UNIVERSA MEDICINA. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: practical experience in 30 subjects
|
|
|
- Brett Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSA MEDICINA October-December, 2008 Vol.27 - No.4 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: practical experience in 30 subjects A. Nurman* ABSTRACT * Department of Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty, Trisakti University Correspondence Dr. A. Nurman, Ph.D, Sp.PD, KGEH Department of Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty, Trisakti University Jl.Kyai Tapa 260-Grogol Jakarta Phone: ext nurman_achmad@yahoo.com Univ Med 2008; 27: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a noninvasive method of imaging the biliary and pancreatic ducts. No special patient preparation is required but the usual contraindications to MR scanning apply. The diagnostic performance of MRCP in most biliary tract diseases is similar to that of more invasive techniques of direct cholangiography such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The objectives of this study were to investigate the diagnostic efficacy of MRCP in patients with abdominal pain with lesser likelihood of having choledochal stone and to determine whether use of MRCP could eliminate the need for purely diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography (ERCP). A total of 30 patients with suspected biliopancreatic pathology from several hospital was studied retrospectiely between January 2007 and December 2008 in Jakarta. The sensitivity and specificity of MRCP was 92.59% (95% Confidence Interval, %) and 66.67% (95% Confidence Interval, %), respectively. The positive predictive value of MRCP for all biliary pathology was 96.15% (95% Confidence Interval, %) The negative predictive value of MRCP was 50.00% (95% Confidence Interval, %). MRCP seems to be effective in diagnosing patients with abdominal pain with lesser likelihood of having choledochal stone. Keywords : Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, biliary, pancreatic INTRODUCTION Cholangiography is often used in patients suspected of having biliary tract and pancreatic disorders to uncover the exact diagnoses of the disease. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was considered the golden standard method for the diagnosis of these diseases, but carries a potential risk of complications, including pancreatitis, haemorrhage, particularly from sphyncterotomy sites, and duodenal perforation. (1-3) The procedure may not always be successful. ERCP is highly sensitive and specific, but is invasive 150
2 Nurman Cholangiopancreatography and inconvenient for the patient, requiring sedation and contrast (with minimal risk of allergic reaction), and associated with significant morbidity (5 10%) and mortality (<1%). (4) At present magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) begins to replace ERCP as a screening method for patients suspected of having biliary obstruction due to biliary calculus. MRCP was first described by Wallner et al. in (5) The use of single-shot fast sequences in a breathhold period provides heavily T2-weighted sequences allowing thick slices and avoiding secondary reconstructions and artifacts. This technologic development has led to its widespread use. (6,7) As a result, MRCP is an easy, quick, noninvasive test accessible to all patients who do not have contraindications. MRCP is also useful in patients with failed or incomplete ERCP. There is also a role for MRCP in the evaluation of patients prior to surgical procedures, to plan what kind of surgical procedure will be undertaken, and to demonstrate the alteration the bile ducts after biliodigestive surgery. MRCP is non-invasive for studying the biliary tree and requires no ionizing radiation or iodinated contrast. It gives high-resolution projectional images of the common bile duct (CBD) with no known hazards in the absence of incompatible foreign bodies. The aim of this study was to investigate the diagnostic validity of MRCP in assessing symptomatic patients suspected of having hepatopancreaticobiliary diseases. METHODS Study design This was a retrospective cohort study of a consecutive group of patients who underwent MRCP during a period of 2 years ( ). Patients Patients were identified from several hospitals in Jakarta over a total period of 24- months. Collected data included clinical presentation, liver function tests, abdominal ultrasound, and MRCP findings, and procedurerelated complications. MRCP Technique All MRCP images were obtained by using a 1.5-T superconducting magnet with a gradient strength of 50 mt/m (General Electric, Milwaukee, Wis, USA), with a body-phased array coil through the liver and pancreas. The mean time of the MRCP examination with evaluation was 15 minutes. MRCP was performed by using thick slab single shot fast spin echo (SSFSE), with selective fat saturation. The first sequence afforded a single image with a dimension of 40 mm, and exhibited the following parameters: TR/TE/FA (2800/1100/ 180), matrix 240 x 256, field of view of 300 mm, and acquisition time of 7 seconds. The second sequence yielded 13 contiguous 5-mm slices and presented the following parameters: TR/TE/FA (10.92/87/180), matrix 256 x 224, field of view of 280 mm, and acquisition time of 19 seconds. Statistical analysis The data were entered in a Microsoft Excel database. The results of MRCP were analysed against laboratory findings, ultrasound examinations and the final diagnoses for the entire study population. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were individually calculated in the usual manner. RESULTS Thirty patients underwent MRCP and were eligible for further evaluation during the 24- month period studied, of whom 15 (50%) were 151
