Chemical classes of antibiotics. Structure. One third of top selling pharmaceuticals are produced from plants or microrganisms
|
|
|
- Joella Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 1 hemical classes of secondary metabolites & Identification and functional analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters ne third of top selling pharmaceuticals are produced from plants or microrganisms Lutz eide Pharmaceutical Institute Tübingen University Germany Taxus sp. 3 3 treptomyces sp. MedIL plit 27: Microbial Genomics and econdary Metabolism Paclitaxel Vancomycin tructure Most frequently prescribed classes of antibiotics (Germany, 25) 1. hemical classes of secondary metabolites 2. Identification and functional analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters hemical classes of antibiotics β-lactam antibiotics (Penicillins, Aminopenicillins, ephalosporins) Peptide antibiotics Glykopeptide antibiotics Lipopeptide antibiotics Fluorquinolones Aminomarins Tetracyclines Makrolides Aminoglycosides Lincosamides xazolidinones ulfonamides itroimidazoles etc. Red = synthetic substances Functional classes of antibiotics biosynthese Bacitracin Vancomycin Mechanism of action blue = antimycotics xazolidinones Daptomycin
2 Biosynthetic classes of antibiotics Polyketide antibiotics (1): Tetracyclines Polyketides (Tetracyclines, Macrolides) on-ribosomal peptides and amino acid derivatives (peptide antibiotics, ß-lactam antibiotics) ligosaccharides (Aminoglycosides) Isoprenoids (Fusidic acid), Meroterpenoids, other isoprenylated componds etc natural compounds from treptomyces semisynthetic Polyketide antibiotics (2): Macrolides Erythromycin and semisynthetic derivatives Amino sugar semisynthetic Lactone Desoxy sugar semisynthetic Roxithromycin Erythromycin A 14-membered lactone Tylosin 16-membered lactone Erythromycin A accharopolyspora erythrea (=treptomyces erythraeus) larithromycin Macrolides: Biosynthesis by modular polyketide synthases Polyketide antibiotics (3): Ansamacrolides Lactam Rifamycin B from Amycolatopsis mediterranei semisynthetic semisynthetic Rifamycin V Rifampicin
3 Rifamycin biosynthesis by modular polyketide synthase starter unit: 3-amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid Rif rf 19 on-ribosomal peptides Rifamycine: : Biosynthese from Amycolatopsis orientalis (= treptomyces orientalis) on-ribosomal peptides Biosynthetic gene cluster of DA 2 R DA = alcium-dependent antibiotic from treptomyces coelicolor A3(2) R A T A T -AMP -AMP R 2 R Amino acid Resistance Regulation synthesis 2kb 82kb 24kb cdap1 cdap2 cdap3 64kb non-ribosomal 2kb peptide synthetases Fatty acid synthesis cdap1 A T A T A T E A T A T A T E M1 (er) M2 (Thr) M3 (Trp) M4 (Asp) M5 (Asp) M6 (PG) DA cdap2 A T A T A T E cdap3 A T A T TE M7 (Asp) M8 (Gly) M9 (Asn) M1 (Glu/Melu) M11 (Trp) A: Adenylatiom domain; T: Thiolation domain ; : condensation domain; E: epimerization domain; TE: thioesterase domain Bacitracin Daptomycin (ubicin ): a lipopeptide fatty acid Bacitracin A from Bacillus licheniformis: a dodeka-peptide Leucine ysteine D-Glutamic L-LysineLysine acid α ε L-LeucineLeucine L-Isoleucine D-rnithine L-Asparagine D-Asparagic acid L-Isoleucine D-Phenylalanine L-istidine from treptomyces roseosporus
