If you do not have time for the entire presentation refer to the following table of contents. To navigate through the slides, right click on your
|
|
|
- Timothy Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Welcome This is an online version of a lecture given by Dr Keith Merritt on gyn cancers. Its purpose is to help women become more aware of early symptoms, risk factors, screening strategies and the importance of knowing their family history of cancers. We hope that you will find this information helpful.
2 If you do not have time for the entire presentation refer to the following table of contents. To navigate through the slides, right click on your mouse and then the slide of interest.
3 Table of Contents Glossary of terms Overview Ovarian cancer Uterine cancer (endometrial) Uterine cancer (sarcoma) Fallopian tube cancer Cervical cancer Vaginal cancer Vulvar cancer
4 Glossary of Terms Ovary- the pelvic organ that contains and releases eggs for reproduction and secretes hormones such as estrogen, progesterone and testosterone. Each woman normally has two ovaries. Fallopian Tube- bilateral tubular structures with one end suspended over an ovary and the other end emptying into the uterine cavity. Its normal function is to capture an the egg released by the ovary, provide a space for fertilization of the egg by sperm and then transport that fertilized egg to the uterine cavity. Uterus- A woman s womb. A pear shaped vessel with a muscular wall and a cavity lined with endometrium. The neck or constricted entry into this vessel is the cervix which protrudes into the vagina.
5 Glossary of Terms Cervix- The constricted entry into or neck of the uterus. It protrudes into the top of the vagina and is the gateway for entry of sperm and exit pathway for menstrual flow. It is the part which must dilate during labor and birth. Its canal is lined with tall cells known as glandular cells which secrete a mucous-like fluid. Its outer vaginal part is coated with flat cells known as squamous cells. These two cell type meet on the outer face of the cervix. The line where these two cell types abut is known as the transformation zone and is the most common area for cervical dysplasia and cancer. This zone and the canal are the cervical parts that are swabbed during a pap smear. Vulva- The mound-like tissue that is the woman s external genitals.
6 Glossary of Terms Endometrium- The lining of the uterine cavity. During a normal 28 day menstrual cycle it thickens during the first 14 days in response to estrogen secreted by the ovary. This growth continues with the thickness increasing as long as estrogen exposure without progesterone continues. After midcycle ovulation, the ovary secretes progesterone in addition to continued estrogen secretion. This tightens and organizes the endometrium in preparation for a fertilized egg to implant. If implantation does nor occur, estrogen and progesterone secretion stop and the endometrium is shed creating the menstrual flow. First degree relative- parent or sibling Second degree relative- grandparents, aunts or uncles.
7 Gyn Cancers
8 Gyn Cancers Ovarian Uterine- endometrial - sarcoma Fallopian Tube Cervical Vaginal Vulvar
9 First A little perspective
10
11 In the first half of the twentieth century cervical cancer was the second most common cause of cancer death in women and lung cancer was rare (as were heart attacks).
12 Then two things changed Pap smears screening began in the 1940 s Tobacco companies discovered that they could effectively market cigarettes to women as women began demanding equal treatment.
13
14
15
16 Ovarian Cancer
17 Ovarian Cancer 2 nd most common gyn cancer -21,000 new cases per year Most deadly gyn cancer -15,000 deaths per year No effective method of screening 70% are advanced at time of diagnosis
18 5 Year Survival 80-90% when confined to ovary 3-80% when spread outside of ovary -varies with degree of spread & type
19
20 Any cell type within the ovary may develop a cancer meaning the ovary may develop a very wide variety of cancers.
21 The Ovary has three basic parts Surface epithelium A thin membrane covering not only the ovary but also every other structure and organ in the abdomen and pelvis. This membrane must rupture and be repaired during each cycle when an egg is released. The cells in this structure are the most common source of ovarian cancers.
22 Germ Cells The eggs. Structures formed from a fertilized egg include the membranes that surround a pregnancy The most common tumors formed by this structure are dermoid cysts.
23 Sex-cord Stroma A matrix of cells that contain the egg follicles and that provide support for the developing eggs. The source of hormone secretion by the ovaries meaning that associated tumors may secrete hormones such as estrogen.
