National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
|
|
|
- Spencer Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation, Inc. received $1,255,581 in formula funds for the grant award period January 1, 2010 through December 31, Accomplishments for the reporting period are described below. Research Project 1: Project Title and Purpose Discovery and Validation of MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Breast and Colon Cancer - Messenger RNA (mrna) expression profiling has yielded useful prognostic tests for breast cancer (e.g., Oncotype DX and MammaPrint ), but has not been very useful in identifying definitive treatment targets. This is because mrna expression profiling does not necessarily provide insight about which changes may be susceptible to therapies. For colon cancer, no clinically useful gene-expression-based prognostic tests exist yet. MicroRNAs (mirnas) are a subset of RNAs which have regulatory functions and, so, could be viewed as master switches for many coordinately regulated genes. This project s purpose is to identify mirnas that are prognostic or predictive of benefit from systemic therapies for breast and colon cancers, using archived tumor tissues from completed NSABP clinical trials. Identified markers may point us to new treatment strategies. Anticipated Duration of Project 1/1/ /31/2013 Project Overview The long-term goal of this research project is to develop biomarkers that will improve the treatment of colon and breast cancers. To achieve this goal, we propose to examine the expression of micrornas (mirnas), which are small, non-coding RNAs that control translation of many mrnas. mirna expression analysis may not only allow for the identification of better biomarkers but may provide a greater understanding of current expression data. One of the fundamental problems associated with the treatment of breast and colon cancers is clinical heterogeneity. Gene-expression mrna signatures that distinguish several subtypes of breast cancer have been identified, and, while no specific signatures currently exist for colon NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 1
2 cancer, the molecular and clinical heterogeneity of colon tumors is known. The subtyping of breast cancers has vastly improved breast cancer treatment because different subtypes respond differently to different breast cancer therapies. Current molecular signatures that distinguish these subtypes of breast cancer involve the profiling of a large number of genes and have primarily been identified by whole genome mrna expression analysis. Whole genome expression analyses are too costly and too complicated, and have too much background interference to be used as routine clinical tests. mirnas may be able to give prognostic and predictive information because they act as major switches that regulate the expression of many mrnas. It may be possible to better characterize a tumor with a small number of mirnas than is possible with mrnas. Colon cancer lacks biomarkers for identifying tumors that have a high risk for recurring, and predicting response to chemotherapy is not possible. Given these considerations, we have adopted the following specific aims: 1) Discover and validate prognostic mirna markers for breast cancer patients with resectable tumors and histologically positive axillary lymph node(s); 2) Discover and validate predictive and prognostic mirna markers for colon cancer patients with stage II and III resectable colon cancer; and 3) Initiate the development of an integrated colon cancer molecular database using mirna data as well as mrna and mutation data from the NSABP clinical trial C-07 samples which will provide unique information for hypothesis generation. Principal Investigator Katherine L. Pogue-Geile, PhD Assistant Director of Molecular Profiling NSABP Foundation, Inc. Four Allegheny Center, 5 th Floor Pittsburgh, PA Other Participating Researchers Soonmyung Paik, MD; Patrick Gavin, BS; Chung Kim, MD employed by NSABP Foundation Expected Research Outcomes and Benefits In this project, we will examine the expression of mirnas in breast and colon cancers. The project has the following expected outcomes: 1) To identify the gene expression profile of mirnas in a large number of colon and breast cancer samples; 2) To determine the prognostic significance of mirnas in colon and breast cancers; 3) To determine the predictive significance of mirnas in colon and breast tumor responses to specific anti-cancer therapies; and 4) To acquire new information for the development of a valuable integrated molecular database of colon tumors. The C-07 colon tumors that will be interrogated for mirna NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 2
3 expression have already been profiled for mrna gene expression by Illumina DASL, arrays and profiled for critical cancer mutations in KRAS, NRAS, PIK3CA, BRAF and MET. This information along with standard histological and clinical information makes this a valuable resource for the discovery of the mechanisms that determine the success or failure of specific cancer treatments and to generate hypotheses regarding control of gene expression and its role in cancer development. Potential benefits include the following: 1) Improved prognostication for patients with diagnoses of breast or colon cancer; 2) Improved prediction of response of patients with colon cancer to oxaliplatin; and 3) Generation of information for the development of integrated molecular databases. C-07 mirna data will add to other molecular information on the same clinical samples, including data on whole genome mrna expression and somatic cancer mutations. This database can be used for hypothesis-generation as it will provide a large database for correlating these molecular characteristics. Summary of Research Completed The Specific Aims addressed in this report period were: 1. Completed mirna expression profiles of 914 cases included in the validation cohort. 2. Identified prognostic and predictive mirnas (mirs) in the discovery cohort of C-08 and began building prognostic models. 3. Identified bevacizumab-predictive mirs and began building predictive models. To achieve the overall goal of this proposal, which was to improve the prognostication and the treatment of colon and breast cancer, we have chosen to focus our efforts on colon cancer both for pragmatic and scientific reasons. Expression profiling of all well-annotated mirs in a large cohort of cases and using the best technology required more budget expenditure than we had originally planned which then necessitated that we choose only one cancer. To maximize the possibility of developing a clinically meaningful signature, we decided to focus on colon cancer because much less molecular data have been collected for colon cancer compared to that for breast cancer. Breast cancer already has prognostic signatures that are used clinically to identify patients who will receive benefit from chemotherapy. We also decided to focus on clinical trial NSABP C-08 because this trial included a control arm of patients who were treated with current standard chemotherapy (mfolfox), and an investigational arm that tested whether the addition of the targeted drug bevacizumab to standard chemotherapy improved the disease-free survival of patients with Stages II or III colon cancer. Even though bevacizumab did not show benefit when added to mfolfox when the entire cohort of C-08 patients was evaluated, it is still possible that a subset of patients did receive benefit from bevacizumab treatment and that these patients could be identified through a molecular test. One of the goals of this project is to develop a mirrna expression signature that is able to identify such a subset. Furthermore, the control arm of C-08 may allow us to develop a prognostic signature that would identify patients who would need more than standard chemotherapy. I. Mir Profiling of the Validation Cohort We have completed the mir expression profiles from 914 cases included in the C-08 validation cohort. This validation cohort consists of cases that were not included in the C-08 discovery NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 3
