World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline
|
|
|
- Brittany Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WGO GUIDELINE World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline Constipation A Global Perspective Greger Lindberg, MD, PhD,* Saeed S. Hamid, MD,w Peter Malfertheiner, MD,z Ole Ostergaard Thomsen, MD, PhD,y Luis Bustos Fernandez, MD,J James Garisch, MD,z Alan Thomson, MD,# Khean-Lee Goh, MD, ** Raesh Tandon, MD, ww Suliman Fedail, MD,zz Benjamin C.Y. Wong, MD,yy Aamir Ghafoor Khan, MD,JJ Justus H. Krabshuis,zz and Anton LeMair, MD## INTRODUCTION Constipation is a chronic problem in many patients all over the world. In some groups of patients such as the elderly, constipation is a significant health care problem, but in the majority of cases chronic constipation is an aggravating, but not life threatening or debilitating, complaint that can be managed in primary care with costeffective control of symptoms. The terminology associated with constipation is problematic. There are 2 pathophysiologies, which differ in principle but overlap: disorders of transit and evacuation disorders. The first can arise secondary to the second, and the second can sometimes follow from the first. This guideline focuses on adult patients and does not specifically discuss children or special groups of patients (such as those with spinal cord injury). Cascades: A Resource-sensitive Approach A gold standard approach is feasible for regions and countries in which the full range of diagnostic tests and medical treatment options are available for the management of all types and subtypes of constipation. A cascade is a hierarchical set of diagnostic, therapeutic, and management options for dealing with ris and disease, raned according to the resources available. DEFINITION AND PATHOGENESIS The word constipation has several meanings, and the way it is used may differ not only between patients but also between different cultures and regions. In a Swedish population study, it was found that a need to tae laxatives From the *Karolinsa Institutet, Stocholm, Sweden; waga Khan University, Karachi, Paistan; zotto von Guerice University, Magdeburg, Germany; yuniversity of Copenhagen, Herlev Hospital, Herlev, Denmar; JHospital Bonorino Udaondo, Buenos Aires, Argentina; zst Georges Hospital, Port Elizabeth, South Africa; #University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada; **University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; wwall India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India; zzuniversity of Khartoum, Khartoum, Sudan; yydepartment of Medicine, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong; JJLady Reading Hospital, Peshawar, Paistan; zzhighland Data, Tourtoirac, France; and ##Highland Data, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. This guideline is written and reviewed by a committee of the WGO chaired by Dr Lindberg. Supported by none. Conflict of interest: None. Copyright r 2011 by Lippincott Williams & Wilins was the most common conception of constipation (57% of respondents). In the same study, women (41%) were twice as liely as men (21%) to regard infrequent bowel motions as representing constipation, whereas equal proportions of men and women regarded hard stools (43%), straining during bowel movements (24%), and pain when passing a motion (23%) as representing constipation. Depending on various factors the diagnostic definition, demographic factors, and group sampling constipation surveys show a prevalence of between 1% and >20% in western populations. In studies of the elderly population, up to 20% of community-dwelling individuals and 50% of institutionalized elderly persons reported symptoms. Functional constipation is generally defined as a disorder characterized by persistent difficult or seemingly incomplete defecation, and/or infrequent bowel movements (once every 3 to 4 d or less) in the absence of alarm symptoms or secondary causes. Differences in the medical definition and variations in the reported symptoms mae it difficult to provide reliable epidemiologic data. Pathogenesis and Ris Factors Functional constipation can have many different causes, ranging from changes in diet, physical activity, or lifestyle to primary motor dysfunctions due to colonic myopathy or neuropathy. Constipation can also be secondary to evacuation disorder. Evacuation disorder may be associated with a paradoxical anal contraction or involuntary anal spasm, which may be an acquired behavioral disorder of defecation in two thirds of patients (Table 1). Although physical exercise and a high-fiber diet may be protective, the following factors increase the ris of constipation (the association may not be causative): Aging (but constipation is not a physiological consequence of normal aging) Depression Inactivity Low calorie intae Low income and low education level Number of medications being taen (independent adverse effect profiles) Physical and sexual abuse Female sex higher incidence of self-reported constipation in women Associated Conditions and Medications (Tables 2 and 3) J Clin Gastroenterol Volume 45, Number 6, July
