Warm Up (Discussion )
|
|
|
- Bonnie Todd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 3: Cells!
2 Warm Up (Discussion ) What is a cell? Where do we find cells? What are cells made up of? What happens in a cell? How are plant and animal cells different?
3 Cell Theory 1. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 2. Cells come from preexisting cells 3. All living things are composed of cells
4 People to Know... Robert Hooke- first to observe a cell- gave cells their name Anton van Leewenhoek- first to observe a living cell Others: Virchow- cells come from preexisting cells Schleiden- all plants are composed of plant cells Schwann- all animals are composed of animal cells
5 2.1 Cell Structure and Function Macromolecules such as PCLN are organized to form the structures that create cells. Cells are the smallest unit of living organisms. Important scientists who discovered cells: 1) Robert Hooke First to observe cells looked at cork (dead cells) and gave individual units the name cells
6 Important Scientists Anton von Leeuwenhoek First to observe living cells looked at scrapings from his cheek and saw live cells
7 4 Structures (organelles) found in all cells: Cell membrane a phospholipid bilayer that separates the inside of the cell from the outside Cytoplasm the inside filling of the cell; mostly water DNA the genetic material to control the cell; organized into chromosomes that are circular in prokaryotes and linear in eukaryotes. Ribosomes an organelle where the DNA code is used to build (synthesize) proteins
8 Types of cells: Prokaryotic: pro means before and kary means nucleus. They do NOT have a central place to store DNA. The DNA is free-floating in the cytoplasm. These cells have all four main organelles to build a cell but are able to perform all STERNGRR life functions. Eukaryotic: eu means true and kary means nucleus. These cells have a membrane that surrounds all the DNA in the cell. The cells have all four main organelles as well as up to 7 additional organelles to perform specific functions.
9 Venn Diagram: Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Place each of the following in a section of the Venn Diagram No nucleus Nucleus Organelles No organelles Simple & small Complex & size varies Unicellular Unicellular or Multicellular Bacteria Cell membrane DNA Ribosomes Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton First cells Cell walls Cytoskeleton Everything but bacteria
10 Warm Up Discussion 1. What is an organelle? 2. What are some similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 3. What kind of cells would I find in plants? 4. Who was Robert Hooke? 5. ARE YOU EXCITED THAT IT S FRIDAY?! a. I am.
11 Cell Organelles- cellular parts that have unique structures and unique functions. There are four that all cells share (see prior page) and up to 9 that are found in plant and animal cells. Prokaryotic cell organelles- in addition to the four common organelles, prokaryotes also have: Plasmids - smaller circular pieces of DNA that can be traded between bacteria Cell wall - structures outside the cell membrane to help protect the cell
12 Eukaryotic cell organelles- in addition to the four common organelles, eukaryotic cells also have the following six organelles: Nucleus the region of eukaryotic cells where DNA is contained by a membrane Lysosome- membrane containing digestive enzymes to digest waste and cell structures ER (endoplasmic reticulum) - membrane to change proteins, detoxify alcohol and communication Golgi Body/Complex - membrane to package proteins for release from a cell Vacuole- a membrane that creates a storage space for food, water or waste Mitochondria a series of folded membranes where carbs are broken down for energy
13 Organelles interact with each other to carry out cell functions: Example: DNA in the nucleus codes for the ribosomes to build proteins. These proteins can then be used as hormones to be released by the cell.
14 Organelles found only in PLANT cells Cellulose cell wall - large carbohydrates create extra support for plants Chloroplast (plants) the organelle that has stacks of membranes to create food during photosynthesis
15 Organelles found ONLY in animal cells Summary: Centrioles proteins that help animal cells divide
16 Cell specialization creates different cells within an organism. A multicellular organism begins its life as an embryo with many cells that have the same DNA and no job other than to grow. As the cells develop, they differentiate or become specialized.
17 Cells are SPECIALIZED, this means their structure fits their function. Cells throughout the organism perform different jobs. The cells of multicellular organisms have the SAME DNA, but some of their genes are turned on, and some turned off. This allows cells to be specialized.
