Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
|
|
|
- Ezra Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
2 Some Terminology: 1. Cells are the smallest living structure 2. Cell = functional unit of the body 3. Cytology = The Study of Cells 4. Ultrastructural Cytology = Cytology at the Electron Microscopic level 5. Histology = the study of tissues (next meeting)
3 Anatomy of a typical cell 1. Cell membrane 2. Cytoplasm = cytosol + organelles 3. Organelles Smallest: Granule cell in cerebellum: 4 µ RBC: 5-7 µ = mm Largest: Anterior horn cell in spinal cord: 135 µ Ovum: 120 µ = 0.12 mm Longest: Pseudounipolar cell (CNS to toe) Fig. 2.1
4 Anatomy of a typical cell, cont d Shapes: Squamous (scale) - flat, capillaries, lungs Cuboidal - lines ducts Columnar - length > width, digestive tract Stratified - many layers Many others will be covered in histology (next two lectures)
5 Cell Membrane = phospholipid bilayer Physical isolation of the cell contents from the environment (interstitium) Regulation of exchange of materials with the environment Sensitivity to changes in the environment Structural support of the cell Organelles, too!
6 Cell Membrane Synonyms: plasma membrane plasmalemma axolemma others! Contains: phospholipids cholesterol proteins carbohydrates
7 Membrane Permeability Diffusion Concentration Gradient of Solutes Osmosis Water (solvent) through semipermeable membrane Filtration Hydrostatic Pressure» Capillaries! Active Transport Requires energy (ATP)
8 Endocytosis = into the cell Pinocytosis Extracellular Fluid Phagocytosis Solid Objects, e.g., bacteria Receptor-mediated Endocytosis Special membrane proteins required
9 Exocytosis = out of the cell Secretory vesicles (e.g. hormones) Fluid and waste removal
10 Cytosol vs. cytoplasm Cytosol = The thick fluid inside any cell Often synonymous with cytoplasm (protoplasm) Cytoplasm = cytosol + organelles Suspends organelles
11 Organelles Structures INSIDE a cell that have specific functions wrt cellular structure, maintenance, or metabolism Membranous» Nucleus» Golgi apparatus» Endoplasmic reticulum» Mitochondria» Vesicles and lysosomes Nonmembranous» Ribosomes» Microtubules (cytoskeleton)» Actin/Myosin in muscle cells
12
13 Nucleus (= center) Visible with LM Membrane bound Many pores DNA 23 Pairs of Chromosomes» Except gametes Nucleolus Most active DNA
14 Nucleus
15 Golgi Apparatus Packaging and shipping of proteins (secretory granules and transport vesicles) Membrane renewal Synthesis of Lysosomes
16 Fig 2.17 Exocytosis
17 Golgi Apparatus
18 Endoplasmic Reticulum Synthesis, Storage, transport Smooth ER Lipid synthesis Rough ER Ribosomes make it rough ER Protein synthesis
19 Mitochondrion / -a Energy Conversion for cellular activities Formation of ATP Double membrane Glycolysis and TCA cycle More prevalent in active cells, e.g., rods and cones Their own genome Self-replicating
20 Lysosomes
21 Ribosomes - RNA 60% RNA + 40% protein Protein Factories Fixed vs. free ribosomes
22 Cytoskeleton 4 major components: 1. Microfilaments (mostly actin) Intermediate filaments Microtubules (composed of tubulin subunits) Function: support & movement of cellular structures & materials
23 Cilium Cilia (pl.) In 9+2 array Compare to microvilli and flagella
24 Actin/Myosin The contractile proteins in muscle cells Striations Skeletal muscle
25 Intercellular Attachments Chapter 4, pp Act as: 1.Seals betw cells Intercellular communication Added strength to resist separation 1. Gap Junctions 2. Tight Junctions 3. Desmosomes 4. Basement Membrane Fig 4-7
26 1) Gap Junctions Channel proteins (connexons) interlock and form pores Abundant in cardiac and smooth muscle Allows efficient intercellular communication
27 2) Tight Junctions Interlocking membrane proteins Found near surface of cells lining the digestive tract. Explain! Adhesive Belt Junctions deep to tight junctions reinforce the seal
28 3) Desmosomes Proteoglycan layer reinforced by transmembrane proteins (cell adhesion molecules or CAMs) Belt, button and hemidesmosomes Found in superficial layers of skin
29 4) Basement Membrane Reticular fibers + Basal Lamina Between epithelium and deeper connective tissue Acts as a filter, and helps epithelial regeneration
30 Fig 2.19 a
31
32 Mitosis (vs. meiosis) Cell Division Interphase Between mitosis Prophase Chromosomes become bunched Metaphase Chromosomes gather at equator Anaphase Chromosomes move to poles Telophase The two new nuclei form Cytokinesis Actual cell separation Two new diploid cells
33 Mitosis
34
35 Some cells Fat cells (adipocytes) Cartilage cells (chondrocytes)
36 More cells Neutrophil Plasma cell
37 Still more cells Columnar cells Sperm cells (spermatozoa)
38 River Cullenagh, Ennistymon, Co Clare, Ireland
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
Chapter 2: The Cell. Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College
 Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells
 Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Chapter 02 Cytology-The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
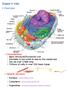 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
1.3 - Cells. Chapter 3 - Cells
 1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells
 Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/human-anatomy-5th-edition-saladin-test-bank/ Chapter 02 - Cytology - The Study of Cells Chapter 02 Cytology -
Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/human-anatomy-5th-edition-saladin-test-bank/ Chapter 02 - Cytology - The Study of Cells Chapter 02 Cytology -
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells
 Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Chapter 02 Cytology - The Study of Cells Multiple Choice Questions 1. Cells of the small intestine and kidney tubule have a "brush border" composed of, which are cell extensions that increase surface area.
