Research Article Silence of NLRP3 Suppresses Atherosclerosis and Stabilizes Plaques in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice
|
|
|
- Godfrey Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mediators of Inflammation, Article ID 5728, 8 pages Research Article Silence of NLRP3 Suppresses Atherosclerosis and Stabilizes Plaques in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fei Zheng, 1 Shanshan Xing, 2 Zushun Gong, 1 Wei Mu, 1 and Qichong Xing 1 1 Department of Cardiology, Qianfoshan Hospital, Shandong University, Jingshi Road, Jinan 2514, China 2 Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 25355, China Correspondence should be addressed to Qichong Xing; xingqichong@126.com Received 1 March 214; Accepted 2 May 214; Published 4 June 214 Academic Editor: TâniaSilviaFröde Copyright 214 Fei Zheng et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Objectives. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis remains controversial. The aim of this study was to determine whether inhibition of NLRP3 signaling by lentivirus-mediated RNA interference could reduce atherosclerosis and stabilizes plaques. We also tried to explore the mechanisms of the impact of NLRP3 inflammasome on atherosclerosis. Methods. Apolipoprotein E- deficient mice aged 8 weeks were fed a high-fat diet and were injected with NLRP3 interfering or mock viral suspension after 4 weeks. Lentivirus transfer was repeated in 2 weeks. Four weeks after the first lentivirus injection, we evaluated the effects of NLRP3 gene silencing on plaque composition and stability and on cholesterol efflux and collagen metabolism, by histopathologic analyses and real-time PCR. Results. Gene silence of NLRP3 prevented plaques progression and inhibited inductions of proinflammatory cytokines. Moreover, this RNA interference reduced plaque content of macrophages and lipid, and increased plaque content of smooth muscle cells and collagen, leading to the stabilizing of atherosclerotic plaques. Conclusions. NLRP3 inflammasomes may play a vital role in atherosclerosis, and lentivirus-mediated NLRP3 silencing would be a new strategy to inhibit plaques progression and to reduce local inflammation. 1. Introduction Atherosclerosis is a complicated inflammatory progress characterized by lipid deposition, leukocyte infiltration, and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the vascular walls [1, 2]. Because inflammation in the atherosclerotic process mostly occurs in the absence of microbial infection, it is considered to be sterile inflammation [3]. Growing evidences suggest that some types of sterile inflammation are mediated by the inflammasome, a large multiprotein complex in the cytosol and a component of the innate immune system [4, 5]. The nod-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, the best characterized inflammasome to date, contains the nod-like receptor scaffold protein NLRP3 associated with the adapter protein, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), which recruits caspase-1 and induces its activation. Caspase-1 induces secretion of interleukin-1β (IL- 1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18), which plays a vital role in promoting the development of lipid plaques and destabilizing the plaques [6, 7]. These findings suggest the involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the development of atherosclerosis. Recent studies have shown that cholesterol crystal activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and release of IL-1β, which indicates that the NLRP3 inflammasome may have a role in the development of atherosclerosis [8, 9]. However, another study of double-mutant mice did not find any differences in atherosclerosis progression with or without the NLRP3 inflammasome [1]. The reason for this discrepancy is unclear. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis remains controversial. Small interfering RNAs (sirnas) have proven effective in silencing target genes and lentivirus can efficiently deliver
2 2 Mediators of Inflammation sirna [11]. In the present study, we constructed lentiviral vectors to knock down NLRP3 to evaluate the role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein (Apo) E-deficient mice, which can develop severe hypercholesterolemia and spontaneous atherosclerosis [12]. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Lentivirus Vectors for NLRP3 RNAi. Three different NLRP3-specific target sequences were chosen using the NLRP3 reference sequence (Gene Bank Accession number NC 77). According to the structure of a pgcsil- GFP viral vector (Genechem gene, Shanghai, China), double-stranded DNA were synthesized and inserted into a linearized vector. The positive clones were identified as lentiviral vectors and pgcsil/nlrp3-1 (sequence: 5 - GGUGAAAUGUACUUAAAUC-3 ) induced the highest levels of downregulation. So pgcsil/nlrp3-1 vector and viral packaging system were cotransfected into 293 cells to replicate competent lentivirus. The mock vector (sequence: 5 -GUGCACAUGAGUGAGAUUU-3 )wasalsopackaged andusedasanegativecontrol,whichhasnosignificant homology to mouse gene sequences Animal Protocol. The animal experimental protocol was reviewed and approved by the Animal Care Committee of Shandong University (Jinan, China). A total of 4 male Apo E-deficient mice aged 8 weeks were purchased from the Beijing University Animal Research Center (Beijing, China) and were housed on a 12-hr light/12-hr dark cycle in plenty of food and water. All mice were fed a high-fat diet (.25% cholesterol and 15% cocoa butter). After 4 weeks, mice were divided into control group and NLRP3 interfering () group, which were injected via tail vein with mock viral suspension ( Tfu, 2 ul) and viral suspension ( Tfu, 2 ul). Lentivirus transfer was repeated in 2 weeks. Four weeks after the first lentivirus injection, mice were anesthetized and perfused with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) for 2 min with needle inserted into the left ventricle. The aortic root vessels were removed and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight and then embedded in optimal cutting temperature (OCT) compound. The rest of aortas were collected for protein extraction and PCR Serum Lipid Level Measurement. Total triglycerides and cholesterol were detected with an automated enzymatic technique (Boehringer Mannheim Diagnostics) [13]. Highdensity lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels were determined with an automated chemically modified technique (Roche Modular DPP System, Roche, Switzerland) Caspase-1 Activity Measurement and ELISA. Caspase-1 activity in protein extracted from aortas in the control and groups was measured using the Caspase-1 Colorimetric Assay Kit (BioVision, Mountain View, CA) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Absorbance reading was taken at 41 nm using a microplate reader. IL-1β and IL- 18 were analysed using IL-1β- and IL-18-specific ELISA kits from R&D Systems Histological Analysis. OCT compound-embedded aortic root vessels were cross-sectioned into pieces 6 μm thickat 5 μm intervals. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histological analysis. The plaque was subdivided into a fibrous cap and a necrotic core on the basis of picrosirius red staining for collagen and oil red O staining for lipids, respectively. Corresponding sections on separate slides were immunostained with monoclonal antibodies. Macrophages and smooth muscle cells (SMCs) were immunostained with monocyte/macrophagespecific antibody (MOMA)-2 (diluted 1 : 25; Abcam, Cambridge, MA) and anti-α-actin antibodies (diluted 1 : 1; Sigma-Aldrich), respectively. The sections were incubated with the appropriate HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (diluted 1 : 1; Zhongshan), followed by incubation with 3,3 - diaminobenzidine and counterstaining with hematoxylin. Sections reacted with nonimmune IgG, secondary antibody only, and no primary and secondary antibodies were used as negative controls. An automated image analysis system (Image-Pro Plus 6.; Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD) was used for quantitative measurements. The positive-staining area of macrophages, SMCs, lipids, and collagen was quantified by computer-assisted color-gated measurement, and the ratio of positive-staining area to intimal area was calculated. The vulnerability index was calculated by the following formula: positive-staining area of (macrophages + lipid)/positivestaining area of (α-smcs + collagen) [14] Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis. After the aortas were collected, total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions. The mrna levels were quantified by the use of SYBR green technology. The house-keeping gene β-actin was quantified as an internal RNA control. The primer sequences for all studied genes are listed in Table 1.The2 ΔΔCT method for comparing relative expression results was applied [15] Data Analysis. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18. (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Quantitative variables are presented as mean ± SD. A 2-tailed Student s t-test was used in the comparison of continuous data. P <.5 was considered statistically significant. 3. Results 3.1. Safety and Efficiency of Lentiviral Transfection. All mice wereapparentlyhealthy,andnomicewerelostbeforethe day of sacrifice. A systemic lentivirus delivery has proven an efficient approach to transferring gene into arterial walls [16]. In order to evaluate the efficacy of lentivirus-mediated gene silencing in vivo, the levels of NLRP3 mrnas expression, the activity of caspase-1, and the protein level of IL-1β and IL-18 (downstream targets of NLRP3 inflammasome) were
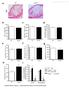
