Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of
|
|
|
- Sophia Carpenter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Supplementary material for: Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of influenza A (H1N2) infection Louise Brogaard, Peter M. H. Heegaard, Lars E. Larsen, Shila Mortensen, Michael Schlegel, Ralf Dürrwald, Kerstin Skovgaard 7
2 8 9 Supplementary Table S1. qpcr primer sequences and experimentally determined PCR efficiencies for all reported genes and mirnas in the present study. Gene/miRNA Forward primer Reverse primer PCR eff. CASP1 GAAGGACAAACCCAAGGTGA TGGGCTTTCTTAATGGCATC 101 % CASP3 AGCAGTTTTATTTGCGTGCTT CAACAGGTCCATTTGTTCCA 99 % CASP9 CTGTGAGGACCTGCTGACC CGGAGGAAATTAAAACAGCCAGG 104 % CCL2 CTTCTGCACCCAGGTCCTT CGCTGCATCGAGATCTTCTT 90 % CCL3 CCAGGTCTTCTCTGCACCAC GCTACGAATTTGCGAGGAAG 104 % CD163 CACATGTGCCAACAAAATAAGAC CACCACCTGAGCATCTTCAA 117 % CXCL2 GAAGATGCTAAACAAGAGCAGTG AGCCAAATGCATGAAACACA 112 % CXCL10 CCCACATGTTGAGATCATTGC GCTTCTCTCTGTGTTCGAGGA 97 % DDX58 ACGAAAGGGGAAGGTTGTCT ATGCCTGCAACTTTGTACCC 96 % FAS CACTGTAACCCTTGCACCAC TGGAACACTTCTCTGCATTTGG 109 % FASLG TTCTGGTGGCCCTGGTTG CTTTGGCTGGCAGACTCTCT 106 % IDO1 GGGCCCATGACTTACAAGAA TTTCCACCAATAGCGAAACC 97 % IFITM1 GCTTTCGCCTACTCCGTGA CCAGGATCAGAGCCCAGATG 106 % IFITM3 TGAACTGCGCTTCCCAGC CACCTCGTGCTCCTCCTTG 104 % IFNA1 TTCCAGCTCTTCAGCACAGA AGCTGCTGATCCAGTCCAGT 101 % IFNG CCATTCAAAGGAGCATGGAT TTCAGTTTCCCAGAGCTACCA 94 % IL8 TTGCCAGAGAAATCACAGGA TGCATGGGACACTGGAAATA 89 % IL10 TACAACAGGGGCTTGCTCTT GCCAGGAAGATCAGGCAATA 108 % IL18 CAATTGCATCAGCTTTGTGG TCCAGGTCCTCATCGTTTTC 100 % IL1RAP TGCATCTTTGACCGAGACAG GGGCTCAGGACAACAATCAT 93 % IL1RN TGCCTGTCCTGTGTCAAGTC GTCCTGCTCGCTGTTCTTTC 103 % IRF1 TGAAGCTGCAACAGATGAGG CTTCCCATCCACGTTTGTCT 102 % IRF2 GATGCTGCCCTTATCTGAGC TGTGCTTCACTCTGTCTTCCTT 91 % IRF3 GCTACACCCTCTGGTTCTGC GAGACACATGGGGACAACCT 96 % IRF9 CATTCAGACTTGGGGAGCAG AAAGGGGCCTCAGTGGTAAC 101 % IFIH1 CAGTGTGCTAGCCTGCTCTG GCAGTGCCTTGTTTCCTCTC 97 % JAK2 CTCAGATATGCAAGGGTATGGAGT CCACCAATATATTCCTTGTTGCCA 104 % MCL1 GAGGCTGGGATGGGTTTGTG TGCCAAACCAGCTCCTACTC 103 % MX1 CCTCCACAGAACTGCCAAG GCAGTACACGATCTGCTCCA 98 % MYD88 AGCTGTAGGGGGAATGTGTG TCAGCTGGTCTGTGGATGTG 98 % NOD1 CTCGACCTGGACAACAACAA TGAGTCTGATGACCGTGAGG 105 % OASL TGGTACCTGAAGTACGTGAAAGC TACCCACTTCCCAGGCATAG 90 % PTGS2 AGGCTGATACTGATAGGAGAAACG GCAGCTCTGGGTCAAACTTC 96 % STAT1 CCTTGCAGAATAGAGAACATGATAC CCTTTCTCTTGTTGTCAAGCATT 98 % TICAM1 CTGCCTTCCCACAGCCTC AGCCCCAGTTGTACCATTTGA 90 % TICAM2 TCTGCTGCAAAATGACTTCGG AGCCATTGACAGCATCGTCT 90 % TLR2 GTTTTACGGAAATTGTGAAACTG TCCACATTACCGAGGGATTT 92 % TLR3 ATTGTGCAAAAGATTCAAGGTG TCTTCGCAAACAGAGTGCAT 104 % TLR4 TTTCCACAAAAGTCGGAAGG CAACTTCTGCAGGACGATGA 95 % TLR7 GGAAATAGCATCAGCCAAGCTC TTCCAGGTTGCGTAGCTCTT 87 % TLR8 GCAAAGACCACCACCAAC ATCCGTCAGTCTGGGAAT 95 % TNF CCCCCAGAAGGAAGAGTTTC CGGGCTTATCTGAGGTTTGA 94 % Genes identified as targeted in MTI network analysis AKT2 CTGCTTAAGAAGGACCCAAAGC CTTCTGTACCACGTCCTGCC 95 % BCL2 GACTCCCTTCACCGCGAG CTCTCCACACACATGACCCC 90 % CDK2 TTGCTGAGATGGTGACCCG GGGTCCCAAGAGTCCGAAAG 106 % CDK4 GGCCAGAATCTACAGCTACCAG TCCACAGGTGTTGCATACGT 90 %
3 10 CCNE2 ATGGTGCTTGCAGTGAAGAGG TGGAGGAAGAGATTTAGCCAGG 107 % CXCR4 CTGCTGGCTGCCATACTACA TCAAACTCACACCCTTGCTG 97 % FOS GGAACAGTTGTCCCCAGAAG TGTCAGTCAGCTCCCTCCTC 100 % FOXO3A CCAGTCTATGCAAACCCTCTCG CAAGTCGCTGGGGAACTTCT 90 % PTEN AGCAAATAAAGACAAGGCCAACC GTTGAACTGCTAGCCTCTGGA 103 % SP1 AAGATAGTGAAGGAAGGGGCTC TACTTTGCCACAACCTTGCATG 106 % TP53 TAAGCGAGCACTGCCCAC TCTCGGAACATCTCGAAGCG 101 % VEGFA CGAAGGTCTGGAGTGTGTGC TCTCTCCTATGTGCTGGCCT 90 % hsa-mir-223- GCGTGTATTTGACAAGCTG GTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAACTCAG 97 % ssc-mir-182 AGTTTGGCAATGGTAGAACTC GTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAGTGTG 96 % ssc-mir-29a GCTAGCACCATCTGAAATCG TCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAACCGA 100 % ssc-mir-31 GGCAAGATGCTGGCA CCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCAGCTATG 92 % ssc-mir-29b CAGTAGCACCATTTGAAATCAG GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAACACT 96 % hsa-mir- AGGTGAAATGTTTAGGACCAC GTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCTAGTG 99 % 203a-3p hsa-mir-449a AGTGGCAGTGTATTGTTAGC GTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTACCAG 90 % ssc-mir-21 TCAGTAGCTTATCAGACTGATG CGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCAAC 101 % hsa-mir-23a- CATCACATTGCCAGGGAT CGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGGAA 109 % 3p ssc-mir-23b AGATCACATTGCCAGGGA CCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGGTAATCC 104 % ssc-mir-30c- CAGTGTAAACATCCTACACTCTC CCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGCTGAG 109 % ssc-mir-423- GGGCAGAGAGCGAGAC GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAAAGTC 90 % hsa-mir-150- GTCTCCCAACCCTTGTAC GTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCACTG 115 % ssc-mir-15a CAGTAGCAGCACATAATGGT TCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTACAAACC 97 % ssc-mir-186 CGCAGCAAAGAATTCTCCT GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAAGC 102 % ssc-mir-22- CAGAGTTCTTCAGTGGCAAG GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAAAGC 90 % ssc-mir-28- CAGAAGGAGCTCACAGTCT GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCTCA 97 % ssc-mir- GCAGTGAGAACTGAATTCCA GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAACC 92 % 146a- hsa-mir-223- CGCAGTGTCAGTTTGTCA CCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGGGGTA 101 % 3p hsa-mir-16- GCAGTAGCAGCACGTA CAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCGCCAA 96 % 11
4 Supplementary Table S2. Sequence comparison of human and porcine homologs of the mirnas reported regulated in the present study. Underlined nucleotides: nucleotides 2-7, i.e. the seed sequence. mirbase accession number mirna mirna sequence MIMAT hsa-mir-29a-3p uagcaccaucugaaaucgguua MIMAT ssc-mir-29a cuagcaccaucugaaaucgguua MIMAT hsa-mir-31- aggcaagaugcuggcauagcu MIMAT ssc-mir-31 aggcaagaugcuggcauagcug MIMAT hsa-mir-29b-3p uagcaccauuugaaaucaguguu MIMAT ssc-mir-29b uagcaccauuugaaaucaguguu MIMAT hsa-mir-21- uagcuuaucagacugauguuga MIMAT ssc-mir-21 uagcuuaucagacugauguuga MIMAT hsa-mir-23a-3p aucacauugccagggauuucc MIMAT ssc-mir-23a aucacauugccagggauuucc MIMAT hsa-mir-30c- uguaaacauccuacacucucagc MIMAT ssc-mir-30c- uguaaacauccuacacucucagc MIMAT hsa-mir-423- ugaggggcagagagcgagacuuu MIMAT ssc-mir-423- ugaggggcagagagcgagacuuu MIMAT hsa-mir-150- ucucccaacccuuguaccagug MIMAT ssc-mir-150 ucucccaacccuuguaccagug MIMAT hsa-mir-186- caaagaauucuccuuuugggcu MIMAT ssc-mir-186 caaagaauucuccuuuugggcuu MIMAT hsa-mir-22- aguucuucaguggcaagcuuua MIMAT ssc-mir-22- aguucuucaguggcaagcuuua MIMAT hsa-mir-28- aaggagcucacagucuauugag MIMAT ssc-mir-28- aaggagcucacagucuauugag MIMAT hsa-mir-146a- ugagaacugaauuccauggguu MIMAT ssc-mir-146a- ugagaacugaauuccauggguu MIMAT hsa-mir-16- uagcagcacguaaauauuggcg MIMAT ssc-mir-16 uagcagcacguaaauauuggcg MIMAT hsa-mir-182- uuuggcaaugguagaacucacacu MIMAT ssc-mir-182 uuuggcaaugguagaacucacacu MIMAT hsa-mir-23b-3p aucacauugccagggauuacc MIMAT ssc-mir-23b aucacauugccagggauuacca MIMAT hsa-mir-15a- uagcagcacauaaugguuugug MIMAT ssc-mir-15a uagcagcacauaaugguuugu
5 Supplementary Table S3. Expression levels of mirna in porcine leukocytes after IAV challenge. Expression is shown as relative levels compared to before challenge. mirna Rel. expression level ±95 % CI p-value 24h pi (n = 12) hsa-mir ssc-mir ssc-mir-29a ssc-mir h pi (n = 9) ssc-mir-29b hsa-mir-203a-3p hsa-mir-449a ssc-mir ssc-mir-29a hsa-mir-23a-3p ssc-mir-23b ssc-mir-30c ssc-mir hsa-mir d pi (n = 6) ssc-mir-15a ssc-mir-29b ssc-mir-29a hsa-mir-449a ssc-mir ssc-mir ssc-mir hsa-mir-203a-3p ssc-mir-146a hsa-mir ssc-mir-23b hsa-mir-223-3p hsa-mir-23a-3p hsa-mir
6 Supplementary Table S4. KEGG Pathway enrichment analysis of experimentally validated targets of the mirnas found to be differentially expressed in the present study. Pathways highlighted in bold text are enriched in at least three of the four gene subsets. Many pathways related to specific cancer types were also enriched in all four gene subsets; these have not been included in the table. KEGG pathway Number of genes involved 1) Enriched in target genes for up-regulated mirnas at 24h and 72h pi Percentage of investigated genes involved P-Value Benjamini- Hochberg adjusted P- Value Pathways in cancer 55 19,3 1,60E-27 1,80E-25 Focal adhesion 36 12,6 2,30E-18 8,50E-17 Cell cycle ,20E-09 3,50E-08 p53 signaling pathway 15 5,3 7,70E-09 7,70E-08 MAPK signaling pathway 26 9,1 2,30E-07 1,80E-06 Apoptosis 13 4,6 8,40E-06 5,50E-05 Neurotrophin signaling pathway 15 5,3 1,60E-05 9,70E-05 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction 22 7,7 2,70E-05 1,60E-04 ErbB signaling pathway 12 4,2 4,70E-05 2,60E-04 TGF-beta signaling pathway 12 4,2 4,70E-05 2,60E-04 T cell receptor signaling pathway 13 4,6 7,70E-05 4,00E-04 Adherens junction 11 3,9 8,30E-05 4,20E-04 ECM-receptor interaction 11 3,9 1,70E-04 8,40E-04 Toll-like receptor signaling pathway 12 4,2 1,90E-04 8,50E-04 Regulation of actin cytoskeleton ,10E-04 2,70E-03 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 10 3,5 9,70E-04 4,10E-03 Gap junction 10 3,5 1,20E-03 5,00E-03 Dilated cardiomyopathy 10 3,5 1,60E-03 5,90E-03 Jak-STAT signaling pathway 13 4,6 2,10E-03 7,80E-03 GnRH signaling pathway 10 3,5 2,40E-03 8,60E-03 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) 9 3,2 3,60E-03 1,20E-02 B cell receptor signaling pathway 8 2,8 6,70E-03 2,20E-02 VEGF signaling pathway 8 2,8 6,70E-03 2,20E-02 Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis 9 3,2 7,10E-03 2,30E-02 2) Enriched in target genes for down-regulated mirnas at 24h and 72h pi Pathways in cancer 37 19,1 8,60E-16 9,70E-14 p53 signaling pathway 14 7,2 3,80E-09 1,40E-07 Focal adhesion 22 11,3 5,50E-09 1,50E-07 Tight junction 12 6,2 2,80E-04 2,20E-03 Adherens junction 9 4,6 4,10E-04 2,80E-03 Cell cycle 11 5,7 6,60E-04 4,20E-03 ECM-receptor interaction 9 4,6 7,40E-04 4,50E-03
7 Notch signaling pathway 7 3,6 7,40E-04 4,20E-03 Apoptosis 9 4,6 9,40E-04 5,10E-03 Jak-STAT signaling pathway 11 5,7 3,40E-03 1,70E-02 Chemokine signaling pathway 12 6,2 4,40E-03 2,10E-02 Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection 7 3,6 5,10E-03 2,40E-02 Viral myocarditis 7 3,6 6,30E-03 2,80E-02 Cysteine and methionine metabolism 5 2,6 7,90E-03 3,40E-02 Neurotrophin signaling pathway 9 4,6 8,60E-03 3,50E-02 Wnt signaling pathway 10 5,2 8,90E-03 3,60E-02 3) Enriched in target genes for up-regulated mirnas at 14d pi Pathways in cancer 63 24,8 8,80E-37 9,50E-35 Focal adhesion 39 15,4 8,10E-22 2,90E-20 Cell cycle 25 9,8 4,90E-14 5,30E-13 Toll-like receptor signaling pathway 22 8,7 4,20E-13 4,10E-12 Neurotrophin signaling pathway 21 8,3 2,10E-10 1,60E-09 MAPK signaling pathway ,30E-09 4,00E-08 Apoptosis 16 6,3 1,80E-08 1,10E-07 p53 signaling pathway 14 5,5 4,60E-08 2,60E-07 T cell receptor signaling pathway 17 6,7 5,50E-08 3,00E-07 ErbB signaling pathway 15 5,9 1,30E-07 6,90E-07 Chemokine signaling pathway 21 8,3 3,00E-07 1,50E-06 B cell receptor signaling pathway 13 5,1 1,20E-06 5,60E-06 Adherens junction 13 5,1 1,60E-06 7,10E-06 Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis 14 5,5 2,60E-06 1,10E-05 VEGF signaling pathway 12 4,7 8,10E-06 3,20E-05 Regulation of actin cytoskeleton 20 7,9 1,10E-05 4,10E-05 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction 22 8,7 1,60E-05 6,10E-05 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 12 4,7 3,10E-05 1,10E-04 Wnt signaling pathway 15 5,9 1,00E-04 3,50E-04 Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection 10 3,9 1,30E-04 4,30E-04 Leukocyte transendothelial migration 13 5,1 1,30E-04 4,30E-04 Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway 10 3,9 3,70E-04 1,20E-03 ECM-receptor interaction 10 3,9 6,40E-04 2,00E-03 mtor signaling pathway 8 3,1 6,60E-04 2,00E-03 TGF-beta signaling pathway 10 3,9 8,30E-04 2,40E-03 Gap junction 10 3,9 9,80E-04 2,80E-03 Axon guidance 12 4,7 1,20E-03 3,20E-03 Jak-STAT signaling pathway 13 5,1 1,60E-03 4,20E-03 NOD-like receptor signaling pathway 8 3,1 1,90E-03 4,90E-03 Type II diabetes mellitus 7 2,8 2,10E-03 5,30E-03 Insulin signaling pathway 11 4,3 5,40E-03 1,30E-02 GnRH signaling pathway 9 3,5 7,10E-03 1,70E-02 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) 8 3,1 1,10E-02 2,60E-02
