Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1
|
|
|
- Alexandra Park
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 1 of 12 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Written by: Orvil Luis Ayala, MD, Pediatric Pain Medicine Fellow, Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center, Department of Anesthesia, Cincinnati, Ohio Reviewed by: Alexandra Szabova, MD, Pediatric Pain Medicine Fellowship, Program Director Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center, Department of Anesthesia, Cincinnati, Ohio REVIEW DATE: December, 2013 Read this article, reflect on the information presented, then go online and complete the lesson post-test and course evaluation before the termination date below. (CME credit is not valid past this date.) You must achieve a score of 80% or better to earn CME credit. TIME TO COMPLETE ACTIVITY: 2 hours RELEASE DATE: February 1, 2014 TERMINATION DATE: January 31, 2015 COPYRIGHT: This material is subject to copyright 2014 Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. All rights reserved. Professional Gaps Although most anesthesiologists appreciate the need to provide perioperative pain relief for their patients, perioperative pain in children remains undertreated. Part 1 of this 2-part series examines the barriers to treatment of pain in children and presents the means of assessing pain as well as other factors affecting acute pain management in the pediatric population. Learning Objectives At the end of this activity, the participant should be able to: 1. Recognize some of the barriers to treating pediatric pain. 2. Discuss the developmental anatomy of nociception. 3. Present the controversies involved with perception of pain. 4. Highlight the development of understanding and reporting of pain by a pediatric patient. 5. Recognize the different tools used to assess pain in the pediatric population. 6. Discuss self-reporting measures used in the assessment of pain in the pediatric population. 7. Discuss the usefulness of observational scales used in the assessment of the nonverbal pediatric patient. 8. Understand other factors affecting the treatment of pain. 9. Discuss some of the techniques available to decrease perioperative anxiety. 10. Present general guidelines for the use of age-appropriate nonpharmacologic techniques in reduction of perioperative anxiety. Case History An 8-year-old boy with a past medical history significant for anorectal malformation and fecal incontinence was scheduled for a continent neo-appendicostomy under general anesthesia. The patient was otherwise healthy. He lived with his parents and had recently completed the third grade.
2 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 2 of 12 He weighed 25 kg, and his vital signs and physical examination were normal. The surgeon noted that postoperative pain could be significant. The surgeon and the parents asked that a plan for postoperative pain relief be in place and explained to them ahead of time The assessment and treatment of pain in the pediatric population present many challenges for perioperative physicians, especially the anesthetic care provider. Since the 1980s, several reports have indicated that pediatric patients in the perioperative setting are undertreated for pain compared with their adult counterparts. 1 Many advances in the care of pediatric patients have occurred, including evidence-based practice guidelines for the treatment of pediatric pain to mitigate gaps in clinical practice. 2 However, excessive pain in the perioperative setting can lead to worse patient outcomes and development of chronic pain syndromes. 3-5 The role of the perioperative physician is to understand and address barriers in pediatric pain management, and to improve pain management and thus patient outcomes (Table 1). 6 Development of Pain Perception Pain, as defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP), is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. The IASP also acknowledges that the inability to communicate verbally does not negate the possibility that an individual is experiencing pain and is in need of appropriate pain-relieving treatment. 7 Some experts have postulated that neonates are born with the ability to perceive pain, given that the neuroanatomical system for pain is considered to be complete by 26 weeks of gestation. 8 Others have argued that the perception of pain requires an actual conscious recognition of noxious stimuli, which has been thought to exist once the thalamocortical pathways have matured and begun to function at around 30 weeks of gestation A brief overview of the developmental anatomy of nociception and pain perception pathways is presented in Table 2. These arguments and findings are relevant when one considers the need for anesthesia for midand end-gestational fetal surgeries in which fetuses are actively treated with opioids to prevent any negative consequences that exposure to pain at such a young age might have. Advances in the field of perinatology have led to an increase in the survival of preterm neonates in neonatal ICUs. 1 Many
3 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 3 of 12 studies have demonstrated that failure to provide adequate analgesia to these patients can lead to negative sequelae, including motor and cognitive deficits, changes in sensory processing, and high susceptibility to growth retardation. 11,14-16 It also is considered substandard and unethical care. Assessment of Perioperative Pain in the Pediatric Population The initial step in successful treatment of perioperative pain in the pediatric population is assessment. Preoperative assessment may elucidate confounding factors, such as the presence of developmental delay, which may make the treatment of pain challenging. It also may provide a platform for discussion between the physician, health care staff, parents, and patients as to what can be expected during the perioperative period. The assessment of pain in the pediatric population has been approached through the use of selfreporting scales, observational scales, and/or physiologic measures. Becoming familiar with the available age-appropriate pediatric pain assessment tools may significantly improve patient care and outcomes (Table 3). 17,18 Self-Reporting Scales The self-reporting scales used in the assessment of pain in the pediatric population rely on the patient s ability to understand and express his or her pain, and thus have to reflect various developmental stages. Success and ease of use of a self-reporting scale depends on how well the implications of the child s understanding of pain are incorporated in the assessment tool. It is important to note that between 36 and 60 months of age, children begin to report both the intensity of their pain and the emotions associated with it. This is the youngest age for which self-reporting scales have been developed, validated, and widely used in pain assessment. In our institution, we use a FACES rating for the younger age group and the numeric rating scale (NRS) for older children and adolescents (Figure). Self-reporting scales are regarded as the gold standard of pain assessment. We recommend choosing 1 or 2 scales, training the medical center staff well, and using the scales
4 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 4 of 12 consistently throughout the perioperative period (Table 4). 19,20 Observational Scales Validated observational scales have been used in the perioperative setting for assessment of pain in the pediatric population (Table 5). 11,19
