Metabolic profiling of Echinostoma caproni and Schistosoma mansoni in their definitive and intermediate hosts
|
|
|
- Angelina Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /s W. Stefański Institute of Parasitology, PAS Acta Parasitologica, 2013, 58(1), 1 5; ISSN REVIEW ARTICLE Metabolic profiling of Echinostoma caproni and Schistosoma mansoni in their definitive and intermediate hosts Ciara O Sullivan, Bernard Fried* and Joseph Sherma Department of Chemistry, *Department of Biology, Lafayette College, Easton, PA Abstract This review examines metabolic profiling of Schistosoma mansoni and Echinostoma caproni in their definitive and intermediate hosts. The earlier coverage of the literature on metabolic profiling was reviewed by Wang et al. 2010, Advances in Parasitology, 73, and covered mainly studies using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The methods focused upon in our review are mainly chromatographic. In the studies reviewed, various metabolites were analyzed in hosts infected with either E. caproni or S. mansoni and compared to the uninfected controls. Keywords Metabolic profiling, trematodes, Schistosoma mansoni, Echinostoma caproni, chromatography Introduction Studies of trematodes are important because millions of humans worldwide suffer from various diseases (trematodiases) associated with different species. These trematodes include blood flukes (Schistosoma), intestinal flukes (Echinostoma), and liver flukes (Fasciola, Clonorchis, and Opisthorchis) (Cox 1993). It is estimated that 40 to 50 million humans worldwide are infected with various food-borne trematodes, which include species of Echinostoma and Fasciola (Fried et al. 2004). Schistosoma infections cause schistosomiasis in humans, and it is estimated that schistosomes infect 200 million people globally (Chitsulo et al. 2000). Current methods of detecting and diagnosing trematodes mainly involve examination of the host feces for the presence of eggs (Fried et al. 2004). This is a time consuming and laborious process, and other methods of detection would be helpful to the biomedical community and to those who suffer from trematodiases. To help solve this problem, research on metabolic profiling has been undertaken to better understand how the presence of these trematodes affect host metabolism. Metabolic profiling determines the presence of certain metabolic reactions to specific outside stimuli (Wang et al. 2010, Holmes 2010). Studies analyzing such metabolic responses have been extensive and vital to the characterization of particular pathologies associated with metabolic and infectious diseases. The most recent review of metabolic profiling studies of trematode infections in humans is that of Wang et al. (2010). That review comprises the salient literature mainly based on nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy methods to profile metabolic markers of major trematode infections. They compiled important information on the metabolic fingerprints of S. mansoni, S. japonicum, E. caproni, and F. hepatica, the major species of trematodes for which metabolic profiling studies are available. There have been several reviews discussing food-borne trematodiasis, mainly on diseases associated with the following trematodes: Echinostoma, Clonorchis, Fasciola, Opisthorchis, and Paragonimus. Infection with these trematodes is usually caused from the consumption of metacercarial cyst contaminated freshwater aquatic animals including fish, frogs, snails, snakes, and tadpoles. The Fried et al. (2004), Fried and Abruzzi (2010) reviews include descriptions of these important trematodes, along with methods of diagnosis and treatment; current statistics on worldwide prevalence of these diseases are also included in these reviews. *Corresponding author: friedb@lafayette.edu
2 2 Ciara O Sullivan et al. In our review, we cover salient studies done after the review of Wang et al. (2010) and some studies not included in that review. The methods used in most of the papers we have included are mainly thin layer chromatography (TLC) or high performance TLC (HPTLC). The difference between these two methods is the type of plate used. In HPTLC, the sorbent particles are smaller and more uniform in size (mean particle size 5 µm), which results in better and faster separations and more sensitive detection of the studied analytes. All of the TLC/HPTLC studies reviewed involved use of a densitometer (CAMAG TLC Scanner 2 or 3 with Cats-3 or wincats software, respectively) to scan standard and sample zones in the reflectance mode and automatically quantify the sample zones based on their scan areas compared to the areas of the standards in a calibration curve. We only consider herein work on S. mansoni and E. caproni, since these two trematodes are the most widely studied for information on metabolic profiling. Within each section of our review, papers that have been covered first are studies of the infection in definitive hosts, followed by papers on the metabolic profiling in the intermediate host. Schistosoma Studies Trematodes of the genus Schistosoma have been extensively studied because they cause schistosomiasis, a tropical disease infecting millions of people globally. Adult schistosomes are white to gray, dioecious worms, 7 20 mm long with two terminal suckers (Gryseels et al. 2006) and live in the mesenteric and hepatic portal blood vessels of their vertebrate hosts. These blood flukes are endemic to 74 countries and territories primarily in Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, South America, and Asia (Chitsulo et al. 2000). The main species infecting humans are S. mansoni, S. japonicum, and S. haematobium (Gryseels et al. 2006). Because the metabolic profiling literature is mainly on S. mansoni, this is the only schistosome we cover here. Muller et al. (2001) examined the effects of S. mansoni infection on the neutral lipid content of the liver, ileum, and serum of mice. Host samples were examined at days 14, 45, and 75 post infection. After sample preparation by the Folch method [extraction of lipids with chloroform-methanol (2:1) followed by purification of the extracts by washing with 0.88% aqueous KCl], lipids were separated by HPTLC on Whatman LHPKDF laned preadsorbent silica gel plates with the Mangold (1969) mobile phase (petroleum ether-diethyl ether-glacial acetic acid, 80:20:1) and detected as dark blue zones on the yellow layer background using 5% ethanolic phosphomolybdic acid (PMA) spray reagent. The most significant finding was that triacylglycerol content in the liver and ileum decreased as the infection progressed, and at the same time cholesterol esters in the liver decreased. O Sullivan et al. (2012) examined the effects of S. mansoni infection on the neutral and polar lipids of the liver, spleen, and small intestine of mice. The samples were analyzed after the mice were necropsied 8 weeks post-infection. Neutral lipids isolated by Folch extraction were separated on preadsorbent, laned Analtech HPTLC-HLF silica gel plates with the Mangold mobile phase and were detected using PMA reagent agent. Polar lipids were separated with the Wagner et al. (1961) mobile phase chloroform-methanol-deionized (DI) water (65:25:4) and detected using 10% cupric sulfate in 8% phosphoric acid spray reagent. These lipids appeared as brown-black spots on a white layer background. No significant differences were found in the neutral lipids of the infected mice compared to the uninfected controls. There was a significantly lower amount of the polar lipid phosphatidylcholine in the liver and small intestine of infected mice compared to uninfected controls. Muller et al. (2000) studied the effects of S. mansoni infection on the neutral lipids of the digestive gland-gonad complex (DGG) of B. glabrata. The lipids were separated on Whatman LHPKDF silica gel HPTLC plates with the Mangold mobile phase and detected with PMA reagent. There was a significant increase in the free sterol and triacylglycerol fractions in the DGG at six and eight weeks post-infection of infected snails compared to the