Lipids. Types of lipids. Fatty acid structure. Lipid functions. Fatty acid structure
|
|
|
- Colin Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lipids Types of lipids lassification of Lipids Fatty Acids Glycerides Nonglycerol Lipids omplex Lipids Structure of Biological Membranes Fatty Acids Saturated Unsaturated omplex Lipids Lipoproteins Glycolipids Glycerides Neutral Phosphoglycerides Nonglycerides Sphingolipids Steroids Waxes Lipid functions Fatty acid structure ell membrane structure reates a barrier for the cell. ontrols flow of materials. Energy storage Fats stored in adipose tissue. ormones and Vitamins ormones - communication between cells. Vitamins - assist in the regulation of biological processes. Long chain monocarboxylic acids 3(2)n Size Range: Always an even number of carbon. Saturated - no double bonds. Unsaturated - one or more double bonds. Fatty acid structure Some common fatty acids Saturated ommon name IUPA name MP o Formula Lauric n-dodecanoic Palmitic n-hexadecanoic Unsaturated cis Stearic n-octadecanoic Palmitoleic cis-9-hexadecenoic leic cis-9-octadecenoic trans - not in nature Linoleic cis,cis,9,12- octadecadienoic Presence of double bonds reduces melting point. In nature, all double bonds are cis.
2 Steric acid leic acid Reactions of fatty acids React like any other carboxylic acid. Esterification R + R ydrolysis R--R + 2 Acid-base R + Na R--R + 2 R-- + R R - Na Reactions of unsaturated fatty acids They can undergo the same reactions. Will also undergo addition. Most common addition is hydrogenation. R-= Ni R Used to convert vegetable oils to margarine. It is during hydrogenation that trans fatty acids can be produced. Unsaturated fatty acids eicosanoids Eicosanoids All are unsaturated. All have twenty carbons. Two are Essential Fatty Acids. an t be produced by the body. examples: linolenic and linoleic acids Prostaglandins riginally isolated from seminal fluid. All are derived from arachidonic acid. Three groups Prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes
3 Arachadonic acid Prostaglandins E 1 F 2 F 1 Prostaglandins Blood clotting Biological effects Stimulation of smooth muscles Regulation of steroid production Inhibition of gastric secretion Inhibition of hormone-sensitive lipases Inhibition / stimulation of plate aggregation Regulation of nerve transmission Sensitization to pain Mediation of inflammatory response Thromboxane A 2 Produced by platelets in blood. Stimulates constriction of blood vessels. Aggregation of platelets. Prostacyclin Produced by cells that line blood vessels. Reverses effects of Thromboxane A 2. Aspirin therapy (1/day) following strokes or MI. Acts as anticoagulent - antiplatelet aggregation. Inflammatory response Smooth muscle contractions Protective mechanism when tissue is damaged. Results in swelling, redness, fever, and pain. Prostaglandins promote this response. Drugs like aspirin and Ibuprofen Anti-inflammatory. Block prostaglandin synthesis. ause reduction in this response. Tylenol - analgesic, not an anti-inflammatory Prostaglandins stimulate contractions in the reproduction system - uterine contractions Dysmenorrhea Painful menstruation. Evidence shows that this may result from an excess of prostaglandins. Physicians often order Motrin (Ibuprofen) for this.
4 Gastrointestinal tract ther uses Prostaglandins will: Inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Increase secretion of mucus layer. Protects mucosa from acid invasion. Aspirin inhibits prostaglandin production Extended use can result in ulceration of the stomach lining. Why? In the kidneys ause renal blood vessels to dilate. Aid in excretion of water and electrolytes. In the respiratory tract Produced by in lungs - leukotrienes. ause constriction of bronchi - asthma ther prostaglandins act as bronchodilators. Neutral glycerides Ester of glycerol and a fatty acid. Principal function is energy storage - fat or oil. Neutral glycerides An example of a triglyceride May have 1-3 fatty acids which need not be the same. 1 - monoglyceride 2 - diglyceride 3 - triglyceride Glycerol 2 2 Ester linkage Fatty acid Fats and oils Both are triglycerides. Fats Typically obtained from animals Solids at room temperature. Made from saturated fatty acids. Fat ils Typically obtained from plants. Liquids at room temperature. Made from unsaturated fatty acids.