5 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 5 of 12 Some of these scales are detailed, labor-intensive, and not practical for routine use, although they work well for intubated and sedated patients in the ICU, such as the Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPS) or COMFORT Scale. For awake patients aged 0 to 18 years, we adopted the FLACC (faces, legs, activity, cry, consolability) scale, whose numeric value correlates with NRS, making interpretation meaningful to all users. A challenge of observational scales is the lack of ability to differentiate between other forms of distress, including hunger, thirst, or anxiety. 19 Physiologic Measures The physiologic measures are not as well validated as other methods of assessing pain but may provide some insight about the body s response to pain. Measures may include heart rate, blood pressure, transcutaneous oxygen, respiratory rate, sweating, and stress response (Table 6). 19 When using physiologic measures, it is important to note that these signs are not specific to pain and they work best when used in conjunction with other methods. Other Factors Affecting Pain Assessment and Treatment in the Pediatric Population Even with the use of age-appropriate pain assessment tools, the potential for failure and complications persists. Factors such as anxiety or medication side effects may alter the treatment of pain in the pediatric population. Perioperative anxiety has been shown to predict higher pain scores and analgesic consumption postoperatively Perioperative anxiety also can lead to long-term maladaptive behaviors. As a result, many studies have focused on interventions to reduce perioperative anxiety in children and their parents. Various pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic techniques have been shown to reduce anxiety, ranging from patient reassurance, distraction, 25 and preoperative videos, 26 as well as complementary and alternative medical therapies such as hypnosis, music therapy, and laughter therapy (Table 7). 27 Parental presence in the induction room is a well-researched technique for reducing anxiety in the pediatric population. 28 It has its limitations, 29 but is most effective when combined with noninstrumental talk between patient and health care providers compared with parental presence alone or in combination with anxiolytics. 30 Distraction is an effective and inexpensive technique to counteract anxiety that can be applied across the age groups. 31 This method probably works through cognitive and motor absorption, as children tend to be oblivious or have a decreased regard for their surroundings. 32 Such tools may include but are not limited to pacifiers, blankets, medical play, video games, and clowns. 30,32
6 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 6 of 12 Table 8. General Guidelines for Nonpharmacologic Techniques Used for Reduction of Perioperative Anxiety in the Pediatric Population Age and Developmental Barriers Techniques Emotional Support Common Reactions Infants (0-1 y) Attachment Basic trust Sensitivity to physical environment Preoperatively: Provide parents with information about the procedure (eg, pamphlets, reading materials, etc) During: Child distraction Music Massage Parental presence Items of comfort (eg, pacifier, blanket) Crying Problems with sleep Generalized increase in irritability Pain Toddlers (1-3 y) Separation anxiety Loss of autonomy Preoperatively: Parental information Child therapeutic play Medical play During: Child distraction Music Massage Same as infants, plus Home routines Simple explanations Pain Verbal responses to pain usually are not reliable When restrained, patient often responds to painless procedures Invasive procedures tend to cause a lot of anxiety Resistance Aggression Regression Preschoolers (4-5 y) Separation anxiety Moral reasoning Good vs bad Allow child to pick coping strategies Provide follow-up to procedures Music distraction Medical play Same as toddlers, plus Choices Positive reinforcement Fears intensified with age/experience Fear of abandonment Guilt Anger/aggression Regression Breaks in schedule, loss of control, and unfamiliar place and people tend to cause more anxiety
7 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 7 of 12 Age and Developmental Barriers Techniques Emotional Support Common Reactions School-aged (6-12 y) Altered body image Loss of privacy Loss of independence Preoperatively: Therapeutic play Medical play Procedure-based images During: Distraction Music Massage Hypnosis Allow child to make more choices Actively involve child in procedure Discuss potential changes in physical appearance Same as preschoolers, plus Positive reinforcement Encourage parental presence Increased ability to identify and localize pain Lack of abstract thinking may cause patient to feel guilt Past experiences/caregiver response can affect pain reactions Capability to exaggerate pain Acting out Aggression Depression Regression Adolescence (13-17 y) Loss of autonomy Loss of privacy Altered body image Preoperatively: Procedure-based instructions During: Distraction Music Guided imagery Hypnosis Discuss possible psychological and physical changes postprocedure Increase chances for involvement in decision making for medical care Same as school children, plus Encourage active participation Can locate and describe pain accurately Increased desire to participate in medical decision making Can be hyper-responsive to pain Has a better understanding of the concept of death May become rebellious to treatment and medical care Depression Regression Aggression Modified from reference 11. Perioperative pain management sometimes can be described as walking a fine line between comfort and medication-related side effects, such as sedation. The risk for adverse drug reactions may double in an overly sedated patient, 21 which is a distressing situation for all involved. Further administration of opioids or other medications under such circumstances should be withheld or tapered. 11 To prevent such incidents, many institutions have implemented routine assessment of sedation in patients on opioids. We use a modified Ramsay Sedation Scale in the assessment of sedation in the perioperative pediatric patient (Table 9). For safety reasons, if the Ramsay score is greater than 3, the administration of opioids or other sedation-enhancing medications is stopped regardless of the patient s pain score. 23
8 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 8 of 12 Conclusion When assessing pain in the pediatric population, the perioperative physician should have a consistent approach to evaluating the patient and to modifying the plan according to confounding factors throughout the perioperative course. Use of age-appropriate pain assessment tools, education of the medical staff on their use, and the creation of treatment guidelines based on assessment, all lead to improved pain management, patient satisfaction, fewer complications, and better outcomes.
9 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 9 of 12 REFERENCES 1. Schechter NL, Allen DA, Hanson K. Status of pediatric pain control: a comparison of hospital analgesic usage in children and adults. Pediatrics. 1986;77(1): MacLaren J, Kain ZN. Research to practice in pediatric pain: what are we missing? Pediatrics. 2008;122(2): Gauthier JC, Finley GA, McGrath PJ. Children s self-report of postoperative pain intensity and treatment threshold: determining the adequacy of medication. Clin J Pain. 1998;14(2): Roth-Isigkeit A, Thyen U, Stoven H, et al. Pain among children and adolescents: restrictions in daily living and triggering factors. Pediatrics. 2005;115(4): Porter FL, Grunau RE, Anand KJ. Long-term effects of pain in infants. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1999;20(4): Golianu B, Krane EJ, Galloway KS, et al. Pediatric acute pain management. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2000;47(3): Goldschneider KR. Long-term consequences of pain in infancy. In: Berde CB, Rowbotham MC, eds. International Association for the Study of Pain: Technical Corner. IASP Newsletter. July/August Lee SJ, Ralston HJP, Drey EA, et al. Fetal pain: a systematic multidisciplinary review of the evidence. JAMA. 2005;294(8): Derbyshire SW. Can fetuses feel pain? BMJ. 2006;332(7546): Lowery CL, Hardman MP, Manning N, et al. Neurodevelopmental changes of fetal pain. Semin Perinatol. 2007;31(5): Gold JI, Townsend J, Jury DL, et al. Current trends in pediatric pain management: from preoperative to the postoperative bedside and beyond. Semin Anesth Periop Med Pain. 2006;25(3): Fitzgerald M. Development of pain pathways and mechanisms. In: Anand KIS, McGrath PJ, eds. Pain Research and Clinical Management. Vol. 5. Pain in Neonates. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1993: Fitzgerald M. The neurobiology of chronic pain. In: McClain BC, Suresh S, eds. Handbook of Pediatric Chronic Pain: Current Science and Integrative Practice. New York, NY:Springer; 2011: Simons SHP, van Djik M, Anand KS, et al. Do we still hurt newborn babies? A prospective study of procedural pain and analgesia in neonates. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003;157(11): Walco GA, Cassidy RC, Schechter NL. Pain, hurt, and harm. The ethics of pain control in infants and children. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(8): Fabrizi L, Slater R. Commentary: exploring the relationship of pain and development in the neonatal intensive care unit. Pain. 2012;153(7): McGrath PJ, Craig KD. Developmental and psychological factors in children s pain. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1989;36(4): Treadwell MJ, Franck LS, Vichinsky E. Using quality improvement strategies to enhance pediatric pain assessment. Int J Qual Health Care. 2002;14(1): McGrath PJ, Unruh AM. Measurement and assessment of pediatric pain. In: Wall & Melzack s Textbook of Pain, 6 th Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; McGrath PJ. Pain measurement in children. International Association for the Study of Pain, Clinical Updates. 