2 WGO Guideline J Clin Gastroenterol Volume 45, Number 6, July 2011 TABLE 1. Pathophysiology of Functional Constipation Pathophysiologic Subtype Slow-transit constipation Colonic inertia Colonic overactivity Evacuation disorder Constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome Main Feature, With Absence of Alarm Symptoms or Secondary Causes Slow colonic transit of stool due to: Decreased colonic activity Increased uncoordinated colon activity Colonic transit may be normal or prolonged, but evacuating stools from the rectum is inadequate/difficult Abdominal pain, bloating, altered bowel habit May appear in combination with any other subtype DIAGNOSIS Constipation is a common condition, and although a minority of patients see medical care, in the United States alone this accounts for several million physician visits per year, whereas in the United Kingdom more than 13 million general practitioner prescriptions were written for laxatives in Gastrointestinal specialist help should focus on efficiently applying health care resources by identifying those patients who are liely to benefit from specialized diagnostic evaluation and treatment. Diagnostic Criteria for Functional Constipation An international panel of experts developed uniform criteria for the diagnosis of constipation the Rome III criteria (Table 4). Patient Evaluation The medical history and physical examination in constipation patients should focus on identifying possible causative conditions and alarm symptoms. Stool consistency: This is regarded as a better indicator of colon transit than stool frequency (Fig. 1). Patient s description of constipation symptoms, symptom diary Bloating, pain, malaise Nature of stools Bowel movements Prolonged/excessive straining Unsatisfactory defecation Laxative use, past and present, frequency and dosage Current conditions, medical history, recent surgery, psychiatric illness Patient s lifestyle, dietary fiber, and fluid intae Use of suppositories or enemas, other medications (prescription or over-the-counter) Physical examination: Gastrointestinal mass Anorectal inspection: Fecal impaction Stricture, rectal prolapse, rectocele Paradoxical or nonrelaxing puborectalis activity Rectal mass If indicated: blood tests biochemical profile, complete blood count, calcium, glucose, and thyroid function Alarm Symptoms (Table 5) Indications for Screening Tests Laboratory studies, imaging or endoscopy, and function tests are only indicated in patients with severe chronic constipation or alarm symptoms (Table 6). Transit Measurement The 5-day marer retention study is a simple method for measuring colonic transit. Marers are ingested on one TABLE 2. Possible Causes and Constipation-associated Conditions Mechanical obstruction Colorectal tumor Diverticulosis Strictures External compression from tumor/other Large rectocele Megacolon Postsurgical abnormalities Anal fissure Neurological disorders/neuropathy Autonomic neuropathy Cerebrovascular disease Cognitive impairment/dementia Depression Multiple sclerosis Parinson disease Spinal cord pathology Endocrine/metabolic conditions Chronic idney disease Dehydration Diabetes mellitus Heavy metal poisoning Hypercalcemia Hypermagnesemia Hyperparathyroidism Hypoalemia Hypomagnesemia Hypothyroidism Multiple endocrine neoplasia II Porphyria Uremia Gastrointestinal disorders and local painful conditions Irritable bowel syndrome Abscess Anal fissure Fistula Hemorrhoids Levator ani syndrome Megacolon Proctalgia fugax Rectal prolapse Rectocele Volvulus Myopathy Amyloidosis Dermatomyositis Scleroderma Systemic sclerosis Dietary Dieting Fluid depletion Low fiber Anorexia, dementia, depression Miscellaneous Cardiac disease Degenerative joint disease Immobility r 2011 Lippincott Williams & Wilins
3 J Clin Gastroenterol Volume 45, Number 6, July 2011 WGO Global Guidelines: Constipation TABLE 3. Medications Associated With Constipation Prescription drugs Antidepressants Antiepileptics Antihistamines Antiparinson drugs Antipsychotics Antispasmodics Calcium channel blocers Diuretics Monoamine oxidase inhibitors Opiates Sympathomimetics Tricyclic antidepressants Self-medication, over-the-counter drugs Antacids (containing aluminium, calcium) Antidiarrheal agents Calcium and iron supplements Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs TABLE 4. Rome III Criteria for Functional Constipation General criteria Presence for at least 3 mo during a period of 6 m Specific criteria apply to at least 1 out of every 4 defecations Insufficient criteria for irritable bowel syndrome No, or rarely, loose stools Specific criteria: 2 or more present Straining Lumpy or hard stools Feeling of incomplete evacuation Sensation of anorectal blocage or obstruction Manual or digital maneuvers applied to facilitate defecation Fewer than 3 defecations per wee TABLE 5. Alarm Symptoms in Constipation Alarm symptoms or situation Change in stool caliber Heme-positive stool Iron-deficiency anemia Obstructive symptoms Patients >50 y of age with no previous colon cancer screening Recent onset of constipation Rectal bleeding Rectal prolapse Weight loss Recommended test: colonoscopy Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Type 4 Type 5 Type 6 Type 7 Separate hard lumps lie nuts (difficult to pass) Sausage-shaped but lumpy Lie a sausage, but with