4 cohort. Mir expression profiles were obtained using the same technology (the TaqMan Array Human MicroRNA Cards) that was used for the expression profiling of the discovery cohort in order to eliminate cross-platform differences between the discovery and validation data sets. Currently, we are performing a quality control (QC) assessment of the validation cohort and may repeat profiling of a few samples that failed our QC. We are still evaluating methods for normalization to compensate for the batch effects, which distinguish the discovery and validation cohorts. Thus, the wet lab portion of the profiling of the validation cohort is nearly completed, but additional bioinformatics work must be done before the validation cohort is complete. II. Statistical Methods of the Mir Expression Data from the C-08 Discovery Cohort We have begun to analyze the mir expression data from the C-08 discovery cohort, which consists of approximately 1000 randomly selected C-08 cases profiled with 754 mirs. C-08 samples were chosen randomly within strata defined by treatment and N-Stage (N0, N1, N2). The proportion of patients in each strata of the sample is the same as the proportion of patients in each strata of the eligible population. A. Quality Control and Normalization Mirs were interrogated with TaqMan Array Human MicroRNA Cards (from Applied Biosystems), which includes 2 cards (A and B). Each card interrogates 381 different mirs. Different QC metrics were required for the two cards because the manufacturer intentionally biased the A card to include more prevalent, better annotated mirs. Quality control of A cards was performed by removing cards with fewer than 150 mirs detected, or more precisely, any A card in which there were fewer than 150 mirs with a Ct value below 37 was removed from the data set. Quality control of B cards was performed by removing cases with an average Ct for U6 snrna of more than 20. The two metrics are highly correlated. Cards failing these criteria were repeated for cases with available RNA. Adequate results were obtained for 966 of 1000 discovery cases for the A card and 953 of 998, for the B card. We selected mirs for normalization by analyzing our data with NormFinder and genorm algorithm. The geometric mean of the 5 normalizers was used to normalize the data. The mirs used for the A card were hsa_mir_140_3p_ , hsa_mir_152_ , hsa_mir_103_ , hsa_mir_99a_ , hsa_mir_93_ , and for the B card were U6, hsa_mir_26b , hsa_mir_18a , hsa_mir_ , and hsa_mir_ Missing values are indicated in the raw data as not defined if their Ct value was 37 cycles or above. B. Identification of Prognostic and Predictive Mirs The prognostic/predictive effect of each mir marker was determined in Cox regression models, which were adjusted for age, sex, nodal status, and t stage. Normalized Ct values were categorized with quartiles to test for possible non-linear effects. Mirs were screened based on the minimum p-values among the three calculated p-values for each subgroup based on the quartile of Ct values for each mir. We also applied a 10-fold jack-knifing technique to determine whether the association p-values were robust. The associations of the p-values for each mir calculated from 10 subsets of the data were averaged. The clinical endpoint for these analyses was time to recurrence (TTR). Forty predictive mirs with minimum p-values below 0.05 were NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 4
5 identified. Table 1 shows the p-values for the top 10 mirs, but the mir names have been changed to anonomous names a-k for proprietary reasons. C. Building and Evaluating Prognostic and Predictive Models We are currently exploring different methods for the building of prognostic and predictive models and are evaluating these models in an effort to pick the best model for validation. Below is a summary of our current efforts to build prognostic and predictive models; however, we have not revealed the identity of specific mirs because these models may be patented. This process is ongoing and we are still building and evaluating these models. Predictive Model 1. The p-values for the top 10 mirs, which were identified as predictive by a categorical analysis, are shown in Table 1, but the mir names have been changed for proprietary reasons. These mirs also were examined for their distinct predictive effect using visual inspection of Kaplan-Meier plots and STEPP analysis. The top 3 mirs (mir-a, mir-b and mir-c) based on the p-value also had a distinct predictive effect. Continuous (linear) interaction p-values for mirs were also calculated using TTR as the clinical endpoint and using a 10-fold jack-knife process. The top four mirs based on the predictive continuous analysis were mir_d (p=0.0162), mir_c (p=0.0269), mir_e (p=0.0434) and mir_f (p=0.0451). The Kaplan-Meier plots were generated for each of these mirs and only the top 2 mirs (mir_d and mir_c) rendered a relatively distinct predictive effect. The top mirs based on the p-values determined by continuous analysis (mir-c and mir-d) and categorical analysis (mir-a, -b, -c) were included in a predictive model. These 4 mirs (mir-c was identified by both continuous and categorical analyses) were used to build a model applying Wald's method. Other classification methods, including average linkage and centroid methods were also applied. All of these methods generated 5 clusters with a differential response to bevacizumab. On the basis of this result, the patients were re-categorized into the following three groups: 1+2, 3, 4+5 (Fig. 1). Only group 1 patients appear to receive benefit from bevacizumab; the adjusted hazard ratio for group 1 was 0.61 (p=0.038). Patients in group 2 and group 3 do not appear to receive benefit, and those in group 2 may have received harm. The interaction p-value for this model was significant (p= 0.018). Even if the number of clusters was reduced, none of the mirs were removed for discrimination for the 3 groups when the stepwise discriminant analysis was performed. When linear discriminant analysis was applied with cross validation, the linear discriminant function with the 4 mirs classified patients into 3 groups with a 10% misclassification rate. Predicitive Model 2 was generated using mirs that have been described to play a role in the immune system. Patients were clustered into 5 groups. Results of this model are shown in Fig. 2. Global p-value for these 5 clusters was 0.011, and if cluster 1 and 2, and cluster 3 and 4 were combined. This model based on this subgrouping was more significant than Predictive Model 1. D. Prognostic Models A prognostic model was built based on the Super Principal Component method and using only the patients who were in the C-08 control group. Mirs included in this analysis had a missing NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 5