18
19 Warm Up 1. What are lysosomes? a. b. c. 2. Golgi Bodies could best be described as: a. b. c Carbohydrates that float in the cell Enzymes that break down waste and food Part of the cell membrane The powerhouse Genetic material The mailroom Where are phospholipids found? Name the 4 structures found in all cells What do chloroplasts do?
20 Word Bank glycerol fatty acids non-polar energy with/down diffusion bilayer plasma around cholesterol proteins integral parts proteins transmembrane perpheral Head tail 4 Functions: 1. cell signaling 2. selective transport 3. excretion of waste 4. structural support
21 Adult organisms still have small reserves of stem cells in some areas of the body. Red blood cells are specialized with the protein hemoglobin to transport oxygen. Muscle cells have LOTS of mitochondria because they need a TON of energy. Sperm cells have a flagella to swim toward the egg Some plants have XYLEM cells, they are long thin tubes to carry water. Nerve cells are long and thin and have extensions to send messages
22 Differentiated cells require cells to collaborate and communicate. Short distance: Cells that touch or have a very small distance can use chemical or electrical signals. Animal nerve cells use both electricity and chemical signals to control body responses.
23 Long distance: communication across long distances require long-lasting chemicals like hormones like insulin. This hormone is released by the pancreas and has effects throughout the mammalian body.
24 Plasma Membrane
25
26 Exit Ticket What types of objects would you look at under a light microscope? What microscope would you use to view a cell? Draw a phospholipid bilayer What does hydrophilic mean? What part of the phospholipid if hydrophilic? What is selective permeability?
27 It s Tuesday... You don t have to be here tomorrow (I do )
28 Warm Up 1. What organelle is considered the powerhouse of the cell? What is its function? 2. If water is moving into and out of the cell, it is: a. Hypotonic b. Hypertonic c. Isotonic 3. True or False: Cells specialize because they have different DNA. 4. What is a plasmid? 5. The fatty acid tails of a phospholipid are a. Hydrophobic b. Hydrophilic
29 Organelle Matching! Groups of 3-4 (see next slide) Match the picture of the organelle to the name and description Raise your hands when you are finished Winner gets Dum Dums #incentive When you are finished and have been checked off, go and help another group!
30 Microscopes Light Small, light Less expensive Use light to view object Less magnification View small objects Can be blurry Electron Large, heavy Expensive Use beam of electrons to view objects Greater magnification View very small objects Clearer picture
31 Microscope Lab Follow instructions on lab. Complete Part A (Intro to Microscope) and Part B (Onion Cell Lab). Materials can be found in the front of classroom If you need anything else, raise your hand silently and Ms. S will come to you! Finish questions for homework! If you finish early, work on the phospholipid cutout (front of class)
32 Exit Ticket Name one difference between an electron and light microscope Where is DNA found in a eukaryotic cell? True or false: Animals have cell walls Which material makes the cell membrane more fluid? a. b. c. d. 5. Cholesterol Glycoproteins Glycolipids Proteins True or false: Peripheral proteins are within the cell membrane
33 Warm Up What is one difference between a light and an electron microscope? What is cell differentiation? Cellulose is found in what plant structure? Ribosomes a. b. c. d. 5. Build lipids Hold nutrients and waste Build proteins Give support The DNA in a prokaryote is found as a (plasmid/nucleus), the DNA in a eukaryote is found as a (plasmid/nucleus)
34 Cell Transport com/legacy/college/boyer/ /animati ons/animations.htm
35 Cell Transport Define the following Osmosis Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Passive diffusion Active Transport
36 Retest We will ALL retest on Friday IT CAN ONLY HELP YOU! You must turn in your test corrections AND the Biochemistry Worksheet to Ms. S in order to retest!
37 Test Corrections On a sheet of looseleaf paper: Name Test: Biochemistry 1. Write the # of the question you got wrong 2. Write your answer 3. Write the correct answer 4. Mark the following a. b. c. d. C=confusing DS= didn t study it F= forgot O=other (describe! Did I not cover it in class?)
