DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
|
|
|
- Buck Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY The histopathological and immunohistochemical study of oral squamous carcinomas PhD Student: DRAGOMIR LUCIAN PAUL Scientific Coordinator: PROF. DR. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA CRAIOVA 2012
2 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION CURRENT STAGE OF KNOWLEDGE CHAPTER I. EPIDEMIOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND RISK FACTORS IN ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMAS 2 I.A. Epidemiological considerations in oral squamous carcinoma 2 I.B. Risk factors in oral squamous carcinoma 4 CHAPTER II. ORAL CARCINOGENESIS: HYPOTHESIS, MECHANISMS 10 CHAPTER III. PROGNOSTIC FACTORS IN ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMAS 26 CHAPTER IV. THE CLASSIFICATION OF ORAL TUMORS 32 PERSONAL CONTRIBUTIONS THE OBJECTIVES OF STUDY 38 CHAPTER V. MATERIAL AND METHODS 39 V.A. Investigated material 39 V.B. Methods 40 CHAPTER VI. RESULTS 45 VI.A. CLINICO-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY OF PACIENTS WITH ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMA 45 VI.B. HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMAS 59 VI.C. IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMAS 89 CHAPTER VII. DISCUSSIONS 111 VII.A. CLINICO-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF PACIENTS WITH ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMA 111 VII.B. HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMAS 122 VII.C. IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF ORAL SQUAMOUS CARCINOMAS 132 CHAPTER VIII. CONCLUSIONS 142 REFERENCES 146
3 INTRODUCTION Oral cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all human cancers and is currently a major health problem worldwide, both in frequency of lesions and their incidence in different age groups as well as by many risk factors involved. Over 90% of malignant tumors with oral location are squamous cell carcinomas (OSC), estimating over 125,000 annual deaths worldwide related to this tumor. Oral carcinogenesis is a multistage process including precursor lesions and invasive and metastatic lesions, and relatively easy access to explore clinicopathologic oral squamous carcinoma tumors designate as an ideal model to investigate the cancerous process. Clinical staging using TNM classification has long been used as a standard tool for planning treatment and estimating prognosis. However, this prognostic method does not provide sufficient predictive information about optimal treatment that would be beneficial for each patient. OSC pathogenesis involving multiple molecular pathways and therefore the molecular changes underlying tumor progression is obscure and is the subject of numerous studies. An important aspect of the OSC is the different biological behavior for patients with similar clinicopathologic features, some tumors having a better prognosis than others. Identification of molecular changes responsible for this process may contribute to a better understanding of tumor behavior. In recent years there have been identified several biomarkers that can provide useful prognostic information in the management of head and neck squamous carcinomas. This study aims to evaluate the expression for several markers in order to identify their role in oral carcinogenesis, also following the possible correlations between these parameters and clinico-morphological analysis and selection of those with statistical significance. Thus, we followed for two categories lesion, dysplasia and carcinomas, the expression of p53, cyclin D1, p16, Ki67, EGFR, Her2/neu and CD44. The study included a total of 224 OSCs that were analyzed clinically and epidemiologically. Subsequently, histopathological analysis followed histological variety, degree of differentiation, inflammatory response, pattern of invasion, presence of vascular and perineural invasion, metastatic adenopathy and status of safety margins. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed on a lot of 44 selected cases and evaluated the immunoexpression in oral squamous carcinoma of proteins involved in cell cycle (p53, cyclin D1, p16), cell proliferation (Ki67), tumor growth (EGFR, Her2/neu ) and tumor- peritumoral matrix relationship (CD44). Also the immunoexpression of analyzed markers was evaluated and compared with clinico-pathological parameters, in this sense using statistical analysis (chi square, ANOVA). 1
4 Keywords: oral squamous cell carcinoma, dysplasia, degree of differentiation, invasion, immunohistochemical expression, prognosis. I. CURRENT STAGE OF KNOWLEDGE Chapter I- Epidemiological considerations and risk factors in oral squamous carcinomas - describes the incidence of oral squamous cell carcinoma in the world in relation to age, sex and oral location and deppending on tumoral pathology in general. There are also analyzed the main risk factors involved in the occurrence of tumors in the oral cavity and squamous cell carcinomas in particular. Chapter II- Oral carcinogenesis: hypothesis, mechanisms - investigate current hypotheses on the initiation and development of oral squamous cell carcinomas and systematizes genetic and proteomic changes in oral carcinogenesis. In this sense refers to genetic alterations