Accuracy of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients; Single Center Experience
|
|
|
- Gabriel Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surgical Science, 2018, 9, ISSN Online: ISSN Print: Accuracy of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients; Single Center Experience Waleed Elnahas 1, Omar Hamdy 1, Khaled Abdel Wahab 1*, Sameh Roshdy 1, Sara Raafat 2, Mohamed Hafez 1, Omar Farouk 1, Mohamed Elmetwally 1 1 Surgical Oncology Unit, Mansoura Oncology Centre, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt 2 Pathology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt How to cite this paper: Elnahas, W., Hamdy, O., Wahab, K.A., Roshdy, S., Raafat, S., Hafez, M., Farouk, O. and Elmetwally, M. (2018) Accuracy of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients; Single Center Experience. Surgical Science, 9, Received: December 8, 2017 Accepted: January 28, 2018 Published: January 31, 2018 Copyright 2018 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0). Open Access Abstract Purpose: Most important factor affecting prognosis of breast cancer is axillary nodal involvement. Several studies evaluated the accuracy of Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients post neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In this study, we will examine accuracy and feasibility of using Sentinel lymph node biopsy in predicting axillary lymph node status in breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Methods: 45 female patients with resectable, nonmetastatic breast carcinoma cases who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy were enrolled in this study according to the routine Mansoura Oncology Center guidelines of management of breast cancer. Methylene blue dye used for detection of Sentinel lymph node. Results: Successful Sentinel lymph node detection was 82.2%. Skin involvement (T4 disease) were linked to a low identification (P = 0.005). False negative rate equals 11/27 = (40.7%).With advancement of the stage of the tumor, the incidence of false negative results increases significantly (p = 0.012) with 95% confidence interval; Conclusion: Sentinel lymph node should be adopted to be the standard method for axillary staging with T1-3 tumors after receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy, in T4 patients, it is associated with low detection rate & high false negative rate making it doubtful technique for axillary staging. Keywords Breast Cancer, Sentinel Lymph Node, Neo Adjuvant Chemotherapy, Blue Dye 1. Introduction The prognosis of breast cancer patients depends mainly on many factors in- DOI: /ss Jan. 31, Surgical Science
2 cluding tumor characteristics especially its size, histological grade, hormonal receptor status & patients age at the time of diagnosis as well as axillary nodal status. However, the most important factor among all of these is axillary nodal involvement, which carries a major impact on 5-year survival rate [1]. For axillary nodal involvement, axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) was considered the optimal care. But, it was also linked with several problems including lymphedema, numbness, pain, impaired shoulder girdle movement and overall affection of quality of life. These complications were a driving force towards a less invasive technique for axillary staging [2]. For years now, Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy in early breast cancer is a routine practice as it provides an accurate & less morbid method for staging preventing the undesirable problems of routine axillary lymph node clearance [3]. Nowadays, neoadjuvant chemotherapy gained popularity and became the first option in dealing with locally advanced breast cancer as well as its progressive usage with T2 breast cancer. Although there was no increase in disease-free survival or overall survival, neoadjuvant chemotherapy has been proven to carry many advantages such as downstaging of inoperable disease & facilitating respectability and conservative breast surgery, in vivo testing of systemic therapy modalities [4] [5]. Accuracy and feasibility of using SNL biopsy after administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is debatable issue; some authors postulated that chemotherapy may change the lymphatic pathway, which can affect on the identification rate [6]. Several studies have assessed the accuracy and feasibility of this technique, but diagnostic accuracy has been varied [7]. In the present study, we will evaluate the feasibility and reliability of SLNB in predicting axillary lymph node status in breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. 2. Methods This is a prospective clinical study done during the period from September 2014 to May 2016 where 45 female patients with resectable, nonmetastatic breast carcinoma cases who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy and appeared to have negative axillae clinically and by radiological assessment were enrolled according to the routine Oncology Center-Mansoura University s guidelines of management of breast cancer. Approval from the ethical committee in Faculty of medicine, Mansoura University was obtained before starting the trial. Patients with the following criteria were excluded from the study: Unfit patients for general anaesthesia. Previous axillary surgery. History of breast surgery or incisional biopsy compromising the breast lymphatic drainage. DOI: /ss Surgical Science
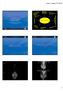
3 Known hypersensitivity to the dye. Patients who received neoadjuvant hormonal therapy. Patients with clinicaly positive or suspicious axilla after neaodjuvant therapy All Patients were assessed carefully on clinical and radiological basis before administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. All patients received doxorubicin and/or Taxan-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Management strategies for those patients were reviewed at the weekly multi-disciplinary breast team in Mansoura oncology center. Patients who satisfied the inclusion criteria were subjected to breast surgery after discussing with the patient and explaining all the available procedures (modified radical mastectomy, conservative breast surgery or immediate reconstruction), sentinel lymph node biopsy and classic axillary lymph node dissection. Intraoperative lymphatic mapping was performed after periareolar injection of 2 to 10 ml of sterile methylene blue dye, and then breast massage for 15 minutes. After the administration of anesthesia, the planned incision was marked on the skin of the affected breast. An incision planned just below the axillary hairline to be used as the same incision for axillary dissection in patients planned for breast conserving surgery or to be extended to perform the mastectomy incision in other cases that were planned to perform a more radical surgery. The blue stained lymphatic pathways were identified (Figure 1) and followed up to the blue SNL which was identified (Figure 2 and Figure 3) by its color and sent for frozen section. Figure 1. Sentinel LN with blue colored lymphatics passing towards it. Figure 2. Sentinel LN identification. DOI: /ss Surgical Science
4 3. Results Figure 3. Specimen including single sentinel LN for HPE. The median patient age at the time of diagnosis was 50.2 years (20-71). As regard the primary tumor size before and after receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy; out of the 45 patients, 23 were T4 before starting chemotherapy, 8 were T3, 13 were T2 and only one was T1 (reported to be metastatic from the time of diagnosis, proved later on to be non-metastatic) with percentage of cases about 51.1%, 17.7%, 28.8%, and 2.2% respectively. After receiving neoadjuvant therapy 4 patients achieved complete clinical response, 12 became T1, number of T2 tumors became 18, T3 and T4 tumors was only one and 10 consequently (Table 1). As regard the state of lymph node pre and post receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy; 18 patients were node negative, 24 were N1, 2 were N2 and one was N3a. All the patients were node negative after neoadjuvant therapy. As regard the tumor pathological response to chemotherapy, 40 patients had residual malignant disease after preoperative chemotherapy, and, in five patients, there was a complete pathological response to chemotherapy. Those forty patients were listed as follow according to their histopathological type: 33 with IDC, 3 patients with invasive lobular carcinoma, 2 patients with DCIS, 1 patient with colloid carcinoma and another one with metaplastic carcinoma. All 45 patients underwent attempted lymphatic mapping with methylene blue dye and SLN biopsy. Overall, there were 37 successful SNL detection (82.2%) and eight unsuccessful detection (17.8%). Univariate analysis of clinicopathologic features revealed that persistent skin involvement (T4 disease) after neoadjuvant therapy was linked significantly with a decreased probability to identify SLN (P = 0.005). if T1-3 & T4 tumors (after NAC) identification rate was calculated independently, the result will differ as follows; T1-3 tumors (after NAC); SLN was identified in 34 out of 35 patients giving percentage of 97.1% while in T4 tumors (after NAC); SLN was identified only in 3 out of 10 patients giving percentage of 30%. Patient age, tumor site and initial lymph node tumor burden were not correlated with successful lymphatic identification. DOI: /ss Surgical Science