3 Mediators of Inflammation 3 Table 1: Primer sequences for real-time PCR. Gene Forward sequence Reverse sequence NLRP3 5 -ATGCCAGGAAGACAGCATTG-3 5 -TCATCGAAGCCGTCCATGAG-3 ABCA1 5 -GCGGACCTCCTGTGGTGTT-3 5 -CAAGAATCTCCGGGCTTTAGG-3 ABCG1 5 -AAGGCCTACTACCTGGCAAAGA-3 5 -GCAGTAGGCCACAGGGAACA-3 P4Hα1 5 -CCCTAAGGCAACTGGATGAA-3 5 -CCCATTTGTTGCCAACTAG-3 MMP-2 5 -ACCCAGATGTGGCCAACTAC-3 5 -TCATTTTAAGGCCCGAGCAA-3 MMP-9 5 -CCTGGAACTCACACGACATCTTC-3 5 -TGGAAACTCACACGCCAGAA-3 β-actin 5 -TCATCACTATTGGCAACGAGC-3 5 -AACAGTCCGCCTAGAAGCAC-3 Table 2: Body weight and serum lipid levels in control group and group. End point (n =2) (n =2) P value Body weight, g 28.8 ± ± 3.8 NS Total cholesterol, mmol/l 2.7 ± ±.64 NS Triglycerides, mg/dl 35.2 ± ± 2.4 NS LDL, mg/dl 6.15 ± ±.73 NS HDL, mg/dl 1.35 ± ± 1.79 NS NS indicates not significant. measured. Compared with the control group, the mrna levels of NLRP3 were significantly downregulated, the caspase-1 activity was strongly decreased, and the content of IL-1β and IL-18 was also decreased after silencing NLRP3 (Figure 1, P<.5) Effects of on Plaque Composition and Stability. Mice transfected with control lentivirus or NLRP3 lentivirus differed in histological and immunohistochemical staining of aortic root vessels (Figure 2). In the atherosclerotic lesion area,smcscontentwashigherby39%andcollagencontent was 46% higher with NLRP3 lentivirus than control transfection. The number of macrophages in the atherosclerotic lesion area, as determined by MOMA-2, was significantly lower by nearly 22% and lipid content was 33% lower with NLRP3 lentivirus than control transfection. Through calculation, the vulnerability index was significantly lower with NLRP3 lentivirus than control transfection Effects of NLRP3 Silencing on Body Weight and Lipids. NLRP3 silencing resulted in no significant differences in comparison with controls in body weight. Likewise, serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, and HDL in the group did not differ significantly from those in the control group (Table 2), suggestingthattheeffectofgenetransferon atherosclerosis was independent of serum lipid levels Effects of on Lipid Efflux. In order to evaluate the effect of NLRP3 interfering on macrophage lipid efflux, we measured the mrna expression of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1, also known as the cholesteroleffluxregulatoryprotein.incomparisonwithcontrol, mrna of ABCA1 and ABCG1 increased significantly in aortas of ApoE-deficient mice treated with NLRP3 silencing (P <.5)(Figure 3) Effects of NLRP3 Silencing on Collagen Synthesis and Degradation. Collagens are main components of fibrous cap in plaques, and prolyl-4-hydroxylases α1 (P4Hα1) are rate limiting for collagen synthesis. On the contrary, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase- 9 (MMP-9) contribute to the breakdown of the collagen. OurdatashowedthatthemRNAexpressionofP4Hα1 was markedly higher in the NRLP3i group than in the control group (P <.5), and the mrna expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 was significantly lower in the treatment group than the control group (P <.5)(Figure 4). These two effects led to the increasing of the collagen and thickness of the fibrous cap. 4. Discussion In the present study, we applied lentivirus-mediated RNA interfering methods to efficiently knock down NLRP3 gene and investigated its role in the pathogenesis of plaque vulnerability in ApoE-deficient mice. Our results demonstrated that mrna expression of NLRP3 was remarkably attenuated by transfected lentiviral sirnas. Plaques of the group showed a higher content of collagen and SMCs, lower content of lipid and macrophages, and lower vulnerability index than didinthecontrolgroup. RNA interference is a powerful technique for selectively silencingmrnaforawiderangeofproteins[17], and using sirna is also more efficient than other gene-specific targeting approaches [18]. Furthermore, gene silencing strategies using sirna have been applied to treat or prevent several diseases [19, 2]. The major limitation for synthetic sirnas and plasmid-based sirnas as a delivering approach is their transient expression and poor transfection efficiency in vivo. In contrast, the lentiviral vector-mediated gene delivery systemappliedinthisstudyhasproveneffectiveandlong lasting in silencing gene function in primary mammalian cells, stem cells, and transgenic mice [21]. In the present study,theefficacyofthismethodwasconfirmednotonly by our observation that NLRP3 mrna expression levels of the treatment group were remarkably downregulated, but also by observation that the caspase-1 activity was strongly reducedandthecontentofdownstreamtargetsofnlrp3