that initiate the cancer, cell cycle alterations that trigger and maintain cell proliferation and disruption of mechanisms that ensure cellular homeostasis and provide tumor progression and metastasis. Chapter III- Prognostic factors in oral squamous carcinomas - analyze clinical factors (age, sex, area of origin, location, tumor size, social status), histopathological factors (tumor stage and grade, pattern of invasion, histological type, margins of resection, presence of vascular invasion and metastases) and molecular factors (alteration of suppressor genes and activation of tumor oncogenes) on which can be appreciated oral squamous carcinoma prognosis. Chapter IV- The classification of oral tumors - presents the last classification by 2005 of the Working Group for head and neck tumors within the World Health Organization. 2
5 II. PERSONAL CONTRIBUTIONS The study proposes an evaluation of carcinogenesis process for squamous carcinomas developed in the oral mucosa and their precursor lesions, using traditional methods of investigation as well as modern techniques such as immunohistochemistry. Identification of the complex mechanisms acting at the molecular level and the interactions between them provides valuable information on tumor initiation and development, and predictions on prognosis. In this study are evaluated markers involved in different stages of carcinogenesis and aims to identify possible prognostic and therapeutic targets. Research in this direction is very actual and achieving the required results can contribute to improve the quality of life and life expectancy of patients. Specific objectives of the study include: Expanding knowledge about the clinical histopathological and immunohistochemical factors, involved in oral carcinogenesis, in order to deepen the mechanisms of initiation and its progression; To identify and define the clinical parameters that characterize oral squamous cell carcinomas and their precursor lesions, for their early diagnosis; To identify and define the morphological parameters that characterize oral squamous cell carcinomas, in order to apply early and differentiated therapies; Identification of mechanisms and markers involved in invasion and aggressivity of oral squamous cell carcinoma; Identification of the most specific markers for prognosis in invasive and metastasing carcinomas. CHAPTER IV- Material and Methods - provides information about the material studied and methods used in research. INVESTIGATED MATERIAL This study was performed over a period of 5 years ( ), including a total of 224 cases of OSC. The studied material was human material from patients hospitalized in the Clinic of Oro-Maxillo-Facial Surgery of the Emergency County Hospital Craiova. Human used material was represented by biopsy fragments or surgical excision pieces. METHODS From the laboratory pathological registers or directly, we obtained data regarding macroscopic aspects (shape, size, number, consistency) and histopathological diagnosis for the cases studied retrospectively. In a first phase I followed to obtain epidemiological and clinical data on patients' sex and age, area of origin, risk factors, time since the onset of illness, symptoms, tumor location, size and their shape, presence of satellite adenopathy. Pieces were processed by the classical technique with paraffin embedding and and Hematoxylin Eosin stain, using also special stains such as Giemsa, which allow a good classification of lesions according to histological appearance. Histopathological analysis was performed on a sample of 224 CSOs and included the following assessment criteria: histological variety, degree of differentiation, the extent of inflammatory response, pattern of tumor invasion, presence of metastatic adenopathy, presence of 3
6 perineural and vessels invasion and presence of residual malignant cells at the safety surgical margins. Immunohistochemical technique was performed for a group of 44 selected cases. Working systems used were the CSA II biotin-free catalyzed Amplification System (code K1497) for EGFR and LSAB + Kits, Universal (code K0679) for the other antibodies, for visualisation using DAB (diaminobenzidine). The panel of antibodies used is presented below: ANTIBODY CLONE DILUTION RETRIEVAL INCUBATION p16 E6H4, ready to use citrate buffer, ph 6 30 min RT CINtec Histology Kit p53 DO-7, Dako 1:50 5 cycles MW in 30 min RT citrate buffer, ph 6 cyclin D1 EP12, Dako 1:100 7 cycles MW în 30 min RT Tris-EDTA buffer, ph 9 ki67 MIB1, Dako 1:50 5 cycles MW în 30 min RT tampon citrat, ph 6 EGFR E30, Dako 1: min RT Her2/neu polyclonal, 1:250 7 cycles MW in 30 min RT Dako citrate buffer, ph 6 CD44 DF1485, Dako 1:50 7 cycles MW in citrate buffer, ph 6 30 min RT The panel of used antibodies For the interpretation of obtained reactions we used a semiquantitative quantification that take into account the percentage of labeled cells and staining intensity, and for Her2/neu was made according to the criteria of the American Society of Clinical Oncology / College of American Pathologists (ASCO / CAP) for breast carcinoma. Primary statistical analysis (mean, standard deviation) and comparison tests of the averages (ANOVA) were useful for assessing differences in the studied groups. To assess the dependence of the two-factor classification chi-square test was used, the results with value less than 0.05 being considered significant. For this purpose were used the module Data Analisys of Microsoft Exceel program and commands such Compare means, Descriptive Statistics and Crosstab within the module Analysis belonging to automatically SPSS 10software. 4