4 ß-Lactams: biosynthesis of penicillins und cephalosporins L-α-Aminoadipinsäure L-ystein L-Valin = A = = V 2 Isopenicillin 1. AV ynthetase: LLL-AV-Tripeptide 2. AV Racemase: LLD-AV-Tripeptid 3. AV yclase = Isopenicillin -ynthase Acyl-oA:IP Acyltransferase (Penicillin-Acylase) Aminopenicillic acid Biosynthesis of Penicillin G 2 Acyl-oA:IP Acyltransferase (Penicillin-Acylase) Isopenicillin oa 2 Benzylpenicillin = Penicillin G 3 3 Biosynthesis of cephalosporins ligosaccharides: Aminoglycosides 2 * Isopenicillin inversion at α- of AA ring expansion hydroxylation acetylation 2 2 ephalosporin similar: ephamycin from treptomyces sp. Acremonium strictum (ephalosporium acremonium), Ascomycetes Aminocyclitoles: Desoxy- deoxy streptamine streptamine treptamin 2 2 plus sugars and aminosugars 2 streptidine treptidin 2 2 Aminoglycosides Meroterpenoids: Polyketide/isoprenoid hybrid compounds treptomycin Kanamycin 3 3 eomycin 2 aphterpin from aus treptomyces sp. strain L19 (oel, alk Institute) Furanonaphthoquinone I from treptomyces sp. Gentamicin
5 on-isoprenoid/isoprenoid hybrids ther structural classes 3 hloramphenicol 2 (l) Lincomycin ovobiocin (an aminomarin antibiotic) Endophenazine A tructure econdary metabolic genes in plant and microbial genomes 1. hemical classes of secondary metabolites Plant genome: Bacterial genome: 2. Identification and functional analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters Biosynthetic genes: scattered over the genome Gene cluster Biosynthetic genes: combined in a cluster oumarin antibiotics: tructural similarities and differences oumarin antibiotics: Inhibitors of gyrase and topoisomerase IV 2 ovobiocin 3 l lorobiocin gyrase GyrA GyrA Fluoroquinolones topoisomerase IV Par Par oumermycin A1 3 3 GyrB Function: GyrB oumarins k D 1 nm introduction of negative supercoils control of DA supercoiling ParE Function: ParE decatenation of daughter chromosomes
6 Biosynthesis: Previous knowledge Deoxysugar Interaction of obiocin with the B subunit of bacterial gyrase Aminomarin ddp-glucose- 4,6-dehydratase Glucose 2 -Adenosyl-methionine Tyrosine?? ovobiocin Tyrosine*?? * resp. 4--phenylpyruvate Pojer et al. JB 278:3661 (23) creening of cosmid bank creening der osmid-genbank A B D E F G A B total 98 cosmids: twenty pools of 48 nes each A B D E F G A B pools of 8 nes single nes creening with dehydratase probe loning of the gene clusters by screening with a ddp-glucose 4,6-dehydratase probe Expect: 4-5 positive cosmids (estimated from genome size = 8.5 Mb and 98 cosmids) found: 4 positive cosmids ovobiocin cluster lorobiocin cluster Probe T gyrb R T gyrb R oumermycin A1 cluster T gyrb R
7 loning of the biosynthetic gene clusters Deoxysugar biosynthesis 2 ovobiocin 3 3 l lorobiocin 2 dtdp-1-glucose synthase 2 dtdp-glucose 4,6-dehydratase dtdp-4-keto- 6-deoxyglucose 3,5 -epimerase - P 3 ovv dtdp ovt dtdp ovw Glucose-1-phosphate oumermycin A Methyltransferase dtdp ovu dtdp-4-keto- 6-desoxy-hexose reductase dtdp ov dtdp EF G I JK L M PQRT UV WgyrBR E F G Y I JKLM halp QR TUVWZ gyrb R pary R pary E G Y I JKLM P R R R R R R gyrb TUVW R R T UVWgyrB R T UVW gyrb R T UVWgyrB R absorbance (UV 35 nm) Inactivation of T : PL examination Wild-type ovobiocin 1 2 T mutant Methylation of iose 3 l ovobiocin lorobiocin oumermycin A time (min) P P P T UVWgyrB R T UVW gyrb R T UVWgyrB R Inactivation of P : PL examination Biosynthesis of aminomarin ring Wild-type oumermycin A1 M- = Tyrosine ov ATP 2 ovi 2 ov P 45 ov P mutant Bis-desmethyl- oumermycin A1 M- = 18 ovj ydroxylation ovk??? 2 ov 2 lo-al R R=-3 R = -l EF G IJKL M PQRT UV WgyrB R E F G Y IJKLM halp QR TUVWZ gyrb R pary R E G Y IJKLM P R RRR RR gyrb TUVW R pary R