4 4 Mediators of Inflammation 3.5 NLRP3 12 Caspase-1 activity 3. 1 Fold induction Relative activity (%) (a) (b) 5 IL-1β 35 IL-18 IL-1β (pg/mg protein) IL-18 (pg/mg protein) (c) (d) Figure 1: Efficiency of lentivirus transfection. (a) NLRP3 interference downregulated NLRP3 mrna expression by 64.3% compared with the control via real-time PCR analyses. (b) Caspase-1 activity in protein extracted from aortas was reduced by 56% after NLRP3 silencing, compared with the control. (c and d) Silence of NLRP3 decreased the downstream proinflammatory factors, IL-1β and IL-18, using ELISA. P <.5 versus control. Values are mean ± SD. inflammasomes, IL-1β and IL-18, was decreased after silencing NLRP3. In addition, the fact that no adverse effects were observed in our mice during the experiment demonstrated that lentivirus transfection was safe in these animals. Thus, we regard that lentiviral vectors expressing sirna provide an efficient, specific, and safe tool to knock down NLPR3 genes. A strong link between inflammation and atherosclerosis is becoming increasingly evident [22].A number of recent landmarkstudieshaveimplicatedtheactivationofthenlrp3 inflammasome, in the progress of atherosclerosis. Cholesterol crystals generated in vitro activate caspase-1 and the cleavage of both IL-1β and IL-18 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and mouse macrophages, and both depend on NLRP3 and ASC [8, 9]. In line with the in vitro data, hypercholesterolemic mice deficient in the receptor for lowdensity lipoprotein (LDL) which are reconstituted with bone marrow from Nlrp3 /, Pycard /,oril1b / mice develop many fewer atherosclerotic plaques than those reconstituted with wild-type bone marrow [8]. However, the critical role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis has been challenged by another study of double-mutant mice generated by crossing Apoe / mice with Nlrp3 /, Pycard /,or Caspase1 / mice [1]. That study did not find any differences in atherosclerosis progression with or without the NLRP3 inflammasome. To clarify these differences, we designed this study, applying RNA interference. Our results demonstrated that silence of NLRP3 suppressed atherosclerosis and stabilized atherosclerotic plaques, as the group of mice consistently exhibited a lower content of macrophages and lipids, a higher content of collagen, and a thicker fibrous cap in atherosclerotic plaques than the control group of mice. All these morphological changes led to a decreased plaque vulnerability index in the group compared to the control group. By incorporating the cumulative effects of protective and destructive factors, plaque vulnerability index has been recognized as a histological marker for vulnerable
5 Mediators of Inflammation 5 HE Macrophage Lipid SMC Collagen (a) Mean cap thickness (μm) Macrophage (%) Lipid (%) (b) (c) (d) SMC (%) Collagen (%) Vulnerability index (e) (f) (g) Figure 2: Cross sections of aortic root vessels from the control and gene interference groups were stained with H&E; vascular smooth muscle cells and collagen were immunostained with α-actin and Sirius red,respectively;and macrophages and lipids were stained with MOMA-2 and oil red O, respectively (a). The mean cap thickness was increased after the NLRP3 silencing, compared with the control (b). Number of macrophages in the atherosclerotic lesion area was significantly lower by nearly 22% and lipid content was 33% lower with NLRP3 lentivirus than control transfection (c and d). SMCs content was higher by 39% and collagen content was 46% higher with NLRP3 lentivirus than control transfection (e and f). The vulnerability index was significantly lower in group than control (g). P <.5 versus control. Values are mean ± SD. Scale bar is 1 μm. plaques. These findings suggested that NLRP3 was critical in the progression of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis progresses through lipid accumulation within macrophages, resulting in the formation of foam cell and necrotic core. Although cholesterol lowering is a way to decrease lipid retention, increasing lipid efflux from macrophages, mostly through ABCA1 and ABCG1, has been regarded as another significant strategy to limit atherosclerosis. Overexpression of ABCA1 and ABCG1 limits atherosclerotic plaque formation, while genetic deletion of these genes promotes foam cell formation and accelerates atherosclerosis in animal models [23 26]. Our data showed that mrna
6 6 Mediators of Inflammation ABCA ABCG1.. (a) (b) Figure 3: ABCA1 and ABCG1 mrna expression levels were determined by real-time PCR analyses. Compared with control, mrna of ABCA1 and ABCG1 increased significantly in aortas of ApoE-deficient mice treated with NLRP3 silencing. P <.5 versus control. Values are mean ± SD P4Hα MMP-2.. (a) (b) 1.2 MMP (c) Figure 4: P4Hα1, MMP-2, and MMP-9 mrna levels in aortas of ApoE-deficient mice were determined with real-time PCR. The mrna expression of P4Hα1 wasmarkedlyhigherinthenrlp3igroupthaninthecontrolgroup,andthemrnaexpressionlevelsofmmp-2and MMP-9 were significantly lower in the treatment group than the control group. P <.5 versus control. Values are mean ± SD.
