Guillain-Barré Syndrome Support Group
|
|
|
- Cody Douglas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guillain-Barré Syndrome Support Group of the United Kingdom Registered Charity A guide for patients, relatives and friends Second Edition 1998 GBS Support Group of the UK LCC Offices Eastgate Sleaford Lincolnshire NG34 7EB Tel/fax: admin@gbs.org.uk Free Helpline: Web site:
2 Information Publications This booklet has been produced by the GBS Support Group of the UK, a registered charity founded in The booklets available from the Group are: Guillain-Barré Syndrome a guide for patients, relatives and friends; The Guillain-Barré Syndrome Patient in Intensive Care a guide for relatives and friends; Childhood Guillain-Barré Syndrome a guide for parents and carers; CIDP a guide for patients, relatives and friends; and Jenny s Story (a beautifully illustrated booklet for children with GBS). The Group s address is: GBS Support Group of the UK, LCC Offices, Eastgate, Sleaford, Lincs, NG34 7EB. Tel/fax: admin@gbs.org.uk. Under certain circumstances, copies may also be obtained by calling the Free Helpline (see below). If you live outside the UK or Irish Republic, see page ii. Free Helpline If you are presently suffering from GBS or a related condition, or are a relative or friend of a sufferer, and wish to talk to talk to someone now about the illness, call the Free GBS Helpline on (UK only). Our Helpline volunteers are themselves former patients or their carers who are able to understand your anxieties and answer your questions. Please do not use the Helpline for routine or administrative calls. Requests for publications by others than patients, relatives or friends should be made to the GBS Office. Hospital visits local and specialist contacts Nothing can boost the morale of a GBS sufferer in hospital more than a visit by a recovered patient. The Group has a network of over 100 local and hospital contacts who carry out this important service and there is probably one in your area. Most importantly, there exists someone locally who understands the sense of isolation that affects all those who come into contact with GBS, and who can offer practical help. There are occasions when local contacts do not have the necessary knowledge for particular cases (eg childhood GBS, CIDP, severe GBS). Under these circumstances, ii
3 the help of one of our specialist contacts can be called upon. The Group s Help Fund The Group s Help Fund exists to provide emergency financial support at the most critical of times. The fund has not been established to pay for care and equipment, provision of which are the responsibilities of the statutory services, nor can it make ongoing grants to supplement statutory benefits. An example of how the Fund may help is the case of a relative having difficulty affording the costs of visiting a GBS patient, especially if the patient is in a hospital many miles from home. Requests to the Fund should be made in writing to the Office and be supported by a covering letter from a health professional. Cost The above information and services are provided absolutely free. There is no obligation to join the Support Group though many who register with us do subsequently become members. Registration If you are a sufferer, or the relative or friend of a sufferer, and have received this booklet directly from the Support Group, then you will be already registered with the Group. Those who are registered receive free copies of the Group s journal Reaching Out for a year. If you received this booklet in some other way (eg from a friend, a hospital or downloaded from the Internet), by registering you too will receive free copies of the Journal. Our records are kept in the strictest confidence and will not be divulged to third parties. To register with the Group, please fill in the form on page iii. Membership If you wish to become a member of the Support Group now, fill in the membership form that accompanied this booklet. If the form is not available, please contact the office for a replacement or visit the Group s Web site. Other countries If you live outside the UK or the Republic of Ireland and are seeking support, we will make every effort to put you in touch with a local support group should one exist. Since the Group s information can be readily downloaded from the Group s Web site ii ii
4 or attached to electronic mail, the Group s publications are not normally posted overseas. If receiving the information in this way is impossible or unsatisfactory, a donation to cover the airmail charges would be much appreciated. The Group regrets that it does not have the resources to register cases from outside the UK or the Republic of Ireland and supply free copies of its journal. However, it is possible to become an Overseas Member of the Group and receive copies of the Group s journal by air mail. Please see the membership form that accompanied this booklet. If the form is not available, contact the office for a replacement or visit the Group s Web site. Disclaimer The GBS Support Group of the UK is not a medically qualified organisation. The information it publishes is for general educational purposes only and should neither be regarded as advice on the diagnosis or treatment of the Guillain-Barré syndrome nor any other medical condition. The information provided by the Group is designed to support, not replace, the relationship that exists between a patient and his/her existing doctor. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the Registration form (UK/Ireland only) Please read the paragraph Registration on the previous page before filling in this form. Please fill in as much detail as possible in the boxes below. Information will be treated with the strictest of confidence. Please add any further details and requests overleaf. YOUR DETAILS: Name Address PATIENT S DETAILS: Name Home address Town County and post code Tel If you would like to receive a call from your local GBS contact, who will be pleased to offer support and/or arrange a hospital visit, please tick box. Send this form to: GBS Support Group of the UK LCC Offices, Eastgate iii iii Town County and post code Tel Hospital Ward/unit Town Relationship to you Date entered hospital Diagnosis (if known) Ventilated YES/NO GBS/CIDP/other(state) Age
5 information, the GBS Support Group of the UK cannot be held responsible for it. Copyright and reproduction The material in this booklet is strictly copyright. However, it may be copied (and translated) in paper form provided that: it is not for commercial gain; the source is acknowledged and copyright notices are reproduced; copies made for circulation in the UK contain the information pages i to iv; and copies made for circulation outside the UK contain suitably amended versions of this paragraph and the previous (disclaimer) paragraph. Placing this publication, or parts of it, on the Internet or in any other electronic medium requires the prior consent of the GBS Support Group of the UK. iv iv
6 CIDP A guide for patients, relatives and friends Introduction This booklet has been written for patients who have been told that they may have CIDP (chronic inflammatory demyelinating poly[radiculo*]neuropathy), and for their relatives and friends. It aims to explain accurately and honestly what CIDP is, and hopefully will answer some of the questions you may have. If you do not understand or are worried by any of the information offered here, do ask your doctor to explain. The degree of severity of CIDP and the way in which it affects people vary enormously from one sufferer to another. There is no typical CIDP. Therefore one general description and one certain prognosis are not possible. This booklet describes symptoms which are common among sufferers. What is CIDP? CIDP is defined thus: chronic refers to the gradual course of the illness; inflammatory means there is strong evidence that it is inflammation that causes the nerve damage; demyelinating means that the damage is primarily to the insulating myelin sheaths around the nerve fibres; and poly[radiculo]neuropathy ; poly means many, [ radiculo means root,] * Radiculo is sometimes omitted. 1