24 Age at Diagnosis Mean age at diagnosis: mid 50 s to 60 s -borderline tumors: mid- 40 s -7 years earlier for hereditary Incidence increases until 80 years old -then declines
25 Risk That an Ovarian Mass is Cancer Premenopausal: 6-11% Postmenopausal: 29-35%
26 Ovarian Cancer Symptoms May occur at early stage -on average 6 months before diagnosis Large majority do not have cancer Consider if symptom is new onset or persistent & occurs daily
27 Ovarian Cancer Symptoms Bloating Increased abdominal girth Urinary urgency or frequency Difficulty eating Feeling full early Pelvic or abdominal pain Leg pain, weakness or numbness
28 Debate Over Origin of Ovarian Cancer Begins at a single point and spreads vs Begins at multiple points (screening pointless)
29 Family History Strongest known risk factor In women who develop ovarian cancer % have a family history (that is % do not)
30 Risk Factors Genetic Lifestyle
31 BRCA 1 & 2 Mutations The most commonly identified ovarian genetic cancer syndromes Also increases the risk of other cancers Autosomal dominant inheritance (all children will be affected)
32 CANCER BRCA1 Risk (Lifetime) BRCA2 Risk (Lifetime) General Population Breast Ca 47-66% 40-57% 12.5% Contralateral Breast Ca 65% 50% 0.5-1% Ovarian Ca 35-46% 13-23% 1.8% Colon Ca Prostate Ca Male Breast Cancer None to very slight inc Increased (unknown) None to very slight inc 5% 35-40% 15% % % 0.1% Pancreatic C <10% <10% 1.3%
33 Lynch II Syndrome Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer -HNPCC 1% of ovarian cancers Lifetime risk -9-12% for ovarian cancer % for endometrial cancer
34 Modifiable Risk Factors for ovarian cancer Nulligravity (no pregnancies) is the greatest known risk factor Risk reduced with -oral contraceptive use, progesterone use -large # of children -breast feeding -tubal ligation
35 Modifiable Risk Factors for ovarian cancer Mounting evidence that the most aggressive form of ovarian cancer originates in the fallopian tubes Consider removal of fallopian tubes instead of tubal ligation Remove tubes if having hysterectomy
36 Risk of Ovarian Cancer Increases with # of reproductive years Decreased with oral contraceptive use -25% decrease in risk for any use -50% reduction for 5 years use -protection persists for up to 30 years
37 Other Risk Factors Endometriosis- younger, better survival Talc- weak, may be due to asbestos Cigarettes- increase in mucinous only Diet- effect not clear Exercise- slight protection with high levels Obesity- slight increase in risk
38 Family ovary ca syndrome 2-3 relatives w ovarian ca (1 st or 2 nd degree relative) 1 relative- 1 st or 2 nd degree 3.1 Relative risk Lifetime ovarian ca probability % unknown 30-50% 4.6 5% (15% if 1 st degree relative) % (5% if 1 st degree relative) No risk factors % Past oral contraceptive use % Past pregnancy % Infertility 2.8 No deliveries 1.6 Past breast feeding 0.8 Tubal ligation 0.6
39 Incidence of ovarian cancer varies with race and with location Western countries 3-7X Japan Japanese Americans approach US rate Caucasians 1.5X African-Americans
40 Screening for Ovarian Cancer To date, no screening strategy effective in reducing ovarian cancer deaths Trials now in progress No effective blood test yet Current recommendation- screen high risk
41 High Risk Patients Age 25-35: every six months -transvaginal ultrasound -Ca-125 Oral contraceptives may not help Surgical removal of ovaries after age 35
42 Endometrial Cancer
43 Endometrial Cancer Most common gyn cancer in the US 6% of all cancers in women 2.5% lifetime risk Usually diagnosed early due to bleeding
44 5 year survivals Localized- 95% (70% of cases) Regional- 67% Metastatic- 23%
45 Endometrial Cancer More common in whites However mortality higher in blacks & Hispanics (7% vs 4%)
46 Has two forms Type I- 80% of cases Type II
47 Type I Due to excessive estrogen stimulation Often associated with hyperplasia
48 Type1 Risk Factors Obesity No pregnancies Diabetes Hypertension Prolonged unopposed estrogen exposure
49 Type II Not associated with estrogen -no preceding hyperplasia Tend to be higher grade tumors -worse outcomes No real known risk factors Those affected tend to be -older -have had multiple children
50 Sources of Excessive Estrogen Unopposed estrogen replacement Tamoxifen Obesity Polycystic ovary syndrome -chronic inability to ovulate Estrogen secreting tumors
51 Unopposed Estrogen Replacement One year of unopposed estrogen -hyperplasia found in 20-50% Absolute risks of endometrial cancer -in general population- 1/1000 -on unopposed estrogen- 1/100
52 Obesity Increases estrogen exposure -fat converts testosterone to estrogen Risk increases with increasing weight Greater weight increases risk of death from endometrial cancer
53 25% occur in premenopausal women 5-10% of these are less than 40 yo Reported in women less than 30 yo Probability of disease if less than 39 yo: 0.05%
54 Characteristics of Younger Women with Endometrial Cancer 89% are type I (high estrogen exposure) 59% are obese 44% have had no pregnancies 23% are hypertensive and/or diabetic 19% had concurrent ovarian cancer
55 Normal Weight Premenopausal Women with Endometrial Cancer Are more likely to Be subfertile Have had no pregnancies Have irregular periods Have a concurrent ovarian cancer Have Lynch Syndrome (9%)
56 Other Risk Factors Slightly higher risk in 1 st degree relatives Lynch Syndrome -consider if family history of colon cancer -breast and ovarian cancers precede colon cancer in 50% (by 11 & 5 years) Prior breast cancer- similar risk factors
57 No Clear Associations Diet Alcohol Early menarche or late menopause Level of physical activity
58 Protective Factors Birth Control Pills 50-80% reduction in risk 12 month use decreases risk by 40% Protective effect lasts at least 15 years Hormone Replacement Therapy Smoking- seen only with postmenopausal
