Protein Structure Klemens Wild, BZH,
|
|
|
- Cassandra Gallagher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Protein Structure
2 recommended books
3 Proteins protein definition From gr. proteios (superior, erstrangig) 1836 JJ Berzelius Functions: structural, enzymes, muscle, transport immune system, Linear polymer of amino acid residues. Connection: peptide bond Polypeptide chain 3D structure: 1950s Myoglobin, hemolobin (Kendrew and Perutz)
4 4 levels of protein structure Primary: the linear sequence of amino acids Secondary: the local organization of parts of a polypeptide chain (α-helix, β-sheet) Tertiary: the overall, three-dimensional arrangement of the polypeptide chain (Domain: folding unit) Quaternary: the assembly of two or more polypeptides into a multisubunit complex
5 Part I protein main chain
6 Amino acids the building blocks In general: 2 functional groups α-amino acids R: side chain: 20 different amino acids encoded
7 the building blocks α-carboxyl group pka 2.0 α-amino group pka 9.5
8 The fractional protonation at a certain ph and the pi can be calculated by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. pka and pi
9 Absolute configuration the building blocks Amino acids contain asymmetric carbons. α-l amino acids S configuration
10 the peptide bond Condensation reaction ΔG = + 10 kj/mol metastable in water Activation by esterification with CCA-end of t-rnas
11 the peptide bond
12 the peptide bond Ramachandran et al., Biochim. Biophys. Acata 339 (1974), 298
13 The peptide bond has partial double bond character (40%) the peptide bond planarity The peptide bond has a constant dipole µ (3.5 Debye) µ
14 cis and trans peptides Configuration of the peptide bond Peptide bonds are mainly in trans Conformation defined by angle ω& Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
15 cis and trans peptides Cis bonds cause sterical hindrance. after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
16 cis and trans peptides Only proline residues are significantly in cis. after Stryer, Biochemistry, Copyright 2002 by W.H. Freeman & Co
17 the peptide bond Each peptide bond formation requires about 4 ATP and 4 GTP molecules for translation and quality control. The peptide planes are relatively oriented by the rotation around the Φ and Ψ angles. Ramachandran plot
18 Φ and ψ angles after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
19 Ramachandran plot Ψ Φ Hoeffken et al., J. Mol. Biol. 204 (1987), 629
20 Ramachandran plot
21 Ramachandran plot Ramachandran plot β-sheet right handed α-helix most favoured regions additionally allowed regions generously allowed regions dis - allowed regions
22 δ+ α - helix 3.6 aar 5.4 Å [ δ-
23 α - helix The α-helix is a helix Helices like to form bundles or coiled coils or transmembrane domains (TMDs)
24 the helical wheel
25 the helical wheel!hydrophobic amphipathic hydrophilic protein core protein surface exposed (membrane) (membrane surface) Branden & Tooze, Protein Structure, 1999 Garland Publ.
26 β-sheet Extended zigzag of peptide chain & Location of side chains alternates & β-sheets form by the alignment of β-strands parallel or antiparallel β-sheets are twisted and like to form β-barrels. after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
27 parallel β-sheet
28 antiparallel β-sheet
29 poly-proline helix Ramachandran plot antiparallel β-sheet parallel β-sheet π-helix 3-10 helix left handed α-helix right handed α-helix most favoured regions additionally allowed regions generously allowed regions dis - allowed regions
30 β II β VIa Ramachandran plot inv. γ β V β I β III β VIb β VIII Rose et al., Adv. Prot. Chem. 37 (1985), 1; Chou & Fasman, J. Mol. Biol. 115 (1977), 135; Wilmot & Thornton, J. Mol. Biol. 203 (1988), 221; Richardson, Adv. Prot. Chem. 34 (1981), 167 β III β I β II γ β V
