Preparation of ph Sensitive Pluronic-Docetaxel Conjugate Micelles to Balance the Stability and Controlled Release Issues
|
|
|
- Timothy McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Materials 2015, 8, ; doi: /ma Article OPEN ACCESS materials ISSN Preparation of ph Sensitive Pluronic-Docetaxel Conjugate Micelles to Balance the Stability and Controlled Release Issues Yanchao Liang, Zhihui Su, Yao Yao and Na Zhang * School of Pharmaceutical Science, Shandong University, 44 Wenhua Xi Road, Ji nan , Shandong, China; s: liangyanchao2012@126.com (Y.L.); suzhihui2013@163.com (Z.S.); yaoyao2y@126.com (Y.Y.) * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; zhangnancy9@sdu.edu.cn; Tel.: ; Fax: Academic Editor: Loo Say Chye Joachim Received: 17 November 2014 / Accepted: 13 January 2015 / Published: 23 January 2015 Abstract: A novel polymer-drug conjugate was prepared by the chemical reaction between the copolymer Pluronic P123 and the docetaxel via a ph sensitive hydrazone bond. These pluronic P123-docetaxel (DTX) conjugates (P123-DTX) could form the stable drug-loaded materials that can self-assemble into the defined nano-micelles in aqueous solution because of their obvious amphiphilic property and low critical micelle concentration. The spherical morphology and particle size of the prepared nano-micelles were characterized by transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering, respectively. Moreover, after the introduction of ph sensitive hydrazone bond, P123-DTX micelle showed a ph dependent drug release behavior. At ph 5.0 (in 48 h), the cumulative release amount of DTX were ~84.9%, which is about six times higher than that at ph 7.4. The prepared novel p123-dtx conjugates may offer a great benefit for drug delivery and controlling the drug release. Keywords: docetaxel; conjugates; nano-micelles; stability; ph controlled release 1. Introduction One purpose to design smart materials is for the sake of its better applications in the field of medicine [1]. Recently, some novel systems designed by smart polymers have been frequently used as drug delivery devices [2 4]. Among these polymeric systems, micelles formed by amphiphilic
2 Materials 2015, copolymers had received more attentions. Composed of two distinct blocks, these copolymers could self-assemble to form two distinct domains in aqueous solution: a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic shell [5]. In this regard, hydrophobic drugs such as anticancer drugs can be entrapped into the hydrophobic core and sheltered by the hydrophilic shell. These covered drug will achieved an improved water solubility capacity and be protected from enzymatic degradation and uptake by mononuclear phagocytes, macrophages and reticuloendothelial systems in the liver, spleen and bone marrow. Hence, their blood circulation time prolonged. More than that, for anticancer drugs, the formed micelles with nano-size will also have the advantages to avoiding the premature elimination via glomerular filtration in the kidneys and stay within the tumor tissues due to the enhanced permeation and retention (EPR) effect [6]. The past decade has witnessed the development of the polymeric micelles and several types of anticancer drug loaded micelles have been applied in hospital or investigated clinical trials [7]. Micelles formed by copolymers have shown its huge potential in anticancer drug delivery. However, these self-assembled micellar carriers often expose inadequate in vivo stability, which leads to premature drug release following intravenous injection. In this respect, polymeric micelles formed by conjugating drugs to the polymer backbone via covalent bonds can be an attractive strategy, which also known as polymer therapeutics, to eliminate the burst and premature release of the drug [8]. The covalent bonds in the polymer-drug conjugates can hold the drug firmly in the circulation, and there will be less anticancer drug released into healthy tissue [9]. In the past several years, various types of polymer-drug conjugates have been explored to enhance the in vivo stability of drug-loaded biodegradable micelles. And many of them have been evaluated in clinical trials [10]. While the release profile of the polymer-drug conjugates still need to be optimized to ensure the therapeutic efficacy. In fact, although a lot of work in the research of the polymer-drug conjugates had showed a superior stability against dilution, these micelles may also adversely influence drug release in the tumor tissues and cells, leading to compromised therapeutic outcomes. To resolve the extracellular stability versus intracellular drug release dilemma, many researchers have dedicated their study to designing the bio-responsive (such as ph and enzyme-sensitive) micelles [11]. In particular, ph-responsive micelles have attracted great attention due to the existence of mildly acidic ph in the tumor tissues than the normal tissues, which may provide a tissues-specific stimulus that can be exploited for selective drug release [12]. In the construction of the ph sensitive conjugates, a range of chemical bonds (orthoester, acetal, hydrazone, imine, cis-aconytil and trityl bonds included) have been developed to show an enhanced degradation or hydrolysis in the presence of slightly acidic media, while being stable at neutral ph level. It is noted that many of the researchers had focused their research on the study of hydrazone group, which had shown favorable ph-responsible ability in antitumor drug delivery [13 15]. Recently, a novel acid-cleavable prodrug of doxorubicin (INNO-206) were reported to be under phase II clinical development [16]. Binding with albumin via the acid-sensitive hydrazone contained linker, the INNO-206 conjugates can release doxorubicin selectively at the tumor site, which showed significantly superior antitumor efficacy and a good safety profile over free doxorubicin [17]. At this stage, the INNO-206 conjugates is evaluated for its effective antitumor therapy against different tumor xenograft models and has the potential to be a promising clinical candidate for treating a broad range of solid tumors [18]. Therefore, developing the
3 Materials 2015, polymeric micelles based on ph-responsive polymer-anticancer drug conjugates can be a potential way to improve the stability and drug release issue. Similar with doxorubicin, docetaxel (DTX) is another one of the most potent chemotherapeutic agents, which exhibits a more effective antitumor activity than paclitaxel. Docetaxel has shown a broad spectrum of activity against a variety of tumors, especially for the treatment of breast, gastric, ovarian, prostate and non-benign lung cancer [19]. In our previous work, conjugates micelles formed by the triblock copolymer Poly (ethylene oxide)-block-poly (propylene oxide)-block-poly (ethylene oxide) (Pluronic) have shown their superior stability capacity in DTX delivery. Without immunogenicity, antigenicity or toxicity, these commercially available Pluronic copolymers can spontaneously form nanosized polymeric micelles in aqueous solution, which is benefit for DTX protection in the circulation. Besides, the effect of Pluronic copolymers in promoting active membrane transport and reversing the multidrug resistance (MDR) effect, may also be helpful to enhance the anticancer therapeutic effect. However, the release profile of these ester bonded conjugates are still suppressed and need to be optimized. Herein, the hydrazone group contained ph sensitive strategy can be utilized to improve their release properties while maintaining their stability in DTX delivery. Under the above considerations, it is important to seek feasible hydrazone linkage construction method to prepare the ph sensitive conjugates. In this study, we chose the widely used triblock copolymer Pluronic P123 (P123) as the carrier to construct our polymer-docetaxel conjugates (P123-DTX). To achieve the ph-dependent characteristic, the hydrazone contained derivative of DTX was prepared via a two-step reaction, so that the hydrazone linker was formed before their combination with the carriers. The micelles formed by these P123-DTX conjugates were also evaluated and investigated to verify its potential to balance the stability and drug release. 2. Results and Discussion The structure and synthesis steps the P123-DTX conjugates is illustrated in Figure 1. The ph sensitive Pluronic P123-DTX conjugates were prepared by the attachment between the DTX and the Pluronic P123. Before the combination with the Pluronic P123, DTX was chemically modified to form the linker contained derivatives, which is important to exhibit its ph sensitive behavior. It had been reported that the modification of taxanes by levulic acid could be an effective way in forming the ph sensitive conjugate to fulfill the issue of stability and controlled release [20 22]. Therefore, the derivatives of the DTX was synthesized: (1) modification of DTX with a levulic acid (DTX-L); (2) synthesized the hydrazone bond contained derivative of DTX (DTX-L-A) by coupling the levulic acid-modified DTX with adipic dihydrazide. To be better conjugated, the carriers were also modified to achieve the Pluronic P123 derivatives: the succinic acid-modified Pluronic P123 (P123-S). The derivatives of DTX and Pluronic P123-DTX conjugates were characterized by 1 H NMR, respectively (Figures 2 and 3). Based on the dialysis method [23], the P123-DTX conjugates can be self-assembled into nano-sized polymeric micelles because of their amphiphilic properties. After the preparation of the conjugates, their drug-loading efficiency was characterized. Based on our previous work [24], the weight percentage (wt%) of DTX in the P123-DTX conjugate was determined using the UV-Visible
4 Materials 2015, spectrophotometer at 230 nm using acetonitrile as solvent. The DTX contents of P123-DTX conjugates were determined to be ~11.18% (wt%). Figure 1. Synthetic routes used for the preparation of Pluronic P123-DTX.
