04_polarity. The formation of synaptic vesicles
|
|
|
- Dwayne Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and some endocrine cells) Dense core secretory vesicles (standard) Tiny secretory vesicles Synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters (acetylcholine, glutamate, GABA) for rapid signaling at chemical synapsis. 58
2 Precursors of lysosomal hydrolases are covalently modified by addition of mannose-6-phosphate in the cis Golgi network. They interact with M6P receptors and are segregated in the trans Golgi network in clathrin-coated vesicles. At the low ph of the late endosome the hydrolases dissociate from the receptors, which are recycled. The M6P is removed from the hydrolyses to prevent return to the Golgi apparatus with the receptors. 59
3 Non polarized cells Polarized cells 60
4 Segregation is thought to occur in the trans-golgi network (TGN) and is mediated by sorting signals embedded within the protein structure. Apical sorting signals include N- and O-linked glycans in the ectodomain, glycosyl phosphatidylinositol and transmembrane anchors, and amino-acid stretches in the cytoplasmic domain. In contrast, basolateral sorting signals usually comprise amino acid stretches in the cytoplasmic domain that typically include tyrosine, dileucine and monoleucine motifs, as well as clusters of acidic amino acids. Early ideas of how epithelial cells generate and maintain c e l l - s u r f a c e polarity: Kreitzer et al. NATURE CELL BIOLOGY VOL 5 FEBRUARY 2003 CAN SORTING AND DELIVERY OF MEMBRANE PROTEINS FROM THE TGN EXPLAIN THE ESTABLISHMENT OF CELL-SURFACE POLARITY? Two groups have shown that apical and basolateral membrane proteins are sorted at the level of the TGN into separate transport vesicles in fibroblasts. However, these proteins had a non-polarized distribution in the plasma membrane, demonstrating that sorting is not sufficient to generate cell-surface polarity. Drubin and Nelson: Origins of cell polarity. Cell 84: 335,
5 Requirement of spatial cues at the surface for biogenesis of epithelial cell polarity Intracellular sorting and delivery are secondary events 62
6 To examine directly the dynamics of E-cadherin in living cells, we constructed a fusion protein composed of fulllength canine E-cadherin fused at the carboxyl terminus to GFP (EcadGFP). EcadGFP was expressed in MDCK cells, HEK 293 EBNA cells and L cells. plasmide E Cadherin cdna GFP Transfection (lipofectamin) Expression of the Fusion protein 63
7 Hek-293 A: apical mb B: basal mb MDCK EcadGFP properties are similar to those of endogenous E- cadherin: it binds catenins, is targeted to cell-cell contacts, promotes adhesion. L-cells after 18h of aggregation in suspension culture in the presence or absence of extracellular Ca++. Parental L-cells do not express E-cadherin EcadGFP plaques 64
8 Redistribution of EcadGFP during cell-cell contact occurs in two stages and correlates with reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. <1 hour >2 hours Actin (rhodamine phalloidin) EcadGFP 65
9 Double immunohistochemistry on formaldehyde fixed cells Rhodamine falloidin E-cadherin mab early EcadGFP puncta were associated with thin cables of actin filaments that emerged from circumferential actin cables oriented parallel to the contact. A diffuse pool of E-cadherin clusters into puncta in response to cell cell contact and those puncta organize and become stabilized around actin filaments located close to the contacting membranes. late EcadGFP plaques were sites at which circumferential actin cables terminated. The gradual increase in the amount of EcadGFP in these plaques could be the result of de novo clustering of EcadGFP around new actin filaments exposed at the margins of the cell cell contact, or from the aggregation and migration of puncta that had preformed along the length of the contact. To distinguish between these two possibilities, time-lapse images of EcadGFP plaques were recorded. Quantitative fluorescence intensities of EcadGFP. The average (gray circles) and maximum (black diamonds) intensities in a 20-mm2 region surrounding a developing plaque area are plotted over a 40-min period. Thus, plaques most likely to arise by lateral clustering of a subset of EcadGFP puncta already formed along the cell cell contact, and are perhaps supplemented by recruitment of additional EcadGFP molecules in the area of plaque formation. It is clear that the peak density(black diamonds), but not the total amount (gray circles) of EcadGFP increased in the region of the membrane containing the forming plaque. 66