cracs on the surface Lie a sausage or snae, smooth and soft Soft blobs with clear-cut edges (passed easily) Fluffy pieces with ragged edges, a mushy stool Watery, no solid pieces (entirely liquid) FIGURE 1. The Bristol Stool Form Scale: A measure to assist patients in reporting on stool consistency. Reproduced from c 1997 Informa Healthcare. occasion and the remaining marers are counted on a plain abdominal radiograph 120 hours later. If >20% of the marers remain in the colon, transit is delayed. Distal accumulation of marers may indicate an evacuation disorder, and in typical cases of slow-transit constipation almost all marers remain and marers are seen in both the right and the left colon. Several companies produce marers, but marers can also be made from a patient-safe radiopaque tube by cutting it into small pieces (2 to 3 mm in length). A suitable number of marers (20 to 24) can be placed in gelatin capsules to facilitate ingestion. Clinical Evaluation Classification of the patient s constipation should be possible on the basis of the medical history and appropriate examination and testing (Table 7). Cascade Options for Investigating Severe and Treatment-refractory Constipation Cascade: a hierarchical set of diagnostic, therapeutic, and management options for dealing with ris and disease, raned according to the resources available. TABLE 6. Physiologic Tests for Chronic Constipation Test Strength Weaness Comment Colonic transit study with radiopaque marers Anorectal manometry Balloon expulsion test Evaluates the presence of slow, normal, or rapid colonic transit; inexpensive and widely available Identifies evacuation disorder, rectal hyposensitivity, rectal hypersensitivity, impaired compliance, Hirschsprung disease Simple, inexpensive, bedside assessment of the ability to expel a simulated stool; identifies evacuation disorder Reproduced with permission from Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2009;19: Inconsistent methodology; validity has been questioned Lac of standardization Lac of standardization Useful for classifying patients according to pathophysiologic subtypes Useful for establishing diagnoses of Hirschsprung disease, evacuation disorder, and rectal hyposensitivity or hypersensitivity Normal balloon expulsion test does not exclude dyssynergia; should be interpreted alongside results of other anorectal tests r 2011 Lippincott Williams & Wilins 485
4 WGO Guideline J Clin Gastroenterol Volume 45, Number 6, July 2011 TABLE 7. Constipation Categories Based on Clinical Evaluation Constipation Type Normal-transit constipation, constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome Slow-transit constipation Evacuation disorder Idiopathic/organic/secondary constipation Typical Findings Patient history, no pathology at physical inspection/ examination Pain and bloating Feeling of incomplete evacuation Slow colonic transit Normal pelvic floor function Prolonged/excessive straining Difficult defecation even with soft stools Patient applies perineal/vaginal pressure to defecate Manual maneuvers to aid defecation High basal sphincter pressure (anorectal manometry) Known drug side effects, contributing medication Proven mechanical obstruction Metabolic disorders abnormal blood tests (b) Anorectal examination, 1-wee bowel habit diary card (c) Transit study using radiopaque marers (d) Balloon expulsion test (b) Anorectal examination, 1-wee bowel habit diary card (c) Transit study using radiopaque marers (d) Balloon expulsion test or defecography (b) Anorectal examination, 1-wee bowel habit diary card (c) Transit study using radiopaque marers (d) Defecography or magnetic resonance proctography (e) Anorectal manometry (f) Sphincter electromyography TREATMENT Scheme for General Management of Constipation (Table 8) Symptomatic Approach If organic and secondary constipation have been evaluated and excluded, most cases can be managed adequately with a symptomatic approach. A graded approach to treatment is based on recommending changes in lifestyle and diet, stopping or reducing medications that cause constipation, and administering fiber supplementation or other bul-forming agents. A gradual increase in fiber (either as standardized supplements or incorporated in the diet) and fluid intae is generally recommended. The second step in the graded approach is to add osmotic laxatives. The best evidence is for the use of polyethylene glycol, but there is also good evidence for lactulose. The new drugs, lubiprostone and linaclotide, act by stimulating ileal secretion and thus increasing fecal water. Prucalopride is also approved in many countries and in Europe. The third step includes stimulant laxatives, enemas, and proinetic drugs. Stimulant laxatives can be given orally or TABLE 8. General Management of Constipation 1. Patient history+physical examination 2. Classify the patient s type of constipation see Table 7 (constipation categories) 3. Medical approach in uncomplicated normal-transit constipation without alarm symptoms 4. In treatment-resistant constipation, specialized investigations can often identify a cause and guide treatment 5. If treatment fails, continue with specialized testing (this may only apply to the extensive resources level) Fiber, mil