8 24 Intestinal immune network for IgA production 6 2,4 1,30E-02 2,90E-02 Oocyte meiosis 9 3,5 1,40E-02 3,10E-02 Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity 10 3,9 1,40E-02 3,10E-02 Tight junction 10 3,9 1,50E-02 3,20E-02 RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway 7 2,8 1,60E-02 3,40E-02 Dilated cardiomyopathy 8 3,1 1,70E-02 3,40E-02 Endocytosis 12 4,7 1,70E-02 3,40E-02 Prion diseases 5 2 1,80E-02 3,50E-02 4) Enriched in target genes for down-regulated mirnas at 14d pi Pathways in cancer 35 23,6 1,40E-16 1,20E-14 p53 signaling pathway 12 8,1 7,30E-08 2,60E-06 Jak-STAT signaling pathway 14 9,5 1,10E-05 1,10E-04 Cell cycle 12 8,1 3,40E-05 3,00E-04 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction 16 10,8 2,00E-04 1,20E-03 Insulin signaling pathway 11 7,4 3,30E-04 2,00E-03 Focal adhesion 13 8,8 6,20E-04 3,50E-03 Chemokine signaling pathway 12 8,1 1,20E-03 6,30E-03 NOD-like receptor signaling pathway 7 4,7 1,40E-03 7,10E-03 Dorso-ventral axis formation 5 3,4 1,40E-03 6,80E-03 ErbB signaling pathway 8 5,4 1,70E-03 7,70E-03 Apoptosis 8 5,4 1,70E-03 7,70E-03 Adipocytokine signaling pathway 7 4,7 2,10E-03 9,30E-03 Notch signaling pathway 6 4,1 2,30E-03 9,90E-03 Neurotrophin signaling pathway 9 6,1 3,20E-03 1,30E-02 VEGF signaling pathway 7 4,7 3,70E-03 1,50E-02 Tight junction 9 6,1 5,20E-03 2,00E-02 MAPK signaling pathway 13 8,8 6,70E-03 2,50E-02 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 7 4,7 7,20E-03 2,60E-02 Wnt signaling pathway 9 6,1 1,00E-02 3,50E-02
9 Supplementary Figure S1. mirna-target interaction networks at A) 24h pi, B) 72h pi, and c) 14d pi. Red circles represent down-regulated mirnas; green circles represent up-regulated mirnas; hexagons represent experimentally validated gene targets. Hexagons with solid grey fill are genes that interact with two or more of the regulated mirnas. Experimentally validated interactions are indicated with arrows from mirna to target. The number of genes with two or more experimentally validated MTIs comprised 6, 65, and 84 at 24h, 72h, and 14d pi, respectively. 31
10 32 a) 24h pi 33 34
11 35 b) 72h pi 36 37
12 38 c) 14d pi 39 40
Pathways of changes in hypermethylation in F1 offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia
 Supplementary Table 1. Pathways of changes in hypermethylation in F1 offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia Pathway Enrichment Score (-log10[p value]) p-value genes Glycosaminoglycan degradation
Supplementary Table 1. Pathways of changes in hypermethylation in F1 offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia Pathway Enrichment Score (-log10[p value]) p-value genes Glycosaminoglycan degradation
fasting blood glucose [mg/dl]
![fasting blood glucose [mg/dl] fasting blood glucose [mg/dl]](/thumbs/80/82129652.jpg) SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Supplemental Figure I body weight [g] 5 5 5 fasting blood glucose [mg/dl] 5 5 5 C total cholesterol [mg/dl] 8 6 4 WT Has -/- Supplemental Figure I: Has-deficient mice exhibited no apparent
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Supplemental Figure I body weight [g] 5 5 5 fasting blood glucose [mg/dl] 5 5 5 C total cholesterol [mg/dl] 8 6 4 WT Has -/- Supplemental Figure I: Has-deficient mice exhibited no apparent
Supplementary Figure 1: Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points
 A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler
 Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Identification of Tissue-Specific Protein-Coding and Noncoding. Transcripts across 14 Human Tissues Using RNA-seq
 Identification of Tissue-Specific Protein-Coding and Noncoding Transcripts across 14 Human Tissues Using RNA-seq Jinhang Zhu 1, Geng Chen 1, Sibo Zhu 1,2, Suqing Li 3, Zhuo Wen 3, Bin Li 1, Yuanting Zheng
Identification of Tissue-Specific Protein-Coding and Noncoding Transcripts across 14 Human Tissues Using RNA-seq Jinhang Zhu 1, Geng Chen 1, Sibo Zhu 1,2, Suqing Li 3, Zhuo Wen 3, Bin Li 1, Yuanting Zheng
Supplementary Files. Novel blood-based microrna biomarker panel for early diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis
 Supplementary Files Novel blood-based microrna biomarker panel for early diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis Lei Xin 1 *, M.D., Jun Gao 1 *, Ph.D., Dan Wang 1 *, M.D., Jin-Huan Lin 1, M.D., Zhuan Liao 1,
Supplementary Files Novel blood-based microrna biomarker panel for early diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis Lei Xin 1 *, M.D., Jun Gao 1 *, Ph.D., Dan Wang 1 *, M.D., Jin-Huan Lin 1, M.D., Zhuan Liao 1,
Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease
 Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease Craig E. Wheelock 1,2*, Åsa M. Wheelock 2,3,4, Shuichi Kawashima 5, Diego Diez 2, Minoru Kanehisa 2,5, Marjan van Erk
Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease Craig E. Wheelock 1,2*, Åsa M. Wheelock 2,3,4, Shuichi Kawashima 5, Diego Diez 2, Minoru Kanehisa 2,5, Marjan van Erk