3 Univ Med Vol.27 - No.4 female and 15 (50%) were male with median age of 56 years (range years). Abdominal pain was the predominant symptom at presentation (90%) with 5 subjects having associated jaundice. Pancreatitis (n=6) and cholangitis (n=22) were the other most common features. Ultrasound Ultrasound scan of the hepatobiliary system was the primary investigation in 30 patients, of whom 10 (33.3%) showed evidence of cholelithiasis and 2 (6.7%) of biliary sludge. Other abnormalities seen were dilated CBD, liver cirrhosis (LC), dilated gall bladder (GB), dilated extrahepatic bile duct (EHBD), dilated intrahepatic bile duct (IHBD), and choledochal cyst in fifteen patients. No abnormality was observed in 3 patients. Figure 1. MRCP in gall bladder stone MRCP Of 30 patients referred, MRCP was successfully performed in all (100.0%) patients. Final diagnosis The final diagnoses of the patients were: i) choledochal cysts in 3 patients (10%); ii) Figure 2. Klatskin tumor choledochal stone/sludge in 5 patients (16.7%); iii) gall bladder stone in 8 patients (26.7%) (Figure 1); iv) intrahepatic stone 1 patient (3.3%);v) distal obstruction of the common bile duct due to mass in 7 cases (23.3%), and follow up CT scan/mri revealed carcinoma of the pancreas in 5 patients (16,7%) and carcinoma of the papilla in 2 patients (6.7%); vi) stricture of the common bile duct post laparoscopic cholecystectomy in 1 patient (3.3%); viii) Klatskin tumor in 1 patient (Figure 2); (3,3%); viii) post hepaticojejunostomy operation in choledochal cyst in 1 patient (3%); and ix) no abnormality in 3 (10%) patients (Figure 3). Figure 3. Normal MRCP 152
4 Nurman Cholangiopancreatography Table 1. Sensitivity and specificity of MRCP as evidenced against gold standard procedures MRCP Final diagnosis Positive Negative Total Positive Negative Total Accuracy of MRCP A total of 30 patients with complete comparative data were considered for detailed analysis. The sensitivity and specificity of MRCP was 92.59% (95% Confidence Interval, %) and 66.67% (95% Confidence Interval, %), respectively. The positive predictive value (having the disease) of MRCP for all biliary pathology was 96.15% (95% Confidence Interval, %) The negative predictive value of MRCP (truly disease free) was 50.00% (95% Confidence Interval, %) (Table 1). There were 18 gall bladder stones, choledochal cyst, and common bile duct sludge among various positive diagnoses, based on all investigations (Table 2). DISCUSSION MRCP is a noninvasive method of imaging the biliary and pancreatic ducts and until now this technique continues to be improved. The basic principle underlying MRCP is that body fluids, such as bile and pancreatic secretions, have high signal intensity in heavily T2- weighted magnetic resonance (i.e. they appear white), whereas background tissues such as the surrounding liver and flowing blood generate little signal (i.e. they appear dark). As a result of this combination of imaging characteristics, MRCP provides optimal contrast between the hyperintense signal of the bile and pancreatic secretions and the hypointense signal of the background tissue (solid organs), while blood vessels have no measurable signal. On these images the intrinsic fluids of the the biliary and pancreatic ducts make up the cholangiogram and pancreatogram. At present, ERCP is considered the gold standard method for the diagnosis of ductal calculus, but carries a potential risk of complications, including pancreatitis, and bleeding, particularly from sphincterotomy sites and duodenal perforation. (8) Most of the patients presented with the chief complaint of right upper quadrant or epigastric pain, with or without jaundice, or were jaundiced patients with or without upper abdominal pain. Abdominal ultrasound (US) and CT scan were mostly used as an initial evaluation in these patients. In these cases the roadmap of the biliary tract and the pancreatic duct is needed. The next examination will be the choice of to decide on ERCP or MRCP. (9) Table 2. Different diagnoses among true positive and false negative of results of MRCP Diagnosis Number True positive Gall bladder stone 13 Choledochal cyst 3 Carcinoma pancreas 7 Obstructed hepatojejunistomy 2 False negative Common bile duct sludge 1 Gall bladder stone 1 Total
5 Univ Med Vol.27 - No.4 If the compaint was due to biliary disease, i.e. choledochal stone or stricture/dilatation obstruction of the bile or pancreatic disease, it was easy to find the dilatation of the bile duct on abdominal US/CT. In these cases ERCP will be the choice because it can be followed by therapeutic endoscopy i.e. sphincterotomy and stone extraction, stent/nasobiliary tube installment etc.the choice of imaging will be ERCP when it is assumed that it will be followed by therapeutic endoscopy. (10) If the complaints were due parenchymal liver disease, there would be no dilatation nor abnormality of the biliary tract or pancreatic duct, such that it will not be followed by therapeutic endoscopy, thus MRCP would be the choice. MRCP would be chosen when the likelihood for therapeutic intervention were less, hence unnecessary ERCP is hereby avoided. This study showed that the sensitivity and positive predictive value of MRCP for the diagnosis is extremely high, being 92.59% (95% Confidence Interval, %) and 96.15% (95% Confidence Interval, %) respectively. A prospective study in Spain found that MRCP had a sensitivity of 91% and positive predictive value of 89%, similar to our study. (11) But the specificity of 66.67% (95% Confidence Interval, %) was lower than that obtained in the study by Calco et al (84%). The negative predictive value in the present study was also low (50.0%; 95% Confidence Interval, %), compared to the Spanish study (88%). No special patient preparation is required, but the usual contraindications to MR