59 Clinical Presentation Bleeding in 90% If postmenopausal- just one drop of blood -5-20% will have endometrial cancer -risk increases with age -risk not related to amount of bleeding
60 Abnormal Premenopausal Bleeding Should also have a biopsy- especially if Obese Diabetic Hypertensive No pregnancies Chronic lack of ovulation Prior tamoxifen use
61 Abnormal Premenopausal Bleeding Risk of endometrial cancer increases with either family or personal history of Breast cancer Ovarian cancer Colon cancer Endometrial cancer Endometrial hyperplasia
62 Diagnosis Office biopsy Ultrasound Sonohystogram Hysteroscopy
63 Screening Only recommended in women with possible Lynch Syndrome Women known to carry the mutation Family member with the mutation Autosomal dominant inheritance of colon cancer without identified gene
64 Who to Test for Lynch Syndrome Endometrial cancer before age 50 plus at least one 1 st degree relative with a related cancer Breast Ovarian Colon
65 Uterine Sarcoma
66 Uterine Sarcoma May arise from either the lining of the uterine cavity or the wall of the uterus Much more aggressive with much worse survival than endometrial cancer Several types Rare- 3.6/100,000 women
67 Uterine Sarcoma 2X more common in African Americans Average age at diagnosis- 60 years Risk may be increased with -prior pelvic radiation therapy -prior tamoxifen use (weak association)
68 Clinical Presentation Bleeding- especially if foul smelling Pelvic pressure, urinary frequency Constipation Enlarged uterus (may be normal size)
69 Cannot distinguish between fibroid and sarcoma by Exam Ultrasound History
70 Suspect In postmenopausal If presumed fibroids bothersome enough to consider hysterectomy -1 to 2% will have a sarcoma In premenopausal Bleeding disproportionate to size of uterus Significant pain
71 Diagnosis Requires either removal or biopsy of mass Office biopsy is not adequate U/S, MRI, CT scan are not adequate
72 Fallopian Tube Cancer
73 Fallopian Tube Cancer Very rare Annual incidence 4.1/1,000,000 women More often due to metastatic spread from -breast, ovary, uterine, colon cancers Shares same risk factors as ovarian -BRCA mutation
74 Clinical Presentation Often in 50 s and 60 s Blood tinged discharge in 50-60% Pelvic pain in 30-50% Pelvic mass in 12-60%
75 Common Presentation Discharge and bleeding with negative endometrial biopsy 10% have abnormal cells on pap with negative cervical & endometrial biopsies
76 Diagnosis Requires removal of the fallopian tube Ca-125 is usually elevated Mass often seen on imaging
77 Cervical Cancer
78 Cervical Cancer Sexually transmitted disease Human papilloma virus (HPV) Over 100 strains of HPV -40 known to infect genital surfaces
79 HPV Infection Affects majority of sexually active humans -majority are low risk HPV (cleared easily) High risk strains more likely to persist & progress to dysplasia then to cancer 5-20 years between infection and cancer
80 HPV Infection There are fifteen high risk strains 70% of cases caused by strains 16 & 18 Thought to interfere with p53 gene -cancer protection
81 Two types of Cervical Cancer Squamous cell cancer -most common Adenocarcinoma -incidence increasing
82 Symptoms Often asymptomatic when early Abnormal bleeding Bleeding after intercourse Discharge- persistent, abnormal
83 When advanced Pelvic or back pain -may radiate along outer sides of legs Bowel or urinary symptoms -pressure & frequency -blood in urine or stool
84 Risk Factors Early age of 1 st intercourse Multiple partners High risk partner STD s Smoking Large number of children Immunosuppression Low socioeconomic class Prolonged use of oral contraceptives Uncircumcised partner
85 Still causes large number of cancer deaths in countries without adequate screening -1.5% risk of death before 65 yo More common in minorities
86
87 Cervical Cancer Prevention Don t ever have sex (good luck with that) Gardisil Condoms Pap smears HPV testing
88 Roden and Wu Nature Reviews Cancer 6, (October 2006) doi: /nrc1973
89 Pap Smears One of the few truly successful screening tests in medicine Reduced cervical cancer from 2 nd to 13 th most common cause of female cancer death Dr George Papanicolaou (Γεώργιος Παπανικολάου)
90
91 Pap Smears Purpose is not to diagnose cancer -not reliable if cancer is suspected Purpose is to find dysplasia -precancerous changes -untreated, 2-70% progress to cancer
92
93 When to Begin Pap Smears Adolescents: 3 years after 1 st intercourse When 20 years old (HPV screening not recommended if < 30)
94 HPV Testing May offer when 30 years old -combine with pap smear -if both are negative, repeat both in 3 yrs (does not apply if HIV +) Follow-up to low level abnormality on pap smear (ASCUS) Still needs annual exam
95 When to Stop Pap Smears After hysterectomy if no prior dysplasia After yo if -no prior dysplasia -no immunosuppression (HIV) -no new sexual partners All women still need annual exam
96 Cervical cancer incidence varies with age Average age at diagnosis- 47 years Incidence at < 20 years: 0/100,000/yr % are > 75 years old
97
98 Vaginal Cancer
99 Vaginal Cancer Squamous cell- 85% of cases Adenocarcinoma- all of cases in < 20 yo s Sarcoma- vaginal mass in childhood Melanoma- seen only in Caucasians
100 Squamous Cell Vaginal Cancer Caused by HPV Much less common than cervical cancer Mean age at diagnosis- 60 years -however can occur in 20 s Ulcer, mass, erosion
101 Vaginal Melanoma Mean age at diagnosis- 58 years Black, brown, blue or skin color Biopsy every new -pigmented area -lump
102 Vulvar Cancer
103 Vulvar Cancer Majority are postmenopausal -mean age has declined from 69 to 55 years HPV causes 60% of cases -strains 16 & 33 Chronic inflammation causes 40% Preceded by dysplasia -treatment prevents cancer
