Original Article Thymidine kinase 1 is a better prognostic marker than Ki-67 for pt1 adenocarcinoma of the lung
|
|
|
- Jessica Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8): /ISSN: /IJCEM Original Article Thymidine kinase 1 is a better prognostic marker than Ki-67 for pt1 adenocarcinoma of the lung Yan Xu 1,2*, Biao Liu 1*, Qun-Li Shi 1, Pei-Lin Huang 2, Xiao-Jun Zhou 1, Heng-Hui Ma 1, Zhen-Feng Lu 1, Yu Bo 1, Staffan Eriksson 3, Ellen He 4, Sven Skog 4 1 Department of Pathology, Jinling Hospital, Nanjing University School of Medicine, Nanjing, P.R.China; 2 Department of Internal Medicine, Zhong Da Hospital Affiliated to Southeast University, Nanjing, P.R.China; 3 Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Biochemistry, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden; 4 Sino- Swed Molecular Bio-Medicine Research Institute, Shenzhen, China. * Equal contributors. Received May 26, 2014; Accepted June 10, 2014; Epub August 15, 2014; Published August 30, 2014 Abstract: Objectives: The sensitivity and reliability of the biomarkers thymidine kinase 1 (TK1) and Ki-67 were studied in relation to clinical features and prognosis of survival for pathological-t1 (pt1) lung adenocarcinoma patients. Methods: TK1 and Ki-67 expression was determined in 80 patients with pt1 adenocarcinoma of the lung and in 20 specimens from normal lung tissues, using immunohistochemistry. Results: TK1 was found in most lung tumor cells both in the cytoplasm and the nuclei. The positive labelling index (LI) for total TK1 was significantly higher than that for Ki-67. There was a significant correlation between the LI of total TK1 and lymph node metastasis, degree of tumor invasion and pathologic stages, which was not found for Ki-67. In addition, the overall 5-year survival of patients was statistically significant different between low and high levels of TK1 expression, but not in cases of Ki-67. A multivariate analysis revealed that expression of TK1, lymph node involvement and TNM pathology staging could serve as independent prognostic factors for the disease progression of pt1 lung adenocarcinoma patients. Conclusions: Compared with Ki-67, TK1 is a more reliable proliferation index in pt1 adenocarcinoma of lung, which can evaluate the invasion and the prognosis of tumor. Keywords: Lung neoplasms, adenocarcinoma, pt1, thymidine kinase 1, TK1, Ki-67, survival Introduction Lung cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death globally. In males, the highest lung cancer incidence rates are found in Eastern and Southern Europe, North America, Micronesia and Polynesia, and Eastern Asia. Among females, it is the fourth most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death. Lung cancer is increasing in countries in Asia, for example in China, and in Africa [1]. In recent years, tomography scanning and imaging technology in combination with pathological TNM staging improved the survival of lung carcinoma patients. The pathologic T stage appeared to have significant impact on predicting patient survival. Patients with pt1-2 type of lung tumor behaved statistically significantly better (P = 0.007) compared to patients with pt3-4 tumor [2]. Microscopic vascular invasion (MVI) is a stronger prognostic indicator than T size in T1a- T2b categories. pt1 lung carcinoma tumor is defined as 3.0 cm in the greatest dimension. Despite complete resection, the prognosis of patients with pt1 lung adenocarcinoma is not consistent. In some cases, the 5-years survival is 100%, while other patients show short-term recurrence and metastasis, and thus poor survival [3]. In a cohort of 20,461 patients with lung cancer, 3,152 patients were identified as non-small lung cancer (NSCLC). The mortality hazard ratios of these patients were calculated during three consecutive time periods following surgery (0-1 month, 1 month-1 year and > 1 year), according to Charlson comorbidity score (CCS 0, 1, 2, 3+). 5-year survival in the NSCLC patients with severe comorbidity was significantly lower (38%, TP1+ CCS 3+) than in patients without comorbid disease (69%, TP1+ CCS 0). Thus, the pt1 classification should be combined with the CCS comorbidity score in
2 Table 1. Clinical and pathological data Type Number of patients Total number 80 Mean age 59.3, Sex Men 41 Female 39 Smoker 22 Non-smoker 58 Lung lobectomy 70 Lobes wedge or segment resection 10 Tumor diameter Histological types: cm, mean 2.3 cm Adenocarcinoma in situ 7 Micro-invasive adenocarcinoma 10 Invasive adenocarcinoma 63 Acinar predominant 34 Lepidic predominant 11 Papillary predominant 9 Micropapillary predominant 2 Solid predominant with mucin production 6 Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma 1 Lymphatic/vascular invasion 17 Lymph node metastasis 18 Pathological stage: IA 60 IIA 15 IIIA 3 IV 2 Proliferation biomarker (LI > 5%) TK1 73 TK1 cyto/nuclei 27 TK1 in cyto only + cyto/nuclei 46 Ki order to identify the patients which are most likely to benefit from surgery and adjuvant therapy [4]. Furthermore, it is also important to evaluate the biological characteristics of pt1 lung tumor and to identify factors related to lymph node metastasis, microscopic vascular invasion and stromal invasion, as well as the invasion of the inner and outer visceral pleura to improve the assessment of prognosis. A multivariate analysis showed that lymph node metastasis is a significant predictor of poor prognosis [5]. Tumor proliferation biomarkers have also been used for determining of the prognosis of lung cancer patients. Proliferation markers reflect the growth rates of a tumor, specifically in relation to un-control regulation of the cell cycle, which is a hallmark of cancer [6]. However, only Ki-67 and TK1 have been shown to be of independent prognostic values. In this study we compared the usefulness of TK1 and Ki-67 in relation to pathological characteristics and over-all 5-years survival of pt1 lung carcinoma patients. TK1 was found to be an independent prognostic factor and more reliable than Ki-67. Although TK1 is classically known as a cytosolic enzyme, several recent studies have demonstrated existence of a nuclear form of TK1 [7, 8] and determinations of both nuclear and cytosolic TK1 in tumor cells were done in this study. Patients and methods Patients The clinical and pathological information about the patients data are summarized in Table 1. pt1 lung adenocarcinoma patients (n = 90) were recruited for this study during 1997~2007 at Jinling Hospital, Nanjing University School of Medicine, China. These patients underwent surgery, and complete clinical and pathological characterization and follow-up results are available. The patients were classified according to the ptnm classification of the International Union Against Cancer (UICC) [9], i.e. having a tumor 3.0 cm in the greatest dimension, being surrounded by lung tissues or visceral pleura, but not involving the main bronchus. Some of these patients (n = 10) who had a medical history of pre-operative radiotherapy and chemotherapy was excluded from this study. The final number of patients investigated in this present study was 80 cases. Specimens from normal lung tissues from 20 patients with trauma (14 male and 6 female; median age, 55 years; range 22-74) served as non-malignant controls Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
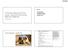
