Interstitial Cystitis
|
|
|
- Brenda Kennedy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
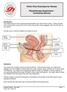
1 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between the navel and the inside of the thighs, front or back. The symptoms range from mild to severe, and intermittent to constant. The more severe cases of IC can have a devastating effect on both sufferers and their loved ones. In the past, IC was believed to be a rare disease that was very difficult to treat. Now we know that IC affects many women and men. The following information should help you discuss this condition with your urologist and understand what treatments are available. What happens under normal conditions? After urine is made in the kidneys, it flows down the ureters into the bladder. The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ. Most of the wall of the bladder is made of muscle. As the bladder fills, the muscle relaxes so that the bladder expands and holds urine. During urination, the bladder muscle contracts to squeeze out the urine. The urethra is the tube through which urine passes from the bladder to the outside. The urethra has a muscle, the sphincter, which is completely different from the bladder muscle. The sphincter normally stays closed and makes a seal to keep urine from leaking. During urination, the sphincter opens and lets urine pass. The bladder and urethra have a specialized lining called the epithelium. The epithelium forms a barrier between the urine and the bladder muscle. The epithelium also helps to keep bacteria from sticking to the bladder, so it helps to prevent bladder infections. What is interstitial cystitis (IC)? IC is a chronic inflammatory condition of the bladder that may also affect the urethra and the prostate. Its symptoms may be mild or severe, occasional or constant. It is not an infection, but its symptoms can feel like those of a bladder infection. What are some risk factors for IC? There are no specific behaviors or exposures (such as smoking) known to increase a person's risk for getting IC. The tendency to get IC may be influenced by a person's genes, and so having a blood relative with IC may increase the risk of getting IC yourself. About 90 percent of people diagnosed with IC are women, which suggests that being female may increase the risk of getting IC. However, the difference in rates of IC for men vs. women may not really be as high as we think, because some men diagnosed with "prostatitis" or similar conditions with different labels may really have IC. How many people in the United States have IC? It is hard to know for certain how many people have IC, because doctors have different opinions about how exactly to diagnose IC. What causes IC? The causes of IC are being studied in medical centers around the world. Many researchers believe that IC is caused by one or more of the following: (1) a defect in the bladder epithelium that allows irritating substances in the urine to penetrate into the bladder; (2) a specific type of inflammatory cell (mast cell) releasing histamine and other chemicals that promote IC symptoms in the bladder; (3) there is something in the urine that damages the bladder; (4) the nerves that carry bladder sensations are changed, so pain is now caused by events that are not normally painful (such as bladder filling); and/or (5) the body's immune system attacks the bladder, similar to other autoimmune conditions. It is likely that different processes occur in different groups of IC patients. It also is likely that these different processes may affect each other (for example, a defect in the bladder epithelium may promote inflammation and stimulate mast cells). Recent research shows that IC patients may have a substance in the urine that inhibits the growth of cells in
2 the bladder epithelium. Therefore, some people may be predisposed to get IC after an injury to the bladder such as an infection. What are the symptoms of IC? The symptoms of IC vary for different patients. If you have IC, you may have urinary frequency/urgency or pain or both. Many people have only pain and no frequency, but most IC patients have all of the symptoms. There have been many reported cases when a person diagnosed with IC was not experiencing substantial pain. Frequency is the need to urinate more often than normal. Normally, the average person urinates no more than seven times a day, and does not have to get up at night to use the bathroom. An IC patient often has to urinate frequently both day and night. As frequency becomes more severe, it leads to urgency. Urgency to urinate is a common IC symptom. Some patients feel a constant urge that never goes away, even right after urinating. While others with IC urinate often, they do not necessarily feel the urge to go all the time. IC patients may have bladder pain that gets worse as the bladder fills. Some IC patients feel the pain in other areas besides the bladder. A person may feel pain in the urethra, lower abdomen, lower back, or the pelvic or perineal area. Women may experience pain in the vulva or the vagina and men may feel the pain in the scrotum, testicle, or penis. The pain may be constant or intermittent. Many IC patients can identify certain things that make their symptoms worse. For example, some people's symptoms are made worse by certain foods or drinks. Many patients find that symptoms are worse if they have stress (either physical or mental stress). The symptoms may vary with the menstrual cycle. Both men and women with IC can experience sexual difficulties due to this condition; women may have pain during intercourse because the bladder is right in front of the vagina, and men may have painful orgasm or pain the next day. How is IC diagnosed? At this time, doctors have different opinions about how to diagnose IC. This is because no test so far has turned out to be completely accurate. All doctors do agree that a medical history, physical exam and urine tests are needed for evaluation. These tests are important to rule out other conditions that might be causing the symptoms. Some doctors believe that IC is present if a patient has IC symptoms and no other cause for those symptoms can be found. Other doctors believe that more tests are necessary to determine whether the patient has IC. One test that many doctors use is simple office cystoscopy, in which the doctor looks inside the bladder with a cystoscope while the patient is not under anesthesia. This test can rule