7 CHAPTER V- Results and CHAPTER VI- Discussions indicate the results obtained in the study, which are reported to recent data from literature. In the clinico-epidemiological study are presented aspects of patients' gender and age, area of origin, risk factors, time since the onset of illness, symptoms, tumor location, size and shape, presence of satellite adenopathy. In this study lesions predominated in males (83.9%), with maximum incidence of diagnosis in the 7 th decade of life (34.8%) in patients from urban areas (72.7%), most commonly being identified ulcerated tumors (37.9%), larger than 2cm (65.3%), with unilateral lymphadenopathy (46.1%) and localized to the lip (35.5%), followed by the lingual lesions (33% ). Also, smoking is indicated to be the main risk factor for oral squamous cell carcinomas and its association with alcohol, irritative factors or precancerous lesions were identified in 45,9% of cases. Most patients were presented to the doctor after a period of between 6-12 months after the desease debut, patients frequently accusing the pain, local discomfort or foreign body sensation. There were statistically significant differences (p <0.05) for the associated risk factors and the degree differentiation of tumor lesions according to their location. Literature data indicate an average age of diagnosis of 64 years, 90% of patients having over 40 years (Jemal A, 2008). American Cancer Society estimated that in 2005 the oral cavity cancers represented approximately 1.9% and 0.9% of new cases of disease in men and women respectively (American Cancer Society, 2007). It is considered that diet rich in raw fruits, vegetables, bread, wheat and other cereals, fish, red wine which is specific to rural areas as compared with the rich in preservatives such as nitrites and nitrates, known to have an increased carcinogenic risk, specific for urban population, plays an important role in establishing rapport neoplasia identified between the two areas of pacients origin (Bosetti C, 2003). Smoking and alcohol abuse are considered dominant risk factors with a strong synergism, its antecedents being found in 75% of patients with cancers of the oral cavity and in the oropharynx (Johnson N, 2001). It is estimated that 30-35% of tumors have lingual location, followed by gingival location in 20-25% cases and much lower percentage of the floor with 5-7%, soft palate with 4-6% and genian mucosa with only 2-3% (Wooglar JA, 1995). The aspects found about macroscopic development pattern and location of oral malignant tumors are similar to literature data (Reichart PA, 2000). Tumour size include diameter, width and depth of the tumor. TNM system considers only the tumor diameter. However, many studies have confirmed that constantly evaluation of all these parameters seems to be the only independent prognostic factor negatively affecting metastases to lymph nodes, local recurrence and survival (Brown B, 1989, Jung J, 2009). Several studies have suggested a quick way classification of a node according to its macroscopic form, such as reniform shape indicate a reactive hyperplasia adenopathy, and round shape or lymph node clustering indicate the neoplastic infiltration (Soames JV, 2005). Histopathological analysis followed histological variety, degree of differentiation, the extent of inflammatory infiltrate, pattern of tumor invasion, presence of metastatic adenopathy, presence of perineural invasion, vessels invasion, the presence of residual malignant cells at the safety surgical margins. OSC with keratinization (50%) or without keratinizations (32.1%), moderately differentiated (41%), with lymphoid infiltrate at the interface of tumors- adjacent matrix (83.4%) and infiltrative pattern of invasion (43.7%) was the most commonly reported. Over the past two decades have been proposed several histologic parameters as prognostic factors including invasion pattern, degree of keratinization, nuclear pleomorphism, mitotic rate and lymphocytic inflammatory response (Bundegaard T, 2002). Despite the development of management overall survival of patients with OSC has not improved significantly in the past 20 years, the survival 5
8 rate at 5 years ranging between 45-50% (Bagan JV, 2007). The literature indicates that basaloid or sarcomatoid forms of carcinomas as more aggressive (Berthelet E, 1994), unlike verrucous carcinoma, a well differentiated and less aggressive tumor (Gnepp D, 1988). The keratinized or not appearance of these lesions is not a prognostic factor in itself, but illustrates the degree of differentiation, important being cytonuclear atypia and mitotic activity. Studies in the literature indicate low prognostic value of the degree of differentiation of oral squamous carcinomas because most are moderately differentiated (Jerjes W, 2010). Several studies have shown an inverse relationship between lymphocytic infiltration and metastatic potential in the lymph nodes (Hiratsuka H, 1997) as well as survival (Kurokawa H). The presence of an invasion front in the form of