Nonoperative Treatment of Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review
|
|
|
- Jessie Dwight Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CRITICAL REVIEW Nonoperative Treatment of Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review Robert A. Magnussen, MD, Warren R. Dunn, MD, MPH, and A. Brian Thomson, MD Objective: The aim of this systematic review is to provide an easily accessible, clear summary of the best available evidence for nonoperative treatment of midportion Achilles tendinopathy. Data Sources: MEDLINE, CINAHL, and Embase through April Search terms: achilles or tendo achilles or triceps surae or tendoachilles or tendo-achilles or achilles AND tendinopathy or tendinosis or itis or tenosynovitis. Study Selection: Of 707 abstracts reviewed, 16 randomized trials met our inclusion criteria. Data Extraction: Data extracted from each paper included: patient demographics (age and sex), duration of symptoms, method of diagnosis, treatments, cohort size, length of follow-up, pain-related outcome data, and secondary outcome data. Data Synthesis: The primary outcome measurement was change in numeric pain score. Focal tenderness, thickness, and validated outcome scores were used secondarily. Eccentric exercises were noted to be equivalent to extracorporeal shockwave therapy (1 study) and superior to wait-and-see treatment (2 trials), traditional concentric exercise (2 of 3 trials), and night splints (1 study). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy was shown to be superior to a wait-and-see method in 1 study but not superior to placebo in another. Sclerosing injections were shown to be superior to placebo in 1 study, but local steroid treatment was beneficial in 2 of 3 studies. Injection of deproteinized hemodialysate and topical glyceryl nitrate application were beneficial in 1 trial each. Conclusions: Eccentric exercises have the most evidence of effectiveness in treatment of midportion Achilles tendinopathy. More investigation is needed into the utility of extracorporeal shockwave therapy, local corticosteroid treatments, injections of sclerosing agents or deproteinized hemodialysate, and topical glyceryl nitrate application. Key Words: Achilles, tendinopathy, midportion, nonoperative treatment (Clin J Sport Med 2009;19:54 64) Submitted for publication February 13, 2008; accepted August 8, From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee. The authors state that they have no financial interest in the products mentioned within this article. Reprints: A. Brian Thomson, MD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, MCE South Tower, Suite 4200, Nashville, TN ( abthom00@hotmail.com). Copyright Ó 2009 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins INTRODUCTION Overuse injuries occur frequently in athletes, with some authors estimating that they account for up to half of all athletic injuries. 1 The Achilles is among the most prone to overuse injury, with problems accounting for up to 18% of injuries in runners and 4% of patients presenting to sports medicine clinics. 2 6 The literature is replete with multiple conservative treatment protocols and results for treating these conditions, but access to and use of the literature is complicated by inconsistent diagnoses and confusing terminology. We will use terminology suggested by Maffulli et al, using the term tendinopathy when referring to a diagnosis based on pain, swelling, and impaired performance and reserving more specific terms, including itis or tendinosis for cases when inflammation or degeneration has been confirmed. 7,8 Achilles tendinopathy has been classified as insertional (within 2 cm of its insertion) and midsubstance (2 to 6 cm its insertion) and is felt by many to represent two distinct clinical entities. 9 Additional discrimination should be made between acute Achilles injuries and more chronic degenerative processes. Multiple risk factors and predispositions to the development of tendinopathy in both locations have been identified and discussed in recent reviews on this subject. 8,10 12 The aim of this systematic review is to provide an easily a0ccessible, clear summary of the best available evidence for nonoperative treatment of midportion Achilles tendinopathy. Our primary focus will be to evaluate data from randomized controlled trials relating to change in numeric pain score. Additionally, we provide a brief summary of other outcome data. MATERIALS AND METHODS Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Papers included in this review are randomized controlled trials for treatment of Achilles tendinopathy. We included only papers that focused on midsubstance Achilles tendinopathy. Retrospective or nonrandomized papers, review papers without original data, and papers examining tendinopathy of multiple s without separate outcome data for Achilles tendinopathy were excluded. Papers that focused on insertional tendinopathy or failed to localize the tendinopathy in the were also excluded (Table 1). Literature Review A MEDLINE search limited to human and English articles for achilles or tendo achilles or triceps surae or 54 Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009