38 Warm Up If there is more salt outside of a cell, where will water move? What materials might plant cells transport? Provide two. True or false: The vacuole digests nutrients. Cytoplasm is made of mostly: a. b. c. d. 5. Plasma Phospholipids Water Salt What is the function of the cell wall?
39 Warm Up 1. Which structure is found in a prokaryotic cell? a. Vacuole b. Chloroplast c. Ribosome d. Mitochondria 2. Plasmids are found in cells a. Prokaryotic b. Eukaryotic c. Plant d. Animal 3. Bacteria are (prokaryotic/eukaryotic) 4. True or false: Cell membrane maintains homeostasis 5. What is the plant organelle responsible for capturing sunlight to make food?
40 About Cell Membranes Cell membranes have pores (holes) in it a. Selectively permeable: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b. The structure helps it be selective! Pores
41 Structure of the Cell Membrane Outside of cell Proteins Lipid Bilayer Transport Protein Animations of membrane Go to structure Section: Carbohydrate chains Phospholipids Inside of cell (cytoplasm)
42 Types of Cellular Transport Animations of Active Transport & Passive Transport Weeee!!! Passive Transport cell doesn t use energy Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis high low Active Transport cell does use energy Protein Pumps Endocytosis Exocytosis This is gonna be hard work!! high low
43 Passive Transport cell uses no energy molecules move randomly Molecules spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (High Low) Three types:
44 3 Types of Passive Transport Diffusion Facilitative Diffusion diffusion with the help of transport proteins Osmosis diffusion of water
45 Passive Transport: 1. Diffusion Simple Diffusion Animation 1. Diffusion: random movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (High to Low) 2. Diffusion continues until all molecules are evenly spaced (equilibrium is reached)-note: molecules will still move around but stay spread out.
46 Passive Transport: 2. Facilitated Diffusion A 2. Facilitated diffusion: diffusion of specific particles through transport proteins found in the membrane Facilitated a. Transport Proteins are diffusion specific they select only certain molecules to (Channel Protein) cross the membrane b. Transports larger or charged molecules Carrier Protein B Diffusion (Lipid Bilayer)
47 Passive Transport: 2. Facilitated Diffusion Glucose molecules Cellular Transport From ahigh Concentration High Channel Proteins animations Cell Membrane Low Concentration Through a Go to Section: Transport Protein Protein channel Low
48 Passive Transport: 3. Osmosis Osmosis animation 3.Osmosis: diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane Water moves from high to low concentrations Water moves freely through pores. Solute (green) to large to move across.
49 Active Transport cell uses energy actively moves molecules to where they are needed Movement from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration (Low High) Three Types:
50 Types of Active Transport 1. Protein Pumps transport proteins that require energy to do work Example: Sodium / Potassium Pumps are important in nerve responses. Sodium Potassium Pumps (Active Transport using proteins) Protein changes shape to move molecules: this requires energy!
51 Types of Active Transport 2. Endocytosis: taking bulky material into a cell Uses energy Cell membrane in-folds around food particle cell eating forms food vacuole & digests food This is how white blood cells eat bacteria!
52 Types of Active Transport 3. Exocytosis: Forces material out of cell in bulk membrane surrounding the material fuses with cell membrane Cell changes shape requires energy EX: Hormones or wastes released from cell Endocytosis & Exocytosis animations
53 Effects of Osmosis on Life Osmosis- diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane Water is so small and there is so much of it the cell can t control it s movement through the cell membrane.
54 Hypotonic Solution Osmosis Animations for isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions Hypotonic: The solution has a lower concentration of solutes and a higher concentration of water than inside the cell. (Low solute; High water) Result: Water moves from the solution to inside the cell): Cell Swells and bursts open (cytolysis)!
55 Hypertonic Solution Osmosis Animations for isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions Hypertonic: The solution has a higher concentration of solutes and a lower concentration of water than inside the cell. (High solute; Low water) shrinks Result: Water moves from inside the cell into the solution: Cell shrinks (Plasmolysis)!
