Cellular Transport. Biology Honors
|
|
|
- Darleen Henderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cellular Transport Biology Honors
2 Review of Concepts and Introduction to the Current Concepts 8hw
3 Passive Active No energy Requires / needs energy
4 Passive Transport- 3 Types Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion
5 What does concentration mean? Concentration is the abundance of something.
6 Diffusion The movement of particles across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high to low concentration; until equilibrium is met. Results in natural motion of particles; which causes the molecules to collide / bump into one another and scatter. Concentration gradient: the difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another.
7 What does diffusion move? Small lipids Nonpolar molecules such as CO 2 and O 2 Water
8
9
10 Osmosis The diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration; until equilibrium is reached.
11 Most cells have special water proteins called aquaporins. Type of channel protein that facilitates the passage of water. The higher the concentration of dissolved particles in a solution, the lower the concentration of water molecules in the same solution. Water diffuses across a membrane from the region of lower solute concentration to the region of higher solute concentration until the solute concentration is equal on both sides.
12 Review Terminology Solute: The substance that is found in the lesser amount. For example, glucose, salt, or potassium. Solvent: The substance that is found in the greatest amount. For example, water.
13 Solutions are described based on their tonicity, or concentration of solutes in the water (inside and outside the cell). Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic
14 A way to remember the direction of the water SALT SUCKS WATER. WHEREVER THERE IS MORE SALT, SUGAR, OR ANY OTHER SOLUTE, THAT IS WHERE THE WATER WILL FLOW. Write this below the table!
15 Isotonic Concentration of water molecules and solutes are the same inside and outside the cell. Animal cells need isotonic solutions to maintain homeostasis. Water does not stop moving. Cells reach dynamic equilibrium.
16 Hypertonic Concentration of water molecules inside the cell is higher than outside the cell. Solutes are higher outside the cell. Therefore, the water moves out of the cell. Causes the cell to shrivel or crenate, because the water is leaving the cell. When plants lose water they wilt. Plasmolysis- process of water moving out of the cell.
17 Hypotonic The concentration of water molecules is higher outside the cell than inside the cell. There are more solutes inside the cell, causing the water to flow into the cell. The cells swell and can burst or lyse. Bursting of cells is cytolysis. Takes in water. Plant cells need this tonicity to maintain homeostasis. Turgor Pressure= results from water inside a plant cell pushing the cell membrane out against the plants cell wall. More solutes inside the cell.
18 Label the diagrams
19 Osmosis Video C6M
20 Facilitated Diffusion The diffusion of molecules across a membrane through transport proteins. Facilitate means to make easier Some bind to only one molecule. Some bind to two different molecules. Examples: glucose, amino acids, ions, and polar / charged molecules.
21 Several Types of Transport Proteins Channel proteins: act like a pore in the membrane that lets water molecules (aquaporins) or small ions through quickly. Carrier proteins: They "carry" the ion, or molecule across the membrane by changing shape. Typically specific to a molecule. Occurs in both passive and active transport. Gated channels: A protein "gate," that allows a molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion, such as glucose. A stimulus initiates the opening and closing of the gate (temperature, chemical signal).
22 Why is it important for glucose to pass through the membrane quickly?
23
24 ACTIVE TRANSPORT Moves materials from areas of low to high concentration. Uses energy / ATP to move the molecules Moves materials against the concentration gradient. The proteins are often referred to as pumps USES ATP Why use active transport?
25
26 Where does the energy come from?
27 Bulk Transport Endocytosis and Exocytosis transports materials across the membrane in vesicles.
28 Endo=within Endocytosis Cytosis= cell Cell takes in large particles by engulfing them. The cell membrane folds into a pouch, called a vesicle. Lysosomes break down the vesicle, releasing the contents. Ex- Large molecules, food, liquids, and other substances.
29 Pinocytosis Cell drinking The process of taking up liquid (just a pinch) from the surrounding environment. Tiny pockets form along the membrane, fill with liquid, and pinch off.
30 phagocytosis Cell eating" key role in your immune system Engulf and destroy particles (bacteria and food). Examples: White blood cells / macrophages
31
32 This image depicts a cancer cell being attacked by a cell of the immune system. Cells of the immune system consistently destroy pathogens by essentially "eating" them. Endocytosis-BIO/
33 Exocytosis Exo= out of Cytosis= cell Release of substances out of the cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane. Ex- cell is exporting proteins, getting rid of toxins, or helping messages travel through nerve cells.