7 neuro means nerve and opathy means disease; so poly[radiculo]neuropathy means a disease of many peripheral nerves [and their roots (which are the points of origin of the peripheral nerves from the spinal cord)]. CIDP is a very rare disease of the peripheral nervous system involving gradual development of weakness and loss of sensation predominantly in the arms and legs. The incidence and prevalence of CIDP are very difficult to determine because of its rarity. Various estimates put the incidence at between 75 and 250 people per year in the UK. The disease may start at any age, but is slightly more common in young adults. It is more common in men than women. For women, relapses are slightly more likely to occur during a pregnancy year. It is not hereditary; ie it is not passed on to children. It is not infectious; ie it is not caught from, or transmitted to, anybody else. It is not a psychiatric or nervous disorder. No-one is sure what causes CIDP. Current research is investigating the role of preceding infections, immunisations and other events before the onset or relapses of CIDP. However, to date there is no general agreement on what causes the disease. Symptoms The severity of CIDP is extremely variable and the symptoms experienced vary considerably between patients. Initial symptoms may be vague and confusing to both the patient and the doctor. Subjective symptoms such as fatigue and sensory disturbance are difficult to communicate. In the early stages it may be difficult for the patient to persuade the doctor that there is anything physically wrong. Early symptoms usually include either tingling (pins and needles) or loss of feeling (numbness) beginning in the toes and fingers, or weakness, so that legs feel heavy and wooden, arms feel limp and hands cannot grip or turn things properly. These symptoms may remain mild and result in only minor disruption the patient s normal life. Alternatively they may become progressively and gradually worse over a period of several weeks, months or even 2
8 years sometimes, but very rarely, to the extent that the patient is bed bound with profound weakness of the arms. CIDP usually presents with both weakness and sensory symptoms, sometimes with weakness alone, and rarely with sensory symptoms alone. The arms and legs are usually affected together, the legs more than the arms. Prickling and tingling sensations in the extremities are common and may be painful. Aching pain in the muscles also occurs. Tendon reflexes are usually lost. As the disease becomes more severe, a tremor may develop, usually in the upper limbs. Very rarely patients may develop facial weakness. Diagnosis CIDP can be difficult to diagnose as there is no conclusive diagnostic test for it. The history of symptoms is often vague with varying signs which could be symptoms of a number of conditions. Therefore a long period of time may elapse before a suggestion of CIDP is made. CIDP is closely related to Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), which is also due to inflammation of the peripheral nerves. Symptoms experienced by patients are similar, but GBS is a more acute condition in which symptoms appear rapidly over a period of days or a few weeks. GBS patients usually make a spontaneous recovery over a period of weeks or months. CIDP is a chronic condition and is only distinguished from GBS by virtue of its pattern of progression. In GBS the low point is reached within four weeks whereas in CIDP the initial progressive phase lasts longer, usually much longer. Some CIDP patients are initially diagnosed as having GBS. Only when the deterioration continues over an extended period, or when one or more relapse(s) occur after a period of improvement, is the illness reclassified as CIDP. The diagnosis is made primarily on clinical grounds, not laboratory tests. This means that the doctor has to rely on the history and clinical examination fitting into the pattern of CIDP. The doctor will particularly want to know of any recent possible toxin exposure (insecticides, solvents), medication, alcohol intake, tick bites, family history of nerve disease, or symptoms of any coincidental illnesses, such as diabetes (thirst, frequent urination, weight loss) 3
9 or arthritis (painful joints). Any of these might lead to a different diagnosis. Essential criteria for a positive diagnosis of CIDP are: progressive weakness in two or more limbs due to a poly[radiculo]neuropathy; loss or diminution of tendon reflexes; progression for more than eight weeks or recurrence or relapse; and evidence of damage to peripheral nerve myelin from nerve conduction tests. Investigations will include blood tests, usually a lumbar puncture and nerve conduction tests with an electromyogram (EMG) machine, and possibly a Magnetic Resonance Image (MRI) scan. A nerve biopsy may also be performed. In cases where CIDP is associated with an abnormal protein in the blood (Paraproteinaemia) a bone marrow examination and X-rays of the bones may be required. The lumbar puncture involves lying on one side and having a needle inserted under local anaesthesia between the vertebrae into the sac of cerebrospinal fluid which surrounds the nerve roots. The idea is worse than the procedure really is and it does not usually hurt. The cerebrospinal fluid often contains much more protein than usual while the cell content remains normal. If different changes are found the doctor has to review the diagnosis with even more care. The EMG is an electrical recording of the muscle activity. If a nerve is stimulated with a brief electrical pulse (felt like a sharp tap or jolt) muscle activity can be recorded and the speed of nerve conduction worked out. Usually in CIDP nerve conduction is markedly slowed or even blocked. The test lasts about half an hour. It is only slightly uncomfortable and quite harmless. The Magnetic Resonance Image (MRI) Scanner is a more recent diagnostic tool and takes X-ray type pictures of the brain and spinal cord (ie of the central nervous system). The procedure involves the patient s upper body being slid into the tunnel-like scanner and remaining absolutely still during the scanning process which lasts about half an hour. It is entirely painless. 4
10 MRI scans are used to eliminate the possibility of damage to the central nervous system. Sometimes a nerve biopsy may also be performed. This involves a small piece of nerve being removed, usually from the side of the heel of the foot, to be examined in the laboratory. This allows the doctor to see any inflammation and the type of nerve damage. Having the biopsy is not painful because local anaesthetic is used, but the skin below may become sore for a week or two afterwards. The patient may be left with some loss of sensation in a very small area on the side of the foot. Progression It is helpful to subdivide CIDP into four sub-categories which are characterised by the pattern of progression of the disease. These are: subacute where symptoms continue to progress and worsen for at least four weeks, but not more than eight weeks before levelling off or improving; chronic progressive where symptoms continue to progress and worsen for a period exceeding eight weeks; chronic relapsing where there is more than one episode in which symptoms progress and worsen for a period greater than four weeks; and recurrent GBS where each bout has a progressive phase of less than four weeks. Clearly the cutoff points used are somewhat arbitrary. The most common form of the disease is the chronic relapsing form largely due to the beneficial effects of treatment but sometimes due to spontaneous remissions. About 80% of patients have this form of the disease. About 10% of patients have the subacute disease which plateaus and then disappears spontaneously. Patients with recurrent GBS form only a small percentage of CIDP patients. Thus some patients only have a single bout of CIDP lasting for several months or years, after which a spontaneous recovery may be made. Others 5