uninfected controls. Pachuski et al. (2002) studied the effects of S. mansoni infection on the amino acid content of the DGG of B. glabrata snails. Amino acids were extracted with ethanol-di water (70:30) and separated on Whatman LHPKDF silica gel HPTLC plates, strong acid cation-exchange sheets (POLY- GRAM IONEX-25 SA-Na; Macherey-Nagel), reversed phase plates with preadsorbant zone (Whatman LKC18F), and HPTLC cellulose F plates (EMD Millipore, a division of Merck KgaA). Three different mobile phases were used: ph 3.3 citrate buffer for the ion exchange sheet, n-propanol-0.5m NaCl (4:6) for the reversed phase layer, and n-butanol-acetic acid-water (3:1:1) for both silica and cellulose gel layers. Detection of the amino acids was done with ninhydrin reagent to produce purple zones for all amino acids except proline, which showed as a yellow zone. There was a significant decrease in the amount of lysine in the infected snails compared to the uninfected controls. In one non-chromatographic study not included in the Wang et al. (2010) review, Ong et al. (2004) used inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) to study the effects of S. mansoni infection on the inorganic elements in B. glabrata snails. A Thermo Jarrell Ash simultaneous-reading ICP-AES instrument was used to measure the concentrations of 28 inorganic elements in both infected and uninfected snail bodies. Elevated concentrations of calcium, cadmium, manganese, and sodium in the bodies of infected snails were found compared to the uninfected controls. Jarusiewicz et al. (2006) studied the glucose and maltose content in the DGG of estivated B. glabrata snails infected with S. mansoni compared to estivated, uninfected controls. The sugars were extracted using 70% aqueous ethanol, and TLC was done on Whatman LK5DF laned preadsorbent silica gel plates developed with ethyl acetate-glacial acetic acidmethanol-di water (60:15:15:10) mobile phase. The carbo-
3 Metabolic profiling of trematodes 3 hydrates were detected using the α-naphthol-sulfuric acid reagent described in Cline et al. (1999). Spots appeared as dark purple zones on a yellow layer background. Both infected and uninfected estivated snails showed significantly decreased maltose and glucose levels compared to the non-estivated infected and uninfected controls. Massa et al. (2007) examined the effects of S. mansoni infection on the carboxylic acids of B. glabrata using ion exclusion high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). They analyzed both the snail DGG and hemolymph. HPLC was carried out using an Aglient 1100 series system with an autosampler, a Bio-Rad Laboratories Aminex ion exclusion HPX-87H column, and an ultraviolet diode array detector. Sulfuric acid (5.0 mm) was the mobile phase with a flow rate of 0.6 ml/min. Retention times of the standard and sample acids were matched to identify each acid. They found that there was a significant reduction in all of the carboxylic acids in the DGG of infected snails compared to uninfected controls. This study suggests that carboxylic acids studied are useful metabolic indicators of infection in the snails. Echinostoma Studies Trematodes in the genus Echinostoma have been extensively studied because they have economic importance in causing food-borne trematodiases. These trematodes are intestinal flukes, 3 10 mm long and 1 3 mm wide with a large ventral sucker (Fried et al. 2004). They are endemic in many Southeastern Asian countries and infect numerous humans who inadvertently ingest the metacercarial cysts of echinostomes in freshwater and brackish water molluscs, fish, crustaceans and amphibians (Fried et al. 2004). The most widely used laboratory model is E. caproni because it has a relatively short time to patency (10 14 days) in mice and is an easy species to maintain in the laboratory since it cycles between B. glabrata and laboratory mice or hamsters (Fried and Huffman 1996). There have been numerous chromatographic studies on the changes in various metabolites associated with E. caproni infection in both mice and snails. Bandstra et al. (2007) used HPTLC to determine the neutral lipid content of mice feces 1 5 weeks postinfection. Samples and standards were chromatographed on either Whatman LHPKDF silica gel plates or EMD Millipore silica gel 60 CF 254 plates developed with the Mangold mobile phase. The neutral lipids were detected using PMA reagent. There was a significant decrease in the triacyglycerol fraction compared to uninfected controls at 3 weeks post-infection. A significant increase in the free sterol fraction at 2 weeks postinfection compared to uninfected controls also occurred. Murray et al. (2007) examined the phospholipid and sphingolipid content in the feces of mice infected with E. caproni using HPTLC. Samples and standards were chromatographed on EMD Millipore silica gel 60 CF 254 plates developed with chloroform-methanol-di water (65:225:4), and polar lipids were detected using a 10% cupric sulfate in 8% phosphoric acid reagent. The fecal polar lipids were not useful to analyze as markers of an E. caproni infection since no significant differences were detected between the infected and uninfected samples. Massa et al. (2008) extended the study of Bandstra et al. (2007) and used the same HPTLC procedures to examine the neutral lipid content of mice feces at 1 7 weeks postinfection. Analysis was done weekly on the fecal samples and consisted of an examination of the free fatty acids, free sterols, triacylglycerols, methyl esters, and steryl esters. At 7 weeks postinfection, the triacylglycerol content was significantly lower in infected mice than in the uninfected controls. Vasta et al. (2008) used HPTLC to examine the neutral lipid content of the mice urine infected with E. caproni. Folch extracted samples and standards were chromatographed on EMD Millipore silica gel 60 CF 254 plates developed with the Mangold mobile phase; bands were detected using PMA reagent as described in Bandstra et al. (2007). To confirm or reject the presence of methyl and steryl esters, the Smith et al. (1995) mobile phase consisting of hexanes-petroleum ether-diethyl ether-glacial acetic acid (50:20:5:1), was used on the samples. Vasta et al. (2008) found that methyl esters were significantly increased at 6 and 7 weeks postinfection compared to the uninfected controls. Massa et al. (2008) analyzed the polar lipid content of human urine, uninfected mouse urine, and urine from mice infected with E. caproni. The purpose of this study was to determine if the mouse model showed comparable polar lipid profiles to human urine. Lipids were separated on Whatman LHPKDF and EMD Millipore silica gel 60 CF 254 HPTLC plates with the Wagner mobile phase and zone detection with 10% cupric sulfate in 8% phosphoric acid reagent. No significant differences in the polar lipids between infected and noninfected mice were found. The polar lipid profiles of human and mouse urine were different. Vasta et al. (2009) used HPTLC to analyze the amino acids in the urine of mice infected with E. caproni. Ethanol-DI water (70:30) sample extracts and standards were chromatographed on both EMD Millipore HPTLC silica gel and cellulose layers. The silica gel layer with a preadsorbent zone was No and the cellulose layer was No Plates were developed with one of two mobile phases: mobile phase A consisted of 2-butanol-pyridine-glacial acetic acid-di water (39:34:10:26) and mobile phase B consisted of 2-butanolpyridine-25% ammonia-di water (39:34:10:26). Zones were detected using ninhydrin reagent and they appeared in various colors on a white to pink background, which aided zone identification. Vasta et al. (2009) found that taurine, alanine, threonine, and lysine were present in mouse urine and that alanine and taurine were present in significantly different amounts in infected and uninfected mice. Some of these findings correlated with the spectroscopic findings of Saric et al. (2008) who suggested that taurine levels in urine may serve as a biological marker for mice infected with E. caproni using spectroscopic methods.