5 Materials 2015, Figure 2. 1 H NMR spectrum of the derivatives of docetaxel (DTX) (DTX, DTX-L, DTX-L-A) in DMSO-d6.
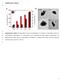
6 Materials 2015, Figure 3. 1 H NMR spectrum of Pluronic P123 and P123-DTX conjugates in DMSO-d6. The particle size is another crucial parameter for drug delivery, which could dramatically affect the in vivo pharmacokinetics and distributions of the conjugate micelles [25]. The particle size and size distribution of P123-DTX conjugate micelles were measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and their morphology were visualized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (Figure 4). These P123-DTX conjugate micelles were well dispersed as individual particles with spherical shape and showed an average diameter about 138 nm. With the limiting size less than 200 nm, these conjugate micelles could beneficial for more drug accumulation in solid tumors due to Enhanced Permeation and Retention effect (EPR effect) [26]. The hydrophobic aggregation ability played an important role to form the micelles and protect the hydrophobic drugs from the cleavage of the system. In this respect, the critical micelle concentrations (CMC) of these conjugates could be used as the fundamental parameter to characterize the thermodynamic stability of micelles (Figure 5). The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of the P123-DTX conjugates was determined using the fluorescence probe technique as we described previously [24]. The fluorescence intensity ratios of pyrene at 373 and 383 nm (I373/I383, I1/I3) were calculated and plotted against the concentration logarithm of the P123-DTX conjugates. It could be seen in Figure 5, as the polymer concentration increased above the CMC, the I1/I3 value experienced a rapid decline process, because the probe pyrene was incorporated into the hydrophobic core of the
7 Materials 2015, micelles. The CMC was determined by taking the inflection point of the pyrene I1/I3 ratio plot. The measured CMC value of the P123-S-A-L-DTX conjugates was ~ mol/l (~502.2 µg/ml). It also indicated that the Pluronic P123-DTX conjugates could form micelles in lower concentration, which would be helpful to form the stable micelles. A B Figure 4. Characterization of P123 DTX conjugate micelles: (A) TEM image and (B) particle size by DLS. Figure 5. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) measurement using pyrene as fluorescent probe: plots of the intensity ratio (I1/I3) from pyrene emission spectra versus the log of concentration for ph sensitive P123-DTX conjugate ([pyrene] = M). In our study, the ph sensitive P123-DTX conjugate micelles were added into rat plasma and the amount of released DTX and DTX-L were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (Figure 6). Although DTX was linked to P123 by covalent hydrazone bond, both of the ph sensitive micelles formed by conjugates still exhibited a sustained release profile within 10 h. After released for 48 h, the cumulative release amount of DTX (and DTX-L) from conjugate micelles was only about 19.5%. These observations showed that our prepared conjugate micelles had a favorable stability around blood circulation.
8 Materials 2015, Figure 6. Stability of P123-DTX conjugate micelles following incubation in mouse plasma in at 37 C for different times. The amount of DTX was calculated as the sum of DTX and DTX-L by HPLC method. Data are expressed as means ± SD (Standard Deviation) (n = 3). We examined the DTX release from the two P123-DTX conjugate micelles at different ph Values. In order to release the drug at target sites (at mildly acidic ph level), the acid-cleavable hydrazone linkage was introduced to combine DTX and Pluronic P123. The P123-DTX conjugate micelles were incubated for 48 h at ph 5.0, 6.5 and 7.4. The total extent of the released drug was calculated as the sum of DTX and DTX-L using the HPLC method. The results showed that the hydrolysis rates of hydrazone linkage in the conjugate micelles were ph-dependent (Figure 7). As expected, DTX released more efficiently at lower acidic ph (ph 5.0), and the release extents of the conjugate micelles could reached above the 80% (~84.9%) at 48 h. It was near six times higher than the release profile at physiological ph level (ph 7.4), which was only about 13.4% released from the conjugate micelles at 48 h. Figure 7. ph-dependent release of DTX from the P123-DTX conjugate micelles. Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3).
9 Materials 2015, Experimental Section 3.1. Materials Pluronic P123 (P123) was purchased from BASF China Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Docetaxel and Duopafei were provided by Qilu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Ji nan, China). 4-oxopentanoic acid (levulic acid, LEV), adipic dihydrazide (ADH), Succinic anhydride (Suc), 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC HCL), N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt (Sulfo-NHS), 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP), and pyrene were all obtained from Aladdin (Shanghai, China). All other chemicals and reagents used were of analytical grade or higher and obtained commercially Synthesis of Levulic Acid Derivatives of DTX (DTX-L) DTX was esterified on 2'-hydroxyl of DTX with LEV to afford the respective ester derivate, designated as DTX-L, with a little difference to the procedure previously reported. Briefly, EDC HCL (24.5 mg) and LEV (17.6 mg) were dissolved in 2 ml Dichloromethane (DCM) and cooled for 20 min to 4 C. Then 3 ml DCM solution of DTX (92.5 mg) and DMAP (18.4 mg) was added dropwisely. The reaction was stirred at 4 C for 8 h. Then DCM was evaporated and ethyl acetate was added to dissolve the product. The organic phase was collected and washed with 10 ml solution of HCl (1%, w/v) and 10 ml of ultrapure water twice, respectively, to remove DMAP and unreacted succinic anhydride. Magnesium sulfate was added to the organic phase and incubated overnight to remove remained water. The final solution was subjected to silica gel column chromatography for purification Synthesis of Hydrazone Contained Derivatives of DTX (DTX-L-A) The hydrazone contained derivatives of DTX was achieved by the reaction of the DTX-L and adipic dihydrazide (ADH). Briefly, DTX-L (20.6 mg) and ADH (40.2 mg) were dissolved in 3 ml anhydrous methanol (MEOH) under stirring at 60 C. The reaction was performed for 4 h after addition of acetic acid (AA, 40 µl/ml of reaction mixture). Then the reaction solution was cooled to 25 C, filtered and recrystallized from methanol. Finally, silica gel column chromatography was used for purification Synthesis of Carboxyl Contained Derivatives of Pluronic P123 (P123-S) To obtain the carboxyl contained derivatives of Pluronic P123, the Succinic anhydride (Suc) was used to react with the hydroxyl group of the Pluronic P123. Briefly, Pluronic P123 (123.5 mg) and Succinic anhydride (45.7 mg) were dissolved in 5 ml DCM, and DMAP (23.9 mg) was added under stirring condition. The reaction was performed for 24 h at 25 C. Then DCM was evaporated and methanol was added to dissolve the product and finally dialyzed against distilled water (Molecular Weight (MW) cutoff 3500 Da) for 48 h and lyophilized Synthesis of Pluronic P123-DTX Conjugate Contained Hydrazone Bond (P123 -DTX) Pluronic P123-DTX conjugates contained one hydrazone bond were synthesized by the reaction between DTX-L-A and P123-S. Briefly, P123-S (89.5 mg), EDC HCL (25.5 mg) and Sulfo-NHS (17.8 mg) were dissolved in 3 ml dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and react for 5 h at 4 C to afford the
10 Materials 2015, Sulfo-NHS-S-P123. Subsequently, 4 ml DMSO solution of DTX-L-A (21.7 mg) and DMAP (19.3 mg) was added dropwisely. The reaction was stirred at 25 C for 24 h. Then the reaction solution was dialyzed against phosphate buffer (ph 7.4) (MW cutoff 3500 Da) for 48 h and lyophilized [24] Preparation and Characterization of ph Sensitive Pluronic P123-DTX Conjugate Micelles The ph sensitive P123-DTX conjugate micelles were prepared by a dialysis method: lyophilized P123-DTX conjugates were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (total concentration 150 mg/ml). The resulting suspension was dialyzed against phosphate buffer (ph 7.4) (MW cutoff 3500 Da) for 36 h. The weight percentage (wt%) of DTX in the two conjugates was determined using an UV-Vis spectrophotometer based on our previous study [24]. The hydrodynamic particle sizes of these conjugate micelles were evaluated by dynamic light scattering (DLS) (Beckman Coulter Inc., Brea, CA, USA). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was employed to visualize the morphology of P123-DTX conjugate micelles with the phosphotungstic acid method Determination of Critical Micelle Concentration The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of the ph sensitive conjugates were determined using the fluorescence probe technique as we described previously [24]. Briefly, P123-DTX conjugate micelles solutions with the concentration ranging from to M were equilibrated with a fixed concentration of pyrene, M. At the fixed excitation wavelength of 334 nm, the emission spectras were scanned from 350 to 500 nm. The fluorescence intensity ratios of pyrene at 373 and 383 nm (I373/I383, I1/I3) were calculated and plotted against the concentration logarithm of the P123-DTX conjugate. The CMC was obtained from the threshold concentration of self-assembled micelles Stability of P123-DTX Conjugate Micelles against Mouse Serum To better determinate the stability of the conjugate micelles, we also detected the drug release situations against the rat plasma. The study were carried out in mouse plasma at 37 C for up to 48 h according to the method another DTX conjugate mentioned [26] with a little difference. Briefly, 0.5 ml solution of the P123-DTX conjugate micelles and DTX/P123 micelles (all with an equivalent DTX concentration of 700 µg/ml) were measured and added into 2.5 ml of rat plasma at 37 C. The amounts of released DTX and DTX-L at different time were quantified by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) analysis (Shimadzu Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan) on a C18 column with acetonitrile/water (50:50) as eluting solution at a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min Assay of in Vitro Drug Release The in vitro release of drug from the P123-DTX conjugate micelles was investigated using the dialysis method we described previously [24]. Briefly, 2 ml of the P123-DTX conjugate micelles solutions (both diluted at an equivalent DTX concentration of ~100 µg/ml) were placed into the pre-swelled dialysis bags (MW 3500 Da) and then dialyzed against 10 ml of phosphate buffer (ph 5.0, 6.5 and 7.4) containing 0.5% Tween 80 at 37 ± 0.5 C under oscillation at 100 r/min. At selected time intervals, the solutions were sampled. Released DTX and DTX-L was analyzed by the HPLC method.
