T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
|
|
|
- Lesley Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Courtheoux et al., S1
2 Figure S2. Visualization of multiple merotelic attachments. (A, top) Kymograph of a rad21-k1 ndc80-gfp cdc11-gfp cell showing two merotelic attachments at the spindle center, each of which is stretched into two dots. (right) A line scan confirms the presence of four dots (2 2 Kts). (bottom) Automated tracking analysis of SPBs (red) and Kt position. (B, top) Kymograph of a rad21-k1 ndc80-gfp cdc11-cfp cell showing three merotelic Kts at the spindle center, each of which is stretched into two dots. (right) A line scan confirms the presence of six dots (2 3 Kts). (bottom) Automated tracking analysis of the SPBs (red) and the Kt position. Green, Kts at the poles; blue, light blue, and purple, the three merotelic Kts. Figure S1. A combination of live cell microscopy and laser ablation to visualize merotelic attachment. (A, top) Live cen1-gfp (red) ndc80-cfp (green) cells during anaphase. (bottom) Representation of an amphitelic Kt attachment. (B, top) Live rad21-k1 cen1-gfp (red) ndc80-cfp (green) cells during anaphase. (bottom) Representation of a merotelic Kt attachment. Schematic representations of fission yeast cell shape are shown (dashed ovals). The boxed region indicates the enlarged region in C. (C) Enlarged images of the merotelic attachment shown in B. (D) Image series of a rad21-k1 ndc80-gfp (green) cdc11-cfp (blue) in live cells stained with Hoechst (DNA; red). Note the presence of a stretched merotelic Kt at the 405-s time point. (E) Quantification of Hoechst signal was performed by integrated intensity on the defined area minus the noise at the 405-s time point. The data shown are representative of a single experiment, which was repeated in several cells (n = 8). (F) Simultaneous laser ablation of cells within the same field is shown. Image series of a field of cells showing eight individual wt SV40-GFP-atb2 mitotic cells (red ovals) before and after laser ablation (blue dots; impact at the 20-s time point). Note that the spindles are simultaneously and reproducibly cut in all cells. S2
3 Figure S3. Merotelic attachment leads to cut/asymmetric division/multipolar spindles and cell death in the absence of Ase1. (A) Image series of a rad21-k1 (MTs) ndc80-gfp (Kts) cell during mitosis. Example of a cell with a merotelic (Mero) attachment (white arrows) during mitotic progression up to the completion of cytokinesis and cell abscission (left, bright field picture). One of the daughter cells (top) undergoes a successful second round of mitosis and cytokinesis, whereas the other (bottom right), although alive, is delayed in G2. (B) Image series of a rad21-k1 ase1 atb2-gfp (MTs) ndc80-gfp (Kts) cell during cell cycle progression after asymmetric spindle collapse. The two SPBs are positioned at one extremity of the cell; mitosis is followed by cytokinesis and abscission (bright field picture). The top cell possesses two sets of chromosomes as judged by the ndc80-gfp signal and undergoes a second round of cytokinesis before cell death. The bottom cell is aneuploid and dies. (C) Image series of a rad21-k1 ase1 ndc80-gfp (Kts) cdc11-cfp (SPBs) Myo2 GFP (ring) after asymmetric spindle collapse and cytokinesis. After replication of the two existing SPBs, cells with multipolar spindles are produced. The inset shows an enlarged view of the SPBs and Kts at 4 min. S3
4 Figure S4. Merotelic attachment leads to cut/asymmetric division and cell death in the absence of Ase1. (A) Percentage of cells with a septum showing defects in chromosome segregation: wt, n = 2,466; rad21-k1, n = 1,966; ase1, n = 2,716; and rad21-k1 ase1, n = 1,368. (B) rad21-k1 is synthetically lethal with ase1 at the semipermissive temperature. rad21-k1, ase1, and rad21-k1 ase1 double mutants were streaked on YEA plates at different temperatures (25, 28, 31, 33, and 36 C). Error bars indicate SD. S4
5 Figure S5. Simulation of multiple merotelic attachments and reduction in spindle force generation during spindle elongation. Simulation of mitotic progression in the presence of two merotelic Kts (green and purple; SPBs are shown in red). The Kt attachment state is indicated for one of the merotelic Kts (purple). (B) Simulation of mitotic progression in the presence of three merotelic Kts (green, purple, and blue). (C) Simulation of a reduction in the spindle force generator (midzone stall force; Table I) at the onset of anaphase A (time 0) until the critical size of the spindle is reached at 7 µm (Loïodice et al., 2005). At this critical size, and as observed in vivo, force is abruptly adjusted to 0. (D) Simulation of Kt dynamics (green) and SPB position (red) when the force produced by the interdigited MTs linearly decreases. Video 1. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of Kt dynamics in a wt S. pombe cell. Wt cells expressing Ndc80 GFP as a marker of the six Kts (green) and Cdc11 CFP as a marker of the two SPBs (red) were analyzed by time-lapse wide field microscopy. Frames were collected every 8 s and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 1 A. Video 2. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of Kt dynamics in rad21-k1 S. pombe cells. Rad21-K1 cells expressing Ndc80 GFP as a marker of the six Kts (green) and Cdc11 CFP as a marker of the two SPBs (red) were analyzed by wide field time-lapse microscopy as in Video 1. Frames were collected every 10 s and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 1 B. S5