4 4 Ciara O Sullivan et al. Counihan et al. (2010) examined the neutral and polar lipids in intestinal and non-intestinal organs of mice infected with E. caproni. The Folch extracted samples and standards were chromatographed on Analtech HPTLC-HLF silica gel plates with the Mangold mobile phase, and detection of zones was carried out with PMA reagent. Polar lipids were developed with the Wagner et al. (1961) mobile phase and detected with 10% cupric sulfate in 8% phosphoric acid reagent. The authors found that there were no significant differences in the neutral lipids of the infected mice compared to the uninfected controls, but the polar lipid phosphatidylethanolamine in the anterior portion of the small intestine was found in significantly higher amounts in the infected mice compared to the uninfected controls. Bandstra et al. (2006) determined neutral lipids and phospholipids in B. glabrata patently infected with E. caproni. The DGG, hemolymph, and shells were analyzed. Folch extracted samples and standards were chromatographed on Whatman LHPKDF-HPTLC silica gel plates with the Mangold mobile phase and zones were detected using PMA reagent. To separate the steryl esters, the Smith et al. (1995) mobile phase was used. Detection was the same as for the other neutral lipids. Phospholipids were developed with the Wagner et al. (1961) mobile phase and detected using 10% cupric sulfate in 8% phosphoric acid reagent. Infected snails had significantly lower amounts of triacylglycerols in the DGG compared to uninfected controls. There were no significant differences in the shells or plasma samples in any of the lipid classes. Concluding Remarks Extensive work has been carried out using various analytical methods on metabolic profiling of E. caproni and S. mansoni. Examining the effects of trematode infections on the different metabolites in both the intermediate and definitive hosts is an important area of work as researchers continue to try and discover simpler and better methods to identify trematode infections in humans and animal. References Bandstra S.R., Murray K.E., Fried B., Sherma J High performance thin layer chromatographic analysis of neutral lipids in the feces of BALB/c mice infected with Echinostoma caproni. Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, 30, DOI: / Bandstra S.R., Fried B., Sherma J High performance thin layer chromatographic analysis of neutral lipids and phospholipids in Biomphalaria glabrata patently infected with Echinostoma caproni. Parasitology Research, 99, DOI: / s Chitsulo L., Engels D., Montresor A., Savioli L The global status of schistosomiasis and its control. Acta Tropica, 77, DOI: /S X(00) Cline D.J., Fried B., Sherma J High performance thin layer chromatography determination of carbohydrates in the hemolymph and digestive gland of Lymnaea elodes (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae). Veliger, 42, Counihan J., Fried B., Sherma J Effects of Echinostoma caproni infection on the neutral and polar lipids of intestinal and non-intestinal organs in the BALB/c mouse as determined by high performance thin layer chromatography. Parasitology Research, 107, DOI: /s y. Cox F.E.G Modern Parasitology: A Textbook for Parasitology. Blackwell Science, Ltd, Oxford, UK. Fried B., Abruzzi A Food borne trematode infections of humans in the United States of America. Parasitology Research, 106, DOI: /s Fried B., Graczyk T.K., Tamang L Food-borne intestinal trematodiasis in humans. Parasitology Research, 93, DOI: /s y. Fried B., Huffman J.E The biology of the intestinal trematode Echinostoma caproni. Advances Parasitology, 38, DOI: /S X(08) Gryseels B., Polman K., Clerinx J., Kestens L Human schistosomiasis. Lancet, 368, DOI: /S (06) Holmes E The evolution of metabolic profiling in parasitology. Parasitology, 137, DOI: /S Jarusiewicz J., Sherma J., Fried B Thin layer chromatographic analysis of glucose and maltose in estivated Biomphalaria glabrata snails and those infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 145B, 3 4, DOI: /j.cbpb Mangold H.K Thin-layer chromatography, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. Massa D.R., Chejlava M.J., Fried B., Sherma J High performance column liquid chromatographic analysis of selected carboxylic acids in Biomphalaria glabrata patently infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology Research, 101, DOI: /s Massa D.R., Vasta J.D., Fried B., Sherma J High performance thin-layer chromatographic analysis of the polar lipid content of human urine and urine from BALB/c mice experimentally infected with Echinostoma caproni. Journal of Planar Chromatography Modern TLC, 21, DOI: / JPC Muller E., Brunet L.R., Fried B., Sherma J Effects on the neutral lipids contents of the liver, ileum and serum during experimental schistosomiasis. International Journal for Parasitology, 31, DOI: /S (00) Muller E., Fried B., Sherma J HPTLC analysis of neutral lipids in Biomphalaria glabrata snails infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Journal of Planar Chromatography Modern TLC, 13, Murray K.E., Fried B., Sherma J Determination of the phospholipid and sphingolipid content in the feces of uninfected BALB/c mice and those infected with Echinostoma caproni by high performance thin layer chromatography with densitometry. Acta Chromatographica, 18, Ong J.H.L., Chejlava M., Fried B., Koehnlein K.M., Bosavage G.L., Sherma J Effects of Schistosoma mansoni infection on the inorganic elements in the snail Biomphalaria glabrata. Journal of Helminthology, 78, DOI: /JOH O Sullivan C., Popovic N., Fried B., Sherma J Effect of Schistosoma mansoni on the neutral and polar lipids in the liver, spleen and small intestine of mice as determined by high performance thin layer chromatography. Journal of Planar Chro-
5 Metabolic profiling of trematodes 5 matography Modern TLC, 25, DOI: / JPC Pachuski J., Fried B., Sherma J HPTLC analysis of amino acids in Biomphalaria glabrata infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, 25, DOI: /JPC Saric J., Li J.V., Wang Y.L., Keiser J., Bundy J.G., Holmes E., Utzinger J Metabolic profiling of an Echinostoma caproni infection in the mouse for biomarker discovery. Plos Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2, No. e 254. DOI: / journal.pntd Smith M.C., Webster C.L., Sherma J., Fried B Determination of neutral lipids in regular and lowfat eggs by high-performance TLC with densitometry. Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, 18, DOI: Vasta J., Fried B., Sherma J High performance thin layer chromatographic analysis of neutral lipids in the urine of BALB/c mice infected with Echinostoma caproni. Parasitology Research, 192, DOI: /s y. Vasta J., Fried B., Sherma J Determination and quantification of amino acids in the urine of BALB/c mice infected with Echinostoma caproni by high performance thin layer chromatography-densitometry. Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, 32, DOI: / Wagner H., Horhammer L., Wolff P Thin-layer chromatography of phosphatides and glycolipids. Biochemische Zeitschrift, 334, 175. Wang Y., Li J.V., Saric J., Keiser J., Wu J., Utzinger J., Holmes E Advances in metabolic profiling of experimental nematode and trematode infections. Advances in Parasitology, 73, DOI: /S X(10) (Accepted October 15, 2012)
DETERMINATION OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID AND SPHINGOLIPID CONTENT IN THE FECES OF UNINFECTED
 ACTA CHROMATOGRAPHICA, NO. 18, 2007 DETERMINATION OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID AND SPHINGOLIPID CONTENT IN THE FECES OF UNINFECTED BALB/c MICE AND THOSE INFECTED WITH Echinostoma caproni BY HIGH PERFORMANCE SILICA
ACTA CHROMATOGRAPHICA, NO. 18, 2007 DETERMINATION OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID AND SPHINGOLIPID CONTENT IN THE FECES OF UNINFECTED BALB/c MICE AND THOSE INFECTED WITH Echinostoma caproni BY HIGH PERFORMANCE SILICA
'.. \ High-performance thin-layer chromatographic analysis of phospholipids in Biomphalaria glabrata snails infected with Scltistosoma mansoni
 '.. \ High-performance thin-layer chromatographic analysis of phospholipids in Biomphalaria glabrata snails infected with Scltistosoma mansoni Quang Ha Dang Bui\ Bernard Fried 1 and Joseph Sherma 1!Department
'.. \ High-performance thin-layer chromatographic analysis of phospholipids in Biomphalaria glabrata snails infected with Scltistosoma mansoni Quang Ha Dang Bui\ Bernard Fried 1 and Joseph Sherma 1!Department
Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica.
 TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム
 Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ON IMPREGNATED CHEMICALLY BONDED STATIONARY PHASES. PART 1
 ACTA CHROMATOGRAPHICA, NO. 17, 2006 CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ON IMPREGNATED CHEMICALLY BONDED STATIONARY PHASES. PART 1 G. Grygierczyk Institute of Chemistry, Silesian University,
ACTA CHROMATOGRAPHICA, NO. 17, 2006 CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ON IMPREGNATED CHEMICALLY BONDED STATIONARY PHASES. PART 1 G. Grygierczyk Institute of Chemistry, Silesian University,
David Bruce Conn. Berry College One Health Center Harvard University Museum of Comparative Zoology
 David Bruce Conn Berry College One Health Center Harvard University Museum of Comparative Zoology From Yang et al, 2012. Global Distribution of Outbreaks of Water Associated Infectious Diseases. PLoS/Neglected
David Bruce Conn Berry College One Health Center Harvard University Museum of Comparative Zoology From Yang et al, 2012. Global Distribution of Outbreaks of Water Associated Infectious Diseases. PLoS/Neglected
UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry. Natura-Brasil. EA Laboratory of Dermatological Research,
 Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18)
 IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18) A. Placed in the subclass Digenea 1. Flukes 2. Digenea refers to having an alternation of hosts in the life cycle B. Characteristics 1. Cuplike suckers without
IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18) A. Placed in the subclass Digenea 1. Flukes 2. Digenea refers to having an alternation of hosts in the life cycle B. Characteristics 1. Cuplike suckers without
Title Revision n date
 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
Overview on the identification of different classes of. lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer. Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer
 Overview on the identification of different classes of lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer Chromatography) Iuliana Popa 1, Marie-Jeanne David 2, Daniel
Overview on the identification of different classes of lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer Chromatography) Iuliana Popa 1, Marie-Jeanne David 2, Daniel
Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes
 1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
FLUNITRAZEPAM Latest Revision: January 24, 2006
 FLUNITRAZEPAM Latest Revision: January 24, 2006 1. SYNONYMS CFR: Flunitrazepam CAS #: 1622-62-4 Other Names: 5-(2-Fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-7-nitro-2H- 1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one Flunitrax Hipnosedon
FLUNITRAZEPAM Latest Revision: January 24, 2006 1. SYNONYMS CFR: Flunitrazepam CAS #: 1622-62-4 Other Names: 5-(2-Fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-7-nitro-2H- 1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one Flunitrax Hipnosedon
Isolation, Separation, and Characterization of Organic Acids*
 In Dashek, William V., ed. Methods in plant biochemistry and molecular biology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press: pp. 107-113. Chapter 9.1997. Isolation, Separation, and Characterization of Organic Acids* William
In Dashek, William V., ed. Methods in plant biochemistry and molecular biology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press: pp. 107-113. Chapter 9.1997. Isolation, Separation, and Characterization of Organic Acids* William
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
TLC SEPARATION OF AMINO ACIDS
 TLC SEPARATION OF AMINO ACIDS LAB CHROM 7 Adapted from Laboratory Experiments for Organic and Biochemistry. Bettelheim & Landesberg (PA Standards for Sci & Tech 3.1.12.D; 3.4.10.A; 3.7.12.B) INTRODUCTION
TLC SEPARATION OF AMINO ACIDS LAB CHROM 7 Adapted from Laboratory Experiments for Organic and Biochemistry. Bettelheim & Landesberg (PA Standards for Sci & Tech 3.1.12.D; 3.4.10.A; 3.7.12.B) INTRODUCTION
130327SCH4U_biochem April 09, 2013
 Option B: B1.1 ENERGY Human Biochemistry If more energy is taken in from food than is used up, weight gain will follow. Similarly if more energy is used than we supply our body with, weight loss will occur.
Option B: B1.1 ENERGY Human Biochemistry If more energy is taken in from food than is used up, weight gain will follow. Similarly if more energy is used than we supply our body with, weight loss will occur.
PURIFICATION OF THE TOXIN IN A ZOAN PALYTHOA TUBERCULOSA.
 Title PURIFICATION OF THE TOXIN IN A ZOAN PALYTHOA TUBERCULOSA Author(s) Kimura, Shoji; Hashimoto, Yoshiro Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1973), 20: 713-718 Issue Date 1973-12-19
Title PURIFICATION OF THE TOXIN IN A ZOAN PALYTHOA TUBERCULOSA Author(s) Kimura, Shoji; Hashimoto, Yoshiro Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1973), 20: 713-718 Issue Date 1973-12-19
CAMAG TLC-MS INTERFACE
 CAMAG TLC-MS INTERFACE 93.1 249.2 40 30 97.1 20 10 250.2 0 200 400 m/z WORLD LEADER IN PLANAR-CHROMATOGRAPHY Identification and elucidation of unknown substances by hyphenation of TLC / HPTLC and MS The
CAMAG TLC-MS INTERFACE 93.1 249.2 40 30 97.1 20 10 250.2 0 200 400 m/z WORLD LEADER IN PLANAR-CHROMATOGRAPHY Identification and elucidation of unknown substances by hyphenation of TLC / HPTLC and MS The
SIMAROUBA CEDRON FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS CEDRON FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 SIMAROUBA CEDRON FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS CEDRON FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Simaba cedron ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy: Simaruba DEFINITION Dried cotyledons
SIMAROUBA CEDRON FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS CEDRON FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Simaba cedron ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy: Simaruba DEFINITION Dried cotyledons
Qualitative and quantitative changes in lipids along the length of female reproductive system of the poultry 'nematode Ascaridia gajli (Schrank 1788)
 Proc, Indian Acad. Sci. (Anim. Sci.), Vol. 96, No.6. November 1987, pp. 683-687. CD Printed in India. Qualitative and quantitative changes in lipids along the length of female reproductive system of the
Proc, Indian Acad. Sci. (Anim. Sci.), Vol. 96, No.6. November 1987, pp. 683-687. CD Printed in India. Qualitative and quantitative changes in lipids along the length of female reproductive system of the
ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) ARTESUNATI COMPRESSI ARTESUNATE TABLETS
 December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
COCHINEAL FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS COCCUS CACTI FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 COCHINEAL FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS COCCUS CACTI FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Coccus cacti ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Whole, dried, female insect, Coccus cacti L. (Dactylopius coccus
COCHINEAL FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS COCCUS CACTI FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Coccus cacti ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Whole, dried, female insect, Coccus cacti L. (Dactylopius coccus
Supporting Information for. Boronic Acid Functionalized Aza-Bodipy (azabdpba) based Fluorescence Optodes for the. analysis of Glucose in Whole Blood
 Supporting Information for Boronic Acid Functionalized Aza-Bodipy (azabdpba) based Fluorescence Optodes for the analysis of Glucose in Whole Blood Yueling Liu, Jingwei Zhu, Yanmei Xu, Yu Qin*, Dechen Jiang*
Supporting Information for Boronic Acid Functionalized Aza-Bodipy (azabdpba) based Fluorescence Optodes for the analysis of Glucose in Whole Blood Yueling Liu, Jingwei Zhu, Yanmei Xu, Yu Qin*, Dechen Jiang*
CHAPTER 9: Preliminary phytochemical analysis of aqueous-ethanol extract of G. lucidum, protein bound polysaccharides and total triterpenes
 CHAPTER 9: Preliminary phytochemical analysis of aqueous-ethanol extract of G. lucidum, protein bound polysaccharides and total triterpenes TABLE OF CONTENTS 9.1. INTRODUCTION 9.2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
CHAPTER 9: Preliminary phytochemical analysis of aqueous-ethanol extract of G. lucidum, protein bound polysaccharides and total triterpenes TABLE OF CONTENTS 9.1. INTRODUCTION 9.2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