non-cohesive cords or islands or isolated neoplastic cells form may be associated with a poor prognosis, with an increased risk of metastasis, whereas tumors with a compact appearance of the invasion front, which grow push (a phenomenon called "pushing"), is associated with a much less aggressive and low risk of metastasis (Thompson DR, 2006). The study indicated vascular invasion (18.3%), perineural invasion (52.6%) and the presence of lymph node metastasis (22.2%) in the case of poorly differentiated carcinomas. Most studies report statistical association between lymphovascular and perineural invasion with prognosis (Chen YW, 2008, Brown B, 1989). In this study, oral squamous carcinomas in tumoral stage I and III were most frequently identified (59.8%). The increased incidence of cervical lymph node metastasis is the most important negative prognostic factor for OSC, at diagnosis more than 40% of patients already have metastases (Chen YW, 2008). Safety margins invasion was identified in 42.5% of cases. The study reported statistically significant differences (p <0.05) of histological type, pattern of invasion, stage and depth of invasion, and perineural and vascular invasion with the degree of tumors differentiation. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed on a group of 44 oral squamous cell carcinomas, for which are investigated the expression of p53, cyclin D1, p16, Ki67, EGFR, Her2/neu and CD44 in tumors and the dysplastic lesions identified in the safety surgical limits. The immunopositive reactions for p53 was present in a proportion of 59% of cases, without obvious correlation with histological type and tumor differentiation grade. The analysis for Cyclin D1immunostain reaction indicated positivity in 59% of the OSC, the most in more than 50% of tumor cells (29.5%) with moderate or high intensity and without correlation with tumor grade. Although were not defined any specific mutations of tumor progression, it was established an experimental model of the process. The first change is the p16 gene inactivation, which is associated with the transition from normal to hyperplasia / hyperkeratosis (Chin Su, 2005). In the next step would appear oncoprotein p53 mutations which are associated with progression to dysplasia lesions. Finally, Cyclin D1 amplification and overexpression is a late event that is associated with invasion. Ki67 index analysis indicated inverse relationship with the degree of differentiation of malignancies, its values are higher when the degree of investigated OSC was lower. In literature it is reported that Ki67 proliferation index is significantly higher in tumors with low histological grade of differentiation (Vicente JC, 2002). EGFR expression did not correlate with the degree of differentiation of the OSC, but was better expressed in well and moderately differentiated tumors, probably because this receptor linked to the degree of differentiation of neoplastic keratinocytes. The literature also confirms EGFR overexpression in three quarters of cases of analyzed OSC, with values up to 75% (Vosoughhosseini S, 2012). Information on positivity for EGFR and the degree of differentiation 6
9 of the OSC reported positivity in 50% of cases, more frequently in well-differentiated forms (Bernardes VF, 2010). The analysis of Her2/neu expression in OSC indicated protein overexpression a small number of tumors (11 cases), all poorly differentiated. The role of HER-2/neu in carcinomas of the head and neck carcinoma is not well defined. Overexpression has been observed in many cancers and is used in cancer therapy regimens. It turned out that HER-2/neu overexpression increases metastatic potential in several stages by promoting invasion and metastatic cascade (Khan AJ, 2002), suggesting that this gene may play an important role in carcinogenesis. The immunoreactions for CD44 indicated a direct proportional relationship with the degree of tumor differentiation, well-differentiated forms revealing the most intense immunostain, moderately differentiated forms with an average immunostaining intensity, while in the poorly differentiated immunostaining was weak. The clinical significance of CD44 expression in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck is that of a tumor marker for diagnosis and prognosis (Assimakopoulos D, 2002). One such study on OSC and dysplastic lesions indicated that immunostain pattern and intensity varied depending on the degree of dysplasia and the degree of differentiation of the OSC (Bahar R, 1997). CHAPTER VII- Conclusions indicates the study conclusions. Analysis of distribution according to age groups indicated that the tumors had an incidence progressively increased with each decade of life, more than three quarters being diagnosed (78.6%) between years; The incidence of lesions by gender revealed a net predominance in males that we found 188 cases (83.9%), most patients being from urban areas respectively 163 cases (72.7%); I noticed that often the risk factors were associated with each other, mostly in alcohol and tobacco (45.9%) or alcohol, smoking, irritation factors and precancerous lesions (16.5%); Most patients, respectively 86 cases (38.4%) were presented to the doctor after a period of between 6-12 months after the onset of disease; As regards the tumor localization, in order of