104 Risk Factors Cigarette smoking Vulvar dystrophy (lichen sclerosis) Immunodeficiency (HIV) HPV infection Northern European heritage History of cervical dysplasia or cancer
105 Symptoms Mass, plaque, ulcer Itching Bleeding, discharge- usually advanced Lump in groin- usually advanced Synchronous malignancy is present in 22% -most commonly cervical
106 In Summary
107 Lifestyle is important Protected sex- insist on condom use Know your partners sexual history Healthy diet is extremely important -vegetables, fruit -limit sugar, processed & refined foods -pasture raised meat Keep your weight under control Don t smoke
108 Remember Get your pap smears Have an annual exam Know your family history If you are trying to decide if you should call your doctor, call!!!!!
109 Report any Changes in bowel movements Urinary symptoms Increase in waist size Weakness of numbness in legs New onset pelvic or back pain Abnormal bleeding or discharge Lumps or scaling Persistent localized itching
110 Back to Acacia Ob/Gyn Website
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers
 Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers
 Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers Jubilee Brown MD and Pamela T. Soliman MD, MPH Department of Gynecologic Oncology and Reproductive Medicine University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers Jubilee Brown MD and Pamela T. Soliman MD, MPH Department of Gynecologic Oncology and Reproductive Medicine University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
Gynecological Cancers
 Gynecological Cancers Outline Ovarian Cancer Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Vaginal Cancer Overian Cancer Ovarian cancer is cancer that forms in the tissue of the ovary and
Gynecological Cancers Outline Ovarian Cancer Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Vaginal Cancer Overian Cancer Ovarian cancer is cancer that forms in the tissue of the ovary and
6 Week Course Agenda. Today s Agenda. Ovarian Cancer: Risk Factors. Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention
 6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Cancer Facts for Women
 Cancer Facts for Women Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colorectal, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancers. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to
Cancer Facts for Women Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colorectal, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancers. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to
Menopause and Cancer risk; What to do overcome the risks? Fatih DURMUŞOĞLU,M.D
 Menopause and Cancer risk; What to do overcome the risks? Fatih DURMUŞOĞLU,M.D Menopause and Cancer How does menopause affect a woman s cancer risk? Ø Menopause does not cause cancer.but risk of developing
Menopause and Cancer risk; What to do overcome the risks? Fatih DURMUŞOĞLU,M.D Menopause and Cancer How does menopause affect a woman s cancer risk? Ø Menopause does not cause cancer.but risk of developing
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
 Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine. Speaker Disclosure:
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Molly A. Brewer DVM, MD, MS Chair and Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Connecticut School of Medicine
 Molly A. Brewer DVM, MD, MS Chair and Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Connecticut School of Medicine Review causes of abnormal uterine bleeding: Adolescent Reproductive
Molly A. Brewer DVM, MD, MS Chair and Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Connecticut School of Medicine Review causes of abnormal uterine bleeding: Adolescent Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Speaker Disclosure: Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine. Controversies in Women s Health
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Sarah Burton. Lead Gynae Oncology Nurse Specialist Cancer Care Cymru
 Sarah Burton Lead Gynae Oncology Nurse Specialist Cancer Care Cymru Gynaecological Cancers Cervical Cancers Risk factors Presentation Early sexual activity Multiple sexual partners Smoking Human Papiloma
Sarah Burton Lead Gynae Oncology Nurse Specialist Cancer Care Cymru Gynaecological Cancers Cervical Cancers Risk factors Presentation Early sexual activity Multiple sexual partners Smoking Human Papiloma
Cancer in Women. Lung cancer. Breast cancer
 Cancer in Women You can get cancer at any age, but it is more likely as you get older. The types of cancer people get and the risk of dying from cancer are not the same for all ethnic groups. Here are
Cancer in Women You can get cancer at any age, but it is more likely as you get older. The types of cancer people get and the risk of dying from cancer are not the same for all ethnic groups. Here are
Protect & Detect: What Women should Know about cancer. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
 Protect & Detect: What Women should Know about cancer The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists A Message From ACOG President Kenneth L. Noller, MD Dr. Noller is the Louis E. Phaneuf professor
Protect & Detect: What Women should Know about cancer The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists A Message From ACOG President Kenneth L. Noller, MD Dr. Noller is the Louis E. Phaneuf professor
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer. Information for Women at Increased Risk
 Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
Ovarian Cancer. What you should know. making cancer less frightening by enlightening
 Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER
 INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
Endometrial Cancer. Incidence. Types 3/25/2019
 Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
What is ovarian cancer?