3 Figure 1. Classification of the lung adenocarcinoma according to the new classification. A. Adenocarcinoma in situ: this tumor grows purely with a lepidic pattern. No foci of invasion or scarring are seen ( 40). B. Micro-invasive adenocarcinoma: This tumor consists mostly of lepidic growth, but there is a scar with small foci of invasion (arrow) at the edge of the scar ( 100). C-F. Invasive adenocarcinoma: C. Papillary predominante ( 100). D. Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma ( 100). E. Micro-papillary predominant ( 100). F. Solid predominant with mucin production (x 100). All sections were hematoxylin and eosine counterstained. Histological and pathological assessment Surgical specimens were fixed in 4% neutral buffered formaldehyde solution. Depending on the size of the tumor, they were embedded in three to six blocks of paraffin from which fourmicrometer-thick slices were cut and stained with hematoxylin-eosine (HE), followed by light microscope pathology assessment. The histological type were classified according to the International Society for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC), the American Thoracic Society 2122 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
4 Figure 2. A. TK1 is simultaneously expressed in cytoplasm and nucleus of the tumor cells, but is also expressed only in the cytoplasm of some tumor cells (black arrows). ( 200, EnVision). B. Ki-67 is expressed in the nuclei of the tumor cells. ( 400, EnVision). (ATS) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) lung cancer multidisciplinary classification scheme published in 2011 (referred to as the new classification ) [10, 11]. Based on the degree of invasion, the tumors were classified as adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), micro-invasive adenocarcinoma (also called minimally invasion adenocarcinoma, MIA) and invasive adenocarcinoma (Figure 1). The histopathological characteristics are shown in Table 1. Follow-up The follow-up information was obtained from the medical records of the clinic, by telephone or written contacts with the patients. The follow-up time was from the date of surgery to death or last follow-up. The follow-up investigation was closed 15 th of July, Immunohistochemistry TK1 and Ki-67 immunohistochemistry were performed on 4 μm thick slices of paraffin blocks. The slices were incubated with antibodies against TK1 and Ki-67 using the EnVision immunohistochemical procedure (DAKO, Denmark). The TK1 Ab was a gift from SSTK Ltd., (Shenzhen, China), Ki-67 Ab was purchased from DAKO, Denmark. TK1 expression was found in both cytoplasm and nuclei (Figure 2A). TK1 expression in some tumor cells was unique in the cytoplasm (Figure 2A). The percentage of these cells varied from about 1% to 10%. For the purpose of this study tumor cells expressing TK1 simultaneously in the cytoplasm and in the nuclei as well as cells where TK1 was found only in the cytoplasm were combined and denoted as total TK1. The tumor cells expressing TK1 in cytoplasma and nuclei simultaneously were denoted cytoplasma/nuclei TK1. Ki-67 was exclusively expressed in the nuclei of the tumor cells (Figure 2B). The numbers of antibody stained tumor and normal cells were counted among 100 cells at 400 magnification and classified into four groups depending on the number of antibody stained cells: 5% - ; 6-25% + ; 26-50% ++ ; 50% +++. The percentages of labeled TK1 and Ki-67 cells were denoted as labeling index (LI). LI index above 5% was denoted as positive LI Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
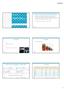
5 Table 2. Expression of TK1 and Ki-67 in relation to clinicopathological features in pt1lung adenocarcinoma. The statistical analysis was done by the non-parametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test Parameters n TK1 Ki-67 P Sex M F Age years > 60 years Smoke yes no Tumor size cm > 2 cm Lymphatic/vascular invasion yes no Lymph node metastasis yes no Histo. New classification < AIS + MIA Invasive adenocarcinoma Path. Stage IA > 1A P Statistical analysis The SPSS17.0 analysis software was used for the statistical calculations, including Chisquare test for comparison of the rate between the two groups, the non-parametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test for comparison of the level of TK1 and Ki-67 expression between the two groups, Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test when comparing survival rate, COX proportional hazard for multivariate analysis. A P-value less than 0.05 was regarded as statistically significance. Results The positive LI of total TK1 and Ki-67 The positive LI of total TK1 and Ki-67 was 91.3% (73/80) and 50.0% (40/80), respectively, which was a statistically significant difference (P = 0.011). There were no significant differences between men and women. TK1 and Ki-67 LIs in relation to clinicopathological features Of the clinicopathological features included, a statistically significant higher total TK1 LI was found in patients with lymph node metastasis (P = 0.009), in patients with invasive adenocarcinoma compared to AIS and MIA (P < 0.001) and in patients with stage above IA compared to stage IA (P = 0.004) (Table 2), which was not found for Ki-67. There was no statistically significant difference in both total TK1 LI and Ki-67 LI according to gender, age, smoking history or vascular invasion (Table 2). Survival analysis The 5-year overall survival (OS) of AIS, MIA and invasive adenocarcinoma were 100%, 90% and 53.7%, respectively (Figure 3A). Log rank analysis showed a statistically significant difference of OS between MIA and invasive adenocarcinoma (P = 0.045). Since no death was found 2124 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
6 similar, whereas better than that of invasive adenocarcinoma. There was a significant difference in the 5-year over-all survival between pathology stage IA and above IA (P < 0.001), with and without lymph node metastasis (P < 0.001) and with and without vascular invasion (P = 0.001) (data not shown). LI of TK1 and Ki-67 in relation to 5-year overall survival Patients were divided into two groups regarding LI, i.e. below 25% and above 25%, denoted as low and high LI, respectively. Mortality The mortalities during the 5-year follow-up of patients with low and high TK1 expression were 35.9% and 73.2%, respectively, which was significantly different (P = 0.003). The corresponding values for low and high Ki-67 were 53.6% and 63.6%, respectively, which was also significantly different (P < 0.001). The differences in mortality levels between TK1 and Ki-67 concerning low (35.9% versus 53.6%) and high (73.2% versus 63.6%) LI groups were also significantly different (P < 0.001). Thus, TK1 is a more sensitive marker for mortality compare to Ki-67. Survival Figure 3. Over-all 5-year survival in relation to: (A) the new pathological stages, (B) total TK1, (C) and Ki-67. among the AIS patients, no log rank analysis could be done. The mortality of AIS, MIA and invasive adenocarcinoma were 0%, 40% and 65.1% during follow-up, respectively. There was a statistically significant difference of mortality between the AIS and invasive adenocarcinoma group (P = 0.001), while no statistically difference was found between the AIS and MIA group. The patient prognosis of AIS and MIA is The 5-year survival rates for low and high TK1 LI was 83.5% and 38.8%, respectively. There was a significant difference between patients with low and high TK1 LI regarding the 5-year survival rates, both in the total TK1 group and in the cytoplasma/nuclei TK1 group of patients (total TK1 χ 2 = 20.47, P < 0.001, Figure 3B; cytoplasm/nuclei χ 2 = 22.05, P < 0.001, data not shown). The corresponding values for low and high Ki-67 LI were 65% and 55%, i.e. no significant difference in the survival was found between low and high Ki-67 LI (Figure 3C). Multivariate COX analyses A COX multivariate analysis was performed with total TK1 LI, invasiveness based on the new classification, pathology stages, lymph node metastasis and lymphatic/vascular invasion. Of these factors, only total TK1 LI, lymph node 2125 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