6 rate of less than 5%. First, ten-fold cross-validation was used to determine the optimum number of genes and Principal Components (PCs) to be included in the models. The median p-values for prognostic effect of the prognostic index (PI) were used in the COX model. The PI is the estimated exponentiated survival time estimated by the model, built in the training set, which is divided into 10 different training sets. The clinical endpoint is TTR. The optimum number of genes and PCs were determined to be 4 and 3, respectively, but only one PC was included in the model because only the first PC contributed to the model (Fig. 3). The top 10 mirs selected in each of the each of the 10 cycles during 10-fold cross validation are shown in Table 2. Mirs included in all 10 cycles have a cv (cross validation) rate of 1. To select the best model, we built 4 models using all samples and the following clinical covariates: nodal status, gender, and age. The models were 1) a model with only the covariates; 2) a model with 1 PC and the top 4 mirs based on their p-values; 3) a model with the covariates and the top mir based on p-value (hsa_mir-l) using forward selection; and 4) a model with covariates and PC1 and the top 4 mirs based on the cv rate (Table 2). These models were evaluated by several statistical measures including a score for deviance. Based on the statistical measures, the best model was model 4. When this model was applied to all samples, the prognostic p-value was , and, in the control samples when adjusted for treatment effect. III. Summary In conclusion, we have nearly completed the wet lab portion of the mir expression profiling of the C-08 validation cohort in this year. Using the separate, non-overlapping discovery cohort, we have shown that it is possible to build prognostic and bevacizumab-predictive models using mir expression data. We are currently evaluating these models in the discovery cohort. NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 6
7 Table 1. Predictive mirs mir minpred_catp hsa_mir_a hsa_mir_b hsa_mir_c hsa_mir_d hsa_mir_e hsa_mir_f hsa_mir_g hsa_mir_h hsa_mir_i hsa_mir_j hsa_mir_k Table 2 Prognostic mirs for Model Buiding mir Pr > ChiSq cvrate hsa_mir-l hsa_mir_m hsa_mir_n hsa_mir_o hsa_mir_p hsa_mir_q hsa_mir_r hsa_mir_s hsa_mir_t hsa_mir_u NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 7
8 Predictive Model 1. Kaplan-Meier Plots of Response (TTR) to Bevacizumab by Cluster Groups NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 8
9 Predictive Model 2. Kaplan-Meier Plots of Response (TTR) to Bevacizumab by Cluster Groups NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 9
10 Model Building for Prognostic Model. Determination of Optimum Number of Principal Components and Genes NSABP Foundation Formula Grant Page 10
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 December 31, 2011 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 December 31, 2011 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The NSABP Foundation
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The NSABP Foundation
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011
 Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease
 Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Assessment of Risk Recurrence: Adjuvant Online, OncotypeDx & Mammaprint
 Assessment of Risk Recurrence: Adjuvant Online, OncotypeDx & Mammaprint William J. Gradishar, MD Professor of Medicine Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University Classical
Assessment of Risk Recurrence: Adjuvant Online, OncotypeDx & Mammaprint William J. Gradishar, MD Professor of Medicine Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University Classical
OVERVIEW OF GENE EXPRESSION-BASED TESTS IN EARLY BREAST CANCER
 OVERVIEW OF GENE EXPRESSION-BASED TESTS IN EARLY BREAST CANCER Aleix Prat, MD PhD Medical Oncology Department Hospital Clínic of Barcelona University of Barcelona esmo.org Disclosures Advisory role for
OVERVIEW OF GENE EXPRESSION-BASED TESTS IN EARLY BREAST CANCER Aleix Prat, MD PhD Medical Oncology Department Hospital Clínic of Barcelona University of Barcelona esmo.org Disclosures Advisory role for
Gene Signatures in Breast Cancer: Moving Beyond ER, PR, and HER2? Lisa A. Carey, M.D. University of North Carolina USA
 Gene Signatures in Breast Cancer: Moving Beyond ER, PR, and HER2? Lisa A. Carey, M.D. University of North Carolina USA When Are Biomarkers Ready To Use? Same Rules for Gene Expression Panels Key elements
Gene Signatures in Breast Cancer: Moving Beyond ER, PR, and HER2? Lisa A. Carey, M.D. University of North Carolina USA When Are Biomarkers Ready To Use? Same Rules for Gene Expression Panels Key elements
Journal: Nature Methods
 Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
8/8/2011. PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant Chemotherapy in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer. Overview
 Overview PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer Jennifer K. Litton, M.D. Assistant Professor The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Using multigene assay
Overview PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer Jennifer K. Litton, M.D. Assistant Professor The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Using multigene assay
COLORECTAL CANCER 44
 COLORECTAL CANCER 44 Colorectal Cancer Highlights from the 2009 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Edited by Stuart M. Lichtman, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Commack,
COLORECTAL CANCER 44 Colorectal Cancer Highlights from the 2009 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Edited by Stuart M. Lichtman, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Commack,
Janet E. Dancey NCIC CTG NEW INVESTIGATOR CLINICAL TRIALS COURSE. August 9-12, 2011 Donald Gordon Centre, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario
 Janet E. Dancey NCIC CTG NEW INVESTIGATOR CLINICAL TRIALS COURSE August 9-12, 2011 Donald Gordon Centre, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario Session: Correlative Studies in Phase III Trials Title: Design
Janet E. Dancey NCIC CTG NEW INVESTIGATOR CLINICAL TRIALS COURSE August 9-12, 2011 Donald Gordon Centre, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario Session: Correlative Studies in Phase III Trials Title: Design
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant
 Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
Basket and Umbrella Trial Designs in Oncology
 Basket and Umbrella Trial Designs in Oncology Eric Polley Biomedical Statistics and Informatics Mayo Clinic Polley.Eric@mayo.edu Dose Selection for Cancer Treatment Drugs Stanford Medicine May 2017 1 /
Basket and Umbrella Trial Designs in Oncology Eric Polley Biomedical Statistics and Informatics Mayo Clinic Polley.Eric@mayo.edu Dose Selection for Cancer Treatment Drugs Stanford Medicine May 2017 1 /
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Profili di espressione genica
 Profili di espressione genica Giampaolo Bianchini MD Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan - Italy Gene expression profiles Transcriptomics Gene DNA mrna mirnas Protein metilation Metabolite Genomics Transcriptomics
Profili di espressione genica Giampaolo Bianchini MD Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan - Italy Gene expression profiles Transcriptomics Gene DNA mrna mirnas Protein metilation Metabolite Genomics Transcriptomics
TITLE: MicroRNA in Prostate Cancer Racial Disparities and Aggressiveness