11 have many bouts in between which spontaneous remission and recovery occurs. After each bout patients may be left with some residual numbness and weakness and sometimes discomfort. For many this will not seriously interfere with their lives, and they are able to continue with or resume their normal occupation. However a very small number are left severely disabled and may be dependent on a wheelchair or even bed bound. There are only a very unfortunate few for whom the disease continues to progress without remission. What is going on? The function of the brain is to interpret sensations and initiate movements and other responses. This activity depends on a complex communication system of nerves running to every part of the body via the spinal cord. Each nerve in this communication system can be compared to an electric cable. The inner part of the nerve, the axon, is made of conductive tissue and carries messages or impulses throughout the body like the wires in an electric cable. The axon is surrounded by a layer of fatty substance, the myelin sheath, like the insulating cover on a cable. The myelin helps the conduction of messages along the nerves as well as insulating and protecting the nerve. The symptoms of CIDP are due to inflammation and damage to the peripheral nerves and their roots. The peripheral nerves connect the central nervous system to the skin and muscle. CIDP is probably an autoimmune disease, ie one in which the immune system attacks its own body. The most likely mechanism is that the immune cells, called lymphocytes, somehow or other make a mistake and attack the nerves. The main part of the nerve which is attacked is the insulating sheath, or myelin. The way in which the lymphocytes are tricked into attacking the body is still the subject of research. The lymphocytes may cause the formation of chemicals called antibodies which circulate in the blood and damage the myelin. Attempts to identify these antibodies have so far been only partially successful. Fortunately the myelin sheath can be replaced within a few weeks or months by the myelin-forming cells, named Schwann cells. If the nerve axons are 6
12 damaged these can also regrow, but this is much slower. Research is continuing into the underlying causes and mechanisms of the disease. Treatment Treatment of CIDP is usually very effective with about 80% of new cases making a dramatic response to therapy, although there is no one shot curative treatment in the way that antibiotics might cure an infection. Drug treatments are generally thought to work by suppressing the autoimmune response. This in turn reduces the disabling symptoms of the disease. Examples are steroids, immunosuppressive drugs, plasma exchange and intravenous immunoglobulin. Obviously suppressing the immune response cannot be undertaken lightly because it runs the risk of suppressing normal immune responses to infections. The decision whether to try these treatments has to be tailored by the doctor to the individual needs of each patient. However it is reassuring to know that treatments are available, that demyelinated nerves can repair themselves, and that some patients get better without treatment. Because of the small number of patients and because most of the treatment methods are quite new, there is limited evidence available of the relative effectiveness of different treatments. Some patients respond to one method of treatment and not to others. There are only a very unfortunate few who cannot be helped by any of these treatments. Steroids Controlled trials have demonstrated that steroids are beneficial in CIDP. A wide range of dosage schedules has been used and no work has been addressed to the question of which is best. The high risks of serious side effects resulting from the prolonged use of high dose steroids are well known. These include osteoporosis (thinning of bones), cataracts, diabetes, hypertension (raised blood pressure), obesity and myopathy (muscle weakness). 7
13 If the dosage levels required to control the CIDP appear unacceptably high or unacceptably prolonged, it may be suggested that other immunosuppressive drugs are used. Immunosuppressive drugs Clinical experience suggests that immunosuppressive drugs help. These include azathioprine, cyclophosphamide and cyclosporin. Azathioprine is the most widely used in the treatment of CIDP. The use of these drugs carries the theoretical side effect of increased risk of developing cancer, but in practice this increased risk is very small. Plasma exchange Plasma exchange involves the patient being connected to a machine which can separate the blood cells from the fluid or plasma. In an on-line process, blood is continuously taken from the patient, separated, the plasma is discarded, the blood cells are mixed with clean plasma and returned to the patient (the process is not unlike that used in kidney dialysis). At each session about two to three litres of plasma are exchanged. The procedure is usually repeated several times over about two weeks until sufficient plasma has been changed. The procedure is safe and the risks are small. It is not painful. However some patients find that it leaves them feeling tired for a day or two. Clinical trials have demonstrated the benefit of plasma exchange for CIDP. For some patients it allows control of the disease to be maintained when immunosuppressive drugs are insufficiently effective. Some patients however do not appear to respond to plasma exchange. Immunoglobulin There is increasing evidence of the effectiveness against CIDP of intravenous infusions of immunoglobulin (also called gamma globulin or antibodies). Antibodies usually react with and neutralise germs which get into the 8
14 body. These are good antibodies. Sometimes antibodies attack the body itself and these bad antibodies, or autoantibodies, may cause CIDP. However there are also anti-autoantibodies, which block these bad antibodies. It may be these anti-autoantibodies in immunoglobulin which help. Whatever the explanation, some people with CIDP do seem to get better after having immunoglobulin. Research is going on to find out which patients. It is given by infusion into a vein, usually every day for five days. Each infusion takes about five hours. The immunoglobulin used in the UK has an excellent safety record. Abroad there have been very rare cases of transmission of hepatitis but considerable care is now taken in the purification and removal of any viral particles which reduces this risk to the absolute minimum. With any blood product there is always a slight risk of transmission of a new infection such as Creutzfeld Jakob disease (CJD) which has received a great deal of recent publicity. For this reason immunoglobulin from British Donors is not currently being used as a source for the manufacture of immunoglobulin until there is confirmation that there is no risk associated with it. This extra safeguard should reduce the concerns of anyone receiving this very effective treatment. There is a rare (about 1 in 40,000) risk of serious allergic reaction at the start of each infusion, so careful monitoring is essential. Some patients only need one course. Others need repeated courses. Physiotherapy Physiotherapy has an important role to play in the assessment and management of CIDP. It helps to maximise a patient s physical potential, particularly where weakness is the predominant problem. The aims of physiotherapy are to: maximise muscle strength and minimise muscle wastage by exercise using strengthening techniques; minimise the development of contractures (or stiffness) around joints; a physiotherapist can advise on passive stretching techniques to help maintain full range movement at joints; 9