of magnesia Add lactulose/peg Add bisacodyl/sodium picosulfate Adjust medication as needed Standard blood test and colonic anatomic evaluation to rule out organic causes; manage the underlying pathology causing constipation The majority of patients will have a normal/negative clinical evaluation and may meet the criteria for constipationpredominant IBS. These patients will probably benefit from treatment with fiber and/or osmotic laxatives Identify STC with a radiopaque marer study Exclude evacuation disorder with anorectal manometry and balloon expulsion test Evaluate anatomic defects with defecography 6. Treatment of STC with aggressive laxative programs Fiber, mil of magnesia, bisacodyl/sodium picosulfate Prucalopride, lubiprostone Add lactulose/peg if no improvement In refractory constipation, a few highly selected patients may benefit from surgery IBS indicates irritable bowel syndrome; PEG, polyethylene glycol; STC, slow-transit constipation r 2011 Lippincott Williams & Wilins
5 J Clin Gastroenterol Volume 45, Number 6, July 2011 WGO Global Guidelines: Constipation TABLE 9. Summary: Evidence Base for the Treatment of Constipation* Treatment Modalities Commonly Used for Constipation Buling agents Psyllium Calcium polycarbophil Bran Methylcellulose Osmotic laxatives Polyethylene glycol Lactulose Wetting agents Dioctyl sulfosuccinate Stimulant laxatives Recommendation Level and Grade of Evidence Level II, grade B Level I, grade A Level II, grade B Bisacodyl/sodium picosulfate Level II, grade B* Senna Others Prucalopride Level I, grade A* Lubiprostone Level I, grade A* Biofeedbac therapy for Level I, grade A evacuation disorder Linaclotide Level II, grade B* Surgery for severe colonic inertia Level II, grade B *Adapted with permission from Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2009;19: Adapted by the present constipation guideline review team. rectally to stimulate colorectal motor activity. Proinetic drugs are also meant to increase the propulsive activity of the colon, but in contrast to stimulant laxatives, which should only be taen occasionally; they are designed to be taen daily. Diet and Supplements Dietary modification may consist of a high-fiber diet (25 g of fiber) and fluid supplementation (up to 1.5 to 2.0 L/d) and may improve stool frequency and decrease the need for laxatives. There is no evidence that dietary and lifestyle measures have any effect on constipation in the elderly persons; fiber supplements and simple osmotic laxatives are usually an adequate approach for constipation in these patients. In patients with colonic dilation, fiber supplementation should be avoided. Psyllium supplements and lactulose may be appropriate for the treatment of chronic constipation. Medication Evacuation disorders respond poorly to standard oral laxative programs. If an evacuation disorder plays a considerable role in constipation, biofeedbac and pelvic muscle training may be considered. Critical success factors are the patient s level of motivation, the frequency of the training program, and participation of a behavioral psychologist and dietitian. If a dietary approach fails, polyethylene glycol (17 g polyethylene glycol laxative for 14 d) or lubiprostone (24 mg twice daily) can be used to promote bowel function in patients with chronic constipation. Proinetic agents (eg, the 5-HT 4 receptor agonist prucalopride) can be used in constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Simple laxative agents, such as mil of magnesia, senna, bisacodyl, and stool softeners are a reasonable choice for treating constipation. Surgery If there is persistent treatment failure in slow-transit constipation, then carefully selected, well-evaluated, and informed patients may benefit from total colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis. The exceptional indication for colectomy must be established in a specialized and experienced tertiary center. Disappointing results may be seen, with fecal incontinence due to surgery and recurrent constipation, especially in patients with evacuation disorder. Only very few patients benefit from a (reversible) colostomy to treat constipation. Evidence-based Summary (Table 9) Cascade Options for Treatment of Chronic Constipation The following cascade is intended for patients with chronic constipation without alarm symptoms and with little or no suspicion of an evacuation disorder. The main symptoms would be hard stools and/or infrequent bowel movements. (b) Fiber supplementation (c) Mil of magnesia (magnesium hydroxide in an aqueous solution) (d) Stimulant laxatives (bisacodyl better than senna) for temporary use (b) Fiber supplementation, psyllium (c) Mil of magnesia, lactulose, macrogol (d) Stimulant laxatives for temporary use (b) Psyllium or lactulose (c) Macrogol or lubiprostone (d) Proinetics (prucalopride) (e) Stimulant laxatives (bisacodyl or sodium picosulfate) Cascade Options for Treatment of Evacuation Disorders This cascade is for patients with chronic constipation without alarm symptoms, but with suspicion of an evacuation disorder. The main symptoms would be prolonged straining, a feeling of incomplete evacuation, thin stools, a feeling of blocage, or failure of treatment for constipation with hard stools. (c) Biofeedbac therapy (c) Biofeedbac therapy (d) Surgical evaluation r 2011 Lippincott Williams & Wilins 487