5 Waxes Water insoluble and hard to hydrolyze ften used to provide a protective coating (leaves, skin, fur, hair...) Beeswax and Sebum are examples. Ester of a fatty acid and a long chain alcohol. Fatty acid lestra Phosphoglycerides Alcohol Phosphoglycerides Lecithin - phosphatidylcholine Lipids that contain a phosphate group. Modified fat where a phosphate replaces one of the fatty acid chain. Uses Production of cell membranes. Emulsifying agents N P 3 2 Non-polar tail Polar head Lecithin Nonglycerol lipids Sphingolipids A type of phospholipid NT derived from fat. Used primarily in nerve tissue - myelin sheath. In people, 25% of all lipids are sphingolipids. Non-polar tail Sphingosine 3(2)12 N holine 2 Polar head Fatty acid P Phosphate Sphingomyelin 3 N
6 Steroids Broad class of compounds that all have the same base structure. Steroids holesterol Principal membrane lipid for fluidity. 3 3 Steroid nucleus holesterol Associated with hardening of the arteries. Appears to coat the arteries - plaque formation. Steroids Some reproductive hormones. 3 3 progesterone Results in increased blood pressure from: Narrowing of arteries Reduced ability to stretch lot formation leading to: Myocardial Infarction Stroke 3 testosterone 3 3 Steroids omplex lipids ortisone Associated with a many biological processes - metabolism of carbohydrates, treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, GI disorders, rashes phospholipid cholesterol protein Lipids bound to other molecules. ombination results in a structure.
7 omplex lipids omposition of complex lipoproteins Four major classes of plasma lipoproteins. hylomicrons Very low-density lypoproteins (VLDL) Low-density lypoproteins (LDL) igh-density lypoproteins (DL) hylomicron VLDL LDL DL Each is composed of several types of lipids. Protein holesterol Phospholipids Triglycerides omposition of complex lipoproteins Lipoprotein Density, g/cm 3 Diameter, nm hylomicron < Very low density Low density igh density Function of lipoproteins hylomicrons Transport triglycerides from intestines to other tissue - except kidneys. (Transport exogenic products.) VLDL Bind triglycerides in liver and released to the blood. LDL arry fat and cholesterol to peripheral tissues. Produced from VLDL in blood. onversion also releases some cholesterol into blood vessels. DL Bound to plasma cholesterol. Transport cholesterol and fat to liver. an pick up chlosterol that has been dumped in the blood stream. Entry of LDL into cells Receptor-mediated endocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis Receptors on cell membrane sense LDL. Pocket forms in membrane - invagination. Takes LDL into cell, forming endosome. Endosome fuses with lysosome. - digestive organelle cholesterol lysozome endosome LDL receptor sites Enzymes digest LDL, releasing cholesterol. cholesterol ester drop
8 Biological membranes Presence of cholesterol in cell Reduces synthesis of more cholesterol. Inhibits production of LDL receptors. ell and organelle membranes are composed of two layers - lipid bilayers. LDL defect in gene coding Allows too much cholesterol to accumulate in the plasma. Excess cholesterol is then deposited artery walls - atherosclerosis. Fluid structure of membranes polar Large number of receptors in liver allow rapid removal of LDL nonpolar Regulation of LDL Mosaic structure of membranes Membranes are not static. Layers move over each other based on percent of unsaturated fatty acids. omponents Peripheral membrane proteins bound only to one side of membrane. lateral diffusion Integral membrane proteins embedded within the membrane. flip-flop Both types of proteins can move around on surface of cell. rare Proteins don t flip in and out or act like revolving door. rotation Mosaic structure of membranes -helix protein Membrane transport carbohydrate ell membrane controls passage of materials in and out of cell. Most transport is controlled by integral membrane transport proteins. Small molecules, like water, pass through membrane on their own - passive transport. cholesterol phospholipids globular protein Larger molecules and ions may require energy to pass through membrane active transport.
9 Passive transport Diffusion Small molecules (2, 2, 2) will simply pass through cell membrane. Entropy is driving force - wants equal concentrations of both sides of membrane. Facilitated diffusion Permeases Specific protein transports materials across a membrane. _ l 3 _ Membrane is considered selectively permeable to these molecules. This concept was discussed last semester. _ l 3 _ smosis Review of hapter 7 smotic pressure The diffusion of a solvent from a dilute solution through a semipermeable membrane to a more concentrated one. Semipermeable membranes nly allow small molecules to go through. ell walls are semipermeable membranes. Three conditions can exist for cells oncentration is the same on both side isotonic oncentration is greater on the inside hypertonic oncentration is greater on the outside hypotonic Isotonic ells in high salt solutions A red blood cell and plasma have the same osmotic pressure If the level of salt in the plasma is too high, the cell collapses. ypotonic cell, hypertonic solution. renation - water is drawn out of the cell.