Lipid Analysis. Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th Introduction to lipid structures
 Lipid Analysis Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th 2005 Introduction to lipid structures Fatty acids Acylglycerols Glycerophospholipids Sterols Strategies involved in lipid
Lipid Analysis Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th 2005 Introduction to lipid structures Fatty acids Acylglycerols Glycerophospholipids Sterols Strategies involved in lipid
Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND. Bridgwater, England LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS. Fourth Edition. Invergowrie, Dundee, Scotland
 Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition WILLIAM W.CHRISTIE MRS Lipid Analysis Unit, Scottish Crop Research Institute, Dundee, Scotland Invergowrie, and
Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition WILLIAM W.CHRISTIE MRS Lipid Analysis Unit, Scottish Crop Research Institute, Dundee, Scotland Invergowrie, and
NEW JERSEY TEA, DRIED FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS CEANOTHUS AMERICANUS SICCUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 NEW JERSEY TEA, DRIED FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS CEANOTHUS AMERICANUS SICCUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Ceanothus americanus siccum ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy
NEW JERSEY TEA, DRIED FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS CEANOTHUS AMERICANUS SICCUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Ceanothus americanus siccum ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy
AMERICAN SPIKENARD FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ARALIA RACEMOSA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 AMERICAN SPIKENARD FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ARALIA RACEMOSA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Aralia racemosa ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Dried, underground part of Aralia racemosa L.
AMERICAN SPIKENARD FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ARALIA RACEMOSA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Aralia racemosa ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Dried, underground part of Aralia racemosa L.
The development of a detection method discriminating for
 1 2 3 The development of a detection method discriminating for mannosylerythritol lipids and acylglycerols Simon Van Kerrebroeck 1, *, Hannes Petit, Joeri Beauprez 1, Inge N.A. Van Bogaert 1, Wim Soetaert
1 2 3 The development of a detection method discriminating for mannosylerythritol lipids and acylglycerols Simon Van Kerrebroeck 1, *, Hannes Petit, Joeri Beauprez 1, Inge N.A. Van Bogaert 1, Wim Soetaert
Study of Phytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Activity of Citrus aurantifolia Seed Extracts
 American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 7, 254-259 Published Online March 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2016.73022 Study of Phytochemical Screening
American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 7, 254-259 Published Online March 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2016.73022 Study of Phytochemical Screening
ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Artemisia absinthium ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy: Artemisia absinthium DEFINITION
ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Artemisia absinthium ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy: Artemisia absinthium DEFINITION
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Tenofoviri disoproxili fumaras)
 C 19 H 30 N 5 O 10 P. C 4 H 4 O 4 Relative molecular mass. 635.5. Chemical names. bis(1-methylethyl) 5-{[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl}-5-oxo-2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-λ 5 - phosphanonanedioate
C 19 H 30 N 5 O 10 P. C 4 H 4 O 4 Relative molecular mass. 635.5. Chemical names. bis(1-methylethyl) 5-{[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl}-5-oxo-2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-λ 5 - phosphanonanedioate
Fatty Acid Methylation Kits
 Methyl esterification kit for fatty acids analysis Fatty Acid Methylation Kits Below are two methods for efficiently preparing fatty acid samples for GC analysis. Neither method requires high temperatures,
Methyl esterification kit for fatty acids analysis Fatty Acid Methylation Kits Below are two methods for efficiently preparing fatty acid samples for GC analysis. Neither method requires high temperatures,
ISOMALT. Stage 4. C 12 H 24 O 11 M r C 12 H 24 O 11, 2H 2 O M r DEFINITION
 1 003-1208PDG.pdf ISOMALT Stage 4 C 12 H 24 O 11 M r 344.3 C 12 H 24 O 11, 2H 2 O M r 380.3 DEFINITION Mixture of 6-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-glucitol (6-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-sorbitol; 1,6- GPS) and 1-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-mannitol
1 003-1208PDG.pdf ISOMALT Stage 4 C 12 H 24 O 11 M r 344.3 C 12 H 24 O 11, 2H 2 O M r 380.3 DEFINITION Mixture of 6-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-glucitol (6-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-sorbitol; 1,6- GPS) and 1-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-D-mannitol
RVC OPEN ACCESS REPOSITORY COPYRIGHT NOTICE
 RVC OPEN ACCESS REPOSITORY COPYRIGHT NOTICE This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced version of an article accepted for publication in Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
RVC OPEN ACCESS REPOSITORY COPYRIGHT NOTICE This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced version of an article accepted for publication in Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases. (Phenolphthalein)
 Introduction Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases (Phenolphthalein) Although a number of different techniques using different chemicals such as fluorescent dyes, starch powder, phenolphthalein powders
Introduction Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases (Phenolphthalein) Although a number of different techniques using different chemicals such as fluorescent dyes, starch powder, phenolphthalein powders
Figure 2. Figure 1. Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules
 Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
SeQuant ZIC -HILIC For all who expect more...
 SeQuant ZIC -ILIC For all who expect more... The better choice for PLC and LC/MS of all types of polar and hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Poor
SeQuant ZIC -ILIC For all who expect more... The better choice for PLC and LC/MS of all types of polar and hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Poor
 Title Spot Test Method Convenient in Column Chromatography for Det Author(s) Morita, Shigeru; Hanai, Tetsuya Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1975), 53(3): 279-283 Issue Date 1975-09-16
Title Spot Test Method Convenient in Column Chromatography for Det Author(s) Morita, Shigeru; Hanai, Tetsuya Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1975), 53(3): 279-283 Issue Date 1975-09-16
Thermal shift binding experiments were carried out using Thermofluor 384 ELS system. Protein
 Supplementary Methods Thermal shift assays Thermal shift binding experiments were carried out using Thermofluor 384 ELS system. Protein unfolding was examined by monitoring the fluorescence of ANS (1-anilinonaphthalene-8-
Supplementary Methods Thermal shift assays Thermal shift binding experiments were carried out using Thermofluor 384 ELS system. Protein unfolding was examined by monitoring the fluorescence of ANS (1-anilinonaphthalene-8-
OLEANDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS NERIUM OLEANDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 OLEANDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS NERIUM OLEANDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Nerium oleander ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homeopathy: Oleander DEFINITION Fresh leaf
OLEANDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS NERIUM OLEANDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Nerium oleander ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homeopathy: Oleander DEFINITION Fresh leaf
SeQuant ZIC -HILIC For all who expect more...