2 Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009 Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy tendoachilles or tendo-achilles or achilles as well as tendinopathy or tendinosis or itis or tenosynovitis, yielding 499 citations. The same search strategy was used to search Embase and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), resulting in 657 and 114 citations, respectively. Finally, a search of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials was undertaken using the search term Achilles located 194 citations. Combining these results and removing duplicate citations yielded a total of 707 papers. The title and abstracts of these studies were reviewed, and 596 were excluded. Reasons for exclusion included: review papers and others with no outcome data (339), papers unrelated to Achilles tendinopathy (135), case series (31), papers describing rupture (42), papers focusing on specific medical conditions associated with Achilles tendinopathy (48), and inability to locate a copy in English (1). Full text of the remaining 111 articles was obtained. Eighty-one papers were then excluded because they were not randomized controlled trials. Two papers that included tendinopathy at multiple sites and failed to report separate outcomes for the Achilles s in the series were also excluded, leaving 28 papers. 5,13 39 The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews was consulted, and no additional papers were located. Finally, an exhaustive review was performed of the reference sections of each paper included in the study as well as all review articles on the subject published in the last 5 years in search of other articles meeting inclusion criteria. One additional paper was identified. 40 From all sources described above, a total of 29 studies were identified. Upon detailed review of the inclusion criteria of the 29 studies, 10 did not specifically localize the tendinopathy to the midportion of the, 14,15,22,23,26,28,32 34,39 and 3 focused primarily on insertional tendinopathy. 21,38,40 All 13 were excluded. The remaining 16 studies are the focus of this review. The search strategy is summarized in Figure 1. Statistical Analyses Statistical analyses from the included studies were used in determining statistical significance of the data, and P values TABLE 1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Inclusion Criteria Randomized controlled trials of treatment of midsubstance Achilles tendinopathy Randomized controlled trials of treatment of tendinopathy in multiple locations with separate outcome reporting for patient with midsubstance Achilles tendinopathy Exclusion Criteria No outcome data reported Review papers without original data Nonrandomized studies and study designs without a comparison group No localization of tendinopathy within the Achilles Papers investigating insertional tendinopathy Papers describing treatment of rupture Focus on patients with another medical condition with Achilles pathology seronegative arthropathies, familial hypercholesterolemia, etc. are reported as calculated by the authors of the original studies. When data were not statistically significant and no specific P values are reported, the data are reported as such. RESULTS Demographics Demographic data from the 16 studies included in this review, including author, journal, publication year, patient age and sex, duration of symptoms, number of patients enrolled and percent follow-up, activity level, and the method of diagnosis of Achilles tendinopathy were recorded. The majority of studies include a predominance of men with a mean age between 30 and 50 years. Most are at least recreational athletes, and about half of the studies use to confirm the diagnosis. Outcomes The studies included in this review used a wide range of outcome measures with little consistency between studies. Most of the studies attempted to quantify pain by using a variety of numeric pain scales. Other common outcomes measures included range of motion, return to activity, peak torque measurements, pain with a variety of provocative tests, and change in diameter when measured with. We chose to focus on change in numeric pain score as our primary outcome variable. Other data are summarized for reference. Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing Eccentric Exercise With Controls Five prospective randomized controlled trials were identified comparing eccentric exercises to controls for midportion Achilles tendinopathy (Table 2). Four trials showed statistically significant improvement in pain score with eccentric exercise compared with control, 24,25,29,36 and one trial showed no significant difference. 5 Randomized Controlled Trials Evaluating Variations of Eccentric Exercises, Splints, or Insoles A recent randomized trial in Sweden demonstrated that restricting running and jumping for 6 in patients undergoing eccentric training for Achilles tendinopathy had no impact on pain scores at 1 year after initiation of treatment. 31 Roos et al found that eccentric exercises resulted in significantly lower pain scores after when compared with night splints alone. 30 In the same study, they were unable to demonstrate any difference in pain score when comparing those who performed eccentric exercises and wore night splints to patients who received either treatment alone. Similarly, Mayer et al demonstrated no difference in pain score when comparing eccentric exercises with custom fit insoles, 25 although the insole group was noted to have significantly better pain scores than controls (Table 3). Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Two randomized controlled trials have evaluated extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) for midportion q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 55