out other problems such as cancer. Whereas simple cystocopy can be performed in the doctor's office, a more invasive test can be performed in the operating room. This involves a basic cystoscopic examination followed by a stretching or distention of the bladder by instilling water under pressure. This can reveal cracks in the bladder in more severe cases. Cystoscopy was once part of the standard IC evaluation, but it is no longer always considered a necessary test for IC because the examination is usually normal. However, during cystoscopy, some IC patients will have small areas of bleeding, or actual ulcers, which the doctor can see through the cystoscope. The ulcers are usually found only in patients who are over the age of 60 years and can often be suspected by the presence of blood in the urine. If a person has symptoms of IC and the cystoscopy shows bleeding or ulcers, the diagnosis is fairly certain. Most people who have IC symptoms do not have these bleeding areas, but they may really have IC after all and may respond to the same treatments. The doctor will often then perform a bladder biopsy, which helps to rule out other bladder diseases. While this procedure is primarily used for testing, some IC patients may experience relief of symptoms afterwards. Some doctors believe that if a person has the typical symptoms of IC, and no other cause for the symptoms is found, then the patient has IC. This is still an area of controversy, and future research may help to resolve it. Urodynamics evaluation is another test that was once considered to be part of the standard IC evaluation, but is no longer believed to be necessary in all cases. This test involves filling the bladder with water through a small catheter, and measuring bladder pressures as the bladder fills and empties. The usual results with IC are that the bladder has a small capacity and perhaps pain with filling.
3 Some doctors use a test called the potassium sensitivity test, in which potassium solution and water are placed into the bladder one at a time, and pain/urgency scores are compared. A person who has IC feels more pain/urgency with the potassium solution than with the water, but patients with normal bladders cannot tell the difference between the two solutions. At this time, there is no definite answer about the best way to diagnose IC. However, if a patient has typical symptoms and a negative urine examination showing no infection or blood, then IC should be suspected. Are there stages of IC? IC is a disease that often starts in a subtle way, usually beginning with urinary frequency that the patient may not notice or recognize as a problem. In other cases, the onset is much more dramatic with severe symptoms occurring within weeks or months. In many cases, the symptoms become chronic but the disease does not tend to progress after the initial 12 to 18 months. In rare cases, the bladder will become progressively smaller over time to the point where there is almost no capacity to store urine. How is IC treated? No one knows the cause of IC. Because there are probably several different causes, no single treatment works for everyone, and no treatment is "the best." Treatment must be chosen individually for each patient, based on his or her symptoms. The usual course is to try different treatments (or combinations of treatments) until good symptom relief occurs. At this time, two treatments are approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat IC. One is oral pentosan polysulfate. No one knows for certain exactly how it works for IC. Many people think that it builds and restores the protective coating on the bladder epithelium. It may also help by decreasing inflammation or by other actions. The usual dose is 100 mg three times a day, although we prescribe it as 200mg twice a day. Possible side effects are very uncommon and the most common are nausea, diarrhea and gastric distress. Occasional hair loss can occur. It often takes at least three to six months of treatment with oral pentosan polysulfate before the patient notices a significant improvement in symptoms. The other FDA-approved treatment is to place dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) into the bladder through a catheter. This is usually done once a week for six weeks, and some people continue using it as maintenance therapy (though at longer intervals; not every week). No one knows for certain how DMSO helps IC. It has several properties including blocking inflammation, decreasing pain sensation and removing a type of toxin called "free radicals" that can damage tissue. Some doctors combine DMSO with other medications such as heparin (similar to pentosan polysulfate) or steroids (to decrease inflammation). No studies have tested whether these combinations work better than dimethyl sulfoxide alone. The main side effect is a garlic-like odor that lasts for several hours after using DMSO. For some patients, DMSO can be painful to place into the bladder. This can often be relieved by first placing a local anesthetic into the bladder through a catheter, or by mixing the local anesthetic with the DMSO. A wide variety of other treatments are used for IC, even though they are not specifically approved by the FDA for this purpose. The most common ones are oral hydroxyzine, oral amitriptyline and instillation of heparin into the bladder through a catheter. Hydroxyzine is an antihistamine. It is thought that some IC patients have too much histamine in the bladder, and that histamine promotes pain and other symptoms. Therefore, an antihistamine can be helpful in treating IC. The usual dose is 10 to 75 mg in the evening. The main side effect is sedation, but that can actually be a benefit because it helps the patient to sleep better at night and get up to urinate less frequently. The only antihistamines that have been specifically studied for IC are hydroxyzine and (more recently) cimetidine. It is unknown whether other antihistamines will also help treat IC. Amitriptyline is described as an antidepressant, but it actually has many effects that may improve IC symptoms. It has antihistamine effects, decreases bladder spasms, and slows the nerves that carry pain messages (for that reason, it is used for many types of pain, not just IC). Amitriptyline is widely used for other types of chronic pain such as cancer and nerve damage. The usual dose is 10 to 75 mg in the evening. The most common side effects are sedation, constipation and possible weight gain.