7 Mediators of Inflammation 7 levels of ABCA1 and ABCG1 were increased after the treatment of, suggesting that NLRP3 gene silencing could be a potentially therapeutic mean to increase macrophage cholesterol efflux for the prevention of atherosclerosis. Collagens are the main components of fibrous cap in atherosclerotic plaques and play a vital role in stabilizing plaques and preventing plaque rupture. Prolyl-4-hydroxylase (P4H) is one of the key enzymes essential for the collagen synthesis. P4Hα1, an isoenzyme of P4H, is a rate-limiting enzyme that folds the procollagen polypeptide chains into the stable triple helical molecules, which is necessary for collagen maturation and secretion [27]. In the present study, we showed that the mrna expression of P4Hα1 was significantly higher, and the mrna expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 that contributed to collagen degradation was markedly lower in the NRLP3 interfering group than in the control group, resulting in the thickness of fibrous cap and the stabilizing of atherosclerotic plaques. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that lentivirus-mediated RNA interference was effective in knocking down NLRP3 genes in ApoE deficient mice, resulting in reduced inflammatory cytokines and plaque content of lipid and macrophages, increased plaque content of collagen, and lowered plaque vulnerability index. NLRP3 inflammasomes play important roles in the pathogenesis of plaque vulnerability. Our findings raised the possibility that lentivirusmediated gene silencing of NLRP3 is a potential therapeutic target for inhibiting progression of atherosclerotic plaques and subsequently preventing cardiovascular events. Conflict of Interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. Acknowledgment This study was supported by the Foundation for Outstanding Young Scientist in Shandong Province (No. 29BSB1312). References [1] P. Libby, P. M. Ridker, and A. Maseri, Inflammation and atherosclerosis, Circulation,vol.15,no. 9, pp ,22. [2] G.K.Hansson, Mechanismsofdisease:inflammation,atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease, The New England Journal of Medicine,vol.352,no.16,pp ,25. [3] G. Y. Chen and G. Nuñez, Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage, Nature Reviews Immunology, vol. 1, no. 12, pp , 21. [4] B.K.Davis,H.Wen,andJ.P.-Y.Ting, TheinflammasomeNLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases, Annual Review of Immunology, vol. 29, pp , 211. [5]T.Strowig,J.Henao-Mejia,E.Elinav,andR.Flavell, Inflammasomes in health and disease, Nature, vol. 481, no. 7381, pp , 212. [6] A.TedguiandZ.Mallat, Cytokinesinatherosclerosis:pathogenic and regulatory pathways, Physiological Reviews, vol. 86, no. 2, pp , 26. [7]H.Kirii,T.Niwa,Y.Yamadaetal., Lackofinterleukin-1ß decreases the severity of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology,vol.23,no.4, pp ,23. [8] P. Duewell, H. Kono, K. J. Rayner et al., NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals, Nature, vol. 464, no. 7293, pp , 21. [9] K. Rajamäki, J. Lappalainen, K. Öörni et al., Cholesterol crystals activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages: a novel link between cholesterol metabolism and inflammation, PLoS ONE,vol.5,no.7,ArticleIDe11765,21. [1]P.Menu,M.Pellegrin,J.-F.Aubertetal., Atherosclerosisin ApoE-deficient mice progresses independently of the NLRP3 inflammasome, Cell Death and Disease,vol.2,no.3,articlee137, 211. [11] K. V. Morris and J. J. Rossi, Lentiviral-mediated delivery of sirnas for antiviral therapy, Gene Therapy, vol.13,no.6,pp , 26. [12] S. Zadelaar, R. Kleemann, L. Verschuren et al., Mouse models for atherosclerosis and pharmaceutical modifiers, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology,vol.27,no.8,pp , 27. [13] J. R. McNamara and E. J. Schaefer, Automated enzymatic standardized lipid analyses for plasma and lipoprotein fractions, Clinica Chimica Acta,vol.166,no.1,pp.1 8,1987. [14] M.Shiomi,T.Ito,Y.Hirouchi,andM.Enomoto, Fibromuscular cap composition is important for the stability of established atherosclerotic plaques in mature WHHL rabbits treated with statins, Atherosclerosis, vol. 157, no. 1, pp , 21. [15] K. J. Livak and T. D. Schmittgen, Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2- ΔΔCT method, Methods, vol. 25, no. 4, pp , 21. [16] Z.-H. Wang, Y.-Y. Shang, S. Zhang et al., Silence of TRIB3 suppresses atherosclerosis and stabilizes plaques in diabetic ApoE / /LDL receptor / mice, Diabetes, vol.61,no.2,pp , 212. [17] S. M. Elbashir, J. Harborth, W. Lendeckel, A. Yalcin, K. Weber, and T. Tuschl, Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells, Nature,vol.411,no. 6836, pp , 21. [18] A. W. Tong, Y.