10 To gain further insight into the assembly dynamics of E-cadherin puncta and plaques, we developed a photobleaching recovery method to measure the diffusion coefficient, mobile fraction, and redistribution of EcadGFP during different stages of contact development Rhodamine falloidin Anti-E-cadherin Ecad-GFP fluorescence of the nonbleached region (red) and the entire cell (green) was monitored during recovery. Images taken before, 0.1 min after, and 10 min after photobleaching a 5.8-mm-diameter circle in a region of membrane not involved in cell cell contact (Membrane), a region of membrane in a, 15-min-old contact (New contact), a region of membrane in the middle of a,60-min-old contact (Puncta), and a membrane at the edge of a.2-h-old contact (Plaque). For each experiment, 300 images were collected every 3.2 s at 0.11 mm/pixel. The relative fluorescence is scaled to the pre-bleach intensity value. The mobile fraction of EcadGFP in the new contact (blue), puncta (green), and plaque (orange) is 100, 50, and,10%, respectively. The circles mark the photobleach region, and the colors correspond to the recovery curves. 67
11 68
12 Factors involved in vesicle delivery from the mother cell into the bud 69
13 S: supernatant P: pellet 70
14 Immunoblotting of postnuclear supernatants from contact-naive and confluent monolayers of MDCK cells showed that similar amounts of Sec6 and Sec8 were present in both non-polarized and polarized cells (Figure 2A), demonstrating that expression of the Sec6/8 complex was not induced by cell cell adhesion. To determine whether the subcellular distribution of the Sec6/8 complex changed during development of epithelial polarity, the fraction of the complex associated with plasma membrane was quantified at different times following initiation of cell cell contacts. E-cadherin, was confined to the top two fractions in Opti- Prep gradients in contact-naive and polarized MDCK cells (Figure 2B). In contact-naive cells,.90% of Sec6 and Sec8 migrated to a position near the bottom of the gradient, indicating that the Sec6/8 complex was largely present in a cytosolic pool. In contrast, Opti-Prep separation of polarized MDCK cell extracts showed that z70% of Sec6 and Sec8 migrated near the top of the gradient, in the same fractions that contained the plasma membrane protein E-cadherin. Therefore, in fully polarized MDCK cell monolayers, the Sec6/8 complex is primarily associated with the plasma membrane. 71
15 The kinetics of recruitment of the Sec6/8 complex to the plasma membrane were assessed by measuring the amounts of Sec6 and Sec8 recovered in the top two fractions from Opti-Prep gradients of homogenates of MDCK cells that had formed cell cell contacts for 3, 6, 12, or 24 hr. This analysis revealed that the Sec6/8 complex is rapidly recruited to the plasma membrane following the onset of cell cell contact with a t1/2» 3 6hr (Figure 2C). Colocalization of Sec6 with E-cadherin and ZO-1 at early cell-cell contacts tightjunction associated protein Sec6 E-cadherin Sec6 ZO-1 methanol Triton X-100 Sec6/8 Complex Associates with Adhesion Protein Complexes at Sites of Early Cell Cell Contacts 72
16 While E-cadherin was broadly distributed along the length of the lateral membrane, both Sec6 and Sec8 were restricted to the apex of the lateral membrane in a distribution similar to that of the tight junction associated protein ZO-1. In budding yeast, the Sec6/8 protein complex has a highly polarized distribution at the bud tip during bud formation (TerBush and Novick, 1995). In polarized MDCKcells, Sec6 and Sec8 were distributed in a circumferential ring around each cell in association with the lateral plasma membrane domain (Figure 4). ZO-1 Anti-sec6 Figure 5. Disruption of Calcium-Dependent Cell Cell Contacts Causes Dissociation of the Sec6/8 Complex from the Plasma Membrane. Polarized MDCK cells cultured on polycarbonate filters were incubated in DMEM containing 1.8 mm calcium (A B) or 5 mm calcium plus 2mM EGTA (C D) for 4 hr at 378C. In (E) (H), cells were cultured in DMEM containing 5 mm calcium plus 2 mm EGTA for 4 hr at 378C, then shifted into medium containing 1.8 mm calcium and incubated for an additional 2.5 hr (E and F) or 7.5 hr (G and H) at 378C. Parallel cultures were fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with antibodies to either ZO-1 (A, C, E, and G) or Sec6 (B, D, F, and H). Antibodies were visualized with fluorescein-labeled donkey anti-rat or anti-membrane, mouse antibodies. control EGTA EGTA then Ca ++ 2,5hr EGTA then Ca ++ 7,5hr 73
17 apical basolateral To synchronize vesicle transport between the Golgi complex and plasma membrane, MDCK cells were infected with recombinant adenoviruses that encode either an apical membrane protein (p75ntr), or a basal-lateral membrane protein (LDL receptor; LDLR). Cells were incubated at 208C for 120 min in the presence of 35S-sulfate to accumulate and label newly synthesized membrane proteins simultaneously in a late Golgi compartment. Cells were permeabilized with streptolysin-o (SLO) and incubated under different conditions. Generalized scheme for the formation of a new membrane domain following induction (cue) of the recruitment of the Sec6/8 complex to the membrane 74
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al.
 Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson
 Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, Please print your name: Instructions:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments
 Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular Compartments and
Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular Compartments and
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
 Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part II 2/3/15
 Name:Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part II 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name:Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part II 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Intracellular vesicular traffic. B. Balen
 Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport
 Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments III. Protein Translocation
 Lecture 3 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments III. Protein Translocation Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular
Lecture 3 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments III. Protein Translocation Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis
 Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells. Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari
 Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Molecular Trafficking
 SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17
 Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17 Exocytosis and endocytosis Transport from the trans-golgi network to the cell exterior: exocytosis. All eukaryotic cells continuously
Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17 Exocytosis and endocytosis Transport from the trans-golgi network to the cell exterior: exocytosis. All eukaryotic cells continuously
Organization of ATPases
 The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
Lectures 18: Biological Membranes: Life in Two Dimensions (contd.)
 Lectures 18: Biological Membranes: Life in Two Dimensions (contd.) Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/
Lectures 18: Biological Membranes: Life in Two Dimensions (contd.) Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes. Reading Assignments. Selective and Semi-permeable Barriers
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion. Richard H. Scheller
 The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion Richard H. Scheller The human brain contains approximately 10 15 connections between nerve cells (Figure 2). The specific formation and modulation
The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion Richard H. Scheller The human brain contains approximately 10 15 connections between nerve cells (Figure 2). The specific formation and modulation
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Apical and Basolateral Endocytic Pathways of MDCK Cells Meet in Acidic Common Endosomes Distinct from a Nearly-Neutral Apical Recycling Endosome
 Traffic 2000 1: 480 493 Munksgaard International Publishers Apical and Basolateral Endocytic Pathways of MDCK Cells Meet in Acidic Common Endosomes Distinct from a Nearly-Neutral Apical Recycling Endosome
Traffic 2000 1: 480 493 Munksgaard International Publishers Apical and Basolateral Endocytic Pathways of MDCK Cells Meet in Acidic Common Endosomes Distinct from a Nearly-Neutral Apical Recycling Endosome
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Rama Abbady. Odai Bani-Monia. Diala Abu-Hassan
 5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation
 Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 3/8/2011 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 3/8/2011 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry. The cell: Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell
 Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles. Hüseyin Çağsın
 Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I
 01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation
 Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Syntaxins 3 and 4 Are Concentrated in Separate Clusters on the Plasma Membrane before the Establishment of Cell Polarity
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 17, 977 989, February 2006 Syntaxins 3 and 4 Are Concentrated in Separate Clusters on the Plasma Membrane before the Establishment of Cell Polarity Seng Hui Low,* Amit
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 17, 977 989, February 2006 Syntaxins 3 and 4 Are Concentrated in Separate Clusters on the Plasma Membrane before the Establishment of Cell Polarity Seng Hui Low,* Amit
10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells eye 100 mm (10 cm) Chicken egg aid n 10 mm
 Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
The Animal Cell. English. Introduction
 R04 (1000523) English The Animal Cell Introduction Cells in animal multicellular organisms principally only occur in groups of similar cells or together with other differentiated cells, or embedded in
R04 (1000523) English The Animal Cell Introduction Cells in animal multicellular organisms principally only occur in groups of similar cells or together with other differentiated cells, or embedded in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Cellular Biochemistry
 Cellular Biochemistry Fall Semester 2013 Sept. 23 Benoit Kornmann Institute of Biochemistry Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry
Cellular Biochemistry Fall Semester 2013 Sept. 23 Benoit Kornmann Institute of Biochemistry Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Cells: The Living Units
 Chapter 3 Part B Cells: The Living Units Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 3.4 Active Membrane Transport Two major
Chapter 3 Part B Cells: The Living Units Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 3.4 Active Membrane Transport Two major
Cell Membranes. Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Cell and Molecular Biology
 Cell Membranes Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Cell and Molecular Biology Organelles 2Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids DNA
Cell Membranes Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Cell and Molecular Biology Organelles 2Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids DNA
Plant Cell, Development & Ultrastructure
 PCDU Lecture Plant Cell, Development & Ultrastructure Plant Cell Biology Labs Download at: http://goo.gl/111tha Microtubules 13 Protofilamente 25nm Plant MT Cytoskeleton Animal MT cytoskeleton Preprophase
PCDU Lecture Plant Cell, Development & Ultrastructure Plant Cell Biology Labs Download at: http://goo.gl/111tha Microtubules 13 Protofilamente 25nm Plant MT Cytoskeleton Animal MT cytoskeleton Preprophase
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, Please print your name:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations Department: BIOLOGY. Title of Exam: Cell Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Active Rab11 and functional recycling endosome are required for E-cadherin trafficking and lumen formation during epithelial morphogenesis
 Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 295: C545 C556, 2008. First published June 25, 2008; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00097.2008. Active Rab11 and functional recycling endosome are required for E-cadherin trafficking and
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 295: C545 C556, 2008. First published June 25, 2008; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00097.2008. Active Rab11 and functional recycling endosome are required for E-cadherin trafficking and
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role in Alzheimer s disease
 Brodeur et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2012, 7:31 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role
Brodeur et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2012, 7:31 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
MCB130 Midterm. GSI s Name:
 1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 8. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18
 Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH INTRACELLULAR PROTEIN TRANSPORT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003
 7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
Microfilaments. myosin. In muscle cells. Microfilaments. Microfilaments. Video: Cytoplasmic Streaming. amoeboid movement. Pseudopodia.
 Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
Chapter 11 Intercellular Communication and Tissue Architecture
 Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter 11 Multicellular organisms such as the human body consist of various tissues such as epithelial tissues, bones and nerves, and organs such as heart and
Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter 11 Multicellular organisms such as the human body consist of various tissues such as epithelial tissues, bones and nerves, and organs such as heart and
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Chapter 12: Membranes. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Rearrangements of the Actin Cytoskeleton and E-Cadherin Based Adherens Junctions Caused by Neoplasic Transformation Change Cell Cell Interactions
 Rearrangements of the Actin Cytoskeleton and E-Cadherin Based Adherens Junctions Caused by Neoplasic Transformation Change Cell Cell Interactions Dmitry V. Ayollo., Irina Y. Zhitnyak., Jury M. Vasiliev,
Rearrangements of the Actin Cytoskeleton and E-Cadherin Based Adherens Junctions Caused by Neoplasic Transformation Change Cell Cell Interactions Dmitry V. Ayollo., Irina Y. Zhitnyak., Jury M. Vasiliev,
GLUT4 is retained by an intracellular cycle of vesicle formation and fusion with endosomes.
 MBC in Press, published on October 31, 2003 as 10.1091/mbc.E03-07-0517 GLUT4 retention by intracellular cycling GLUT4 is retained by an intracellular cycle of vesicle formation and fusion with endosomes.
MBC in Press, published on October 31, 2003 as 10.1091/mbc.E03-07-0517 GLUT4 retention by intracellular cycling GLUT4 is retained by an intracellular cycle of vesicle formation and fusion with endosomes.
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Maintenance of Golgi structure and function depends on the integrity of ER export
 JCB Article Published November 12, 2001 Maintenance of Golgi structure and function depends on the integrity of ER export Theresa H. Ward, Roman S. Polishchuk, Steve Caplan, Koret Hirschberg, and Jennifer
JCB Article Published November 12, 2001 Maintenance of Golgi structure and function depends on the integrity of ER export Theresa H. Ward, Roman S. Polishchuk, Steve Caplan, Koret Hirschberg, and Jennifer
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human
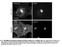 Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014
 Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