4 Heparin is similar to pentosan polysulfate and probably helps the bladder by similar mechanisms. Heparin is not absorbed by the stomach and long-term injections can cause osteoporosis (bone thinning), and so it must be placed into the bladder by a catheter. The usual dose is 10,000 to 20,000 units daily or three times a week. Side effects are rare because the heparin remains only in the bladder and does not usually affect the rest of the body. Many other IC treatments are also used, but less frequently than the ones described. Some patients do not respond to any IC therapy but can still have significant improvement in the quality of life with adequate pain management. Pain management can include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, moderate strength opiates and stronger long-acting opiates in addition to nerve blocks, acupuncture and other non-drug therapies. Professional pain management may often be helpful in more severe cases. What can be expected after IC treatment? The most important thing to remember is that none of the IC treatments works immediately. It usually takes weeks to months before symptoms improve. Even with successful treatment, the condition is not "cured;" it is simply "in remission." Most patients need to continue treatment indefinitely, or else the symptoms return. Some patients have flare-ups of symptoms even on treatment. Although most patients will find that their symptoms improve as they are treated for IC, not all patients will become completely symptom-free. Many patients still have to urinate more frequently than normal, or have some degree of persistent discomfort and/or have to avoid certain foods or activities that make symptoms worse. Is it possible for IC to recur after successful treatment? How can recurrences be prevented? It is possible for IC symptoms to recur even if the disease has been in remission for a long time. It is not known what causes recurrences. Also, there is no known way to prevent recurrences for certain. Some things that patients do to try to prevent recurrence include: (1) stay on their medical treatments even after remission; (2) avoid certain foods that may irritate the bladder; and (3) avoid certain activities or stresses that may worsen IC. The specific foods or activities that affect IC are different for different patients, and so each person has to form his/her own individual plan. Frequently Asked Questions: How does diet affect IC? Most (but not all) people with IC find that certain foods make their symptoms worse. There are four foods that patients most often find irritating to their bladders: citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate and coffee. All four of these foods are rich in potassium. Other foods that bother the bladder in many patients are alcoholic beverages, spicy foods and some carbonated beverages. The list of foods that have been reported to affect IC is quite long, but not all foods affect all patients the same way. For this reason, each patient must find out how foods affect his or her own bladder. The simplest way to find out whether any foods bother your bladder is to try an "elimination diet" for one to two weeks. On an elimination diet, you stop eating all of the foods that could irritate your bladder. IC food lists are available from many sources ( or If your bladder symptoms improve while you are on the elimination diet, this means that at least one of the foods was irritating your bladder. The next step is to find out exactly which foods cause bladder problems for you. After one to two weeks on the elimination diet, try eating one food from the IC food list. If this food does not bother your bladder within 24 hours, this food is probably safe and can be added back into your regular diet. The next day, try eating a second food from the list, and so on. In this way, you will add the foods back into your diet one at a time, and your bladder symptoms will tell you if any food causes problems for you. Be sure to add only one new food to your diet each day. If a person eats a banana, strawberries and tomatoes all in the same day,
5 and the IC symptoms get bad that evening, he/she will not know which of the three foods caused the symptom to flare up Does stress cause IC? At this time, there is no evidence that stress makes a person get IC in the first place. However, it is well known that if a person has IC, physical or mental stress can make the symptoms worse. Is IC hereditary? There is some research that indicates that there is a genetic pattern. It is important to discuss the symptoms of IC with the family, especially the females, so that any other affected members can be screened and treated early in the disease process.