-A. Zhang, and J. Nemunaitis, Small interfering RNA for experimental cancer therapy, Current Opinion in Molecular Therapeutics,vol.7,no.2,pp ,25. [19] A. de Fougerolles, H.-P. Vornlocher, J. Maraganore, and J. Lieberman, Interfering with disease: a progress report on sirna-based therapeutics, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, vol. 6, no. 6, pp , 27. [2] L. Zender, S. Hütker, C. Liedtke et al., Caspase 8 small interfering RNA prevents acute liver failure in mice, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 1, no. 13, pp , 23. [21] H. Matta, B. Hozayev, R. Tomar, P. Chugh, and P. M. Chaudhary, Use of lentiviral vectors for delivery of small interfering RNA, Cancer Biology and Therapy,vol.2,no.2,pp.26 21,23. [22] G. K. Hansson and A. Hermansson, The immune system in atherosclerosis, Nature Immunology, vol. 12, no. 3, pp , 211. [23] M. Van Eck, R. R. Singaraja, D. Ye et al., Macrophage ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 overexpression inhibits atherosclerotic lesion progression in low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology,vol.26,no.4,pp ,26.
8 8 Mediators of Inflammation [24]X.Wang,H.L.Collins,M.Ranallettaetal., Macrophage ABCA1 and ABCG1, but not SR-BI, promote macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in vivo, Clinical Investigation, vol. 117, no. 8, pp , 27. [25] R. Out, M. Hoekstra, K. Habets et al., Combined deletion of macrophage ABCA1 and ABCG1 leads to massive lipid accumulation in tissue macrophages and distinct atherosclerosis at relatively low plasma cholesterol levels, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, vol.28,no.2,pp , 28. [26] L. Yvan-Charvet, M. Ranalletta, N. Wang et al., Combined deficiency of ABCA1 and ABCG1 promotes foam cell accumulation and accelerates atherosclerosis in mice, Clinical Investigation,vol.117,no.12,pp ,27. [27] K. L. Gorres and R. T. Raines, Prolyl 4-hydroxylase, Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, vol.45,no.2, pp , 21.
9 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3150
 Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
 ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy. Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L.
 Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
About OMICS International Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of making the information
About OMICS Group OMICS Group is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of making the information
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report of Neoadjuvant Use Enabling Complete Surgical Resection
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 197328, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.11/13/197328 Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan G. Andocs, 1 Y. Okamoto,
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 197328, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.11/13/197328 Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan G. Andocs, 1 Y. Okamoto,
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Research Article The Effect of Elevated Triglycerides on the Onset and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease: A Retrospective Chart Review
 Cholesterol Volume 2015, Article ID 292935, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/292935 Research Article The Effect of Elevated Triglycerides on the Onset and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease:
Cholesterol Volume 2015, Article ID 292935, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/292935 Research Article The Effect of Elevated Triglycerides on the Onset and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease:
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism
 Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories
 The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 187835, 3 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187835 Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia Meggyesházi Nóra, 1 Andócs
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 187835, 3 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187835 Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia Meggyesházi Nóra, 1 Andócs
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT MATERIAL. CD70 limits atherosclerosis and promotes macrophage function.