5 Table 1. Illustrates the tumor and lymph node staging before and after neo adjuvant chemotherapy characteristics. T stage Before chemotherapy (no) After chemotherapy (no) T0 (ccr) 0 4 T T T3 8 1 T N stage Before chemotherapy (no) After chemotherapy (no) N N N2 2 0 N3 1 0 Among the 37 cases where SLN could be detected and sent for histopathological examination, the result in 27 patients was negative for tumor deposits while was positive in 10 patients only (one of them showed micrometastasis) and it was the only positive node in one patient. On the other hand, as regard the final pathology of axillary lymph node dissection (ALND), 17 patients showed negative axillae, while 20 patients showed positive tumor deposits in the dissected axillary LNs. One of them was the only positive node. This means that the total false negative rate equals 11/21 = (52%). Calculating false negative results according to the stage revealed that with advancement of the stage of the tumor, the incidence of false negative results increases significantly (P = 0.012) with 95% confidence interval; ; When false negative rate was calculated separately for patients who were T4 before NAC, the results were as follow: T4 group: fnr equals 9/13 = 69% while in T1-3 group: fnr equals 2/7 = 28%. The accuracy of frozen section in examination of sentinel LNs was 100%. All the frozen section results were exactly as the paraffin. No allergic reactions, short or long-term complications were recorded for the maneuver. 4. Discussion Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy in early breast cancer is referred to nowadays as the standard of care as it provides an accurate & less morbid method for staging avoiding the undesirable complications of routine axillary clearance [3]. SLN identification can be performed with equal success rates using methylene blue and patent blue dyes. Methylene blue can be used as a cost-effective technique in economically less developed countries [8]. Methylene blue dye is a cheap, efficient alternative for patent blue dye with DOI: /ss Surgical Science
6 less allergic reactions in performing sentinel LN biopsy. The technique was first described for axillary staging in breast cancer using blue dye in 1994 by Giuliano et al. with identification rate in 66% of cases & accuracy rate of 96% [9]. Usage of Gamma probe to identify SLN was performed in 1993 by Krag et al. 82% identification rate [10]. It has also been proved that the combination between two methods is much more sensitive, specific & accurate in prediction of the axillary nodal status [11]. As regard the method used for lymphatic mapping in our study, it was methylene blue due to non-availability of either radioactive material or patent blue dye. Although the combined technique offers more rapid identification of SLN, the methylene blue dye technique alone can be used efficiently in centers which do not own nuclear medicine facilities [12]. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy was considered as a contraindication to SLNB. Schwartz et al, in 2003, suggested that neoadjuvant chemotherapy should not be an absolute contraindication to SLNB. Their study conducted on 21 patients showed an identification percent of 95% and a false negative result in only one patient [13]. The first published meta-analysis was that of Xing et al. They included articles discussing the issue of the accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy in cases that have received neo adjuvant chemotherapy. Articles that fit their inclusion criteria were 21 comprising about 1273 patients. The identification rates reported ranged from 72 to 100%, with reported sensitivity of about 67% to 100%. They stated at the end of their study that we can use SNLB in patients that had received neoadjuvant chemotherapy with good reliability [14]. Also, Kelly and his team collected results of about 24 trials with a total number of cases of about 1799 subjects. They found an identification rate of about 89.6% with the false-negative rate was about 8.4%. They had a conclusion that such a technique after neoadjuvant chemotherapy showed high accuracy and feasibility for axillary staging [15]. This was nearly the same conclusion that was stated by Van Deurzen et al. where the SLN identification rate was 90.9% with false-negative rate was about 10.5%. They just added that there is still inadequate evidence to recommend it as the standard procedure [16]. A Prospective German, multi-institutional SENTINA-Trial performed on cases that were converted from positive to negative nodes post neo adjuvant chemo therapy declared that detection rate for the SLNB was significantly lower when these cases were compared to others who underwent SLNB before any other treatment. They clearly stated in their conclusion that administration of systemic therapy significantly affects the accuracy of SLNB [17]. Issues that may affect detection of sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be: a proposed change in the lymphatic channels post systemic therapy. Recent study showed that although the location of sentinel nodes DOI: /ss Surgical Science
7 was not affected by NAC, nearly one third of the sentinel lymphatic pathways were modified [18]. In our study, the identification rate in Stage III B & C (tumors with skin involvement) was nearly 30%. In 2000, two studies were published concerning the issue of SNLB post neoadjuvant chemotherapy; Nason et al. published their study on 82 patients who underwent SLNB followed by level I-II ALND. SLNs were successfully identified in 80% of patients with a false negative rate of 33% (3 patients). They had a conclusion that NAC was associated with high false negative rate [19]. Breslin et al. reported their study conducted on 51 patients with stage II or III breast cancer who received doxorubicin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The study was conducted from 1994 to 1999 with detection rate improving from 64.7% to 94.1% and a false-negative rate of 6% [20]. Stearns et al., in 2002, reported their study conducted on 34 patients with breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy with detection rate of 85 and a false-negative rate of 14%. Among the subgroup without inflammatory breast cancer, the detection and false-negative rates were 89% and 6%, respectively. They concluded that SLNB after neoadjuvant chemotherapy may accurately predict axillary staging except in inflammatory breast cancer [21]. In our study, the detection rate equals 82.2% (37/45). The only significant non-technical factor which could be identified as a possible cause for non-identification of sentinel LNs was persistence of skin manifestations (especially peau de orange) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients who were first presented by T4 lesions before chemotherapy. When T1-3 & T4 tumors (after NAC) identification rate was calculated independently, the result differed radically; in T1-3 tumors (after NAC); SLN was identified in 34 out of 35 patients giving percentage of 97.1% and in T4 tumors (after NAC); SLN was identified only in 3 out of 10 patients giving percentage of 30%. The most probable explanation for that result is that one of the pathological characters of T4 breast cancer is invasion of dermal lymphatic by tumor emboli, which can lead to lymphatic obstruction causing the clinical picture of peau d orange, rapid breast enlargement and diffuse erythema [22]. This copes with the recently published systematic review and meta-analysis of the accuracy & feasibility of SLNB after NAC in locally advanced breast cancer enrolling 7451 patients were included. Identification rate was 89.6%, which is lower than the 95% identification rate observed in recent series of early breast cancer. These findings highlight the limits of SNB performance in this population [23]. The factors affecting the rate of false negative results during are multiple including SLNB technique, variability in lymphatic drainage pathway, level of surgeon experience and patient selection [24]. Among many factors affecting false negative result (fnr), increased surgical experience as well as choosing suitable technique of SLNB may bring down the high fnr to an acceptable minimum [25]. According to the ACOSOG Z1071 trial, factors affecting the accuracy of SLNB DOI: /ss Surgical Science
8 after neoadjuvant chemotherapy could be identified. Tumor factors (clinical T or N stage), patient factors (age, BMI), length of chemotherapy treatment, nodal response to chemotherapy and site of injection did not significantly affect the SLN identification rate. The SLN identification rate was higher when mapping was performed using a dual-agent mapping technique vs a single-agent mapping technique. It was also found that the false negative rate was lower when 3 or more SLNs are examined vs only 2 SLNs [26] [27]. Reports from the Dutch breast cancer trialists group (BOOG), on their study on 657 patients, showed that in patients who converted after neoadjuvant chemotherapy from cn+ to cn0, the false negative rate was 20% [28]. In our study, false negative rate equals 52% which is too high in comparison to other published studies. False negative rate for T4 group equals 69% while in T1-3 group equals 28% This may be attributed to: Relatively small sample size, Lymphatic obstruction in the T4 group and, may be, the presence of learning curve; the two false negative cases in T1-3 group were in the first half of the study, in the second half, the fnr for T1-3 group was 0%. The main Limitations of our study were the relative small sample size, Lymphatic obstruction in the T4 group which represents 22 patients out of the 45 included in the study (48.8%). This high ratio can be explained by absence of widely applied screening programs and delayed seeking of medical advice by many patients which lead to facing an advanced tumor at the time of diagnosis, and lastly, Presence of learning curve; the two false negative cases in T1-3 group were in the first half of the study, in the second half, the fnr for T1-3 group was 0%. 5. Conclusion SLNB should be adopted to be the standard method for axillary staging in breast cancer patients with T1-3 tumors after receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy while SLNB is patients with T4 breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is associated with low detection rate & high false negative rate making it doubtful technique for axillary staging. References [1] Gherghe, M., Bordea, C. and Blidaru, A. (2014) Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB) vs. Axillary Lymph Node Dissection (ALND) in the Current Surgical Treatment of Early Stage Breast Cancer. Journal of Medicine and Life, 8, [2] Khavanin, N., Gart, M.S., Berry, T., Thornton, B., Saha, S. and Kim, J.Y. (2014) Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy versus Axillary Lymphadenectomy in Patients Treated with Lumpectomy: An Analysis of Short-Term Outcomes. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 21, [3] Tsujimoto, M. (2015) Recent Advances in Sentinel Node Biopsy in Breast Surgery. Breast Cancer, 22, [4] Holmes, D., Colfry, A., Czerniecki, B., Dickson-Witmer, D., Espinel, C. F., Feldman, E. and Kuerer, H. (2015) Performance and Practice Guideline for the Use of DOI: /ss Surgical Science
9 Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy in the Management of Breast Cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 22, [5] Mamounas, E.P. (2015) Impact of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Locoregional Surgical Treatment of Breast Cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 22, [6] Benson, J.R. and Jatoi, I. (2014) Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Future Oncology, 10, [7] Yagata, H., Yamauchi, H., Tsugawa, K., Hayashi, N., Yoshida, A., Kajiura, Y. and Nakamura, S. (2013) Sentinel Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Cytologically Proven Node-Positive Breast Cancer. Clinical Breast Cancer, 13, [8] Srivastava, A. and Misra, M. (2012) In Search of a Cost-Effective Sentinel Node Biopsy Technique: A Randomized Trial Comparing the Use of Methylene Blue and Patent Blue Violet to Identify Sentinel Node in Breast Cancer. Cancer Research, 72, [9] Giuliano, A.E., Kirgan, D.M., Guenther, J.M. and Morton, D.L. (1994) Lymphatic Mapping and Sentinel Lymphadenectomy for Breast Cancer. Annals of Surgery, 220, [10] Krag, D., Weaver, D., Alex, J., Fairbank, J., et al. (1993) Surgical Resection and Radiolocalization of the Sentinel Lymph Node in Breast Cancer Using a Gamma Probe. Surgical Oncology, 2, [11] Motomura, K. (2015) Sentinel Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer: Past, Present, and Future. Breast Cancer, 22, [12] Varghese, P., Mostafa, A., Abdel-Rahman, A., Akberali, S., Gattuso, J., Canizales, A. and Carpenter, R. (2007) Methylene Blue Dye versus Combined Dye-Radioactive Tracer Technique for Sentinel Lymph Node Localisation in Early Breast Cancer. European Journal of Surgical Oncology (EJSO), 33, [13] Schwartz, G.F. and Meltzer, A.J. (2003) Accuracy of Axillary Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Following Neoadjuvant (Induction) Chemotherapy for Carcinoma of the Breast. The Breast Journal, 9, [14] Xing, Y., Foy, M., Cox, D., Kuerer, H., Hunt, K. and Cormier, J. (2006) Meta-Analysis of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Preoperative Chemotherapy in Patients with Breast Cancer. British Journal of Surgery, 93, [15] Kelly, A.M., Dwamena, B., Cronin, P. and Carlos, R.C. (2009) Breast Cancer: Sentinel Node Identification and Classification after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Academic radiology, 16, [16] van Deurzen, C.H., Vriens, B.E., Tjan-Heijnen, V.C., van der Wall, E., Albregts, M., van Hilligersberg, R. and Diest, P.J. (2009) Accuracy of Sentinel Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review. European Journal of Cancer, 45, [17] Kuehn, T., Bauerfeind, I., Fehm, T., Fleige, B., Helms, G., Lebeau, A. and Schrenk, P. (2012) Abstract S2-2: Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Before or after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Final Results from the Prospective German, Multiinstitutional DOI: /ss Surgical Science
10 SENTINA-Trial. Cancer Research, 72, S2-2-S [18] Tsuyuki, S., Yamaguchi, A., Kawata, Y. and Kawaguchi, K. (2015) Assessing the Effects of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Lymphatic Pathways to Sentinel Lymph Nodes in Cases of Breast Cancer: Usefulness of the Indocyanine Green-Fluorescence Method. The Breast, 24, [19] Nason, K.S., Anderson, B.O., Byrd, D.R., Dunnwald, L.K., Eary, J.F., Mankoff, D.A. and Yeung, R.S. (2000) Increased False Negative Sentinel Node Biopsy Rates after Preoperative Chemotherapy for Invasive Breast Carcinoma. Cancer, 89, [20] Breslin, T.M., Cohen, L., Sahin, A., Fleming, J.B., Kuerer, H.M., Newman, L.A. and Feig, B.W. (2000) Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Is Accurate after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 18, [21] Stearns, V., Ewing, C.A., Slack, R., Penannen, M.F., Hayes, D.F. and Tsangaris, T.N. (2002) Sentinel Lymphadenectomy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer May Reliably Represent the Axilla except for Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Annals of surgical oncology, 9, [22] Kwon, S., Agollah, G., Wu, G. and Sevick-Muraca, E.M. (2015) Abstract P : In vivo Lymphatic Imaging of a Human Inflammatory Breast Cancer Model. Cancer Research, 75, P [23] Mocellin, S., Goldin, E., Marchet, A. and Nitti, D. (2015) Sentinel Node Biopsy Performance after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Cancer, 138, [24] Wang, Y., Dong, H., Wu, H., Zhang, L., Yuan, K., Chen, H. and Fu, R. (2015) Improved False Negative Rate of Axillary Status Using Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Ultrasound-Suspicious Lymph Node Sampling in Patients with Early Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer, 15, [25] Sekhar, G.C., Vamseedhar, K. and Babu, M.H. (2015) A Study of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Early Breast Cancer Using Methylene Blue in a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS), Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences, Vijayawada. [26] Boughey, J.C., Suman, V.J., Mittendorf, E.A., Ahrendt, G.M., Wilke, L.G., Taback, B. and Bowling, M. (2015) Factors Affecting Sentinel Lymph Node Identification Rate after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer Patients Enrolled in ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance). Annals of Surgery, 261, [27] Boughey, J.C., Suman, V.J., Mittendorf, E.A., Ahrendt, G.M., Wilke, L.G., Taback, B. and Flippo-Morton, T.S. (2013) Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Node-Positive Breast Cancer: The ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) Clinical Trial. JAMA, 310, [28] Tjan-Heijnen, V.C., Vriens, B.E., Aarts, M.J., Kroep, J.R., van de Velde, C.J., Liefers, G.-J. and de Boer, M. (2015) Abstract P : Sentinel Node Procedure before or after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Clinically Node Negative or Positive Patients; Results from 3 Phase III Studies of the Dutch Breast Cancer Trialists Group (BOOG). Cancer Research, 75, P DOI: /ss Surgical Science
Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer
 - Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
- Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
Targeting Surgery for Known Axillary Disease. Abigail Caudle, MD Henry Kuerer, MD PhD Dept. Surgical Oncology MD Anderson Cancer Center
 Targeting Surgery for Known Axillary Disease Abigail Caudle, MD Henry Kuerer, MD PhD Dept. Surgical Oncology MD Anderson Cancer Center Nodal Ultrasound at Diagnosis Whole breast and draining lymphatic
Targeting Surgery for Known Axillary Disease Abigail Caudle, MD Henry Kuerer, MD PhD Dept. Surgical Oncology MD Anderson Cancer Center Nodal Ultrasound at Diagnosis Whole breast and draining lymphatic
The Role of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Axillary Dissection
 The Role of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Axillary Dissection Henry Mark Kuerer, MD, PhD, FACS Department of Surgical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center SLN Biopsy Revolutionized surgical
The Role of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy and Axillary Dissection Henry Mark Kuerer, MD, PhD, FACS Department of Surgical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center SLN Biopsy Revolutionized surgical
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
 Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer Registrar Tutorial Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar The Royal Melbourne Hospital Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Axillary LN status important prognostic factor
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer Registrar Tutorial Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar The Royal Melbourne Hospital Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Axillary LN status important prognostic factor
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Should be Performed BEFORE Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
 The London Cancer Alliance West and South Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Should be Performed BEFORE Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Dimitri J Hadjiminas, MD, MPhil, FRCS (Consultant Breast & Endocrine Surgeon Imperial
The London Cancer Alliance West and South Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Should be Performed BEFORE Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Dimitri J Hadjiminas, MD, MPhil, FRCS (Consultant Breast & Endocrine Surgeon Imperial
Breast Cancer: Management of the Axilla in Greg McKinnon MD FRCSC SON Vancouver Oct 2016
 Breast Cancer: Management of the Axilla in 2016 Greg McKinnon MD FRCSC SON Vancouver Oct 2016 No Disclosures Principle #1 There is no point talking about surgical therapy in isolation. From a patient
Breast Cancer: Management of the Axilla in 2016 Greg McKinnon MD FRCSC SON Vancouver Oct 2016 No Disclosures Principle #1 There is no point talking about surgical therapy in isolation. From a patient
EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY
 EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY AXILLARY LYMPH NODE METASTASIS Axillary lymph node metastasis is one of the most
EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY AXILLARY LYMPH NODE METASTASIS Axillary lymph node metastasis is one of the most
16/09/2015. ACOSOG Z011 changing practice. Presentation outline. Nodal mets #1 prognostic tool. Less surgery no change in oncologic outcomes
 ACOSOG Z011 changing practice The end of axillary US/FNA? Preoperative staging of the axilla in the era of Z011 Adena S Scheer MD MSc FRCSC Surgical Oncologist, St. Michael s Hospital Assistant Professor,
ACOSOG Z011 changing practice The end of axillary US/FNA? Preoperative staging of the axilla in the era of Z011 Adena S Scheer MD MSc FRCSC Surgical Oncologist, St. Michael s Hospital Assistant Professor,
Updates on management of the axilla in breast cancer the surgical point of view
 Updates on management of the axilla in breast cancer the surgical point of view Edwige Bourstyn Centre des maladies du sein Hôpital Saint Louis Paris Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is the standard of
Updates on management of the axilla in breast cancer the surgical point of view Edwige Bourstyn Centre des maladies du sein Hôpital Saint Louis Paris Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is the standard of
Is Complete Axillary Dissection Needed Following Mastectomy and Sentinel Node Biopsy for N1 disease?
 Is Complete Axillary Dissection Needed Following Mastectomy and Sentinel Node Biopsy for N1 disease? Mylin A. Torres, MD Director, Glenn Family Breast Center Louis and Rand Glenn Family Chair in Breast
Is Complete Axillary Dissection Needed Following Mastectomy and Sentinel Node Biopsy for N1 disease? Mylin A. Torres, MD Director, Glenn Family Breast Center Louis and Rand Glenn Family Chair in Breast
Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study
 [ABS-0078] GBCC 2018 Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study Eun Young Kim 1, Kwan Ho Lee 1, Yong
[ABS-0078] GBCC 2018 Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study Eun Young Kim 1, Kwan Ho Lee 1, Yong
Surgical Considerations in Breast Cancer treated with Neoadjuvant Therapy
 Surgical Considerations in Breast Cancer treated with Neoadjuvant Therapy Rebecca Warburton MD Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia Mount Saint Joseph Hospital, Providence Health Care
Surgical Considerations in Breast Cancer treated with Neoadjuvant Therapy Rebecca Warburton MD Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia Mount Saint Joseph Hospital, Providence Health Care
Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 15: 927-931, 2005 927 Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy YOSUKE TANAKA 1, HIRONORI MAEDA 2, YASUHIRO OGAWA 3, AKIHITO NISHIOKA 3, SATOSHI
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 15: 927-931, 2005 927 Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy YOSUKE TANAKA 1, HIRONORI MAEDA 2, YASUHIRO OGAWA 3, AKIHITO NISHIOKA 3, SATOSHI
Practice of Axilla Surgery
 Summer School of Breast Disease 2016 Practice of Axilla Surgery Axillary Lymph Node Dissection & Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy 연세의대외과 박세호 Contents Anatomy of the axilla Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND)
Summer School of Breast Disease 2016 Practice of Axilla Surgery Axillary Lymph Node Dissection & Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy 연세의대외과 박세호 Contents Anatomy of the axilla Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND)
Donna Plecha, MD 1, Shiyu Bai, BS 2, Helen Patterson 3, Cheryl Thompson, PhD 4, and Robert Shenk, MD 5
 Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-015-4527-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Improving the Accuracy of Axillary Lymph Node Surgery in Breast Cancer with Ultrasound-Guided Wire Localization of Biopsy Proven
Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-015-4527-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Improving the Accuracy of Axillary Lymph Node Surgery in Breast Cancer with Ultrasound-Guided Wire Localization of Biopsy Proven
Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Node-Positive Breast Cancer The ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) Clinical Trial
 Research Original Investigation Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Node-Positive Breast Cancer The ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) Clinical Trial Judy C. Boughey, MD; Vera
Research Original Investigation Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Node-Positive Breast Cancer The ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) Clinical Trial Judy C. Boughey, MD; Vera
Surgical Issues in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
 14 th Bossche Mamma Congress Ruwenbergstraat 7 5271 AG Sint Michielsgestel June 14, 2016 Surgical Issues in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Tari A. King MD FACS Chief, Breast Surgery Dana Farber/Brigham and Women
14 th Bossche Mamma Congress Ruwenbergstraat 7 5271 AG Sint Michielsgestel June 14, 2016 Surgical Issues in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Tari A. King MD FACS Chief, Breast Surgery Dana Farber/Brigham and Women
Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial
 DCIS and Early Breast Cancer Symposium JUNE 15-17 2012 CAPPADOCIA Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Professor of Surgery Axillary Node Dissection Staging, Regional control, Survival
DCIS and Early Breast Cancer Symposium JUNE 15-17 2012 CAPPADOCIA Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Professor of Surgery Axillary Node Dissection Staging, Regional control, Survival
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer
 Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation
 Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm
 Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
Breast Surgery When Less is More and More is Less. E MacIntosh, MD June 6, 2015
 Breast Surgery When Less is More and More is Less E MacIntosh, MD June 6, 2015 Presenter Disclosure Faculty: E. MacIntosh Relationships with commercial interests: None Mitigating Potential Bias Not applicable
Breast Surgery When Less is More and More is Less E MacIntosh, MD June 6, 2015 Presenter Disclosure Faculty: E. MacIntosh Relationships with commercial interests: None Mitigating Potential Bias Not applicable
Review Article Controversial Indications for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Patients
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 405949, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/405949 Review Article Controversial Indications for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Patients
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 405949, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/405949 Review Article Controversial Indications for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Patients
Recent Update in Surgery for the Management of Breast Cancer
 Recent Update in Surgery for the Management of Breast Cancer Wonshik Han, MD, PhD Professor, Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine Chief of Breast Care Center, Seoul National
Recent Update in Surgery for the Management of Breast Cancer Wonshik Han, MD, PhD Professor, Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine Chief of Breast Care Center, Seoul National
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Is Valuable For All Cancer. Surgery Grand Rounds Debate October 6, 2008 Joel Baumgartner
 Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Is Valuable For All Cancer Surgery Grand Rounds Debate October 6, 2008 Joel Baumgartner History Lymphatics first described by Rasmus Bartholin in 1653 Rudolf Virchow postulated
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Is Valuable For All Cancer Surgery Grand Rounds Debate October 6, 2008 Joel Baumgartner History Lymphatics first described by Rasmus Bartholin in 1653 Rudolf Virchow postulated
Surgical Management of the Axilla
 Surgical Management of the Axilla Jean-Francois Boileau, MD, MSc, FRCSC Surgical Oncologist, Montreal Jewish General Hospital Segal Cancer Centre Associate Member, Department of Oncology, McGill University
Surgical Management of the Axilla Jean-Francois Boileau, MD, MSc, FRCSC Surgical Oncologist, Montreal Jewish General Hospital Segal Cancer Centre Associate Member, Department of Oncology, McGill University
CURRENT CONTROVERSIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Less or more!?
 CURRENT CONTROVERSIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Less or more!? I have no Disclosures Wolfgang Gatzemeier Breast Unit Milan, Italy 17th ESO-ESMO- EONS Masterclass in Clinical Oncology 24-29 MARCH 2018 Optimal
CURRENT CONTROVERSIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Less or more!? I have no Disclosures Wolfgang Gatzemeier Breast Unit Milan, Italy 17th ESO-ESMO- EONS Masterclass in Clinical Oncology 24-29 MARCH 2018 Optimal
Is Sentinel Node Biopsy Practical?
 Breast Cancer Is Sentinel Node Biopsy Practical? Benefits and Limitations JMAJ 45(10): 444 448, 2002 Shigeru IMOTO *1, Satoshi EBIHARA *2 and Noriyuki MORIYAMA *3 *1 Breast Surgery Division, National Cancer
Breast Cancer Is Sentinel Node Biopsy Practical? Benefits and Limitations JMAJ 45(10): 444 448, 2002 Shigeru IMOTO *1, Satoshi EBIHARA *2 and Noriyuki MORIYAMA *3 *1 Breast Surgery Division, National Cancer
Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath
 DOI 10.1007/s00268-014-2752-3 BRIEF ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath E.
DOI 10.1007/s00268-014-2752-3 BRIEF ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath E.
M D..,., M. M P.. P H., H, F. F A.. A C..S..
 Implications of NSABP B-32 and Loco-Regional Therapy Considerations After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H, F.A.C.S. Professor of Surgery Northeastern Ohio Medical University Medical
Implications of NSABP B-32 and Loco-Regional Therapy Considerations After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H, F.A.C.S. Professor of Surgery Northeastern Ohio Medical University Medical
Surgical Advances in the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Laura Kruper, MD, MSCE Chief, Breast Surgery
 Surgical Advances in the Treatment of Breast Cancer Laura Kruper, MD, MSCE Chief, Breast Surgery Nothing to disclose DISCLOSURE LESS IS MORE Radiation Lymph nodes Reconstruction Less is More! Radiation
Surgical Advances in the Treatment of Breast Cancer Laura Kruper, MD, MSCE Chief, Breast Surgery Nothing to disclose DISCLOSURE LESS IS MORE Radiation Lymph nodes Reconstruction Less is More! Radiation
Debate Axillary dissection - con. Prof. Dr. Rodica Anghel Institute of Oncology Bucharest
 Debate Axillary dissection - con Prof. Dr. Rodica Anghel Institute of Oncology Bucharest Summer School of Oncology, third edition Updated Oncology 2015: State of the Art News & Challenging Topics Bucharest,
Debate Axillary dissection - con Prof. Dr. Rodica Anghel Institute of Oncology Bucharest Summer School of Oncology, third edition Updated Oncology 2015: State of the Art News & Challenging Topics Bucharest,
Sentinel Node Biopsy, Introduction and Application of the Technique in a Senology Unit of a District Hospital - Prospective Study.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 20 Number 2 Sentinel Node Biopsy, Introduction and Application of the Technique in a Senology Unit of a District Hospital - Prospective Study. Z Sidiropoulou,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 20 Number 2 Sentinel Node Biopsy, Introduction and Application of the Technique in a Senology Unit of a District Hospital - Prospective Study. Z Sidiropoulou,
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Correspondence should be addressed to Donald R. Lannin;
 Hindawi Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 5924802, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5924802 Research Article Intraoperative Injection of Technetium-99m Sulfur Colloid for Sentinel
Hindawi Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 5924802, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5924802 Research Article Intraoperative Injection of Technetium-99m Sulfur Colloid for Sentinel
Indications and Technical Considerations for Adjuvant Radiation after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
 Indications and Technical Considerations for Adjuvant Radiation after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Wendy A. Woodward, M.D. Ph.D. A sociate Profesor Section Chief, Breast Radiation Oncology
Indications and Technical Considerations for Adjuvant Radiation after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Wendy A. Woodward, M.D. Ph.D. A sociate Profesor Section Chief, Breast Radiation Oncology
Management of the Axilla at Initial Surgery Manejo da Axila em Cirurgia Inicial
 DISCIPLINA DE MASTOLOGIA ESCOLA PAULISTA DE MEDICINA UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE SÃO PAULO Management of the Axilla at Initial Surgery Manejo da Axila em Cirurgia Inicial Disciplina de Mastologia Prof. Dr.
DISCIPLINA DE MASTOLOGIA ESCOLA PAULISTA DE MEDICINA UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE SÃO PAULO Management of the Axilla at Initial Surgery Manejo da Axila em Cirurgia Inicial Disciplina de Mastologia Prof. Dr.
Yue Yu 1,2, Ning Cui 1,2, Heng-Yu Li 1,2, Yan-Mei Wu 1,2,LuXu 1,2, Min Fang 1,2 and Yuan Sheng 1,2*
 Yu et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:808 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2829-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: retrospective comparative evaluation of clinically
Yu et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:808 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2829-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: retrospective comparative evaluation of clinically
Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 160:387 391 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-4017-3 EDITORIAL Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery Monika Brzezinska 1 Linda J.
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 160:387 391 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-4017-3 EDITORIAL Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery Monika Brzezinska 1 Linda J.
Axillary ultrasound is frequently used to assess axillary nodes at
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification and Resection of Clipped Node Decreases the False-negative Rate of Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery in Patients Presenting With Node-positive Breast Cancer (T0 T4, N1 N2) Who
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification and Resection of Clipped Node Decreases the False-negative Rate of Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery in Patients Presenting With Node-positive Breast Cancer (T0 T4, N1 N2) Who
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Radionuclide detection of sentinel lymph node
 Radionuclide detection of sentinel lymph node Sophia I. Koukouraki Assoc. Professor Department of Nuclear Medicine Medicine School, University of Crete 1 BACKGROUND The prognosis of malignant disease is
Radionuclide detection of sentinel lymph node Sophia I. Koukouraki Assoc. Professor Department of Nuclear Medicine Medicine School, University of Crete 1 BACKGROUND The prognosis of malignant disease is
Savitri Krishnamurthy, MD 1
 EVOLVING TRENDS IN PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES IN BREAST CANCER Savitri Krishnamurthy, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center AXILLARY
EVOLVING TRENDS IN PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES IN BREAST CANCER Savitri Krishnamurthy, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center AXILLARY
EDITORIAL. Ann Surg Oncol (2011) 18: DOI /s
 Ann Surg Oncol (2011) 18:2407 2412 DOI 10.1245/s10434-011-1593-7 EDITORIAL Multidisciplinary Considerations in the Implementation of the Findings from the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (ACOSOG)
Ann Surg Oncol (2011) 18:2407 2412 DOI 10.1245/s10434-011-1593-7 EDITORIAL Multidisciplinary Considerations in the Implementation of the Findings from the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (ACOSOG)
Role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in assessing the cancer spread to axilla in early breast cancer
 International Surgery Journal Gumber A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jan;4(1):53-57 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20164445
International Surgery Journal Gumber A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jan;4(1):53-57 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20164445
BREAST CANCER SURGERY. Dr. John H. Donohue
 Dr. John H. Donohue HISTORY References to breast surgery in ancient Egypt (ca 3000 BCE) Mastectomy described in numerous medieval texts Petit formulated organized approach in 18 th Century Improvements
Dr. John H. Donohue HISTORY References to breast surgery in ancient Egypt (ca 3000 BCE) Mastectomy described in numerous medieval texts Petit formulated organized approach in 18 th Century Improvements
Use of the dye guided sentinel lymph node biopsy method alone for breast cancer metastasis to avoid unnecessary axillary lymph node dissection
 456 Use of the dye guided sentinel lymph node biopsy method alone for breast cancer metastasis to avoid unnecessary axillary lymph node dissection TOMOKO TAKAMARU 1, GORO KUTOMI 1, FUKINO SATOMI 1, HIROAKI
456 Use of the dye guided sentinel lymph node biopsy method alone for breast cancer metastasis to avoid unnecessary axillary lymph node dissection TOMOKO TAKAMARU 1, GORO KUTOMI 1, FUKINO SATOMI 1, HIROAKI
Introduction. Hy-De Lee, MD, PhD 1 Sung Gwe Ahn, MD 1 Seung Ah Lee, MD 2 Hak Min Lee, MD 1 Joon Jeong, MD, PhD 1
 pissn 1598-2998, eissn 2005-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 2015;47(1):26-33 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.208 Open Access Prospective Evaluation of the Feasibility of Sentinel Lymph Node
pissn 1598-2998, eissn 2005-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 2015;47(1):26-33 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.208 Open Access Prospective Evaluation of the Feasibility of Sentinel Lymph Node
Surgical Considera0ons with Neoadjuvant Treatment in Breast Cancer
 Surgical Considera0ons with Neoadjuvant Treatment in Breast Cancer David R McCready MD MSc FRCSC FACS GaAuso Chair in Breast Surgical Oncology Professor of Surgery, University of Toronto Princess Margaret
Surgical Considera0ons with Neoadjuvant Treatment in Breast Cancer David R McCready MD MSc FRCSC FACS GaAuso Chair in Breast Surgical Oncology Professor of Surgery, University of Toronto Princess Margaret
Salem, Tamilnadu, India. )
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. V (June. 2016), PP 30-36 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Accuracy of Sentinel Node
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. V (June. 2016), PP 30-36 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Accuracy of Sentinel Node
IJC International Journal of Cancer
 IJC International Journal of Cancer Sentinel node biopsy performance after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis Simone Mocellin, Elena Goldin,
IJC International Journal of Cancer Sentinel node biopsy performance after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis Simone Mocellin, Elena Goldin,
Canadian Scientific Journal. Intraoperative color detection of lymph nodes metastases in thyroid cancer
 Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Intraoperative color detection of lymph nodes metastases in thyroid
Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Intraoperative color detection of lymph nodes metastases in thyroid
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Page 1. AHN-JHU Breast Cancer Symposium. Novel Local Regional Clinical Trials. Background. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Benefit.
 AHN-JHU Breast Cancer Symposium Novel Local Regional Clinical Trials March 22, 2019 Thomas B. Julian, MD, FACS Associate Medical Director, Cancer Program Development, ANH Cancer Institute Background In
AHN-JHU Breast Cancer Symposium Novel Local Regional Clinical Trials March 22, 2019 Thomas B. Julian, MD, FACS Associate Medical Director, Cancer Program Development, ANH Cancer Institute Background In
Evolution of Breast Surgery
 Evolution of Breast Surgery Natasha Rueth MD Surgical Oncologist Piper Breast Center and Alina Health Surgical Specialists Minneapolis, MN Definitions Radical Mastectomy: Removal of breast, chest muscles,
Evolution of Breast Surgery Natasha Rueth MD Surgical Oncologist Piper Breast Center and Alina Health Surgical Specialists Minneapolis, MN Definitions Radical Mastectomy: Removal of breast, chest muscles,
Page 1. AD vs. no AD. Survival. Randomized Trials. All trials reported higher survival in the AD group. Years. Node-NegativeNegative
 Sentinel Node Biopsy: The Past, The Present, and The Future Thomas B. Julian, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Human Oncology Drexel University College of Medicine Director of Breast Surgical Oncology
Sentinel Node Biopsy: The Past, The Present, and The Future Thomas B. Julian, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Human Oncology Drexel University College of Medicine Director of Breast Surgical Oncology
Breast Imaging. Jamie L. Wagner, DO, FACOS. Digital vs Analog Mammography (2-D) Surgical Oncologist. Patient with Cancer. Radiology/ Interventional
 Breast Cancer Prevention, Treatment, and Survivorship Jamie L. Wagner, DO, FACOS Assistant Professor Chief, Division of Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Anesthesiology Surgical Oncologist Patient with
Breast Cancer Prevention, Treatment, and Survivorship Jamie L. Wagner, DO, FACOS Assistant Professor Chief, Division of Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Anesthesiology Surgical Oncologist Patient with
Sentinel lymph node biopsy under local anesthesia in patients with breast cancer
 Review Article Sentinel lymph node biopsy under local anesthesia in patients with breast cancer Prakasit Chirappapha 1,2, Visnu Lohsiriwat 1,3, Youwanush Kongdan 2, Panuwat Lertsithichai 2, Thongchai Sukarayothin
Review Article Sentinel lymph node biopsy under local anesthesia in patients with breast cancer Prakasit Chirappapha 1,2, Visnu Lohsiriwat 1,3, Youwanush Kongdan 2, Panuwat Lertsithichai 2, Thongchai Sukarayothin
Prospective study found that peripheral lymph node sampling reduced the false negative rate of sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-016-0099-x Chinese Journal of Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Prospective study found that peripheral lymph node sampling reduced the false negative rate of sentinel lymph node biopsy
DOI 10.1186/s40880-016-0099-x Chinese Journal of Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Prospective study found that peripheral lymph node sampling reduced the false negative rate of sentinel lymph node biopsy
Quality ID #264: Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #264: Sentinel Lymph de Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Quality ID #264: Sentinel Lymph de Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Relevance. Axillary Node Recurrence. Purpose. Case Presentation: Is axillary staging required? Two trends have emerged:
 Axillary Node Recurrence N.L. Davis Associate Professor of Surgery, UBC Head of Surgical Oncology, BCCA Relevance In an attempt to minimize long term complications and to maximize cancer control, the management
Axillary Node Recurrence N.L. Davis Associate Professor of Surgery, UBC Head of Surgical Oncology, BCCA Relevance In an attempt to minimize long term complications and to maximize cancer control, the management
Problems in staging breast carcinoma
 Problems in staging breast carcinoma Primary systemic therapy (PST) of breast carcinoma pathologists tasks Dr. Janina Kulka, 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Budapest Austro-Hungarian
Problems in staging breast carcinoma Primary systemic therapy (PST) of breast carcinoma pathologists tasks Dr. Janina Kulka, 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Budapest Austro-Hungarian
2019 COLLECTION TYPE: MIPS CLINICAL QUALITY MEASURES (CQMS) MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #264: Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Appropriate Use of Healthcare 2019 COLLECTION TYPE:
Quality ID #264: Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Appropriate Use of Healthcare 2019 COLLECTION TYPE:
Applicability of the ACOSOG Z0011 Criteria in Women with High-Risk Node-Positive Breast Cancer Undergoing Breast Conserving Surgery
 Ann Surg Oncol (2015) 22:1128 1132 DOI 10.1245/s10434-014-4090-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Applicability of the ACOSOG Z0011 Criteria in Women with High-Risk Node-Positive Breast Cancer Undergoing
Ann Surg Oncol (2015) 22:1128 1132 DOI 10.1245/s10434-014-4090-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Applicability of the ACOSOG Z0011 Criteria in Women with High-Risk Node-Positive Breast Cancer Undergoing
Sentinel Lymph Node Detection in Early Carcinoma Breast: A Comparative Study Between Intralesional and Perilesional Dye Injection
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 11 (2015) pp: 11-15 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Sentinel Lymph Node
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 2~ Issue 11 (2015) pp: 11-15 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Sentinel Lymph Node
Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary Lymph Node Involvement In Breast Carcinoma
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema
 Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema Nathalie Johnson,MD,FACS Medical Director, Legacy Cancer Institute and Breast Health Centers Portland,Oregon Objectives for Learning Understand
Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema Nathalie Johnson,MD,FACS Medical Director, Legacy Cancer Institute and Breast Health Centers Portland,Oregon Objectives for Learning Understand
Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma. Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA)
 The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) 6 th leading cause of cancer among men and women 68,720 new cases of invasive melanoma in 2009 8,650 deaths from melanoma
The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) 6 th leading cause of cancer among men and women 68,720 new cases of invasive melanoma in 2009 8,650 deaths from melanoma
Sentinel Node Biopsy. Is There Any Role for Axillary Dissection? JCCNB Nov 20, Stephen B. Edge, MD
 Sentinel Node Biopsy Is There Any Role for Axillary Dissection? JCCNB Nov 20, 2010 Tokyo, Japan Stephen B. Edge, MD Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Buffalo, NY USA SNB with Clinically
Sentinel Node Biopsy Is There Any Role for Axillary Dissection? JCCNB Nov 20, 2010 Tokyo, Japan Stephen B. Edge, MD Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Buffalo, NY USA SNB with Clinically
Mehmet Eser 1, Metin Kement 1,4*, Levent Kaptanoglu 1, Melin Gecer 2, Evrim Abamor 3, Firat Tutal 1, Salim Balin 1, Necmi Kurt 1 and Huseyin Uzun 1
 Eser et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:13 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A prospective comparative study to assess the contribution of radioisotope tracer method to dye-only method in the detection of sentinel
Eser et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:13 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A prospective comparative study to assess the contribution of radioisotope tracer method to dye-only method in the detection of sentinel
Update on Sentinel Node Biopsy in Endometrial Cancer: Feasibility, Technique, Impact
 Update on Sentinel Node Biopsy in Endometrial Cancer: Feasibility, Technique, Impact Bjørn Hagen, MD, PhD St Olavs Hospital Trondheim University Hospital Trondheim, Norway Endometrial Cancer (EC) The most
Update on Sentinel Node Biopsy in Endometrial Cancer: Feasibility, Technique, Impact Bjørn Hagen, MD, PhD St Olavs Hospital Trondheim University Hospital Trondheim, Norway Endometrial Cancer (EC) The most
Clinical Outcome of Reconstruction With Tissue Expanders for Patients With Breast Cancer and Mastectomy
 Clinical Outcome of Reconstruction With Tissue Expanders for Patients With Breast Cancer and Mastectomy Mitsui Memorial Hospital Department of Breast and Endocine surgery Daisuke Ota No financial support
Clinical Outcome of Reconstruction With Tissue Expanders for Patients With Breast Cancer and Mastectomy Mitsui Memorial Hospital Department of Breast and Endocine surgery Daisuke Ota No financial support
Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
 Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-0005-4 Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-0005-4 Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
Educational Goals and Objectives for Rotations on: Breast, Wound and Plastic Surgery
 Educational Goals and Objectives for Rotations on: Breast, Wound and Plastic Surgery Goal The goal of the Breast Surgery rotation is to develop the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary to evaluate,
Educational Goals and Objectives for Rotations on: Breast, Wound and Plastic Surgery Goal The goal of the Breast Surgery rotation is to develop the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary to evaluate,
Measure #264: Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #264: Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY DESCRIPTION: The percentage
Measure #264: Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY DESCRIPTION: The percentage
Evaluating the Z011 study and how local-regional therapy for early breast cancer may change
 Evaluating the Z011 study and how local-regional therapy for early breast cancer may change Karen Hoffman, M.D., M.H.Sc., M.P.H. Dept of Radiation Oncology The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
Evaluating the Z011 study and how local-regional therapy for early breast cancer may change Karen Hoffman, M.D., M.H.Sc., M.P.H. Dept of Radiation Oncology The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
ALND. Dr. MJ Vrancken
 ALND Dr. MJ Vrancken ALND in primary surgery se1ng Axillary lymph node dissec8on (ALND) Very nice opera8on; dorsal approach 2 ALND in primary surgery se1ng Axillary lymph node dissec8on (ALND) Very nice
ALND Dr. MJ Vrancken ALND in primary surgery se1ng Axillary lymph node dissec8on (ALND) Very nice opera8on; dorsal approach 2 ALND in primary surgery se1ng Axillary lymph node dissec8on (ALND) Very nice
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy. Issued by the Breast Team
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Issued by the Breast Team Why do my Lymph Nodes require investigation? The lymphatic system is a pathway of lymph vessels and
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Issued by the Breast Team Why do my Lymph Nodes require investigation? The lymphatic system is a pathway of lymph vessels and
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF COLON AND RECTAL CANCERS IN SENTINEL LYMPH NODE MAPPING
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp 10-14, 2007 Copyright 2007 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF COLON AND
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp 10-14, 2007 Copyright 2007 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF COLON AND
Implications of ACOSOG Z11 for Clinical Practice: Surgical Perspective
 :$;7)#*8'-87*4BCD'E7)F'31$4.$&'G$H'E7)F&'GE'>??ID >?,"'@4,$)4*,#74*8'!74/)$++'74',"$'A.,.)$'7%'()$*+,'!*42$)!7)74*67&'!3 6 August 2011 Implications of ACOSOG Z11 for Clinical
:$;7)#*8'-87*4BCD'E7)F'31$4.$&'G$H'E7)F&'GE'>??ID >?,"'@4,$)4*,#74*8'!74/)$++'74',"$'A.,.)$'7%'()$*+,'!*42$)!7)74*67&'!3 6 August 2011 Implications of ACOSOG Z11 for Clinical
Clinical outcomes after sentinel lymph node biopsy in clinically node-negative breast cancer patients
 Original Article Radiat Oncol J 4;():-7 http://dx.doi.org/.857/roj.4... pissn 4-9 eissn 4-56 Clinical outcomes after sentinel lymph node biopsy in clinically node-negative breast cancer patients Hee Ji