8 FRT FRT FRT FRT Inactivation of hal by PR targeting Inactivation of hal: PL analysis ~2,5 kb ~2,5 kb wild-type cosmid D1A8-h-773 integration mutant probe Eco19I Eco19I start hal Eco19I start hal Eco19I hal 14 bp orit orit Paac neo Paac Eco19I aac(3)iv 1662 bp stop hal double crossover Eco19I aac(3)iv stop hal 8576 bp 7427 bp 616 bp 4899 bp 3639 bp 2799 bp 1953 bp 1882 bp 1515 bp 1482 bp 1164 bp 992 bp MWT outhern Blot analysis. WT = wild-type 1, 2, 3 = hal - mutant 3 3 hal - mutant [M-] - : m/z = ovbiocin µg/ml 3 Wild type [M-] - : m/z = 695. l lorobiocin 2-25 µg/ml Gust et al., PA 1:1541 (23) 1662 bp Eustaquio et al. hem Biol 1:279 (23) Eustaquio et al. hem Biol 1:279 (23) Expression of the methyl transferase ov in the hal - mutant Biosynthesis of prenylated benzoate moiety 3 3 hal - mutant [M-] - : m/z = hal - mutant + empty vector ovbiocin µg/ml 3 hal - mutant + vector with [M-] - : m/z = ovbiocin µg/ml Eustaquio et al. hem Biol 1:279 (23) l ovobiocin lorobiocin oumermycin A1 E F G I JK L M PQRT UV WgyrB R E F G Y I JKLM halp QR T U VW Z gyrb R pary R E G Y I JKLM P R RRR RR gyrb TUVW R pary R Biosynthesis of prenylated benzoate moiety: ypothesis 1 Biosynthesis of prenylated benzoate moiety: ypothesis 1 2 Tyr 3 - lyase ß-oxidation prenyl transferase 2 Tyr 3 - lyase ß-oxidation prenyl transferase Tyrosine 4-oumarate Prenylated 4-hydroxybenzoate () Tyrosine 4-oumarate 4-ydroxybenzoate 4-ydroxybenzoate Prenylated 4-hydroxybenzoate () similar to: Brad Moore and coworkers Enterocin biosynthesis J Bacteriol 23 EF G I JK L M PQRT UV WgyrBR Database comparison: o PAL, no ß-oxidation enzymes! o prenyltransferase!
9 ounts (DPM) Biosynthesis of prenylated benzoate moiety Biosynthesis of prenylated benzoate moiety ovobiocin 3 l lorobiocin 2 l ovobiocin lorobiocin Database comparison: 3 3 oumermycin A1 Dehydrogenase o sequence homology lass II aldolase E F G I JK L M PQRT UV WgyrB R E F G Y I JKLM halp QR T U VW Z gyrb R pary R E G Y I JKLM P R RRR RR gyrb TUVW R pary R E F G I JK L M PQRT UV WgyrB R E F G Y I JKLM halp QR T U VW Z gyrb R pary R E G Y I JKLM P R RRR RR gyrb TUVW R pary R Biosynthesis of prenylated benzoate moiety ypothesis 2 (hen & Walsh 21) Inactivation of Q 2 ov ov 2 ovi ov 2 2 A Wild-type (WT) I Bam PvuII probe Q (975 bp) B/P PvuII 1469 bp B Pojer et al. PA 1: 2316 (23) pfp4 WT Q8 Q mutant 3.6-kb 2.8-kb 1.9-kb Tyr Retro-aldol (a) ovf? ovr? ovq? R pfp4 Q - mutant B/P B/P III PvuII ind Bam I Pst I thio loq* (165 bp) PvuII I Bam 223 bp double cross-over recombination PvuII 2947 bp 1.5-kb robiocin wild-type Q - mutant Q - mutant + Q is involved in biosynthesis 696, 589, 58, , 589, 58, , 589, 58, 226 min Purification of loq and prenylation assays 3-dimethylallyl- 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde PRTEI: total soluble purified 97 kda 66 kda 45 kda 3 kda Tyr loq -GT 2 ov loq 2 ov ovi a 2 loq DMAPP loq ov DMAPP loq DMAPP (A) loq + DMAPP + [U- ] ß--Tyr--ov tyrosine 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde ß-tyrosine 4.5 min min. Retention time (min.) RingA Pojer et al. PA 1: 2316 (23) 4 A Wild-type (WT) pew2 I - mutant indiii / / / coi Inactivation of I probe I (1221 bp) coi thio PstI coi coi loj 858 bp coi 1987bp XbaI double cross-over recombination loj coi loj loi* (12 bp) 858 bp B 1.9-kb.9-kb pew2 WT I4 loi mutant 34 nm 254 nm 696, 589, 58, 226 robiocin wild-type I - mutant 696, 589, 58, 226 D wild-type wild-type I - mutant 2 5, 1 61, , 1 61, 16 min. min I - mutant still produces prenylated 4-hydroxybenzoate Pojer et al. PA 1: 2316 (23)