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary figure 1: Pathway enrichment for each comparison. The first column shows enrichment with differentially expressed genes between the diet groups at t = 0, the second
Supplementary figures Supplementary figure 1: Pathway enrichment for each comparison. The first column shows enrichment with differentially expressed genes between the diet groups at t = 0, the second
Supplementary Material. Part I: Sample Information. Part II: Pathway Information
 Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
# of transcr ipts FDR q- value transcripts PGF,CTNNB1,AKT2,FARP2,VEGFB,PDGFRA,DRD 2,CSF1,CDH1,ITGB1,SRC,KRAS,RASGRP3,MAP2. Pathway
 Supplementary Table 9. Pathways and biological processes associated with transcripts specific to SEB in both the pre- and post- RASP leukocytes (transcripts included in the Reactome Function Interaction
Supplementary Table 9. Pathways and biological processes associated with transcripts specific to SEB in both the pre- and post- RASP leukocytes (transcripts included in the Reactome Function Interaction
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID
 Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Deconvolution of Heterogeneous Wound Tissue Samples into Relative Macrophage Phenotype Composition via Models based on Gene Expression
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information for: Deconvolution of Heterogeneous Wound Tissue Samples into
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information for: Deconvolution of Heterogeneous Wound Tissue Samples into
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk
 Contact Technical Support BRCsupport@QIAGEN.COM 1-800-362-7737 Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk Jesse Liang, Ph.D. Legal disclaimer QIAGEN products shown here are intended for molecular biology
Contact Technical Support BRCsupport@QIAGEN.COM 1-800-362-7737 Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk Jesse Liang, Ph.D. Legal disclaimer QIAGEN products shown here are intended for molecular biology
Supplementary information. Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by mir-204 controls
 Supplementary information Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by mir-204 controls angiogenesis in breast cancer Ali Flores-Pérez, Laurence A. Marchat, Sergio Rodríguez-Cuevas, Verónica Bautista-Piña,
Supplementary information Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by mir-204 controls angiogenesis in breast cancer Ali Flores-Pérez, Laurence A. Marchat, Sergio Rodríguez-Cuevas, Verónica Bautista-Piña,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Retinal expression of small non-coding RNAs in a murine model of proliferative retinopathy Chi-Hsiu Liu 1, Zhongxiao Wang 1, Ye Sun 1, John Paul SanGiovanni 2, Jing Chen 1, * 1 Department
Supporting Information Retinal expression of small non-coding RNAs in a murine model of proliferative retinopathy Chi-Hsiu Liu 1, Zhongxiao Wang 1, Ye Sun 1, John Paul SanGiovanni 2, Jing Chen 1, * 1 Department
The Role of micrornas in Pain. Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan
 The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
Contribution of the intronic mir-338-3p and its Hosting Gene AATK to Compensatory β-cell Mass Expansion
 Contribution of the intronic mir-338-3p and its Hosting Gene AATK to Compensatory β-cell Mass Expansion Cécile Jacovetti 1, Veronica Jimenez 2, Eduard Ayuso 2#, Ross Laybutt 3, Marie-Line Peyot 4, Marc
Contribution of the intronic mir-338-3p and its Hosting Gene AATK to Compensatory β-cell Mass Expansion Cécile Jacovetti 1, Veronica Jimenez 2, Eduard Ayuso 2#, Ross Laybutt 3, Marie-Line Peyot 4, Marc
Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL).
 Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL). (b) Depiction of a MTZ array generated by NAFL. (c-e) IgG production
Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL). (b) Depiction of a MTZ array generated by NAFL. (c-e) IgG production
Pathway Map Reference Guide
 Pathway Map Reference Guide Focus Attention-grabber Your Pathway The most popular cell signaling pathways Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents AKT Signaling 4 camp Signaling 5 Cellular Apoptosis