10 ells in low salt solutions If the level of salt in the plasma is too low, the cell swells and ruptures. Active transport When a cell must expend energy to move needed materials across the cell membrane. K + Na + ypertonic cell, hypotonic solution. emolysis - water is drawn into the cell. K + ADP+ P i ATP Na+ Na + - K + ATPase pump Passing Na + out of cell. This system is used to pump sodium out of the cell and potassium into it. Two protein subunits span the cell membrane. Energy as ATP is required as the energy source. Extracellular side ytoplasm Na + - K + ATPase pump membrane bilayer Extracellular side ytoplasm Energy is used to shift the position of the proteins, releasing the sodium Extracellular side ytoplasm 3 Na + move into the unit where they bind. P ATP ADP
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Chapter 17: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons
 hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Section 8: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons. Outline
 hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
Chapter 20 Lipids. Organic and Biochem
 Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Functions of Lipids. - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g).
 Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Chapter 19 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 19 Lecture utline Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Lipids! Introduction to Lipids! Lipids are biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in
Chapter 19 Lecture utline Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Lipids! Introduction to Lipids! Lipids are biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in
Lipids. Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids.
 Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Roles of Lipids in the body
 Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Experiment 12 Lipids. Structures of Common Fatty Acids Name Number of carbons
 Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12
 BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds.
 Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Organism. Organ and organ systems. Tissue. Cells. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids
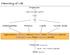 hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
CH 3. Lipids CHAPTER SUMMARY
 H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Chemistry B11 Chapters 15 Lipids
 Chapters 15 ipids ipids: are family of biomolecules that have the common property of being soluble in organic solvents but not in water. Role of lipids: they have three important roles in nature: 1. They
Chapters 15 ipids ipids: are family of biomolecules that have the common property of being soluble in organic solvents but not in water. Role of lipids: they have three important roles in nature: 1. They
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
Chapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids
 common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
Nebal Al - Gallab. Shatha Al - Jabri. Mamoon Ahram
 10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
Classification of Lipids
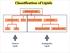 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
Sphingolipids. Sphingolipids are an additional type of membrane lipids, after glycerophospholipids, galactolipids and sulfolipids
 Lipids 2 Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Bioinformatics Department of Biology and Environmental Sciences University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: Bioinformatics Lab NCN#343B Tel:
Lipids 2 Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Bioinformatics Department of Biology and Environmental Sciences University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: Bioinformatics Lab NCN#343B Tel:
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature
 GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS:
 LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
Plasma Membrane Function
 Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Topic 3: Molecular Biology
 Topic 3: Molecular Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids Essen=al Understanding: Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are used to supply and store energy. Carbohydrates CARBOHYDRATES CHO sugars Primarily consist
Topic 3: Molecular Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids Essen=al Understanding: Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are used to supply and store energy. Carbohydrates CARBOHYDRATES CHO sugars Primarily consist
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Lipids. Lipids: Defined. ClassificaCon by FuncCon 10/19/09. Chapter 21
 Lipids Chapter 21 Lipids: Defined They are a family of substances that are insoluble in water, but soluble in non polar solvents and solvents of low polarity ClassificaCon by FuncCon Energy storage Lipids
Lipids Chapter 21 Lipids: Defined They are a family of substances that are insoluble in water, but soluble in non polar solvents and solvents of low polarity ClassificaCon by FuncCon Energy storage Lipids
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Organic molecules highly hydrophobic and water insoluble.
 UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
The Plasma Membrane. 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane. Phospholipid Bilayer. The Plasma Membrane
 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
Seminar 6 Theoretical part
 Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport. 阮雪芬 May/9/2004
 Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport 阮雪芬 May/9/2004 Outline Introduction Fatty Acids Triacylglycerols Polar lipids Steroids and other lipids Biological membranes Membrane transport Examples
Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport 阮雪芬 May/9/2004 Outline Introduction Fatty Acids Triacylglycerols Polar lipids Steroids and other lipids Biological membranes Membrane transport Examples
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
Lipids are used to store and excess energy from extra carbohydrates in animals
 Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
3.9 Carbohydrates. Provide building materials and energy storage. Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
 3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202
 General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
Chemistry Chapter 21
 Chemistry 2100 Chapter 21 Lipids Fa3y Acids CH oleic acid (mp 4 C) CH stearic acid (mp 70 C) Triacylglycerols Fatty Acids! The fatty acid components of triglycerides have certain things in common: 1.