6 Video 3. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of a single merotelic Kt after laser ablation. Wt (left) and rad21-k1 (right) cells expressing SV40-GFP-atb2 as a marker of -tubulin (green) and Cdc11 CFP as a marker of the two SPBs (red). Both cells were analyzed simultaneously by time-lapse microscopy as in Video 1. At the 140-s time point, cells were subjected simultaneously to laser ablation (white dots; pulse time of 35 ms). Frames were collected every 10 s and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 2. Video 4. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of an ase1 S. pombe cell expressing -tubulin. ase1 cell expressing SV40-GFP-atb2 as a marker of -tubulin (spindle) and Ndc80-GFP as a marker of the Kts (Kts are at the poles) were analyzed as in Video 1. Frames were collected every 2 s and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 4 B (left). Video 5. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of an ase1 rad21-k1 S. pombe cell expressing -tubulin. ase1 rad21-k1 cell expressing SV40-GFP-atb2 analyzed as in Video 1. Frames were collected every 2 s and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 4 B (right). Video 6. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of Kt dynamic and cytokinesis in a wt S. pombe cell. Wt cells expressing Myo2 GPF as a marker of the actomyosin ring (green), Ndc80 GFP as a marker of the six Kts (green), and Cdc11 CFP as a marker of the two SPBs (red) were analyzed by time-lapse microscopy as in Video 1. Frames were collected every 1 min and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 5 A. Video 7. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of Kt dynamic and cytokinesis in a rad21-k1 S. pombe cell. rad21-k1 cells expressing Myo2 GFP as a marker of the actomyosin ring (green), Ndc80-GFP as a marker of the six Kts (green), and Cdc11 CFP as a marker of the two SPBs (red) were analyzed as in Video 1. Frames were collected every 1 min and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 5 B. Video 8. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of Kt dynamics and cytokinesis in a rad21-k1 ase1 S. pombe cell. rad21-k1 ase1 cells expressing Myo2 GFP as a marker of the actomyosin ring (green), Ndc80-GFP as a marker of the six Kts (green), and Cdc11 CFP as a marker of the two SPBs (red) were analyzed by time-lapse microscopy as in Video 1. Frames were collected every 1 min and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 5 C. Video 9. Fluorescent time-lapse imaging of Kt dynamics and cytokinesis in a rad21-k1 ase1 S. pombe cell. rad21-k1 ase1 cells expressing Myo2 GFP as a marker of the actomyosin ring (green), Ndc80-GFP as a marker of the six Kts (green), and Cdc11 CFP as a marker of the two SPBs (red) were analyzed by time-lapse microscopy as in Video 1. Frames were collected every 1 min and are shown at a rate of 60 frames/min. Representative frames from this video are shown in Fig. 5 D. S6
7 Table S1. S. pombe strains used in this study Strain number Genotype References TCX189 rad21-k1 cen1(d107)-kanr-ura4-laco his7-laci-gfp ndc80-cfp::kanr This study TCX177 ndc80-cfp::kanr cen1(d107)- kanr-ura4-laco his7+-laci-gfp This study ST102 ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr ura4-d18 leu1-32 Tournier et al. (2004) TCX113 rad21-k1 ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr This study TCX246 lys1::nmt1 atb2-gfp cdc11-cfp::kanr This study ST754 ase1::kanr Loïodice et al. (2005) TCX218 rad21-k1 ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr ase1::kanr This study TCX220 rad21-k1 ase1::kanr ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr SV40-gfp-atb2 This study TCX221 rad21-k1 ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr SV40-gfp-atb2 This study ST430 rad21-k1 Tomonaga et al. (2000) TCX284 rad21-k1 ase1::kanr This study TCX276 ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr myo2-gfp::kanr This study TCX272 rad21-k1 ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr myo2-gfp::kanr This study TCX278 rad21-k1 ase1:: kanr ndc80-gfp::kanr cdc11-cfp::kanr myo2-gfp::kanr This study References Loïodice, I., J. Staub, T.G. Setty, N.P. Nguyen, A. Paoletti, and P.T. Tran Ase1p organizes antiparallel microtubule arrays during interphase and mitosis in fission yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell. 16: doi: /mbc.e Tomonaga, T., K. Nagao, Y. Kawasaki, K. Furuya, A. Murakami, J. Morishita, T. Yuasa, T. Sutani, S.E. Kearsey, F. Uhlmann, et al Characterization of fission yeast cohesin: essential anaphase proteolysis of Rad21 phosphorylated in the S phase. Genes Dev. 14: doi: /gad Tournier, S., Y. Gachet, V. Buck, J.S. Hyams, and J.B. Millar Disruption of astral microtubule contact with the cell cortex activates a Bub1, Bub3, and Mad3- dependent checkpoint in fission yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell. 15: doi: /mbc.e S7
Supplementary table 1
 Supplementary table 1 S. pombe strain list Fig. 1A JX38 h + ade6-m216 nda3-km311 PX476 PW775 PX545 PX546 h- ade6-m216 sgo2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h 9 mad2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h + ade6-m21 nda3-km311 rad21 +
Supplementary table 1 S. pombe strain list Fig. 1A JX38 h + ade6-m216 nda3-km311 PX476 PW775 PX545 PX546 h- ade6-m216 sgo2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h 9 mad2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h + ade6-m21 nda3-km311 rad21 +
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
Latrunculin A delays anaphase onset in fission yeast by disrupting an Ase1-independent pathway controlling mitotic spindle stability
 Latrunculin A delays anaphase onset in fission yeast by disrupting an Ase1-independent pathway controlling mitotic spindle stability John C. Meadows * and Jonathan B.A. Millar * * Division of Yeast Genetics,