3 Magnussen et al Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009 FIGURE 1. Search strategy. Achilles tendinopathy. With placebo ESWT as a control group, Costa et al were unable to demonstrate a statistically significant effect after 3 of treatment. 17 Rompe et al did demonstrate statistically significant improvements in pain at 16 when compared with a wait-and-see group, but no benefit of ESWT over eccentric exercises was noted (Table 4). 29 Local Injections Steroid Injections Two randomized controlled trials used local steroid injections for midportion Achilles tendinopathy. Fredberg et al found decreased pain with ambulation 4 after -guided injection of triamcinalone around the Achilles when compared with placebo. 20 However, DaCruz et al were unable to demonstrate any improvement in pain or more rapid return to function after methylprednisolone injection (Table 5). 18 Fredberg et al noted 1 rupture in their experimental group and none in the control, and DaCruz et al noted no ruptures in either the experimental or treatment groups. Other Injections One randomized controlled trial demonstrated significant improvements in visual analog pain score after injection with Polidocanol, a sclerosing agent, into areas of neovascularization when compared with injection of local anesthetic. 13 Brown et al compared peritendinous injections of aprotinin with placebo injections and were unable to detect any significant differences in pain or return to sport in 1 year of follow-up. 16 Pforringer et al demonstrated decreased thickness and decreased pain overall under stress conditions and with palpation with local injection of deproteinized hemodialysate into patients with acute midportion Achilles tendinopathy (Table 5). 37 Other Conservative Treatments Neeter et al noted decreases in pain with stairs and pain after activity 6 after iontophoresis with dexamethasone compared with saline. 35 Paoloni et al investigated the use of topical glycerol nitrate and found significantly less pain with activity relative to control 24 after treatment (Table 5) q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
4 q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 57 TABLE 2. Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing Eccentric Exercises With Controls Author, Journal, and Year Mayer 2007 Rompe AJSM, 2007 Silbernagel SJMSS, 2001 Mafi KSSTA, 2001 Niesen- Vertommen CJSM, 1992 Mean Patient Age (Range) and Sex 38 (18 to 50); 100% male Duration of Symptoms Mean = 14 Method of Diagnosis Intervention 1 Intervention 2 Painful nodule or pain over midportion of Achilles 48; 39% male All,.6 degenerative change noted on 44 (19 to 77); 73% male All,.4 insertion of 44; 55% male All,.3 degenerative change noted on 35 (22 to 49); 59% male Mean = 3.7 NR Physiotherapy: friction massage, (1.5 W/cm 2 ), ice, and exercises (eccentric training, balance) 3 10 sessions over 4 Eccentric exercises: Eccentric exercises: Eccentric exercises: Eccentric exercises: Control: normal activity Control: wait-and-see Control: concentric exercises Control: concentric exercises Control: concentric exercises Cohort Size* and Length of Follow-up Decrease in Pain Score Other Outcome Data 19/21 (90%); 4 46/50 (92%); 16 37/49 (76%); 52 44/44 (100%); 17/17 (100%); Decrease in PES, P, 0.05 Physiotherapy (eccentric exercises) = 55% Control = 10% Decrease in pain with loading,{ P, Eccentric exercises = 3.2 points Wait and see = 2.0 points Decrease in median VAS pain score, NS Eccentric exercises = 28 points Concentric exercises = 18 points Decrease in VAS pain score, P, Eccentric exercises = 51 points Concentric exercises = 22 points Decrease in pain score,{ P, 0.01 Eccentric exercises = 4.7 points Concentric exercises = 3.0 points Increase in peak torque, NS Physiotherapy (eccentric exercises) = 15% Control = 5% Subjective improvement, P = Eccentric exercises = 60% Wait and see = 24% VISA-A** score, P = Eccentric exercises = 75.6 Wait and see = 55.0 Subjective full recovery, P, 0.05 Eccentric exercises = 60% Concentric exercises = 25% Patient satisfied with outcome, P, 0.05 Eccentric exercises = 70% Concentric exercises = 38% Have pain during activity, P, 0.05 Eccentric exercises = 26% Concentric exercises = 46% Return to initial activity level, NS Eccentric exercises = 55% Concentric exercises = 34% Resumed previous activity, P, Eccentric exercises = 82% Concentric exercises = 36% NR, not reported. *Number of s included (some patients had bilateral involvement). Both Mayer et al and Rompe et al included a third group in their study (Table 3). Pain Experience Scale: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates greater pain. Decrease in pain score reported as a percentage only by the primary authors. Not Significant: specific P value not reported in the original paper. {Numeric Pain Scale: range, 0 to 10; higher score indicates greater pain. **Victorian Institute of Sports Assessment, Achilles: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates less severe symptoms. Visual Analogue Scale: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates greater pain. Not reported in the original paper. Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009 Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