11 Materials 2015, Conclusions We synthesized the ph sensitive Pluronic P123-DTX conjugates by the combination between the Pluronic P123 and the drug docetaxel via acid-cleavage hydrazone bonds. With a low critical micelle concentration (CMC), these ph sensitive P123-DTX conjugates could self-assemble into nano-size polymeric micelles in aqueous solution. The spherical morphology and particle size of the prepared nano-micelles were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS), respectively. With the introduction of the covalent hydrazone bonds, these ph sensitive polymeric conjugate micelles exhibited their stability against the rat plasma, and showed a ph dependent drug release behavior. These results showed that our prepared ph sensitive Pluronic P123-DTX conjugate micelles had the potential to balance the stability and drug release. And they might offer a great benefit for drug delivery and controlling the drug release. Author Contributions Yanchao Liang contributed to the whole process of the preparation of conjugate micelles, characterization, drug-release tests, interpretation of the results and preparation of the manuscript. Na Zhang supervised the whole procedure and also contributed to the data interpretation and preparation of the manuscript. Zhihui Su contributed to the preparation of the micelles and the drug-release tests. Yao Yao contributed to characterization tests and data extraction. Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1. Rodriguez, L.C.; Chari, J.; Aghyarian, S.; Gindri, I.M.; Kosmopoulos, V.; Rodrigues, D.C. Preparation and characterization of injectable brushite filled-poly (methyl methacrylate) bone cement. Materials 2014, 7, Keller, S.; Wilson, J.T.; Patilea, G.I.; Kern, H.B.; Convertine, A.J.; Stayton, P.S. Neutral polymer micelle carriers with ph-responsive, endosome-releasing activity modulate antigen trafficking to enhance CD8 + T cell responses. J. Controll. Release 2014, 191, Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Tan, L.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, F.; Wei, Y.; Qian, Z. PEG PCL based micelle hydrogels as oral docetaxel delivery systems for breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Tao, W.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Mei, L.; Feng, S.-S. The effect of autophagy inhibitors on drug delivery using biodegradable polymer nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2014, 35, Chen, W.; Zhang, J.Z.; Hu, J.; Guo, Q.; Yang, D. Preparation of amphiphilic copolymers for covalent loading of paclitaxel for drug delivery system. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2014, 52, Ke, X.; Ng, V.W.L.; Ono, R.J.; Chan, J.M.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Wang, Y.; Hedrick, J.L.; Yang, Y.Y. Role of non-covalent and covalent interactions in cargo loading capacity and stability of polymeric micelles. J. Controll. Release 2014, 193, 9 26.
12 Materials 2015, Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K. Progress of drug-loaded polymeric micelles into clinical studies. J. Controll. Release 2014, 190, Sun, Q.; Radosz, M.; Shen, Y. Challenges in design of translational nanocarriers. J. Controll. Release 2012, 164, Kopeček, J. Polymer-drug conjugates: Origins, progress to date and future directions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, Deng, C.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, R.; Meng, F.; Zhong, Z. Biodegradable polymeric micelles for targeted and controlled anticancer drug delivery: Promises, progress and prospects. Nano Today 2012, 7, Hoffman, A.S. Stimuli-responsive polymers: Biomedical applications and challenges for clinical translation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, Gao, G.H.; Li, Y.; Lee, D.S. Environmental ph-sensitive polymeric micelles for cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy. J. Controll. Release 2013, 169, Quader, S.; Cabral, H.; Mochida, Y.; Ishii, T.; Liu, X.; Toh, K.; Kinoh, H.; Miura, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Selective intracellular delivery of proteasome inhibitors through ph-sensitive polymeric micelles directed to efficient antitumor therapy. J. Controll. Release 2014, 188, Nakamura, H.; Etrych, T.; Chytil, P.; Ohkubo, M.; Fang, J.; Ulbrich, K.; Maeda, H. Two step mechanisms of tumor selective delivery of N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide copolymer conjugated with pirarubicin via an acid-cleavable linkage. J. Controll. Release 2014, 174, Li, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, J.; Huang, Y. Doxorubicin-loaded, charge reversible, folate modified HPMA copolymer conjugates for active cancer cell targeting. Biomaterials 2014, 35, Elsadek, B.; Graeser, R.; Warnecke, A.; Unger, C.; Saleem, T.; El-Melegy, N.; Madkor, H.; Kratz, F. Optimization of an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin that is cleaved by prostate-specific antigen. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, Kratz, F. INNO-206 (DOXO-EMCH), an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin under development for phase II studies. Curr. Bioact. Comp. 2011, 7, Graeser, R.; Esser, N.; Unger, H.; Fichtner, I.; Zhu, A.; Unger, C.; Kratz, F. INNO-206, the (6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin), shows superior antitumor efficacy compared to doxorubicin in different tumor xenograft models and in an orthotopic pancreas carcinoma model. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, Zhao, P.; Astruc, D. Docetaxel nanotechnology in anticancer therapy. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, Etrych, T.S.; S i rova, M.; Starovoytova, L.; R i hova, B.; Ulbrich, K. HPMA copolymer conjugates of paclitaxel and docetaxel with ph-controlled drug release. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, Journo-Gershfeld, G.; Kapp, D.; Shamay, Y.; Kopeček, J.; David, A. Hyaluronan oligomers-hpma copolymer conjugates for targeting paclitaxel to CD44-overexpressing ovarian carcinoma. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, Alani, A.W.; Bae, Y.; Rao, D.A.; Kwon, G.S. Polymeric micelles for the ph-dependent controlled, continuous low dose release of paclitaxel. Biomaterials 2010, 31,
13 Materials 2015, Liu, F.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, N. Tumor-specific delivery and therapy by double-targeted DTX-CMCS-PEG-NGR conjugates. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N. Pluronic P123-docetaxel conjugate micelles: Synthesis, characterization, and antitumor activity. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Watanabe, W. Physical and chemical stability of drug nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, Liu, F.; Feng, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N. Synthesis, characterization and antitumor evaluation of CMCS DTX conjugates as novel delivery platform for docetaxel. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 451, by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (
Dual-Responsive Polymer Micelles for. Target-Cell-Specific Anticancer Drug Delivery
 Dual-Responsive Polymer Micelles for Target-Cell-Specific Anticancer Drug Delivery Xing Guo, Chunli Shi, Guang Yang, Jie Wang, Zhenghong Cai, and Shaobing Zhou,, * Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies
Dual-Responsive Polymer Micelles for Target-Cell-Specific Anticancer Drug Delivery Xing Guo, Chunli Shi, Guang Yang, Jie Wang, Zhenghong Cai, and Shaobing Zhou,, * Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information For Intracellularly Acid-Switchable Multifunctional Micelles for Combinational Photo/Chemotherapy of the Drug Resistant Tumor Tingting Wang +,#, Dangge Wang +,#, Haijun Yu +, *,
Supporting Information For Intracellularly Acid-Switchable Multifunctional Micelles for Combinational Photo/Chemotherapy of the Drug Resistant Tumor Tingting Wang +,#, Dangge Wang +,#, Haijun Yu +, *,
# Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems # This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2005
 Supporting Information Multifunctional Polymeric Micelles with Folate-Mediated Cancer Cell Targeting and ph-triggered Drug Releasing Properties for Active Intracellular Drug Delivery Younsoo Bae, Woo-Dong
Supporting Information Multifunctional Polymeric Micelles with Folate-Mediated Cancer Cell Targeting and ph-triggered Drug Releasing Properties for Active Intracellular Drug Delivery Younsoo Bae, Woo-Dong
Title: Calcium phosphate-reinforced reduction-sensitive hyaluronic acid micelles for
 Title: Calcium phosphate-reinforced reduction-sensitive hyaluronic acid micelles for delivering paclitaxel in cancer therapy Bing Deng a,1, Mengxin Xia a,1, Jin Qian a, Rui Li a, Lujia Li a,b, Jianliang
Title: Calcium phosphate-reinforced reduction-sensitive hyaluronic acid micelles for delivering paclitaxel in cancer therapy Bing Deng a,1, Mengxin Xia a,1, Jin Qian a, Rui Li a, Lujia Li a,b, Jianliang
Supporting information
 S1 Supporting information Biodegradable Injectable Polymer Systems Exhibiting Temperature-Responsive Irreversible Sol-to-Gel Transition by Covalent Bond Formation Yasuyuki YOSHIDA 1,2, Keisuke KAWAHARA
S1 Supporting information Biodegradable Injectable Polymer Systems Exhibiting Temperature-Responsive Irreversible Sol-to-Gel Transition by Covalent Bond Formation Yasuyuki YOSHIDA 1,2, Keisuke KAWAHARA
Coordination-responsive Selenium-containing Polymer Micelles for. Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science Coordination-responsive Selenium-containing Polymer Micelles for Controlled Drug Release Wei Cao, a Yang Li, b Yu Yi, a Shaobo Ji, a Lingwu
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science Coordination-responsive Selenium-containing Polymer Micelles for Controlled Drug Release Wei Cao, a Yang Li, b Yu Yi, a Shaobo Ji, a Lingwu
Electronic Supplementary Material
 Electronic Supplementary Material PAMAM Dendrimers Bearing Electron-Donating Chromophores: Fluorescence and Electrochemical Properties Bing-BingWang a, Xin Zhang a, Ling Yang a, Xin-Ru Jia* a, Yan Ji a,
Electronic Supplementary Material PAMAM Dendrimers Bearing Electron-Donating Chromophores: Fluorescence and Electrochemical Properties Bing-BingWang a, Xin Zhang a, Ling Yang a, Xin-Ru Jia* a, Yan Ji a,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Polymer Micelles Stabilization-n-Demand through Reversible Photocrosslinking 1. Synthesis and Characterization of Diblock Copolymers Materials. Cu(I)Br, 2-Bromo-2-methylpropionyl
Supporting Information Polymer Micelles Stabilization-n-Demand through Reversible Photocrosslinking 1. Synthesis and Characterization of Diblock Copolymers Materials. Cu(I)Br, 2-Bromo-2-methylpropionyl
Characterization and Modification of Low Molecular Water-Soluble Chitosan for Pharmaceutical Application
 Characterization and Modification of Low Molecular Water-Soluble Chitosan Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2003, Vol. 24, No. 9 1303 Characterization and Modification of Low Molecular Water-Soluble Chitosan for
Characterization and Modification of Low Molecular Water-Soluble Chitosan Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2003, Vol. 24, No. 9 1303 Characterization and Modification of Low Molecular Water-Soluble Chitosan for
2. Block Copolymers. 2.1 Micelle and gel formation in amphiphilic block copolymers. 2.2 Phase behavior in the bulk. 2.3 Structures in thin films
 2. Block Copolymers 2.1 Micelle and gel formation in amphiphilic block copolymers 2.2 Phase behavior in the bulk 2.3 Structures in thin films I.W. Hamley, Block Copolymers in Solution. Wiley 2005. 1 Block
2. Block Copolymers 2.1 Micelle and gel formation in amphiphilic block copolymers 2.2 Phase behavior in the bulk 2.3 Structures in thin films I.W. Hamley, Block Copolymers in Solution. Wiley 2005. 1 Block
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 278 (2006) 60 66
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 278 (2006) 60 66 Synthesis and characterization of polyion complex micelles between poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted poly(aspartic acid) and cetyltrimethyl
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 278 (2006) 60 66 Synthesis and characterization of polyion complex micelles between poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted poly(aspartic acid) and cetyltrimethyl
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information ph- and Amylase-Responsive Carboxymethyl Starch/Poly(2-Isobutyl-acrylic acid) Hybrid Microgels as Effective Enteric Carriers for Oral Insulin Delivery Liang Liu, a,b Ying Zhang,
Supporting Information ph- and Amylase-Responsive Carboxymethyl Starch/Poly(2-Isobutyl-acrylic acid) Hybrid Microgels as Effective Enteric Carriers for Oral Insulin Delivery Liang Liu, a,b Ying Zhang,
ph Switchable and Fluorescent Ratiometric Squarylium Indocyanine Dyes as Extremely Alkaline Sensors
 ph Switchable and Fluorescent Ratiometric Squarylium Indocyanine Dyes as Extremely Alkaline Sensors Jie Li, Chendong Ji, Wantai Yang, Meizhen Yin* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
ph Switchable and Fluorescent Ratiometric Squarylium Indocyanine Dyes as Extremely Alkaline Sensors Jie Li, Chendong Ji, Wantai Yang, Meizhen Yin* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Tenofoviri disoproxili fumaras)
 C 19 H 30 N 5 O 10 P. C 4 H 4 O 4 Relative molecular mass. 635.5. Chemical names. bis(1-methylethyl) 5-{[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl}-5-oxo-2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-λ 5 - phosphanonanedioate
C 19 H 30 N 5 O 10 P. C 4 H 4 O 4 Relative molecular mass. 635.5. Chemical names. bis(1-methylethyl) 5-{[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl}-5-oxo-2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-λ 5 - phosphanonanedioate
DELFIA Eu-DTPA ITC Chelate & Europium Standard
 AD0026P-3 (en) 1 DELFIA Eu-DTPA ITC Chelate & AD0021 Europium Standard For Research Use Only INTRODUCTION DELFIA Eu-DTPA ITC Chelate is optimized for the europium labelling of proteins and peptides for
AD0026P-3 (en) 1 DELFIA Eu-DTPA ITC Chelate & AD0021 Europium Standard For Research Use Only INTRODUCTION DELFIA Eu-DTPA ITC Chelate is optimized for the europium labelling of proteins and peptides for
DELFIA Tb-N1 DTA Chelate & Terbium Standard
 AD0029P-1 (en) 1 DELFIA Tb-N1 DTA Chelate & AD0012 Terbium Standard For Research Use Only INTRODUCTION DELFIA Tb-N1 DTA Chelate is optimized for the terbium labeling of proteins and peptides for use in
AD0029P-1 (en) 1 DELFIA Tb-N1 DTA Chelate & AD0012 Terbium Standard For Research Use Only INTRODUCTION DELFIA Tb-N1 DTA Chelate is optimized for the terbium labeling of proteins and peptides for use in
A New Design for Light-Breakable Polymer Micelles
 Supporting Information A New Design for Light-Breakable Polymer Micelles 1. Synthesis and Characterization of Diblock Copolymer Materials. Dioxane and THF were purified by distillation from sodium with
Supporting Information A New Design for Light-Breakable Polymer Micelles 1. Synthesis and Characterization of Diblock Copolymer Materials. Dioxane and THF were purified by distillation from sodium with
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A single design strategy for dual sensitive ph probe with a suitable range to map ph in living cells Kang-Kang Yu, Ji-Ting Hou, Kun Li, * Qian Yao, Jin Yang, Ming-Yu Wu, Yong-Mei
Supporting Information A single design strategy for dual sensitive ph probe with a suitable range to map ph in living cells Kang-Kang Yu, Ji-Ting Hou, Kun Li, * Qian Yao, Jin Yang, Ming-Yu Wu, Yong-Mei
EFFECT OF COMPRESSED CO 2 ON THE PROPERTIES OF AOT IN ISOOCTANE REVERSE MICELLAR SOLUTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO RECOVER NANOPARTICLES
 EFFECT OF COMPRESSED CO 2 ON THE PROPERTIES OF AOT IN ISOOCTANE REVERSE MICELLAR SOLUTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO RECOVER NANOPARTICLES Dongxia Liu, Jianling Zhang, Tiancheng Mu, Jing Chen, Weize Wu, Jun