Latrunculin A delays anaphase onset in fission yeast by disrupting an Ase1-independent pathway controlling mitotic spindle stability John C. Meadows * and Jonathan B.A. Millar * * Division of Yeast Genetics,
Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach
![klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach](/thumbs/91/104639484.jpg) DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Supplementary information. The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic. Spindle Orientation
 Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
BIOLOGY 4/6/2015. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza
 Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza Polarity of tubulin polymerization Nuclei Tubulin > C C Preferential addition of tubulin ar (+) ends Tubulin < C C Preferential loss of tubulin ar (+) ends Kinesin
Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza Polarity of tubulin polymerization Nuclei Tubulin > C C Preferential addition of tubulin ar (+) ends Tubulin < C C Preferential loss of tubulin ar (+) ends Kinesin
Mitosis vs. microtubule
 Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
9 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell division plays
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell division plays
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities
 Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
10.2 The Cell Cycle *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m52672 1 10.2 The Cell Cycle * Shannon McDermott Based on The Cell Cycle by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m52672 1 10.2 The Cell Cycle * Shannon McDermott Based on The Cell Cycle by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
BIOLOGY. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
How Cells Divide. Chapter 10
 How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Self-Organization of Dynein Motors Generates Meiotic Nuclear Oscillations
 Generates Meiotic Nuclear Oscillations PLoS BIOLOGY Sven K. Vogel 1[, Nenad Pavin 2,3[, Nicola Maghelli 1, Frank Jülicher 2, Iva M. Tolić-Nørrelykke 1* 1 Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology
Generates Meiotic Nuclear Oscillations PLoS BIOLOGY Sven K. Vogel 1[, Nenad Pavin 2,3[, Nicola Maghelli 1, Frank Jülicher 2, Iva M. Tolić-Nørrelykke 1* 1 Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Growth and Division. Chapter 10
 Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Cell Division Before a cell becomes too large, it undergoes cell division, in which the cell divides and becomes 2 daughter cells. Before cell division occurs, the cell
Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Cell Division Before a cell becomes too large, it undergoes cell division, in which the cell divides and becomes 2 daughter cells. Before cell division occurs, the cell
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
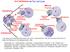 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS
 Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Mad2 and Mad3 Cooperate to Arrest Budding Yeast in Mitosis
 Mad2 and Mad3 Cooperate to Arrest Budding Yeast in Mitosis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published
Mad2 and Mad3 Cooperate to Arrest Budding Yeast in Mitosis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Cell Division. During interphase, a cell s DNA is in a loose form called. It condenses into tightly coiled structures called chromosomes during.
 Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Essential Questions. Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase?
 Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Key Concepts in Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Video: Sea Urchin Embryonic Development (time-lapse)
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Name. A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
Cell Division and Mitosis
 Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Meiosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Cellular Reproduction
 Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages )
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS SECOND EDITION URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview. Cellular Organization of the Genetic Material. Distribution of Chromosomes During Eukaryotic Cell Division
 CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair
 Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Cell division and mitosis
 Cell division and mitosis Universal functions of the cell cycle Replicate the DNA. Segregate it into daughter cells. Replicate and/or distribute organelles into daughter cells. Grow. The Cell Cycle Growth
Cell division and mitosis Universal functions of the cell cycle Replicate the DNA. Segregate it into daughter cells. Replicate and/or distribute organelles into daughter cells. Grow. The Cell Cycle Growth
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Supplementary Information for. Shi and King, Chromosome Nondisjunction Yields Tetraploid Rather than Aneuploid Cells in Human Cell Lines.
 Supplementary Information for Shi and King, Chromosome Nondisjunction Yields Tetraploid Rather than Aneuploid Cells in Human Cell Lines Contains Supplementary Methods Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary
Supplementary Information for Shi and King, Chromosome Nondisjunction Yields Tetraploid Rather than Aneuploid Cells in Human Cell Lines Contains Supplementary Methods Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
Why do cells reproduce?
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother
 Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