Original Article Radiat Oncol J 4;():-7 http://dx.doi.org/.857/roj.4... pissn 4-9 eissn 4-56 Clinical outcomes after sentinel lymph node biopsy in clinically node-negative breast cancer patients Hee Ji
Ines Buccimazza 16 TH UP CONTROVERSIES AND PROBLEMS IN SURGERY SYMPOSIUM
 BILATERAL MASTECTOMY IS NOT ROUTINELY JUSTIFIED IN PATIENTS WITH BILATERAL AXILLARY LYMPHADENOPATHY AND ONLY ONE DETECTABLE PRIMARY BREAST CANCER LESION SURGERY SYMPOSIUM Ines Buccimazza Breast Unit Department
BILATERAL MASTECTOMY IS NOT ROUTINELY JUSTIFIED IN PATIENTS WITH BILATERAL AXILLARY LYMPHADENOPATHY AND ONLY ONE DETECTABLE PRIMARY BREAST CANCER LESION SURGERY SYMPOSIUM Ines Buccimazza Breast Unit Department
Surgery for Breast Cancer
 Surgery for Breast Cancer 1750 Mastectomy - Petit 1894 Radical mastectomy Halsted Extended, Super radical mastectomy 1948 Modified radical mastectomy Patey 1950-60 WLE & RT Baclesse, Mustakallio 1981-85
Surgery for Breast Cancer 1750 Mastectomy - Petit 1894 Radical mastectomy Halsted Extended, Super radical mastectomy 1948 Modified radical mastectomy Patey 1950-60 WLE & RT Baclesse, Mustakallio 1981-85
Financial Disclosure. Learning Objectives. None. To understand the clinical applicability of the NCDB Breast Cancer PUF
 Preoperative Prediction of Node Negative Disease After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients Presenting with Node Negative or Node Positive Breast Cancer Brittany L Murphy MD, Tanya Hoskin MS, Courtney
Preoperative Prediction of Node Negative Disease After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients Presenting with Node Negative or Node Positive Breast Cancer Brittany L Murphy MD, Tanya Hoskin MS, Courtney
Journal of Breast Cancer
 Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2013 December; 16(4): 378-385 Reliability of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients Ahram Han 1, *,
Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2013 December; 16(4): 378-385 Reliability of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients Ahram Han 1, *,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY. Ann Surg Oncol (2010) 17: DOI /s x
 Ann Surg Oncol (2010) 17:2690 2695 DOI 10.1245/s10434-010-1052-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Discordance of Intraoperative Frozen Section Analysis with Definitive Histology of Sentinel Lymph Nodes
Ann Surg Oncol (2010) 17:2690 2695 DOI 10.1245/s10434-010-1052-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Discordance of Intraoperative Frozen Section Analysis with Definitive Histology of Sentinel Lymph Nodes
Welcome to. American College of Surgeons. Clinical Research Program (ACS-CRP) Breast Surgical Trial Webinar
 American College of Surgeons Clinical Research Program Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Program Director Welcome to American College of Surgeons Clinical Research Program (ACS-CRP) Breast Surgical Trial Webinar Moderator:
American College of Surgeons Clinical Research Program Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Program Director Welcome to American College of Surgeons Clinical Research Program (ACS-CRP) Breast Surgical Trial Webinar Moderator:
San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium 2010: Highlights from a Surgical Perspective. Disclosures
 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium 2010: Highlights from a Surgical Perspective January 18, 2011 Association of Northern California Oncologists Steven Chen, MD, MBA Chief, Breast Surgery University of
San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium 2010: Highlights from a Surgical Perspective January 18, 2011 Association of Northern California Oncologists Steven Chen, MD, MBA Chief, Breast Surgery University of
What you should know about Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
 What you should know about Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy AFFILIATED WITH GENESIS MEDICAL CENTER 1228 East Rusholme Street, Suite 210 Davenport, Iowa 52803 (563) 421-7625 1-800-215-1444 www.genesishealth.com
What you should know about Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy AFFILIATED WITH GENESIS MEDICAL CENTER 1228 East Rusholme Street, Suite 210 Davenport, Iowa 52803 (563) 421-7625 1-800-215-1444 www.genesishealth.com
Implications of ACOSOG Z11 for Clinical Practice: Surgical Perspective
 Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065 10th International Congress on the Future of Breast Cancer Coronado, CA 6 August 2011 Implications of ACOSOG Z11 for Clinical
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065 10th International Congress on the Future of Breast Cancer Coronado, CA 6 August 2011 Implications of ACOSOG Z11 for Clinical
Evaluation of Pathologic Response in Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy
 Evaluation of Pathologic Response in Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy Eun Yoon Cho, MD, PhD Department of Pathology and Translational Genomics Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University
Evaluation of Pathologic Response in Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy Eun Yoon Cho, MD, PhD Department of Pathology and Translational Genomics Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University
The Value of Intraoperative Examination of Axillary Sentinel Nodes in Carcinoma of the Breast.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pathology, Anatomy, and Cell Biology Faculty Papers Department of Pathology, Anatomy, and Cell Biology 11-1-2008 The Value of Intraoperative
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pathology, Anatomy, and Cell Biology Faculty Papers Department of Pathology, Anatomy, and Cell Biology 11-1-2008 The Value of Intraoperative
Clinical Study Sentinel Lymph Node Detection Using Laser-Assisted Indocyanine Green Dye Lymphangiography in Patients with Melanoma
 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2013, Article ID 904214, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/904214 Clinical Study Sentinel Lymph Node Detection Using Laser-Assisted Indocyanine Green Dye Lymphangiography
International Surgical Oncology Volume 2013, Article ID 904214, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/904214 Clinical Study Sentinel Lymph Node Detection Using Laser-Assisted Indocyanine Green Dye Lymphangiography
Axillary Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Carcinoma of the Breast
 Axillary Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Carcinoma of the Breast Gordon F. Schwartz, MD, MBA 1 ; Jonathan E. Tannebaum, MD 1 ; Amelia M. Jernigan, MD 1 ; and Juan P. Palazzo,
Axillary Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Carcinoma of the Breast Gordon F. Schwartz, MD, MBA 1 ; Jonathan E. Tannebaum, MD 1 ; Amelia M. Jernigan, MD 1 ; and Juan P. Palazzo,
Treatment of the Axilla for Breast Cancer:
 Treatment of the Axilla for Breast Cancer: V. Suzanne Klimberg, M.D., Ph.D. Courtney M Townsend, Jr. M.D. Distinguished Chair in General Surgery Chief of Surgical Oncology and Medical Director of the University
Treatment of the Axilla for Breast Cancer: V. Suzanne Klimberg, M.D., Ph.D. Courtney M Townsend, Jr. M.D. Distinguished Chair in General Surgery Chief of Surgical Oncology and Medical Director of the University
Radiotherapy Implications of ACOSOG Z-11 for Clinical Practice. Julia White, MD Professor of Radiation Oncology Medical College of Wisconsin
 1 Radiotherapy Implications of ACOSOG Z-11 for Clinical Practice Julia White, MD Professor of Radiation Oncology Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosures: none Agenda 1. ACOSOG Z-11: Another perspective
1 Radiotherapy Implications of ACOSOG Z-11 for Clinical Practice Julia White, MD Professor of Radiation Oncology Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosures: none Agenda 1. ACOSOG Z-11: Another perspective
Maria João Cardoso, MD, PhD
 Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Specific Issues in LocorregionalTreatment Surgery, MD, PhD Head Breast Surgeon Breast Unit, Champalimaud Foundation Lisbon, Portugal 1 Conflict of Interest Disclosure No
Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Specific Issues in LocorregionalTreatment Surgery, MD, PhD Head Breast Surgeon Breast Unit, Champalimaud Foundation Lisbon, Portugal 1 Conflict of Interest Disclosure No
Correlation of Imprint Cytology of Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Carcinoma with the Histopathological Diagnosis
 Occupational Correlation Health of Hazards Imprint Correlation of Imprint Cytology of Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Carcinoma with the Histopathological Diagnosis Ranabhat SK a, Karki A b, Shah GJ c and
Occupational Correlation Health of Hazards Imprint Correlation of Imprint Cytology of Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Carcinoma with the Histopathological Diagnosis Ranabhat SK a, Karki A b, Shah GJ c and