Pathway Map Reference Guide Focus Attention-grabber Your Pathway The most popular cell signaling pathways Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents AKT Signaling 4 camp Signaling 5 Cellular Apoptosis
Eosinophils! 40! 30! 20! 10! 0! NS!
 A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene
 OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
 Table S1. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracelluarly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene expression in
Table S1. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracelluarly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene expression in
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 *** Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Pten pc-/- ;Zbtb7a pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Pml pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Trp53 pc-/-
 Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3745
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental settings. (a) Experimental setup and bioinformatic data analysis of transcriptomic changes induced in neonatal and adult monocytes by stimulation with 10 ng/ml LPS for
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental settings. (a) Experimental setup and bioinformatic data analysis of transcriptomic changes induced in neonatal and adult monocytes by stimulation with 10 ng/ml LPS for
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Applied Biosystems models 7500 (Fast block), 7900HT (Fast block), StepOnePlus, ViiA 7 (Fast block)
 RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
K-means Clustering of a subset of five datasets that were identified as. TNBC by IHC. Since TNBCs are not identified by GE in the clinical setting, we
 Supplemental Results K-means Clustering of a subset of five datasets that were identified as TNBC by IHC. Since TNBCs are not identified by GE in the clinical setting, we performed a similar GE analysis
Supplemental Results K-means Clustering of a subset of five datasets that were identified as TNBC by IHC. Since TNBCs are not identified by GE in the clinical setting, we performed a similar GE analysis
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
How Will New Therapies Affect HCC Development?
 How Will New Therapies Affect HCC Development? July 6, 2018 Scott Friedman, M.D. Fishberg Professor of Medicine Dean for Therapeutic Discovery Chief, Division of Liver Diseases Icahn School of Medicine
How Will New Therapies Affect HCC Development? July 6, 2018 Scott Friedman, M.D. Fishberg Professor of Medicine Dean for Therapeutic Discovery Chief, Division of Liver Diseases Icahn School of Medicine
Considering a new paradigm for Alzheimer s disease research a response
 Considering a new paradigm for Alzheimer s disease research a response Martin Hofmann Apitius Department of Bioinformatics Fraunhofer Institute for Algorithms and Scientific Computing (SCAI) BioMed 21
Considering a new paradigm for Alzheimer s disease research a response Martin Hofmann Apitius Department of Bioinformatics Fraunhofer Institute for Algorithms and Scientific Computing (SCAI) BioMed 21
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
An integrated transcriptomic and functional genomic approach identifies a. type I interferon signature as a host defense mechanism against Candida
 Supplementary information for: An integrated transcriptomic and functional genomic approach identifies a type I interferon signature as a host defense mechanism against Candida albicans in humans Sanne
Supplementary information for: An integrated transcriptomic and functional genomic approach identifies a type I interferon signature as a host defense mechanism against Candida albicans in humans Sanne
Pathway enrichment analysis of human osteosarcoma U-2 OS bone cells expose to dexamethasone
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Pathway enrichment analysis of human osteosarcoma U-2 OS bone cells expose to dexamethasone 2014; 18: 2631-2639 J. CHEN, J. XIA, S.-Q. WANG, Y.-B.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Pathway enrichment analysis of human osteosarcoma U-2 OS bone cells expose to dexamethasone 2014; 18: 2631-2639 J. CHEN, J. XIA, S.-Q. WANG, Y.-B.