frequency they were located in the: lips (35.2%), tongue (33%), floor (16.9%), gingiva (8.4%) and palate (6 2%); There were significant statistically differences (p <0.05) for risk factors associated and the degree of differentiation of tumor lesions according to tumors localization; The analysis tumor size indicated that 72,4% of cases corresponded to T1/T2 categories; The most common OSC histological varieties were the forms without keratinization (50%) and the keratinized ones (32.1%); The analysis of differentiation in OSC indicated predominance of moderately differentiated forms in 92 cases (41%), followed in 75 cases (33.5%) of well differentiated OSC and 57 cases (25.5%) with poorly differentiated OSC; The analysis of lymphoid infiltrate at the interface tumor / adjacent matrix indicated its presence in almost half of cases (102 cases or 45.5%) with medium intensity; Classification of tumors regarding the pattern of tumor invasion revealed predominance of infiltrative pattern, respectively in 73 cases (43.7%); Perineural and vascular space invasion was present predominantly in moderately and poorly differentiated OSC and in 23 cases (13.7%) was associated with metastatic adenopathy; The analysis of the clinico-anatomical stage indicated that most cases corresponded to stage I and III, each with 50 cases; Surgical safety limits invasion was identified in 42.5% of cases. 7
10 Were found statistically significant differences (p <0.05) of histological type, pattern of invasion, stage and depth of invasion, and perineural and vessels invasion with the degree of tumor differentiation; The analyzed markers expression in both carcinomas and dysplasia indicates their intervention in oral carcinogenesis in its early stage, at least for some of these tumors; The immunostain appreciation for p53 oncoprotein indicated p53 gene mutations involved in neoplastic transformation that can occur early in oral carcinogenesis; The positivity for p53 may be an indicator of tumor progression, but can not be used as a factor for predicting malignant potential of oral squamous carcinomas; The positivity for p16, used as a surrogate marker for identifying OSC HPV positive was low and inversely proportional to the expression of p53, suggesting that different mechanisms involved in oral carcinogenesis; P16 and p53 positivity in dysplastic adjacent OSC areas indicate that these changes are the beginning of malignant transformation; also p53 and p16 positivity in both lesions, dysplasia and carcinomas, and increase the proportion of p53 positive cases from dysplasia to carcinoma suggests that p53 and p16 gene mutations are involved in neoplastic transformation and may occur early in oral carcinogenesis; The analysis of Ki67 index indicated inverse relationship with the degree of tumor differentiation; Overexpression of p53 and Ki-67 appear to be reliable indicators of tumor progression in OSC; While p53 immunoexpression dominated the poorly differentiated OSC group, p16 and EGFR immunoexpression dominated the well differentiated OSC group; The analysis of Her2/neu expression in OSC indicated the protein overexpression for a small number of tumors (11 cases), all poorly differentiated; Statistical analysis indicated differences in Ki67 proliferation index, as well as HER2/neu and CD44 reactions depending on the degree of tumors differentiation; There were statistical relations between p53reactions and cyclin D1, respectively EGFR and also between HER2/neu and EGFR, indicating cooperation of growth factors involved in the regulation of cell cycle proteins in oral carcinogenesis; Ki67 and CD44 are useful markers for assessing the degree and risk of progression of oral dysplastic lesions. 8
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Catholic University of Louvain, St - Luc University Hospital Head and Neck Oncology Programme. Anatomopathology. Pathology 1 Sept.
 Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY ANGIOGENESIS ROLE IN LIPS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA PROGRESSION - CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY PhD Student:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY ANGIOGENESIS ROLE IN LIPS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA PROGRESSION - CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY PhD Student:
Table of Contents. 1. Overview. 2. Interpretation Guide. 3. Staining Gallery Cases Negative for CINtec PLUS
 Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor survival in breast cancer patients
 Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies. Agenda
 Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY
 Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS.
 NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Physician to Physician AJCC 8 th Edition. Head and Neck. Summary of Changes. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7 th Ed. Head and Neck Chapters
 Physician to Physician Head and Neck William M. Lydiatt, MD Chair of Surgery Nebraska Methodist Hospital Clinical Professor of Surgery, Creighton University Validating science. Improving patient care.
Physician to Physician Head and Neck William M. Lydiatt, MD Chair of Surgery Nebraska Methodist Hospital Clinical Professor of Surgery, Creighton University Validating science. Improving patient care.
