number (PEN) here. Place only pre-printed PEN label here. STUDENT INSTRUCTINS 1. Place the stickers with your Personal Education Number (PEN) in the allotted spaces above. Under
Place Personal Education Number (PEN) here. Place only pre-printed PEN label here. STUDENT INSTRUCTINS 1. Place the stickers with your Personal Education Number (PEN) in the allotted spaces above. Under
Why do cells reproduce?
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Ch 4 BIOL 100 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Ch 4 BIOL 100 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview. Cellular Organization of the Genetic Material. Distribution of Chromosomes During Eukaryotic Cell Division
 CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle
 Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function. The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Chromosome loci. Organization of the Chromatin. Nucleotide Structure
 Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP
 Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT
 HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART 1 - BACKGROUND: 1. Heterozygous means. A. Information about heritable traits B. Unique/ different molecular forms of a gene that are possible at a given locus C. Having
HEREDITY SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART 1 - BACKGROUND: 1. Heterozygous means. A. Information about heritable traits B. Unique/ different molecular forms of a gene that are possible at a given locus C. Having
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Biology 12. Examination Booklet 2008/09 Released Exam June 2009 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EXAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO.
 Biology 12 Examination Booklet 2008/09 Released Exam June 2009 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. FOR FURTHER INSTRUCTIONS REFER TO THE RESPONSE BOOKLET. Contents: 32
Biology 12 Examination Booklet 2008/09 Released Exam June 2009 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. FOR FURTHER INSTRUCTIONS REFER TO THE RESPONSE BOOKLET. Contents: 32
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
TRANSLATION: 3 Stages to translation, can you guess what they are?
 TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Biology 12. Examination Booklet August 2007 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EXAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO.
 Biology 12 Examination Booklet August 2007 Form A D NT PEN ANY EAMINATIN MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED T D S. FR FURTHER INSTRUCTINS REFER T THE RESPNSE BKLET. Contents: 28 pages Examination: 2 hours 67 multiple-choice
Biology 12 Examination Booklet August 2007 Form A D NT PEN ANY EAMINATIN MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED T D S. FR FURTHER INSTRUCTINS REFER T THE RESPNSE BKLET. Contents: 28 pages Examination: 2 hours 67 multiple-choice
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
AN INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS. The First Ankle in a Series about the Significance of Genetic Science for Catholic Health Care
 AN INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS The First Ankle in a Series about the Significance of Genetic Science for Catholic Health Care BY JEFFREY G.SHAW Jeffrey Shaw is genetics counselor, Cancer Center, Penrose-St.
AN INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS The First Ankle in a Series about the Significance of Genetic Science for Catholic Health Care BY JEFFREY G.SHAW Jeffrey Shaw is genetics counselor, Cancer Center, Penrose-St.
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division
 2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