10 ounts (DPM) ounts (DPM) Biosynthesis of prenylated benzoate moiety Q encodes a 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate 3-dimethylallyltransferase ypothesis 2 hen & Walsh 21 Tyr?? 2 lo 2 lo loi Retro-aldol (a) lof? lor? 2 lo loj/k? loq? R I is not involved in biosynthesis 2 4PP k m= 25 µm loq DMAPP k m= 35 µm loq + [1 14 ]DMAPP + 4PP Retention time (min.) a loq + [1 14 ]DMAPP + 4PP; after a treatment 3-dimethylallyl- 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid min. min 3-dimethylallyl- 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde min min Retention time (min.) 4 Pojer et al. PA 1: 2316 (23) loq represents a el prenyltransferase UbiA (ubiquinone) Lepgt 1 (shikonin) loq (robiocin) lor encodes a el bifunctional non-heme iron (II) dependent dioxygenase kda lor-gt (56.5 kda) lor (3.5 kda).. 4PP.. 179, 135, 17 3DMA-4MA 235, 191, 189, , 161, 15, 15 3DMA-4PP 247, 23, membrane-bound (D/)DxxD motif Mg 2+ dependent n soluble protein no (D/)DxxD motif Mg 2+ independent loq DMAPP lor lor + Fe 2+ + Fe 2+ Melzer et al. BBA 1994 Mühlenweg et al. Planta 1998 Pojer et al. PA 23 Kuzuyama et al. ature 25 4PP 3DMA-4PP 3DMA-4MA Pojer et al. JB 278: 3661 (23) Primary metabolism Biosynthesis of and Prephenate lof Tyr Transaminase 2 lo loq DMAPP 2 lo loi lor 2 2 lor 4PP E F G IJKL M PQRT UV WgyrB 2 lo loj/k? 2 R E F G Y IJKLM halp QR T U VW Z gyrb R pary R 2 2 Linkage of rings 3 TDP ovv ovt ovw ovu ov ov ovi ovj ovk? ov ovf? ovq ovr Glucose Tyr Prephenate
11 Linkage of rings Linkage of rings Amide synthetase ovl ATP AMP Glycosyl transferase ovm Amide synthetase ovl ATP AMP 3 TDP ovl lol oul MW [kda] TDP ovm: Thorson group: rg Lett 5: 933 (23) Walsh group: Biochemistry 42: 4179 (23) teffensky et al. JB 275: (2); Galm et al. hem & Biol 11: 173 (24) Tayloring reactions: ovobiocin Tayloring reactions: lorobiocin Methyltransferase ovp arbamoyl transferase ov AM Xu et al. MGG 268: 387 (22) Xu et al. hem & Biol 11: (24) P 2 3 Li et al. Microbiology 148: 3317 (22) Acyl transfer: APs lo1 & lo5 Transferases lo2 & lo7 Xu et al. hem & Biol 24 Freitag et al. hembiochem 25 Walsh group Biochemistry 26 3 Methyl transferase lo6 Westrich et al. hembiochem 4: 1 (23) 3 3 -lo5 Proline l lo5 Xu et al. MGG 268: 387 (22) lo4 lo3 Wang et al. AA 44: 34 (2) entral pyrrole unit of mermycin Functional analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters 3 l ovobiocin lorobiocin oumermycin A1 EF G I JK L M PQRT UV WgyrB R E F G Y I JKLM halp QR TUVWZ gyrb R pary R pary E G Y I JKLM P R RRR RR gyrb TUVW R R Regulation E F G E G 3 E F G ovobiocin 3 3 oumermycin A1 3 l IJKL M P QR T UV W IJK L M P R R R R IJKLM hal P QR T U VW lorobiocin R 6 TUVW
12 Functional analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters ovobiocin 3 l lorobiocin Acknowledgements Pharmaceutical Biology Team, Tübingen Dr. B. Gust Prof..-M. Li oumermycin A1 3 E F G IJKL M P QR T UV WgyrB R Resistance Regulation E F G Y IJKLM hal P QR T U VW ZgyrB R pary R E G Y IJK L M P R R R R R R gyrb pary 6 TUVW R R 5 ooperation partners L. Wessjohann, alle A. Maxwell, JI orwich, UK G. Bringmann, Würzburg Basilea AG, witzerland B. Kammerer, Tübingen Funding Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft European ommission
Secondary metabolites: structure, biosynthesis, enzymology and genetics
 econdary metabolites: structure, biosynthesis, enzymology and genetics ne third of top selling pharmaceuticals are produced from plants or microrganisms Lutz eide Pharmaceutical Institute Tübingen University
econdary metabolites: structure, biosynthesis, enzymology and genetics ne third of top selling pharmaceuticals are produced from plants or microrganisms Lutz eide Pharmaceutical Institute Tübingen University
Table removed due to copyright reasons.