 SeQuant ZIC -ILIC For all who expect more... The better choice for PLC and LC/MS of all types of polar and hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore is a division of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Poor retention
SeQuant ZIC -ILIC For all who expect more... The better choice for PLC and LC/MS of all types of polar and hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore is a division of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Poor retention
Development and Validation of HPTLC Method for Estimation of Tramadol HCl in Bulk and in Capsule Dosage Form
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.4, No.3, pp 1261-1265, July-Sept 2012 Development and Validation of HPTLC Method for Estimation of Tramadol HCl in Bulk
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.4, No.3, pp 1261-1265, July-Sept 2012 Development and Validation of HPTLC Method for Estimation of Tramadol HCl in Bulk
CONTENTS Determination of cholinesterase inhibitory activity High performance Thin Layer Chromatography
 Chapter VI Bioactive guided fractionation and identification of active compounds from Gelidiella acerosa CONTENTS 8.1. 8.2. Abstract Introduction 8.3. Materials and Methods 8.3.1. Preparation of seaweed
Chapter VI Bioactive guided fractionation and identification of active compounds from Gelidiella acerosa CONTENTS 8.1. 8.2. Abstract Introduction 8.3. Materials and Methods 8.3.1. Preparation of seaweed
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products)
 Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
Standardization of Milagathi Choornam
 2014; 1 (6): 69-74 ISSN 2321-2187 IJHM 2014; 1 (6): 69-74 Received: 19-12-2013 Accepted: 16-01-2014 Priya F Government Siddha Medical College, Anna Hospital Campus, Shakila R Siddha Central Research Institute
2014; 1 (6): 69-74 ISSN 2321-2187 IJHM 2014; 1 (6): 69-74 Received: 19-12-2013 Accepted: 16-01-2014 Priya F Government Siddha Medical College, Anna Hospital Campus, Shakila R Siddha Central Research Institute
Simple Densitometric-TLC Analysis of Non-Chromophore Containing Bioactive Constituents in Medicinal Plant Extracts
 PTLC Symposium Basel 2011 Simple Densitometric-TLC Analysis of Non-Chromophore Containing Bioactive Constituents in Medicinal Plant Extracts Wanchai De-Eknamkul Department of Pharmacognosy and Pharmaceutical
PTLC Symposium Basel 2011 Simple Densitometric-TLC Analysis of Non-Chromophore Containing Bioactive Constituents in Medicinal Plant Extracts Wanchai De-Eknamkul Department of Pharmacognosy and Pharmaceutical
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
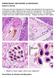 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable. Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors
 Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
SACCHARIDES (Liquid Chromatography)
 Corn Syrup Analysis E-61-1 PRINCIPLE SCOPE A corn syrup solution is passed through a metal ion-modified cation exchange column. The individual sugars are separated by molecular exclusion and ligand exchange.
Corn Syrup Analysis E-61-1 PRINCIPLE SCOPE A corn syrup solution is passed through a metal ion-modified cation exchange column. The individual sugars are separated by molecular exclusion and ligand exchange.
BIOCHEMISTRY & MEDICINE:
 BIOCHEMISTRY & MEDICINE: INTRODUCTION Biochemistry can be defined as the science of the chemical basis of life (Gk bios "life"). The cell is the structural unit of living systems. Thus, biochemistry can
BIOCHEMISTRY & MEDICINE: INTRODUCTION Biochemistry can be defined as the science of the chemical basis of life (Gk bios "life"). The cell is the structural unit of living systems. Thus, biochemistry can
LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis on QTRAP Instruments
 LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis on QTRAP Instruments Junhua Wang and Paul RS Baker SCIEX LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis Topics Covered Lipid extraction techniques Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)
LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis on QTRAP Instruments Junhua Wang and Paul RS Baker SCIEX LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis Topics Covered Lipid extraction techniques Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)
Chromatography Vacuum Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Application Note Differentiation and Determination Differentiation and Determination of Fatty Acid Methyl of Fatty Esters Acid by Gas Methyl Chromatography Esters by Vacuum Gas Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
Application Note Differentiation and Determination Differentiation and Determination of Fatty Acid Methyl of Fatty Esters Acid by Gas Methyl Chromatography Esters by Vacuum Gas Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
JPSBR: Volume 4, Issue 6: 2014 ( ) ISSN NO
 Analytical Method Development and Validation for Simultaneous Estimation of Timolol Maleate and Brimonidine in Bulk and Marketed Ophthalmic Formulation Suketa K. Mehta*, Dr. Dilip G. Maheshwari Department
Analytical Method Development and Validation for Simultaneous Estimation of Timolol Maleate and Brimonidine in Bulk and Marketed Ophthalmic Formulation Suketa K. Mehta*, Dr. Dilip G. Maheshwari Department
Available online at Universal Research Publications. All rights reserved. Original Article
 Available online at http://www.urpjournals.com International Journal of Analytical and Bioanalytical chemistry Universal Research Publications. All rights reserved Original Article Application of HPTLC
Available online at http://www.urpjournals.com International Journal of Analytical and Bioanalytical chemistry Universal Research Publications. All rights reserved Original Article Application of HPTLC
Study of the British Pharmacopeia method on methimazole (thiamazole) content in carbimazole tablets
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 16 (1998) 785 792 Study of the British Pharmacopeia method on methimazole (thiamazole) content in carbimazole tablets Maria Aletrari *, Popi Kanari, Dora
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 16 (1998) 785 792 Study of the British Pharmacopeia method on methimazole (thiamazole) content in carbimazole tablets Maria Aletrari *, Popi Kanari, Dora
Variation in amino acid and lipid composition of latent fingerprints
 Variation in amino acid and lipid composition of latent fingerprints Croxton, R. S., Baron, M. G., Butler, D., Kent, T. and Sears, V. G. Variation in amino acid and lipid composition of latent fingerprints.
Variation in amino acid and lipid composition of latent fingerprints Croxton, R. S., Baron, M. G., Butler, D., Kent, T. and Sears, V. G. Variation in amino acid and lipid composition of latent fingerprints.