5 58 q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins TABLE 3. Randomized Controlled Trials Evaluating Variations of Eccentric Exercises, Splints, or Insoles Author, Journal, and Year Silbernagel AJSM, 2007 de Vos 2006 Roos SJMSS, 2004 Roos SJMSS, 2004 Roos SJMSS, 2004 Mayer 2007 Mayer 2007 Mean Patient Age (Range) and Sex 46 (30 to 58); 53% male 45 (26 to 59); sex not reported 46 (26 to 60); 48% male 46 (26 to 60); 48% male 46 (26 to 60); 48% male 38 (18 to 50); 100% male 38 (18 to 50); 100% male Duration of Symptoms All,.2 All,.2 86%,.3 86%,.3 86%,.3 Mean = 14 Mean = 14 Method of Diagnosis Intervention 1 Intervention 2 Painful nodule or pain over mid-portion of Achilles Pain 2 to 7 cm insertion insertion of insertion of insertion of Painful nodule or pain over mid-portion of Achilles Painful nodule or pain over mid-portion of Achilles Eccentric exercise program including eccentric exercises 3 12 ; no limits on physical activity Eccentric exercises 3 12 Eccentric exercises 3 12 Eccentric exercises 3 12 Night splints 3 Individually fit semi-rigid insoles during all activities Individually fit semi-rigid insoles during all activities Eccentric exercise program including eccentric exercises 3 12 ; no running or jumping allowed for the first 6 Night splints 3 12 Night splints 3 12 Both eccentric exercises and night splints 3 12 Both eccentric exercises and night splints 3 12 Cohort Size* and Length of Follow-up 53/57 (93%); 52 63/70 (90%); 23/29 (79%); 23/29 (79%); 23/30 (77%); Physiotherapy: friction 19/21 (90%); massage, 4 (1.5W/cm 2 ), ice, and exercises (eccentric training, balance) 3 10 sessions over 4 Control: normal activity 18/20 (90%); 4 Decrease in Pain Score Decrease in median VAS pain score, NS Full activity = 3.5 points Limited activity = 4.0 points Decrease in mean pain score, P = 0.04 Eccentric exercises = 22 points Night splints = 7 points Decrease in mean pain score, NS Eccentric exercises = 22 points Both treatments = 14 points Decrease in mean pain score, NS Night splints = 7 points Both treatments = 14 points Decrease in PES, NS Insoles = 65% Physiotherapy (eccentric exercises) = 55% Decrease in PES, P, 0.05 Insoles = 65% Control = 10% Other Outcome Data VISA-A score, NS Full activity = 85 Limited activity = 91 Toe raise (total work), NS Full activity = 2431 Joules Limited activity = 2058 Joules Range of motion, dorsiflexion, NS Full activity = 35 degrees Limited activity = 35 degrees Subjective patient satisfaction,{ NS** Eccentric exercises, night splint = 48% Eccentric exercises = 63% VISA-A score, NS Eccentric exercises, night splint = 67.0 Eccentric exercises = 68.8 Difficulty with sports, NS Eccentric exercises = 27% Night splints = 50% Difficulty with sports, NS Eccentric exercises = 27% Both treatments = 58% Difficulty with sports, NS Night splints = 50% Both treatments = 58% Increase in peak torque, NS Insoles = 20% Physiotherapy (eccentric exercises) = 15% Increase in peak torque, NS Insoles = 20% Control = 5% *Number of s included (some patients had bilateral involvement). Visual Analog Scale: range 0 to 10; higher score indicates greater pain. Victorian Institute of Sports Assessment, Achilles: range 0 to 100, higher score indicates less severe symptoms. Follow-up was carried longer (52 ), but crossover was allowed after the 12-week point. {Subjective patient satisfaction score: 100% indicates completely satisfied. **Not significant, P values not reported in the original paper. Numeric Pain Scale: range, 0 to 10; higher score indicates greater pain. Pain Experience Scale: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates greater pain. Decrease in pain score reported as a percentage only by the primary authors. Magnussen et al Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009
6 q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 59 TABLE 4. Randomized Controlled Trials Evaluating ESWT Author, Journal, and Year Rompe AJSM, 2007 Rompe AJSM, 2007 Costa CORR, 2005 Mean Patient Age and Sex 48; 39% male 48; 39% male 52; 43% male Duration of Symptoms All,.6 All,.6 All,.4 Method of Diagnosis Intervention 1 Intervention 2 degenerative change noted on degenerative change noted on Pain with dorsiflexion and palpation of Achilles ESWT: 2000 pulses of 0.1 mj/mm 2 at 8 pulses/s weekly 3 3 treatments ESWT: 2000 pulses of 0.1 mj/mm 2 at 8 pulses/s weekly 3 3 treatments ESWT: 1500 pulses of 0.2 mj/mm 2 monthly 3 3 treatments Control: wait-and-see Eccentric exercises: Placebo shockwave (air bubble interposition to dissipate shockwaves) Cohort Size* and Length of Follow-up Decrease in Pain Score Other Outcome Data 46/50 (92%); 16 47/50 (94%); 16 43/49 (88%); 13 Decrease in pain with loading, P = ESWT = 3.0 points Wait and see = 2.0 points Decrease in pain with loading, P = ESWT = 3.0 points Eccentric exercises = 3.2 Decrease in pain score, NS ESWT = 14 points Placebo = 25 points Subjective improvement, P = ESWT = 53% Wait and see = 24% VISA-A score,{ P = ESWT = 70.4 Wait and see = 55.0 Subjective improvement, NS** ESWT = 53% Eccentric exercises = 60% VISA-A score, P = 0.26 ESWT = 70.4 Eccentric exercises = 75.6 Pain during walking, P = 0.12 ESWT = 21 points Placebo = 5 points Pain during sport, NS ESWT = 20 points Placebo = 4 points *Number of s included (some patients had bilateral involvement). For results of eccentric exercise versus control, see Table 2. Millijoules per square millimeter. Numeric Pain Scale: range, 0 to 10; higher score indicates greater pain. {Victorian Institute of Sports Assessment, Achilles: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates less severe symptoms. **Not Significant, specific P value not reported in the original paper. Pain Scale: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates greater pain. Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009 Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
7 60 q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins TABLE 5. Randomized Controlled Trials Evaluating Local Injection or Topical Application of Steroids, Slerosing Agents, Aprotinin, or Deproteinized Hemodialysate, or Glyceryl Nitrate Author, Journal, and Year Fredberg SJR, 2004 DaCruz 1988 Neeter SJMSS, 2003 Alfredson KSSTA, 2005 Brown 2006 Mean Patient Age (Range) and Sex 35 (18 to 58); 62% male 28 (22 to 46); 64% male 38 (18 to 76); 60% male 50 (38 to 66); 45% male 46 (30 to 73); 64% male Duration of Symptoms 50%,.2 NR All,.3 All,.3 All,.6 Method of Diagnosis Intervention 1 Intervention 2 Tenderness noted 2to4cm mass noted on Pain in the midportion of the Achilles insertion of Tenderness noted 2to4cm mass noted on Pain on Achilles palpation and with activity, noninsertional Injection of 20 mg triamcinolone in 4mL3 1 Injection of methylprednisolone (40 mg) 3 1 Dexamtheasone iontophoresis: 20-min treatment every 3 to 4 days 3 4 treatments Injection of sclerosing agent polidocanol (5 mg/ml) into neovascularized areas of under guidance 3 2 injections Injection of 30,000 IU aprotinin weekly 3 3 treatments Injection of 4 ml of placebo 3 1 Placebo injection 3 1 Saline iontophoresis: 20-min treatment every 3 to 4 days 3 4 treatments Injection of nonsclerosing lidocaine and epinephrine into neovascularized areas of under guidance 3 2 injections Injection of placebo 3 3 treatments Cohort Size* and Length of Follow-up Decrease in Pain Score Other Outcome Data 24/24 (100%); 4 34/42 (81%); 25/25 (100%); 26 20/20 (100%): 26/33 (79%); 52 Decrease in walking pain score, P, 0.02 Triamcinolone = 2.9 points Placebo = 0.5 points Decrease in pain score, NS{ Methylprednisolone = 11 points Placebo = 11 points Pain after activity,** P, 0.05 Dexamethasone = 17% Saline = 64% Pain with walking,** NS Dexamethasone = 14% Saline = 36% Pain with stairs,** P, 0.05 Dexamethasone = 0% Saline = 36% Decrease in VAS pain score, P, Sclerosing injection = 48 points Placebo injection = 2 points Decrease in VAS pain score, NS Aprotinin = 36.3 points Placebo = 32.3 points Tendon thickness, P = NR Triamcinolone = 8.0 mm Placebo = 9.4 mm Local pain threshold, P =NR Triamcinolone = 599 kpa Placebo = 460 kpa Complete resolution of symptoms, NS Methylprednisolone = 32% Placebo = 33% Returned to at least 50% of normal activity, NS Methylprednisolone = 77% Placebo = 70% Number of toe lifts performed, NS Dexamethasone = 14 Saline = 10 Percent of patients satisfied, P = NR Sclerosing injection = 90% Placebo injection = 50% Returned to sport, NS Aprotinin = 77% Placebo = 85% Number of hops before pain, NS Aprotinin = 7.4 Placebo = 5.5 Magnussen et al Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009
8 q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 61 TABLE 5. (continued) Randomized Controlled Trials Evaluating Local Injection or Topical Application of Steroids, Slerosing Agents, Aprotinin, or Deproteinized Hemodialysate, or Glyceryl Nitrate Author, Journal, and Year Pforringer CJSM, 1994 Paoloni JBJS Am, 2004 Mean Patient Age (Range) and Sex 33 (18 to 55); sex not reported 49 (24 to 77); 62% male Duration of Symptoms All,,3 All,.4 Method of Diagnosis Intervention 1 Intervention 2 Thickened Achilles by.2 mm compared to contralateral or mean on Tender nodule 2to6cm no tear by Injection of 5 ml mepivacaine and 5 ml of deproteinized hemodialysate 3 3at0,3,and 10 days Transdermal glyceryl trinitrate 1.25 mg q24h for 24 Injection of 5 ml mepivacaine and 5 ml of saline at 0, 3, and 10 days Transdermal placebo patch q24h for 24 Cohort Size* and Length of Follow-up Decrease in Pain Score Other Outcome Data 60/60 (100%); 3 58/65 (89%); 24 Decrease in pain score, P, Deprotein hemodialysate = 4.8 points Placebo = 1.5 points Decrease in activity pain,{{ P = 0.03 Glyceryl trinitrate = 1.9 points Placebo = 1.4 points Decrease in night pain, NS Glyceryl trinitrate = 0.7 points Placebo = 0.5 points Decrease in thickness, P, Deprotein hemodialysate = 27.2% Placebo = 14.2% Pain: stress conditions, P, 0.02 Deprotein hemodialysate = 0% Placebo = 25.0% Local tenderness, P, Deprotein hemodialysate = 16.7% Placebo = 70.0% Hop test pain, P = 0.01 Glyceryl trinitrate = 0.5 Placebo = 1.6 Decrease in local tenderness, NS Glyceryl trinitrate = 1.5 points Placebo = 1.3 points NR, not reported. *Number of s included (some patients had bilateral involvement). Pain score: range, 0 to 10; higher score indicates increased pain. Not reported by original author. Pain Scale: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates increased pain. {Not significant, specific P values not reported by original author. **Pain reported as either present or absent, no pain score utilized. Visual Analogue Scale: range, 0 to 100; higher score indicates increased pain. International Units. Numeric Pain Scale: range, 0 to 10; higher score indicates increased pain. {{Scale: 0 to 4; higher score indicates greater pain. Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009 Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