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation
 Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Constipation an Old Friend. Presented by Dr. Keith Harris
 Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management
 UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
Constipation. (Medical Aspects)
 Constipation (Medical Aspects) By Dr. Ehab Abdel Khalik MD. Anatomy of the anorectum The rectum is 12-15 15 cm. long. It connects with the sigmoid colon by the rectosigmoid junction which is believed to
Constipation (Medical Aspects) By Dr. Ehab Abdel Khalik MD. Anatomy of the anorectum The rectum is 12-15 15 cm. long. It connects with the sigmoid colon by the rectosigmoid junction which is believed to
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
Chronic constipation in the elderly
 Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Constipation. Disease Review
 bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly
 Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Constipation. H. David Vargas, MD. Overview
 Constipation H. David Vargas, MD Overview Constipation is a very common complaint affecting upwards of 15% of all Americans. Fortunately, constipation usually is simple to avoid and easy to treat when
Constipation H. David Vargas, MD Overview Constipation is a very common complaint affecting upwards of 15% of all Americans. Fortunately, constipation usually is simple to avoid and easy to treat when
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone. Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club
 Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Scoop on the poop: Constipation in the Elderly
 Scoop on the poop: Constipation in the Elderly Laurie Archbald-Pannone, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Medicine, Geriatrics, & Palliative Care Division of Infectious Diseases and International
Scoop on the poop: Constipation in the Elderly Laurie Archbald-Pannone, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Medicine, Geriatrics, & Palliative Care Division of Infectious Diseases and International
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mustafa Giaffer March 2017
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
10/10/16. Disclosures. Educational Objectives
 Nimish Vakil, MD, FACP, FACG, AGAF, FASGE Clinical Adjunct Professor University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin Disclosures All faculty, course directors, planning committee, content reviewers and others
Nimish Vakil, MD, FACP, FACG, AGAF, FASGE Clinical Adjunct Professor University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin Disclosures All faculty, course directors, planning committee, content reviewers and others
CONSTIPATION OR STYPSIS. Prof. G. Zuliani
 CONSTIPATION OR STYPSIS Prof. G. Zuliani How Do We Define Constipation? The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) definition of constipation: Unsatisfactory defecation characterized by infrequent
CONSTIPATION OR STYPSIS Prof. G. Zuliani How Do We Define Constipation? The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) definition of constipation: Unsatisfactory defecation characterized by infrequent
A 27-Year-Old Woman With Constipation: Diagnosis and Treatment
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:838 842 EDUCATION PRACTICE A 27-Year-Old Woman With Constipation: Diagnosis and Treatment ARNOLD WALD Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:838 842 EDUCATION PRACTICE A 27-Year-Old Woman With Constipation: Diagnosis and Treatment ARNOLD WALD Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA
 OMED 17 OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA 29.5 Category 1-A CME credits anticipated ACOFP / AOA s 122 nd Annual Osteopathic Medical Conference & Exposition Joint Session with ACOFP and Cleveland
OMED 17 OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA 29.5 Category 1-A CME credits anticipated ACOFP / AOA s 122 nd Annual Osteopathic Medical Conference & Exposition Joint Session with ACOFP and Cleveland
Anorectal physiology test
 Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Are you aware there are many different reasons for having irregular bowels? This chart is to help you get back into balance during and post detox.
 BRISTOL POOP CHART The Bristol Poop Chart was created in the United Kingdom by a group of gastroenterologists at the University of Bristol. This chart is designed to help you determine the health of your
BRISTOL POOP CHART The Bristol Poop Chart was created in the United Kingdom by a group of gastroenterologists at the University of Bristol. This chart is designed to help you determine the health of your
Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS OVERVIEW
 Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS A major medical conditions that commonly is seen among persons with IDD and may lead to serious complications is constipation.
Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS A major medical conditions that commonly is seen among persons with IDD and may lead to serious complications is constipation.
Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence
 The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview
 Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines. Version 1 November 2016
 Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Associated with
 Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
 Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System. Antidiarrheal and Laxatives
 Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antidiarrheal and Laxatives Diarrhea Abnormal frequent passage of loose stools or Abnormal passage of stools with increased frequency, fluidity, and weight,
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antidiarrheal and Laxatives Diarrhea Abnormal frequent passage of loose stools or Abnormal passage of stools with increased frequency, fluidity, and weight,
Don t let. Irritable irregularity 2.0
 Don t let constipation Over 2 million Americans visit their health care providers each year for constipationrelated problems, yet constipation is often overlooked until it becomes serious. We ll help you
Don t let constipation Over 2 million Americans visit their health care providers each year for constipationrelated problems, yet constipation is often overlooked until it becomes serious. We ll help you
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation
 3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
3D Dynamic Ultrasound In Obstructed Defecation By Ramy Salahudin Abdelkader Assist. Lecturer of General Surgery Cairo University Introduction Pelvic floor is complex system, with passive and active components
Is one of the most common chronic disorders. causing patients to seek medical treatment.
 ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
Managing constipation in adults with co-morbidities
 Managing constipation in adults with co-morbidities Angela Gardiner and Andrea Hilton Constipation can be described in a number of ways but in general it is related to straining, reduced frequency of defecation
Managing constipation in adults with co-morbidities Angela Gardiner and Andrea Hilton Constipation can be described in a number of ways but in general it is related to straining, reduced frequency of defecation
Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
MANAGING CONSTIPATION
 MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests
 Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now. George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, :35 4:05 PM
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, 2017 3:35 4:05 PM Dr. Logan indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. He does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, 2017 3:35 4:05 PM Dr. Logan indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. He does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
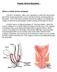 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Emerging Treatments for IBS-C and Clinical Trial Endpoints
 Emerging Treatments for IBS-C and Clinical Trial Endpoints Lin Chang, M.D. Oppenheimer Family Center for Neurobiology of Stress David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Learning Objectives Describe current
Emerging Treatments for IBS-C and Clinical Trial Endpoints Lin Chang, M.D. Oppenheimer Family Center for Neurobiology of Stress David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Learning Objectives Describe current
Constipation. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Constipation National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Constipation is defined as having a bowel
Constipation National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Constipation is defined as having a bowel
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination
 Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Opioid Induced Constipation Lisa Clince Acute Pain CNS Palmerston North Hospital
 Opioid Induced Constipation Lisa Clince Acute Pain CNS Palmerston North Hospital 21-04-2016 MidCentral District Health Board 1 Overview Patient Experience Opioid Collaborative Constipation defined Opioid
Opioid Induced Constipation Lisa Clince Acute Pain CNS Palmerston North Hospital 21-04-2016 MidCentral District Health Board 1 Overview Patient Experience Opioid Collaborative Constipation defined Opioid
4) Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Shaikhani. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Burden. Diagnosis
 4) Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Shaikhani Epidemiology A common disorder, with a 7% prevalence. Women are 1.5 times more likely to be affected than men, most commonly between ages 20-40 years. Onset
4) Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Shaikhani Epidemiology A common disorder, with a 7% prevalence. Women are 1.5 times more likely to be affected than men, most commonly between ages 20-40 years. Onset
Current Pharmacological Treatment Options in Chronic Constipation and IBS with Constipation
 Current Pharmacological Treatment Options in Chronic Constipation and IBS with Constipation Anthony Lembo, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Center Beth
Current Pharmacological Treatment Options in Chronic Constipation and IBS with Constipation Anthony Lembo, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Center Beth
Managing constipation in residential care
 Managing constipation in residential care Amanda Lee Lecturer, Hull University ; PhD Candidate, Gastroesophageal cancers Key Points Constipation is a major problem in residential care Early detection and
Managing constipation in residential care Amanda Lee Lecturer, Hull University ; PhD Candidate, Gastroesophageal cancers Key Points Constipation is a major problem in residential care Early detection and
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS
 BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
Measurement of colonic transit time with the Transit-Pellets TM method
 Measurement of colonic transit time with the Transit-Pellets TM method Measurement of colonic transit time is an important investigation in clinical gastroenterology. The measurement is indicated particularly
Measurement of colonic transit time with the Transit-Pellets TM method Measurement of colonic transit time is an important investigation in clinical gastroenterology. The measurement is indicated particularly
Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida
 Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private
Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private
Antidiarrheals Antidiarrheal
 Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
 HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
Human Anatomy rectum
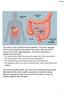 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES
 OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
Effect of biofeedback therapy on anorectal physiological parameters among patients with fecal evacuation disorder
 DOI 10.1007/s12664-017-0731-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of biofeedback therapy on anorectal physiological parameters among patients with fecal evacuation disorder Abhai Verma 1 & Asha Misra 1 & Uday C Ghoshal
DOI 10.1007/s12664-017-0731-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of biofeedback therapy on anorectal physiological parameters among patients with fecal evacuation disorder Abhai Verma 1 & Asha Misra 1 & Uday C Ghoshal
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders What are functional GI disorders?