Supporting Information
 Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
Supplementary Information. Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid on Metabolic Profiles in Brain and Liver of Mouse by a
 Supplementary Information Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid on Metabolic Profiles in Brain and Liver of Mouse by a High-throughput Targeted Metabolomics Approach Nanyang Yu, Si Wei, *, Meiying Li, Jingping
Supplementary Information Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid on Metabolic Profiles in Brain and Liver of Mouse by a High-throughput Targeted Metabolomics Approach Nanyang Yu, Si Wei, *, Meiying Li, Jingping
Development and Validation of Stability Indicating HPTLC Method for Estimation of Seratrodast
 ARC Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (AJPS) Volume 2, Issue 3, 2016, PP 15-20 ISSN 2455-1538 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-1538.0203004 www.arcjournals.org Development and Validation of Stability
ARC Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (AJPS) Volume 2, Issue 3, 2016, PP 15-20 ISSN 2455-1538 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-1538.0203004 www.arcjournals.org Development and Validation of Stability
PAPRIKA EXTRACT SYNONYMS DEFINITION DESCRIPTION FUNCTIONAL USES CHARACTERISTICS
 PAPRIKA EXTRACT Prepared at the 77 th JECFA, published in FAO JECFA Monographs 14 (2013), superseding tentative specifications prepared at the 69 th JECFA (2008). An ADI of 0-1.5 mg/kg bw was allocated
PAPRIKA EXTRACT Prepared at the 77 th JECFA, published in FAO JECFA Monographs 14 (2013), superseding tentative specifications prepared at the 69 th JECFA (2008). An ADI of 0-1.5 mg/kg bw was allocated
Detection Rate of Urinary Schistosomiasis in El khiar Villages White Nile State, Sudan
 Pyrex Journal of Biomedical Research Vol 3 (5) pp. 34-38 June, 2017 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.pyrexjournals.org/pjbr ISSN: 2579-1222 Copyright 2017 Pyrex Journals Full Length
Pyrex Journal of Biomedical Research Vol 3 (5) pp. 34-38 June, 2017 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.pyrexjournals.org/pjbr ISSN: 2579-1222 Copyright 2017 Pyrex Journals Full Length
Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes
 Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes A. The information on the Platyhelminthes provided in the previous section should be reviewed, as it still applies. B. Adult trematodes are parasites of vertebrates.
Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes A. The information on the Platyhelminthes provided in the previous section should be reviewed, as it still applies. B. Adult trematodes are parasites of vertebrates.
 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ HIGH PERFORMANCE THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHOD FOR QUANTIFICATION OF PIPERINE
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ HIGH PERFORMANCE THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHOD FOR QUANTIFICATION OF PIPERINE
Core E Analysis of Neutral Lipids from Human Plasma June 4, 2010 Thomas J. Leiker and Robert M. Barkley
 Core E Analysis of Neutral Lipids from Human Plasma June 4, 2010 Thomas J. Leiker and Robert M. Barkley This protocol describes the extraction and direct measurement of cholesterol esters (CEs) and triacylglycerols
Core E Analysis of Neutral Lipids from Human Plasma June 4, 2010 Thomas J. Leiker and Robert M. Barkley This protocol describes the extraction and direct measurement of cholesterol esters (CEs) and triacylglycerols
LAVENDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS LAVANDULA VERA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 LAVENDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS LAVANDULA VERA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Lavandula angustifolia ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Fresh, blooming, flower-heads of Lavandula angustifolia
LAVENDER FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS LAVANDULA VERA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Lavandula angustifolia ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Fresh, blooming, flower-heads of Lavandula angustifolia
IAM Chromatography. Introduction
 IAM Chromatography IAM Drug Discovery Columns Introduction References: 1. Regis 1998-99 Chromatography Catalog A simple, rapid method to predict drug transport across biological barriers has been a long
IAM Chromatography IAM Drug Discovery Columns Introduction References: 1. Regis 1998-99 Chromatography Catalog A simple, rapid method to predict drug transport across biological barriers has been a long
3. PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING
 93 3. PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING 3.1 INTRODUCTION All the drugs- Ayurvedic, Unani and Herbal extracts were subjected to preliminary phytochemical screening to test the presence of alkaloids, carbohydrates
93 3. PRELIMINARY PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING 3.1 INTRODUCTION All the drugs- Ayurvedic, Unani and Herbal extracts were subjected to preliminary phytochemical screening to test the presence of alkaloids, carbohydrates
Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine. Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics
 Page 11 of 32 Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics James W. Antoon, Jiawang Liu, Adharsh P. Ponnapakkam,
Page 11 of 32 Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics James W. Antoon, Jiawang Liu, Adharsh P. Ponnapakkam,
DriSolv. Anhydrous solvents for organic synthesis. EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
 DriSolv Anhydrous solvents for organic synthesis EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany DriSolv Anhydrous solvents for organic synthesis EMD Millipore is a recognized leader
DriSolv Anhydrous solvents for organic synthesis EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany DriSolv Anhydrous solvents for organic synthesis EMD Millipore is a recognized leader
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016.
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Aspartame This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Aspartame This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive
Metabolomics: quantifying the phenotype
 Metabolomics: quantifying the phenotype Metabolomics Promises Quantitative Phenotyping What can happen GENOME What appears to be happening Bioinformatics TRANSCRIPTOME What makes it happen PROTEOME Systems
Metabolomics: quantifying the phenotype Metabolomics Promises Quantitative Phenotyping What can happen GENOME What appears to be happening Bioinformatics TRANSCRIPTOME What makes it happen PROTEOME Systems
THE ANALYSIS OF CAROTENOIDS FROM MINT EXTRACTS. Abstract
 M. Ciurea, et al. Scientifical Researches. Agroalimentary Processes and Technologies, Volume XI, No. 2 (2005), 261-266 THE ANALYSIS OF CAROTENOIDS FROM MINT EXTRACTS Mihaela Ciurea 1, I. Jianu 2 1 Aurel
M. Ciurea, et al. Scientifical Researches. Agroalimentary Processes and Technologies, Volume XI, No. 2 (2005), 261-266 THE ANALYSIS OF CAROTENOIDS FROM MINT EXTRACTS Mihaela Ciurea 1, I. Jianu 2 1 Aurel
Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column
 Application Note Pharmaceutical and Food Testing Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column Author Lu Yufei Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract A liquid chromatographic
Application Note Pharmaceutical and Food Testing Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column Author Lu Yufei Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract A liquid chromatographic
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths
 Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS. Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012)
 July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010)
 June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Schistosomiasis. Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University
 Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
INTRODUCTION. safety and efficacy throughout all phases of its shelf life, including storage. In
 INTRODUCTION Analytically monitoring of a pharmaceutical product is necessary to ensure its safety and efficacy throughout all phases of its shelf life, including storage. In Simultaneous processing of
INTRODUCTION Analytically monitoring of a pharmaceutical product is necessary to ensure its safety and efficacy throughout all phases of its shelf life, including storage. In Simultaneous processing of
Student Handout. This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have
 Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
notes on methodology Rapid separation of lipid classes in high yield and purity using bonded phase columns
 notes on methodology Rapid separation of lipid classes in high yield and purity using bonded phase columns M. A. Kaluzny, * L. A. Duncan,* * M. V. Merritt,' and D. E. Eppse.* Physical and Analytical Chemisty
notes on methodology Rapid separation of lipid classes in high yield and purity using bonded phase columns M. A. Kaluzny, * L. A. Duncan,* * M. V. Merritt,' and D. E. Eppse.* Physical and Analytical Chemisty
ISSN: ; CODEN ECJHAO E-Journal of Chemistry 2011, 8(3),
 ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(3), 1275-1279 Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Phenylephrine Hydrochloride, Oxolamine Citrate and Chlorpheniramine
ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(3), 1275-1279 Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Phenylephrine Hydrochloride, Oxolamine Citrate and Chlorpheniramine
A New HILIC/RP Mixed-Mode Column and Its Applications in Surfactant Analysis
 A New HILIC/RP Mixed-Mode Column and Its Applications in Surfactant Analysis X. Liu, C. Pohl, Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA, USA ABSTRACT Although reversed-phase (RP) silica columns (e.g., C18 and
A New HILIC/RP Mixed-Mode Column and Its Applications in Surfactant Analysis X. Liu, C. Pohl, Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA, USA ABSTRACT Although reversed-phase (RP) silica columns (e.g., C18 and
For example, monosaccharides such as glucose are polar and soluble in water, whereas lipids are nonpolar and insoluble in water.
