34 Cancer. Lecture Outline, 11/30/05. Cancer is caused by mutant genes. Changes in growth properties of cancer cells
|
|
|
- Trevor Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 34 Cancer Lecture Outline, 11/30/05 Review the Cell cycle Cancer is a genetic disease Oncogenes and roto-oncogenes Normally romote cell growth. Become oncogenic after oint mutations, dulications, deletion of silencer, etc Tumor Suressor genes Normally inhibit cell growth. Allow cell growth when damaged or deleted. Mutator genes The multi-ste model of cancer Cancer is caused by mutant genes Changes in growth roerties of cancer cells Mutations in regulatory genes lead to uncontrolled cell growth Understanding gene regulation is one key to understanding cancer All cancers trace back to single cell Must accumulate multile mutations, all in the same cell lineage 1
2 The incidence of human cancers increases markedly with age It takes a long time for the causative mutations to accumulate in a cell The Human Cell Cycle ~ 1 hour ~ 4 hours ~ 10 hours ~ 9 hours Cell Cycle Regulators and Cancer Rb reresses E2F Free E2F is a transcrition activator Cyclin/Cdk inactivates Rb by hoshorylation 2
3 GTP Ras GTP Ras P53 is a transcrition factor that activates 21, an inhibitor of cyclin/cdk2 Signaling athways that regulate cell division (a) Cell cycle stimulating athway. This athway is triggered by 1 a growth factor that binds to 2 its recetor in the lasma membrane. The signal is relayed to 3 a G rotein called Ras. Like all G roteins, Ras is active when GTP is bound to it. Ras asses the signal to 4 a series of rotein kinases. The last kinase activates 5 a transcrition activator that turns on one or more genes for roteins that stimulate the cell cycle. If a mutation makes Ras or any other athway comonent abnormally active, excessive cell division and cancer may result. 1 Growth factor 3 G rotein Hyeractive Ras rotein MUTATION (roduct of oncogene) issues signals on its own 4 Protein kinases 2 Recetor (hoshorylation cascade) NUCLEUS 5 Transcrition factor (activator) DNA Gene exression Protein that stimulates the cell cycle (b) Cell cycle inhibiting athway. In this athway, 1 DNA damage is an intracellular signal that is assed via 2 rotein kinases and leads to activation of Activated 53 romotes transcrition of the gene for a rotein that inhibits the cell cycle. The resulting suression of cell division ensures that the damaged DNA is not relicated. Mutations causing deficiencies in any athway comonent can contribute to the develoment of cancer. UV light 2 Protein kinases 3 Active form of 53 1 DNA damage in genome DNA MUTATION Defective or missing transcrition factor, such as 53, cannot activate transcrition Protein that inhibits the cell cycle (c) Effects of mutations. Increased cell division, ossibly leading to cancer, can result if the cell cycle is overstimulated, as in (a), or not inhibited when it normally would be, as in (b). Protein overexressed EFFECTS OF MUTATIONS Protein absent Figure Cell cycle overstimulated Increased cell division Cell cycle not inhibited Stimulation versus inhibition of G1 rogression Stimulation of G1 rogression myc RB Inhibition S-hase entry mitogens ras cyclin D / cdk4 oncogenes RB P P P S-hase entry allowed PKB 27 DNA-damage Inhibition of G1 rogression RB Inhibition S-hase entry anti-mitogen (TGF-β) 15 cyclin D / cdk4 RB P P P S-hase entry allowed tumor suressor genes? 16 Oncogenes All are involved in ositive control of cell growth and division. About 100 different oncogenes have been identified Can be various kinds of roteins: Growth factors, regulatory genes involved in the control of cell multilication. Protein kinases, add hoshate grous to target roteins, imortant in signal transduction athways. Proto-oncogenes Normal form of the gene that is involved in ositive regulation of the cell cycle 3
4 Genetic changes that can turn roto-oncogenes into oncogenes Translocation uts abl under the control of a different romoter Proto-oncogene DNA Translocation or transosition: gene moved to new locus, under new controls Gene amlification Point mutation within a control element Point mutation within the gene New romoter Oncogene Oncogene Normal growth-stimulating rotein in excess Normal growth-stimulating rotein in excess Normal growth-stimulating Hyeractive or rotein in excess degradationresistant rotein Figure Translocation uts bcl near a new enhancer Ras Proto-oncogene Mutated in 30% of all cancers. A molecular switch in the signal transduction athway leading from growth factors to gene exression controlling cell roliferation: GF recetor Ras TF target genes growth. A single amino acid change in Ras rotein can cause constant stimulation of the athway, even in the absence of growth factors. 4
5 Recetor tyrosine kinases can activate ras ras is a monomeric G-rotein molecular switch You ve seen RAS before... PROBLEMS IN CANCER: - broken ras won t shut off Ras activation sets off a hoshorylation cascade MAPKK 1,000 MAPK 100,000 MAPKKK Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases MAPKs Controls: -Transcrition Factors -Translation Factors -Cell Division Oncogenes act cooeratively in tumor-induction - Broken recetor thinks ligand there even when it isn t -broken MAPK on all the time, even when not hoshorylated RESULT: continuous signal for cell to divide 5