34 Endocytosis/lesson/Exocytosis-and- Endocytosis-BIO/
35
36 Sodium potassium pump Exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions across the cell membrane of animal cells. Uses ATP to pump molecules through a carrier protein. Pumping the molecules through. Three sodium ions bind with the protein pump inside the cell. In doing so, it pumps the three sodium ions out of the cell. At that point, two potassium ions from outside the cell bind to the protein pump. The potassium ions are then transported into the cell, and the process repeats ( Pump/lesson/Sodium-Potassium-Pump-BIO/).
37 002/node/4182
38 Identify the Process
39 Bellwork / exit slip COMPARE/CONTRAST the kinds of transport DIFFUSION Active (ATP) or Passive (KINETIC ENERGY) What does it use to help: Membrane proteins? Vesicles? Needs no help (phospholipids)? Example of substance(s) that use this kind of transport in cells FACILITATED DIFFUSION OSMOSIS SODIUM-POTASSIUM (NA+ -K + ) PUMP (ANIMALS) ENDOCYTOSIS (PHAGOCYTOSIS) ENDOCYTOSIS (PINOCYTOSIS) EXOCYTOSIS
40 Identify the Diagrams
41
42
43
44
45
46
CELL BOUNDARIES. Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants
 CELL BOUNDARIES CELL BOUNDARIES Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants TYPES OF MEMBRANES Some substances = too large or
CELL BOUNDARIES CELL BOUNDARIES Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants TYPES OF MEMBRANES Some substances = too large or
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport
 Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport 5.1 Homeostasis & Permeability Homeostasis ability of cell to maintain balance needed for life To maintain balance: cells must transport needed materials into cells &
Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport 5.1 Homeostasis & Permeability Homeostasis ability of cell to maintain balance needed for life To maintain balance: cells must transport needed materials into cells &
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane. Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5
 Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE. SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion).
 CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES
 Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook TYPES OF TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE: What do you remember? Complete the chart with what you
Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook TYPES OF TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE: What do you remember? Complete the chart with what you
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY
 Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
II. Active Transport (move molecules against conc. gradient - cell must expend energy) (uses carrier proteins)
 Chapter 5 - Homeostasis and Transport I. Passive Transport (no energy from cell required) A. Diffusion 1. movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration a.
Chapter 5 - Homeostasis and Transport I. Passive Transport (no energy from cell required) A. Diffusion 1. movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration a.
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Example - Paramecium contain contractile vacuoles that collect and remove excess water, thereby helping to achieve homeostasis
 Homeostasis Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment; All organisms have ranges that are tolerated (i.e. ph and temperature) Example - Paramecium contain contractile
Homeostasis Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment; All organisms have ranges that are tolerated (i.e. ph and temperature) Example - Paramecium contain contractile
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Movement of Substances in the Cell
 Movement of Substances in the Cell The Marble Memories Biology All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane (also called cell membrane). This membrane regulates the entry and exit of substances into and
Movement of Substances in the Cell The Marble Memories Biology All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane (also called cell membrane). This membrane regulates the entry and exit of substances into and
Equilibrium is a condition of balance. Changes in temperature, pressure or concentration can cause a shift in the equilibrium.
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Passive Transport Objectives Relate concentration gradients, diffusion, and equilibrium. Predict the direction of water
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Passive Transport Objectives Relate concentration gradients, diffusion, and equilibrium. Predict the direction of water
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT
 CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT Homeostasis: Maintaining a Balance Organisms must adjust to changes in their environment. If not DEATH! A formal definition is maintaining a stable internal condition despite
CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT Homeostasis: Maintaining a Balance Organisms must adjust to changes in their environment. If not DEATH! A formal definition is maintaining a stable internal condition despite
Plasma Membrane Function
 Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Review: Cellular Transport
 Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
PASSIVE TRANSPORT. Diffusion Facilitative Diffusion diffusion with the help of transport proteins Osmosis diffusion of water
 PASSIVE TRANSPORT cell uses no energy molecules move randomly Molecules spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (High Low) Three types: Diffusion Facilitative Diffusion
PASSIVE TRANSPORT cell uses no energy molecules move randomly Molecules spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (High Low) Three types: Diffusion Facilitative Diffusion
Section 4: Cellular Transport. Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell.