 The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
IBS - Definition. Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by:
 IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
management of this patient within the Enhanced Primary Care Pathway is appropriate, without need for specialist consultation at this time.
 TRIAGE CATEGORY: Enhanced Primary Care Pathway CONSTIPATION Dear Colleague, The clinical and diagnostic information you have provided for the above-named patient is consistent with a diagnosis of chronic
TRIAGE CATEGORY: Enhanced Primary Care Pathway CONSTIPATION Dear Colleague, The clinical and diagnostic information you have provided for the above-named patient is consistent with a diagnosis of chronic
Motility Disorders. Pelvic Floor. Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 701) January 2010 November 2011
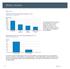 Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Protectives and Adsorbents. Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry
 Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Practical Approaches Towards Improving Patient Outcomes for Chronic Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation (IBS-C) Among Older
 Practical Approaches Towards Improving Patient Outcomes for Chronic Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation (IBS-C) Among Older Adults Educational Learning Objectives Describe the elements
Practical Approaches Towards Improving Patient Outcomes for Chronic Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation (IBS-C) Among Older Adults Educational Learning Objectives Describe the elements
SYMPROIC (naldemedine tosylate) oral capsule
 SYMPROIC (naldemedine tosylate) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
SYMPROIC (naldemedine tosylate) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Constipation in Children. Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG*
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 19 No. 1 January, 2013 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2013.19.1.78 Original Article Successful
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 19 No. 1 January, 2013 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2013.19.1.78 Original Article Successful
Opioid constipation treatment dulcolax
 P ford residence southampton, ny Opioid constipation treatment dulcolax Posts about how to relieve constipation instantly written by gbrese1958. Official Web site for MOVANTIK (naloxegol) tablets, for
P ford residence southampton, ny Opioid constipation treatment dulcolax Posts about how to relieve constipation instantly written by gbrese1958. Official Web site for MOVANTIK (naloxegol) tablets, for
I ve had it with you and your emotional constipation.
 I ve had it with you and your emotional constipation. Washington Irving If Mother had to be told not to put the entire brick of ivory up Junior s hindquarters, constipation is the least of his problems.
I ve had it with you and your emotional constipation. Washington Irving If Mother had to be told not to put the entire brick of ivory up Junior s hindquarters, constipation is the least of his problems.
Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in Canada. A Special Report from the Canadian Digestive Health Foundation
 Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in Canada A Special Report from the Canadian Digestive Health Foundation February 2014 Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in
Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in Canada A Special Report from the Canadian Digestive Health Foundation February 2014 Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in
SIMULATORS, ANATOMICAL MODELS AND CHARTS FOR CLINICAL SKILLS AND TRAINING AR321/AR321-B. Rectal Examination Model. Instruction Manual
 SIMULATORS, ANATOMICAL MODELS AND CHARTS FOR CLINICAL SKILLS AND TRAINING AR321/AR321-B Rectal Examination Model Instruction Manual Thank you for purchasing this AR321/AR321-B Rectal Examination Model.
SIMULATORS, ANATOMICAL MODELS AND CHARTS FOR CLINICAL SKILLS AND TRAINING AR321/AR321-B Rectal Examination Model Instruction Manual Thank you for purchasing this AR321/AR321-B Rectal Examination Model.
Zaponex Fact Sheet Constipation
 Important Information The information provided in this fact sheet is intended for healthcare professionals and should not be used as a patient information leaflet. The information in this document is not
Important Information The information provided in this fact sheet is intended for healthcare professionals and should not be used as a patient information leaflet. The information in this document is not
11/04/2011 OVERVIEW. Neurogenic Bowel Management. in adults with Spinal Cord Injury (S.C.I.) Sequence of events in normal Defecation
 Neurogenic Bowel Management in adults with Spinal Cord Injury (S.C.I.) Dimitrios D. Ergeletzis MD Physiatrist Director of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Dept.- GIROKOMEION ATHENS, Greece OVERVIEW Anatomy
Neurogenic Bowel Management in adults with Spinal Cord Injury (S.C.I.) Dimitrios D. Ergeletzis MD Physiatrist Director of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Dept.- GIROKOMEION ATHENS, Greece OVERVIEW Anatomy
Hemorrhoids. Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery
 Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
In the evaluation and management of chronic
 HOW TO IDENTIFY, COUNSEL, AND TREAT PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC CONSTIPATION AND IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME * Anthony J. Lembo, MD ABSTRACT Though not a life-threatening condition, chronic constipation has a substantial
HOW TO IDENTIFY, COUNSEL, AND TREAT PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC CONSTIPATION AND IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME * Anthony J. Lembo, MD ABSTRACT Though not a life-threatening condition, chronic constipation has a substantial
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION. Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital
 ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?'
 Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 77 July 1984 559 Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?' M R B Keighley MS FRCS P Shouler FRCS Department of Surgery, General Hospital, Birmingham
Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 77 July 1984 559 Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?' M R B Keighley MS FRCS P Shouler FRCS Department of Surgery, General Hospital, Birmingham
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists
 Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Episode 3.2 Show Notes Constipation
 Episode 3.2 Show Notes Constipation Presented by: Dr Jo Preston, Dr Iain Wilkinson & Mairéad O Malley Faculty: Clare Watson, Wendy Grosvenor Guest faculty: Dr Gaggandeep Singh Alg Broadcast Date: 28th
Episode 3.2 Show Notes Constipation Presented by: Dr Jo Preston, Dr Iain Wilkinson & Mairéad O Malley Faculty: Clare Watson, Wendy Grosvenor Guest faculty: Dr Gaggandeep Singh Alg Broadcast Date: 28th
Constipation in children
 Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014
 Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430
 Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
CENTENE PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS DRUG REVIEW 3Q17 July August
 BRAND NAME Symproic GENERIC NAME Naldemedine MANUFACTURER Shionogi Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL March 23, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE Anticipated to launch mid-summer 2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug
BRAND NAME Symproic GENERIC NAME Naldemedine MANUFACTURER Shionogi Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL March 23, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE Anticipated to launch mid-summer 2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Functional gastrointestinal disorders Definition A variable combination of chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms (attributed to the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, biliary
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Functional gastrointestinal disorders Definition A variable combination of chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms (attributed to the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, biliary
A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence
 Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Angie Jefferson Registered Dietitian & Consultant Nutritionist
 Angie Jefferson Registered Dietitian & Consultant Nutritionist Constipation & Haemorrhoids are two of the most common problems experienced by pregnant women Incidence increases dramatically 40% women reportedto
Angie Jefferson Registered Dietitian & Consultant Nutritionist Constipation & Haemorrhoids are two of the most common problems experienced by pregnant women Incidence increases dramatically 40% women reportedto
Constipation is a ubiquitous problem. Physicians and patients often perceive. Management of Chronic Constipation Nicholas J. Talley, MD, PhD, FRACP
 MANAGEMENT UPDATE Management of Chronic Constipation Nicholas J. Talley, MD, PhD, FRACP Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology and Center for Enteric Neurosciences Translational and Epidemiological
MANAGEMENT UPDATE Management of Chronic Constipation Nicholas J. Talley, MD, PhD, FRACP Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology and Center for Enteric Neurosciences Translational and Epidemiological
Prof. Dr. Mufti Munsurar Rahman Dept. of Medicine Enam Medical College Hospital
 Prof. Dr. Mufti Munsurar Rahman Dept. of Medicine Enam Medical College Hospital Functional constipation : prevalence and life style factors in a district of Bangladesh Perveen I, Rahman MM, Saha M, Parvin
Prof. Dr. Mufti Munsurar Rahman Dept. of Medicine Enam Medical College Hospital Functional constipation : prevalence and life style factors in a district of Bangladesh Perveen I, Rahman MM, Saha M, Parvin
Relief, true to form
 For adults with Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) or Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) Relief, true to form When It Comes to Constipation Relief, Form Matters Trulance can help you
For adults with Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) or Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) Relief, true to form When It Comes to Constipation Relief, Form Matters Trulance can help you
Primary Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Primary Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Instructor, Division of Gastroenterology Current Concepts in Drug Therapy CME Course April 23, 2015 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Primary Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Instructor, Division of Gastroenterology Current Concepts in Drug Therapy CME Course April 23, 2015 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider
 Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence)
 Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Evidence-based Treatment Strategies for
 Evidence-based Treatment Strategies for Chronic Constipation William D. Chey, MD Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Rome III criteria*: Chronic constipation Must include 2 of the following (>25%
Evidence-based Treatment Strategies for Chronic Constipation William D. Chey, MD Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Rome III criteria*: Chronic constipation Must include 2 of the following (>25%
Bloating, Flatulence, and
 A 45-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Abdominal Pain, Bloating, Flatulence, and Intermittent Loose Stools Anthony J. Lembo, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Laboratory
A 45-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Abdominal Pain, Bloating, Flatulence, and Intermittent Loose Stools Anthony J. Lembo, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Laboratory