EFFECT OF COMPRESSED CO 2 ON THE PROPERTIES OF AOT IN ISOOCTANE REVERSE MICELLAR SOLUTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO RECOVER NANOPARTICLES Dongxia Liu, Jianling Zhang, Tiancheng Mu, Jing Chen, Weize Wu, Jun
A ph-sensitive prodrug micelle self-assembled from multi-doxorubicin-tailed. PCFM Lab of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 A ph-sensitive prodrug micelle self-assembled from multi-doxorubicin-tailed polyethylene glycol
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 A ph-sensitive prodrug micelle self-assembled from multi-doxorubicin-tailed polyethylene glycol
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE (SF298) (Continuation Sheet)
 REPRT DCUMENTATIN PAGE (SF298) (Continuation Sheet) Key Features of the Report: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) We have synthesized a polymer that could form both unimolecular micelles and inverse micelles, depending
REPRT DCUMENTATIN PAGE (SF298) (Continuation Sheet) Key Features of the Report: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) We have synthesized a polymer that could form both unimolecular micelles and inverse micelles, depending
DELFIA Tb-DTPA ITC Chelate & Terbium Standard
 AD0035P-2 (en) 1 DELFIA Tb-DTPA ITC Chelate & AD0029 Terbium Standard For Research Use Only INTRODUCTION DELFIA Tb-DTPA ITC Chelate is optimized for the terbium labelling of proteins and peptides for use
AD0035P-2 (en) 1 DELFIA Tb-DTPA ITC Chelate & AD0029 Terbium Standard For Research Use Only INTRODUCTION DELFIA Tb-DTPA ITC Chelate is optimized for the terbium labelling of proteins and peptides for use
Auto-assemblage de copolymères à blocs amphiphiles Suming LI
 Auto-assemblage de copolymères à blocs amphiphiles Suming LI Institut Européen des Membranes Université de Montpellier 34095 Montpellier, France Self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers Colloidal
Auto-assemblage de copolymères à blocs amphiphiles Suming LI Institut Européen des Membranes Université de Montpellier 34095 Montpellier, France Self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers Colloidal
Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic. etching of gold nanorods
 Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic etching of gold nanorods Xin Liu, Shuya Zhang, Penglong Tan, Jiang Zhou, Yan Huang, Zhou Nie* and Shouzhuo Yao State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic etching of gold nanorods Xin Liu, Shuya Zhang, Penglong Tan, Jiang Zhou, Yan Huang, Zhou Nie* and Shouzhuo Yao State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
UV Tracer TM Maleimide NHS ester
 UV Tracer TM Maleimide HS ester Product o.: 1020 Product ame: UV-Tracer TM Maleimide-HS ester Chemical Structure: Chemical Composition: C 41 H 67 5 18 Molecular Weight: 1014.08 Appearance: Storage: Yellow
UV Tracer TM Maleimide HS ester Product o.: 1020 Product ame: UV-Tracer TM Maleimide-HS ester Chemical Structure: Chemical Composition: C 41 H 67 5 18 Molecular Weight: 1014.08 Appearance: Storage: Yellow
LANCE Eu-W1024 ITC Chelate & Europium Standard AD0013 Development grade
 AD0017P-4 (en) 1 LANCE Eu-W1024 ITC Chelate & Europium Standard AD0013 Development grade INTRODUCTION Fluorescent isothiocyanato-activated (ITC-activated) Eu-W1024 chelate is optimized for labelling proteins
AD0017P-4 (en) 1 LANCE Eu-W1024 ITC Chelate & Europium Standard AD0013 Development grade INTRODUCTION Fluorescent isothiocyanato-activated (ITC-activated) Eu-W1024 chelate is optimized for labelling proteins
An Orthogonal Array Optimization of Lipid-like Nanoparticles for. mrna Delivery in Vivo
 Supporting Information An rthogonal Array ptimization of Lipid-like Nanoparticles for mrna Delivery in Vivo Bin Li, Xiao Luo, Binbin Deng, Junfeng Wang, David W. McComb, Yimin Shi, Karin M.L. Gaensler,
Supporting Information An rthogonal Array ptimization of Lipid-like Nanoparticles for mrna Delivery in Vivo Bin Li, Xiao Luo, Binbin Deng, Junfeng Wang, David W. McComb, Yimin Shi, Karin M.L. Gaensler,
Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information A Novel and Facile Zn-mediated Intramolecular Five-membered Cyclization of β-tetraarylporphyrin Radicals from β-bromotetraarylporphyrins Dong-Mei Shen, Chao Liu, Qing-Yun
Electronic Supplementary Information A Novel and Facile Zn-mediated Intramolecular Five-membered Cyclization of β-tetraarylporphyrin Radicals from β-bromotetraarylporphyrins Dong-Mei Shen, Chao Liu, Qing-Yun
Hydrogel patterning by diffusion through the matrix and subsequent light-triggered chemical immobilization
 Supporting Information ydrogel patterning by diffusion through the matrix and subsequent light-triggered chemical immobilization Zheyi Yi, Yu Zhang, Sujit Kootala, Jöns ilborn, and Dmitri A. ssipov* Science
Supporting Information ydrogel patterning by diffusion through the matrix and subsequent light-triggered chemical immobilization Zheyi Yi, Yu Zhang, Sujit Kootala, Jöns ilborn, and Dmitri A. ssipov* Science
TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010)
 June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable. Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors
 Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
Self-assembled ZnO nanoparticle capsules for carrying and delivering isotretinoin to cancer cells
 Supporting Information Self-assembled ZnO nanoparticle capsules for carrying and delivering isotretinoin to cancer cells Wei Zhao, Ji-Shi Wei, Peng Zhang, Jie Chen, Ji-Lie Kong,,, * Lian-Hua Sun, Huan-Ming
Supporting Information Self-assembled ZnO nanoparticle capsules for carrying and delivering isotretinoin to cancer cells Wei Zhao, Ji-Shi Wei, Peng Zhang, Jie Chen, Ji-Lie Kong,,, * Lian-Hua Sun, Huan-Ming
Supporting Information for. Boronic Acid Functionalized Aza-Bodipy (azabdpba) based Fluorescence Optodes for the. analysis of Glucose in Whole Blood
 Supporting Information for Boronic Acid Functionalized Aza-Bodipy (azabdpba) based Fluorescence Optodes for the analysis of Glucose in Whole Blood Yueling Liu, Jingwei Zhu, Yanmei Xu, Yu Qin*, Dechen Jiang*
Supporting Information for Boronic Acid Functionalized Aza-Bodipy (azabdpba) based Fluorescence Optodes for the analysis of Glucose in Whole Blood Yueling Liu, Jingwei Zhu, Yanmei Xu, Yu Qin*, Dechen Jiang*
Development of Degradable Stealth Nanospheres for Controlled Delivery of Anticancer Drugs
 Development of Degradable Stealth Nanospheres for Controlled Delivery of Anticancer Drugs Emmanuel. Akala, R.Ph., Ph.D. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy First Generation Polymeric
Development of Degradable Stealth Nanospheres for Controlled Delivery of Anticancer Drugs Emmanuel. Akala, R.Ph., Ph.D. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy First Generation Polymeric
Caution: For Laboratory Use. A product for research purposes only. Eu-W1024 ITC Chelate & Europium Standard. Product Number: AD0013
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET Lance Caution: For Laboratory Use. A product for research purposes only. Eu-W1024 ITC Chelate & Europium Standard Product Number: AD0013 INTRODUCTION: Fluorescent isothiocyanato-activated
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET Lance Caution: For Laboratory Use. A product for research purposes only. Eu-W1024 ITC Chelate & Europium Standard Product Number: AD0013 INTRODUCTION: Fluorescent isothiocyanato-activated
Caution: For Laboratory Use. A product for research purposes only. Eu-W1284 Iodoacetamido Chelate & Europium Standard. Product Number: AD0014
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET Lance Caution: For Laboratory Use. A product for research purposes only. Eu-W1284 Iodoacetamido Chelate & Europium Standard Product Number: AD0014 INTRODUCTION: Iodoacetamido-activated