Supplementary Figure 1. Dynamic Response of WT and mir-21 -/- mice to caerulein. (a) Representative histological sections of mouse pancreas stained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Dynamic Response of WT and mir-21 -/- mice to caerulein. (a) Representative histological sections of mouse pancreas stained with hematoxylin from caerulein-treated WT and mir-21
Supplementary Figure 1. Dynamic Response of WT and mir-21 -/- mice to caerulein. (a) Representative histological sections of mouse pancreas stained with hematoxylin from caerulein-treated WT and mir-21
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
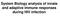 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Chapter 11 CYTOKINES
 Chapter 11 CYTOKINES group of low molecular weight regulatory proteins secreted by leukocytes as well as a variety of other cells in the body (8~30kD) regulate the intensity and duration of the immune
Chapter 11 CYTOKINES group of low molecular weight regulatory proteins secreted by leukocytes as well as a variety of other cells in the body (8~30kD) regulate the intensity and duration of the immune
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Virchow s Hypothesis lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation
 Virchow s Hypothesis 1863 lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation Barrett s esophagus/ Esophageal adenocarcinoma PSC / Cholangiocarcinoma Viral hepatitis
Virchow s Hypothesis 1863 lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation Barrett s esophagus/ Esophageal adenocarcinoma PSC / Cholangiocarcinoma Viral hepatitis
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
Integrative analysis of genetic data sets reveals a shared innate immune component in autism spectrum disorder and its co-morbidities
 Integrative analysis of genetic data sets reveals a shared innate immune component in autism spectrum disorder and its co-morbidities The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share
Integrative analysis of genetic data sets reveals a shared innate immune component in autism spectrum disorder and its co-morbidities The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Dysregulated MicroRNA Expression and Chronic Lung Allograft Rejection in Recipients With Antibodies to Donor HLA
 American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 1933 1947 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C Copyright 2015 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 10.1111/ajt.13185
American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 1933 1947 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C Copyright 2015 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 10.1111/ajt.13185
Signal transduction camp signaling pathway ko Signal transduction MAPK signaling pathway ko
 Table S2 - Summary of the KEGG pathway annotation results for the P transcriptome. Pathway Hierarchy1 Pathway Hierarchy2 KEGG Pathway Pathway ID Gene Metabolism Amino acid metabolism Lysine degradation
Table S2 - Summary of the KEGG pathway annotation results for the P transcriptome. Pathway Hierarchy1 Pathway Hierarchy2 KEGG Pathway Pathway ID Gene Metabolism Amino acid metabolism Lysine degradation
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
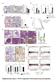 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Diseases of Immunity CL Davis General Pathology. Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc
 Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 6 th Ed Veterinary Immunology,
Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 6 th Ed Veterinary Immunology,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Bioinformatics: A personal perspective
 Bioinformatics: A personal perspective Jake Chen, Ph.D. Associate Director & Professor The Informatics Institute UAB School of Medicine Email: jakechen@uab.edu 1 Challenges in analyzing Genomic big data
Bioinformatics: A personal perspective Jake Chen, Ph.D. Associate Director & Professor The Informatics Institute UAB School of Medicine Email: jakechen@uab.edu 1 Challenges in analyzing Genomic big data
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Hippocampal sections from new-born Pten+/+ and PtenFV/FV pups were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and were imaged at (a) low and (b) high
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Hippocampal sections from new-born Pten+/+ and PtenFV/FV pups were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and were imaged at (a) low and (b) high
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017
 mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease In Ebola Virus-Infected Pigs
 Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease In Ebola Virus-Infected Pigs Charles Nfon 1, Anders Leung 2, Greg Smith 1, Carissa Embury-Hyatt 1, Gary Kobinger 2,3,4 and Hana Weingartl 1,3 1 National Centre for Foreign
Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease In Ebola Virus-Infected Pigs Charles Nfon 1, Anders Leung 2, Greg Smith 1, Carissa Embury-Hyatt 1, Gary Kobinger 2,3,4 and Hana Weingartl 1,3 1 National Centre for Foreign
Irf1 fold changes (D) 24h 48h. p-p65. t-p65. p-irf3. t-irf3. β-actin SKO TKO 100% 80% 60% 40% 20%
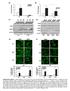 Irf7 Fold changes 3 1 Irf1 fold changes 3 1 8h h 8h 8h h 8h p-p6 p-p6 t-p6 p-irf3 β-actin p-irf3 t-irf3 β-actin TKO TKO STKO (E) (F) TKO TKO % of p6 nuclear translocation % % 1% 1% % % p6 TKO % of IRF3
Irf7 Fold changes 3 1 Irf1 fold changes 3 1 8h h 8h 8h h 8h p-p6 p-p6 t-p6 p-irf3 β-actin p-irf3 t-irf3 β-actin TKO TKO STKO (E) (F) TKO TKO % of p6 nuclear translocation % % 1% 1% % % p6 TKO % of IRF3