7 Table 3. COX multi-variate analysis Variables p-values Hazard risk 95% CV Total TK Pathology stage < Lymphnode metastasis lymphatic/vascular invasion New pathology stage metastasis and pathology stage showed significance. Thus, these three parameters are independent prognostic factors for overall survival (Table 3). Discussion Thymidine kinase (EC ) (TK) is a key enzyme in the pyrimidine salvage pathway, catalysing transfer of the terminal phosphate from ATP to 5 -hydroxyl group of thymidine (dtdr), producing dtmp, which is subsequently incorporated into DNA. There are two forms cellular TK enzymes, one cytoplasmic form, thymidine kinase 1 (TK1), and one mitochondrial form, thymidine kinase 2 (TK2). TK2 is cell-cycle independent, while TK1 protein level is tightly correlated to S-G2 phases of the cell cycle and thus to overall cell proliferation. TK1 plays a role in regulating the intracellular thymidine pools throughout the cell cycle, but is probably also involved DNA repair process [12]. In proliferating normal cells and tumor cells, the synthesis of TK1 starts at the latter stage of the G1 phase and significantly increases until the late S-G2 phases [7]. TK1 in non-proliferating cells and in serum of healthy persons is minimal or undetectable [7]. TK1 also provides information on recurrence, on 5-years survival of cancer patients and for monitoring the outcome of tumor therapy in lung, rectal, breast and cervical cancer patients [7, 12]. Thus, elevated TK1 is an important risk factor indicating a high proliferation capacity of tumors, leading to shorter survival. Ki-67 is a frequently used proliferation biomarker expressed in all stages of the cell cycle, except in the G0 phase [13, 14]. Several studies show that Ki-67, but not PCNA, is a good prognostic factor for recurrence in patients with NSCLC [15]. A multivariate analysis showed that EGFR and Ki-67 were independent negative prognostic factors for survival of squamous cell lung cancer patients [15], while lymph-node metastasis and Ki-67 were independent prognostic parameters for overall survival in patients with NSCLC [16, 17]. Multivariate COX regression analysis also showed that the Mini-chromosome maintenance factor (MCM7) is an independent prognostic marker, but not MCM2 or Ki-67, in pt1 lung adenocarcinoma patients [18]. TK1 was recently shown to increase earlier during the G1 to S transition of the cell cycle than Ki-67 [6], suggesting that TK1 is a very efficient proliferating marker [6]. In a privious study we also found that TK1 was a more reliable and sensitive proliferating marker than Ki-67 in lung adenocarcinoma patients [19]. In our previous study on pt1 lung carcinoma patients [20], we showed for the first time that TK1 expression in tumor tissues correlated positively to 5-year survival. TK1 also improved the stromal invasion grading system for prognostic evaluation and gave a further reliable assessment for prognosis. Even when the tumor reaches grade 3 of stromal invasion in patients with pt1 lung adenocarcinoma, as long as the TK1 expression still is low, these patients have a good prognosis. This explain why some patients with grade 3 stromal invasion show better survival than others, i.e. their lung tumor may still have lower proliferation rates. In a multivariate analysis, TK1 expression was also found to be an independent prognostic factor. Here we extended the previous study by comparing TK1 with Ki-67 and found that TK1 has some advantages over this ususal used proliferation marker. Total TK1-LI correlated to lymph node metastasis, tumor invasion, pathological stage and 5-year survival, whereas these was not observed for Ki-67. Multivariate analysis showed that total TK1 LI, lymph node metastasis and pathology stage were independent prognostic factors, but not Ki-67. In a recent study on patients with cervical carcinoma we found that TK1 expression in the nuclei correlated to decreased 5-year survival [12]. Tumor cells with almost no TK1 expression in the nuclei (Cervical intraepithelial neoplasias type) showed good survival, while tumor cells with high TK1 expression in the nuclei (invasive carcinoma type) showed worse survival [12]. However, the results in the present study on the pt1 lung carcinoma did not con Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
8 firm that observation. The physiological significance of TK1 in these two compartments, i.e. cytoplasm/nuclei, is the subject of a separate investigation. It is possible that TK1 re-localized into the nuclei directly participates in repair of DNA, which could improve the survival of the tumor cells and consequently reduces the survival of the patients [12]. However, it is also known that TK1 accumulates in late S and G2 cells, particularly, when cells are subjected to DNA damage [21]. A fraction of TK1 may constantly be transferred into the nuclei through co-transport processes. This may be is not linked to any functional role for nuclear TK1, but simply allow the detection of this form of TK1 by immunohistochemical methods once it exceeds a certain threshold level in the cytoplasma. Further studies are needed to clarify this interesting question. Disclosure of conflict of interest YX, BL, QS, PH, XZ, HM, ZL, YB and SE do not declare any conflicts of interest, EH and SS are consulters to SSTK Ltd, Shenzhen, China. Address correspondence to: Dr. Qun-Li Shi, Department of Pathology, Jinling Hospital, Nanjing University School of Medicine, 305 Zhongshangdong Road, Nanjing , Jiangsu Province, China. shiqunli2011@126.com; Dr. Sven Skog, Sino-Swed Molecular Bio-Medicine Research Institute, Shenzhen, China. Tel: ; Fax: ; svenisak@hotmail. com References [1] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: [2] Collaud S, Stahel R, Inci I, Hillinger S, Schneiter D, Kestenholz P, Weder W. Survival of patients treated surgically for synchronous single-organ metastatic NSCLC and advanced pathologic TN stage. Lung Cancer 2012; 78: [3] Kawakami T, Nabeshima K, Makimoto Y, Hamasaki M, Iwasaki A, Shirakusa T, Iwasaki H.Micropapillary pattern and grade of stromal invasion in pt1 adenocarcinoma of the lung: usefulness as prognostic factors. Mod Pathol 2007; 20: [4] Lüchtenborg M, Jakobsen E, Krasnik M, Linklater KM, Mellemgaard A, Møller H. The effect of comorbidity on stage-specific survival in resected non-small cell lung cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 2012; 48: [5] Hamasaki M, Kato F, Koga K, Hayashi H, Aoki M, Miyake Y, Iwasaki A, Nabeshima K. Invasion of the inner and outer layers of the visceral pleura in pt1 size lung adenocarcinoma measuring 3 cm: correlation with malignant aggressiveness and prognosis. Virchows Arch 2012; 461: [6] Gasparri F, Wang N, Skog S, Galvani A, Eriksson S. Thymidine kinase 1 expression defines an activated G1 state