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET Lance Caution: For Laboratory Use. A product for research purposes only. Eu-W1284 Iodoacetamido Chelate & Europium Standard Product Number: AD0014 INTRODUCTION: Iodoacetamido-activated
Organic Semiconducting Nanoparticles as Efficient Photoacoustic Agents for Lightening Early Thrombus and
 Supporting Information rganic Semiconducting anoparticles as Efficient Photoacoustic Agents for Lightening Early Thrombus and Monitoring Thrombolysis in Living Mice Cao Cui,, Zhen Yang,, Xiang Hu, Jinjun
Supporting Information rganic Semiconducting anoparticles as Efficient Photoacoustic Agents for Lightening Early Thrombus and Monitoring Thrombolysis in Living Mice Cao Cui,, Zhen Yang,, Xiang Hu, Jinjun
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information ovel pseudo[2]rotaxanes constructed by selfassembly of dibenzyl
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information ovel pseudo[2]rotaxanes constructed by selfassembly of dibenzyl
Protection of Photoactivity of Photosensitizers by Amphiphilic Polysaccharide Micelles *
 Chinese Journal of Polymer Science Vol. 32, No. 10, (2014), 1413 1418 Chinese Journal of Polymer Science Chinese Chemical Society Institute of Chemistry, CAS Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2014 Note
Chinese Journal of Polymer Science Vol. 32, No. 10, (2014), 1413 1418 Chinese Journal of Polymer Science Chinese Chemical Society Institute of Chemistry, CAS Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2014 Note
Supporting Information for. Interaction of Spin-Labeled HPMA-based Nanoparticles with Human Blood Plasma Proteins
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Interaction of Spin-Labeled HPMA-based Nanoparticles with Human Blood
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Interaction of Spin-Labeled HPMA-based Nanoparticles with Human Blood
Supporting Information. Silver Nanoparticle-Gated Mesoporous Silica-Coated Gold Nanorods. Low Premature Release and Multifunctional
 Supporting Information Silver Nanoparticle-Gated Mesoporous Silica-Coated Gold Nanorods (AuNR@MS@AgNPs): Low Premature Release and Multifunctional Cancer Theranostic Platform Zhehua Zhang, a, Changhui
Supporting Information Silver Nanoparticle-Gated Mesoporous Silica-Coated Gold Nanorods (AuNR@MS@AgNPs): Low Premature Release and Multifunctional Cancer Theranostic Platform Zhehua Zhang, a, Changhui
ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) ARTESUNATI COMPRESSI ARTESUNATE TABLETS
 December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Naoya Takahashi, Keiya Hirota and Yoshitaka Saga* Supplementary material
 Supplementary material Facile transformation of the five-membered exocyclic E-ring in 13 2 -demethoxycarbonyl chlorophyll derivatives by molecular oxygen with titanium oxide in the dark Naoya Takahashi,
Supplementary material Facile transformation of the five-membered exocyclic E-ring in 13 2 -demethoxycarbonyl chlorophyll derivatives by molecular oxygen with titanium oxide in the dark Naoya Takahashi,
RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS. Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012)
 July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging
 General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging Sheng Huang, Min Bai, Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging Sheng Huang, Min Bai, Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long. Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supplementary materials. Multivalent mannose displaying nanoparticles constructed from
 Supplementary materials Multivalent mannose displaying nanoparticles constructed from poly{styrene-co-[(maleic anhydride)-alt-styrene]} Rongming Su a, Lei Li b, Xiaoping Chen a, Jiahuai Han c, Shoufa Han*,a
Supplementary materials Multivalent mannose displaying nanoparticles constructed from poly{styrene-co-[(maleic anhydride)-alt-styrene]} Rongming Su a, Lei Li b, Xiaoping Chen a, Jiahuai Han c, Shoufa Han*,a
DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR THE INTERNATIONAL PHARMACOPOEIA: CARBAMAZEPINI COMPRESSI - CARBAMAZEPINE TABLETS
 December 2015 Draft document for comment 1 2 3 4 5 6 DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR THE INTERNATIONAL PHARMACOPOEIA: CARBAMAZEPINI COMPRESSI - CARBAMAZEPINE TABLETS (December 2015) REVISED DRAFT FOR COMMENT Should
December 2015 Draft document for comment 1 2 3 4 5 6 DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR THE INTERNATIONAL PHARMACOPOEIA: CARBAMAZEPINI COMPRESSI - CARBAMAZEPINE TABLETS (December 2015) REVISED DRAFT FOR COMMENT Should
Supporting Information
 Investigation of self-immolative linkers in the design of hydrogen peroxide metalloprotein inhibitors Jody L. Major Jourden, Kevin B. Daniel, and Seth M. Cohen* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Investigation of self-immolative linkers in the design of hydrogen peroxide metalloprotein inhibitors Jody L. Major Jourden, Kevin B. Daniel, and Seth M. Cohen* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Supporting information to Amino-functional polyester dendrimers based on bis-mpa as nonviral vectors for sirna delivery
 Supporting information to Amino-functional polyester dendrimers based on bis-mpa as nonviral vectors for sirna delivery P. Stenström, D. Manzanares, Y. Zhang, V. Ceña and M. Malkoch* * To whom correspondence
Supporting information to Amino-functional polyester dendrimers based on bis-mpa as nonviral vectors for sirna delivery P. Stenström, D. Manzanares, Y. Zhang, V. Ceña and M. Malkoch* * To whom correspondence
Cytosolar delivery of large proteins using nanoparticlestabilized
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Cytosolar delivery of large proteins using nanoparticlestabilized nanocapsules
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Cytosolar delivery of large proteins using nanoparticlestabilized nanocapsules
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information The Effects of Spacer Length and Composition on Aptamer-Mediated Cell-Specific Targeting with Nanoscale PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Hang Xing +, [a] Ji Li +, [a] Weidong Xu,
Supporting Information The Effects of Spacer Length and Composition on Aptamer-Mediated Cell-Specific Targeting with Nanoscale PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Hang Xing +, [a] Ji Li +, [a] Weidong Xu,
Supporting Information
 Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus
 University of Groningen Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus Published in: Chemistry DOI: 10.1002/chem.201001816
University of Groningen Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus Published in: Chemistry DOI: 10.1002/chem.201001816
Europium Labeling Kit
 Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Novel ph-responsive nanovectors for controlled release of ionisable drugs
 Supplementary Information Novel ph-responsive nanovectors for controlled release of ionisable drugs Francesca Mastrotto, a Stefano Salmaso a, Cameron Alexander, b Giuseppe Mantovani b and Paolo Caliceti
Supplementary Information Novel ph-responsive nanovectors for controlled release of ionisable drugs Francesca Mastrotto, a Stefano Salmaso a, Cameron Alexander, b Giuseppe Mantovani b and Paolo Caliceti
Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Active Gold Nanoparticles. with Enzyme-Mimicking Activities for Measuring Glucose and
 Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Active Gold Nanoparticles with Enzyme-Mimicking Activities for Measuring Glucose and Lactate in Living Tissues Yihui Hu, Hanjun Cheng, Xiaozhi Zhao, Jiangjiexing Wu, Faheem
Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Active Gold Nanoparticles with Enzyme-Mimicking Activities for Measuring Glucose and Lactate in Living Tissues Yihui Hu, Hanjun Cheng, Xiaozhi Zhao, Jiangjiexing Wu, Faheem
An Investigative Study of Reactions Involving Glucosinolates and Isothiocyanates