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0477 TITLE: MicroRNA in Prostate Cancer Racial Disparities and Aggressiveness PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Cathryn Bock CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Wayne State University REPORT DATE:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0477 TITLE: MicroRNA in Prostate Cancer Racial Disparities and Aggressiveness PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Cathryn Bock CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Wayne State University REPORT DATE:
Classification of cancer profiles. ABDBM Ron Shamir
 Classification of cancer profiles 1 Background: Cancer Classification Cancer classification is central to cancer treatment; Traditional cancer classification methods: location; morphology, cytogenesis;
Classification of cancer profiles 1 Background: Cancer Classification Cancer classification is central to cancer treatment; Traditional cancer classification methods: location; morphology, cytogenesis;
Use of Archived Tissues in the Development and Validation of Prognostic & Predictive Biomarkers
 Use of Archived Tissues in the Development and Validation of Prognostic & Predictive Biomarkers Richard Simon, D.Sc. Chief, Biometric Research Branch National Cancer Institute http://brb.nci.nih.gov Different
Use of Archived Tissues in the Development and Validation of Prognostic & Predictive Biomarkers Richard Simon, D.Sc. Chief, Biometric Research Branch National Cancer Institute http://brb.nci.nih.gov Different
The 21 Gene Oncotype DX Assay and The NCI-Sponsored TAILORx Trial. Steven Shak Chief Medical Officer Genomic Health October 4, 2007
 The 21 Gene Oncotype DX Assay and The NCI-Sponsored TAILORx Trial Steven Shak Chief Medical Officer Genomic Health October 4, 2007 Biomarkers - 1999 Thousands of publications on biomarkers in cancer Few
The 21 Gene Oncotype DX Assay and The NCI-Sponsored TAILORx Trial Steven Shak Chief Medical Officer Genomic Health October 4, 2007 Biomarkers - 1999 Thousands of publications on biomarkers in cancer Few
Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:
 Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:7332-7341 Presented by Deming Mi 7/25/2006 Major reasons for few prognostic factors to
Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:7332-7341 Presented by Deming Mi 7/25/2006 Major reasons for few prognostic factors to
Assessment of omicsbased predictor readiness for use in a clinical trial
 Assessment of omicsbased predictor readiness for use in a clinical trial Lisa Meier McShane Biometric Research Branch Division of Cancer Treatment & Diagnosis U.S. National Cancer Institute Biopharmaceutical
Assessment of omicsbased predictor readiness for use in a clinical trial Lisa Meier McShane Biometric Research Branch Division of Cancer Treatment & Diagnosis U.S. National Cancer Institute Biopharmaceutical
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz H-J, et al. Effect of first-line chemotherapy combined with cetuximab or bevacizumab on overall survival in patients with KRAS wild-type advanced
Supplementary Online Content Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz H-J, et al. Effect of first-line chemotherapy combined with cetuximab or bevacizumab on overall survival in patients with KRAS wild-type advanced
Supplementary. properties of. network types. randomly sampled. subsets (75%
 Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Design considerations for Phase II trials incorporating biomarkers
 Design considerations for Phase II trials incorporating biomarkers Sumithra J. Mandrekar Professor of Biostatistics, Mayo Clinic Pre-Meeting Workshop Enhancing the Design and Conduct of Phase II Studies
Design considerations for Phase II trials incorporating biomarkers Sumithra J. Mandrekar Professor of Biostatistics, Mayo Clinic Pre-Meeting Workshop Enhancing the Design and Conduct of Phase II Studies
FISH mcgh Karyotyping ISH RT-PCR. Expression arrays RNA. Tissue microarrays Protein arrays MS. Protein IHC
 Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Summary BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3
 ESMO 2016 Congress 7-11 October, 2016 Copenhagen, Denmark Table of Contents Summary... 2 BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3 Large data analysis reveals similar survival outcomes with sequential
ESMO 2016 Congress 7-11 October, 2016 Copenhagen, Denmark Table of Contents Summary... 2 BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3 Large data analysis reveals similar survival outcomes with sequential
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer
 Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Impact of Prognostic Factors
 Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
University of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 University of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Research Project 1: Project Title and Purpose Small Molecule Inhibitors of HIV Nef Signaling
University of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Research Project 1: Project Title and Purpose Small Molecule Inhibitors of HIV Nef Signaling
Breast Cancer Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue
 Breast Cancer Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.12.009 12/02/2008 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date Section: 05/25/2018 Other Miscellaneous
Breast Cancer Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.12.009 12/02/2008 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date Section: 05/25/2018 Other Miscellaneous
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo. Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale
 Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
Gene Expression Profiling for Managing Breast Cancer Treatment. Policy Specific Section: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental
 Medical Policy Gene Expression Profiling for Managing Breast Cancer Treatment Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Laboratory/Pathology Original Policy Date:
Medical Policy Gene Expression Profiling for Managing Breast Cancer Treatment Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Laboratory/Pathology Original Policy Date:
BreastPRS is a gene expression assay that stratifies intermediaterisk Oncotype DX patients into high- or low-risk for disease recurrence
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2013) 139:705 715 DOI 10.1007/s10549-013-2604-0 PRECLINICAL STUDY BreastPRS is a gene expression assay that stratifies intermediaterisk Oncotype DX patients into high- or low-risk
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2013) 139:705 715 DOI 10.1007/s10549-013-2604-0 PRECLINICAL STUDY BreastPRS is a gene expression assay that stratifies intermediaterisk Oncotype DX patients into high- or low-risk
-- Kaiser Permanente Presents Results from Large Community-Based Study Consistent with NSABP Recurrence Study Findings
 www.genomichealth.com Contacts: Kathleen Rinehart/GHI: 408/460-9116 Jim Weiss/GHI: 415/609-3680 Lori Garvey/NSABP: 412/330-4621 The National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) and Genomic
www.genomichealth.com Contacts: Kathleen Rinehart/GHI: 408/460-9116 Jim Weiss/GHI: 415/609-3680 Lori Garvey/NSABP: 412/330-4621 The National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) and Genomic
Clinical Trial Design to Expedite Drug Development Mary W. Redman, Ph.D.
 Clinical Trial Design to Expedite Drug Development Mary W. Redman, Ph.D. What do we mean by expediting drug development? Phase I Single Arm Phase II (expansion cohort) Randomized Phase II Phase III Necessary?