31 Which secondary structure is formed? propensities Secondary structures can be predicted.
32 side chains amino acid side chains
33 Amino acid classification: amino acid classes 1. Aliphatic 2. Proline (imino acid) 3. Hydroxyl (polar) 4. Acidic 5. Amide (polar) 6. Basic 7. Histidine 8. Aromatic 9. Sulfur containing
34 G Gly Glycine 1. Aliphatic Glycine R: -H Glycine is not asymmetric High conformational flexibility molecular mass: 57 dalton frequency: 7.2 % All aliphatic residues are chemically inert. Structural role (hydrophobic core) after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
35 1. Aliphatic Alanine R: -CH 3 A Ala Alanine molecular mass: 71 dalton frequency: 8.3 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
36 1. Aliphatic Valine R: -CH-(CH 3 ) 2 V Val Valine molecular mass: 99 dalton frequency: 6.6 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
37 1. Aliphatic Leucine R: -CH 2 -CH-(CH 3 ) 2 L Leu Leucine molecular mass: 113 dalton frequency: 9.0 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
38 1. Aliphatic Isoleucine I Ile Isoleucine molecular mass: 113 dalton frequency: 5.2 % Note: Additional asymmetric β-carbon. after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
39 1. Proline (imino acid) R: -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 - Side chain is bonded to main chain nitrogen. Rigid breaks secondary structures P Pro Proline molecular mass: 97 dalton frequency: 5.1 % black = protein main chain after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
40 2. Hydroxyl (polar) Serine R: -CH 2 -OH Hydroxyl group is polar but chemically inert. S Ser Serine molecular mass: 87 dalton frequency: 6.9 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
41 2. Hydroxyl (polar) Threonine R: -CH(-CH) 3 (-OH) Note: Additional asymmetric β-carbon. T Thr Threonine molecular mass: 101 dalton frequency: 5.8 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
42 3. Acidic D Asp Aspartate Aspartic acid (Aspartate) R: -CH 2 -COOH Used for ionic and polar interactions molecular mass: (active sites, metal chelating) 115 dalton frequency: 5.3 % pka: 4.0 shaded = partial double bond after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
43 E Glu Glutamate 3. Acidic Glutamic acid (Glutamate) R: -CH 2 -CH 2 -COOH Used for ionic and polar interactions molecular mass: 129 dalton frequency: 6.2 % pka: 4.4 shaded = partial double bond after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
44 N Asn Asparagine 5. Amide (polar) Asparagine R: -CH 2 -CONH 2 Amid form of aspartic acid black = double bond relatively inert but amide is labile molecular mass: 114 dalton frequency: 4.4 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
45 5. Amide (polar) Glutamine R: -CH 2 -CH 2 -CONH 2 Amid form of glutamic acid Q Gln Glutamine molecular mass: 128 dalton frequency: 4 % black = double bond after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
46 5. Amide (polar) Glutamine spontaneously cyclises at N-terminus pyrrolidone carboxylic acid Q Gln Glutamine Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
47 6. Basic K Lys Lysine Lysine R: -(CH 2 ) 4 -NH 2 non-ionised Lys is a potent nucleophile! molecular mass: frequency: 128 dalton 5.7 % pka: after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
48 6. Basic Arylation K Lys Lysine 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonate absorbance at 367 nm Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
49 6. Basic acetylation by anhydrides (reversible) K Lys Lysine Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
50 K Lys Lysine reversible Schiff base with Aldehydes Example: PLP (Vit. B6) Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
51 6. Basic Arginine R: -(CH 2 ) 3 -NH-C-(NH 2 ) 2 used for ionic and polar interactions (i.e. nucleotides) R Arg Arginine molecular mass: 156 dalton frequency: 5.7 % shaded = partial double bond pka: 12 Guanidinium group planar after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
52 H His Histidine 7. Histidine Contains very reactive imidazole ring Nucleophilic and acid-base reactions active site molecular mass: 137 dalton black = double bond pka: 6-7 frequency: 2.2 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
53 pka: 6-7 H His Histidine an aromatic heterocycle with one pyrrole N (δ 1 ) and one pyridine N (ε 2 ) The two nitrogens contribute 3 valence electrons to the aromatic ring. In the neutral imidazole ring, six π-electrons are de-localised over five p-orbitals in the five atoms of the imidazole ring. This makes for three bonding molecular orbitals. after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co and Kyte, Structure in Protein Chemistry, 1995 by Garland Publ. Inc.
54 + H His Histidine - after Kyte, Structure in Protein Chemistry, 1995 by Garland Publ. Inc.
55 F Phe Phenylalanine 8. Aromatic Phenylalanine Hydrophobic and inert protein core molecular mass: 147 dalton shaded = partial double bond frequency: 3.9 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
56 Y Tyr Tyrosine 8. Aromatic Tyrosine Less hydrophobic due to hydroxyl group Used for ligand interactions Absorbs at 280 nm shaded = partial double bond molecular mass: 163 dalton frequency: 3.2 % pka: 11 after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
57 W Trp Tryptophane 8. Aromatic Tryptophane Indole ring important for absorption and flourescence molecular mass: 186 dalton shaded = partial double bond frequency: 1.3 % black = double bond after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
58 Phe Trp Tyr Wetlaufer, Adv. Protein Chem. 17 (1962), 303
59 Phe Trp Tyr Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
60 C Cys Cysteine 9. Sulfur containing Cysteine R: -CH 2 -SH Thiol group is most reactive side chain active sites Thiolate is a potent nucleophile! Sensitive to oxidation! pka: molecular mass: 103 dalton frequency: 1.7 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
61 C Cys Cysteine 9. Sulfur containing cysteine oxidation disulfide formation Cellular system to prevent oxidation: Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
62 C Cys Cysteine 9. Sulfur containing thiole-disulfide exchange Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
63 9. Sulfur containing Cleland s reagent C Cys Cysteine DTT Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
64 C Cys Cysteine 9. Sulfur containing Ellman Assay DTNB di-thio-bis-nitrobenzoic acid after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
65 9. Sulfur containing C Cys Cysteine alkylation at basic ph pka: Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
66 9. Sulfur containing C Cys Cysteine p-mercuribenzoic acid Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
67 9. Sulfur containing Methionine R: -CH 2 -CH 2 -S-CH 3 Long and flexible and hydrophobic M Met Methionine less sensitive to oxidation molecular mass: 131 dalton frequency: 2.4 % after Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co; amino acid frequency McCaldon & Argos, Proteins 4 (1988), 99
68 9. Sulfur containing M Met Methionine methionine oxidation by air Creighton, Proteins, Copyright 1993 by W.H. Freeman & Co
69 A Venn diagram showing the relationship of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids Taylor, W. R. The Classification of Amino Acid Conservation. J. Theor. Biol. 119 (1986), ; Livingstone & Barton, Meth. Enzymol. 266 (1996),
70 Essential amino acids I Ile, L Leu, V Val, W Trp, F Phe, M Met, K Lys, T Thr
71 Modified amino acids
72 phosphorylation O-phosphonoserine, O-phosphonothreonine, O-phosphonotyrosine, O-phosphonoglutamate, N-phosphonolysine, N-phosphonohistidine, N-phosphonoarginine, S-phosphonocysteine Jack Kyte, Structure in Protein Chemistry, 1995 by Garland Publ. Inc.; Uy, R. & Wood, F., Science 198 (1977),
73 glycosylation O-(polymannosyl)serine, O-(polymannosyl)threonine, O-[oligo(α1,2)galactosyl]serine, O-(3-O-(β-glucosyl)-α-fucosyl]threonine, O-[2-O-(α-glucosyl)-β-galactosyl)-5-hydroxylysine, O-(β-xylosyl)serine, O-[4-O-(β-galactosyl)-β-xylosyl]serine, S-digalactosylcysteine, S-triglucosylcysteine, O-(glucosylarabinosyl)hydroxyproline, O-(N-acetylglucosaminyl)serine Jack Kyte, Structure in Protein Chemistry, 1995 by Garland Publ. Inc.; Uy, R. & Wood, F., Science 198 (1977),
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Review II: The Molecules of Life
 Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2007 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2007 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids
Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2007 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2007 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Judy Wieber. Department of Computational Biology. May 27, 2008
 Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2008 Department of Computational Biology University it of Pittsburgh School of Medicine i May 27, 2008 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates
Review II: The Molecules of Life Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2008 Department of Computational Biology University it of Pittsburgh School of Medicine i May 27, 2008 Outline Introduction Proteins Carbohydrates
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
Amino Acids. Lecture 4: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where?
 Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
PROTEINS. Building blocks, structure and function. Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties
 PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection
 Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Bioinformatics for molecular biology
 Bioinformatics for molecular biology Structural bioinformatics tools, predictors, and 3D modeling Structural Biology Review Dr Research Scientist Department of Microbiology, Oslo University Hospital -
Bioinformatics for molecular biology Structural bioinformatics tools, predictors, and 3D modeling Structural Biology Review Dr Research Scientist Department of Microbiology, Oslo University Hospital -
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Maha AbuAjamieh. Tamara Wahbeh. Mamoon Ahram
 12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids.
 Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Amino acids. (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi
 Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids. You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures.
 Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
Introduction. Basic Structural Principles PDB
 BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
Amino Acids االحماض األمينية
 Amino Acids االحماض األمينية Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cell Structure Amino Acids The study of
Amino Acids االحماض األمينية Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cell Structure Amino Acids The study of
Raghad Abu Jebbeh. Amani Nofal. Mamoon Ahram
 ... 14 Raghad Abu Jebbeh Amani Nofal Mamoon Ahram This sheet includes part of lec.13 + lec.14. Amino acid peptide protein Terminology: 1- Residue: a subunit that is a part of a large molecule. 2- Dipeptide:
... 14 Raghad Abu Jebbeh Amani Nofal Mamoon Ahram This sheet includes part of lec.13 + lec.14. Amino acid peptide protein Terminology: 1- Residue: a subunit that is a part of a large molecule. 2- Dipeptide:
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology:
 The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
Chem Lecture 2 Protein Structure
 Chem 452 - Lecture 2 Protein Structure 110923 Proteins are the workhorses of a living cell and involve themselves in nearly all of the activities that take place in a cell. Their wide range of structures
Chem 452 - Lecture 2 Protein Structure 110923 Proteins are the workhorses of a living cell and involve themselves in nearly all of the activities that take place in a cell. Their wide range of structures
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011
 Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes
 Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions. Proteins
 Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. DATE: Oct. 22, 2002 Midterm EXAMINATION. PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO.: 2.277/60.
 PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS You must mark the answer sheet with pencil (not pen). Put your name and enter your student number on the answer sheet. The examination consists of multiple
PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS You must mark the answer sheet with pencil (not pen). Put your name and enter your student number on the answer sheet. The examination consists of multiple
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay
 Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
PHAR3316 Pharmacy biochemistry Exam #2 Fall 2010 KEY
 1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Bio Factsheet. Proteins and Proteomics. Number 340
 Number 340 Proteins and Proteomics Every living thing on the planet is composed of cells, and cells in turn are made of many types of molecules, including the biological molecules carbohydrates, lipids,
Number 340 Proteins and Proteomics Every living thing on the planet is composed of cells, and cells in turn are made of many types of molecules, including the biological molecules carbohydrates, lipids,
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination #5: Section Five December 7, Name: (print) Section:
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Metabolic Classification of the Amino Acids
 Metabolic Classification of the Amino Acids *Essential and Non-essential * Glucogenic and Ketogenic 1 Essential Amino Acids Of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins 10 of them can be synthesized by
Metabolic Classification of the Amino Acids *Essential and Non-essential * Glucogenic and Ketogenic 1 Essential Amino Acids Of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins 10 of them can be synthesized by
Human Biochemistry Option B
 Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Head. Tail. Carboxyl group. group. group. air water. Hydrocarbon chain. lecture 5-sa Seth Copen Goldstein 2.
 Lipids Some lipid structures Organic compounds Amphipathic Polar head group (hydrophilic) Non-polar tails (hydrophobic) Lots of uses Energy storage Membranes Hormones Vitamins HO O C H 2 C CH 2 H 2 C CH
Lipids Some lipid structures Organic compounds Amphipathic Polar head group (hydrophilic) Non-polar tails (hydrophobic) Lots of uses Energy storage Membranes Hormones Vitamins HO O C H 2 C CH 2 H 2 C CH
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Different levels of protein structure
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Proteins and its function Amino acids: building blocks Different levels of protein structure Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary 2 Proteomics ourse PTEL 1 Derived from Greek
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Proteins and its function Amino acids: building blocks Different levels of protein structure Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary 2 Proteomics ourse PTEL 1 Derived from Greek
Lecture 3: 8/24. CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids
 Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Date: EXERCISE 4. Figure 1. Amino acid structure.
 Student s name: Date: Points: Assistant s signature: Index numer: /6 EXERISE 4 AMIN AIDS AND PRTEINS. Amino acids are structural units (monomers) of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids coded for
Student s name: Date: Points: Assistant s signature: Index numer: /6 EXERISE 4 AMIN AIDS AND PRTEINS. Amino acids are structural units (monomers) of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids coded for
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL
 Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
COO - l. H 3 N C a H l R 1
 COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks)
 Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
2. Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found on the outer surface of a properly folded protein?
 Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
So where were we? But what does the order mean? OK, so what's a protein? 4/1/11
 So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels. Supplementary Information
 Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit
 Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
 Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
 AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
Tala Saleh. Tamer Barakat. Diala Abu-Hassan
 13 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat Diala Abu-Hassan Biochemical application of monosodium glutamate MSG MSG is a glutamic acid derivative, used as a flavor enhancer in Asian food. Chinese restaurant syndrome
13 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat Diala Abu-Hassan Biochemical application of monosodium glutamate MSG MSG is a glutamic acid derivative, used as a flavor enhancer in Asian food. Chinese restaurant syndrome
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Proteins consist of joined amino acids They are joined by a Also called an Amide Bond
 Lecture Two: Peptide Bond & Protein Structure [Chapter 2 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in Red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Proteins consist of joined amino acids
Lecture Two: Peptide Bond & Protein Structure [Chapter 2 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in Red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Proteins consist of joined amino acids
Polypeptides. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Protein Structure Monday, March
 Michael Morales ffice: 204/202 ary; knock hard if you visit as my office is some door. Lab: 238 & 205 ary ffice hours Either make an appointment or just drop by Phone: 829-3965 E-Mail: moralesm@buffalo.edu
Michael Morales ffice: 204/202 ary; knock hard if you visit as my office is some door. Lab: 238 & 205 ary ffice hours Either make an appointment or just drop by Phone: 829-3965 E-Mail: moralesm@buffalo.edu
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
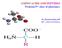 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
I) Choose the best answer: 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine.
 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
PAPER No. : 16, Bioorganic and biophysical chemistry MODULE No. : 22, Mechanism of enzyme catalyst reaction (I) Chymotrypsin
 Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