 What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that forms in tissues of the ovary. Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial cancers (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface
What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that forms in tissues of the ovary. Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial cancers (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer
 What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
A patient s guide to understanding. Cancer. Screening
 A patient s guide to understanding Cancer Screening Contents 04 06 10 12 Cancer Screening Who Should Go For Cancer Screening 05 Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Colorectal Cancer 08 Lung Cancer Liver Cancer Breast
A patient s guide to understanding Cancer Screening Contents 04 06 10 12 Cancer Screening Who Should Go For Cancer Screening 05 Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Colorectal Cancer 08 Lung Cancer Liver Cancer Breast
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know
 Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
41a Pathology: Reproductive System
 41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
RAISING THE AWARENESS OF GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER. Penny Bognuda CNS Gynaecologic Oncology ADHB. June 2015.
 RAISING THE AWARENESS OF GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER Penny Bognuda CNS Gynaecologic Oncology ADHB. June 2015. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES OF THE NEXT ½ HOUR. Brief overview of the different types of gynaecological cancers
RAISING THE AWARENESS OF GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER Penny Bognuda CNS Gynaecologic Oncology ADHB. June 2015. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES OF THE NEXT ½ HOUR. Brief overview of the different types of gynaecological cancers
Ohio Northern University HealthWise. Authors: Alexis Dolin, Andrew Duska, Hannah Lamb, Eric Miller, Pharm D Candidates 2018 May 2018
 Women s Health Authors: Alexis Dolin, Andrew Duska, Hannah Lamb, Eric Miller, Pharm D Candidates 2018 May 2018 Let Your Body Empower You! National Women s Health Week Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Page 2 Breast
Women s Health Authors: Alexis Dolin, Andrew Duska, Hannah Lamb, Eric Miller, Pharm D Candidates 2018 May 2018 Let Your Body Empower You! National Women s Health Week Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Page 2 Breast
THE MODERN GYNECOLOGIC EXAMINATION & SCREENING FOR GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
 THE MODERN GYNECOLOGIC EXAMINATION & SCREENING FOR GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Denise Uyar, MD Associate Professor OB/GYN Chief Gynecologic Oncology Medical College of Wisconsin April 12, 2019 NO DISCLOSURES
THE MODERN GYNECOLOGIC EXAMINATION & SCREENING FOR GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Denise Uyar, MD Associate Professor OB/GYN Chief Gynecologic Oncology Medical College of Wisconsin April 12, 2019 NO DISCLOSURES
Bursting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
 www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
patient education Fact Sheet
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans.
 Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
Understanding and Managing Lynch Syndrome
 Understanding and Managing Lynch Syndrome Princess Margaret For women who may have Lynch syndrome and their family members Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca
Understanding and Managing Lynch Syndrome Princess Margaret For women who may have Lynch syndrome and their family members Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca
Major tips: The importance of early detection: Hx, risk factors
 Cancer Chapter 3 Introduction Cancer ranks 2nd to cardiovascular disease as the leading cause of death in the Gaza Strip. Death rate increased from 10.3% in 2007 to 13.6 in 2012. Some related factors :
Cancer Chapter 3 Introduction Cancer ranks 2nd to cardiovascular disease as the leading cause of death in the Gaza Strip. Death rate increased from 10.3% in 2007 to 13.6 in 2012. Some related factors :
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS
 Polycystic heart, blood vessels, and appearance. Women with PCOS have these characteristics: Ovarian high levels of male hormones, also called androgens an irregular or no menstrual cycle Syndrome may
Polycystic heart, blood vessels, and appearance. Women with PCOS have these characteristics: Ovarian high levels of male hormones, also called androgens an irregular or no menstrual cycle Syndrome may
Cancer Prevention and Early Detection Worksheet for Women
 Page 1 of 8 Cancer Prevention and Early Detection Worksheet for Women While a tremendous amount of progress has been made in cancer research, we still don t understand exactly what causes most cancers.
Page 1 of 8 Cancer Prevention and Early Detection Worksheet for Women While a tremendous amount of progress has been made in cancer research, we still don t understand exactly what causes most cancers.
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Bursting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
 www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
Pathology of the female genital tract
 Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Estimated New Cancers Cases 2003
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz Estimated New Cancers Cases 2003 Images removed due to copyright reasons.
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz Estimated New Cancers Cases 2003 Images removed due to copyright reasons.
Birth Control- an Overview. Keith Merritt, MD. Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy
 Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates
 University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
Screening tests. When you need them and when you don t
 Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
Gynecologic Malignancies. Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18
 Gynecologic Malignancies Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18 Outline Female Cancer Statistics Uterine Cancer Adnexal Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Uterine Cancer Endometrial Cancer Uterine Sarcoma Endometrial
Gynecologic Malignancies Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18 Outline Female Cancer Statistics Uterine Cancer Adnexal Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Uterine Cancer Endometrial Cancer Uterine Sarcoma Endometrial
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions.
 Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
FERTILITY & TCM. On line course provided by. Taught by Clara Cohen
 FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
Female Genital Tract Lab. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan
 Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer
 Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer Cervical Ovarian Uterine Vaginal Vulvar Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer www.cdc.gov/cancer/knowledge 1-800-CDC-INFO About This Booklet This booklet was developed
Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer Cervical Ovarian Uterine Vaginal Vulvar Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer www.cdc.gov/cancer/knowledge 1-800-CDC-INFO About This Booklet This booklet was developed
UTERINE LEIOMYOSARCOMA. About Uterine leiomyosarcoma
 UTERINE LEIOMYOSARCOMA Uterine Lms, Ulms Or Just Lms Rare uterine malignant tumour that arises from the smooth muscular part of the uterine wall. Diagnosis Female About Uterine leiomyosarcoma Uterine LMS
UTERINE LEIOMYOSARCOMA Uterine Lms, Ulms Or Just Lms Rare uterine malignant tumour that arises from the smooth muscular part of the uterine wall. Diagnosis Female About Uterine leiomyosarcoma Uterine LMS
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Hormone Treatments and the Risk of Breast Cancer
 Cornell University Program on Breast Cancer and Environmental Risk Factors in New York State (BCERF) Updated July 2002 Hormone Treatments and the Risk of Breast Cancer 1) Hormone Treatment After Menopause
Cornell University Program on Breast Cancer and Environmental Risk Factors in New York State (BCERF) Updated July 2002 Hormone Treatments and the Risk of Breast Cancer 1) Hormone Treatment After Menopause
Evaluation of the Infertile Couple
 Overview and Definition Infertility is defined as the inability of a couple to fall pregnant after one year of unprotected intercourse. Infertility is a very common condition as in any given year about
Overview and Definition Infertility is defined as the inability of a couple to fall pregnant after one year of unprotected intercourse. Infertility is a very common condition as in any given year about
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
HEALTH HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE. Family Risk Assessment Program
 HEALTH HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Family Risk Assessment Program Name DOB Current Age Address Home Phone Cell Phone Business Phone Best time to contact you Day Evening E-mail Address (Email will only be used
HEALTH HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Family Risk Assessment Program Name DOB Current Age Address Home Phone Cell Phone Business Phone Best time to contact you Day Evening E-mail Address (Email will only be used
Cancer Awareness Talk ICPAK 2014
 Cancer Awareness Talk ICPAK 2014 F. Chite Asirwa, MB ChB. MD. MSc. Internist. Medical Oncologist & Hematologist Asst. Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology/Oncology Indiana University Email: fasirwa@iu.edu
Cancer Awareness Talk ICPAK 2014 F. Chite Asirwa, MB ChB. MD. MSc. Internist. Medical Oncologist & Hematologist Asst. Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology/Oncology Indiana University Email: fasirwa@iu.edu
Gynecologic Cancers. Marcella Williams, MS, RN, AOCN
 This material is protected by U.S. copyright law. Unauthorized reproduction is prohibited. To purchase quantity reprints, please e-mail reprints@ons.org or to request permission to reproduce multiple copies,
This material is protected by U.S. copyright law. Unauthorized reproduction is prohibited. To purchase quantity reprints, please e-mail reprints@ons.org or to request permission to reproduce multiple copies,
HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH
 HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH W H O THEME FOR 2017 D E P R E S S I O N : L E T S TA L K WHAT IS DEPRESSION? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness, and loss of interest in activities that
HEALTH AWARENESS MONTH W H O THEME FOR 2017 D E P R E S S I O N : L E T S TA L K WHAT IS DEPRESSION? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness, and loss of interest in activities that
What is a Pap smear?
 Pap smear What is a Pap smear? A Pap smear is a test that checks for changes in the cells of your cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. Developed over forty years
Pap smear What is a Pap smear? A Pap smear is a test that checks for changes in the cells of your cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. Developed over forty years
Cervical Cancer - Suspected
 Cervical Cancer - Suspected Presentation for patients Asymptomatic presentation Symptomatic presentation History and examination Consider differential diagnoses RED FLAG! Cervix appears normal after examination
Cervical Cancer - Suspected Presentation for patients Asymptomatic presentation Symptomatic presentation History and examination Consider differential diagnoses RED FLAG! Cervix appears normal after examination
What Causes Cervical Cancer? Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
 Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Kimberley A. Schroeder, D.O. 115 Baker Drive Tomball, TX
 Kimberley A. Schroeder, D.O. 115 Baker Drive Tomball, TX 77375 281.290.0531 www.feelwellagain.com FEMALE MEDICAL QUESTIONNAIRE (POSTMENOPAUSAL) NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: CHIEF COMPLAINT What is your primary
Kimberley A. Schroeder, D.O. 115 Baker Drive Tomball, TX 77375 281.290.0531 www.feelwellagain.com FEMALE MEDICAL QUESTIONNAIRE (POSTMENOPAUSAL) NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: CHIEF COMPLAINT What is your primary
Gynecologic Cancers. What is Gynecologic Cancer. Who is at risk for GYN cancer? 3/1/2018 1
 What is Gynecologic Cancer Gynecologic Cancers Marge Ramsdell RN, MN, OCN Madigan Army Medical Center Any cancer that starts in a woman s reproductive organs Each GYN cancer is unique 5 main types Cervical
What is Gynecologic Cancer Gynecologic Cancers Marge Ramsdell RN, MN, OCN Madigan Army Medical Center Any cancer that starts in a woman s reproductive organs Each GYN cancer is unique 5 main types Cervical
Chronic Pelvic Pain. AP099, December 2010
 AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
Cervical Cancer Prevention Month. January 2011 Morehouse College
 Cervical Cancer Prevention Month January 2011 Morehouse College What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical Cancer begins in the cervix (lower part of the womb, called the uterus). Cervical Cancer, at one point,
Cervical Cancer Prevention Month January 2011 Morehouse College What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical Cancer begins in the cervix (lower part of the womb, called the uterus). Cervical Cancer, at one point,
Center for Reproductive Medicine Advanced Reproductive Technologies
 Center for Reproductive Medicine Advanced Reproductive Technologies www.ivfminnesota.com Recessive Disease Screening Recessive conditions are conditions that result from two recessive genes being passed
Center for Reproductive Medicine Advanced Reproductive Technologies www.ivfminnesota.com Recessive Disease Screening Recessive conditions are conditions that result from two recessive genes being passed
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
Ovaries: In Sickness and Health. Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital
 Ovaries: In Sickness and Health Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital Topics for discussion How to assess ovarian function? AMH PCOS Ovarian pain Ovarian cysts Ovarian screening Menopause
Ovaries: In Sickness and Health Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital Topics for discussion How to assess ovarian function? AMH PCOS Ovarian pain Ovarian cysts Ovarian screening Menopause
 Understanding ovarian cancer An information sheet for women with ovarian cancer, their family and friends If you or someone you love has recently been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, you re sure to have
Understanding ovarian cancer An information sheet for women with ovarian cancer, their family and friends If you or someone you love has recently been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, you re sure to have
Change your Lifestyle to prevent Epidemic of Non Communicable Diseases Principles of Nutrition and Physical Activity in Cancer Control
 Change for the better Dr. Arun Kurkure Change your Lifestyle to prevent Epidemic of Non Communicable Diseases Principles of Nutrition and Physical Activity in Cancer Control Scientific evidence suggests
Change for the better Dr. Arun Kurkure Change your Lifestyle to prevent Epidemic of Non Communicable Diseases Principles of Nutrition and Physical Activity in Cancer Control Scientific evidence suggests
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
GET THE FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCER. Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer
 GET THE FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCER Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer C E R V I C A L OVA R I A N U T E R I N E VAG I N A L V U LVA R ABOUT THIS BOOKLET This booklet was developed in support of
GET THE FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCER Get the Facts About Gynecologic Cancer C E R V I C A L OVA R I A N U T E R I N E VAG I N A L V U LVA R ABOUT THIS BOOKLET This booklet was developed in support of
Chronic Pelvic Pain Case Study
 Case Study Chronic Pelvic Pain Case Study Melissa, a 28 year old veteran comes to your office complaining of lower abdominal pain for the past 6 months. She has tried acetaminophen and ibuprofen but they
Case Study Chronic Pelvic Pain Case Study Melissa, a 28 year old veteran comes to your office complaining of lower abdominal pain for the past 6 months. She has tried acetaminophen and ibuprofen but they
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Gynecological Cancers in Primary Care
 Gynecological Cancers in Primary Care Nora M. Lersch MSN CRNP AOCNP Division of Gynecological Oncology Objectives Identify the incidence of ovarian, cervical, vulvar and endometrial cancer Identify common
Gynecological Cancers in Primary Care Nora M. Lersch MSN CRNP AOCNP Division of Gynecological Oncology Objectives Identify the incidence of ovarian, cervical, vulvar and endometrial cancer Identify common
Types of Hysterectomy for Non-cancerous Conditions: Understanding Your Doctor s Recommendations
 Types of Hysterectomy for Non-cancerous Conditions: Understanding Your Doctor s Recommendations Who can benefit from this information? The decision to have a hysterectomy is one of the many important decisions
Types of Hysterectomy for Non-cancerous Conditions: Understanding Your Doctor s Recommendations Who can benefit from this information? The decision to have a hysterectomy is one of the many important decisions
The Female Reproductive System
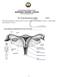 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Gray Davis, Governor State of California
 Gray Davis, Governor State of California Grantland Johnson, Secretary California Health and Human Services Agency Diana M. Bonta, R.N., Dr.P.H., Director California Department of Health Services ` This
Gray Davis, Governor State of California Grantland Johnson, Secretary California Health and Human Services Agency Diana M. Bonta, R.N., Dr.P.H., Director California Department of Health Services ` This
Endometriosis Information Leaflet
 Endometriosis Information Leaflet What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the womb (endometrium) is found outside the womb. About 1 out of 10 women of
Endometriosis Information Leaflet What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the womb (endometrium) is found outside the womb. About 1 out of 10 women of
BREAST CANCER & CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING
 BREAST CANCER & CERVICAL CANCER 1 BREAST Cancer WHAT IS BREAST CANCER? Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast begin to grow in an uncontrolled way and build up to form a lump (also known as a tumour).
BREAST CANCER & CERVICAL CANCER 1 BREAST Cancer WHAT IS BREAST CANCER? Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast begin to grow in an uncontrolled way and build up to form a lump (also known as a tumour).
CERVICAL CANCER FACTSHEET. What is cervical cancer?
 CERVICAL CANCER FACTSHEET What is cervical cancer? ENGAGe is releasing a series of factsheets to raise awareness of gynaecological cancers and to support its network to work at a grassroots level. Take-up
CERVICAL CANCER FACTSHEET What is cervical cancer? ENGAGe is releasing a series of factsheets to raise awareness of gynaecological cancers and to support its network to work at a grassroots level. Take-up
Preventive Care Risk Assessment
 Preventive Care Risk Assessment Name: DOB Date Lung Cancer (please check all that apply) You currently smoke cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. You have a history of second-hand smoke exposure. You have been
Preventive Care Risk Assessment Name: DOB Date Lung Cancer (please check all that apply) You currently smoke cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. You have a history of second-hand smoke exposure. You have been
CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS
 CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS Click on the link below to access the checklist sheet. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Adenomyosis Chronic Abdominal or Pelvic Pain Endometriosis Fibroids General Guidelines
CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS Click on the link below to access the checklist sheet. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Adenomyosis Chronic Abdominal or Pelvic Pain Endometriosis Fibroids General Guidelines
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
and treating joins with the top of canal). at risk for cervical carcinomas, cervix.
 CERVICAL CANCER Worldwide, cervical cancer is twelfth most common and the fifth most deadly cancer in women. It affects about 16 per 100,000 women per year and kills about 9 per 100,000 per year. Cervical
CERVICAL CANCER Worldwide, cervical cancer is twelfth most common and the fifth most deadly cancer in women. It affects about 16 per 100,000 women per year and kills about 9 per 100,000 per year. Cervical
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY Ph fax
 Page 1 of 9 16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY 10016 Ph 212-679-2289 fax 212-679-2288 Please complete the following: Fertility Evaluation Name: Date of birth: Age: Partner s Name: Date of birth: Age:
Page 1 of 9 16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY 10016 Ph 212-679-2289 fax 212-679-2288 Please complete the following: Fertility Evaluation Name: Date of birth: Age: Partner s Name: Date of birth: Age:
Acute Salpingitis. Fallopian Tubes. Uterus
 Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary
 Subfertility Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary Infertility affects about 15 % of couples. age of the female. Other factors that
Subfertility Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary Infertility affects about 15 % of couples. age of the female. Other factors that
Endometriosis: An Overview
 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
What is PCOS? PCOS THE CONQUER PCOS E-BOOK. You'll be amazed when you read this...
 PCOS What is PCOS? You'll be amazed when you read this... What is PCOS?. Who is at risk? How to get tested? What are the complications. Is there a cure? What are the right ways to eat? What lifestyle changes
PCOS What is PCOS? You'll be amazed when you read this... What is PCOS?. Who is at risk? How to get tested? What are the complications. Is there a cure? What are the right ways to eat? What lifestyle changes
Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cancer
 Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cancer The American Cancer Society recommends these cancer screening guidelines for most adults. Screening tests are used to find cancer before a person has any symptoms.
Guidelines for the Early Detection of Cancer The American Cancer Society recommends these cancer screening guidelines for most adults. Screening tests are used to find cancer before a person has any symptoms.