Clinical Trial Design to Expedite Drug Development Mary W. Redman, Ph.D. What do we mean by expediting drug development? Phase I Single Arm Phase II (expansion cohort) Randomized Phase II Phase III Necessary?
Oral Communications & Posters
 Carcinoma uroteliale: Current and future directions of treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder cancer/ Multimodality approach of bladder cancer Oral Communications & Posters CRISTINA MASINI Oncologia Medica
Carcinoma uroteliale: Current and future directions of treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder cancer/ Multimodality approach of bladder cancer Oral Communications & Posters CRISTINA MASINI Oncologia Medica
The Oncotype DX Assay in the Contemporary Management of Invasive Early-stage Breast Cancer
 The Oncotype DX Assay in the Contemporary Management of Invasive Early-stage Breast Cancer Cancer The Biology Century Understanding and treating the underlying tumor biology Cancer genetic studies demonstrate
The Oncotype DX Assay in the Contemporary Management of Invasive Early-stage Breast Cancer Cancer The Biology Century Understanding and treating the underlying tumor biology Cancer genetic studies demonstrate
Oncotype DX tools User Guide
 Oncotype DX tools User Guide This guide provides an overview of the data and quick access to the Oncotype DX tools Oncotype DX tools offers two quantitative calculator tools that may be used together with
Oncotype DX tools User Guide This guide provides an overview of the data and quick access to the Oncotype DX tools Oncotype DX tools offers two quantitative calculator tools that may be used together with
Emerald City Communications
 For Release: Immediate Contact: Frank Catanzano Emerald City Communications 412-965-5269 fcatanzano@truebaseline.com Ground-Breaking Study by the Pittsburgh Based National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and
For Release: Immediate Contact: Frank Catanzano Emerald City Communications 412-965-5269 fcatanzano@truebaseline.com Ground-Breaking Study by the Pittsburgh Based National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and
Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD
 Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Review
Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Review
IRESSA (Gefitinib) The Journey. Anne De Bock Portfolio Leader, Oncology/Infection European Regulatory Affairs AstraZeneca
 IRESSA (Gefitinib) The Journey Anne De Bock Portfolio Leader, Oncology/Infection European Regulatory Affairs AstraZeneca Overview The Drug The Biomarker and Clinical Trials Sampling Lessons Learned The
IRESSA (Gefitinib) The Journey Anne De Bock Portfolio Leader, Oncology/Infection European Regulatory Affairs AstraZeneca Overview The Drug The Biomarker and Clinical Trials Sampling Lessons Learned The
The Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant
 The Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology
The Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology
Supplementary Figure 1: Experimental design. DISCOVERY PHASE VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) (N = 20) Healthy = 20. Healthy = 6. Endometriosis = 33
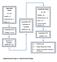 DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
Evaluation of public cancer datasets and signatures identifies TP53 mutant signatures with robust prognostic and predictive value
 Lehmann et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:179 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1102-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of public cancer datasets and signatures identifies TP53 mutant signatures with robust prognostic
Lehmann et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:179 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1102-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of public cancer datasets and signatures identifies TP53 mutant signatures with robust prognostic
MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC)
 PERSPECTIVE 1 LARGE SCALE DATASET EXAMPLES MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) BC Cancer Agency, Vancouver Samuel Aparicio, PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair
PERSPECTIVE 1 LARGE SCALE DATASET EXAMPLES MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) BC Cancer Agency, Vancouver Samuel Aparicio, PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair
ISPOR 4 th Asia Pacific Conference IP2 Gilberto de Lima Lopes
 Health Economic Considerations for Personalized Medicine in Asia: Using Genomic Profiling to Guide Treatment Decisions in Early Breast Cancer Gilberto de Lima Lopes, Jr., M.D., M.B.A Assistant Director
Health Economic Considerations for Personalized Medicine in Asia: Using Genomic Profiling to Guide Treatment Decisions in Early Breast Cancer Gilberto de Lima Lopes, Jr., M.D., M.B.A Assistant Director
Relevancia práctica de la clasificación de subtipos intrínsecos en cáncer de mama Miguel Martín Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Gregorio Marañón
 Relevancia práctica de la clasificación de subtipos intrínsecos en cáncer de mama Miguel Martín Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Gregorio Marañón Universidad Complutense Madrid The new technologies
Relevancia práctica de la clasificación de subtipos intrínsecos en cáncer de mama Miguel Martín Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Gregorio Marañón Universidad Complutense Madrid The new technologies
Defining Actionable Novel Discoveries, Annotating Genomes, and Reanalysis in Cancer A Laboratory Perspective
 Integrating Large-Scale Genomic Information into Clinical Practice: A Workshop Defining Actionable Novel Discoveries, Annotating Genomes, and Reanalysis in Cancer A Laboratory Perspective Federico A. Monzon
Integrating Large-Scale Genomic Information into Clinical Practice: A Workshop Defining Actionable Novel Discoveries, Annotating Genomes, and Reanalysis in Cancer A Laboratory Perspective Federico A. Monzon
T. R. Golub, D. K. Slonim & Others 1999
 T. R. Golub, D. K. Slonim & Others 1999 Big Picture in 1999 The Need for Cancer Classification Cancer classification very important for advances in cancer treatment. Cancers of Identical grade can have
T. R. Golub, D. K. Slonim & Others 1999 Big Picture in 1999 The Need for Cancer Classification Cancer classification very important for advances in cancer treatment. Cancers of Identical grade can have
Comparative Effectiveness Research (CER) and Personalized Medicine: Policy, Science, and Business
 Comparative Effectiveness Research (CER) and Personalized Medicine: How a comprehensive CER system can support personalized medicine Amy P. Abernethy, MD October 28, 2009 CER in Cancer Care? 2 Friends
Comparative Effectiveness Research (CER) and Personalized Medicine: How a comprehensive CER system can support personalized medicine Amy P. Abernethy, MD October 28, 2009 CER in Cancer Care? 2 Friends
Reliable Evaluation of Prognostic & Predictive Genomic Tests
 Reliable Evaluation of Prognostic & Predictive Genomic Tests Richard Simon, D.Sc. Chief, Biometric Research Branch National Cancer Institute http://brb.nci.nih.gov Different Kinds of Biomarkers Prognostic
Reliable Evaluation of Prognostic & Predictive Genomic Tests Richard Simon, D.Sc. Chief, Biometric Research Branch National Cancer Institute http://brb.nci.nih.gov Different Kinds of Biomarkers Prognostic
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles
 On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
Comprehensive Genomic Profiling, in record time. Accurate. Clinically Proven. Fast.