15 facilitate mobility and function; sometimes, if muscles are very weak, function can be improved by the use of splints and provide a physical assessment which may help in planning future management. Living with CIDP Coping with uncertainty CIDP may follow a pattern of relapses and remissions or a more gradual increase in symptoms. During a relapse new symptoms occur or old symptoms which had previously subsided may recur. Relapses can last for several months and may be relatively slight or quite severe. A remission occurs when the symptoms experienced during the relapse disappear either partially or completely over a period of time which may last weeks, months or even years. CIDP does not always have these patterns of being better or worse ; sometimes symptoms can gradually increase over a period of many years and it may be difficult to identify better or worse times. It is impossible to predict with certainty how CIDP is going to affect an individual in the future. The pattern of relapses and remissions varies greatly from person to person. A period of relapse can be very disturbing but many people make a good recovery. Coping with this uncertainty is one of the most difficult aspects of living with CIDP. You should try and accept this variability without getting too worried about it. You and your family and friends A diagnosis such as CIDP of a chronic condition with an uncertain prognosis, may well throw a strain on family and other relationships. You may find 10
16 it difficult to accept help when you need it, or your family and friends may feel that they cannot give help or become overprotective toward you. It is difficult to carry on family life as if nothing has happened. Everyone concerned may have to take on new roles. If you and your family and friends are able to speak openly and honestly with each other you will probably find that you are able to help each other through difficult times with the result that the bonds are strengthened. Instinctively children are aware that something is wrong and that you are worried. It is important that their questions are answered as and when they occur. Older children can become surprisingly mature and a source of strength. Trying to keep your problems to yourself will not spare them any anxiety. You and your doctor It is important to build a good relationship with your doctors, both GP and specialist. Because of the rarity of the illness, many doctors will not have encountered it before. The symptoms are difficult to describe and may not be taken seriously at first. Each case of CIDP is different, and relapses, if they occur, may bring new symptoms and problems. Because of the variability in severity and progression of the disease, the doctor will not be able to give you a definite prognosis. Although there is not one single overall treatment for CIDP, there is much that your doctor can do to help. Each person responds in different ways to different treatments. A period of experimentation with different treatment regimes is likely to be necessary in order to discover the regime which is most appropriate for you. Attitude to life It is important to be as positive as possible about everything. Our emotional state plays a large part in our health and although the norms of life may have to change for a while, the majority of patients with CIDP can expect a good quality of life. 11
17 Modification of ones lifestyle may be necessary but it is better to emphasise strengths, undertaking what can be achieved rather than failing to achieve the impossible. It is a natural reaction to become frustrated but the acceptance and understanding of the problem is more than half the battle. Addressing the problems of CIDP can be seen as bringing a new challenge. Being positive can take a lot of effort, determination and even courage and can be helped by a similar attitude in those that support and help you. What you can do to help yourself You should follow as healthy a lifestyle as possible. This will help to prevent other illnesses and infections which have been shown to trigger relapses. A nutritionally balanced diet will ensure you are getting all the vitamins and minerals you require. There is no evidence of any special dietary requirements for CIDP sufferers. It is sensible to keep your weight down, since more weight is more difficult for weak legs to carry. Regular exercise is important for overall health and should be taken according to individual limits and capabilities. Over exertion causes fatigue. However a little regular exercise will help to minimise muscle wastage and give you a good feeling of wellbeing. Any form of exercise that you enjoy and can comfortably follow will prove beneficial. Ask your physiotherapist to show you. Adequate rest periods are essential to avoid fatigue. Stress and tension may irritate the symptoms of CIDP and therefore relaxation will allow you to unwind and recharge. Some patients find it useful to record their progress in a diary so that they can discuss changes of treatment in the light of their recent progress. Others find that this can increase their anxiety about the disease and is counter productive. Original text by Eileen Evers and Professor Richard Hughes. Second edition June Revised by Ronald Munro and Dr John Winer. Copyright 1998 GBS Support Group of the United Kingdom. Registered Charity
Support and information
 Support and information for those affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome, CIDP & associated inflammatory neuropathies Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy & Associated Chronic Variants Helpline:
Support and information for those affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome, CIDP & associated inflammatory neuropathies Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy & Associated Chronic Variants Helpline:
Coping with. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) Patient information
 Coping with Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) Patient information What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)? Your doctor will have told you that you may have a disease that affects the nerves of your arms and
Coping with Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) Patient information What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)? Your doctor will have told you that you may have a disease that affects the nerves of your arms and
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (C.I.D.P.)
 University Teaching Trust Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (C.I.D.P.) Neurology 0161 206 2323 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout. Information about Chronic Inflammatory
University Teaching Trust Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (C.I.D.P.) Neurology 0161 206 2323 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout. Information about Chronic Inflammatory
5: Family, children and friends
 5: Family, children and friends This section will help you to manage difficult conversations as people close to you adjust to your diagnosis of MND. The following information is an extracted section from
5: Family, children and friends This section will help you to manage difficult conversations as people close to you adjust to your diagnosis of MND. The following information is an extracted section from
Certificate of Merit in Disorders of the Body Lesson 2: Epilepsy, Diabetes and Multiple Sclerosis
 Certificate of Merit in Disorders of the Body Lesson 2: Epilepsy, Diabetes and Multiple Sclerosis Epilepsy Epilepsy is a condition in which there is a sudden burst of electrical energy in the brain, which
Certificate of Merit in Disorders of the Body Lesson 2: Epilepsy, Diabetes and Multiple Sclerosis Epilepsy Epilepsy is a condition in which there is a sudden burst of electrical energy in the brain, which
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS INTRODUCTION Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the nervous system. Multiple sclerosis causes inflammation and damage to the protective coatings in the brain and the nerves.
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS INTRODUCTION Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the nervous system. Multiple sclerosis causes inflammation and damage to the protective coatings in the brain and the nerves.
CT guided nerve root injections
 CT guided nerve root injections Providing support and information for patients and their families A CT guided nerve root injection is used to relieve pain in the neck, shoulder, arm, back and leg, which
CT guided nerve root injections Providing support and information for patients and their families A CT guided nerve root injection is used to relieve pain in the neck, shoulder, arm, back and leg, which
Multiple Sclerosis. What is multiple sclerosis? What is the cause? What are the symptoms?