of the cell cycle as revealed with site-specific antibodies and Array- Scan assays. Eur J Cell Biol 2009; 88: [7] Zhou J, He E, Skog S. The proliferation marker thymidine kinase 1 (TK1) in clinical use (Review). Mol Clin Oncol 2013; 1: [8] Brockenbrough JS, Morihara JK, Hawes SE, Stern JE, Rasey JS, Wiens LW, Feng Q, Vesselle H. Thymidine kinase 1 and thymidine phosphorylase expression in non-small-cell lung carcinoma in relation to angiogenesis and proliferation. J Histochem Cytochem 2009; 57: [9] Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind CH. International Union Against Cancer (UICC): TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 7th ed. New York: Wiley-Liss Press; pp [10] Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ, Van Schil PE, Garg K, Austin JH, Asamura H, Rusch VW, Hirsch FR, Scagliotti G, Mitsudomi T, Huber RM, Ishikawa Y, Jett J, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Sculier JP, Takahashi T, Tsuboi M, Vansteenkiste J, Wistuba I, Yang PC, Aberle D, Brambilla C, Flieder D, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Gould M, Hasleton P, Henderson D, Johnson B, Johnson D, Kerr K, Kuriyama K, Lee JS, Miller VA, Petersen I, Roggli V, Rosell R, Saijo N, Thunnissen E, Tsao M, Yankelewitz D. International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thoracic Oncol 2011; 6: [11] Yoshizawa A, Motoi N, Riely GJ, Sima CS, Gerald WL, Kris MG, Park BJ, Rusch VW, Travis WD. Impact of proposed IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of lung adenocarcinoma: prognostic subgroups and implications for further revision of staging based on analysis of 514 stage I cases. Mod Pathol 2011; 24: [12] Chen G, He C, Li L, Lin A, Zheng X, He E, Skog S. Nuclear TK1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for survival in pre-malignant and malignant lesions of the cervix. BMC Cancer 2013; 13: [13] Scholzen T and Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 2000; 182: Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
9 [14] Ciancio N, Galasso MG, Campisi R, Bivona L, Migliore M, Di Maria GU. Prognostic value of p53 and Ki67 expression in fiberoptic bronchial biopsies of patients with non small cell lung cancer. Multidiscip Respir Med 2012; 14: 29. [15] Oka S, Uramoto H, Shimokawa H, Iwanami T, Tanaka F. The Expression of Ki-67, but Not Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen, Predicts Poor Disease Free Survival in Patients with Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. Anticancer Res 2011; 31: [16] Niemiec J, Kolodziejski L, Dyczek S. EGFR LI and Ki-67 LI are independent prognostic parameters influencing survivals of surgically treated squamous cell lung cancer patients. Neoplasma 2005; 52: [17] Sun JG, Wang Y, Chen ZT, Zhuo WL, Zhu B, Liao RX, Zhang SX. Detection of lymph angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer and its prognostic value. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2009; 28: 21. [18] Fujioka S, Ito H, Shomori K, Nishihara K, Yamaga K, Nosaka K, Araki K, Haruki T, Taniguchi Y, Nakamura H, Ito H. Expression of minichromosome maintenance 7 (MCM7) in small lung adenocarcinoma (pt1): Prognostic implication. Lung Cancer 2009; 65: [19] Mao Y, Wu J, Skog S, Eriksson S, Zhao Y, Zhou J, He Q. Expression of cell proliferating genes in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by immunohistochemistry and cdna profiling. Oncology Report 2005; 13: [20] Xu Y, Shi QL, Ma H, Zhou H, Lu Z, Yu B, Zhou X, Eriksson S, He E, Skog S. High thymidine kinase 1 (TK1) expression is a predictor of poor survival in patients with pt1 of lung adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol 2012; 33: [21] Skog S, Tribukait B. Analysis of cell flow and cell loss following X-irradiated using sequential investigation of the total number of cells in the various parts of the cell cycle. Cell Tissue Kinet 1985; 18: Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(8):
Classification of non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC)
 Classification of non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC) 1. NordiQC Conference on Standardization in Applied Immunohistochemistry 4-7 June 2013 Birgit Guldhammer Skov, MD. DMeSci, Dept. Of Pathology, Rigshospitalet,
Classification of non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC) 1. NordiQC Conference on Standardization in Applied Immunohistochemistry 4-7 June 2013 Birgit Guldhammer Skov, MD. DMeSci, Dept. Of Pathology, Rigshospitalet,
Pulmonary adenocarcinoma Issues, Issues and more issues. Why the headache?
 Issues Pulmonary adenocarcinoma Issues, Issues and more issues. Why the headache? Classification Multiple nodules Invasive size Alain Borczuk, MD Weill Cornell Medicine Chronic headache - Classification
Issues Pulmonary adenocarcinoma Issues, Issues and more issues. Why the headache? Classification Multiple nodules Invasive size Alain Borczuk, MD Weill Cornell Medicine Chronic headache - Classification
Lung cancer is now a major cause of death in developed
 Original Article New IASLC/ATS/ERS Classification and Invasive Tumor Size are Predictive of Disease Recurrence in Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma Naoki Yanagawa, MD, PhD,* Satoshi Shiono, MD, PhD, Masami Abiko,
Original Article New IASLC/ATS/ERS Classification and Invasive Tumor Size are Predictive of Disease Recurrence in Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma Naoki Yanagawa, MD, PhD,* Satoshi Shiono, MD, PhD, Masami Abiko,
MOLECULAR PREDICTIVE MARKERS OF LUNG CARCINOMA: KFSH&RC EXPERIENCE
 25 th IAP-Arab Division Conference 07-09 November 2013, Amman, Jordan MOLECULAR PREDICTIVE MARKERS OF LUNG CARCINOMA: KFSH&RC EXPERIENCE Fouad Al Dayel, MD, FRCPA, FRCPath Professor and Chairman Department
25 th IAP-Arab Division Conference 07-09 November 2013, Amman, Jordan MOLECULAR PREDICTIVE MARKERS OF LUNG CARCINOMA: KFSH&RC EXPERIENCE Fouad Al Dayel, MD, FRCPA, FRCPath Professor and Chairman Department
Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma
 Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
Original Article Correlation of EGFR mutation and histological subtype according to the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of lung adenocarcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(11):8039-8045 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0002211 Original Article Correlation of EGFR mutation and histological subtype according to the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(11):8039-8045 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0002211 Original Article Correlation of EGFR mutation and histological subtype according to the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Minor Components of Micropapillary and Solid Subtypes in Lung Adenocarcinoma are Predictors of Lymph Node Metastasis and Poor Prognosis
 Ann Surg Oncol (2016) 23:2099 2105 DOI 10.1245/s10434-015-5043-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY Minor Components of Micropapillary and Solid Subtypes in Lung Adenocarcinoma are Predictors of Lymph
Ann Surg Oncol (2016) 23:2099 2105 DOI 10.1245/s10434-015-5043-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE THORACIC ONCOLOGY Minor Components of Micropapillary and Solid Subtypes in Lung Adenocarcinoma are Predictors of Lymph
Should minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma be transferred from stage IA1 to stage 0 in future updates of the TNM staging system?