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT MATERIAL CD7 limits atherosclerosis and promotes macrophage function. Holger Winkels* 1,2, Svenja Meiler* 1,2, Esther Smeets* 2, Dirk Lievens 1, David Engel 3, Charlotte Spitz 1, Christina
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT MATERIAL CD7 limits atherosclerosis and promotes macrophage function. Holger Winkels* 1,2, Svenja Meiler* 1,2, Esther Smeets* 2, Dirk Lievens 1, David Engel 3, Charlotte Spitz 1, Christina
Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies
 Scientifica Volume 2016, Article ID 2698362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2698362 Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies Vani Chandrashekar
Scientifica Volume 2016, Article ID 2698362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2698362 Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies Vani Chandrashekar
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers
 Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis with Comorbid Conditions
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27
 Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 2005 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-30, 2005
 Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Supplemental Material. Results
 Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features
 Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
Familial hypercholesterolaemia in children and adolescents
 Familial hypercholesterolaemia in children and adolescents Rationale and recommendations for early identification and treatment European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel Slide deck adapted from:
Familial hypercholesterolaemia in children and adolescents Rationale and recommendations for early identification and treatment European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel Slide deck adapted from:
Research Article Clinical and Epidemiological Investigation of TCM Syndromes of Patients with Coronary Heart Disease in China
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 714517, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/714517 Research Article Clinical and Epidemiological Investigation of TCM Syndromes of Patients
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 714517, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/714517 Research Article Clinical and Epidemiological Investigation of TCM Syndromes of Patients
Spherical Nucleic Acids For Advanced Wound Healing Applications Chad A. Mirkin
 Spherical Nucleic Acids For Advanced Wound Healing Applications Chad A. Mirkin Departments of Chemistry, Infectious Disease, Materials Science & Engineering, Chemical & Biological Engineering, and Biomedical
Spherical Nucleic Acids For Advanced Wound Healing Applications Chad A. Mirkin Departments of Chemistry, Infectious Disease, Materials Science & Engineering, Chemical & Biological Engineering, and Biomedical
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
INFLAMMATION AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Rob Greenfield MD FACC FAHA FNLA California Heart Associates University of California, Irvine
 INFLAMMATION AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS Rob Greenfield MD FACC FAHA FNLA California Heart Associates University of California, Irvine What determines who will develop atherosclerosis? LDL-CHOLESTEROL?? OTHER
INFLAMMATION AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS Rob Greenfield MD FACC FAHA FNLA California Heart Associates University of California, Irvine What determines who will develop atherosclerosis? LDL-CHOLESTEROL?? OTHER
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
sirna-mediated silencing of Wnt5a regulates inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis through the MAPK/NF-κB pathways
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 34: 1147-1152, 2014 sirna-mediated silencing of Wnt5a regulates inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis through the MAPK/NF-κB pathways LEI YANG 1, YINGJIE
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 34: 1147-1152, 2014 sirna-mediated silencing of Wnt5a regulates inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis through the MAPK/NF-κB pathways LEI YANG 1, YINGJIE
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Protective effect of the polarity of macrophages regulated by IL-37 on atherosclerosis
 Protective effect of the polarity of macrophages regulated by IL-37 on atherosclerosis J. Huang 1, F.L. Hou 2, A.Y. Zhang 1 and Z.L. Li 2 1 Department of Cardiology, Weifang People s Hospital, Weifang,
Protective effect of the polarity of macrophages regulated by IL-37 on atherosclerosis J. Huang 1, F.L. Hou 2, A.Y. Zhang 1 and Z.L. Li 2 1 Department of Cardiology, Weifang People s Hospital, Weifang,
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Ebrahim Abbasi Oshaghi 1,2
 1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Abhd2 regulates alveolar type Ⅱ apoptosis and airway smooth muscle remodeling: a key target of COPD research
 Abhd2 regulates alveolar type Ⅱ apoptosis and airway smooth muscle remodeling: a key target of COPD research Shoude Jin Harbin Medical University, China Background COPD ------ a silent killer Insidious,
Abhd2 regulates alveolar type Ⅱ apoptosis and airway smooth muscle remodeling: a key target of COPD research Shoude Jin Harbin Medical University, China Background COPD ------ a silent killer Insidious,
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
determination of Triglyceride in Serum Amal Alamri
 determination of Triglyceride in Serum Amal Alamri Triglyceride are fatty acid esters of glycerol,and are the main lipids in the diet. They broken down(by lipase) in the small intestine to a mixture of
determination of Triglyceride in Serum Amal Alamri Triglyceride are fatty acid esters of glycerol,and are the main lipids in the diet. They broken down(by lipase) in the small intestine to a mixture of
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit
 Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit Catalog Number KA4541 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit Catalog Number KA4541 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Wnt7a Inhibits Cartilage Matrix Degradation in a Mouse In Vivo Osteoarthritis Model
 Wnt7a Inhibits Cartilage Matrix Degradation in a Mouse In Vivo Osteoarthritis Model Averi Leahy, Andrea Foote, Tomoya Uchimura, Li Zeng, PhD. Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA. Disclosures: A. Leahy: None.