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome
 page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC)
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Coping with urges and leaks?
 OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information
 Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
You have been booked for a. Flexible Cystoscopy. Under Local Anaesthetic
 You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use Bladder Control Does Matter
 Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Overactive bladder. Information for patients from Urogynaecology
 Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar. Part I: The Physical Impact
 Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar Tuesday, December 1, 2015 Part I: The Physical Impact Presented by LaShon Day received her Masters of Science as a Physician s Assistant at
Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar Tuesday, December 1, 2015 Part I: The Physical Impact Presented by LaShon Day received her Masters of Science as a Physician s Assistant at
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
BLADDER CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY. Learn more at
 BLADDER CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK TO YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents WHAT IS BLADDER CANCER? 4 TYPES OF BLADDER CANCER 5 GRADING AND STAGING 8 TREATMENT OVERVIEW
BLADDER CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK TO YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents WHAT IS BLADDER CANCER? 4 TYPES OF BLADDER CANCER 5 GRADING AND STAGING 8 TREATMENT OVERVIEW
Intravesical Botox Injections
 Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
Lee Jackson, M.D. Post-Operation Information and Instructions
 Post-Operation Information and Instructions While a robotic prostatectomy is performed routinely, it is still a relatively major surgery that will take some time and effort to recover from. The following
Post-Operation Information and Instructions While a robotic prostatectomy is performed routinely, it is still a relatively major surgery that will take some time and effort to recover from. The following
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Cystoscopy. Your cystoscopy is scheduled at the Ambulatory Procedure Center at Altru Clinic - Main, 4-south waiting room.
 Improving Health, Enriching Life Cystoscopy Your cystoscopy is scheduled at the Ambulatory Procedure Center at Altru Clinic - Main, 4-south waiting room. Arrival Time: Appointment Date: Normal Female Urinary
Improving Health, Enriching Life Cystoscopy Your cystoscopy is scheduled at the Ambulatory Procedure Center at Altru Clinic - Main, 4-south waiting room. Arrival Time: Appointment Date: Normal Female Urinary
Having prostate surgery
 Having prostate surgery Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk The most common operation on the prostate is known as a Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP). Sometimes, it is necessary
Having prostate surgery Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk The most common operation on the prostate is known as a Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP). Sometimes, it is necessary
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE
 TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
Kelly procedure. How does the urinary system work? What is a Kelly procedure and why does my child need one?
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Kelly procedure This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains the Kelly procedure used
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Kelly procedure This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains the Kelly procedure used
ONE IN THREE WOMEN WHO EVER HAD A BABY WET THEMSELVES EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD DO PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING.
 08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. About Your Surgery DRAFT
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Surgery Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) This handout describes a transurethral resection of the prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Surgery Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) This handout describes a transurethral resection of the prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before
Trans Urethral Resection of Bladder Tumour
 Trans Urethral Resection of Bladder Tumour Department of Urology 2 Patient Information Contents Where is the bladder and what does it do? 3 What is non invasive cancer of the bladder? 4 How is bladder
Trans Urethral Resection of Bladder Tumour Department of Urology 2 Patient Information Contents Where is the bladder and what does it do? 3 What is non invasive cancer of the bladder? 4 How is bladder
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
About Your Procedure
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Procedure UroLift This handout describes a UroLift procedure to treat an enlarged prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before and after your procedure.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Procedure UroLift This handout describes a UroLift procedure to treat an enlarged prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before and after your procedure.
Incontinence. Urinary. In Adults. THIS PUBLICATION IS OUT OF DATE. For most current information:
 Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help
 Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Having a Flexible Cystoscopy
 ENDOSCOPY DEPARTMENT Patient Information Having a Flexible Cystoscopy Endoscopy Unit North Wing Entrance 1 Dorset County Hospital Williams Avenue Dorchester DT1 2JY If you need this information in large
ENDOSCOPY DEPARTMENT Patient Information Having a Flexible Cystoscopy Endoscopy Unit North Wing Entrance 1 Dorset County Hospital Williams Avenue Dorchester DT1 2JY If you need this information in large
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Information for Patients. Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English
 Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
Patient Information. Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms. pubic bone. urethra. scrotum. bladder. vaginal canal
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Returning Home After Prostatectomy
 Returning Home After Prostatectomy Catholic Medical Center in conjunction with Manchester Urology Associates is proud to be one of the few hospitals in the United States to offer Robotic Assisted radical
Returning Home After Prostatectomy Catholic Medical Center in conjunction with Manchester Urology Associates is proud to be one of the few hospitals in the United States to offer Robotic Assisted radical
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence
 Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises
 MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients
 Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer
 Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy
 Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Anterior And Posterior Repair
 gynaecology program Pre- and Post-operative Instructions: Anterior And Posterior Repair Informed Consent As part of informed consent, your doctor will talk to you about: What will be done during the surgery
gynaecology program Pre- and Post-operative Instructions: Anterior And Posterior Repair Informed Consent As part of informed consent, your doctor will talk to you about: What will be done during the surgery
Prostatitis - A straight forward guide to
 Prostatitis - A straight forward guide to inflammation of the prostate and Pelvic Pain Syndrome What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate and it is usually about the size of a walnut. Around the age
Prostatitis - A straight forward guide to inflammation of the prostate and Pelvic Pain Syndrome What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate and it is usually about the size of a walnut. Around the age
Information about your Urodynamics Test
 Gynaecology Department Patient Information Information about your Urodynamics Test This information booklet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about having an urodynamic
Gynaecology Department Patient Information Information about your Urodynamics Test This information booklet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about having an urodynamic
Prostate surgery. What is the prostate? What is a TURP? Why is a TURP operation necessary? Deciding to have a TURP operation.
 What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
A Patient s Guide to HIVEC Treatment HIVECTM
 A Patient s Guide to HIVEC Treatment HIVECTM Contents Pages 1. Understanding Bladder Cancer 1. Understanding Bladder Cancer 2. Tumour Stages 3. What is HIVEC Treatment? 4. How Does it Work? 5. Before Your
A Patient s Guide to HIVEC Treatment HIVECTM Contents Pages 1. Understanding Bladder Cancer 1. Understanding Bladder Cancer 2. Tumour Stages 3. What is HIVEC Treatment? 4. How Does it Work? 5. Before Your
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
Stress. incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES.
 Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
 What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
Urinary incontinence. Urology Department. Patient Information Leaflet
 Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It
 Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
Bladder Cancer Knowing the Risks and Warning Signs. Part II: Warning Signs
 Bladder Cancer Knowing the Risks and Warning Signs Part II: Warning Signs May 8, 2018 Presented by: is the Director of Urologic Oncology at MedStar Washington Hospital Center and an Assistant Professor
Bladder Cancer Knowing the Risks and Warning Signs Part II: Warning Signs May 8, 2018 Presented by: is the Director of Urologic Oncology at MedStar Washington Hospital Center and an Assistant Professor
Chronic Pelvic Pain. AP099, December 2010
 AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. What Is IBS?
 1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant
 Page 1 of 5 What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant This information will help you understand the risks, benefits and possible complications involved in a kidney transplant. Please read it carefully.
Page 1 of 5 What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant This information will help you understand the risks, benefits and possible complications involved in a kidney transplant. Please read it carefully.
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Can xanax cause bed wetting
 Can xanax cause bed wetting Search 12-12-2011 I had the Monarc bladder sling surgery a month ago. I am voiding fine, and don't appear to have the stress incontinence anymore; however, I am in constant.
Can xanax cause bed wetting Search 12-12-2011 I had the Monarc bladder sling surgery a month ago. I am voiding fine, and don't appear to have the stress incontinence anymore; however, I am in constant.
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Cystoscopy. Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Cystoscopy Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 8 What is a cystoscopy? A cystoscopy is a procedure to look inside the bladder using a thin camera called a cystoscope. A cystoscope is inserted
Cystoscopy Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 8 What is a cystoscopy? A cystoscopy is a procedure to look inside the bladder using a thin camera called a cystoscope. A cystoscope is inserted
Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope
 Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, 2018 Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope Chris Morash MD FRCSC Associate Professor, University of Ottawa Head, Urological Oncology Bladder
Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, 2018 Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope Chris Morash MD FRCSC Associate Professor, University of Ottawa Head, Urological Oncology Bladder
Indwelling urinary catheter
 Indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is a catheter? A catheter is a hollow flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following
Indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is a catheter? A catheter is a hollow flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following
Uroformation. Prostate Surgery. Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy (RALP)
 Uroformation Prostate Surgery Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy (RALP) The Uroformation series is a co-operative venture in patient centered urological information. June 2014 What is the Prostate?