 Biology 4A Laboratory Biologically Important Molecules Objectives Perform tests to detect the presence of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Recognize the importance of a control in a biochemical
Biology 4A Laboratory Biologically Important Molecules Objectives Perform tests to detect the presence of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Recognize the importance of a control in a biochemical
10 Sulfaquinoxaline H N O S O. 4-amino-N-quinoxalin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide C 14 H 12 N 4 O 2 S MW: CAS No.:
 10 Sulfaquinoxaline N N H N O S O NH 2 4-amino-N-quinoxalin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide C 14 H 12 N 4 O 2 S MW: 300.33 CAS No.: 59-40-5 Outline of sulfaquinoxaline Sulfaquinoxaline is light yellow to brownish
10 Sulfaquinoxaline N N H N O S O NH 2 4-amino-N-quinoxalin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide C 14 H 12 N 4 O 2 S MW: 300.33 CAS No.: 59-40-5 Outline of sulfaquinoxaline Sulfaquinoxaline is light yellow to brownish
In this study, effect of different high-boiling-organic solvent (ethanolamine, diethylene glycol and
 ISESCO JOURNAL of Science and Technology Vol. 12 No 21 High Boiling Solvent Pre-treatment of Hazelnut Shells for Enzymatic Hydrolysis Emir Zafer Hoşgün, Berrin Bozan Anadolu University, Engineering Faculty,
ISESCO JOURNAL of Science and Technology Vol. 12 No 21 High Boiling Solvent Pre-treatment of Hazelnut Shells for Enzymatic Hydrolysis Emir Zafer Hoşgün, Berrin Bozan Anadolu University, Engineering Faculty,
Lutein Esters from Tagetes Erecta
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Lutein Esters from Tagetes Erecta This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Lutein Esters from Tagetes Erecta This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Mercury Speciation Determinations in Asian Dietary Supplements
 Mercury Speciation Determinations in Asian Dietary Supplements Terri Christison, Deepali Mohindra, Frank Hoefler, and Linda Lopez, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, California, USA Overview Purpose:
Mercury Speciation Determinations in Asian Dietary Supplements Terri Christison, Deepali Mohindra, Frank Hoefler, and Linda Lopez, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, California, USA Overview Purpose:
CHEMICAL STANDARDIZATION AND QUANTIFICATION OF PIPERIN FROM METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF PIPER NIGRUM BY HPLC METHOD ON THE BASIS OF ISOLATED MARKERS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 6(4), 2008, 1726-1733 CHEMICAL STANDARDIZATION AND QUANTIFICATION OF PIPERIN FROM METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF PIPER NIGRUM BY HPLC METHOD ON THE BASIS OF ISOLATED MARKERS RAJANI CHAUHAN,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 6(4), 2008, 1726-1733 CHEMICAL STANDARDIZATION AND QUANTIFICATION OF PIPERIN FROM METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF PIPER NIGRUM BY HPLC METHOD ON THE BASIS OF ISOLATED MARKERS RAJANI CHAUHAN,
ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Artemisia absinthium ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy: Artemisia absinthium DEFINITION
ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ABSINTHIUM FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Artemisia absinthium ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy: Artemisia absinthium DEFINITION
COMMON BARBERRY FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS BERBERIS VULGARIS FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 COMMON BARBERRY FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS BERBERIS VULGARIS FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Berberis vulgaris ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy : Berberis DEFINITION
COMMON BARBERRY FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS BERBERIS VULGARIS FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Berberis vulgaris ad praeparationes homoeopathicas Other Latin name used in homoeopathy : Berberis DEFINITION
Fast and simultaneous analysis of ethanol metabolites and barbiturates using the QTRAP 4500 LC-MS/MS system
 Fast and simultaneous analysis of ethanol metabolites and barbiturates using the QTRAP 4500 LC-MS/MS system Xiang He 1, Adrian Taylor 2 and Alexandre Wang 1 1 SCIEX, Redwood City, USA. 2 SCIEX, Concord,
Fast and simultaneous analysis of ethanol metabolites and barbiturates using the QTRAP 4500 LC-MS/MS system Xiang He 1, Adrian Taylor 2 and Alexandre Wang 1 1 SCIEX, Redwood City, USA. 2 SCIEX, Concord,
Rapid and Robust Detection of THC and Its Metabolites in Blood
 Rapid and Robust Detection of THC and Its Metabolites in Blood Application Note Forensics/Doping Control Author Stephan Baumann Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara CA 95051 USA Abstract A robust method
Rapid and Robust Detection of THC and Its Metabolites in Blood Application Note Forensics/Doping Control Author Stephan Baumann Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara CA 95051 USA Abstract A robust method
Determination of tramadol in capsules by high performance thin layer chromatography - densitometry
 Determination of tramadol in capsules by high performance thin layer chromatography - densitometry Venkateshwarlu K 1,3, Reddy YN 3 *, Srisailam K 2, Rajkumar V 2 and Pai MG 1 1 Department of Pharmaceutical
Determination of tramadol in capsules by high performance thin layer chromatography - densitometry Venkateshwarlu K 1,3, Reddy YN 3 *, Srisailam K 2, Rajkumar V 2 and Pai MG 1 1 Department of Pharmaceutical
Isolation of five carotenoid compounds from tangerine tomatoes
 Isolation of five carotenoid compounds from tangerine tomatoes Thesis Thomas Haufe Advisor: Steven J. Schwartz, Ph.D Department of Food Science and Technology Presented in fulfillment of the requirements
Isolation of five carotenoid compounds from tangerine tomatoes Thesis Thomas Haufe Advisor: Steven J. Schwartz, Ph.D Department of Food Science and Technology Presented in fulfillment of the requirements
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Participation of Endogenous Fatty Acids in Ca 2+ Release Activation from Mitochondria
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1985), 4, 549 556 549 Participation of Endogenous Fatty Acids in Ca 2+ Release Activation from Mitochondria B. I. MEDVEDEV, E. P. SEVERINA, V. G. GOGVADZE, E. A. CHUKHLOVA and Yu.
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1985), 4, 549 556 549 Participation of Endogenous Fatty Acids in Ca 2+ Release Activation from Mitochondria B. I. MEDVEDEV, E. P. SEVERINA, V. G. GOGVADZE, E. A. CHUKHLOVA and Yu.
Supporting Information (SI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information (SI) Title: Optimization of Metabolite Extraction of Human Vein Tissue for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information (SI) Title: Optimization of Metabolite Extraction of Human Vein Tissue for
Main Functions maintain homeostasis
 The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