6 Tumor Suressor Genes Normally inhibit cell growth Examle: retinoblastoma RB rotein normally blocks a transcrition factor, E2F 53 Gene Detects DNA damage The Last Gatekeeer Aotosis = controlled cell death Involved in 50% of cancers Often not malignant desite other cancer-causing mutations until 53 is inactivated by mutation. Two ossible resonses to DNA damage: 1) Acts as a Transcrition Factor to activate exression of 21, which inhibits CDK/G1 cyclin to halt the cell cycle; then activates DNA reair. 2) Triggers Aotosis (rogrammed cell death) if damage can t be reaied. executioner roteins (casases) break down the cell Reduced cell death can also lead to cancer 6
7 Aotosis athways htt:// Mutator genes Cancer is caused by mutations, so factors that increase mutation rate will increase cancer rate. What kinds of genes would increase mutation rate? Examle: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Many environmental factors (carcinogens) also cause DNA damage or mutations, that can lead to cancer A multiste model for the develoment of colorectal cancer Colon 1 Loss of tumor-suressor Colon wall gene APC (or other) Normal colon eithelial cells (1) The clonal origin of tumors: each individual cancer is a clone that arises from a single cell. The rogeny cells have growth advantage over the surrounding normal cells. (2) Cancer develoment is a multi-ste rocess. Multile mutations accumulated over eriods of many years ---- multi-hit model. Small benign growth (oly) 2 Activation of Ras oncogene 3 Loss of tumorsuressor gene DCC Larger benign growth (adenoma) 4 Loss of tumor-suressor gene 53 5 Additional mutations Malignant tumor (carcinoma) Figure
A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
 Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer
 CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
cis-9,trans-11-conjugated linoleic acid down- regulates phorbol ester-induced d NF- B activation and subsequent COX-2 expression in hairless mouse
 cis-9,trans-11-conjugated linoleic acid down- regulates horbol ester-induced d NF-B activation and subsequent COX-2 exression in hairless mouse skin by targeting IB kinase and PI3K-Akt Introduction Inflammation
cis-9,trans-11-conjugated linoleic acid down- regulates horbol ester-induced d NF-B activation and subsequent COX-2 exression in hairless mouse skin by targeting IB kinase and PI3K-Akt Introduction Inflammation
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Peng Zhang 1, Michelle Yueqin Chen 1, Diana Caridha 1, William J. Smith 2 & Peter K. Chiang 1
 Peng Zhang 1, Michelle Yueqin Chen 1, Diana Caridha 1, William J. Smith 2 & Peter K. Chiang 1 1 Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, 2 United States Army Medical Research Institute of Chemical Defense
Peng Zhang 1, Michelle Yueqin Chen 1, Diana Caridha 1, William J. Smith 2 & Peter K. Chiang 1 1 Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, 2 United States Army Medical Research Institute of Chemical Defense
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Gene Regulation. Bacteria. Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II. Prof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department
 Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer: key epigenetic players
 Editorial Neuroendocrine differentiation in rostate cancer: key eigenetic layers Karishma Guta 1,2, Sanjay Guta 1,2,3,4,5 1 Deartment of Urology, Case Western Reserve University, School of Medicine, Cleveland,
Editorial Neuroendocrine differentiation in rostate cancer: key eigenetic layers Karishma Guta 1,2, Sanjay Guta 1,2,3,4,5 1 Deartment of Urology, Case Western Reserve University, School of Medicine, Cleveland,
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Fels Institute For Cancer Research And Molecular Biology, Temple University, School Of Medicine, 3307 North Broad Street. Philadelphia, PA 19140
 Frontiers in Bioscience 5, d1-19, January 1, 2000] CELL CYCLE CONTROL OF PANCREATIC BETA CELL PROLIFERATION Sushil G. Rane and E. Premkumar Reddy Fels Institute For Cancer Research And Molecular Biology,
Frontiers in Bioscience 5, d1-19, January 1, 2000] CELL CYCLE CONTROL OF PANCREATIC BETA CELL PROLIFERATION Sushil G. Rane and E. Premkumar Reddy Fels Institute For Cancer Research And Molecular Biology,
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Regarding techniques of proteomics, there is:
 Molecular الحلقة biology 14 واألخيرة To put you back in the context; the discussion was about Trancriptomics (the study of transcription). The following topic will be PROTEOMICS, which is the study of
Molecular الحلقة biology 14 واألخيرة To put you back in the context; the discussion was about Trancriptomics (the study of transcription). The following topic will be PROTEOMICS, which is the study of
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division
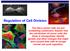 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Mohammed El-Khateeb. Tumor Genetics. MGL-12 July 21 st 2013 台大農藝系遺傳學 Chapter 22 slide 1
 Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 July 21 st 2013 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cellular Basis of Cancer Cancer is a collection of diseases characterized by abnormal and uncontrolled growth
Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 July 21 st 2013 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cellular Basis of Cancer Cancer is a collection of diseases characterized by abnormal and uncontrolled growth
Oncogenes and Tumor. supressors
 Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
target effector enzyme is Phospholipase C A. target protein adenylate cyclase camp-> PKA B. target protein phospholipase C two 2nd Messengers:
 COR 011 Cell Communication II Lect 19 Lecture Outline Signal molecule Activated Ras-GT A G-rotein And they tell friends And they tell friends And they tell friends 1. Finish Trimeric G-rotein: hospholipase
COR 011 Cell Communication II Lect 19 Lecture Outline Signal molecule Activated Ras-GT A G-rotein And they tell friends And they tell friends And they tell friends 1. Finish Trimeric G-rotein: hospholipase
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer
 Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Mohammed El-Khateeb. Tumor Genetics. MGL-12 May 13 th Chapter 22 slide 1 台大農藝系遺傳學
 Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 May 13 th 2014 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cancer Genetics Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer Multistage Model
Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 May 13 th 2014 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cancer Genetics Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer Multistage Model
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Cell Cycle Regulation. Adrian R. Black
 Cell Cycle Regulation Adrian R. Black 845-3090 Adrian.black@roswellpark.org Loss of Growth Control Block of Apoptosis Evasion of Senescence Angiogenesis Invasion hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome
Cell Cycle Regulation Adrian R. Black 845-3090 Adrian.black@roswellpark.org Loss of Growth Control Block of Apoptosis Evasion of Senescence Angiogenesis Invasion hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
General Biology 1004 Chapter 11 Lecture Handout, Summer 2005 Dr. Frisby
 Slide 1 CHAPTER 11 Gene Regulation PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Slide 1 CHAPTER 11 Gene Regulation PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Section D. Genes whose Mutation can lead to Initiation
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Received: 12 June 2012; in revised form: 26 July 2012 / Accepted: 1 August 2012 / Published: 10 August 2012
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9980-9991; doi:10.3390/ijms13089980 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdi.com/journal/ijms Combined Phoshatase and Tensin Homolog
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9980-9991; doi:10.3390/ijms13089980 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdi.com/journal/ijms Combined Phoshatase and Tensin Homolog
Ch 7 Mutation. A heritable change in DNA Random Source of genetic variation in a species may be advantageous, deleterious, neutral
 Ch 7 Mutation A heritable change in DNA Random Source of genetic variation in a species may be advantageous, deleterious, neutral Mutation (+ sexual reproduction) + natural selection = evolution Types
Ch 7 Mutation A heritable change in DNA Random Source of genetic variation in a species may be advantageous, deleterious, neutral Mutation (+ sexual reproduction) + natural selection = evolution Types
HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED. Patterns of Gene Expression in Differentiated Cells
 HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 5 HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 6 Every somatic cell in an organism contains identical genetic instructions. They all share the same genome. So what makes cells different
HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 5 HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 6 Every somatic cell in an organism contains identical genetic instructions. They all share the same genome. So what makes cells different
Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
 Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS To understand the concept of the hallmarks of cancer and that they are phenotypic changes needed in all cancer cells. To list the tumor enablers
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS To understand the concept of the hallmarks of cancer and that they are phenotypic changes needed in all cancer cells. To list the tumor enablers
Emerging" hallmarks of cancer, a. Reprogramming of energy metabolism b. Evasion of the immune system, Enabling characteristics, a.
 HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
Hormone Resistance and Hypersensitivity
 Endocrine Develoment 24 Hormone Resistance and Hyersensitivity From Genetics to Clinical Management Worksho, Genoa, May 2012. Bearbeitet von M. Maghnie, S. Loche, M. Caa, L. Ghizzoni, R. Lorini, P.-E.