 atural Product Biosynthesis Relevance of natural products in the pharmaceutical industry (see Table 2 in Butler J. at. Prod. 2004, 67, 2141-2153.)) Table removed due to copyright reasons. 2 * a phosphopantetheinyl
atural Product Biosynthesis Relevance of natural products in the pharmaceutical industry (see Table 2 in Butler J. at. Prod. 2004, 67, 2141-2153.)) Table removed due to copyright reasons. 2 * a phosphopantetheinyl
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function
 Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Avermectin. 2. Physical data (Avermectin B1a) White powder. C 48 H 72 O 14 ; mol wt Sol. in CHCl 3, acetone, MeOH. Insol. in H 2 O.
 Chapter Chapter 1 Avermectin 1. Discovery, producing organism and structures 1,) The discovery of avermectins was the result of a collaboration with Merck harp & Dohm Research Laboratories. Natural products
Chapter Chapter 1 Avermectin 1. Discovery, producing organism and structures 1,) The discovery of avermectins was the result of a collaboration with Merck harp & Dohm Research Laboratories. Natural products
Amino Acid Catabolism
 Amino Acid atabolism 3-1 Lec #8 To date we have considered the catabolism of carbohydrates and lipids with the object of generating energy in the form of ATP. Both give rise to AcoA which is fed through
Amino Acid atabolism 3-1 Lec #8 To date we have considered the catabolism of carbohydrates and lipids with the object of generating energy in the form of ATP. Both give rise to AcoA which is fed through
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Chapter 4. Erythronolide B and the Erythromycins
 124 Chapter 4 Erythronolide B and the Erythromycins Isolation and tructure Isolated in 1952 from the soil bacteria actinomycetes, 1 the erythromycins are a distinguished family of natural products by virtue
124 Chapter 4 Erythronolide B and the Erythromycins Isolation and tructure Isolated in 1952 from the soil bacteria actinomycetes, 1 the erythromycins are a distinguished family of natural products by virtue
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Assembly and Clustering of Natural Antibiotics Guides Target Identification Chad W. Johnston 1,2, Michael A. Skinnider 1,2, Chris A. Dejong 1,2, Philip N. Rees 1,2, Gregory M.
Supplementary Information Assembly and Clustering of Natural Antibiotics Guides Target Identification Chad W. Johnston 1,2, Michael A. Skinnider 1,2, Chris A. Dejong 1,2, Philip N. Rees 1,2, Gregory M.
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 30 Amino Acid Degradation and the Urea Cycle 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 30 Outline Amino acids are obtained from the
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 30 Amino Acid Degradation and the Urea Cycle 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 30 Outline Amino acids are obtained from the
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Distribution of the amino acids in Nature Frequency in proteins (%)
 Distribution of the amino acids in ature Amino Acid Frequency in proteins (%) Leucine Alanine Glycine erine Valine Glutamic acid Threonine Arginine Lysine Aspartic acid Isoleucine Proline Asparagine Glutamine
Distribution of the amino acids in ature Amino Acid Frequency in proteins (%) Leucine Alanine Glycine erine Valine Glutamic acid Threonine Arginine Lysine Aspartic acid Isoleucine Proline Asparagine Glutamine
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Antibiotics for Research
 Antibiotics for Research Natural antibiotics have existed for centuries prior to scientists identifying and isolating active moieties responsible for antibacterial activity. Today antibiotics are widely
Antibiotics for Research Natural antibiotics have existed for centuries prior to scientists identifying and isolating active moieties responsible for antibacterial activity. Today antibiotics are widely
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
 Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 16. Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III
 Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Amino Acid Metabolism (Nitrogen Metabolism) Dec Dr. Robert Lyons
 1 Amino Acid Metabolism (itrogen Metabolism) Dec 9-11 008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary (non-required) course materials. Medical relevance of amino acid
1 Amino Acid Metabolism (itrogen Metabolism) Dec 9-11 008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary (non-required) course materials. Medical relevance of amino acid
Dental Students Biochemistry Exam V Questions ( Note: In all cases, the only correct answer is the best answer)
 Dental Students Biochemistry Exam V Questions - 2006 ( Note: In all cases, the only correct answer is the best answer) 1. Essential fatty acids are: A. precursors of biotin B. precursors of tyrosine C.