Wnt7a Inhibits Cartilage Matrix Degradation in a Mouse In Vivo Osteoarthritis Model Averi Leahy, Andrea Foote, Tomoya Uchimura, Li Zeng, PhD. Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA. Disclosures: A. Leahy: None.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /07/$32.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.081
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.081
Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
Thematic review series: The Immune System and Atherogenesis
 thematic review Thematic review series: The Immune System and Atherogenesis Lipoprotein-associated inflammatory proteins: markers or mediators of cardiovascular disease? Alan Chait, 1 Chang Yeop Han, John
thematic review Thematic review series: The Immune System and Atherogenesis Lipoprotein-associated inflammatory proteins: markers or mediators of cardiovascular disease? Alan Chait, 1 Chang Yeop Han, John
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome. and Type-2 Diabetes
 A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
Relationship between serum glutathione peroxidase-1activity with endothelial dysfunction level in patients with coronary artery diseases
 Relationship between serum glutathione peroxidase-1activity with endothelial dysfunction level in patients with coronary artery diseases Introduction Reactive oxygen species (ROS),such as superoxide and
Relationship between serum glutathione peroxidase-1activity with endothelial dysfunction level in patients with coronary artery diseases Introduction Reactive oxygen species (ROS),such as superoxide and
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
Child born in year /3 will die before parents in US (diabetes)
 Child born in year 2000-1/3 will die before parents in US (diabetes) ATP III identified 6 components of the metabolic syndrome that relate to CVD 1. Abdominal obesity 2. Atherogenic dyslipidemia (elevated
Child born in year 2000-1/3 will die before parents in US (diabetes) ATP III identified 6 components of the metabolic syndrome that relate to CVD 1. Abdominal obesity 2. Atherogenic dyslipidemia (elevated
Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ
 Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
Tracking a Killer Molecule
 Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
APOB (Human) ELISA Kit
 APOB (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA4330 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
APOB (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA4330 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
Study of the NLRP3 inflammasome component genes and downstream cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with carotid atherosclerosis
 Lee et al. Lipids in Health and Disease (2017) 16:217 DOI 10.1186/s12944-017-0595-2 RESEARCH Open Access Study of the NLRP3 inflammasome component genes and downstream cytokines in patients with type 2
Lee et al. Lipids in Health and Disease (2017) 16:217 DOI 10.1186/s12944-017-0595-2 RESEARCH Open Access Study of the NLRP3 inflammasome component genes and downstream cytokines in patients with type 2
Basic Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis and Plaque Rupture: Clinical Implications
 12 th Annual Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Symposium February 8, 2013 KEYNOTE ADDRESS Basic Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis and Plaque Rupture: Clinical Implications Ira Tabas, M.D., Ph.D. Richard J.
12 th Annual Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Symposium February 8, 2013 KEYNOTE ADDRESS Basic Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis and Plaque Rupture: Clinical Implications Ira Tabas, M.D., Ph.D. Richard J.
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
III. Results and Discussion
 III. Results and Discussion 1. Histological findings in the coronary artery Twenty-four swine had surgical treatments performed in two of the coronary arteries, LAD as well as either the LCX or RCA. A
III. Results and Discussion 1. Histological findings in the coronary artery Twenty-four swine had surgical treatments performed in two of the coronary arteries, LAD as well as either the LCX or RCA. A
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Research Article The Hyperlipidemia Caused by Overuse of Glucocorticoid after Liver Transplantation and the Immune Adjustment Strategy
 Hindawi Immunology Research Volume 2017, Article ID 3149426, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3149426 Research Article The Hyperlipidemia Caused by Overuse of Glucocorticoid after Liver Transplantation
Hindawi Immunology Research Volume 2017, Article ID 3149426, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3149426 Research Article The Hyperlipidemia Caused by Overuse of Glucocorticoid after Liver Transplantation
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/389/ra79/dc1 Supplementary Materials for HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P 1 to limit vascular
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/389/ra79/dc1 Supplementary Materials for HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P 1 to limit vascular
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Research Article Challenges in Assessing Outcomes among Infants of Pregnant HIV-Positive Women Receiving ART in Uganda
 Hindawi AIDS Research and Treatment Volume 2017, Article ID 3202737, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3202737 Research Article Challenges in Assessing Outcomes among Infants of Pregnant HIV-Positive
Hindawi AIDS Research and Treatment Volume 2017, Article ID 3202737, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3202737 Research Article Challenges in Assessing Outcomes among Infants of Pregnant HIV-Positive