 An Investigative Study of Reactions Involving Glucosinolates and Isothiocyanates Alzea Chrisel H. Alea 1, Diane Elaine T. Co 2 and Marissa G Noel 3* 1,2,3Chemistry Department, De La Salle University, 2401
An Investigative Study of Reactions Involving Glucosinolates and Isothiocyanates Alzea Chrisel H. Alea 1, Diane Elaine T. Co 2 and Marissa G Noel 3* 1,2,3Chemistry Department, De La Salle University, 2401
Title Revision n date
 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
Analysis of fatty acid metabolism using Click-Chemistry and HPLC-MS
 Analysis of fatty acid metabolism using Click-Chemistry and HPLC-MS Alexander J. Pérez and Helge B. Bode -Supporting Information- Contents Experimental section Supplementary figures NMR spectra Page S2
Analysis of fatty acid metabolism using Click-Chemistry and HPLC-MS Alexander J. Pérez and Helge B. Bode -Supporting Information- Contents Experimental section Supplementary figures NMR spectra Page S2
mm C3a. 1 mm C3a Time (s) C5a. C3a. Blank. 10 mm Time (s) Time (s)
 125 I-C5a (cpm) Fluorescnece Em 520nm a 4000 3000 2000 1000 c 0 5000 4000 3000 2000 Blank C5a C3a 6 0.3 mm C3a 7 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 0.3 mm C5a 0 300 600 900 1200 Time (s) 17 Fluorescnece Em 520nm Fluorescnece
125 I-C5a (cpm) Fluorescnece Em 520nm a 4000 3000 2000 1000 c 0 5000 4000 3000 2000 Blank C5a C3a 6 0.3 mm C3a 7 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 0.3 mm C5a 0 300 600 900 1200 Time (s) 17 Fluorescnece Em 520nm Fluorescnece
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products)
 Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
L-Carnosine-Derived Fmoc-Tripeptides Forming ph- Sensitive and Proteolytically Stable Supramolecular
 Supporting Information: L-Carnosine-Derived Fmoc-Tripeptides Forming ph- Sensitive and Proteolytically Stable Supramolecular Hydrogels Rita Das Mahapatra, a Joykrishna Dey* a, and Richard G. Weiss b a
Supporting Information: L-Carnosine-Derived Fmoc-Tripeptides Forming ph- Sensitive and Proteolytically Stable Supramolecular Hydrogels Rita Das Mahapatra, a Joykrishna Dey* a, and Richard G. Weiss b a
Student Handout. This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have
 Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
SYNTHESIS OF DOXORUBICIN-CYCLODEXTRIN CONJUGATES
 VOL.47 NO.9 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 1025 SYNTHESIS OF DOXORUBICIN-CYCLODEXTRIN CONJUGATES Hiroshi Tanaka, Kaichiro Kominato, Reiko Yamamoto, Takeo Yoshioka, Hiroshi Nishida, Hiroshi Tone and Rokuro
VOL.47 NO.9 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 1025 SYNTHESIS OF DOXORUBICIN-CYCLODEXTRIN CONJUGATES Hiroshi Tanaka, Kaichiro Kominato, Reiko Yamamoto, Takeo Yoshioka, Hiroshi Nishida, Hiroshi Tone and Rokuro
SUCROSE OLIGOESTERS TYPE I
 SUCROSE OLIGOESTERS TYPE I Prepared at the 71 st JECFA (2009) and published in FAO JECFA Monographs 7 (2009). A group ADI of 0-30 mg/kg bw for this substance together with sucrose esters of fatty acids,
SUCROSE OLIGOESTERS TYPE I Prepared at the 71 st JECFA (2009) and published in FAO JECFA Monographs 7 (2009). A group ADI of 0-30 mg/kg bw for this substance together with sucrose esters of fatty acids,
Catalytic decarboxylative alkylation of β-keto acids with sulfonamides via the cleavage of carbon nitrogen and carbon carbon bonds
 Catalytic decarboxylative alkylation of β-keto acids with sulfonamides via the cleavage of carbon nitrogen and carbon carbon bonds Cui-Feng Yang, Jian-Yong Wang and Shi-Kai Tian* Joint Laboratory of Green
Catalytic decarboxylative alkylation of β-keto acids with sulfonamides via the cleavage of carbon nitrogen and carbon carbon bonds Cui-Feng Yang, Jian-Yong Wang and Shi-Kai Tian* Joint Laboratory of Green
Thiol-Ene Photoimmobilization of Chymotrypsin on Polysiloxane Gels for Enzymatic Peptide Synthesis
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information for: Thiol-Ene Photoimmobilization of Chymotrypsin on Polysiloxane Gels
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information for: Thiol-Ene Photoimmobilization of Chymotrypsin on Polysiloxane Gels
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information X-Ray Responsive Nanoparticles with Triggered Release of Nitrite, a Precursor
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information X-Ray Responsive Nanoparticles with Triggered Release of Nitrite, a Precursor
Preparation and Characterization of Candesartan Cilexetil Solid Lipid Nanoparticulate Capsules
 Research Article Preparation and Characterization of Candesartan Cilexetil Solid Lipid Nanoparticulate Capsules *Surya Kiran Vuddisa, Subramanian S., Sindhu Raavi Department of Pharmaceutics, PSG College
Research Article Preparation and Characterization of Candesartan Cilexetil Solid Lipid Nanoparticulate Capsules *Surya Kiran Vuddisa, Subramanian S., Sindhu Raavi Department of Pharmaceutics, PSG College
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Developing Activity Localization Fluorescence Peptide Probe Using Thiol-Ene Click Reaction for Spatially Resolved Imaging of Caspase-8 in Live Cells Wei Liu,, Si-Jia Liu,, Yong-Qing
Supporting Information Developing Activity Localization Fluorescence Peptide Probe Using Thiol-Ene Click Reaction for Spatially Resolved Imaging of Caspase-8 in Live Cells Wei Liu,, Si-Jia Liu,, Yong-Qing
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation of Abacavir Sulphate in Bulk and Tablet Dosage Form
 RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation of Abacavir Sulphate in Bulk and Tablet Dosage Form S. LAVANYA* 1, SK. MANSURA BEGUM 1, K. NAGAMALLESWARA RAO 2, K. GAYATHRI DEVI 3 Department of pharmaceutical
RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation of Abacavir Sulphate in Bulk and Tablet Dosage Form S. LAVANYA* 1, SK. MANSURA BEGUM 1, K. NAGAMALLESWARA RAO 2, K. GAYATHRI DEVI 3 Department of pharmaceutical
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
Thermal shift binding experiments were carried out using Thermofluor 384 ELS system. Protein
 Supplementary Methods Thermal shift assays Thermal shift binding experiments were carried out using Thermofluor 384 ELS system. Protein unfolding was examined by monitoring the fluorescence of ANS (1-anilinonaphthalene-8-
Supplementary Methods Thermal shift assays Thermal shift binding experiments were carried out using Thermofluor 384 ELS system. Protein unfolding was examined by monitoring the fluorescence of ANS (1-anilinonaphthalene-8-
Electronic Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Chemistry Frontiers. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2018 Electronic Supporting Information Tetraphenylpyrazine-based luminogens with full-colour
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Chemistry Frontiers. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2018 Electronic Supporting Information Tetraphenylpyrazine-based luminogens with full-colour
Masatoshi Shibuya,Takahisa Sato, Masaki Tomizawa, and Yoshiharu Iwabuchi* Department of Organic Chemistry, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
 Oxoammonium ion/naclo 2 : An Expedient, Catalytic System for One-pot Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Carboxylic Acid with Broad Substrate Applicability Masatoshi Shibuya,Takahisa Sato, Masaki Tomizawa,
Oxoammonium ion/naclo 2 : An Expedient, Catalytic System for One-pot Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Carboxylic Acid with Broad Substrate Applicability Masatoshi Shibuya,Takahisa Sato, Masaki Tomizawa,
p-toluenesulfonic Acid-Mediated 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of
 Supporting Information for: p-toluenesulfonic Acid-Mediated 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Nitroolefins with NaN 3 for Synthesis of 4-Aryl-NH-1,2,3-triazoles Xue-Jing Quan, Zhi-Hui Ren, Yao-Yu Wang, and
Supporting Information for: p-toluenesulfonic Acid-Mediated 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Nitroolefins with NaN 3 for Synthesis of 4-Aryl-NH-1,2,3-triazoles Xue-Jing Quan, Zhi-Hui Ren, Yao-Yu Wang, and