scanning apply. (1,12) Patients with cardiac pacemakers, neurostimulators, or ferromagnetic aneurysm clips are excluded. The examination is usually performed after the patient has fasted for several hours to allow filling of the gallbladder and emptying of the stomach. No sedation is required, and no hospitalization is needed. In some patients claustrophobia might be a problem. (13) Oral contrast agents are not administered, no intravenous contrast agents are needed, and there is no radiation exposure. (10) MRCP is an ideal imaging method for patients with allergies to iodide/iodine-based contrast, or those with a general history of atopy, and for preventing the occurence of contrast nephropathy. (10) In this study as in that from a different center, (10) the procedures were performed with the indication as screening in patients with right upper quadrant/epigastric pain with no dilatation/equivocal dilatation of the common bile duct with/without gall bladder stone, or with normal/disturbed liver function test, with the goal to avoid unnecessary ERCP. In acute pancreatitis ERCP is avoided, because ERCP carries potential risk of complication including pancreatitis, bleeding particularly from sphincterotomy sites, and duodenal perforation. (14) If dilatation of bile duct was found then ERCP would be the choice and subsequent sphincterotomy and extraction of choledochal stone will be retrogradely performed. MRCP is an alternative to diagnostic ERCP for the imaging of the bile tree and the pancreatic ducts. A major feature of MRCP is that is not a therapeutic procedure, while in contrast ERCP is used for both diagnosis and treatment. (1) MRCP is the only modality that allows imaging of these ducts in the basal state, as extrinsic contrast agents are not used, (10) hence more accurately displays the native calibre of the duct than ERCP. Because of its noninvasive nature, it does not carry the risks and complications associated with ERCP and Percutaeous Transhepatic Cholangiography (PTC). (1) In MRCP there is no morbidity nor mortality like in ERCP/PTC. MRCP is particularly useful where ERCP is difficult, hazardous or impossible (12) to perform, ie in patients with 154
6 Nurman Cholangiopancreatography anatomical/structural abnormalities, such as gastroenteric anastomosis or gastrojejunostomy. In this series MRCP was performed in a patient after hepaticojejunostomy because it was impossible to perform ERCP in this setting. In some situations MRCP maybe preferable to ERCP, such as situations where MRCP may give more informations than ERCP (eg hilar biliary strictures, lesions associated with complete pancreatic or biliary duct cut-off). MRCP is a non invasive tool that is suitable in patients suspected of having to have pancreaticobiliary disease, where there is no likelihood or little possibility to perform therapeutic intervention, eg patients with asymptomatic cholelithiasis without clinical evidence of clinical bile duct disease, like the presence of jaundice and abnormalities of liver fuction tests. MRCP is a non invasive imaging technique, seems to be highly accurate for the presense of obstruction, (15,16) but is less accurate at differentiating malignant from benign causes of obstruction. (10) It is almost as good as ERCP in the diagnoses of common bile duct stones (CBDS), although the ability of MR to detect small stones in nondilated ducts may be limited. (10,17) MRCP may be considered as a new gold standard for the investigation of CBDS and permits reservation of ERCP to patients with a high probability of therapeutic intervention. (10) The Eropean Association of Laparoscopic Surgeons consider MRCP to be the standard diagnostic test for patients with an intermediate probability of CBDS. (17) The presence of intracranial metallic clips, claustrophobia, or morbid obesity might preclude MRCP. (4,15) CONCLUSIONS Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography seems to be effective in the diagnosis of patients with abdominal pain with lesser likelihood of having choledochal stone. It plays a fundamental role in patients with a low or intermediate risk of choledocholithiasis, contributing to the avoidance of purely diagnostic ERCP. REFERENCES 1. Mac Eneaney P, Mitchell MT, Mc Dermoth R. Update on magnetic resonance cholagio pancreatography. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 2002; 31: Ballinger PW, Frank ED. Biliary tract and gallbladder. In: Merrill s atlas at radiographic position and radiologic procedures. Vol. II. Missouri: Mosby; p Karani J. The biliary tract. In: Sutton D, editor. Textbook of radiology and imaging. Vol.1. London: Churchill Livingstone; p Shanmugam AV, Beattie GC, Yule SR, Reid W, London MA. Is magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography the new goldstandard in biliary imaging? Br J Radiol 2005; 78: Wallner BK, Schumacher KA, Weidenmaier W, Friedrich JM. Dilated biliary tract: evaluation with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with a T2-weighted contrast-enhanced fast sequence. Radiology 1991; 18: Mougenel JL, Hudziak H, Ernst O. Evaluation of a new sequence of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in thick cut and one shot acquisition. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 2000; 24: Gallix BP, Régent D, Bruel JM. Use of magnetic resonance cholangiography in the diagnosis of choledocholithiasis. Abdom Imaging 2001; 26: Topal B, Van de Moortel M, Fieuws S, Vanbeckevoort D. The value of magnetic resonance cholangio pancratography in predicting common bile duct stones in patients with gallstone disease. Br J Surg 2003; 90: Wijaya PM. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography for biliary obstruction. 7 th Hepatobiliary Surgical Update and Workshop on Therapeutic Endoscopy. Jakarta; Barrish MA, Yuccel EK, Ferrucci JT. Magnetic resonance cholangio pancreatography. N Engl J Med 1999; 341:
7 Univ Med Vol.27 - No Calco MM, Bufanda L, Calderon A, Heras I, Cabriada JL, Bernal A, et al. Role of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in patients with suspected choledocholithiasis. Mayo Clin Proc 2002; 77: Romagnuolo J, Bardon M, Rahme E, Joseph L, Reinhold C, Barkun AN. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: a meta analysis of test performance in suspected biliary disease. Ann Inter Med 2003; 139-7: Kaltenhaler E, Vergel YB, Chilcot J, Thomas S, Blakeborough T, Walters SJ, et al. A systemic review and economic evaluation of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography compare with diagnostic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopan-creatography. Health Technology Assessment; Availabe at: /summ810.htm. Accessed August 1, Leung J. Fundamentals of ERCP, in advanced digestive endoscopy: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. In: Cotton PB, Leung J, editors. 1 st Ed. Massachusets: Blackwell Publishing; p Georgopulos SK, Schwartz LH, Jarnagin WR, Gerdes H, Breite I, Fong Y, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance and endoscopic retrograde cholangiography in malignant pancreaticobiliary obstruction. Arch Surg 1999; 134: Fulcher AS,Turner MA, Capps GW, Zfass AM, Baker K. Half-Fourier RARE magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: experience in 300 subjects. Radiology 1998; 207: Williams EJ, Green J, Beckingham I, Park R, Martin D, Lombard M. Guidelines of the management of common bile duct stones. GUT 2008; 57:
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 10, by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN /01/$20.00
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 10, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02807-6 Can Endoscopic
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 10, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02807-6 Can Endoscopic
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Predictors of abnormalities on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: is there a role when the biliary tree is normal on previous imaging?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2019) 32, 1-6 Predictors of abnormalities on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: is there a role when the biliary tree is normal on previous imaging?
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2019) 32, 1-6 Predictors of abnormalities on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: is there a role when the biliary tree is normal on previous imaging?
ACCURACY OF MRCP COMPARED WITH ERCP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF BILE DUCT STONES
 ejpmr, 2016,3(8), 27-32 SJIF Impact Factor 3.628 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF European PHARMACEUTICAL Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical Research AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2394-3211 www.ejpmr.com
ejpmr, 2016,3(8), 27-32 SJIF Impact Factor 3.628 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF European PHARMACEUTICAL Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical Research AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2394-3211 www.ejpmr.com
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Endoscopic Retrograde Pancreatography and Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. TEAM 1 Janix M. De Guzman, MD Presentor
 Endoscopic Retrograde Pancreatography and Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy TEAM 1 Janix M. De Guzman, MD Presentor Premise 40F Jaundice Abdominal pain US finding of gallstones with apparently normal common
Endoscopic Retrograde Pancreatography and Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy TEAM 1 Janix M. De Guzman, MD Presentor Premise 40F Jaundice Abdominal pain US finding of gallstones with apparently normal common
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Role of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in diagnosing pancreatobiliary pathologies: a prospective study
 International Surgery Journal Nirhale DS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Jun;5(6):2233-2237 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20182228
International Surgery Journal Nirhale DS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Jun;5(6):2233-2237 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20182228
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE
 ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital
 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
Research Article The Diagnostic Accuracy of Linear Endoscopic Ultrasound for Evaluating Symptoms Suggestive of Common Bile Duct Stones
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 6957235, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6957235 Research Article The Diagnostic Accuracy of Linear Endoscopic Ultrasound for Evaluating
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 6957235, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6957235 Research Article The Diagnostic Accuracy of Linear Endoscopic Ultrasound for Evaluating
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP
 R.C. Chen, K.Y. Lin, J.M. Lii, et al MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP Ran-Chou Chen, 1,2 Kuang-Yang Lin, 3
R.C. Chen, K.Y. Lin, J.M. Lii, et al MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP Ran-Chou Chen, 1,2 Kuang-Yang Lin, 3
Management of Gallstone Pancreatitis: Effects of Deviation from Clinical Guidelines
 Management of Gallstone Pancreatitis: Effects of Deviation from Clinical Guidelines Kevin Sargen, Andrew N Kingsnorth Department of Surgery, Plymouth Postgraduate Medical School, Derriford Hospital. Plymouth.
Management of Gallstone Pancreatitis: Effects of Deviation from Clinical Guidelines Kevin Sargen, Andrew N Kingsnorth Department of Surgery, Plymouth Postgraduate Medical School, Derriford Hospital. Plymouth.
Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-6 Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria Ankit Chhoda
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-6 Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria Ankit Chhoda
UTILITY OF THREE DIMENSIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BILIARY OBSTRUCTION IN ADULTS
 - 842 - UTILITY OF THREE DIMENSIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BILIARY OBSTRUCTION IN ADULTS Moanes M. Enaba MD *Tarek H. ELKammash**MD,, Mansour M. Morsy ***MD * Department
- 842 - UTILITY OF THREE DIMENSIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BILIARY OBSTRUCTION IN ADULTS Moanes M. Enaba MD *Tarek H. ELKammash**MD,, Mansour M. Morsy ***MD * Department
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Versus Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Findings in the Postorthotopic Liver Transplant Population Authors: *Ashok Shiani,
Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Versus Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Findings in the Postorthotopic Liver Transplant Population Authors: *Ashok Shiani,
Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions
 November 2014 Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions Colin Nevins, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Initial course and work-up Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
November 2014 Cholangiocarcinoma: Radiologic evaluation and interventions Colin Nevins, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Initial course and work-up Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Downloaded from jssu.ssu.ac.ir at 13:10 IRST on Saturday October 28th 2017
 Journal of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences Vol. 21, No. 5, Nov-Dec 2013 Pages: 675-681 1392 5 21 675-681 : 3 2* 1 1392/8/ : -1-2 -3 1391/8/24 : (). :. 1390 200 :.. SPSS (%0/5) 200 (8%) (%9/5)19
Journal of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences Vol. 21, No. 5, Nov-Dec 2013 Pages: 675-681 1392 5 21 675-681 : 3 2* 1 1392/8/ : -1-2 -3 1391/8/24 : (). :. 1390 200 :.. SPSS (%0/5) 200 (8%) (%9/5)19
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging. technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts,
 SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion
 Acta Med Kindai Univ Vol.43, No.1 1-8, 2018 1 MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion Shojiro Hidaka 1,2,
Acta Med Kindai Univ Vol.43, No.1 1-8, 2018 1 MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion Shojiro Hidaka 1,2,
The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP
 The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP Mauro Giuliani, MD, Specialist in Visceral Surgery, Vice Head Physician, Surgical Ward, Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Alberto Fasoli, MD,
The campaign on laboratory: focus on Gallstone Disease and ERCP Mauro Giuliani, MD, Specialist in Visceral Surgery, Vice Head Physician, Surgical Ward, Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Alberto Fasoli, MD,
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment
 State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
Management of Gallbladder Disease
 Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do?
 ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
Role of MRCP in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Causes of Biliary Obstruction
 Original Article Role of MRCP in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Causes of Biliary Obstruction DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/14174.6771 Radiology Section Meena Suthar 1, Sunita Purohit 2, Vivek Bhargav
Original Article Role of MRCP in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Causes of Biliary Obstruction DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/14174.6771 Radiology Section Meena Suthar 1, Sunita Purohit 2, Vivek Bhargav
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico
 Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
Treatment for cancer of the gall bladder
 Treatment for cancer of the gall bladder Hepatobiliary Services Information for Patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction The aim of this booklet is to help you understand more about
Treatment for cancer of the gall bladder Hepatobiliary Services Information for Patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction The aim of this booklet is to help you understand more about
Hepatobiliary investigations
 Hepatobiliary investigations Hepatobiliary Services Information for patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction You have been referred to the Hepatobiliary Unit. We specialise in procedures
Hepatobiliary investigations Hepatobiliary Services Information for patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction You have been referred to the Hepatobiliary Unit. We specialise in procedures
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons
 General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options
 Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons
 General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: UPPER GI & HPB - HEPATIC, PANCREATIC & BILIARY
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Gall bladder cancer. Information for patients Hepatobiliary
 Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst
 Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis of common bile duct stones Vanja Giljaca University Hospital Center Rijeka Department of Gastroenterology
 Evidencebased guidelines for diagnosis of common bile duct stones Vanja Giljaca University Hospital Center Rijeka Department of Gastroenterology Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health. Outline
Evidencebased guidelines for diagnosis of common bile duct stones Vanja Giljaca University Hospital Center Rijeka Department of Gastroenterology Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health. Outline
BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II
 CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
CME Pretest BILIARY TRACT & PANCREAS, PART II VOLUME 41 1 2015 A pretest is mandatory to earn CME credit on the posttest. The pretest should be completed BEFORE reading the overview. Both tests must be
Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management
 Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Department of General Surgery, Al Khor Hospital, Hamad Medical Corporation, Qatar 2
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 469013, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/469013 Clinical Study Laparoscopic Intraoperative Cholangiography Interpretation
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 469013, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/469013 Clinical Study Laparoscopic Intraoperative Cholangiography Interpretation
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Clinical Impact. Giancarlo Caletti. Gastroenterologia Università di Bologna. Caletti
 Clinical Impact Giancarlo Gastroenterologia Università di Bologna AUSL di Imola,, Castel S. Pietro Terme (BO) 1982 Indications Diagnosis of Submucosal Tumors (SMT) Staging of Neoplasms Evaluation of Pancreato-Biliary
Clinical Impact Giancarlo Gastroenterologia Università di Bologna AUSL di Imola,, Castel S. Pietro Terme (BO) 1982 Indications Diagnosis of Submucosal Tumors (SMT) Staging of Neoplasms Evaluation of Pancreato-Biliary
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Study between Laparoscopic and Open Cholecystectomy for Dr. B. Hemasankararao 1,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Study between Laparoscopic and Open Cholecystectomy for Dr. B. Hemasankararao 1,
Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas
 CASE REPORT Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas Anand Patel, Louis Lambiase, Antonio Decarli, Ali Fazel Division of Gastroenterology
CASE REPORT Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas Anand Patel, Louis Lambiase, Antonio Decarli, Ali Fazel Division of Gastroenterology
ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT OF A BILE DUCT
 HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
ERCP / PTC Surgical Laparoscopic vs open Timing and order of approach
 Choledocholithiasis Which Approach and When? Lygia Stewart, MD University of California, San Francisco 2010 Naffziger Post-Graduate Course Clinical Manifestations of Choledocholithiasis Asymptomatic (no
Choledocholithiasis Which Approach and When? Lygia Stewart, MD University of California, San Francisco 2010 Naffziger Post-Graduate Course Clinical Manifestations of Choledocholithiasis Asymptomatic (no
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018) Commissioning Statement Asymptomatic Gallstones Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018) Commissioning Statement Asymptomatic Gallstones Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Diagnosis of tumor extension in biliary carcinoma has. Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
Gallstones Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Gutscharity.org.uk
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
Title: The best approach to treat concomitant gallstones and. Authors: Jesús García-Cano, Francisco Domper
 Title: The best approach to treat concomitant gallstones and common bile duct stones. Is ERCP still needed? Authors: Jesús García-Cano, Francisco Domper DOI: 10.17235/reed.2019.6226/2019 Link: PubMed (Epub
Title: The best approach to treat concomitant gallstones and common bile duct stones. Is ERCP still needed? Authors: Jesús García-Cano, Francisco Domper DOI: 10.17235/reed.2019.6226/2019 Link: PubMed (Epub
Personal Profile. Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history. Hepatitis B carrier
 Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis
 Original Article Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis Pradhan S 1, Shah S 2, Maharjan S 2, Shah JN 3 1 2 2 3 Professor, Patan hospital Correspondence:
Original Article Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis Pradhan S 1, Shah S 2, Maharjan S 2, Shah JN 3 1 2 2 3 Professor, Patan hospital Correspondence:
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are epithelial invaginations in the gallbladder wall that from as a result of increased gallbladder pressures.
 Anatomy The complexity of the biliary tree can be broken down into much simpler segments. The intrahepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts which exit the liver and join to become
Anatomy The complexity of the biliary tree can be broken down into much simpler segments. The intrahepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts which exit the liver and join to become
Intraductal papillary neoplasms in the bile ducts
 Intraductal papillary neoplasms in the bile ducts Seok Hwa Youn Myunghee Yoon Dong Hoon Shin Kosin University Gospel Hospital Department of general surgery Hepato-biliary-pancreatic division Introduction
Intraductal papillary neoplasms in the bile ducts Seok Hwa Youn Myunghee Yoon Dong Hoon Shin Kosin University Gospel Hospital Department of general surgery Hepato-biliary-pancreatic division Introduction
EVALUATION OF MRCP IN BILIARY OBSTRUCTION WITH ERCP, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 EVALUATION OF MRCP IN BILIARY OBSTRUCTION WITH ERCP, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE TAMIL NADU Dr. M.G.R MEDICAL UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REGULATIONS
EVALUATION OF MRCP IN BILIARY OBSTRUCTION WITH ERCP, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE TAMIL NADU Dr. M.G.R MEDICAL UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REGULATIONS
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Quality & Safety Committee 17 th August 2017 Agenda item: 6.2
 SUMMARY REPORT ABM University Health Board Quality & Safety Committee 17 th August 2017 Agenda item: 6.2 Subject Improvements in the management of gallstone disease Prepared by Approved & presented by:
SUMMARY REPORT ABM University Health Board Quality & Safety Committee 17 th August 2017 Agenda item: 6.2 Subject Improvements in the management of gallstone disease Prepared by Approved & presented by:
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master
 Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures
 Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. BHARADWAZ; AARHUS, Re/DK Keywords: Obstruction
Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. BHARADWAZ; AARHUS, Re/DK Keywords: Obstruction
Type of intervention Treatment. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Preoperative endoscopic sphincterotomy versus laparoendoscopic rendezvous in patients with gallbladder and bile duct stones Morino M, Baracchi F, Miglietta C, Furlan N, Ragona R, Garbarini A Record Status
Preoperative endoscopic sphincterotomy versus laparoendoscopic rendezvous in patients with gallbladder and bile duct stones Morino M, Baracchi F, Miglietta C, Furlan N, Ragona R, Garbarini A Record Status
Bilirubin levels predict malignancy in patients with obstructive jaundice
 DOI:1.1111/j.1477-2574.211.312.x HPB ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bilirubin levels predict malignancy in patients with obstructive jaundice Giuseppe Garcea, Wee Ngu, Christopher P. Neal, Ashley R. Dennison & David
DOI:1.1111/j.1477-2574.211.312.x HPB ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bilirubin levels predict malignancy in patients with obstructive jaundice Giuseppe Garcea, Wee Ngu, Christopher P. Neal, Ashley R. Dennison & David
CBD stones & strictures (Obstructive jaundice)
 1 CBD stones & strictures (Obstructive jaundice) Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz
1 CBD stones & strictures (Obstructive jaundice) Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz
Disclosures. Overview. Case 1. Common Bile Duct Sizes 10/14/2016. General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis
 Disclosures General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis 123 Blank Blank, LLC Aldo Maspons, MD Assistant Professor Director of Endoscopy Department of Pediatrics Texas Tech University Health
Disclosures General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis 123 Blank Blank, LLC Aldo Maspons, MD Assistant Professor Director of Endoscopy Department of Pediatrics Texas Tech University Health
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Assessment for Ampullary and Bile Duct Malignancy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (79)
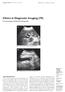 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(11) : 591-596 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (79) P Lerttumnongtum, M Muttarak, K Wasanavijit 1a Fig. 1a Subcostal US scan taken at the porta
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(11) : 591-596 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (79) P Lerttumnongtum, M Muttarak, K Wasanavijit 1a Fig. 1a Subcostal US scan taken at the porta
General Surgery PURPLE SERVICE MUHC-RVH Site
 Preamble HPB is a clinical teaching unit with several different vocations: It regroups all solid organ Transplantation as well as most advanced Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic clinical activities performed
Preamble HPB is a clinical teaching unit with several different vocations: It regroups all solid organ Transplantation as well as most advanced Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic clinical activities performed
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Accuracy of ASGE criteria for the prediction of choledocholithiasis
 1130-0108/2016/108/6/309-314 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2016 Arán Ediciones, S. L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig (Madrid) Vol. 108, N.º 6, pp. 309-314, 2016 ORIGINAL PAPERS Accuracy of
1130-0108/2016/108/6/309-314 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2016 Arán Ediciones, S. L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig (Madrid) Vol. 108, N.º 6, pp. 309-314, 2016 ORIGINAL PAPERS Accuracy of
Biliary Tract Disease. Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010
 Biliary Tract Disease Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010 Overview Gallstones Biliary tract tumours Other conditions Acute acalculous cholecystitis Mirizzi s syndrome Primary Biliary
Biliary Tract Disease Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010 Overview Gallstones Biliary tract tumours Other conditions Acute acalculous cholecystitis Mirizzi s syndrome Primary Biliary
Post Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Biloma in a Child Managed by Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography and Stenting: A Case Report