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Cells & Tissues. Chapter 3
 Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS
 CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology
 A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology Form A Name Lab 1. Pinocytosis would allow the intake of a. solid b. gas c. liquids d. all of these answers are true 2. Which of the following
A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology Form A Name Lab 1. Pinocytosis would allow the intake of a. solid b. gas c. liquids d. all of these answers are true 2. Which of the following
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and function
 Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Theory. Passive Transport
 Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic
 Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Plasma membrane The Nucleus Control center of the cell Contains genetic material (DNA) Three regions Nuclear envelope (membrane) Nucleolus
 Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy
Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Goals. Cells. Cells: The Living Units. By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe.
 C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
6 functions of membrane proteins integral & peripheral proteins Membrane Junctions
 Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma membrane?
 Chapter 3 Reading Guide The Cellular Level of Organization Name 1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. Section 3.1 Parts of a Cell 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma
Chapter 3 Reading Guide The Cellular Level of Organization Name 1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. Section 3.1 Parts of a Cell 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis!
 Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
The Cell. The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
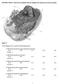 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
Cell Structure and Function
 C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
Cell Structure & Interactions
 Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
Overview. Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions. The Cell. Key Terms. Microscopes. Microscopes. Cytology The study of cells
 Overview Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Key Terms The Cell active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic
Overview Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Key Terms The Cell active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
basic unit structure and function
 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Microanatomy-Cytology (cells)
 Microanatomy-Cytology (cells) Levels of Organization least complex most complex Chemical level>cellular level>tissue level>organ level>organ system level>organism level Cytology Cytology-the study of the
Microanatomy-Cytology (cells) Levels of Organization least complex most complex Chemical level>cellular level>tissue level>organ level>organ system level>organism level Cytology Cytology-the study of the
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 3
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 3 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 3 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Name 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of
 Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Name: Per/row: Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology
 Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
4. A phospholipid is an example of organization at the level.
 1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units
 Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Cell. ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange
 Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things
 Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure
Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cytology. Cell Anatomy. Cell Theory - A good place to start! The generalized cell contains: Cell membrane Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytosol Organelles
 Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Cytology. Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges
 Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Cells. Introduction: Composite Cell: Bi100 Chapter 3
 Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
Homeostatic Control Systems
 Homeostatic Control Systems In order to maintain homeostasis, control system must be able to Detect deviations from normal in the internal environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate
Homeostatic Control Systems In order to maintain homeostasis, control system must be able to Detect deviations from normal in the internal environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
I. Introduction. Unit One. PROKARYOTIC CELL (bacterium Escherichia coli) TYPICAL PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL CELLS OF THE SIX KINGDOMS
 3 CELLS OF THE SIX KINGDOMS ARCHAEA EUBACTERIA PROTISTA Karen Webb Smith Unit One FUNGI PLANTAE ANIMALIA PROKARYOTIC CELL (bacterium Escherichia coli) TYPICAL PLANT CELL nucleoid cytoplasm cell wall ANIMAL
3 CELLS OF THE SIX KINGDOMS ARCHAEA EUBACTERIA PROTISTA Karen Webb Smith Unit One FUNGI PLANTAE ANIMALIA PROKARYOTIC CELL (bacterium Escherichia coli) TYPICAL PLANT CELL nucleoid cytoplasm cell wall ANIMAL