Dental Students Biochemistry Exam V Questions - 2006 ( Note: In all cases, the only correct answer is the best answer) 1. Essential fatty acids are: A. precursors of biotin B. precursors of tyrosine C.
Lecture 4. Grouping Amino Acid 7/1/10. Proteins. Amino Acids. Where Are Proteins Located. Nonpolar Amino Acids
 Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Fate of Dietary Protein
 Fate of Dietary Protein Dietary protein Stomach: l, pepsin Denatured and partially hydrolyzed protein (large polypeptides) small intestine: proteases Amino acids and dipeptides intestinal lining: proteases
Fate of Dietary Protein Dietary protein Stomach: l, pepsin Denatured and partially hydrolyzed protein (large polypeptides) small intestine: proteases Amino acids and dipeptides intestinal lining: proteases
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Fate of Dietary Protein Dietary protein Stomach: l, pepsin Denatured and partially hydrolyzed protein (large polypeptides) small intestine: proteases Amino acids and dipeptides intestinal
Amino Acid Metabolism Fate of Dietary Protein Dietary protein Stomach: l, pepsin Denatured and partially hydrolyzed protein (large polypeptides) small intestine: proteases Amino acids and dipeptides intestinal
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
AMINO ACID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
antibiotics from microbial sources
 antibiotics from microbial sources 14-15/ 11/ 07 Margherita osio KtedoGen outline 1. antibiotics producers: treptomyces and related actinomycetes 2. antibiotic biosynthesis 3. earch for novel antibiotics
antibiotics from microbial sources 14-15/ 11/ 07 Margherita osio KtedoGen outline 1. antibiotics producers: treptomyces and related actinomycetes 2. antibiotic biosynthesis 3. earch for novel antibiotics
Welcome to Class 14! Class 14: Outline and Objectives. Overview of amino acid catabolism! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Welcome to Class 14 Introductory Biochemistry Class 14: Outline and Objectives Amino Acid Catabolism Fates of amino groups transamination urea cycle Fates of carbon skeletons important cofactors metabolic
Welcome to Class 14 Introductory Biochemistry Class 14: Outline and Objectives Amino Acid Catabolism Fates of amino groups transamination urea cycle Fates of carbon skeletons important cofactors metabolic
Chapter 26. Outline. Nitrogen. Nitrogen and Amino Acid Metabolism. BCH 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 26 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2
 BCH 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 26 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 26 Nitrogen and Amino Acid Metabolism 2 utline No time to cover entire chapter, therefore concentrate on a few focal points Assimilation of inorganic
BCH 4054 Spring 2001 Chapter 26 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 26 Nitrogen and Amino Acid Metabolism 2 utline No time to cover entire chapter, therefore concentrate on a few focal points Assimilation of inorganic
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle
 Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Supplementary Results
 upplementary Results upplementary Table 1. Primers used in this study. upplementary Figure 1. PCP3-TE assay in the absence of ul. upplementary Figure 2. Multiple alignment of the sulfazecin TE, highlighting
upplementary Results upplementary Table 1. Primers used in this study. upplementary Figure 1. PCP3-TE assay in the absence of ul. upplementary Figure 2. Multiple alignment of the sulfazecin TE, highlighting
TA Section Day/Time. Organic Chemistry FINAL EXAM A (250 points)
 UCSC, Binder ame TA Section Day/Time rganic Chemistry FIAL EXAM A (250 points) D T BEGI TE EXAM TU TE PAGE UTIL ISTUCTED T D S. In the meantime, please read the instructions below. Use your knowledge of
UCSC, Binder ame TA Section Day/Time rganic Chemistry FIAL EXAM A (250 points) D T BEGI TE EXAM TU TE PAGE UTIL ISTUCTED T D S. In the meantime, please read the instructions below. Use your knowledge of
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
PAPER No. : 16 Bioorganic and biophysical chemistry MODULE No. : 25 Coenzyme-I Coenzyme A, TPP, B12 and biotin
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 16, Bio organic and Bio physical chemistry 25, Coenzyme-I : Coenzyme A, TPP, B12 and CHE_P16_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 16, Bio organic and Bio physical chemistry 25, Coenzyme-I : Coenzyme A, TPP, B12 and CHE_P16_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS
 Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS 2. The fate of the carbon sceleton 3 N + C R Active C 1 intermediers The folate derivatives structure s Folate (F) - vitamin Folate, 2 F, 4 F Dihydrofolate ( 2
Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS 2. The fate of the carbon sceleton 3 N + C R Active C 1 intermediers The folate derivatives structure s Folate (F) - vitamin Folate, 2 F, 4 F Dihydrofolate ( 2
TA Section Day/Time. Organic Chemistry FINAL EXAM B (250 points)