 Comprehensive Genomic Profiling, in record time Accurate. ly Proven. Fast. PCDx advantages Comprehensive genomic profiling, in record time PCDx Comprehensive Genomic Profiling (CGP) provides precise information
Comprehensive Genomic Profiling, in record time Accurate. ly Proven. Fast. PCDx advantages Comprehensive genomic profiling, in record time PCDx Comprehensive Genomic Profiling (CGP) provides precise information
11th Annual Population Health Colloquium. Stan Skrzypczak, MS, MBA Sr. Director, Marketing Genomic Health, Inc. March 15, 2011
 11th Annual Population Health Colloquium Stan Skrzypczak, MS, MBA Sr. Director, Marketing Genomic Health, Inc. March 15, 2011 Agenda Personalized medicine in oncology healthcare Clinical relevance of personalized
11th Annual Population Health Colloquium Stan Skrzypczak, MS, MBA Sr. Director, Marketing Genomic Health, Inc. March 15, 2011 Agenda Personalized medicine in oncology healthcare Clinical relevance of personalized
Prognostic significance of K-Ras mutation rate in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Bruno Vincenzi Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma
 Prognostic significance of K-Ras mutation rate in metastatic colorectal cancer patients Bruno Vincenzi Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma Colorectal cancer 3 rd most common cancer worldwide Approximately
Prognostic significance of K-Ras mutation rate in metastatic colorectal cancer patients Bruno Vincenzi Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma Colorectal cancer 3 rd most common cancer worldwide Approximately
The 70-Gene Signature (MammaPrint) As a Guide for the Management of Early Stage Breast Cancer. California Technology Assessment Forum
 TITLE: The 70-Gene Signature (MammaPrint) As a Guide for the Management of Early Stage Breast Cancer AUTHOR: Jeffrey A. Tice, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of General Internal Medicine Department
TITLE: The 70-Gene Signature (MammaPrint) As a Guide for the Management of Early Stage Breast Cancer AUTHOR: Jeffrey A. Tice, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of General Internal Medicine Department
Are We Ready to Predict Who is at Risk For What Kind of Breast Cancer? NOT YET NO DISCLOSURES 3/7/2015. Laura Esserman MD MBA
 Are We Ready to Predict Who is at Risk For What Kind of Breast Cancer? NOT YET But soon.... Laura Esserman MD MBA 2 Breast Cancer Gene Expression Profiling Prognostic Tests 1. OncotypeDX Recurrence Score
Are We Ready to Predict Who is at Risk For What Kind of Breast Cancer? NOT YET But soon.... Laura Esserman MD MBA 2 Breast Cancer Gene Expression Profiling Prognostic Tests 1. OncotypeDX Recurrence Score
Genomic Profiling of Tumors and Loco-Regional Recurrence
 1 Genomic Profiling of Tumors and Loco-Regional Recurrence Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H., F.A.C.S. Medical Director, Comprehensive Breast Program UF Health Cancer Center at Orlando Health Professor of Surgery,
1 Genomic Profiling of Tumors and Loco-Regional Recurrence Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H., F.A.C.S. Medical Director, Comprehensive Breast Program UF Health Cancer Center at Orlando Health Professor of Surgery,
Cetuximab with Chemotherapy as Treatment for Stage III Colon or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
 Cetuximab with Chemotherapy as Treatment for Stage III Colon or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cetuximab with Chemotherapy (CT) as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mcrc): Analysis of
Cetuximab with Chemotherapy as Treatment for Stage III Colon or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cetuximab with Chemotherapy (CT) as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mcrc): Analysis of
Adjuvant endocrine therapy (essentials in ER positive early breast cancer)
 Adjuvant endocrine therapy (essentials in ER positive early breast cancer) Giuseppe Curigliano MD, PhD Breast Cancer Program Division of Experimental Therapeutics Outline Picking optimal adjuvant endocrine
Adjuvant endocrine therapy (essentials in ER positive early breast cancer) Giuseppe Curigliano MD, PhD Breast Cancer Program Division of Experimental Therapeutics Outline Picking optimal adjuvant endocrine
8/1/2017. Imaging and Molecular Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Prognosis. Disclosures. The Era of Precision Oncology
 Imaging and Molecular Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Prognosis Ruijiang Li, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiation Oncology 08/01/2017 Stanford University Department of Radiation Oncology School of Medicine Disclosures
Imaging and Molecular Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Prognosis Ruijiang Li, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiation Oncology 08/01/2017 Stanford University Department of Radiation Oncology School of Medicine Disclosures
2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Review
 2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Review HER2 Positive Disease 01-10-2015 Elisavet Paplomata, MD Assistant Professor Hematology & Medical Oncology Emory University Winship Cancer Institute S6-01
2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Review HER2 Positive Disease 01-10-2015 Elisavet Paplomata, MD Assistant Professor Hematology & Medical Oncology Emory University Winship Cancer Institute S6-01
Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue as a Technique to Determine Prognosis in Patients with Breast Cancer
 Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue as a Technique to Determine Prognosis in Patients with Breast Cancer Policy Number: 2.04.36 Last Review: 1/2019 Origination: 1/2006 Next Review: 9/2019 Policy
Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue as a Technique to Determine Prognosis in Patients with Breast Cancer Policy Number: 2.04.36 Last Review: 1/2019 Origination: 1/2006 Next Review: 9/2019 Policy
Survival Prediction Models for Estimating the Benefit of Post-Operative Radiation Therapy for Gallbladder Cancer and Lung Cancer
 Survival Prediction Models for Estimating the Benefit of Post-Operative Radiation Therapy for Gallbladder Cancer and Lung Cancer Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer PhD 1, William Hersh, MD 1, Jong Song Kim, PhD
Survival Prediction Models for Estimating the Benefit of Post-Operative Radiation Therapy for Gallbladder Cancer and Lung Cancer Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer PhD 1, William Hersh, MD 1, Jong Song Kim, PhD
CHMP Type II variation assessment report