 Original Article Should minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma be transferred from stage to stage 0 in future updates of the TNM staging system? Tianxiang Chen 1,2#, Jizhuang Luo 3#, Haiyong Gu 3, Yu Gu
Original Article Should minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma be transferred from stage to stage 0 in future updates of the TNM staging system? Tianxiang Chen 1,2#, Jizhuang Luo 3#, Haiyong Gu 3, Yu Gu
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer
 original article Why Do Pathological Stage IA Lung Adenocarcinomas Vary from Prognosis? A Clinicopathologic Study of 176 Patients with Pathological Stage IA Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on the IASLC/ATS/ERS
original article Why Do Pathological Stage IA Lung Adenocarcinomas Vary from Prognosis? A Clinicopathologic Study of 176 Patients with Pathological Stage IA Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on the IASLC/ATS/ERS
Ratio of maximum standardized uptake value to primary tumor size is a prognostic factor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
 Original Article Ratio of maximum standardized uptake value to primary tumor size is a prognostic factor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Fangfang Chen 1 *, Yanwen Yao 2 *, Chunyan
Original Article Ratio of maximum standardized uptake value to primary tumor size is a prognostic factor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Fangfang Chen 1 *, Yanwen Yao 2 *, Chunyan
The 2015 World Health Organization Classification for Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Practical Approach
 The 2015 World Health Organization Classification for Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Practical Approach Dr. Carol Farver Director, Pulmonary Pathology Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Institute Objectives Discuss
The 2015 World Health Organization Classification for Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Practical Approach Dr. Carol Farver Director, Pulmonary Pathology Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Institute Objectives Discuss
Research Article Prognostic Implication of Predominant Histologic Subtypes of Lymph Node Metastases in Surgically Resected Lung Adenocarcinoma
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 64568, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/64568 Research Article Prognostic Implication of Predominant Histologic Subtypes of Lymph Node Metastases in Surgically
BioMed Research International, Article ID 64568, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/64568 Research Article Prognostic Implication of Predominant Histologic Subtypes of Lymph Node Metastases in Surgically
The histological grading of lung cancer is a significant
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Interobserver Agreement in the Nuclear Grading of Primary Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma Yoshimasa Nakazato, MD,* Akiko Miyagi Maeshima, MD, Yuichi Ishikawa, MD, Yasushi Yatabe, MD, Junya Fukuoka,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Interobserver Agreement in the Nuclear Grading of Primary Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma Yoshimasa Nakazato, MD,* Akiko Miyagi Maeshima, MD, Yuichi Ishikawa, MD, Yasushi Yatabe, MD, Junya Fukuoka,
ORIGINAL PAPER. Marginal pulmonary function is associated with poor short- and long-term outcomes in lung cancer surgery
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 37 ~ 42, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.1.37 ORIGINAL PAPER Marginal pulmonary function is associated with poor short- and long-term outcomes in lung cancer surgery Naoki Ozeki, Koji
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 37 ~ 42, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.1.37 ORIGINAL PAPER Marginal pulmonary function is associated with poor short- and long-term outcomes in lung cancer surgery Naoki Ozeki, Koji
Visceral pleural involvement (VPI) of lung cancer has
 Visceral Pleural Involvement in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer: Prognostic Significance Toshihiro Osaki, MD, PhD, Akira Nagashima, MD, PhD, Takashi Yoshimatsu, MD, PhD, Sosuke Yamada, MD, and Kosei Yasumoto,
Visceral Pleural Involvement in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer: Prognostic Significance Toshihiro Osaki, MD, PhD, Akira Nagashima, MD, PhD, Takashi Yoshimatsu, MD, PhD, Sosuke Yamada, MD, and Kosei Yasumoto,
Second predominant subtype predicts outcomes of intermediatemalignant invasive lung adenocarcinoma
 European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 51 (2017) 218 222 doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezw318 Advance Access publication 6 October 2016 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cite this article as: Ito M, Miyata Y, Yoshiya T, Tsutani
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 51 (2017) 218 222 doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezw318 Advance Access publication 6 October 2016 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cite this article as: Ito M, Miyata Y, Yoshiya T, Tsutani
Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Validation of the T descriptor in the new 8th TNM classification for non-small cell lung cancer
 Original Article Validation of the T descriptor in the new 8th TNM classification for non-small cell lung cancer Hee Suk Jung 1, Jin Gu Lee 2, Chang Young Lee 2, Dae Joon Kim 2, Kyung Young Chung 2 1 Department
Original Article Validation of the T descriptor in the new 8th TNM classification for non-small cell lung cancer Hee Suk Jung 1, Jin Gu Lee 2, Chang Young Lee 2, Dae Joon Kim 2, Kyung Young Chung 2 1 Department
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Yang Zhang 1,2, Yihua Sun 1,2, Haiquan Chen 1,2,3,4
 /, Vol. 7, No. 12 A propensity score matching analysis of survival following segmentectomy or wedge resection in early-stage lung invasive adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma Yang Zhang 1,2, Yihua
/, Vol. 7, No. 12 A propensity score matching analysis of survival following segmentectomy or wedge resection in early-stage lung invasive adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma Yang Zhang 1,2, Yihua
Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 23 (2003) 865 869 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q Jeong-Han Kang, Kil Dong Kim, Kyung
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 23 (2003) 865 869 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Prognostic value of visceral pleura invasion in non-small cell lung cancer q Jeong-Han Kang, Kil Dong Kim, Kyung
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Predictive risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with small size non-small cell lung cancer
 Original Article Predictive risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with small size non-small cell lung cancer Feichao Bao, Ping Yuan, Xiaoshuai Yuan, Xiayi Lv, Zhitian Wang, Jian Hu Department
Original Article Predictive risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with small size non-small cell lung cancer Feichao Bao, Ping Yuan, Xiaoshuai Yuan, Xiayi Lv, Zhitian Wang, Jian Hu Department
HRCT features distinguishing minimally invasive adenocarcinomas from invasive adenocarcinomas appearing as mixed ground-glass nodules
 Original Article HRCT features distinguishing minimally invasive adenocarcinomas from invasive adenocarcinomas appearing as mixed ground-glass nodules Wei Yu 1, Zhaoyu Wang 2, Liyong Qian 2, Shanjun Wang
Original Article HRCT features distinguishing minimally invasive adenocarcinomas from invasive adenocarcinomas appearing as mixed ground-glass nodules Wei Yu 1, Zhaoyu Wang 2, Liyong Qian 2, Shanjun Wang
Lung cancer is a major cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Factors in 3315 Completely Resected Cases of Clinical Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Teruaki Koike, MD,* Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, Yasunori Sohara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Factors in 3315 Completely Resected Cases of Clinical Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Teruaki Koike, MD,* Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, Yasunori Sohara,
Differing histopathology and prognosis in pulmonary adenocarcinoma at central and peripheral locations
 Original Article Differing histopathology and prognosis in pulmonary adenocarcinoma at central and peripheral locations Youngkyu Moon 1, Kyo Young Lee 2, Sook Whan Sung 1, Jae Kil Park 1 1 Department of
Original Article Differing histopathology and prognosis in pulmonary adenocarcinoma at central and peripheral locations Youngkyu Moon 1, Kyo Young Lee 2, Sook Whan Sung 1, Jae Kil Park 1 1 Department of