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
Immunohistochemical determinations in evaluating the prognostic in patient with urinary bladder tumors
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(2):175 179 ORIGINAL PAPER Immunohistochemical determinations in evaluating the prognostic in patient with urinary bladder tumors E. TRAŞCĂ 1), R.
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(2):175 179 ORIGINAL PAPER Immunohistochemical determinations in evaluating the prognostic in patient with urinary bladder tumors E. TRAŞCĂ 1), R.
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas
 Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
Studies of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Tongue (TSCC), with Focus on Histological Factors
 Studies of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Tongue (TSCC), with Focus on Histological Factors Oskar Jonsson Filip Papic Supervised by Karin Nylander, professor Department of Medical Biosciences Umeå University.
Studies of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Tongue (TSCC), with Focus on Histological Factors Oskar Jonsson Filip Papic Supervised by Karin Nylander, professor Department of Medical Biosciences Umeå University.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Afrah A. Khalil, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Seta A. Sarkis, B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D. (2) ABSTRACT Background: Understanding the
Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Afrah A. Khalil, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Seta A. Sarkis, B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D. (2) ABSTRACT Background: Understanding the
Diseases of oral cavity
 Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION OF ENLARGED LYMPH NODE: Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
 Case Scenario 1 HNP: A 70 year old white male presents with dysphagia. The patient is a current smoker, current user of alcohol and is HPV positive. A CT of the Neck showed mass in the left pyriform sinus.
Case Scenario 1 HNP: A 70 year old white male presents with dysphagia. The patient is a current smoker, current user of alcohol and is HPV positive. A CT of the Neck showed mass in the left pyriform sinus.
Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14
 Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14 Contents 14. Neuroendocrine Tumours 161 14.1. Diagnostic algorithm
Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14 Contents 14. Neuroendocrine Tumours 161 14.1. Diagnostic algorithm
Head and Neck SCC. HPV in Tumors of the Head and Neck. Overview. Role of HPV in Pathogenesis of Head & Neck Tumors
 HPV in Tumors of the Head and Neck Christina Kong, M.D. Associate Professor, Stanford Dept of Pathology Director, Cytopathology Laboratory & Cytopathology Fellowship ckong@stanford.edu Head and Neck SCC
HPV in Tumors of the Head and Neck Christina Kong, M.D. Associate Professor, Stanford Dept of Pathology Director, Cytopathology Laboratory & Cytopathology Fellowship ckong@stanford.edu Head and Neck SCC
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Case Scenario. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
This form may provide more data elements than required for collection by standard setters such as NCI SEER, CDC NPCR, and CoC NCDB.
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Salivary Gland FNA ATYPICAL : Criteria and Controversies
 Salivary Gland FNA ATYPICAL : Criteria and Controversies W.C. Faquin, M.D., Ph.D. Director, Head and Neck Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School
Salivary Gland FNA ATYPICAL : Criteria and Controversies W.C. Faquin, M.D., Ph.D. Director, Head and Neck Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors)
 Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors) Kael Mikesell, DO McKay-Dee Hospital May 14, 2015 Outline Update to DNA Testing
Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors) Kael Mikesell, DO McKay-Dee Hospital May 14, 2015 Outline Update to DNA Testing
Gynecologic Malignancies. Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18
 Gynecologic Malignancies Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18 Outline Female Cancer Statistics Uterine Cancer Adnexal Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Uterine Cancer Endometrial Cancer Uterine Sarcoma Endometrial
Gynecologic Malignancies Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18 Outline Female Cancer Statistics Uterine Cancer Adnexal Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Uterine Cancer Endometrial Cancer Uterine Sarcoma Endometrial
Her-2/neu expression and its correlation with ER status and various clinicopathological parameters
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00106.X Her-2/neu expression and its correlation with ER status and various clinicopathological parameters Kriti Chauhan 1,*, Monika Garg 2, Abhimanyu
Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00106.X Her-2/neu expression and its correlation with ER status and various clinicopathological parameters Kriti Chauhan 1,*, Monika Garg 2, Abhimanyu
Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization with Colorectal Carcinoma: A Pilot Study
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67 and p53 Expressions to Histopathology Grading of Breast Cancer in Makassar, Indonesia
 Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
Case Scenario 1. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Penile cancer teams in UK. Common variants. Penile cancer teams. Basaloid squamous carcinoma. The Pathology of Penile Tumours
 The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients
 HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients Financial Disclosure: None November 8, 2013 Steven J. Wang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients Financial Disclosure: None November 8, 2013 Steven J. Wang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY)
 Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 05 Page May 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.92 Clinicopathological Profile & Correlation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.92 Clinicopathological Profile & Correlation
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Study of expression of P53 in Gastric Carcinoma As a prognostic indicator
 Original Research Article Study of expression of P53 in Gastric Carcinoma As a prognostic indicator K. Padma Malini 1*, Srivani 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
Original Research Article Study of expression of P53 in Gastric Carcinoma As a prognostic indicator K. Padma Malini 1*, Srivani 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
6. Cervical Lymph Nodes and Unknown Primary Tumors of the Head and Neck
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 11 Page November 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.78 A Histomorphological Study of Carcinoma
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.78 A Histomorphological Study of Carcinoma
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
(formalin fixed) 6 non-neoplastic spots (6 spots) Corresponding normal tissues with cancers: Yes Diameter: 1. 0 mm
 CBA729-Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 6 Tissue type: Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues No. of spots: 6 spots from each
CBA729-Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 6 Tissue type: Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues No. of spots: 6 spots from each
FCDS Annual Educational Conference Orlando, Florida July 28, Steven Peace, CTR
 FCDS Annual Educational Conference Orlando, Florida July 28, 2017 Steven Peace, CTR 1 Outline 2018 Transition from CS SSFs to Individual Site Specific Prognostic Factor Fields (SSFs) Locating SSFs in the
FCDS Annual Educational Conference Orlando, Florida July 28, 2017 Steven Peace, CTR 1 Outline 2018 Transition from CS SSFs to Individual Site Specific Prognostic Factor Fields (SSFs) Locating SSFs in the
3/27/2017. Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical History:
 Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative breast lesions adjacent to malignancy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES)
 NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat Page 1
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Tongue: A Case Report Authors: Nanayakkara PR*, Arudchelvam JD** Ariyaratne JC*, Mendis K*, Jayasekera
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Tongue: A Case Report Authors: Nanayakkara PR*, Arudchelvam JD** Ariyaratne JC*, Mendis K*, Jayasekera
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF GENERAL MEDICINE DOCTOR S DEGREE THESIS ABSTRACT
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF GENERAL MEDICINE DOCTOR S DEGREE THESIS ABSTRACT CLINICAL, HISTOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY IN A GROUP OF PATIENTS WITH BREAST CANCERS
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF GENERAL MEDICINE DOCTOR S DEGREE THESIS ABSTRACT CLINICAL, HISTOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY IN A GROUP OF PATIENTS WITH BREAST CANCERS
WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER?
 CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts
 Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק
 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק 26.06.09 Lecture outlines WHO histological classification Macro/Micro assessment Early diagnosis Minimal pathology Main subtypes SCC, AdCa, LCLC
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק 26.06.09 Lecture outlines WHO histological classification Macro/Micro assessment Early diagnosis Minimal pathology Main subtypes SCC, AdCa, LCLC
Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva Malignant melanoma sho
 Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
10. HPV-Mediated (p16+) Oropharyngeal Cancer
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013
 EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT. Robin Billet, MA, CTR, Head & Neck CTAP Member May 9, 2013 Head and Neck Coding and Staging Head and Neck Coding and Staging Anatomy & Primary Site Sequencing and MPH
P16 INK4A EXPRESSION AS A POTENTIAL PROGNOSTIC MARKER IN CERVICAL PRECANCEROUS AND CANCEROUS LESIONS IN MOROCCO
 P16 INK4A EXPRESSION AS A POTENTIAL PROGNOSTIC MARKER IN CERVICAL PRECANCEROUS AND CANCEROUS LESIONS IN MOROCCO Yassine Zouheir Laboratory of histo-cytopathology of Institut Pasteur of Morocco, Casablanca,
P16 INK4A EXPRESSION AS A POTENTIAL PROGNOSTIC MARKER IN CERVICAL PRECANCEROUS AND CANCEROUS LESIONS IN MOROCCO Yassine Zouheir Laboratory of histo-cytopathology of Institut Pasteur of Morocco, Casablanca,
Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland
 Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Objectives. Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System. Role of Salivary Gland FNA 04/26/2018
 Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients
 BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour
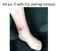 64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour Case History Excision with split-skin grafting Histology moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with large areas of necrosis and brisk mitotic activity.
64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour Case History Excision with split-skin grafting Histology moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with large areas of necrosis and brisk mitotic activity.