1995;3(2): Vila H, Smith RA, Augustyniak MJ, et al. The efficacy and safety of pain management before and after implementation of hospital-wide pain management standards: is patient safety compromised by treatment based solely on numerical pain ratings? Anesth Analg. 2005;101(2); Lentschener C, Tostivint P, White PF, et al. Opioid-induced sedation in the postanesthesia care unit does not insure adequate pain relief: a case-control study. Anesth Analg. 2007;105(4): Ramsay MAE. How to use the Ramsay score to assess the level of ICU sedation. edation.htm. Accessed September 8, Kain ZN, Mayes LC, Caldwell-Andrews AA, et al. Preoperative anxiety, postoperative pain, and behavioral recovery in young children undergoing surgery. Pediatrics. 2006;18(2): Lee J, Lee J, Lim H, et al. Cartoon distraction alleviates anxiety in children during induction of anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2012;115(5): McEwen A, Moorthy C, Quantock C, et al. The effect of videotaped preoperative information on parental anxiety during anesthesia induction for elective pediatric procedures. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007;17(6): Evans S, Tsao JC, Zeltzer LK. Complementary and alternative medicine for acute procedural pain in children. Altern Ther Health Med. 2008;14(5): Powers KS, Rubenstein JS. Family presence during invasive procedure in the pediatric intensive care unit: a prospective study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153(9): Cameron JA, Bond MJ, Pointer SC. Reducing the anxiety of children undergoing surgery: parental presence during anesthetic
10 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 10 of 12 induction. J Paediatr Child Health. 1996;32(1): Vagnoli L, Caprilli S, Messeri A. Parental presence, clowns or sedative premedication to treat preoperative anxiety in children: what could be the most promising option? Paediatr Anaesth. 2010;20(10): Kleiber C, Harper DC. Effects of distraction on children s pain and distress during medical procedures: a meta-analysis. Nurs Res. 1999;48(1): Patel A, Schieble T, Davidson M, et al. Distraction with a hand-held videogame reduces pediatric preoperative anxiety. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006;16(10):
11 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 11 of 12 Visit today for instant online processing of your CME post-test and evaluation form. There is a registration fee of $15 for this non industry-supported activity. For assistance with technical problems, including questions about navigating the Web site, call toll-free customer service at (888) or send an to Customer.Support@ProCEO.com. For inquiries about course content only, send an to ram.roth@mssm.edu. Ram Roth, MD, is director of PreAnesthetic Assessment Online and assistant professor of anesthesiology at The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY. Post-test 1. Which of the following is an example of an observational measure used to assess pain in a pediatric patient? a. Poker Chips b. Visual analog scale c. FLACC Scale d. FACES Scale 2. Which of the following scales may be used to assess pain in sedated patients? a. COMFORT Scale b. Numeric Rating Scale c. The Oucher scale d. Poker Chips 3. Which of the following is an example of the nonpharmacologic techniques involved in the treatment of pediatric patients? a. Massages b. Blowing bubbles c. Music therapy d. All of the above 4. Examples of barriers to the treatment of pain in the pediatric population include all of the following except. a. lack of familiarity with appropriate assessment tools b. lack of familiarity with drug options and dosing c. lack of parental/patient education d. presence of child life specialist on an inpatient unit 5. The treatment of pain should be withheld in which of the following scenarios? a. A 3-month-old boy undergoing elective circumcision b. A 13-year-old boy s/p pectus excavatum repair with patient-controlled analgesia and respiratory rate of 6 who requires supplemental oxygen to maintain saturation above 94% c. A 6-month-old girl undergoing congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation repair d. An 18-month-old boy undergoing pyeloplasty
12 Lesson 308: PreAnesthetic Assessment of the Pediatric Patient With Pain: Part 1 Page 12 of Which of the following is not part of the FLACC Scale? a. Face b. Labs c. Activity d. Cry 7. What Ramsay Sedation Scale (RSS) score does the following patient have: a 6-year-old boy s/p left inguinal hernia repair currently in the postanesthesia care unit, who is asleep but awakens to voice commands? a. RSS 6 b. RSS 8 c. RSS 1 d. RSS 3 8. Which of the following are some of the consequences of administering opioids or other sedation-inducing medications to an overly sedated person? a. Severe hypercarbia b. Hypoxia c. Respiratory arrest d. All of the above 9. High levels of parental anxiety may lead to higher anxiety levels in the pediatric patient during the perioperative period. a. Almost always b. It is unrelated c. Never d. Depends entirely on the preoperative mental condition of the child 10. Which of the following will help reduce anxiety during the perioperative period in an adolescent patient? a. Involving patient in decision making b. Hypnosis c. Procedure-based instructions d. All of the above
Avoiding premedication in children a practical approach
 Preoperative preparation and communication in children Avoiding premedication in children a practical approach J. Berghmans M.D. Department of Anesthesia, ZNA Middelheim, Queen Paola Children s Hospital,
Preoperative preparation and communication in children Avoiding premedication in children a practical approach J. Berghmans M.D. Department of Anesthesia, ZNA Middelheim, Queen Paola Children s Hospital,
Clowns for the prevention of preoperative anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial
 Pediatric Anesthesia 2009 19: 262 266 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9592.2008.02903.x Clowns for the prevention of preoperative anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial G. GOLAN PhD*, P. TIGHE MD, N. DOBIJA
Pediatric Anesthesia 2009 19: 262 266 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9592.2008.02903.x Clowns for the prevention of preoperative anxiety in children: a randomized controlled trial G. GOLAN PhD*, P. TIGHE MD, N. DOBIJA
THE EFFECT OF CHILDREN S TEMPERAMENT ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PARENTAL ANXIETY AND POSTOPERATIVE PAIN
 THE EFFECT OF CHILDREN S TEMPERAMENT ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PARENTAL ANXIETY AND POSTOPERATIVE PAIN Nguyen, Therese Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Care Michelle Fortier, PhD The intent
THE EFFECT OF CHILDREN S TEMPERAMENT ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PARENTAL ANXIETY AND POSTOPERATIVE PAIN Nguyen, Therese Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Care Michelle Fortier, PhD The intent
Guidance on competencies for Paediatric Pain Medicine reviewed 2017
 Guidance on competencies for Paediatric Pain Medicine reviewed 2017 Endorsed by: Contents Introduction A: Core competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine Page 2 4 Appendix A: Curriculum 5 B: Competencies
Guidance on competencies for Paediatric Pain Medicine reviewed 2017 Endorsed by: Contents Introduction A: Core competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine Page 2 4 Appendix A: Curriculum 5 B: Competencies
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures
 Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Using Pediatric Pain Scales
 Using Pediatric Pain Scales We care about your child s comfort. You are an important member of your child s healthcare team. You know your child best. We want to partner with you to help control your child
Using Pediatric Pain Scales We care about your child s comfort. You are an important member of your child s healthcare team. You know your child best. We want to partner with you to help control your child
Pain Control in the NICU
 Pain Control in the NICU By Robert Cicco, MD Introduction There is ample documentation in the literature that newborn infants experience pain and exhibit a variety of both physiologic and behavioral responses
Pain Control in the NICU By Robert Cicco, MD Introduction There is ample documentation in the literature that newborn infants experience pain and exhibit a variety of both physiologic and behavioral responses
Background Music Used to Reduce Anxiety in Infants during an Ear Examination
 Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Hospital & Medical Management ISSN 2471-9781 DOI: 10.4172/2471-9781.100046 Background Music Used to Reduce Anxiety in Infants during an Ear
Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Hospital & Medical Management ISSN 2471-9781 DOI: 10.4172/2471-9781.100046 Background Music Used to Reduce Anxiety in Infants during an Ear
EFFECTS OF CHILDREN S TEMPERAMENT ON THE AMOUNT OF ANALGESICS ADMINISTERED BY PARENTS AFTER SURGERY
 EFFECTS OF CHILDREN S TEMPERAMENT ON THE AMOUNT OF ANALGESICS ADMINISTERED BY PARENTS AFTER SURGERY Zolghadr, Sheeva Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Care Michelle Fortier, PhD Temperament,
EFFECTS OF CHILDREN S TEMPERAMENT ON THE AMOUNT OF ANALGESICS ADMINISTERED BY PARENTS AFTER SURGERY Zolghadr, Sheeva Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Care Michelle Fortier, PhD Temperament,
revision Nov 2011 Andrew Triebwasser Department of Anesthesiology Hasbro Children s Hospital
 revision Nov 2011 Andrew Triebwasser Department of Anesthesiology Hasbro Children s Hospital safety efficiency acceptance outcome evaluation and preparation decision to use premedication involvement of
revision Nov 2011 Andrew Triebwasser Department of Anesthesiology Hasbro Children s Hospital safety efficiency acceptance outcome evaluation and preparation decision to use premedication involvement of
ROTATION SUMMARY PEDIATRIC PAIN MANAGEMENT
 ROTATION SUMMARY PEDIATRIC PAIN MANAGEMENT Rotation Contacts and Scheduling Details Rotation Director: Srinivas Naidu, M.D. Administrative Assistant: Kathryn De Rama To set up elective: Contact Srinivas
ROTATION SUMMARY PEDIATRIC PAIN MANAGEMENT Rotation Contacts and Scheduling Details Rotation Director: Srinivas Naidu, M.D. Administrative Assistant: Kathryn De Rama To set up elective: Contact Srinivas
Anesthetic-Induced Neuronal Brain Injury in Infants: Finding an Answer with Clinical Studies
 Anesthetic-Induced Neuronal Brain Injury in Infants: Finding an Answer with Clinical Studies Andrew Davidson Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne AUSTRALIA Local anesthesia infiltration by the surgeon has
Anesthetic-Induced Neuronal Brain Injury in Infants: Finding an Answer with Clinical Studies Andrew Davidson Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne AUSTRALIA Local anesthesia infiltration by the surgeon has
Sonoma Valley Hospital Sonoma Valley Healthcare District Policy and Procedure Organizational. Page: 1
 Title: PAIN MANAGEMENT Sonoma Valley Hospital Organizational Number: PC-104 Page: 1 Effective Date: 3/96 Mary Kelly, R.N., M.P.A. 12/07 Approved By Date Revision Dates: 07/01, 02/02 Signature on file Signature
Title: PAIN MANAGEMENT Sonoma Valley Hospital Organizational Number: PC-104 Page: 1 Effective Date: 3/96 Mary Kelly, R.N., M.P.A. 12/07 Approved By Date Revision Dates: 07/01, 02/02 Signature on file Signature
The operative experience can
 Ronald Zuwala, CRNA, MS Flint, Michigan Kimberly R. Barber, MS Lennon, Michigan Reducing anxiety in parents before and during pediatric anesthesia induction Fear and anxiety in a child undergoing surgery
Ronald Zuwala, CRNA, MS Flint, Michigan Kimberly R. Barber, MS Lennon, Michigan Reducing anxiety in parents before and during pediatric anesthesia induction Fear and anxiety in a child undergoing surgery
The Participant will be able to: All Better!: Pediatric Adenotonsillectomy Pain Management
 All Better!: Pediatric Adenotonsillectomy Pain Management Deborah Scalford, RN, MSN The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Objectives The Participant will be able to: Identify reasons why pain is unrelieved.
All Better!: Pediatric Adenotonsillectomy Pain Management Deborah Scalford, RN, MSN The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Objectives The Participant will be able to: Identify reasons why pain is unrelieved.
Pain assessment: When self-report conflicts with observation or context
 Pain assessment: When self-report conflicts with observation or context Carl L von Baeyer, PhD www.usask.ca/childpain/pubs/ 4 Nov 2013 This version of the presentation has been edited for online distribution.
Pain assessment: When self-report conflicts with observation or context Carl L von Baeyer, PhD www.usask.ca/childpain/pubs/ 4 Nov 2013 This version of the presentation has been edited for online distribution.
Nonpharmacologic pain management
 Nonpharmacologic pain management Kathy Davis, PhD, MSEd University of Kansas SoM; Dept of Pediatrics kdavis2@kumc.edu Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of
Nonpharmacologic pain management Kathy Davis, PhD, MSEd University of Kansas SoM; Dept of Pediatrics kdavis2@kumc.edu Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of
Preoperative Anxiety
 Alyssa Brzenski Case You are called by a parent of a child who you took care of a week and a half ago. The child, a 4 year old boy, came to IR for the first of many sclerotherapy of a Venous Malformation
Alyssa Brzenski Case You are called by a parent of a child who you took care of a week and a half ago. The child, a 4 year old boy, came to IR for the first of many sclerotherapy of a Venous Malformation
Baby It Hurts. Deb Fraser, MN, RNC
 Baby It Hurts Deb Fraser, MN, RNC Outline What is pain? Misconceptions about pain Problems with neonatal pain management Pain assessment Our view of pain? definitions Pain: An unpleasant sensory or emotional
Baby It Hurts Deb Fraser, MN, RNC Outline What is pain? Misconceptions about pain Problems with neonatal pain management Pain assessment Our view of pain? definitions Pain: An unpleasant sensory or emotional
SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES
 SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES Sinno Simons Erasmus MC Sophia Children s Hospital Rotterdam, the Netherlands s.simons@erasmusmc.nl SEDATION in newborns How and when How to evaluate How to dose Why to use
SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES Sinno Simons Erasmus MC Sophia Children s Hospital Rotterdam, the Netherlands s.simons@erasmusmc.nl SEDATION in newborns How and when How to evaluate How to dose Why to use
Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions to alleviate anxiety before pediatric anesthesia: a survey of current practice in Korea
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 55-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.1.55 Clinical Research Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions to alleviate anxiety before pediatric anesthesia: a survey
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 55-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.1.55 Clinical Research Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions to alleviate anxiety before pediatric anesthesia: a survey
Distress at induction: prevention and consequences Andrew Davidson a,b,c and Ian McKenzie a
 Distress at induction: prevention and consequences Andrew Davidson a,b,c and Ian McKenzie a a Department of Anaesthesia, Royal Children s Hospital, b Anaesthesia Research Group, Murdoch Childrens Research
Distress at induction: prevention and consequences Andrew Davidson a,b,c and Ian McKenzie a a Department of Anaesthesia, Royal Children s Hospital, b Anaesthesia Research Group, Murdoch Childrens Research
DOCTORAL DISSERTATION
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL DOCTORAL DISSERTATION - Summary - METHODS OF ANALGESIA AND SEDATION IN THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD PhD SUPERVISER: PH. D. PROFESSOR : VALENTIN C#RLIG
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL DOCTORAL DISSERTATION - Summary - METHODS OF ANALGESIA AND SEDATION IN THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD PhD SUPERVISER: PH. D. PROFESSOR : VALENTIN C#RLIG
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines Intravenous Sedation and General Anesthesia Coverage for Dental Services
 Policy: Intravenous sedation and general anesthesia are considered medically necessary for individuals undergoing needed dental procedures who are unable to tolerate the dental procedures using behavior
Policy: Intravenous sedation and general anesthesia are considered medically necessary for individuals undergoing needed dental procedures who are unable to tolerate the dental procedures using behavior
BRITISH ASSOCIATION FOR EMERGENCY MEDICINE Registered Charity No
 BRITISH ASSOCIATION FOR EMERGENCY MEDICINE Registered Charity No 273876 AT THE ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS OF ENGLAND 35-43 LINCOLN'S INN FIELDS, LONDON, WC2A 3PE, UNITED KINGDOM Telephone: +44 (0)20 7831
BRITISH ASSOCIATION FOR EMERGENCY MEDICINE Registered Charity No 273876 AT THE ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS OF ENGLAND 35-43 LINCOLN'S INN FIELDS, LONDON, WC2A 3PE, UNITED KINGDOM Telephone: +44 (0)20 7831
Sedation is a dynamic process.
 19th Annual Mud Season Nursing Symposium Timothy R. Lyons, M.D. 26 March 2011 To allow patients to tolerate unpleasant procedures by relieving anxiety, discomfort or pain To expedite the conduct of a procedure
19th Annual Mud Season Nursing Symposium Timothy R. Lyons, M.D. 26 March 2011 To allow patients to tolerate unpleasant procedures by relieving anxiety, discomfort or pain To expedite the conduct of a procedure
Dr. Ali D. Abbas.
 Pain Management Dr. Ali D. Abbas Instructor, Fundamentals of Nursing Department, College of Nursing, University of Baghdad ali_dukhan@yahoo.com LEARNING OBJECTIVES After mastering the contents of this
Pain Management Dr. Ali D. Abbas Instructor, Fundamentals of Nursing Department, College of Nursing, University of Baghdad ali_dukhan@yahoo.com LEARNING OBJECTIVES After mastering the contents of this
Global public health can be improved with effective management of needle fear. Pain, Pain Buzz Away: Bee ating Needle Phobia
 Global public health can be improved with effective management of needle fear. Pain, Pain Buzz Away: Bee ating Needle Phobia Needle Phobia Definition Defined as needle fear that is: Persistent Excessive
Global public health can be improved with effective management of needle fear. Pain, Pain Buzz Away: Bee ating Needle Phobia Needle Phobia Definition Defined as needle fear that is: Persistent Excessive
Palliative Care. And Pain Management
 Palliative Care And Pain Management Revised: bw/september 2010 Palliative Care Symptom management is a primary goal of palliative care. Pain is one of the most feared symptoms experienced by patients.
Palliative Care And Pain Management Revised: bw/september 2010 Palliative Care Symptom management is a primary goal of palliative care. Pain is one of the most feared symptoms experienced by patients.
Perioperative Pain Management
 Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
Pain Assessment. Cathy Murray MSN RN OCNS-C Clinical Nurse Specialist December /21/2014 1
 Pain Assessment Cathy Murray MSN RN OCNS-C Clinical Nurse Specialist December 2013 3/21/2014 1 Objectives Articulate pain assessment strategies. Identify appropriate assessment tools for patients. Describe
Pain Assessment Cathy Murray MSN RN OCNS-C Clinical Nurse Specialist December 2013 3/21/2014 1 Objectives Articulate pain assessment strategies. Identify appropriate assessment tools for patients. Describe
Pediatric Anesthesia Historical Perspective 573 Andrew T. Costarino, Jr and John J. Downes
 PEDIATRIC ANESTHESIOLOGY Foreword Lee A. Fleisher xiii Preface Andrew T. Costarino, Jr and B. Randall Brenn xv Pediatric Anesthesia Historical Perspective 573 Andrew T. Costarino, Jr and John J. Downes
PEDIATRIC ANESTHESIOLOGY Foreword Lee A. Fleisher xiii Preface Andrew T. Costarino, Jr and B. Randall Brenn xv Pediatric Anesthesia Historical Perspective 573 Andrew T. Costarino, Jr and John J. Downes
Tarek M Sarhan, Assistant professor of Anesthesiology, Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University
 7 ANALGESIA FOR TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULA REPAIR IN NEONATES : A COMPARISON OF SINGLE SHOT THORACIC PARAVERTEBRAL BLOCK AND EPIDURAL BLOCK WITH ROPIVACAINE Tarek M Sarhan, Assistant professor of Anesthesiology,
7 ANALGESIA FOR TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULA REPAIR IN NEONATES : A COMPARISON OF SINGLE SHOT THORACIC PARAVERTEBRAL BLOCK AND EPIDURAL BLOCK WITH ROPIVACAINE Tarek M Sarhan, Assistant professor of Anesthesiology,
Clinical Study A Comparison of Two Pain Scales in the Assessment of Dental Pain in East Delhi Children
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume, Article ID 7, pages doi:.//7 Clinical Study A Comparison of Two Pain Scales in the Assessment of Dental Pain in East Delhi Children Amit
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume, Article ID 7, pages doi:.//7 Clinical Study A Comparison of Two Pain Scales in the Assessment of Dental Pain in East Delhi Children Amit
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Guideline for the management of pain in children Kieran O Connor Anaesthetics ATICS Date Uploaded: 1 September 2016 Review
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Guideline for the management of pain in children Kieran O Connor Anaesthetics ATICS Date Uploaded: 1 September 2016 Review
HPNA Position Statement Pain Management
 HPNA Position Statement Pain Management Background Pain is a common symptom in most serious or life-threatening illnesses. Pain is defined as an unpleasant subjective sensory and emotional experience associated
HPNA Position Statement Pain Management Background Pain is a common symptom in most serious or life-threatening illnesses. Pain is defined as an unpleasant subjective sensory and emotional experience associated
Distraction techniques in children during venipuncture: an Italian experience
 J prev med hyg 2012; 53: 44-48 The nurses point of view Distraction techniques in children during venipuncture: an Italian experience A. BAGNASCO, E. PEZZI, F. ROSA, L. FORNONI *, L. SASSO Health Sciences
J prev med hyg 2012; 53: 44-48 The nurses point of view Distraction techniques in children during venipuncture: an Italian experience A. BAGNASCO, E. PEZZI, F. ROSA, L. FORNONI *, L. SASSO Health Sciences
Generic Pain Assessment Tools 1
 Generic Pain Assessment Tools 1 Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described by the person in terms of such damage, with chronic
Generic Pain Assessment Tools 1 Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described by the person in terms of such damage, with chronic
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guideline Guideline Intravenous Sedation and General Guideline # UM_DEN 01. Date
 IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guideline Guideline Intravenous Sedation and General Guideline # UM_DEN 01 Anesthesia for Dental Services Original Effective Date 01/26/06 Section Dental Revision
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guideline Guideline Intravenous Sedation and General Guideline # UM_DEN 01 Anesthesia for Dental Services Original Effective Date 01/26/06 Section Dental Revision
Oral Preanesthetic Medication In Children: A Comparison of Midazolam Syrup Versus Midazolam Syrup Plus Fentanyl Lozenge.
 13 Oral Preanesthetic Medication In Children: A Comparison of Midazolam Syrup Versus Midazolam Syrup Plus Fentanyl Lozenge. Tarek Atef Tawfic MD Lecturer of anesthesia, faculty of medicine, Alexandria
13 Oral Preanesthetic Medication In Children: A Comparison of Midazolam Syrup Versus Midazolam Syrup Plus Fentanyl Lozenge. Tarek Atef Tawfic MD Lecturer of anesthesia, faculty of medicine, Alexandria
Treating Pain in Pediatrics: Safety First. Nicole Ralston, RN Jamie Sperduto, RN, BSN
 Treating Pain in Pediatrics: Safety First Nicole Ralston, RN Jamie Sperduto, RN, BSN Background Information Due to the current opioid crisis that most states are experiencing, it is necessary to institute
Treating Pain in Pediatrics: Safety First Nicole Ralston, RN Jamie Sperduto, RN, BSN Background Information Due to the current opioid crisis that most states are experiencing, it is necessary to institute
Original Articles. Effects of Parent's Presence on Pain Tolerance in Children during Venipuncture: A Randomised Controlled Trial
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2011;16:247-252 Original Articles Effects of Parent's Presence on Pain Tolerance in Children during Venipuncture: A Randomised Controlled Trial M OZCETIN, M SUREN, E KARAASLAN,
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2011;16:247-252 Original Articles Effects of Parent's Presence on Pain Tolerance in Children during Venipuncture: A Randomised Controlled Trial M OZCETIN, M SUREN, E KARAASLAN,
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Sedation in Children
 CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
Pain in the Pediatric Population
 Objective Pain in the Pediatric Population Noor Daghistani, Pharm.D. Define and discuss types of Discuss barriers in the treatment of in the pediatric population Describe age appropriate strategies and
Objective Pain in the Pediatric Population Noor Daghistani, Pharm.D. Define and discuss types of Discuss barriers in the treatment of in the pediatric population Describe age appropriate strategies and
Wild Child in the PACU: Update on Emergence Agitation
 Wild Child in the PACU: Update on Emergence Agitation Constance S. Houck, MD Senior Associate in Perioperative Anesthesia Children s Hospital, Boston Assistant Professor of Anaesthesia Harvard Medical
Wild Child in the PACU: Update on Emergence Agitation Constance S. Houck, MD Senior Associate in Perioperative Anesthesia Children s Hospital, Boston Assistant Professor of Anaesthesia Harvard Medical
Spinal Anesthesia in Infants
 The heart and science of medicine. UVMHealth.org/Childrens Spinal Anesthesia in Infants Robert Williams, MD Professor of Anesthesia and Pediatrics College of Medicine University of Vermont Conflicts of
The heart and science of medicine. UVMHealth.org/Childrens Spinal Anesthesia in Infants Robert Williams, MD Professor of Anesthesia and Pediatrics College of Medicine University of Vermont Conflicts of
Managing post-operative pain in children
 Managing post-operative pain in children Dr Alison Twycross, Reader in Children s Nursing Faculty of Health and Social Care Sciences, Kingston University and St George s, University of London. Overview
Managing post-operative pain in children Dr Alison Twycross, Reader in Children s Nursing Faculty of Health and Social Care Sciences, Kingston University and St George s, University of London. Overview
Pharmacological methods of behaviour management
 Pharmacological methods of behaviour management Pharmacological methods CONCIOUS SEDATION?? Sedation is the use of a mild sedative (calming drug) to manage special needs or anxiety while a child receives
Pharmacological methods of behaviour management Pharmacological methods CONCIOUS SEDATION?? Sedation is the use of a mild sedative (calming drug) to manage special needs or anxiety while a child receives
Pediatric Patient Selection for Ambulatory Surgery Centers
 Pediatric Patient Selection for Ambulatory Surgery Centers 2017 Dr. Alan Jay Schwartz: Hello. This is Alan Jay Schwartz, Editor-in-Chief of the American Society of Anesthesiologists 2017 Refresher Courses
Pediatric Patient Selection for Ambulatory Surgery Centers 2017 Dr. Alan Jay Schwartz: Hello. This is Alan Jay Schwartz, Editor-in-Chief of the American Society of Anesthesiologists 2017 Refresher Courses
The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children
 The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children Guided Notes for Online Learning Name: Date: 1 Table of Contents Section 1: The Opioid Crisis Page 3 Section 2: Addiction Page 4 Section 3: Trauma Informed Care
The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children Guided Notes for Online Learning Name: Date: 1 Table of Contents Section 1: The Opioid Crisis Page 3 Section 2: Addiction Page 4 Section 3: Trauma Informed Care
Pediatric Grand Rounds - University of TX Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX 9/30/2016. Why is this important?
 Why is this important? Risk of Neurotoxicity in Children from General Anesthesia Marisa Earley, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology UTHSCSA Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery September 30, 2016
Why is this important? Risk of Neurotoxicity in Children from General Anesthesia Marisa Earley, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology UTHSCSA Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery September 30, 2016
(ADULT) Refer to policy MC.E.48 for neonatal to pediatric pain assessment and management.
 Department: Policy/Procedure: PATIENT CARE PAIN ASSESSMENT AND DOCUMENTATION (ADULT) Refer to policy MC.E.48 for neonatal to pediatric pain assessment and management. Definition: Pain can be described
Department: Policy/Procedure: PATIENT CARE PAIN ASSESSMENT AND DOCUMENTATION (ADULT) Refer to policy MC.E.48 for neonatal to pediatric pain assessment and management. Definition: Pain can be described
Difficult Situations in the NICU. Esther Chon, PhD, EdM Miller Children s Hospital NICU Small Baby Unit Training July, 2016
 Difficult Situations in the NICU Esther Chon, PhD, EdM Miller Children s Hospital NICU Small Baby Unit Training July, 2016 TOPICS Compassion Fatigue, Burnout and PTSD Dealing with Death and Loss Moral
Difficult Situations in the NICU Esther Chon, PhD, EdM Miller Children s Hospital NICU Small Baby Unit Training July, 2016 TOPICS Compassion Fatigue, Burnout and PTSD Dealing with Death and Loss Moral
Emotional Development
 Emotional Development How Children Develop Chapter 10 Emotional Intelligence A set of abilities that contribute to competent social functioning: Being able to motivate oneself and persist in the face of
Emotional Development How Children Develop Chapter 10 Emotional Intelligence A set of abilities that contribute to competent social functioning: Being able to motivate oneself and persist in the face of
Maternal Mental Health: Risk Factors, Ramifications, and Roles. Anna Glezer MD UCSF Assistant Clinical Professor Founder, Mind Body Pregnancy
 Maternal Mental Health: Risk Factors, Ramifications, and Roles Anna Glezer MD UCSF Assistant Clinical Professor Founder, Mind Body Pregnancy Disclosures None Objectives for Today Review major maternal
Maternal Mental Health: Risk Factors, Ramifications, and Roles Anna Glezer MD UCSF Assistant Clinical Professor Founder, Mind Body Pregnancy Disclosures None Objectives for Today Review major maternal
Conflict of Interest Disclosure
 Monitoring for Opioid Induced Respiratory Depression: Paradigm Shift from Threshold Monitoring to Trend Monitoring Carla R. Jungquist, ANP BC, PhD Assistant Professor University at Buffalo J. Paul Curry,
Monitoring for Opioid Induced Respiratory Depression: Paradigm Shift from Threshold Monitoring to Trend Monitoring Carla R. Jungquist, ANP BC, PhD Assistant Professor University at Buffalo J. Paul Curry,
Preoperative evaluation, premedication, and induction of anesthesia in infants and children
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Preoperative evaluation, premedication, and induction of anesthesia in infants and children Suzanne Strom Purpose of review Preparation for and induction of anesthesia in children
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Preoperative evaluation, premedication, and induction of anesthesia in infants and children Suzanne Strom Purpose of review Preparation for and induction of anesthesia in children
Relationships Relationships
 PRENATAL OPIATE EXPOSURE IMPACT ON EARLY CHILDHOOD LEARNING AND BEHAVIOR Ira J. Chasnoff, MD NTI Upstream www.ntiupstream.com Children grow and develop in the context of Attachment: Basic Concept Attachment:
PRENATAL OPIATE EXPOSURE IMPACT ON EARLY CHILDHOOD LEARNING AND BEHAVIOR Ira J. Chasnoff, MD NTI Upstream www.ntiupstream.com Children grow and develop in the context of Attachment: Basic Concept Attachment:
Curricular Components for Cardiology EPA
 Curricular Components for Cardiology EPA 1. EPA Title 2. Description of the Activity Diagnosis and management of patients with acute congenital or acquired cardiac problems requiring intensive care. Upon
Curricular Components for Cardiology EPA 1. EPA Title 2. Description of the Activity Diagnosis and management of patients with acute congenital or acquired cardiac problems requiring intensive care. Upon
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
NHS Training for AHP Support Workers. Workbook 5 Pain control awareness
 NHS Training for AHP Support Workers Workbook 5 Pain control awareness Contents Workbook 5 Pain control awareness 1 5.1 Aim 3 5.3 What is pain and why does it occur? 4 5.4 Pain rating scales 11 5.5 Pain
NHS Training for AHP Support Workers Workbook 5 Pain control awareness Contents Workbook 5 Pain control awareness 1 5.1 Aim 3 5.3 What is pain and why does it occur? 4 5.4 Pain rating scales 11 5.5 Pain
Guideline for the management of pain in children
 The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
The Vine Assessment System by LifeCubby
 The Vine Assessment System by LifeCubby A Fully Integrated Platform for Observation, Daily Reporting, Communications and Assessment For Early Childhood Professionals and the Families that they Serve Alignment
The Vine Assessment System by LifeCubby A Fully Integrated Platform for Observation, Daily Reporting, Communications and Assessment For Early Childhood Professionals and the Families that they Serve Alignment
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of
 Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
Effect of Kaleidoscope on Pain Perception of Children Aged 4-6 Years During Intravenous Cannulation
 American Journal of Nursing Science 2018; 7(4): 137-142 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajns doi: 10.11648/j.ajns.20180704.14 ISSN: 2328-5745 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5753 (Online) Effect of Kaleidoscope
American Journal of Nursing Science 2018; 7(4): 137-142 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajns doi: 10.11648/j.ajns.20180704.14 ISSN: 2328-5745 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5753 (Online) Effect of Kaleidoscope
Pediatric Patient Overview
 Emergency Medical Services Seattle/King County Public Health 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 206.296.4863 Last Updated December 14, 2015 Pediatric Patient Overview Contents PEDIATRIC BASICS...
Emergency Medical Services Seattle/King County Public Health 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 206.296.4863 Last Updated December 14, 2015 Pediatric Patient Overview Contents PEDIATRIC BASICS...
Comparison of Drug Clonidine and Midazolam as Premedication s in Children: An Institutional Based Study
 Original article: Comparison of Drug Clonidine and Midazolam as Premedication s in Children: An Institutional Based Study Dr. Gurdeep Singh Jheetay Associate Professor, Department of Anaesthesia, Shri
Original article: Comparison of Drug Clonidine and Midazolam as Premedication s in Children: An Institutional Based Study Dr. Gurdeep Singh Jheetay Associate Professor, Department of Anaesthesia, Shri
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy
 Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
Cross-validation of a composite pain scale for preschool children within 24 hours of surgery
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 87 (3): 400±5 (2001) Cross-validation of a composite pain scale for preschool children within 24 hours of surgery S. Suraseranivongse*, U. Santawat, K. Kraiprasit, S. Petcharatana,
British Journal of Anaesthesia 87 (3): 400±5 (2001) Cross-validation of a composite pain scale for preschool children within 24 hours of surgery S. Suraseranivongse*, U. Santawat, K. Kraiprasit, S. Petcharatana,
Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation. Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016
 Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016 Introduction Repetitive collapse of the upper airway > sleep fragmentation, > hypoxemia, hypercapnia, > marked variations in intrathoracic
Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016 Introduction Repetitive collapse of the upper airway > sleep fragmentation, > hypoxemia, hypercapnia, > marked variations in intrathoracic
Chapter 19. Pain Management, Rest, and Restorative Sleep. Fundamentals of Nursing Care Concepts, Connections, & Skills, Second Edition
 Chapter 19 Pain Management, Rest, and Restorative Sleep Presented by Farahnaz Danandeh, Nursing Educator @ GHOC Classifications of Pain Acute: Sudden pain; short duration of less than 6 months Chronic:
Chapter 19 Pain Management, Rest, and Restorative Sleep Presented by Farahnaz Danandeh, Nursing Educator @ GHOC Classifications of Pain Acute: Sudden pain; short duration of less than 6 months Chronic:
James J. Mooney * and Ashley McDonell ** Introduction
 Opioid Administration as Predictor of Pediatric Epidural Failure James J. Mooney * and Ashley McDonell ** Background: Increasing use of regional analgesia in pediatric populations requires a better understanding
Opioid Administration as Predictor of Pediatric Epidural Failure James J. Mooney * and Ashley McDonell ** Background: Increasing use of regional analgesia in pediatric populations requires a better understanding
Therapies for Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers
 Therapies for Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers Is This Guide Right for the Child in My Care? Yes, if: The child you care for is 0 to 12 years old
Therapies for Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder A Review of the Research for Parents and Caregivers Is This Guide Right for the Child in My Care? Yes, if: The child you care for is 0 to 12 years old
PAIN MANAGEMENT IN CHILDREN
 SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education (ICON 2016) Presentation Date: 23 rd January 2016 PAIN MANAGEMENT IN CHILDREN Aziza Shad, MD Ellen Wasserman Chair of Pediatrics Chief, Division of Pediatric Hematology
SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education (ICON 2016) Presentation Date: 23 rd January 2016 PAIN MANAGEMENT IN CHILDREN Aziza Shad, MD Ellen Wasserman Chair of Pediatrics Chief, Division of Pediatric Hematology
Pain Assessment in Children
 Pain Assessment in Children Professor Alison Twycross Head of Department for Children s Nursing September 2016 Learning outcomes By the end of the session participants will: Be able to describe the different
Pain Assessment in Children Professor Alison Twycross Head of Department for Children s Nursing September 2016 Learning outcomes By the end of the session participants will: Be able to describe the different
Sleep: What s the big deal?
 Rise & Shine: The Importance of Sleep Sleep: What s the big deal? Sleep affects every aspect of a child s physical, emotional, cognitive, and social development. 1 Sleep is the Primary Activity of the
Rise & Shine: The Importance of Sleep Sleep: What s the big deal? Sleep affects every aspect of a child s physical, emotional, cognitive, and social development. 1 Sleep is the Primary Activity of the
Persistent post surgical pain. Jim Olson Waitemata DHB Auckland
 Persistent post surgical pain Jim Olson Waitemata DHB Auckland Declaration Within the last five years I have accepted hospitality from the pharmaceutical industry, received honoraria from Mundipharma NZ
Persistent post surgical pain Jim Olson Waitemata DHB Auckland Declaration Within the last five years I have accepted hospitality from the pharmaceutical industry, received honoraria from Mundipharma NZ
ANESTHESIA. Planning Your Childbirth: Pain Relief During Labor and Delivery EACH WOMAN S LABOR IS
 ANESTHESIA & YOU Planning Your Childbirth: Pain Relief During Labor and Delivery EACH WOMAN S LABOR IS UNIQUE T he amount of pain a woman feels during labor may differ from that felt by another woman.
ANESTHESIA & YOU Planning Your Childbirth: Pain Relief During Labor and Delivery EACH WOMAN S LABOR IS UNIQUE T he amount of pain a woman feels during labor may differ from that felt by another woman.
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR) ISSN (Online): Index Copernicus Value (2013): 6.14 Impact Factor (2013): 4.
 Effectiveness of Two Distraction Techniques in Altering Behaviour Response to Pain among Children (1-3 years) Receiving Immunisation at Selected Immunisation Clinics in Mangalore Mukesh Chandra Sharma
Effectiveness of Two Distraction Techniques in Altering Behaviour Response to Pain among Children (1-3 years) Receiving Immunisation at Selected Immunisation Clinics in Mangalore Mukesh Chandra Sharma
Outcomes of Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
 Outcomes of Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Caroline O. Chua, MD, FAAP Medical Director, Division of Neonatology Director, Neonatal Follow Up Clinic Nemours Children s Hospital Orlando, Florida
Outcomes of Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Caroline O. Chua, MD, FAAP Medical Director, Division of Neonatology Director, Neonatal Follow Up Clinic Nemours Children s Hospital Orlando, Florida
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
1. Influence of isoflurane exposure in pregnant rats on the learning and memory of offspring
 1. Influence of isoflurane exposure in pregnant rats on the learning and memory of offspring Huang W, Dong Y, Zhao G, et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2018 18:5 Concerns remain about possible effects of general
1. Influence of isoflurane exposure in pregnant rats on the learning and memory of offspring Huang W, Dong Y, Zhao G, et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2018 18:5 Concerns remain about possible effects of general
Preoperative Interactive Communication Program to Children and Effects at Induction of General Anaesthesia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Preoperative Interactive Communication Program to Children and Effects at Induction of General Anaesthesia NAZIA AKHTAR 1, MUHAMMAD ANWAR-UL-HAQ 2 ABSTRACT Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Preoperative Interactive Communication Program to Children and Effects at Induction of General Anaesthesia NAZIA AKHTAR 1, MUHAMMAD ANWAR-UL-HAQ 2 ABSTRACT Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness
Immunisations under sedation at a tertiary paediatric hospital in Melbourne, Australia from
 Immunisations under sedation at a tertiary paediatric hospital in Melbourne, Australia from 2012-2016 Dr Kirsten Perrett Paediatrician, Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne NHMRC Research Fellow, Murdoch
Immunisations under sedation at a tertiary paediatric hospital in Melbourne, Australia from 2012-2016 Dr Kirsten Perrett Paediatrician, Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne NHMRC Research Fellow, Murdoch
Pain Management at Stony Brook Medicine
 Pain Management at Stony Brook Medicine Pain Management Policy All patients must have effective pain management Appropriate screening and pain assessment Documentation Care and treatment Pain education
Pain Management at Stony Brook Medicine Pain Management Policy All patients must have effective pain management Appropriate screening and pain assessment Documentation Care and treatment Pain education
Management of Pain in Children. The Royal College of Emergency Medicine. Best Practice Guideline
 The Royal College of Emergency Medicine Best Practice Guideline Management of Pain in Children Revised Management of pain in children (REV July 2017) 1 July 2017 Summary of recommendations 1. Recognition
The Royal College of Emergency Medicine Best Practice Guideline Management of Pain in Children Revised Management of pain in children (REV July 2017) 1 July 2017 Summary of recommendations 1. Recognition
Preemptive Analgesia in Children with Caudal Blocks
 Article ID: WMC001679 2046-1690 Preemptive Analgesia in Children with Caudal Blocks Corresponding Author: Dr. Antigona Hasani, Anesthesiology and Reanimation, Pediatric Anesthesiologist, University Clinical
Article ID: WMC001679 2046-1690 Preemptive Analgesia in Children with Caudal Blocks Corresponding Author: Dr. Antigona Hasani, Anesthesiology and Reanimation, Pediatric Anesthesiologist, University Clinical
Disclosures: This presenter has no financial relationships with commercial interests.
 Session: L127 Session: L308 Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy in a Child With Down Syndrome: More to It Than You Think! Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children s Hospital, Houston, TX Disclosures: This
Session: L127 Session: L308 Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy in a Child With Down Syndrome: More to It Than You Think! Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children s Hospital, Houston, TX Disclosures: This
Neonatal Stress, Pain and Cognitive. Anne Synnes MDCM, MHSc BC Women s Hospital University of British Columbia
 Neonatal Stress, Pain and Cognitive Deficits Anne Synnes MDCM, MHSc BC Women s Hospital University of British Columbia Learning objectives Scope of pain and stress in the preterm baby in the NICU Effect
Neonatal Stress, Pain and Cognitive Deficits Anne Synnes MDCM, MHSc BC Women s Hospital University of British Columbia Learning objectives Scope of pain and stress in the preterm baby in the NICU Effect
Colonic (Large Intestine) Manometry
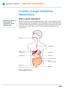 Patient and Family Education Colonic (Large Intestine) Manometry Manometry measures the pressure of contractions of the digestive tract. What is colonic manometry? The colon (also known as the large intestine)
Patient and Family Education Colonic (Large Intestine) Manometry Manometry measures the pressure of contractions of the digestive tract. What is colonic manometry? The colon (also known as the large intestine)
Learning when to treat repetitive behaviors in autism
 VIEWPOINT Learning when to treat repetitive behaviors in autism BY CLARE HARROP 10 NOVEMBER 2015 Autism spectrum disorder involves two core deficits: problems with social communication and restricted and
VIEWPOINT Learning when to treat repetitive behaviors in autism BY CLARE HARROP 10 NOVEMBER 2015 Autism spectrum disorder involves two core deficits: problems with social communication and restricted and
CURRICULUM VITAE ANDREW S. TRIEBWASSER, MD
 CURRICULUM VITAE ANDREW S. TRIEBWASSER, MD Department of Anesthesiology Rhode Island Hospital 593 Eddy Street Providence, RI 02903 Tel: (401) 444-5142 Fax: (401) 444-5083 Email: atriebwasser@lifespan.org
CURRICULUM VITAE ANDREW S. TRIEBWASSER, MD Department of Anesthesiology Rhode Island Hospital 593 Eddy Street Providence, RI 02903 Tel: (401) 444-5142 Fax: (401) 444-5083 Email: atriebwasser@lifespan.org
Interaction between Sedation and Weaning: How to Balance Them? Guillermo Castorena MD Fundacion Clinica Medica Sur Mexico
 Interaction between Sedation and Weaning: How to Balance Them? Guillermo Castorena MD Fundacion Clinica Medica Sur Mexico Balance is not that easy! Weaning Weaning is the liberation of a patient from
Interaction between Sedation and Weaning: How to Balance Them? Guillermo Castorena MD Fundacion Clinica Medica Sur Mexico Balance is not that easy! Weaning Weaning is the liberation of a patient from
Peri-Operative Management: Guidelines for Inpatient Management of Children with Sickle Cell Disease
 Version 02 Approved by Interprofessional Patient Care Committee: September 16, 2016 1.0 Background Children with Sickle Cell are at risk of developing post-operative Acute Chest Syndrome. With improvements
Version 02 Approved by Interprofessional Patient Care Committee: September 16, 2016 1.0 Background Children with Sickle Cell are at risk of developing post-operative Acute Chest Syndrome. With improvements
Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view
 Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view 1st Geneva International SCIENTIFIC DAY February 3 rd 2010 E. Schiffer Dept APSI, HUG 1 Fast-Track in colorectal
Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view 1st Geneva International SCIENTIFIC DAY February 3 rd 2010 E. Schiffer Dept APSI, HUG 1 Fast-Track in colorectal
The effect of intravenous ketamine versus thiopental in the preoperative holding area on the separation anxiety and emergence agitation in children
 Journal of Anesthesiology 2014; 2(2): 13-17 Published online April 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ja) doi: 10.11648/j.ja.20140202.11 The effect of intravenous ketamine versus thiopental
Journal of Anesthesiology 2014; 2(2): 13-17 Published online April 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ja) doi: 10.11648/j.ja.20140202.11 The effect of intravenous ketamine versus thiopental
Anesthesia and You. Planning Your Childbirth
 Anesthesia and You Planning Your Childbirth Anesthesia Options for Labor and Delivery There are many medications available to women during labor and childbirth. However, some pain relief choices may be
Anesthesia and You Planning Your Childbirth Anesthesia Options for Labor and Delivery There are many medications available to women during labor and childbirth. However, some pain relief choices may be
Understanding the impact of pain and dementia
 Understanding the impact of pain and dementia Knowing how to identify and manage the symptoms of pain in people living with dementia is an important part of a carer s role. This guide provides an overview
Understanding the impact of pain and dementia Knowing how to identify and manage the symptoms of pain in people living with dementia is an important part of a carer s role. This guide provides an overview
Disclosures. Objectives. OSA Death and Near Miss Registry The path to creation.
 OSA Death and Near Miss Registry The path to creation. October 23, 2015 Norman Bolden, M.D. Vice-Chairman, Department of Anesthesiology Associate Professor, Case Western Reserve University n None Disclosures
OSA Death and Near Miss Registry The path to creation. October 23, 2015 Norman Bolden, M.D. Vice-Chairman, Department of Anesthesiology Associate Professor, Case Western Reserve University n None Disclosures