 26 January 2017 EMA/CHMP/59238/2017 Invented name: Avastin International non-proprietary name: bevacizumab Procedure No. EMEA/H/C/000582/II/0093 Marketing authorisation holder (MAH): Roche Registration
26 January 2017 EMA/CHMP/59238/2017 Invented name: Avastin International non-proprietary name: bevacizumab Procedure No. EMEA/H/C/000582/II/0093 Marketing authorisation holder (MAH): Roche Registration
Prognostic and predictive biomarkers. Marc Buyse International Drug Development Institute (IDDI) Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium
 Prognostic and predictive biomarkers Marc Buyse International Drug Development Institute (IDDI) Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium marc.buyse@iddi.com 1 Prognostic biomarkers (example: gene signature) 2 PROGNOSTIC
Prognostic and predictive biomarkers Marc Buyse International Drug Development Institute (IDDI) Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium marc.buyse@iddi.com 1 Prognostic biomarkers (example: gene signature) 2 PROGNOSTIC
IPA Advanced Training Course
 IPA Advanced Training Course October 2013 Academia sinica Gene (Kuan Wen Chen) IPA Certified Analyst Agenda I. Data Upload and How to Run a Core Analysis II. Functional Interpretation in IPA Hands-on Exercises
IPA Advanced Training Course October 2013 Academia sinica Gene (Kuan Wen Chen) IPA Certified Analyst Agenda I. Data Upload and How to Run a Core Analysis II. Functional Interpretation in IPA Hands-on Exercises
Correlation of pretreatment surgical staging and PET SUV(max) with outcomes in NSCLC. Giancarlo Moscol, MD PGY-5 Hematology-Oncology UTSW
 Correlation of pretreatment surgical staging and PET SUV(max) with outcomes in NSCLC Giancarlo Moscol, MD PGY-5 Hematology-Oncology UTSW BACKGROUND AJCC staging 1 gives valuable prognostic information,
Correlation of pretreatment surgical staging and PET SUV(max) with outcomes in NSCLC Giancarlo Moscol, MD PGY-5 Hematology-Oncology UTSW BACKGROUND AJCC staging 1 gives valuable prognostic information,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue as a Technique Page 1 of 67 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue
Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue as a Technique Page 1 of 67 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Assays of Genetic Expression in Tumor Tissue
Lecture Outline. Biost 590: Statistical Consulting. Stages of Scientific Studies. Scientific Method
 Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies; Approach to Consulting Lecture Outline Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies Statistical Tasks Approach to
Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies; Approach to Consulting Lecture Outline Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies Statistical Tasks Approach to
ASSESSING LONG-TERM BENEFITS OF IMMUNOTHERAPY BASED ON EARLY TUMOR ASSESSMENT DATA
 ASSESSING LONG-TERM BENEFITS OF IMMUNOTHERAPY BASED ON EARLY TUMOR ASSESSMENT DATA PRALAY MUKHOPADHYAY AstraZeneca, Gaithersburg, USA XUEKUI ZHANG University of Victoria, Victoria, Canada Disclosures Pralay
ASSESSING LONG-TERM BENEFITS OF IMMUNOTHERAPY BASED ON EARLY TUMOR ASSESSMENT DATA PRALAY MUKHOPADHYAY AstraZeneca, Gaithersburg, USA XUEKUI ZHANG University of Victoria, Victoria, Canada Disclosures Pralay
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Hormone therapyduration: Can weselectthosepatientswho benefitfromtreatmentextension?
 Hormone therapyduration: Can weselectthosepatientswho benefitfromtreatmentextension? Ivana Sestak, PhD Centre for Cancer Prevention Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine Queen Mary University London
Hormone therapyduration: Can weselectthosepatientswho benefitfromtreatmentextension? Ivana Sestak, PhD Centre for Cancer Prevention Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine Queen Mary University London
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer
 Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer Kathy S. Albain, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Dean s Scholar Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Cardinal Bernardin
Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer Kathy S. Albain, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Dean s Scholar Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Cardinal Bernardin
HAVE YOU BEEN recently DIAGNOSED with stage II or stage III colon cancer?
 To learn more about the Oncotype DX Colon Cancer Test, please visit www. oncotypedx.com and talk to your health care team. For insurance, financial aid or other questions about the Oncotype DX test, please
To learn more about the Oncotype DX Colon Cancer Test, please visit www. oncotypedx.com and talk to your health care team. For insurance, financial aid or other questions about the Oncotype DX test, please
Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer. Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
Application of Artificial Neural Network-Based Survival Analysis on Two Breast Cancer Datasets
 Application of Artificial Neural Network-Based Survival Analysis on Two Breast Cancer Datasets Chih-Lin Chi a, W. Nick Street b, William H. Wolberg c a Health Informatics Program, University of Iowa b
Application of Artificial Neural Network-Based Survival Analysis on Two Breast Cancer Datasets Chih-Lin Chi a, W. Nick Street b, William H. Wolberg c a Health Informatics Program, University of Iowa b
Multi-omics data integration colon cancer using proteogenomics approach
 Dept. of Medical Oncology Multi-omics data integration colon cancer using proteogenomics approach DTL Focus meeting, 29 August 2016 Thang Pham OncoProteomics Laboratory, Dept. of Medical Oncology VU University
Dept. of Medical Oncology Multi-omics data integration colon cancer using proteogenomics approach DTL Focus meeting, 29 August 2016 Thang Pham OncoProteomics Laboratory, Dept. of Medical Oncology VU University
Sesiones interhospitalarias de cáncer de mama. Revisión bibliográfica 4º trimestre 2015
 Sesiones interhospitalarias de cáncer de mama Revisión bibliográfica 4º trimestre 2015 Selected papers Prospective Validation of a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer TAILORx. NEJM 2015 OS for fulvestrant
Sesiones interhospitalarias de cáncer de mama Revisión bibliográfica 4º trimestre 2015 Selected papers Prospective Validation of a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer TAILORx. NEJM 2015 OS for fulvestrant
Statistical validation of biomarkers and surogate endpoints
 Statistical validation of biomarkers and surogate endpoints Marc Buyse, ScD IDDI, Louvain-la-Neuve & Hasselt University, Belgium marc.buyse@iddi.com OUTLINE 1. Setting the scene: definitions and types
Statistical validation of biomarkers and surogate endpoints Marc Buyse, ScD IDDI, Louvain-la-Neuve & Hasselt University, Belgium marc.buyse@iddi.com OUTLINE 1. Setting the scene: definitions and types
University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute UPMC CancerCenter. Uma Chandran, MSIS, PhD /21/13
 University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute UPMC CancerCenter Uma Chandran, MSIS, PhD chandran@pitt.edu 412-648-9326 2/21/13 University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute Founded in 1985 Director Nancy Davidson,
University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute UPMC CancerCenter Uma Chandran, MSIS, PhD chandran@pitt.edu 412-648-9326 2/21/13 University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute Founded in 1985 Director Nancy Davidson,
Classification. Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day Five. Rainer Spang
 Classification Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day Five Rainer Spang Ms. Smith DNA Chip of Ms. Smith Expression profile of Ms. Smith Ms. Smith 30.000 properties of Ms. Smith The expression
Classification Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day Five Rainer Spang Ms. Smith DNA Chip of Ms. Smith Expression profile of Ms. Smith Ms. Smith 30.000 properties of Ms. Smith The expression
Clinical Utility of Diagnostic Tests
 Clinical Utility of Diagnostic Tests David A. Eberhard MD, PhD Director, Pre-Clinical Genomic Pathology, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center Associate Professor, Depts. of Pathology and Pharmacology
Clinical Utility of Diagnostic Tests David A. Eberhard MD, PhD Director, Pre-Clinical Genomic Pathology, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center Associate Professor, Depts. of Pathology and Pharmacology
Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
 Implementing a National Cancer Clinical Trials System for the 21 st Century, Workshop #2 Session #5: Accelerating Innovation Through Effective Partnerships Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
Implementing a National Cancer Clinical Trials System for the 21 st Century, Workshop #2 Session #5: Accelerating Innovation Through Effective Partnerships Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
School of Medicine success with new HRB Applying Research into Policy and Practice (ARPP) Postdoctoral Fellowships 2018 programme
 School of Medicine success with new HRB Applying Research into Policy and Practice (ARPP) Postdoctoral Fellowships 2018 programme The School of Medicine is delighted to congratulate 5 researchers from
School of Medicine success with new HRB Applying Research into Policy and Practice (ARPP) Postdoctoral Fellowships 2018 programme The School of Medicine is delighted to congratulate 5 researchers from
April 5, :45 AM 1:45 PM MARRIOTT MARQUIS HOTEL & MARINA, MIRAMAR VIGNETTE 1 VIGNETTE 2 VIGNETTE 3* VIGNETTE 4* VIGNETTE 5*
 April 5, 2016 11:45 AM 1:45 PM MARRIOTT MARQUIS HOTEL & MARINA, MIRAMAR CHAIR: DANNY A. MILNER, JR., BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL, BOSTON, MA VIGNETTE 1 VIGNETTE 2 VIGNETTE 3* VIGNETTE 4* VIGNETTE 5* *VIGNETTES
April 5, 2016 11:45 AM 1:45 PM MARRIOTT MARQUIS HOTEL & MARINA, MIRAMAR CHAIR: DANNY A. MILNER, JR., BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL, BOSTON, MA VIGNETTE 1 VIGNETTE 2 VIGNETTE 3* VIGNETTE 4* VIGNETTE 5* *VIGNETTES
The TAILORx Trial: A review of the data and implications for practice
 The TAILORx Trial: A review of the data and implications for practice Angela DeMichele, MD, MSCE Jill & Alan Miller Endowed Chair in Breast Cancer Excellence Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology University
The TAILORx Trial: A review of the data and implications for practice Angela DeMichele, MD, MSCE Jill & Alan Miller Endowed Chair in Breast Cancer Excellence Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology University
The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer
 The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer Laura Spring, MD Breast Medical Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Primary Mentor: Dr. Aditya Bardia
The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer Laura Spring, MD Breast Medical Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Primary Mentor: Dr. Aditya Bardia
Introduction to Discrimination in Microarray Data Analysis
 Introduction to Discrimination in Microarray Data Analysis Jane Fridlyand CBMB University of California, San Francisco Genentech Hall Auditorium, Mission Bay, UCSF October 23, 2004 1 Case Study: Van t
Introduction to Discrimination in Microarray Data Analysis Jane Fridlyand CBMB University of California, San Francisco Genentech Hall Auditorium, Mission Bay, UCSF October 23, 2004 1 Case Study: Van t
National Cancer Policy Forum Workshop on Multi-Center Phase 3 Clinical Trials and NCI Cooperative Groups
 National Cancer Policy Forum Workshop on Multi-Center Phase 3 Clinical Trials and NCI Cooperative Groups Session 3: Data Collection Standards to Establish Safety and Efficacy: How Much Data Is Enough?
National Cancer Policy Forum Workshop on Multi-Center Phase 3 Clinical Trials and NCI Cooperative Groups Session 3: Data Collection Standards to Establish Safety and Efficacy: How Much Data Is Enough?
Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical Informatics (CoSBBI) Outline. Molecular Biology of Cancer AND. Goals/Expectations. David Boone 7/1/2015
 Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
She counts on your breast cancer expertise at the most vulnerable time of her life.
 HOME She counts on your breast cancer expertise at the most vulnerable time of her life. Empowering the right treatment choice for better patient outcomes. The comprehensive genomic assay experts trust.
HOME She counts on your breast cancer expertise at the most vulnerable time of her life. Empowering the right treatment choice for better patient outcomes. The comprehensive genomic assay experts trust.
Jules Bordet Institute, Brussels, Belgium Université Libre de Bruxelles Breast International Group (BIG aisbl), Chair ESMO President
 Symposium «Evaluation of the Belgian Cancer Plan» Brussels, November 26th, 2012 Personalized oncology in Europe: only a dream if national health systems do not get involved in diagnostics and pivotal cancer
Symposium «Evaluation of the Belgian Cancer Plan» Brussels, November 26th, 2012 Personalized oncology in Europe: only a dream if national health systems do not get involved in diagnostics and pivotal cancer