CHAPTER-6 IDENTIFICATION, AND CHARACTERISATION OF DEGRADATION IMPURITY IN VALSARTAN TABLETS
 129 CHAPTER-6 IDENTIFICATION, AND CHARACTERISATION OF DEGRADATION IMPURITY IN VALSARTAN TABLETS 130 6.1. Introduction Valsartan is an orally active specific angiotensin II blocker effective in lowering
129 CHAPTER-6 IDENTIFICATION, AND CHARACTERISATION OF DEGRADATION IMPURITY IN VALSARTAN TABLETS 130 6.1. Introduction Valsartan is an orally active specific angiotensin II blocker effective in lowering
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 7 8 Supplementary Figure Intracellular fusion and degradation. (a) Changes of intracellular metal ion concentrations. Intracellular ion concentrations were normalized by total protein
Supplementary Figures 7 8 Supplementary Figure Intracellular fusion and degradation. (a) Changes of intracellular metal ion concentrations. Intracellular ion concentrations were normalized by total protein
A New HILIC/RP Mixed-Mode Column and Its Applications in Surfactant Analysis
 A New HILIC/RP Mixed-Mode Column and Its Applications in Surfactant Analysis X. Liu, C. Pohl, Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA, USA ABSTRACT Although reversed-phase (RP) silica columns (e.g., C18 and
A New HILIC/RP Mixed-Mode Column and Its Applications in Surfactant Analysis X. Liu, C. Pohl, Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA, USA ABSTRACT Although reversed-phase (RP) silica columns (e.g., C18 and
Core-Shell Microneedle Gel for Self-Regulated Insulin Delivery
 Supporting Information Core-Shell Microneedle Gel for Self-Regulated Insulin Delivery Jinqiang Wang,,, Yanqi Ye,,, Jicheng Yu,, Anna R. Kahkoska, Xudong Zhang,, Chao Wang,, Wujin Sun,, Ria D. Corder, #
Supporting Information Core-Shell Microneedle Gel for Self-Regulated Insulin Delivery Jinqiang Wang,,, Yanqi Ye,,, Jicheng Yu,, Anna R. Kahkoska, Xudong Zhang,, Chao Wang,, Wujin Sun,, Ria D. Corder, #
Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine. Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics
 Page 11 of 32 Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics James W. Antoon, Jiawang Liu, Adharsh P. Ponnapakkam,
Page 11 of 32 Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics James W. Antoon, Jiawang Liu, Adharsh P. Ponnapakkam,
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SEVERAL AMPHIPHILIC CHITOSAN DERIVATIVES NADHRATUN NAIIM MOBARAK & MD. PAUZI ABDULLAH
 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SEVERAL AMPHIPHILIC CHITOSAN DERIVATIVES NADHRATUN NAIIM MOBARAK & MD. PAUZI ABDULLAH School of Chemistry Science and Food Technology, Faculty of Science and Technology,
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SEVERAL AMPHIPHILIC CHITOSAN DERIVATIVES NADHRATUN NAIIM MOBARAK & MD. PAUZI ABDULLAH School of Chemistry Science and Food Technology, Faculty of Science and Technology,
CYCLOSERINI CAPSULAE - CYCLOSERINE CAPSULES (AUGUST 2015)
 August 2015 Document for comment 1 2 3 4 5 CYCLOSERINI CAPSULAE - CYCLOSERINE CAPSULES DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR THE INTERNATIONAL PHARMACOPOEIA (AUGUST 2015) DRAFT FOR COMMENT 6 Should you have any comments
August 2015 Document for comment 1 2 3 4 5 CYCLOSERINI CAPSULAE - CYCLOSERINE CAPSULES DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR THE INTERNATIONAL PHARMACOPOEIA (AUGUST 2015) DRAFT FOR COMMENT 6 Should you have any comments
Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells
 Supporting Information for Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells Sasa Zhu, Weiying Lin,* Lin Yuan State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Supporting Information for Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells Sasa Zhu, Weiying Lin,* Lin Yuan State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information 1. General Information...S2 a. Materials b. HPLC
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information 1. General Information...S2 a. Materials b. HPLC
Cross-Linked Small-Molecule Micelle-Based Drug Delivery System: Concept, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation
 Supporting Information for Cross-Linked Small-Molecule Micelle-Based Drug Delivery System: Concept, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation Chunyan Liao,, Yun Chen, Yongchao Yao, Shiyong Zhang,*,, Zhongwei
Supporting Information for Cross-Linked Small-Molecule Micelle-Based Drug Delivery System: Concept, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation Chunyan Liao,, Yun Chen, Yongchao Yao, Shiyong Zhang,*,, Zhongwei
Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids
 0 out of 9 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 84th meeting 2017 Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids This monograph was also published in:
0 out of 9 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 84th meeting 2017 Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids This monograph was also published in:
Supramolecular micelles with dual temperature and redox responses. for multi-controlled drug release
 Electronic Supplementary Information for: Supramolecular micelles with dual temperature and redox responses for multi-controlled drug release Weizhong Yuan* ab, Hui Zou a, Wen Guo a,tianxiang Shen a and
Electronic Supplementary Information for: Supramolecular micelles with dual temperature and redox responses for multi-controlled drug release Weizhong Yuan* ab, Hui Zou a, Wen Guo a,tianxiang Shen a and
Determination of Tetracyclines in Chicken by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Determination of Tetracyclines in Chicken by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Application ote Food Safety Authors Chen-Hao Zhai and Yun Zou Agilent Technologies Co. Ltd.
Determination of Tetracyclines in Chicken by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Application ote Food Safety Authors Chen-Hao Zhai and Yun Zou Agilent Technologies Co. Ltd.
Preparation, isolation and characterization of N α -Fmoc-peptide isocyanates: Solution synthesis of oligo-α-peptidyl ureas
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Preparation, isolation and characterization of N α -Fmoc-peptide isocyanates: Solution synthesis of oligo-α-peptidyl ureas Vommina V. Suresh Babu*, Basanagoud S. Patil, and Rao Venkataramanarao
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Preparation, isolation and characterization of N α -Fmoc-peptide isocyanates: Solution synthesis of oligo-α-peptidyl ureas Vommina V. Suresh Babu*, Basanagoud S. Patil, and Rao Venkataramanarao
Dual aggregation-induced emission for enhanced fluorescence. sensing of furin activity in vitro and in living cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Dual aggregation-induced emission for enhanced fluorescence
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Dual aggregation-induced emission for enhanced fluorescence
Comprehensive Study of SLE as a Sample. Preparation Tool for Bioanalysis
 Comprehensive Study of SLE as a Sample Preparation Tool for Bioanalysis Wan Wang, Warren Chen, Jerry Wang Bonna-Agela Technologies 179 Southern Street, West TEDA, Tianjin, China Abstract A simple, fast,
Comprehensive Study of SLE as a Sample Preparation Tool for Bioanalysis Wan Wang, Warren Chen, Jerry Wang Bonna-Agela Technologies 179 Southern Street, West TEDA, Tianjin, China Abstract A simple, fast,
Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C18 MM & FLARE C18+ Columns
 Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C8 MM & FLARE C8+ Columns Introduction Diamond Analytics Technical Note: T05- Avermectins are a series of 6-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives
Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C8 MM & FLARE C8+ Columns Introduction Diamond Analytics Technical Note: T05- Avermectins are a series of 6-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives