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.4.281 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2016 December 19(4):281-285 Case Report PGHN Post Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Biloma in
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.4.281 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2016 December 19(4):281-285 Case Report PGHN Post Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Biloma in
Title: Fasciola hepatica in the common bile duct: spyglass visualization and endoscopic extraction
 Title: Fasciola hepatica in the common bile duct: spyglass visualization and endoscopic extraction Authors: Edson Guzmán Calderón, Augusto Vera Calderón, Ramiro Díaz Ríos, Ronald Arcana López, Edgar Alva
Title: Fasciola hepatica in the common bile duct: spyglass visualization and endoscopic extraction Authors: Edson Guzmán Calderón, Augusto Vera Calderón, Ramiro Díaz Ríos, Ronald Arcana López, Edgar Alva
Clinical Spectrum of Presentation of Obstructive Jaundice in Inflammation, Stone Disease, and Malignancy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/326 Clinical Spectrum of Presentation of Obstructive Jaundice in Inflammation, Stone Disease, and Malignancy R Selvasekaran
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/326 Clinical Spectrum of Presentation of Obstructive Jaundice in Inflammation, Stone Disease, and Malignancy R Selvasekaran
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
IMAGING OF LIVER, BILIARY TREE, PANCREAS
 IMAGING OF LIVER, BILIARY TREE, PANCREAS Department of Radiology West China Hospital, Sichuan University Yao Jin Learning Points The methodology for imaging the LBP (liver, biliary tree, and pancreas )
IMAGING OF LIVER, BILIARY TREE, PANCREAS Department of Radiology West China Hospital, Sichuan University Yao Jin Learning Points The methodology for imaging the LBP (liver, biliary tree, and pancreas )
Diagnostic Imaging of the Liver
 S. Sakuma T. Ishigaki T. Takeuchi Diagnostic Imaging of the Liver Biliary Tract and Pancreas Data Analysis and Diagnostic Procedures With 312 Figures in 932 Separate Illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin
S. Sakuma T. Ishigaki T. Takeuchi Diagnostic Imaging of the Liver Biliary Tract and Pancreas Data Analysis and Diagnostic Procedures With 312 Figures in 932 Separate Illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Lutheran Medical Center. Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005
 Lutheran Medical Center Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005 History xx y.o. pt with primary CBD stones s/p ERCP xx months earlier for attempted stone extraction resulting in post ERCP pancreatitis. Patient
Lutheran Medical Center Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005 History xx y.o. pt with primary CBD stones s/p ERCP xx months earlier for attempted stone extraction resulting in post ERCP pancreatitis. Patient
Biliary MRI w Eovist
 Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis
 The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium 10 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass SPEAKER DECLARATIONS This presenter has the following
The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium 10 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass SPEAKER DECLARATIONS This presenter has the following
Pre-operative prediction of difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy
 International Surgery Journal http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151083 Pre-operative prediction of difficult laparoscopic
International Surgery Journal http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151083 Pre-operative prediction of difficult laparoscopic
Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction
 Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Appendix A: Summary of evidence from surveillance
 Appendix A: Summary of evidence from surveillance 2018 surveillance of Gallstone disease: diagnosis and management (2014) NICE guideline CG188 Summary of evidence from surveillance Studies identified in
Appendix A: Summary of evidence from surveillance 2018 surveillance of Gallstone disease: diagnosis and management (2014) NICE guideline CG188 Summary of evidence from surveillance Studies identified in
4/9/2018 OBJECTIVES PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS
 PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
ACUTE CHOLANGITIS AS a result of an occluded
 Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
Bile Duct Injury during Lap Chole. Bile Duct Injury during cholecystectomy TOPICS. 1. Prevalence, mechanisms, prevention and diagnosis
 Bile Duct Injury during cholecystectomy Catherine HUBERT Jean-Fran François GIGOT Benoît t NAVEZ Division of Hepato-Biliary Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery Department of Abdominal Surgery and Transplantation
Bile Duct Injury during cholecystectomy Catherine HUBERT Jean-Fran François GIGOT Benoît t NAVEZ Division of Hepato-Biliary Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery Department of Abdominal Surgery and Transplantation
What can you expect after your ERCP?
 ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases
 Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
Management of Cholangiocarcinoma. Roseanna Lee, MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital
 Management of Cholangiocarcinoma Roseanna Lee, MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital Case Presentation 37 year old male from Yemen presented with 2 week history of epigastric pain, anorexia, jaundice and puritis.
Management of Cholangiocarcinoma Roseanna Lee, MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital Case Presentation 37 year old male from Yemen presented with 2 week history of epigastric pain, anorexia, jaundice and puritis.
Having an ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangio pancreatogram)
 Having an ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangio pancreatogram) The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having an ERCP. It explains what it is, why it
Having an ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangio pancreatogram) The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having an ERCP. It explains what it is, why it