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Department of Pathology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India 2
 original article Oman Medical Journal [2016], Vol. 31, No. 3:165 169 Transition of Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and Vimentin from Premalignant to Malignant Lesions of Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
original article Oman Medical Journal [2016], Vol. 31, No. 3:165 169 Transition of Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and Vimentin from Premalignant to Malignant Lesions of Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
Barriers to Understanding
 Behind the Scenes: The Critical Importance of Cancer Cell Pathology and the Pathologist Sherry T. Emery, M.D., Chief of Pathology Northeast Health System Barriers to Understanding Questions for 2010 What
Behind the Scenes: The Critical Importance of Cancer Cell Pathology and the Pathologist Sherry T. Emery, M.D., Chief of Pathology Northeast Health System Barriers to Understanding Questions for 2010 What
Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Head and Neck Squamous Subtypes
 1 Head and Neck Squamous Subtypes Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas HNSCC 5 th -6 th most common cancer 400,000/year 50% mortality Considerable
1 Head and Neck Squamous Subtypes Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas HNSCC 5 th -6 th most common cancer 400,000/year 50% mortality Considerable
Da Costa was the first to coin the term. Marjolin s Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Report. Introduction
 E-Da Medical Journal 2016;3(2):24-28 Case Report Marjolin s Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature Review Yue-Chiu Su 1, Li-Ren Chang 2 Marjolin s ulcer is an aggressive cutaneous malignancy, which is common
E-Da Medical Journal 2016;3(2):24-28 Case Report Marjolin s Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature Review Yue-Chiu Su 1, Li-Ren Chang 2 Marjolin s ulcer is an aggressive cutaneous malignancy, which is common
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
Genetic Testing: When should it be ordered? Julie Schloemer, MD Dermatology
 Genetic Testing: When should it be ordered? Julie Schloemer, MD Dermatology Outline Germline testing CDKN2A BRCA2 BAP1 Somatic testing Gene expression profiling (GEP) BRAF Germline vs Somatic testing
Genetic Testing: When should it be ordered? Julie Schloemer, MD Dermatology Outline Germline testing CDKN2A BRCA2 BAP1 Somatic testing Gene expression profiling (GEP) BRAF Germline vs Somatic testing
Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 2010
 Original Article Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 21 * DMRT clinical oncology, MSc. pathology. Summary:
Original Article Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 21 * DMRT clinical oncology, MSc. pathology. Summary:
UPDATE ON RADIOTHERAPY
 1 Miriam Kleiter UPDATE ON RADIOTHERAPY Department for Companion Animals and Horses, Plattform Radiooncology and Nuclear Medicine, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna Introduction Radiotherapy has
1 Miriam Kleiter UPDATE ON RADIOTHERAPY Department for Companion Animals and Horses, Plattform Radiooncology and Nuclear Medicine, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna Introduction Radiotherapy has
Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
 Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas SEMINARS IN DIAGNOSTIC PATHOLOGY 31 (2014) 443 451 Ralph H.Hruban, MD, David S. Klimstra, MD Paola Parente Anatomia Patologica Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza San Giovanni
Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas SEMINARS IN DIAGNOSTIC PATHOLOGY 31 (2014) 443 451 Ralph H.Hruban, MD, David S. Klimstra, MD Paola Parente Anatomia Patologica Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza San Giovanni
MDJ The Role of K-Ras and PI3Kcb Expression in Oral Vol.:10 No.:2 2013
 MDJ The Role of K-Ras and PI3Kcb Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Dr. Asseel Mohammed ghazi. B.D.S Dr.Muna S. Merza. B.D.S, M.Sc. Ph.D Abstract Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma is an
MDJ The Role of K-Ras and PI3Kcb Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Dr. Asseel Mohammed ghazi. B.D.S Dr.Muna S. Merza. B.D.S, M.Sc. Ph.D Abstract Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma is an
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer 2 The So Called Pre-Neoplastic Lesions and Carcinoma In Situ
 Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Clinico-pathological Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Keywords :
 29 2 14 4 Clinico-pathological Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Yasuhiko Tsuyama, Takashi Nakatsuka, Yoshiyuki Mori, Tsuyoshi Takato (Department of Plastic
29 2 14 4 Clinico-pathological Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Yasuhiko Tsuyama, Takashi Nakatsuka, Yoshiyuki Mori, Tsuyoshi Takato (Department of Plastic
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System
 Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K)
 Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES. 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH)
 INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH) Biopsy-Indications Diffuse/multifocal lesions (neoplastic, inflammatory, etc) Etiology of the
INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH) Biopsy-Indications Diffuse/multifocal lesions (neoplastic, inflammatory, etc) Etiology of the
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