 What is multiple sclerosis? Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). Many people with multiple sclerosis are only mildly affected
What is multiple sclerosis? Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). Many people with multiple sclerosis are only mildly affected
Dr. Terry Wahls Interview pitch. Bio
 Bio Dr. Terry L. Wahls is professor of Medicine at the University of Iowa where she teaches primary care and conducts clinical trials. She also has secondary progressive multiple sclerosis and in 2003
Bio Dr. Terry L. Wahls is professor of Medicine at the University of Iowa where she teaches primary care and conducts clinical trials. She also has secondary progressive multiple sclerosis and in 2003
Keep moving. Self-help and daily living Keep moving. and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis.
 Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
Peripheral Nerve Disorders
 Helping people affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome, CIDP & associated inflammatory neuropathies Peripheral Nerve Disorders Helpline: 0800 374803 (UK) 1800 806152 (ROI) Peripheral Nerve Disorders - Page
Helping people affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome, CIDP & associated inflammatory neuropathies Peripheral Nerve Disorders Helpline: 0800 374803 (UK) 1800 806152 (ROI) Peripheral Nerve Disorders - Page
Support for Kidney Cancer
 Page 1 Fact sheet Introduction Our series of kidney cancer fact sheets have been developed to help you understand more about kidney cancer. This fact sheet provides support information for people affected
Page 1 Fact sheet Introduction Our series of kidney cancer fact sheets have been developed to help you understand more about kidney cancer. This fact sheet provides support information for people affected
Peripheral Nerve Disorders - P a g e 1. Introduction
 Peripheral Nerve Disorders - P a g e 1 Introduction The peripheral nerves connect the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) to the periphery (the sensory receptors and muscles). An illness
Peripheral Nerve Disorders - P a g e 1 Introduction The peripheral nerves connect the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) to the periphery (the sensory receptors and muscles). An illness
Get on with life, we ll see you. in 6 months. Living your life your way with MS
 Get on with life, we ll see you in 6 months. Living your life your way with MS If you re one of the 4000 New Zealanders affected by MS, ask your doctor or nurse if OCREVUS is right for you. Contents What
Get on with life, we ll see you in 6 months. Living your life your way with MS If you re one of the 4000 New Zealanders affected by MS, ask your doctor or nurse if OCREVUS is right for you. Contents What
This section will help you to identify and manage some of the more difficult emotional responses you may feel after diagnosis.
 4: Emotional impact This section will help you to identify and manage some of the more difficult emotional responses you may feel after diagnosis. The following information is an extracted section from
4: Emotional impact This section will help you to identify and manage some of the more difficult emotional responses you may feel after diagnosis. The following information is an extracted section from
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT - A TREATMENT OPTION
 KIDNEY TRANSPLANT - A TREATMENT OPTION Page 1/5 WHAT IS A KIDNEY TRANSPLANT? When kidney failure becomes very advanced, your kidneys are so damaged they can no longer do their job. A transplant is a treatment
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT - A TREATMENT OPTION Page 1/5 WHAT IS A KIDNEY TRANSPLANT? When kidney failure becomes very advanced, your kidneys are so damaged they can no longer do their job. A transplant is a treatment
Dorsal root ganglion block / Transforaminal epidural / Nerve root block
 Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Dorsal root ganglion block / Transforaminal epidural / Nerve root block What is the aim of this information sheet? for the Treatment of Pain The aim of
Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Dorsal root ganglion block / Transforaminal epidural / Nerve root block What is the aim of this information sheet? for the Treatment of Pain The aim of
Choices. Diagnosis. Multiple sclerosis information.
 Choices Diagnosis Multiple sclerosis information www.ms-uk.org Welcome to this Choices leaflet about diagnosis... MS-UK believes we must listen to the voices of people affected by multiple sclerosis (MS)
Choices Diagnosis Multiple sclerosis information www.ms-uk.org Welcome to this Choices leaflet about diagnosis... MS-UK believes we must listen to the voices of people affected by multiple sclerosis (MS)
Non-epileptic attacks
 Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
Acute kidney injury. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Acute kidney injury Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals page 2 of 12 Acute kidney injury You have been given this leaflet because you have had an episode of acute kidney injury (AKI).
Acute kidney injury Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals page 2 of 12 Acute kidney injury You have been given this leaflet because you have had an episode of acute kidney injury (AKI).
Infosheet. Peripheral neuropathy. What is peripheral neuropathy? The peripheral nervous system
 Infosheet Peripheral neuropathy What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral neuropathy is the term used to describe damage to the nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system. In myeloma the nerves
Infosheet Peripheral neuropathy What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral neuropathy is the term used to describe damage to the nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system. In myeloma the nerves
Total ankle replacement. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Total ankle replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Total ankle replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
All about Leukaemia. An Easy Read Document
 All about Leukaemia An Easy Read Document What is in this booklet About this booklet and leukaemia Page 4 How are blood cells made Page 5 Different types of leukaemia Page 9 Things that might mean you
All about Leukaemia An Easy Read Document What is in this booklet About this booklet and leukaemia Page 4 How are blood cells made Page 5 Different types of leukaemia Page 9 Things that might mean you
Disability. Fibromyalgia. An advice guide for Usdaw reps
 Disability Fibromyalgia An advice guide for Usdaw reps What is fibromyalgia? Fibromyalgia is a long-term health condition where people experience chronic, widespread pain all over their body. The pain
Disability Fibromyalgia An advice guide for Usdaw reps What is fibromyalgia? Fibromyalgia is a long-term health condition where people experience chronic, widespread pain all over their body. The pain
Section 11: Nerve damage associated with an operation under general anaesthetic
 Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 11: Nerve damage associated with an operation under Summary This leaflet explains why it is possible that some nerve damage may occur during your. This is
Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 11: Nerve damage associated with an operation under Summary This leaflet explains why it is possible that some nerve damage may occur during your. This is
Spinal cord compression: what it means and how it can be treated
 Spinal cord compression: what it means and how it can be treated Patient Information Oncology Department Author ID: Acute Oncology Nurse Specialist Leaflet Number: CC 036 Version: 2.1 Name of Leaflet:
Spinal cord compression: what it means and how it can be treated Patient Information Oncology Department Author ID: Acute Oncology Nurse Specialist Leaflet Number: CC 036 Version: 2.1 Name of Leaflet:
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome
 Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
 What is Rheumatoid Arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the joint tissue causing inflammation, stiffness, pain and extreme fatigue. If left
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the joint tissue causing inflammation, stiffness, pain and extreme fatigue. If left
Epidural steroid injection
 Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Epidural steroid injection for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this information sheet is to provide you with
Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Epidural steroid injection for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this information sheet is to provide you with
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE
 SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
How to Exercise with CFS
 How to Exercise with CFS To equip people affected by CFS / ME with the skills for self-management towards a better quality of life. Adult CFS / ME Service January 2018 Review January 2019 HOW CAN I EXERCISE
How to Exercise with CFS To equip people affected by CFS / ME with the skills for self-management towards a better quality of life. Adult CFS / ME Service January 2018 Review January 2019 HOW CAN I EXERCISE
Peripheral neuropathy
 Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in myeloma patients, how it is treated and some tips for selfmanagement. What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral
Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in myeloma patients, how it is treated and some tips for selfmanagement. What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral
Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Medications (DMARDS) Monitoring Clinic
 Department of Rheumatology Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Medications (DMARDS) Monitoring Clinic Patient Information Leaflet Specialist Support This leaflet can be made
Department of Rheumatology Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Medications (DMARDS) Monitoring Clinic Patient Information Leaflet Specialist Support This leaflet can be made
Mild memory problems
 Symptoms and lifestyle Mild memory problems Mild memory and thinking problems, also known as 'mild cognitive impairment' can affect some people with Parkinson s. This information sheet explains the symptoms
Symptoms and lifestyle Mild memory problems Mild memory and thinking problems, also known as 'mild cognitive impairment' can affect some people with Parkinson s. This information sheet explains the symptoms
This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request.