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Urodynamic recording of BOO-induced LUTD patients. (A) DO group. BOO patients with increased detrusor pressure and reduced urine flow during pressure flow in combination
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Urodynamic recording of BOO-induced LUTD patients. (A) DO group. BOO patients with increased detrusor pressure and reduced urine flow during pressure flow in combination
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
qpcr-array Analysis Service
 qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Case Study - Informatics
 bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
Immunology of aging #1: Why older adults are at increased risk of vaccine-preventable diseases
 Immunology of aging #1: Why older adults are at increased risk of vaccine-preventable diseases Bonnie B. Blomberg Dept. of Microbiology and Immunology U Miami Miller School of Medicine Immunization in
Immunology of aging #1: Why older adults are at increased risk of vaccine-preventable diseases Bonnie B. Blomberg Dept. of Microbiology and Immunology U Miami Miller School of Medicine Immunization in
Profiling micrornas in lung tissue from pigs infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
 Podolska et al. BMC Genomics 2012, 13:459 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Profiling micrornas in lung tissue from pigs infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Agnieszka Podolska 1,2, Christian Anthon
Podolska et al. BMC Genomics 2012, 13:459 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Profiling micrornas in lung tissue from pigs infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Agnieszka Podolska 1,2, Christian Anthon
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
Kerdiles et al - Figure S1
 Kerdiles et al - Figure S1 a b Homo sapiens T B ce ce l ls c l M ls ac r PM oph N ag es Mus musculus Foxo1 PLCγ Supplementary Figure 1 Foxo1 expression pattern is conserved between mouse and human. (a)
Kerdiles et al - Figure S1 a b Homo sapiens T B ce ce l ls c l M ls ac r PM oph N ag es Mus musculus Foxo1 PLCγ Supplementary Figure 1 Foxo1 expression pattern is conserved between mouse and human. (a)
4. Th1-related gene expression in infected versus mock-infected controls from Fig. 2 with gene annotation.
 List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Profiling of the Exosomal Cargo of Bovine Milk Reveals the Presence of Immune- and Growthmodulatory Non-coding RNAs (ncrna)
 Animal Industry Report AS 664 ASL R3235 2018 Profiling of the Exosomal Cargo of Bovine Milk Reveals the Presence of Immune- and Growthmodulatory Non-coding RNAs (ncrna) Eric D. Testroet Washington State
Animal Industry Report AS 664 ASL R3235 2018 Profiling of the Exosomal Cargo of Bovine Milk Reveals the Presence of Immune- and Growthmodulatory Non-coding RNAs (ncrna) Eric D. Testroet Washington State
T cell-mediated immunity
 T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
REACTOME: Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) REACTOME:72764 Eukaryotic Translation Termination. REACTOME:72737 Cap dependent Translation Initiation
 A REACTOME:975957 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:975956 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:927802
A REACTOME:975957 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:975956 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:927802
Original Article Detection of mirna differential expression of necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns by high-throughput sequencing
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1025-1033 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0037332 Original Article Detection of mirna differential expression of necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns by high-throughput
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1025-1033 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0037332 Original Article Detection of mirna differential expression of necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns by high-throughput
Supplementary Figure 1. PCA separated RA and OA FLS isolated from (a) knees and (b) hips. by corresponding DMLs.
 Supplementary Figure 1. PCA separated RA and OA FLS isolated from (a) knees and (b) hips by corresponding DMLs. Supplementary Table 1. Enriched biological pathways identified between 19 RA and 5 OA in
Supplementary Figure 1. PCA separated RA and OA FLS isolated from (a) knees and (b) hips by corresponding DMLs. Supplementary Table 1. Enriched biological pathways identified between 19 RA and 5 OA in
Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study. February 2018
 Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study February 2018 Precision Medicine Therapies designed to target the molecular alteration that aids cancer development 30 TARGET gene alterations
Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study February 2018 Precision Medicine Therapies designed to target the molecular alteration that aids cancer development 30 TARGET gene alterations
SIRT6 histone deacetylase functions as a potential oncogene in human melanoma -
 SIRT6 histone deacetylase functions as a potential oncogene in human melanoma - Garcia-Peterson et al Supplementary Figure S:Tissue microarray (TMA) staining and organization. A) Diagram of the TMA indicating
SIRT6 histone deacetylase functions as a potential oncogene in human melanoma - Garcia-Peterson et al Supplementary Figure S:Tissue microarray (TMA) staining and organization. A) Diagram of the TMA indicating