Uroformation Prostate Surgery Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy (RALP) The Uroformation series is a co-operative venture in patient centered urological information. June 2014 What is the Prostate?
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME
 Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
WHAT EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS IN WOMEN. By Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., FACG
 WHAT EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS IN WOMEN By Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., FACG Originally published in October 2002. Updated by Dr. Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., MACG in April 2007.
WHAT EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS IN WOMEN By Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., FACG Originally published in October 2002. Updated by Dr. Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., MACG in April 2007.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
Chronic pelvic pain has many different characteristics. Signs and symptoms may include:
 Pelvic Pain in Women Pelvic pain in women refers to pain in the lowest part of your abdomen and pelvis. If asked to locate your pain, you might sweep your hand over that entire area rather than point to
Pelvic Pain in Women Pelvic pain in women refers to pain in the lowest part of your abdomen and pelvis. If asked to locate your pain, you might sweep your hand over that entire area rather than point to
flow resulting from damage to blood vessels can also contribute to sexual dysfunction.
 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Troublesome bladder symptoms and changes in sexual function are common health problems as people age. Having diabetes can mean
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Troublesome bladder symptoms and changes in sexual function are common health problems as people age. Having diabetes can mean
Retropubic Prostatectomy
 2014 Retropubic Prostatectomy Retropubic Prostatectomy What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland that makes a fluid that helps sperm move. It also gives nourishment for the sperm. It is about the size
2014 Retropubic Prostatectomy Retropubic Prostatectomy What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland that makes a fluid that helps sperm move. It also gives nourishment for the sperm. It is about the size
Sexual Concerns. Mental Health Topics
 Sexual Concerns A lot of people have concerns about their sex life. Common concerns and problems that affect one or both sex partners Talk to your partner about your include: sexual concerns. n Little
Sexual Concerns A lot of people have concerns about their sex life. Common concerns and problems that affect one or both sex partners Talk to your partner about your include: sexual concerns. n Little
Open Radical Prostatectomy Surgery
 To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
PATIENT INFORMATION HANDOUT Dr Joseph K Johnson KG Medical Centre
 PATIENT INFORMATION HANDOUT Dr Joseph K Johnson KG Medical Centre Chronic Pelvic Pain What is Chronic Pelvic Pain? Chronic pelvic pain refers to pain in the lower half of your abdomen, lasting six months,
PATIENT INFORMATION HANDOUT Dr Joseph K Johnson KG Medical Centre Chronic Pelvic Pain What is Chronic Pelvic Pain? Chronic pelvic pain refers to pain in the lower half of your abdomen, lasting six months,
Treatment for bladder tumours (transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT))
 Treatment for bladder tumours (transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT)) Information for patients from the Urology Department You have had a cystoscopy or other examination that has shown that
Treatment for bladder tumours (transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT)) Information for patients from the Urology Department You have had a cystoscopy or other examination that has shown that
Multiple Sclerosis. What is multiple sclerosis? What is the cause? What are the symptoms?
 What is multiple sclerosis? Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). Many people with multiple sclerosis are only mildly affected
What is multiple sclerosis? Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). Many people with multiple sclerosis are only mildly affected
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide
 Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide Introduction The urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys, helps maintain stable chemical conditions in the body, stores, and eliminates
Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide Introduction The urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys, helps maintain stable chemical conditions in the body, stores, and eliminates
CYSTOSCOPY AND URETHRAL BULKING INJECTIONS INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
 The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk CYSTOSCOPY
The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk CYSTOSCOPY
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder
 www.olarts.com Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS.
www.olarts.com Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS.
HOLEP (HOLMIUM LASER ENUCLEATION OF PROSTATE )
 HOLEP (HOLMIUM LASER ENUCLEATION OF PROSTATE ) What does the procedure involve? Removal of obstructing prostate tissue using a telescope and a laser. What are the alternatives to this procedure? Alternatives
HOLEP (HOLMIUM LASER ENUCLEATION OF PROSTATE ) What does the procedure involve? Removal of obstructing prostate tissue using a telescope and a laser. What are the alternatives to this procedure? Alternatives