9 Magnussen et al Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009 DISCUSSION Eccentric Exercises Eccentric muscle training for treatment of Achilles tendinopathy has been recommended since the mid 1980s. 41 Theories on the mechanism of eccentric exercises in decreasing pain include more rapid strengthening of the calf muscle, stiffening and lengthening of the myotendinous unit, and decreased neovascularization in the region. 24,30,42 44 Regardless of the mechanism, significant improvement in patient satisfaction and decreased pain were seen in 60% to 90% of patients, and it has been demonstrated to be superior to controls in 4 of the 5 randomized controlled trials outlined above. Performance of a meta-analysis on these data was prohibited by the heterogeneity of treatment groups, interventions, and outcome measures across the prospective trials evaluating eccentric exercises. A recent randomized controlled trial attempting to reproduce the beneficial effects of eccentric exercise on Achilles tendinopathy showed mild improvement from baseline with eccentric exercises at 3 and 1 year, but it was not able to demonstrate superiority of this technique to stretching. 26 This study included patients with midportion as well as insertional tendinopathy. Other work by the same authors has demonstrated insertional tendinopathy to be less responsive to eccentric exercises than midportion tendinopathy. 45,46 Careful distinction between these conditions should be made in any future trials. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy The two randomized controlled trials of ESWT included in this review suggest that it may be of utility in the treatment of chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy. These trials employ low- to medium-energy ESWT ( mj/mm 2 ) without the use of general anesthesia. Significantly greater effect was noted in the Rompe et al study, but its use of a waitand-see group as a control raises concerns of a placebo effect with treatment. 29 In the Costa et al study, patients were blinded to the treatment they received, and the treatment effect was not significant. 17 A recent randomized controlled trial investigating highenergy ESWT for insertional Achilles tendinopathy showed significant pain relief at 1 year. 21 Investigation of the effect of ESWT therapy for tendinopathy in other anatomic locations has been extensive and contradictory, with numerous randomized trials showing success, as well as multiple randomized trials failing to show an effect Interpretation of these data are complicated by inconsistent definition of low- and highenergy ESWT and the use of multiple techniques to generate the pulses. Clear definition of terms and consistent technique will be necessary in future randomized controlled trials in this area. Local Steroid Therapy The 3 randomized controlled trials described above present a mixed picture of the effect of local steroids on healing, with 2 studies indicating some benefit 20,35 and the other detecting none. 18 Accurate placement of the injection was confirmed by by Fredberg et al, and the iontophoresis method used by Neeter et al does not require accurate injection. DaCruz et al did not confirm the injection site with imaging, instead relying on the experience of the senior author for accurate placement. The difficulty of obtaining appropriate placement without imaging is noted by Fredberg et al and may contribute to the failure of DaCruz et al to show an effect of the steroid injection relative to placebo. The relatively short follow-up (4 ) obtained by Fredberg et al should also be considered when evaluating these data; short-term improvement may not correlate with longterm outcomes. A major concern for the use of corticosteroid injections in the treatment of opathies is subsequent rupture, as was observed in 1 study cited in this review. The mechanism behind any positive effect of local steroids on chronic Achilles tendinopathy remains unclear. A recent paper questioning the prevailing opinion that inflammation is not present in chronic tendinopathy may point to an antiinflammatory mechanism. 61 Several authors have hypothesized that any beneficial effects of corticosteroids in this condition are owed to other local steroid effects rather than suppression of inflammation, including lysis of peritenon adhesions or alteration of the function of paingenerating nocioceptors in the region At this time, there is not significant evidence from which to draw firm conclusions on the utility of local steroid treatments for midportion Achilles tendinopathy. Previous reviews on this subject have come to the same conclusion. 63,64 Sclerosing Injections As alluded to above, the presence of neovascularization has been associated with painful midportion Achilles tendinopathy. 