 UCSC, Binder ame TA Section Day/Time rganic Chemistry FIAL EXAM B (250 points) D T BEGI TE EXAM TU TE PAGE UTIL ISTUCTED T D S. In the meantime, please read the instructions below. Use your knowledge of
UCSC, Binder ame TA Section Day/Time rganic Chemistry FIAL EXAM B (250 points) D T BEGI TE EXAM TU TE PAGE UTIL ISTUCTED T D S. In the meantime, please read the instructions below. Use your knowledge of
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism
 Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
CHEM-643 Biochemistry Mid-term Examination 8:00 10:00, Friday, 2 November 2007
 EM-643 Biochemistry Mid-term Examination 8:00 10:00, Friday, 2 November 2007 Name Dr.. White - Instructor There are 10 pages to this examination including this page. Write your name on each new page. Read
EM-643 Biochemistry Mid-term Examination 8:00 10:00, Friday, 2 November 2007 Name Dr.. White - Instructor There are 10 pages to this examination including this page. Write your name on each new page. Read
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites
 Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites Secondary Metabolism Secondary metabolism, metabolic pathways that are not essential for growth, development or reproduction. Secondary metabolites are those chemical
Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites Secondary Metabolism Secondary metabolism, metabolic pathways that are not essential for growth, development or reproduction. Secondary metabolites are those chemical
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the
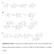 Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Structure and Function In Biochemistry
 University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
E.coli Core Model: Metabolic Core
 1 E.coli Core Model: Metabolic Core 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Each student should be able to: Describe the glycolysis pathway in the core model. Describe the TCA cycle in the core model. Explain gluconeogenesis.
1 E.coli Core Model: Metabolic Core 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Each student should be able to: Describe the glycolysis pathway in the core model. Describe the TCA cycle in the core model. Explain gluconeogenesis.
Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism
 Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction 2 Proteins are degraded into amino acids. Protein
Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction 2 Proteins are degraded into amino acids. Protein
Nitrogen Metabolism. Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Lecture 16. Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III
 Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Amino acid metabolism I
 Amino acid metabolism I Jana Novotná Department of the Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry The 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univ. Metabolic relationship of amino acids DIETARY PROTEINS GLYCOLYSIS
Amino acid metabolism I Jana Novotná Department of the Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry The 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univ. Metabolic relationship of amino acids DIETARY PROTEINS GLYCOLYSIS
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
Antibiotics.. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol
 Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Post-PKS tailoring steps of the spiramycin. macrolactone ring in Streptomyces ambofaciens
 Post-PKS tailoring steps of the spiramycin macrolactone ring in Streptomyces ambofaciens Hoang-Chuong NGUYEN, Emmanuelle DARBN, Robert THAI, Jean-Luc PERNDET, Sylvie LAUTRU SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Figure
Post-PKS tailoring steps of the spiramycin macrolactone ring in Streptomyces ambofaciens Hoang-Chuong NGUYEN, Emmanuelle DARBN, Robert THAI, Jean-Luc PERNDET, Sylvie LAUTRU SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Figure
Chemistry 5.07 Problem Set 5 (redox cofactors and oxidation reactions; carbohydrate chemistry, and introduction to metabolism)
 Chemistry 5.07 Problem Set 5 (redox cofactors and oxidation reactions; carbohydrate chemistry, and introduction to metabolism) Problem 1 Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) is a heterotetramer enzyme complex
Chemistry 5.07 Problem Set 5 (redox cofactors and oxidation reactions; carbohydrate chemistry, and introduction to metabolism) Problem 1 Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) is a heterotetramer enzyme complex
Aminocoumarin antibiotics (Fig. 1) are very potent inhibitors
 CloQ, a prenyltransferase involved in clorobiocin biosynthesis Florence Pojer*, Emmanuel Wemakor*, Bernd Kammerer, Huawei Chen, Christopher T. Walsh, Shu-Ming Li*, and Lutz Heide* *Pharmazeutische Biologie,
CloQ, a prenyltransferase involved in clorobiocin biosynthesis Florence Pojer*, Emmanuel Wemakor*, Bernd Kammerer, Huawei Chen, Christopher T. Walsh, Shu-Ming Li*, and Lutz Heide* *Pharmazeutische Biologie,
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
7.05 Spring 2004 May 7, Recitation #11