 Section 4: Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell. Essential Questions What are the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active
Section 4: Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell. Essential Questions What are the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active
Constant Motion of Molecules. Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers
 CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
9/20/2016 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES. Section Objectives. Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions.
 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes
 Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Lesson Overview. 7.3 Cell Transport
 7.3 THINK ABOUT IT When thinking about how cells move materials in and out, it can be helpful to think of a cell as a nation. The boundaries of a nation are its borders, and nearly every country tries
7.3 THINK ABOUT IT When thinking about how cells move materials in and out, it can be helpful to think of a cell as a nation. The boundaries of a nation are its borders, and nearly every country tries
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
WAYS MOLECULES MOVE. Chapter 7-3.
 WAYS MOLECULES MOVE Chapter 7-3 http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_main.html See a video clip about DIFFUSION-7A Diffusion http://lhs.lps.org/staff/sputnam/biology/u3cell/diffusion_1.png Animatioin
WAYS MOLECULES MOVE Chapter 7-3 http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_main.html See a video clip about DIFFUSION-7A Diffusion http://lhs.lps.org/staff/sputnam/biology/u3cell/diffusion_1.png Animatioin
Movement across the Membrane
 Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane 2003-2004 1 Cell membrane Cells have an inside & an outside Cell membrane is the boundary Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO! Why not? The cell needs materials
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane 2003-2004 1 Cell membrane Cells have an inside & an outside Cell membrane is the boundary Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO! Why not? The cell needs materials
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT. Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018
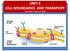 UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018 Cell Wall CELL BOUNDARIES support protect & the cell cell membrane Lies outside of the Is made of & carbohydrates proteins Plant cell
UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018 Cell Wall CELL BOUNDARIES support protect & the cell cell membrane Lies outside of the Is made of & carbohydrates proteins Plant cell
Passive Transport. Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place. Ex-rolling down a hill
 Passive Transport Fluid Mosaic Model Passive Transport Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place Ex-rolling down a hill Parts of a Solution Solute: what gets dissolved Solvent: What
Passive Transport Fluid Mosaic Model Passive Transport Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place Ex-rolling down a hill Parts of a Solution Solute: what gets dissolved Solvent: What
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries
 Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Transport. Slide 1 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 & Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
& Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
WEDNESDAY 10/18/17. Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes.
 WEDNESDAY 10/18/17 Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes. THE PLASMA MEMBRANE - 2 Gateway to Cell HOMEOSTASIS Balanced
WEDNESDAY 10/18/17 Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes. THE PLASMA MEMBRANE - 2 Gateway to Cell HOMEOSTASIS Balanced
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8. Cell Membrane Section 1
 Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
The Transport of Materials Across Cell Membranes
 The Transport of Materials Across Cell Membranes EK 2.B.1.b. LO 2.10 The Plasma Membrane 2 EK 2.B.1.b. LO 2.10 The Plasma Membrane The cell membrane is said to be semi permeable or selectively permeable
The Transport of Materials Across Cell Membranes EK 2.B.1.b. LO 2.10 The Plasma Membrane 2 EK 2.B.1.b. LO 2.10 The Plasma Membrane The cell membrane is said to be semi permeable or selectively permeable
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Chapter 5 Homeostasis and Cell Transport
 Chapter 5 Homeostasis and Cell Transport Palabra Palooza! Role #1: The Definer says: The word can be explained as Role #2: The Re-stater says: Then I understand (word) to mean Words: Passive transport
Chapter 5 Homeostasis and Cell Transport Palabra Palooza! Role #1: The Definer says: The word can be explained as Role #2: The Re-stater says: Then I understand (word) to mean Words: Passive transport
The Cell Membrane. Why cells must control materials. Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival.
 The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
Each cell has its own border, which separates the cell from its surroundings and also determines what comes in and what goes out.
 7.3 Cell Transport Wednesday, December 26, 2012 10:02 AM Vocabulary: Diffusion: process in which cells become specialized in structure and function Facilitated diffusion: process of diffusion in which
7.3 Cell Transport Wednesday, December 26, 2012 10:02 AM Vocabulary: Diffusion: process in which cells become specialized in structure and function Facilitated diffusion: process of diffusion in which
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Image from: http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/ge22/03.gif Slide show modified from: http://www.explorebiology.com/pptap/2005/ http://facstaff.bloomu.edu/gdavis/links%20100.htm
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Image from: http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/ge22/03.gif Slide show modified from: http://www.explorebiology.com/pptap/2005/ http://facstaff.bloomu.edu/gdavis/links%20100.htm
Controlled via the Cell Membrane
 CELL TRANSPORT 1 Controlled via the Cell Membrane Passive Transport Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations Active Transport DOES require energy, moves from LOW concentrations
CELL TRANSPORT 1 Controlled via the Cell Membrane Passive Transport Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations Active Transport DOES require energy, moves from LOW concentrations
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3
 Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Equilibrium when two areas have the same concentration or are filled evenly
 Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function. Biology 12 Chapter 4
 Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Membrane Structure and Function. Cell Membranes and Cell Transport
 Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membranes and Cell Transport 1895 1917 1925 Membrane models Membranes are made of lipids Phospholipids can form membranes Its actually 2 layers - there are proteins
Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membranes and Cell Transport 1895 1917 1925 Membrane models Membranes are made of lipids Phospholipids can form membranes Its actually 2 layers - there are proteins
FLEXIBLE, SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE boundary that helps control what enters and leaves the cell. Composed of: a. Two layers of PHOSPHOLIPIDS molecules
 FLEXIBLE, SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE boundary that helps control what enters and leaves the cell. Composed of: a. Two layers of PHOSPHOLIPIDS molecules arranged with POLAR HEADS facing outside and NON-POLAR
FLEXIBLE, SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE boundary that helps control what enters and leaves the cell. Composed of: a. Two layers of PHOSPHOLIPIDS molecules arranged with POLAR HEADS facing outside and NON-POLAR
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells
 Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Cell Transport. Movement of molecules
 Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Membrane Structure and Function - 1
 Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
The Cell Membrane. Lecture 3a. Overview: Membranes. What is a membrane? Structure of the cell membrane. Fluid Mosaic Model. Membranes and Transport
 Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
BELLRINGER DAY In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane?
 BELLRINGER DAY 01 1. In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane? THE CELL MEMBRANE S T R U C T U R E A N D F U N C T I O N CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS Cell
BELLRINGER DAY 01 1. In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane? THE CELL MEMBRANE S T R U C T U R E A N D F U N C T I O N CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS Cell
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Chapter 8 KEY CONCEPTS Cellular s are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Membrane structure results in selective permeability Passive transport is diffusion of a substance
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Chapter 8 KEY CONCEPTS Cellular s are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Membrane structure results in selective permeability Passive transport is diffusion of a substance
What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast.
 1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast.
 1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function
 Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
FIGURE A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged) and hydrophilic (attracted to water).
 PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
Cell Structure and Function. Cell Membrane and Osmosis
 Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane and Osmosis Cell Membrane All living things must maintain homeostasis. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and the environment that surrounds the
Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane and Osmosis Cell Membrane All living things must maintain homeostasis. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and the environment that surrounds the
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function
 Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Chapter 7. Movement across the Cell Membrane
 Chapter 7 Movement across the Cell Membrane 2005-2006 Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems u Universe tends towards disorder Diffusion u movement from high low concentration Diffusion
Chapter 7 Movement across the Cell Membrane 2005-2006 Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems u Universe tends towards disorder Diffusion u movement from high low concentration Diffusion
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
How Things Get In and Out of Cells, or gummy bears, zip lock bags or whatever!
 How Things Get In and Out of Cells, or gummy bears, zip lock bags or whatever! SC.912.L.14.3 Benchmark Clarifications: Students will compare and/or contrast the structures found in plant cells and in animal
How Things Get In and Out of Cells, or gummy bears, zip lock bags or whatever! SC.912.L.14.3 Benchmark Clarifications: Students will compare and/or contrast the structures found in plant cells and in animal
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
Cell Biology. The Plasma Membrane
 Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
What do you remember about the cell membrane?
 Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
The Cell Membrane. Also known as the Plasma Membrane
 Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Movement across the Cell Membrane (Ch. 7.3)
 Movement across the Cell Membrane (Ch. 7.3) 2007-2008 Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems universe tends towards disorder (entropy) Diffusion movement from HIGH LOW concentration
Movement across the Cell Membrane (Ch. 7.3) 2007-2008 Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems universe tends towards disorder (entropy) Diffusion movement from HIGH LOW concentration
Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport
 Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport Name: Class key Period: Page 1 of 39 Topic 7.4 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Page 2 of 39 Topic: Membrane Channels Objective: Why do molecules move
Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport Name: Class key Period: Page 1 of 39 Topic 7.4 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Page 2 of 39 Topic: Membrane Channels Objective: Why do molecules move
Cellular Transport Notes. Ch. 7.3
 Cellular Transport Notes Ch. 7.3 About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions: a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides
Cellular Transport Notes Ch. 7.3 About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions: a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides
Chapter 3.4 & 3.5 Cell Transport (Osmosis and Diffusion) = only some molecules can get in or out of the cell
 Chapter 3.4 & 3.5 Cell Transport (Osmosis and Diffusion) I. Cell Membrane (cells need an inside and outside) a. separate cell from its environment b. cell membrane is the boundary c. cell membrane controls
Chapter 3.4 & 3.5 Cell Transport (Osmosis and Diffusion) I. Cell Membrane (cells need an inside and outside) a. separate cell from its environment b. cell membrane is the boundary c. cell membrane controls
Membrane Structure and Function. Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function
 Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Passive Cellular Transport. Unit 2 Lesson 4
 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Students will be able to: Define passive transport Enumerate the three types of passive transport Described each type of passive transport: osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Students will be able to: Define passive transport Enumerate the three types of passive transport Described each type of passive transport: osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion
[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution
![[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution [S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution](/thumbs/88/115710711.jpg) Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
Movement across the Cell Membrane
 Movement across the Cell Membrane Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems universe tends towards disorder (entropy) Diffusion u movement from HIGH LOW concentration Simple Diffusion
Movement across the Cell Membrane Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems universe tends towards disorder (entropy) Diffusion u movement from HIGH LOW concentration Simple Diffusion
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane. diffusion. Diffusion of 2 solutes. Cell (plasma) membrane. Diffusion 9/7/2012
 Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane Diffusion Diffusion of 2 solutes Each substance diffuses down its own concentration gradient, independent of concentration gradients of other substances Diffusion
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane Diffusion Diffusion of 2 solutes Each substance diffuses down its own concentration gradient, independent of concentration gradients of other substances Diffusion
Movement Through the Cell Membrane
 Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
Chapter 4. Membrane Structure and Function. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 4 Membrane Structure and Function Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Regulates the entrance
Chapter 4 Membrane Structure and Function Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Regulates the entrance
In groups of 3, half the class will conduct factors affecting diffusion lab while the others are working on osmosis
 Factors Affecting Diffusion & Osmosis In groups of 3, half the class will conduct factors affecting diffusion lab while the others are working on osmosis 1 THE CELL IN ACTION! 2 Passive Transport The net
Factors Affecting Diffusion & Osmosis In groups of 3, half the class will conduct factors affecting diffusion lab while the others are working on osmosis 1 THE CELL IN ACTION! 2 Passive Transport The net
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
 Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Lipids: Non-polar substances such as fat that contain C, H, O. Phospholipids: Lipid with phosphate group, very abundant in plasma
Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Lipids: Non-polar substances such as fat that contain C, H, O. Phospholipids: Lipid with phosphate group, very abundant in plasma
Bio Chapter 7.3 Notes. Cellular Movement
 Bio Chapter 7.3 Notes Cellular Movement I.Background Information A. Solution- a mixture in which the solute (molecules being dissolved) never settle out in the solvent (water). B. In a 25% Koolaid solution,
Bio Chapter 7.3 Notes Cellular Movement I.Background Information A. Solution- a mixture in which the solute (molecules being dissolved) never settle out in the solvent (water). B. In a 25% Koolaid solution,
Membrane structure & function
 Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy.
 1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy. ATP is the primary energy molecule for the cell. It is produced in the mitochondria during cellular respiration, which breaks down
1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy. ATP is the primary energy molecule for the cell. It is produced in the mitochondria during cellular respiration, which breaks down
Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer. Membrane Structure and Function. Fluid Mosaic Model. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Cells & Transport. Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4
 Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Biology, Friday, September 29
 Biology, Friday, September 29 On page 62 of your INB, in the top box, write the following questions on the left and answer it on the right. What is the function of the cell membrane? Your Answer Here Micrographs
Biology, Friday, September 29 On page 62 of your INB, in the top box, write the following questions on the left and answer it on the right. What is the function of the cell membrane? Your Answer Here Micrographs