43 Sensory nerves traveling with these vessels have been implicated as possible pain generators, leading to the hypothesis that destruction of the vessels and nerves will lead to pain relief If other authors can demonstrate success in using sclerotherapy similar to Alfredson et al, it may prove to be a useful alternative therapy. 13 However, the demonstration that less invasive eccentric exercises are also capable of decreasing neovascularization relegate sclerosing injection therapy to those that fail or are not capable of performing eccentric exercises. 44 Other Conservative Treatments Aprotinin injections have been used for treatment of tendinopathy throughout the body, with a placebo-controlled randomized controlled trial showing improved outcomes of patellar tendinopathy. 68 A drawback of aprotinin therapy is the formation of antibodies to the medication, possibly limiting its subsequent use. 69 Both deproteinized hemodialysate injections and topical glycerol nitrate application showed positive results in one study each. Both are believed to influence Achilles tendinopathy through their effects on fibroblasts ability to synthesize collagen. Deproteinized hemodialysate is believed to make the environment of fibroblasts in the region more conducive to anabolic pathways Topical glyceryl nitrate application increases local tissue nitric oxide concentrations, which are believed to improve fibroblast function and wound healing. 27,73,74 The relatively short duration of symptoms and short follow-up in the Pforringer et al paper 62 q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
10 Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January 2009 Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy limit conclusions that can be made regarding deproteinized hemodialysate treatment. Mayer et al demonstrated decreased pain relative to controls at 4 with custom insoles, but no improvement was noted relative to physical therapy, including eccentric exercises. 25 The use of heel pads in Achilles tendinopathy was evaluated in the mid 1980s by Lowdon et al and found to be ineffective. 23 This earlier study did not differentiate between insertional and midportion Achilles tendinopathy, and the heel pads used were not custom-fit, possibly influencing outcome. However, the relatively short follow-up in the Mayer study weakened their finding of a positive effect of custom insoles. CONCLUSION There is currently more evidence in support of eccentric exercises than the other interventions included in this review. This evidence, combined with their low cost and low risk, makes these exercises ideal first-line therapy. Alternative treatment should be considered in patients who are unable or unwilling to perform or have failed treatment with these exercises. ESWT, injections of sclerosing agents or deproteinized hemodialysate, and topical glyceryl nitrate application show promise in early studies without known complications to date, but significant additional study is needed. More investigation is needed into the utility of local steroid therapy. REFERENCES 1. Jarvinen M. Epidemiology of injuries in sports. Clin Sports Med. 1992;11: Clement DB, Taunton JE, Smart GW. Achilles itis and periitis: etiology and treatment. Am J Sports Med. 1984;12: Devereaux MD, Lachmann SM. Athletes attending a sports injury clinic - a review. Br J Sports Med. 1983;17: Rolf C. Overuse injuries in runners. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1995;5: Silbernagel KG, Thomee R, Thomee P, et al. Eccentric overload training for patients with chronic Achilles pain - a randomised controlled study with reliability testing of the evaluation methods. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2001;11: Soma CA, Mendelbaum BR. Achilles disorders. Clin Sports Med. 1994;13: Maffulli N, Khan KM, Puddu G. Overuse conditions: time to change a confusing terminology. Arthroscopy. 1998;14: Sayana MK, Maffulli N. Insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Clin N Am. 2005;10: Clain MR, Baxter DE. Achilles itis. Foot Ankle. 1992;13: Aronow MS. Posterior heel pain (retrocalcaneal bursitis, insertional and noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy). Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2005;22: Maffulli N, Kader D. Tendinopathy of tendo Achillis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84: Sella EJ. Disorders of the Achilles at its insertion. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2005;22: Alfredson H, Ohberg L. Sclerosing injections to areas of neovascularisation reduce pain in chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a doubleblind randomised controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2005;13: Astrom M, Westlin N. No effect of piroxicam on Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized study of 70 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63: Bjordal JM, Lopes-Martins RAB, Iversen VV. A randomised, placebo controlled trial of low level laser therapy for activated Achilles itis with microdialysis measurements of peritendinous prostaglandin E 2 concentrations. Br J Sports Med. 2006;40: Brown R, Orchard J, Kinchington M, et al. Aprotinin in the management of Achilles