 Information for patients This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request. This leaflet tells you about acupuncture
Information for patients This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request. This leaflet tells you about acupuncture
Managing your pain
 Managing your pain www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic pain Anxiety and stress can make
Managing your pain www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic pain Anxiety and stress can make
Understanding your Tecfidera. treatment. Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera.
 Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. Contents Treatment with Tecfidera About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Multiple sclerosis A brief
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. Contents Treatment with Tecfidera About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Multiple sclerosis A brief
Changes to your behaviour
 Life after stroke Changes to your behaviour Together we can conquer stroke Because there is so much to deal with after a stroke, it s normal for your behaviour to change in some way. In this booklet we
Life after stroke Changes to your behaviour Together we can conquer stroke Because there is so much to deal with after a stroke, it s normal for your behaviour to change in some way. In this booklet we
DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS
 YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
Scoliosis. This leaflet gives you information on scoliosis and what you can do to help manage the symptoms you are experiencing.
 Scoliosis This leaflet gives you information on scoliosis and what you can do to help manage the symptoms you are experiencing. What is Scoliosis? The term scoliosis refers to the abnormal twisting and
Scoliosis This leaflet gives you information on scoliosis and what you can do to help manage the symptoms you are experiencing. What is Scoliosis? The term scoliosis refers to the abnormal twisting and
Spinal cord stimulation
 Spinal cord stimulation Pain Management Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Welcome to The Dudley Group Pain Management Service. This leaflet will provide you and your relatives with information about
Spinal cord stimulation Pain Management Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Welcome to The Dudley Group Pain Management Service. This leaflet will provide you and your relatives with information about
Multiple Sclerosis , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. nr Last reviewed: 04/17/2017 1
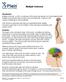 Multiple Sclerosis Introduction Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a disease of the brain and spinal cord. Most patients with multiple sclerosis are able to lead a very functional life. However, MS causes a
Multiple Sclerosis Introduction Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a disease of the brain and spinal cord. Most patients with multiple sclerosis are able to lead a very functional life. However, MS causes a
How to Talk to Your Doctor About Psoriatic Arthritis
 How to Talk to Your Doctor About Psoriatic Arthritis Preparing for your Doctor s Appointment Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that often occurs with psoriasis of the skin, a condition that features
How to Talk to Your Doctor About Psoriatic Arthritis Preparing for your Doctor s Appointment Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that often occurs with psoriasis of the skin, a condition that features
Coccygeal Denervation
 Coccygeal Denervation 1 Introduction Before you agree to have your coccygeal denervation, it is sensible to know all you can about it. This means knowing why you may need coccygeal denervation, what the
Coccygeal Denervation 1 Introduction Before you agree to have your coccygeal denervation, it is sensible to know all you can about it. This means knowing why you may need coccygeal denervation, what the
Carpal tunnel syndrome
 Condition Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this condition. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely
Condition Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this condition. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely
Eastman Dental Hospital. About Face Pain management programme. Facial Pain Team
 Eastman Dental Hospital About Face Pain management programme Facial Pain Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an interpreter contact us on
Eastman Dental Hospital About Face Pain management programme Facial Pain Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an interpreter contact us on
Facet Joint Rhizolysis/Radio Frequency Lesioning (Denervation)
 Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Facet Joint Rhizolysis/Radio Frequency Lesioning (Denervation) for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this information
Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Facet Joint Rhizolysis/Radio Frequency Lesioning (Denervation) for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this information
The road to recovery. The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke
 The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline on 0303 3033
The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline on 0303 3033
Watch and Wait. A Guide for Patients
 Watch and Wait A Guide for Patients Introduction Some blood cancers progress rapidly and therefore require treatment straightaway. Others progress slowly and the patient may not experience any symptoms
Watch and Wait A Guide for Patients Introduction Some blood cancers progress rapidly and therefore require treatment straightaway. Others progress slowly and the patient may not experience any symptoms
Epidurals and spinals: information about their operation for anyone who may benefit from an epidural or spinal
 Information for patients pidurals and spinals: information about their operation for anyone who may benefit from an epidural or spinal This leaflet has been made using information from the Royal College
Information for patients pidurals and spinals: information about their operation for anyone who may benefit from an epidural or spinal This leaflet has been made using information from the Royal College
Seldom Heard Voices Visual & Hearing Sensory Loss Prepared by: South Lincs Blind Society
 Seldom Heard Voices Visual & Hearing Sensory Loss Prepared by: South Lincs Blind Society Healthwatch Lincolnshire Supporting Seldom Heard Voices Healthwatch Lincolnshire was formed under the Health and
Seldom Heard Voices Visual & Hearing Sensory Loss Prepared by: South Lincs Blind Society Healthwatch Lincolnshire Supporting Seldom Heard Voices Healthwatch Lincolnshire was formed under the Health and
Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Spinal Cord. Peripheral Nerves
 Multiple Sclerosis Introduction Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a disease of the brain and spinal cord. It affects about 400,000 Americans at any one time. Most patients with multiple sclerosis are able
Multiple Sclerosis Introduction Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a disease of the brain and spinal cord. It affects about 400,000 Americans at any one time. Most patients with multiple sclerosis are able
Peripheral neuropathy
 Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what the peripheral nervous system is, what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, its symptoms and treatments and tips for self-management.
Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what the peripheral nervous system is, what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, its symptoms and treatments and tips for self-management.
Welcome to NHS Highland Pain Management Service
 Welcome to NHS Highland Pain Management Service Information from this questionnaire helps us to understand your pain problem better. It is important that you read each question carefully and answer as
Welcome to NHS Highland Pain Management Service Information from this questionnaire helps us to understand your pain problem better. It is important that you read each question carefully and answer as
Creutzfelt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
 Creutzfelt-Jakob Disease (CJD) Introduction Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is an illness of the nervous system that causes damage to the brain. (The disease is named after 2 German scientists). CJD is
Creutzfelt-Jakob Disease (CJD) Introduction Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is an illness of the nervous system that causes damage to the brain. (The disease is named after 2 German scientists). CJD is
Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
Deep brain stimulation
 About insertion of a deep brain stimulator The deep brain stimulator sends electrical impulses to the brain interrupting the abnormal signals that are causing the symptoms. The impulses are adjusted by
About insertion of a deep brain stimulator The deep brain stimulator sends electrical impulses to the brain interrupting the abnormal signals that are causing the symptoms. The impulses are adjusted by
Piriformis Syndrome. Midwest Bone & Joint Institute 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL Phone: Fax:
 A Patient s Guide to Piriformis Syndrome 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Piriformis Syndrome 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure LIVING WELL
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure LIVING WELL Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 Who is affected by kidney failure? 6 How does kidney failure affect
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure LIVING WELL Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 Who is affected by kidney failure? 6 How does kidney failure affect
A handbook for people who have injected drugs
 A handbook for people who have injected drugs Introduction This handbook has been written for current and ex-drug injectors. It gives information and advice about the hep C virus, and the tests you can
A handbook for people who have injected drugs Introduction This handbook has been written for current and ex-drug injectors. It gives information and advice about the hep C virus, and the tests you can
Autoimmune Liver Disease
 Autoimmune Liver Disease A Guide An explanation of what autoimmune liver diseases are including autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune sclerosis cholangitis What are autoimmune diseases?... 4 What is autoimmune
Autoimmune Liver Disease A Guide An explanation of what autoimmune liver diseases are including autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune sclerosis cholangitis What are autoimmune diseases?... 4 What is autoimmune
Caudal epidural. Information for patients Pain Management Service
 Caudal epidural Information for patients Pain Management Service As part of your treatment it has been suggested that you may benefit from a caudal epidural. It is difficult to say how much this treatment
Caudal epidural Information for patients Pain Management Service As part of your treatment it has been suggested that you may benefit from a caudal epidural. It is difficult to say how much this treatment
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent
 Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent ER_OS02 Total Knee Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of November 2018 Local Informa#on For further informa0on locally you can contact the Pa0ent Advice & Liaison Service
Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent ER_OS02 Total Knee Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of November 2018 Local Informa#on For further informa0on locally you can contact the Pa0ent Advice & Liaison Service
Parkinson s UK Brain Bank: answering your questions about brain donation. In association with
 Parkinson s UK Brain Bank: answering your questions about brain donation In association with Version 6/2015 Contents About the tissue we collect 4 How brain tissue is used in Parkinson s research 6 Becoming
Parkinson s UK Brain Bank: answering your questions about brain donation In association with Version 6/2015 Contents About the tissue we collect 4 How brain tissue is used in Parkinson s research 6 Becoming
Living Life with Persistent Pain. A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain
 Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
Occupational therapy after stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke This guide explains how occupational therapy can help your recovery and rehabilitation after a stroke.
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke This guide explains how occupational therapy can help your recovery and rehabilitation after a stroke.
Bone density scanning and osteoporosis
 Bone density scanning and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break
Bone density scanning and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery. (Minor procedure in Primary Care)
 Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery (Minor procedure in Primary Care) Information for Patients Gateshead Upper Limb Unit Page 1 of 5 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery (Minor procedure in Primary Care) Information for Patients Gateshead Upper Limb Unit Page 1 of 5 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition
Beyond Cancer Moving On
 Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
Living well with and beyond cancer Information, support and practical advice to help you through treatment and beyond
 Living well with and beyond cancer Information, support and practical advice to help you through treatment and beyond Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction to this booklet Receiving
Living well with and beyond cancer Information, support and practical advice to help you through treatment and beyond Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction to this booklet Receiving
A CT guided cervical nerve block (Root block)
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust A CT guided cervical nerve block (Root block) Radiology Department The leaflet tells you about having a computerised tomography
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust A CT guided cervical nerve block (Root block) Radiology Department The leaflet tells you about having a computerised tomography
If you would like to find out more about this service:
 Step by Step Information for parents and carers This guidance forms part of Samaritans Step by Step resources for communities working with and supporting young people. Step by Step is a Samaritans service
Step by Step Information for parents and carers This guidance forms part of Samaritans Step by Step resources for communities working with and supporting young people. Step by Step is a Samaritans service
Worried about your memory?
 Worried about your memory? Find out more about memory problems and what you can do next alzheimers.org.uk Worried about memory problems? Everybody forgets things from time to time. But if you or other
Worried about your memory? Find out more about memory problems and what you can do next alzheimers.org.uk Worried about memory problems? Everybody forgets things from time to time. But if you or other
STROKE INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 STROKE INTRODUCTION Stroke is the medical term for a specific type of neurological event that causes damage to the brain. There are two types of stroke, but both types of stroke cause the same type of
STROKE INTRODUCTION Stroke is the medical term for a specific type of neurological event that causes damage to the brain. There are two types of stroke, but both types of stroke cause the same type of
Pars Injection for Lumbar Spondylolysis
 Pars Injection for Lumbar Spondylolysis Issue 4: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent investigations and consultation with your spinal surgeon, a possible cause for your symptoms
Pars Injection for Lumbar Spondylolysis Issue 4: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent investigations and consultation with your spinal surgeon, a possible cause for your symptoms
Unit 3: EXPLORING YOUR LIMITING BELIEFS
 Unit 3: EXPLORING YOUR LIMITING BELIEFS Beliefs and Emotions Bring to mind a negative belief you hold about money. Perhaps it is I don t believe I can win with money or Money is hard to come by. While
Unit 3: EXPLORING YOUR LIMITING BELIEFS Beliefs and Emotions Bring to mind a negative belief you hold about money. Perhaps it is I don t believe I can win with money or Money is hard to come by. While
CT guided lung biopsy explained
 CT guided lung biopsy explained Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as a CT (computerised tomography) guided lung biopsy.
CT guided lung biopsy explained Lung Investigation Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as a CT (computerised tomography) guided lung biopsy.
Angiogram. Information for patients
 Angiogram Information for patients What is an Angiogram? What is an angiogram? An angiogram is used to take detailed pictures of arteries using x-ray guidance. Normally blood vessels do not show up on
Angiogram Information for patients What is an Angiogram? What is an angiogram? An angiogram is used to take detailed pictures of arteries using x-ray guidance. Normally blood vessels do not show up on
Information for potential living kidney donors
 Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Optic neuritis. Information for patients Ophthalmology
 Optic neuritis Information for patients Ophthalmology page 2 of 8 What is optic neuritis? Optic neuritis is a common cause of acute visual loss in young people. The optic nerve is like a cable of electric
Optic neuritis Information for patients Ophthalmology page 2 of 8 What is optic neuritis? Optic neuritis is a common cause of acute visual loss in young people. The optic nerve is like a cable of electric
Your visit to the Breast Clinic. Information for patients Breast Services
 Your visit to the Breast Clinic Information for patients Breast Services This leaflet will provide you with information about the Breast Clinic and what might happen during your appointment. If after reading
Your visit to the Breast Clinic Information for patients Breast Services This leaflet will provide you with information about the Breast Clinic and what might happen during your appointment. If after reading
Acute Liver Failure. A Guide. An explanation of what Acute Liver Failure is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
 A Guide An explanation of what is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Introduction... 4 What is ALF?... 4 What can cause ALF?... 4 What are the signs and symptoms of ALF?... 5 Why does my child need to
A Guide An explanation of what is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Introduction... 4 What is ALF?... 4 What can cause ALF?... 4 What are the signs and symptoms of ALF?... 5 Why does my child need to
Botulinum Toxin Injections
 KAISER PERMANENTE SAN FRANCISCO DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY Office Procedures included: - Botulinum Toxin Injections - Electroencephalogram (EEG) - Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Condition Studies (NCS)
KAISER PERMANENTE SAN FRANCISCO DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY Office Procedures included: - Botulinum Toxin Injections - Electroencephalogram (EEG) - Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Condition Studies (NCS)
Lumbar sympathetic block (lumbar sympathectomy) with local anaesthetic
 Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Lumbar sympathetic block (lumbar sympathectomy) with local anaesthetic for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this
Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Lumbar sympathetic block (lumbar sympathectomy) with local anaesthetic for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
 PATIENT INFORMATION SHEET RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Page 1 of 8 INTRODUCTION A hip replacement is an extremely successful operation. At least 95% of patients are satisfied with their
PATIENT INFORMATION SHEET RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Page 1 of 8 INTRODUCTION A hip replacement is an extremely successful operation. At least 95% of patients are satisfied with their
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS
 INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
risk factors for falling
 Resource # 10 Page 1 of 8 1. Dizziness- What Can Cause Dizziness? Not eating regularly Change in body position (e.g. from sitting to standing) Low blood pressure High blood pressure Medication side effects
Resource # 10 Page 1 of 8 1. Dizziness- What Can Cause Dizziness? Not eating regularly Change in body position (e.g. from sitting to standing) Low blood pressure High blood pressure Medication side effects
MS Ireland s Opinion On The Introduction of Sativex
 MS Ireland s Opinion On The Introduction of Sativex Introduction Multiple Sclerosis Ireland is the national organization providing information, support and advocacy services to the MS community people
MS Ireland s Opinion On The Introduction of Sativex Introduction Multiple Sclerosis Ireland is the national organization providing information, support and advocacy services to the MS community people
High dose (radical) radiotherapy to the lung or bronchus
 The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust High dose (radical) radiotherapy to the lung or bronchus Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When radiotherapy is given... 1 Chemotherapy
The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust High dose (radical) radiotherapy to the lung or bronchus Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When radiotherapy is given... 1 Chemotherapy
Diagnostic Lumbar Medial Branch Block: Summary and Discharge Instructions
 Scheduled Date:! 2012 / /!! Arrival time:!!!! am / pm What is going to be done today and why? Today, you will have a procedure called a diagnostic lumbar medial branch block. The term diagnostic is used
Scheduled Date:! 2012 / /!! Arrival time:!!!! am / pm What is going to be done today and why? Today, you will have a procedure called a diagnostic lumbar medial branch block. The term diagnostic is used
Peripheral Nerve Injections: General Information
 Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Peripheral Nerve Injections: General Information for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this information sheet
Information sheet for adult patients undergoing: Peripheral Nerve Injections: General Information for the Treatment of Pain What is the aim of this information sheet? The aim of this information sheet
Osteoarthritis of the neck
 1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
A Patient s Guide to Dropped Head Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Dropped Head Syndrome 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It
A Patient s Guide to Dropped Head Syndrome 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts
 A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts
 A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
If you have dementia, you may have some or all of the following symptoms.
 About Dementia Dementia may be caused by a number of illnesses that affect the brain. Dementia typically leads to memory loss, inability to do everyday things, difficulty in communication, confusion, frustration,
About Dementia Dementia may be caused by a number of illnesses that affect the brain. Dementia typically leads to memory loss, inability to do everyday things, difficulty in communication, confusion, frustration,
Arthroscopy of the ankle. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Arthroscopy of the ankle Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Arthroscopy of the ankle Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Large granular lymphocytic leukaemia (LGLL)
 Bloodwise Patient Information Large granular lymphocytic leukaemia (LGLL) For anyone affected by blood cancer Large granular lymphocytic leukaemia (LGLL) This fact sheet will help you to understand LGLL,
Bloodwise Patient Information Large granular lymphocytic leukaemia (LGLL) For anyone affected by blood cancer Large granular lymphocytic leukaemia (LGLL) This fact sheet will help you to understand LGLL,