Histopathology of NSCLC, IHC markers and ptnm classification
 ESMO Preceptorship on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer November 15 th & 16 th 2017 Singapore Histopathology of NSCLC, IHC markers and ptnm classification Prof Keith M Kerr Department of Pathology, Aberdeen University
ESMO Preceptorship on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer November 15 th & 16 th 2017 Singapore Histopathology of NSCLC, IHC markers and ptnm classification Prof Keith M Kerr Department of Pathology, Aberdeen University
The new international multidisciplinary lung adenocarcinoma
 Eur Respir J 2011; 38: 239 243 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00026711 CopyrightßERS 2011 EDITORIAL Paradigm shifts in lung cancer as defined in the new IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma classification W.D. Travis*,"",
Eur Respir J 2011; 38: 239 243 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00026711 CopyrightßERS 2011 EDITORIAL Paradigm shifts in lung cancer as defined in the new IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma classification W.D. Travis*,"",
Lung Neoplasia II Resection specimens Pathobasic. Lukas Bubendorf Pathology
 Lung Neoplasia II Resection specimens Pathobasic Lukas Bubendorf Pathology Agenda Preneoplastic lesions Histological subtypes of lung cancer Histological patterns of AC Cells of origin and characteristic
Lung Neoplasia II Resection specimens Pathobasic Lukas Bubendorf Pathology Agenda Preneoplastic lesions Histological subtypes of lung cancer Histological patterns of AC Cells of origin and characteristic
A nonresponding small cell lung cancer combined with adenocarcinoma
 Case Report A nonresponding small cell lung cancer combined with adenocarcinoma Hongyang Lu 1,2, Shifeng Yang 3 1 Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Diagnosis & Treatment Technology on Thoracic Oncology (Lung
Case Report A nonresponding small cell lung cancer combined with adenocarcinoma Hongyang Lu 1,2, Shifeng Yang 3 1 Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Diagnosis & Treatment Technology on Thoracic Oncology (Lung
The Prognostic Value of Ratio-Based Lymph Node Staging in Resected Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer
 Original Article The Prognostic Value of Ratio-Based Lymph Node Staging in Resected Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Chen Qiu, MD,* Wei Dong, MD,* Benhua Su, MBBS, Qi Liu, MD,* and Jiajun Du, PhD Introduction:
Original Article The Prognostic Value of Ratio-Based Lymph Node Staging in Resected Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Chen Qiu, MD,* Wei Dong, MD,* Benhua Su, MBBS, Qi Liu, MD,* and Jiajun Du, PhD Introduction:
Proposal of a prognostically relevant grading scheme for pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG CANCER Proposal of a prognostically relevant grading scheme for pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma Wilko Weichert 1,2,3, Claudia Kossakowski 1, Alexander Harms 1, Peter Schirmacher
ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG CANCER Proposal of a prognostically relevant grading scheme for pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma Wilko Weichert 1,2,3, Claudia Kossakowski 1, Alexander Harms 1, Peter Schirmacher
Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
THE IASLC/ERS/ATS ADENOCARCINOMA CLASSIFICATION RATIONALE AND STRENGTHS
 THE IASLC/ERS/ATS ADENOCARCINOMA CLASSIFICATION RATIONALE AND STRENGTHS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY SOCIETY USCAP, BALTIMORE, March 2, 2013 William D. Travis, M.D. Dept of Pathology, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer
THE IASLC/ERS/ATS ADENOCARCINOMA CLASSIFICATION RATIONALE AND STRENGTHS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY SOCIETY USCAP, BALTIMORE, March 2, 2013 William D. Travis, M.D. Dept of Pathology, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer
International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory
 International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. William Travis, Elisabeth
International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. William Travis, Elisabeth
The 8th Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer Background, Innovations and Implications for Clinical Practice
 The 8th Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer Background, Innovations and Implications for Clinical Practice University of Torino Lecture 28th June 2017 Torino, Italy Ramón Rami-Porta Thoracic
The 8th Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer Background, Innovations and Implications for Clinical Practice University of Torino Lecture 28th June 2017 Torino, Italy Ramón Rami-Porta Thoracic
Survival of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma before and after approved use of gefitinib in China
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma before and after approved use of gefitinib in China Yu-Tao Liu, Xue-Zhi Hao, Jun-Ling Li, Xing-Sheng
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma before and after approved use of gefitinib in China Yu-Tao Liu, Xue-Zhi Hao, Jun-Ling Li, Xing-Sheng
Negative prognostic influence of micropapillary pattern in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma
 European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 49 (2016) 293 299 doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezv058 Advance Access publication 11 March 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cite this article as: Tsubokawa N, Mimae T, Sasada S, Yoshiya
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 49 (2016) 293 299 doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezv058 Advance Access publication 11 March 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cite this article as: Tsubokawa N, Mimae T, Sasada S, Yoshiya
I appreciate the courtesy of Kusumoto at NCC for this presentation. What is Early Lung Cancers. Early Lung Cancers. Early Lung Cancers 18/10/55
 I appreciate the courtesy of Kusumoto at NCC for this presentation. Dr. What is Early Lung Cancers DEATH Early period in its lifetime Curative period in its lifetime Early Lung Cancers Early Lung Cancers
I appreciate the courtesy of Kusumoto at NCC for this presentation. Dr. What is Early Lung Cancers DEATH Early period in its lifetime Curative period in its lifetime Early Lung Cancers Early Lung Cancers
Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection
 Original Article Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection Mingjian Yang 1,2, Hongdian Zhang 1,2, Zhao Ma 1,2, Lei Gong 1,2, Chuangui Chen
Original Article Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection Mingjian Yang 1,2, Hongdian Zhang 1,2, Zhao Ma 1,2, Lei Gong 1,2, Chuangui Chen
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Steering Committee. Waiting on photo. Paul A. Bunn, Jr., MD Kavita Garg, MD Kim Geisinger, MD Fred R. Hirsch, Gregory Riely, MD, PhD.
 Steering Committee Paul A. Bunn, Jr., MD Kavita Garg, MD Kim Geisinger, MD Fred R. Hirsch, Gregory Riely, MD, PhD MD, PhD Waiting on photo Paul Van Schil, MD, PhD William D. Travis, MD Ming-Sound Tsao,
Steering Committee Paul A. Bunn, Jr., MD Kavita Garg, MD Kim Geisinger, MD Fred R. Hirsch, Gregory Riely, MD, PhD MD, PhD Waiting on photo Paul Van Schil, MD, PhD William D. Travis, MD Ming-Sound Tsao,
A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Correlation in histological subtypes with high resolution computed tomography signatures of early stage lung adenocarcinoma
 Original Article Correlation in histological subtypes with high resolution computed tomography signatures of early stage lung adenocarcinoma Yingying Miao 1,2 *, Jianya Zhang 1,2 *, Jiawei Zou 1,2, Qingqing
Original Article Correlation in histological subtypes with high resolution computed tomography signatures of early stage lung adenocarcinoma Yingying Miao 1,2 *, Jianya Zhang 1,2 *, Jiawei Zou 1,2, Qingqing
Nuclear TK1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for survival in pre-malignant and malignant lesions of the cervix
 Chen et al. BMC Cancer 2013, 13:249 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Nuclear TK1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for survival in pre-malignant and malignant lesions of the cervix Gang Chen 1*,
Chen et al. BMC Cancer 2013, 13:249 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Nuclear TK1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for survival in pre-malignant and malignant lesions of the cervix Gang Chen 1*,
The Spectrum of Management of Pulmonary Ground Glass Nodules
 The Spectrum of Management of Pulmonary Ground Glass Nodules Stanley S Siegelman CT Society 10/26/2011 No financial disclosures. Noguchi M et al. Cancer 75: 2844-2852, 1995. 236 surgically resected peripheral
The Spectrum of Management of Pulmonary Ground Glass Nodules Stanley S Siegelman CT Society 10/26/2011 No financial disclosures. Noguchi M et al. Cancer 75: 2844-2852, 1995. 236 surgically resected peripheral
Frequencies of actionable mutations and survival in variants of invasive adenocarcinoma of lung
 Original Article Frequencies of actionable mutations and survival in variants of invasive adenocarcinoma of lung Zhengbo Song 1,2 *, Tangfeng Lv 1 *, Yiping Zhang 2, Yong Song 1 1 Department of Respiratory
Original Article Frequencies of actionable mutations and survival in variants of invasive adenocarcinoma of lung Zhengbo Song 1,2 *, Tangfeng Lv 1 *, Yiping Zhang 2, Yong Song 1 1 Department of Respiratory
Factors that predict lymph node status in clinical stage T1aN0M0 lung adenocarcinomas
 Ye et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:42 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Factors that predict lymph node status in clinical stage T1aN0M0 lung adenocarcinomas Bo
Ye et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:42 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Factors that predict lymph node status in clinical stage T1aN0M0 lung adenocarcinomas Bo
Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between mucinous gastric carcinoma and signet-ring cell carcinoma
 Original Article Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between mucinous gastric carcinoma and signet-ring cell carcinoma Zhaode Bu, Zhixue Zheng, Ziyu Li, Xiaojiang Wu, Lianhai Zhang, Aiwen Wu,
Original Article Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between mucinous gastric carcinoma and signet-ring cell carcinoma Zhaode Bu, Zhixue Zheng, Ziyu Li, Xiaojiang Wu, Lianhai Zhang, Aiwen Wu,
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18538-18542 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012561 Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18538-18542 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012561 Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast
Original Articles. Current Evidence Does Not Warrant Frozen Section Evaluation for the Presence of Tumor Spread Through Alveolar Spaces
 Original Articles Current Evidence Does Not Warrant Frozen Section Evaluation for the Presence of Tumor Spread Through Alveolar Spaces Ann E. Walts, MD; Alberto M. Marchevsky, MD Context. Tumor spread
Original Articles Current Evidence Does Not Warrant Frozen Section Evaluation for the Presence of Tumor Spread Through Alveolar Spaces Ann E. Walts, MD; Alberto M. Marchevsky, MD Context. Tumor spread
Evaluation of the new TNM staging system proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer at a single institution
 Evaluation of the new TNM staging system proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer at a single institution Kotaro Kameyama, MD, a Mamoru Takahashi, MD, a Keiji Ohata, MD, a
Evaluation of the new TNM staging system proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer at a single institution Kotaro Kameyama, MD, a Mamoru Takahashi, MD, a Keiji Ohata, MD, a
Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis
 19 th Congress of APSR PG of Lung Cancer (ESAP): Update of Lung Cancer Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis Kazuma Kishi, M.D. Department of Respiratory Medicine,
19 th Congress of APSR PG of Lung Cancer (ESAP): Update of Lung Cancer Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis Kazuma Kishi, M.D. Department of Respiratory Medicine,
Accepted Manuscript. Risk stratification for distant recurrence of resected early stage NSCLC is under construction. Michael Lanuti, MD
 Accepted Manuscript Risk stratification for distant recurrence of resected early stage NSCLC is under construction Michael Lanuti, MD PII: S0022-5223(17)32392-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.10.063 Reference:
Accepted Manuscript Risk stratification for distant recurrence of resected early stage NSCLC is under construction Michael Lanuti, MD PII: S0022-5223(17)32392-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.10.063 Reference:
The prognostic significance of central fibrosis of adenocarcinoma
 Prognostic Significance of the Size of Central Fibrosis in Peripheral Adenocarcinoma of the Lung Kenji Suzuki, MD, Tomoyuki Yokose, MD, Junji Yoshida, MD, Mitsuyo Nishimura, MD, Kenro Takahashi, MD, Kanji
Prognostic Significance of the Size of Central Fibrosis in Peripheral Adenocarcinoma of the Lung Kenji Suzuki, MD, Tomoyuki Yokose, MD, Junji Yoshida, MD, Mitsuyo Nishimura, MD, Kenro Takahashi, MD, Kanji
OBJECTIVES. Solitary Solid Spiculated Nodule. What would you do next? Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules.
 Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
Xiaohuan Pan 1,2 *, Xinguan Yang 1,2 *, Jingxu Li 1,2, Xiao Dong 1,2, Jianxing He 2,3, Yubao Guan 1,2. Original Article
 Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
Rare Small Cell Carcinoma in Genitourinary Tract: Experience from E-Da Hospital
 E-Da Medical Journal 20;():-5 Original Article Rare Small Cell Carcinoma in Genitourinary Tract: Experience from E-Da Hospital Wei-Ting Kuo, I-Wei Chang2, Kevin Lu, Hua-Pin Wang, Tsan-Jung u, Victor C.
E-Da Medical Journal 20;():-5 Original Article Rare Small Cell Carcinoma in Genitourinary Tract: Experience from E-Da Hospital Wei-Ting Kuo, I-Wei Chang2, Kevin Lu, Hua-Pin Wang, Tsan-Jung u, Victor C.
In 1989, Deslauriers et al. 1 described intrapulmonary metastasis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Intrapulmonary Metastases Kanji Nagai, MD,* Yasunori Sohara, MD, Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, and Etsuo Miyaoka,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Intrapulmonary Metastases Kanji Nagai, MD,* Yasunori Sohara, MD, Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, and Etsuo Miyaoka,
Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells in lung-cancer-associated pleural effusion
 Received: 1 May 2016 Revised: 19 June 2016 Accepted: 10 July 2016 DOI: 10.1111/crj.12527 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells
Received: 1 May 2016 Revised: 19 June 2016 Accepted: 10 July 2016 DOI: 10.1111/crj.12527 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
In the mid 1970s, visceral pleural invasion (VPI) was included
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tumor Invasion of Extralobar Soft Tissue Beyond the Hilar Region Does Not Affect the Prognosis of Surgically Resected Lung Cancer Patients Hajime Otsuka, MD,* Genichiro Ishii, MD, PhD,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tumor Invasion of Extralobar Soft Tissue Beyond the Hilar Region Does Not Affect the Prognosis of Surgically Resected Lung Cancer Patients Hajime Otsuka, MD,* Genichiro Ishii, MD, PhD,*
Visceral pleura invasion (VPI) was adopted as a specific
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visceral Pleura Invasion Impact on Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patient Survival Its Implications for the Forthcoming TNM Staging Based on a Large-Scale Nation-Wide Database Junji Yoshida,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visceral Pleura Invasion Impact on Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patient Survival Its Implications for the Forthcoming TNM Staging Based on a Large-Scale Nation-Wide Database Junji Yoshida,
Analysis of Prognosis and Prognostic Factors of Cervical Adenocarcinoma and Adenosqumous Carcinoma of the Cervix
 DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0133-8 133 Analysis of rognosis and rognostic Factors of Cervical Adenocarcinoma and Adenosqumous Carcinoma of the Cervix Guangwen Yuan Lingying Wu Xiaoguang Li Manni Huang Department
DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0133-8 133 Analysis of rognosis and rognostic Factors of Cervical Adenocarcinoma and Adenosqumous Carcinoma of the Cervix Guangwen Yuan Lingying Wu Xiaoguang Li Manni Huang Department
Early-stage locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Clinical Case Discussion
 Early-stage locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Clinical Case Discussion Pieter Postmus The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre Liverpool Heart and Chest Hospital Liverpool, United Kingdom 1 2
Early-stage locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Clinical Case Discussion Pieter Postmus The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre Liverpool Heart and Chest Hospital Liverpool, United Kingdom 1 2
Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng, Hui Wang, Yinyan Li, Dongsheng Huang, Jian Zheng,
 The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
3/23/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Pathologic Staging Updates in Lung Cancer T STAGE OUTLINE SURVIVAL ACCORDING TO SIZE ONLY