Chemistry 2100 Chapter 21 Lipids Fa3y Acids CH oleic acid (mp 4 C) CH stearic acid (mp 70 C) Triacylglycerols Fatty Acids! The fatty acid components of triglycerides have certain things in common: 1.
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Chapter 10 Homework Assignment
 hapter 10 Homework Assignment I have decided to alter the homework assignment for hapter 10. The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 2, 4, 5, 6, 9 Lipids are Good (and not always
hapter 10 Homework Assignment I have decided to alter the homework assignment for hapter 10. The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 2, 4, 5, 6, 9 Lipids are Good (and not always
Chapter 11: Lipids. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: AP Biology
 Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Lipids and Biological Membranes
 Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition. phospholipids. Sphingolipids. Cholesterol. db=books&itool=toolbar
 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble
 Lipids Lipids Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble Lipids They act like this because of their molecular structure (non-polar) Lipids are made mostly of C and H atoms, with O
Lipids Lipids Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble Lipids They act like this because of their molecular structure (non-polar) Lipids are made mostly of C and H atoms, with O
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules. KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life.
 KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. Carbon-based
KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. Carbon-based
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Inorganic compounds: Usually do not contain carbon H 2 O Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 NaCl Carbon containing molecules not considered organic: CO 2
 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
Lipids. Chapter 11: Outline. Fatty Acids. Lipid Classes. Fatty Acids-2. Fatty Acids-3. General Types eg. A fatty acid
 Chapter 11: utline Lipid Classes Fatty Acids and Derivatives Triacylglycerols Phospholipids Isoprenoids Membranes Membrane Structure Membrane Function Wax Esters Sphingolipids Lipoproteins Lipids General
Chapter 11: utline Lipid Classes Fatty Acids and Derivatives Triacylglycerols Phospholipids Isoprenoids Membranes Membrane Structure Membrane Function Wax Esters Sphingolipids Lipoproteins Lipids General
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules CARBON BASED MOLECULES
 CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids
 WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids PART A: Understanding Lipids Lipids are more commonly known as fats and include triglycerides,
WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids PART A: Understanding Lipids Lipids are more commonly known as fats and include triglycerides,
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Saba Al Fayoumi. Nour Hamdan. Bann Khraisat. Dr. Mamoun Ahram
 9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
What are the molecules of life?
 Molecules of Life What are the molecules of life? Organic Compounds Complex Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Organic Compounds Carbon- hydrogen based molecules From Structure to Function Ø Carbon
Molecules of Life What are the molecules of life? Organic Compounds Complex Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Organic Compounds Carbon- hydrogen based molecules From Structure to Function Ø Carbon
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
3150:112 SAMPLE TEST 2. Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck!
 SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
Ahmad O. Olimat. Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh. Dr.Mamoun
 10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
Transport Movement across the Cell Membrane
 Transport Movement across the Cell Membrane Lipids of cell membrane Membrane consists primarily of phosphos phospho bilayer inside cell phosphate hydrophilic outside cell hydrophobic S1 The Fluidity of
Transport Movement across the Cell Membrane Lipids of cell membrane Membrane consists primarily of phosphos phospho bilayer inside cell phosphate hydrophilic outside cell hydrophobic S1 The Fluidity of
Lipids. Water vsoil. Water is a Polar Molecule δ + Polarity vs Nonpolarity H O
 Water vsil SCBC203 Lipids Jirundon Yuvaniyama, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science Mahidol University Figure taken from https://www.healthtap.com/user_questions/558342 Figures taken from
Water vsil SCBC203 Lipids Jirundon Yuvaniyama, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science Mahidol University Figure taken from https://www.healthtap.com/user_questions/558342 Figures taken from
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membrane structure.
 Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membranebound organelles. In this topic, we will examine the structure and
Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membranebound organelles. In this topic, we will examine the structure and
The Components of Life
 The omponents of Life Section 1.2 Organic hemistry Pre-View 1.2 hemistry Review MAAP-EO Biology I 8 Section 1.2 The omponents of Life Section 1.2, continued Organic hemistry Each line represents a bond.
The omponents of Life Section 1.2 Organic hemistry Pre-View 1.2 hemistry Review MAAP-EO Biology I 8 Section 1.2 The omponents of Life Section 1.2, continued Organic hemistry Each line represents a bond.
Membrane Structure and Function - 1
 Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
/ The following functional group is a. Aldehyde c. Carboxyl b. Ketone d. Amino
 Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