Endocrine Develoment 24 Hormone Resistance and Hyersensitivity From Genetics to Clinical Management Worksho, Genoa, May 2012. Bearbeitet von M. Maghnie, S. Loche, M. Caa, L. Ghizzoni, R. Lorini, P.-E.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17
 Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17 INTRODUCTION - Our genes underlie every aspect of human health, both in function and
Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17 INTRODUCTION - Our genes underlie every aspect of human health, both in function and
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
BIOLOGY. Cell Communication. Outline. Evolution of Signaling. Overview: Cellular Messaging. Local and Long-Distance Signaling
 11 CAMBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Cell Communication Lecture resentation by Dr Burns NVC Biol 120 Outline I. Cell Signaling II. Forms of cell signaling III. Quick
11 CAMBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Cell Communication Lecture resentation by Dr Burns NVC Biol 120 Outline I. Cell Signaling II. Forms of cell signaling III. Quick
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits)
 Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
C) The graph should look exactly like the graph on the left (Mut1 cells + Mating Pheromone for 3 hours at 25 degrees). The cells arrest in G1.
 706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
Cancer Cells. It would take another 20 years and a revolution in the techniques of biological research to answer these questions.
 Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Matrix abnormalities in pulmonary fibrosis
 LUNG SCIENCE CONFERENCE MATRIX ABNORMALITIES Matrix abnormalities in ulmonary fibrosis Chandak Uaguta, Chiko Shimbori, Rahmah Alsilmi and Martin Kolb Affiliation: Firestone Institute for Resiratory Health,
LUNG SCIENCE CONFERENCE MATRIX ABNORMALITIES Matrix abnormalities in ulmonary fibrosis Chandak Uaguta, Chiko Shimbori, Rahmah Alsilmi and Martin Kolb Affiliation: Firestone Institute for Resiratory Health,
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2)
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November
 Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Control of Cell Cycle. Unit 2 Part f III
 Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer.
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of November
 Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer
 BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer Topics we will cover today Introduction to normal and cancer cells Characteristics of cells in culture Cancerous changes in cells Viruses can harbor transforming
BioSci 145A Lecture 15 - Oncogenes and Cancer Topics we will cover today Introduction to normal and cancer cells Characteristics of cells in culture Cancerous changes in cells Viruses can harbor transforming
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Hormones and Cancer Research Unit Department of Medicine, McGill University Dr. Jean-Jacques Lebrun
 Hormones and Cancer Research Unit Department of Medicine, McGill University www.hcru.mcgill.ca Dr. Jean-Jacques Lebrun TGF /Smad signaling pathways CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Institut de recherches
Hormones and Cancer Research Unit Department of Medicine, McGill University www.hcru.mcgill.ca Dr. Jean-Jacques Lebrun TGF /Smad signaling pathways CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Institut de recherches
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
CANCER. Inherited Cancer Syndromes. Affects 25% of US population. Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease)
 CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
REVIEW. The regulation of TGF-β/SMAD signaling by protein deubiquitination. Protein & Cell
 Protein Cell 2014, 5(7):503 517 DOI 10.1007/s13238-014-0058-8 The regulation of TGF-β/SMAD signaling by rotein deubiquitination Juan Zhang 1,2, Xiaofei Zhang 2, Feng Xie 1, Zhengkui Zhang 1, Hans van Dam
Protein Cell 2014, 5(7):503 517 DOI 10.1007/s13238-014-0058-8 The regulation of TGF-β/SMAD signaling by rotein deubiquitination Juan Zhang 1,2, Xiaofei Zhang 2, Feng Xie 1, Zhengkui Zhang 1, Hans van Dam
Cell Communication. Cell Communication. Cell Communication. Cell Communication. Cell Communication. Chapter 9. Communication between cells requires:
 Chapter 9 Communication between cells requires: ligand: the signaling molecule receptor protein: the molecule to which the receptor binds -may be on the plasma membrane or within the cell 2 There are four
Chapter 9 Communication between cells requires: ligand: the signaling molecule receptor protein: the molecule to which the receptor binds -may be on the plasma membrane or within the cell 2 There are four
BL 424 Test pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points.
 BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS. D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH
 E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
THE EUKARYOTIC CELL CYCLE AND CANCER
 THE EUKARYOTIC CELL CYCLE AND CANCER ABOUT THIS WORKSHEET This worksheet complements the Click and Learn The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer developed in conjunction with the 2013 Holiday Lectures on
THE EUKARYOTIC CELL CYCLE AND CANCER ABOUT THIS WORKSHEET This worksheet complements the Click and Learn The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer developed in conjunction with the 2013 Holiday Lectures on
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2
 p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
'''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
 '''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Anggraini'Barlian,' Iriawa-' Tjandra'Anggraeni' SITH4ITB' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
'''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Anggraini'Barlian,' Iriawa-' Tjandra'Anggraeni' SITH4ITB' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test
 Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division. Making new cells. Getting the right stuff. Overview of mitosis 1/5/2015
 Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 210, and for Concept 11.1, read from the first full paragraph on p. 212. Read all of Concept 11.2. Pay
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 210, and for Concept 11.1, read from the first full paragraph on p. 212. Read all of Concept 11.2. Pay