 Pathologic Staging Updates in Lung Cancer Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME
Pathologic Staging Updates in Lung Cancer Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Expression and significance of Bmi-1 and Ki67 in colorectal carcinoma tissues
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:12, 568-573; December Expression 2008]; 2008 and significance Sun Yat-sen of University Bmi-1 and Cancer Ki67 in Center colorectal carcinoma tissues Clinical Research Paper
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:12, 568-573; December Expression 2008]; 2008 and significance Sun Yat-sen of University Bmi-1 and Cancer Ki67 in Center colorectal carcinoma tissues Clinical Research Paper
Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai, China
 www.springerlink.com Chin J Cancer Res 23(4):265 270, 2011 265 Original Article Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai,
www.springerlink.com Chin J Cancer Res 23(4):265 270, 2011 265 Original Article Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai,
The right middle lobe is the smallest lobe in the lung, and
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Superior Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastases on Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Located in the Right Middle Lobe Yukinori Sakao, MD, PhD,* Sakae Okumura, MD,* Mun Mingyon,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Superior Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastases on Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Located in the Right Middle Lobe Yukinori Sakao, MD, PhD,* Sakae Okumura, MD,* Mun Mingyon,
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Prudence Anne Russell 1,2, Gavin Michael Wright 3,4
 Editorial Page 1 of 7 Predominant histologic subtype in lung adenocarcinoma predicts benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in completely resected patients: discovery of a holy grail? Prudence Anne Russell
Editorial Page 1 of 7 Predominant histologic subtype in lung adenocarcinoma predicts benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in completely resected patients: discovery of a holy grail? Prudence Anne Russell
Higher expression of deoxyuridine triphosphatase (dutpase) may predict the metastasis potential of colorectal cancer
 1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kurume University Hospital, Kurume, Japan; 2 Department of Surgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan; 3 Biostatistics Center, Kurume University,
1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kurume University Hospital, Kurume, Japan; 2 Department of Surgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan; 3 Biostatistics Center, Kurume University,
A Multi-Resolution Deep Learning Framework for Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth Pattern Classification
 MIUA2018, 053, v4 (final): Multi-Resolution CNN for Lung Growth Pattern Classification 1 A Multi-Resolution Deep Learning Framework for Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth Pattern Classification Najah Alsubaie
MIUA2018, 053, v4 (final): Multi-Resolution CNN for Lung Growth Pattern Classification 1 A Multi-Resolution Deep Learning Framework for Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth Pattern Classification Najah Alsubaie
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
The 8th Edition Lung Cancer Stage Classification
 The 8th Edition Lung Cancer Stage Classification Elwyn Cabebe, M.D. Medical Oncology, Hematology, and Hospice and Palliative Care Valley Medical Oncology Consultants Director of Quality, Medical Oncology
The 8th Edition Lung Cancer Stage Classification Elwyn Cabebe, M.D. Medical Oncology, Hematology, and Hospice and Palliative Care Valley Medical Oncology Consultants Director of Quality, Medical Oncology
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Surgical pathology of early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma
 Review Article Page 1 of 8 Surgical pathology of early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma Mary Beth Beasley 1, Francine R. Dembitzer 1, Raja M. Flores 2 1 Department of Pathology, 2 Department of Thoracic
Review Article Page 1 of 8 Surgical pathology of early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma Mary Beth Beasley 1, Francine R. Dembitzer 1, Raja M. Flores 2 1 Department of Pathology, 2 Department of Thoracic
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Including Various Adenocarcinoma Subtypes
 doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.18-00163 Original Article PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Including Various Adenocarcinoma Subtypes Tomoyuki Miyazawa, MD, 1 Hideki Marushima, MD, PhD, 1 Hisashi Saji,
doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.18-00163 Original Article PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Including Various Adenocarcinoma Subtypes Tomoyuki Miyazawa, MD, 1 Hideki Marushima, MD, PhD, 1 Hisashi Saji,
Molly Boyd, MD Glenn Mills, MD Syed Jafri, MD 1/1/2010
 LSU HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER NSCLC Guidelines Feist-Weiller Cancer Center Molly Boyd, MD Glenn Mills, MD Syed Jafri, MD 1/1/2010 Initial Evaluation/Intervention: 1. Pathology Review 2. History and Physical
LSU HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER NSCLC Guidelines Feist-Weiller Cancer Center Molly Boyd, MD Glenn Mills, MD Syed Jafri, MD 1/1/2010 Initial Evaluation/Intervention: 1. Pathology Review 2. History and Physical
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma - Myers
 Role of Routine Histology and Special Testing in Managing Patients with Non- Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor Director, Anatomic Pathology & MLabs University of
Role of Routine Histology and Special Testing in Managing Patients with Non- Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor Director, Anatomic Pathology & MLabs University of
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules
 Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
Xiang Hu*, Liang Cao*, Yi Yu. Introduction
 Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Prognostic prediction of clinical stage IA lung cancer presenting as a pure solid nodule
 Original Article Prognostic prediction of clinical stage IA lung cancer presenting as a pure solid nodule Jong Hui Suh 1, Jae Kil Park 2, Youngkyu Moon 2 1 Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery,
Original Article Prognostic prediction of clinical stage IA lung cancer presenting as a pure solid nodule Jong Hui Suh 1, Jae Kil Park 2, Youngkyu Moon 2 1 Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 8: , 2014
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 8: 813-818, 2014 Investigation of the epidermal growth factor receptor mutation rate in non small cell lung cancer patients and the analysis of associated risk factors using logistic regression
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 8: 813-818, 2014 Investigation of the epidermal growth factor receptor mutation rate in non small cell lung cancer patients and the analysis of associated risk factors using logistic regression
Lung cancer pleural invasion was recognized as a poor prognostic
 Visceral pleural invasion classification in non small cell lung cancer: A proposal on the basis of outcome assessment Kimihiro Shimizu, MD a Junji Yoshida, MD a Kanji Nagai, MD a Mitsuyo Nishimura, MD
Visceral pleural invasion classification in non small cell lung cancer: A proposal on the basis of outcome assessment Kimihiro Shimizu, MD a Junji Yoshida, MD a Kanji Nagai, MD a Mitsuyo Nishimura, MD
The lung adenocarcinoma guidelines: what to be considered by surgeons
 Review Article The lung adenocarcinoma guidelines: what to be considered by surgeons Rodrigo A. S. Sardenberg 1, Evandro Sobroza Mello 1, Riad N. Younes 2 1 Hospital Alemão Oswaldo Cruz, São Paulo, Brazil;
Review Article The lung adenocarcinoma guidelines: what to be considered by surgeons Rodrigo A. S. Sardenberg 1, Evandro Sobroza Mello 1, Riad N. Younes 2 1 Hospital Alemão Oswaldo Cruz, São Paulo, Brazil;
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Mutation and prognostic analyses of PIK3CA in patients with completely resected lung adenocarcinoma
 Cancer Medicine ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Mutation and prognostic analyses of PIK3CA in patients with completely resected lung adenocarcinoma Zhengbo Song 1,2, Xinmin Yu 1 & Yiping Zhang 1,2 1 Department
Cancer Medicine ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Mutation and prognostic analyses of PIK3CA in patients with completely resected lung adenocarcinoma Zhengbo Song 1,2, Xinmin Yu 1 & Yiping Zhang 1,2 1 Department