 Recitation #11 ontact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, 2-132 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, 2-132 Unit 4 Schedule Recitation/Exam Date Topic Recitation #11 Friday,
Recitation #11 ontact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, 2-132 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, 2-132 Unit 4 Schedule Recitation/Exam Date Topic Recitation #11 Friday,
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
LIPID METABOLISM
 LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
3.0 Fatty Acids and Polyketides : Biosynthesis and Engineering
 3.0 Fatty Acids and Polyketides : Biosynthesis and Engineering Chemical tructure Chemical Formula: C 16 32 2 Palmitic Acid = LAD aponification Na Na = AP Present in animal and plant fats as triacyl glycerols
3.0 Fatty Acids and Polyketides : Biosynthesis and Engineering Chemical tructure Chemical Formula: C 16 32 2 Palmitic Acid = LAD aponification Na Na = AP Present in animal and plant fats as triacyl glycerols
CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003
 CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003 1. A cell in an active, catabolic state has a. a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD + ) ratio b. a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD + ) ratio c. a
CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003 1. A cell in an active, catabolic state has a. a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD + ) ratio b. a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD + ) ratio c. a
life-threatening infections
 Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn
 Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn Research Mentors: Dr. Taifo Mahmud, Dr. Kerry McPhail A Bioresource Research Thesis Seminar Presentation Streptomyces pactum produces the antitumor
Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn Research Mentors: Dr. Taifo Mahmud, Dr. Kerry McPhail A Bioresource Research Thesis Seminar Presentation Streptomyces pactum produces the antitumor
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Figure S3 Differentially expressed fungal and plant genes organised by catalytic activity ontology Organisation of E. festucae (A) and L.
 sak WT Number of branches 3 WT sak Figure S1 Vasculature of plants infected with the E. festucae sak mutant. Light micrographs of perennial ryegrass blade tissue showing branching between the vasculature
sak WT Number of branches 3 WT sak Figure S1 Vasculature of plants infected with the E. festucae sak mutant. Light micrographs of perennial ryegrass blade tissue showing branching between the vasculature
Polypeptides. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids.
 Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
A Novel Lantibiotic Acting on Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Produced by the Uncommon FLAVIA MARINELLI. DBSM, University of Insubria, Varese Italy
 A Novel Lantibiotic Acting on Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Produced by the Uncommon Actinomycete Planomonospora sp. FLAVIA MARINELLI DBSM, University of Insubria, Varese Italy Vicuron Pharmaceuticals,
A Novel Lantibiotic Acting on Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Produced by the Uncommon Actinomycete Planomonospora sp. FLAVIA MARINELLI DBSM, University of Insubria, Varese Italy Vicuron Pharmaceuticals,
Lecture 17: Nitrogen metabolism 1. Urea cycle detoxification of NH 3 2. Amino acid degradation
 Lecture 17: Nitrogen metabolism 1. Urea cycle detoxification of NH 3 2. Amino acid degradation Reference material Biochemistry 4 th edition, Mathews, Van Holde, Appling, Anthony Cahill. Pearson ISBN:978
Lecture 17: Nitrogen metabolism 1. Urea cycle detoxification of NH 3 2. Amino acid degradation Reference material Biochemistry 4 th edition, Mathews, Van Holde, Appling, Anthony Cahill. Pearson ISBN:978
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination #5: Section Five December 7, Name: (print) Section:
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Math for Life BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES. LIPIDS: Fatty acids Triglycerides Phospholipids Steroids
 REFERENE TABLES BILIAL MARMLEULES LIIDS: Fatty acids Triglycerides hospholipids Steroids ARBYDRATES: Mono and Disaccharides olysaccharides Derivative carbohydrates RTEINS: Amino acids roteins NULEI AIDS:
REFERENE TABLES BILIAL MARMLEULES LIIDS: Fatty acids Triglycerides hospholipids Steroids ARBYDRATES: Mono and Disaccharides olysaccharides Derivative carbohydrates RTEINS: Amino acids roteins NULEI AIDS:
18 Amino Acid Oxidation and Production of Urea W. H. Freeman and Company
 18 Amino Acid Oxidation and Production of Urea 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Last Class of Biomolecules For Energy 1. Production of acetyl-coa. Glucose. To pyruvate via glycolysis. To acetyl-coa by
18 Amino Acid Oxidation and Production of Urea 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Last Class of Biomolecules For Energy 1. Production of acetyl-coa. Glucose. To pyruvate via glycolysis. To acetyl-coa by
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