56 Isotonic Solution Osmosis Animations for isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions Isotonic: The concentration of solutes in the solution is equal to the concentration of solutes inside the cell. Result: Water moves equally in both directions and the cell remains same size! (Dynamic Equilibrium)
57 What type of solution are these cells in? A B C Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic
58 Cell Defense! com/gamesandlabs/cellgames/celldefen se.html
59 Exit Ticket What is the difference between active and passive transport? Diffusion is the transport of and osmosis is the transport What do lysosomes do? Integral proteins are found where? What are the two parts of a phospholipid? Draw the bilayer.
60 Warm Up Water always moves with Define solute. How is facilitated diffusion similar to active transport? Where would you find a peripheral protein? What is selective permeability?
61 Demonstration Selective Membrane!
62 Station Review Station 1: Matching Station 2: Identify the organelle and write it s function Station 3: Compare prokaryotes vs. eukaryote Station 4: Create a cell membrane Station 5: Cell Transport Game Station 6: Overview
63 Kahoot =)
64 Exit Ticket STUDY FOR YOUR TEST. STUDY FOR YOUR TEST. STUDY FOR YOUR TEST. STUDY FOR YOUR TEST. STUDY FOR YOUR TEST.
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Controlled via the Cell Membrane
 CELL TRANSPORT 1 Controlled via the Cell Membrane Passive Transport Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations Active Transport DOES require energy, moves from LOW concentrations
CELL TRANSPORT 1 Controlled via the Cell Membrane Passive Transport Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations Active Transport DOES require energy, moves from LOW concentrations
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7
 Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
Cellular Transport Notes. Ch. 7.3
 Cellular Transport Notes Ch. 7.3 About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions: a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides
Cellular Transport Notes Ch. 7.3 About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions: a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
Movement Through the Cell Membrane
 Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Name Class Date. cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell. MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
 Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Name Date Class. Cellular Structure
 Concept Mapping Cellular Structure Complete the network tree about cellular structure. These terms may be used more than once: animals, bacteria, chloroplasts, eukaryotes, a large central vacuole, plants,
Concept Mapping Cellular Structure Complete the network tree about cellular structure. These terms may be used more than once: animals, bacteria, chloroplasts, eukaryotes, a large central vacuole, plants,
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cells & Transport. Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4
 Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life
 AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Cell Structure and Function. The Basic Unit of Life
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
3.1. Cell Structure and Function CHAPTER 3. Cells are the basic unit of life. CELL THEORY Study Guide KEY CONCEPT
 SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell Early studies led to the development of the
SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell Early studies led to the development of the
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Equilibrium when two areas have the same concentration or are filled evenly
 Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Cells are the smallest units of life CH 3
 Cells are the smallest units of life CH 3 The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced only from
Cells are the smallest units of life CH 3 The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced only from
CH 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7
 A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7 CELL THEORY Before microscopes, people thought diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits They had no idea microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses existed
A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7 CELL THEORY Before microscopes, people thought diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits They had no idea microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses existed
Interest Grabber. All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells.
 Interest Grabber Section 7-1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1. What are the advantages
Interest Grabber Section 7-1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1. What are the advantages
NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? cell unicellular multicellular DISCOVERY OF CELLS Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek THE CELL THEORY
 NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? A cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. Living things can be either unicellular (made up entirely of only one cell) or
NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? A cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. Living things can be either unicellular (made up entirely of only one cell) or
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function
 Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Biology 30 Mr. Oosterom Development of the Cell Theory People have known about the existence of cells for approximately 300 yrs Early microscopes allowed scientists to
Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Biology 30 Mr. Oosterom Development of the Cell Theory People have known about the existence of cells for approximately 300 yrs Early microscopes allowed scientists to
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
The Discovery of the Cell
 The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
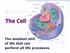 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell Basics. Basic Unit of Life. Prokaryotic. Eukaryotic. Plant Cell. Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Bacteria. Very Complex.
 Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function
 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell
 Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and function
 Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
The Cell. The basic unit of life
 The Cell The basic unit of life Cell Theory: states the following 1) all living things are cellular 3 things 2) cells are the smallest functioning unit in all living things and 3) cells come from preexisting
The Cell The basic unit of life Cell Theory: states the following 1) all living things are cellular 3 things 2) cells are the smallest functioning unit in all living things and 3) cells come from preexisting
CELL THEORY- EQ: What are the 3 facts of the cell theory? - pp191. EQ- Which Scientists are connected to cell discovery?
 UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8. Cell Membrane Section 1
 Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Written Response #1: True/False
 Written Response #1: True/False 1. Osmosis means to absorb something. 2. Cells are able to excrete waste. 3. Cells obtain energy by gaining nutrition from food. 4. Plants use sunlight for food. 5. Plants
Written Response #1: True/False 1. Osmosis means to absorb something. 2. Cells are able to excrete waste. 3. Cells obtain energy by gaining nutrition from food. 4. Plants use sunlight for food. 5. Plants
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided.
 Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Cell Structure and Function
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Cell Boundaries. Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h
 Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Also, how substances are transported throughout the cell.
 Also, how substances are transported throughout the cell. Why Study Cells? Cells are as fundamental to Biology as the atom is to chemistry. All organisms are made of cells. The cell is the simplest collection
Also, how substances are transported throughout the cell. Why Study Cells? Cells are as fundamental to Biology as the atom is to chemistry. All organisms are made of cells. The cell is the simplest collection
Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
KEY CONCEPT VOCABULARY
 SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development
SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic
 Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK
 NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems. Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells
 IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE. SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion).
 CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Cytology I Study of Cells
 Cytology I Study of Cells Biology 20 Which cell type has organelles such as mitochondria, nuclues, Golgi bodies, etc? A) prokaryotic B) eukaryotic C) bacterial D) viral E) none of these Cellular Basis
Cytology I Study of Cells Biology 20 Which cell type has organelles such as mitochondria, nuclues, Golgi bodies, etc? A) prokaryotic B) eukaryotic C) bacterial D) viral E) none of these Cellular Basis
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis What is the cell membrane? A quick review A. Cell Membrane and Cell Transport. Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport
 Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Transport Name: Directions: Go to https://shimkoscience.weebly.com/ and on the Biology page, find the document labelled Cell Membrane and Cell Transport
Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Transport Name: Directions: Go to https://shimkoscience.weebly.com/ and on the Biology page, find the document labelled Cell Membrane and Cell Transport
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Transport. Slide 1 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 & Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
& Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
Cells. Cell as a basic unit of life. Activity: Observing onion cells. Cells
 1 Cells Cell as a basic unit of life In the year 1665, Robert Hooke observed a honeycomb like structure consisting of many compartments in a thin slice of cork. He called these boxes as cells. Cell in
1 Cells Cell as a basic unit of life In the year 1665, Robert Hooke observed a honeycomb like structure consisting of many compartments in a thin slice of cork. He called these boxes as cells. Cell in
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per:
 Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
PASSIVE TRANSPORT. Diffusion Facilitative Diffusion diffusion with the help of transport proteins Osmosis diffusion of water
 PASSIVE TRANSPORT cell uses no energy molecules move randomly Molecules spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (High Low) Three types: Diffusion Facilitative Diffusion
PASSIVE TRANSPORT cell uses no energy molecules move randomly Molecules spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (High Low) Three types: Diffusion Facilitative Diffusion
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function. Biology 12 Chapter 4
 Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT. Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018
 UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018 Cell Wall CELL BOUNDARIES support protect & the cell cell membrane Lies outside of the Is made of & carbohydrates proteins Plant cell
UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018 Cell Wall CELL BOUNDARIES support protect & the cell cell membrane Lies outside of the Is made of & carbohydrates proteins Plant cell
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Biology, Friday, September 29
 Biology, Friday, September 29 On page 62 of your INB, in the top box, write the following questions on the left and answer it on the right. What is the function of the cell membrane? Your Answer Here Micrographs
Biology, Friday, September 29 On page 62 of your INB, in the top box, write the following questions on the left and answer it on the right. What is the function of the cell membrane? Your Answer Here Micrographs
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2010, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Cells Most basic unit of living system Arise by cell division from existing cell Make up
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2010, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Cells Most basic unit of living system Arise by cell division from existing cell Make up