tendinopathy: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2006;40: Costa ML, Shepstone L, Donnell ST, et al. Shock wave therapy for chronic Achilles pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;440: DaCruz DJ, Geeson M, Allen MJ, et al. Achilles paraitis: an evaluation of steroid injection. Br J Sports Med. 1988;22: de Vos RJ, Weir A, Visser RJ, et al. The additional value of a night splint to eccentric exercises in chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41:e5. Epub 2006 Dec Fredberg U, Bolvig L, Pfeiffer-Jensen M, et al. Ultrasonography as a tool for diagnosis, guidance of local steroid injection and, together with pressure algometry, monitoring of the treatment of athletes with chronic jumper s knee and Achilles itis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33: Furia JP. High-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a treatment for insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34: Larsen AI, Egfjord M, Jelsdorff HM. Low-dose heparin in the treatment of calcaneal peritendinitis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1987;16: Lowdon A, Bader DL, Mowat AG. The effect of heel pads on the treatment of Achilles itis: a double blind trial. Am J Sports Med. 1984;12: Mafi N, Lorentzon R, Alfredson H. Superior short-term results with eccentric calf muscle training compared to concentric training in a randomized prospective multicenter study on patients with chronic Achilles tendinosis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2001;9: Mayer F, Hirschmueller A, Muller S, et al. The effects of short-term treatment strategies over 4 in Achilles tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41:e6. Epub 2007 Jan Norregaard J, Larsen CC, Bieler T, et al. Eccentric exercise in treatment of Achilles tendinopathy. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2007;17: Paoloni JA, Appleyard RC, Nelson J, et al. Topical glyceryl trinitrate treatment of chronic noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86: Read MTF, Motto SG. Tendo Achilles pain: steroids and outcome. Br J Sports Med. 1992;26: Rompe JD, Nafe B, Furia JP, et al. Eccentric loading, shock-wave treatment, or wait-and-see policy for tendinopathy of the main body of tendo Achilles. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35: Roos EM, Engstrom M, Lagerquist A, et al. Clinical improvement after 6 of eccentric exercise in patients with mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy - a randomized trial with 1-year follow-up. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2004;14: Silbernagel KG, Thomee R, Eriksson BI, et al. Continued sports activity, using a pain-monitoring model, during rehabilitation in patients with Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled study. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35: Sundqvist H, Forsskahl B, Kvist M. A promising novel therapy for Achilles peritendinitis: double blind comparison of glycosaminoglycan polysulfate and high-dose indomethacin. Int J Sports Med. 1987;8: Auclair J, Georges M, Grapton X, et al. A double-blind controlled multicenter study of percutaneous niflumic acid gel and placebo in the treatment of Achilles heel tendinitis. Curr Ther Res. 1989;46: Chapman-Jones D, Hill D. Novel microcurrent treatment is more effective than conventional therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: randomised comparative trial. Physiotherapy. 2002;88: Neeter C, Thomee R, Silbernagel KG, et al. Iontophoresis with or without dexamethasone in the treatment of acute Achilles pain. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2003;13: Niesen-Vertommen SL, Taunton JE, Clement DB, et al. The effect of eccentric versus concentric exercises in the management of Achilles itis. Clin J Sport Med. 1992;2: Pforringer W, Pfister A, Kuntz G. The treatment of Achilles paratendinitis: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled study with a deproteinized hemodialysate. Clin J Sport Med. 1994;4: Constantino C, Pogliacomi F, Vaienti E. Cryo therapy and itis in athletes: a comparative evaluation versus laser CO2 and t.e.ca.r.therapy. Acta Biomed. 2005;76: q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 63
11 Magnussen et al Clin J Sport Med Volume 19, Number 1, January Jakobsen TJ, Petersen L, Christiansen S, et al. Tenoxicam vs placebo in the treatment of tendinitis, periostitis, and sprains. Curr Ther Res. 1989; 45: Capasso G, Maffulli N, Testa V, et al. Preliminary results with peritendinous protease inhibitor injections in the management of Achilles tendinitis. J Sports Traumtol Rel Res. 1993;15: Stanish WD, Rubinovich RM, Curwin S. Eccentric exercise in chronic tendinitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; Porter MM, Andersson M, Hellstrom U, et al. Passive resistive torque of the plantar flexors following eccentric loading as assessed by isokinetic dynamanometry. Can J Appl Physiol. 2002;27: Ohberg L, Lorentzon R, Alfredson H. Neovascularisation in Achilles s with painful tendinosis but not in normal s: an ultrasonographic investigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2001;9: Ohberg L, Lorentzon R, Alfredson H. Eccentric training in patients with chronic Achilles tendinosis: normalised structure and decreased thickness at follow up. Br J Sports Med. 2004;38: Alfredson H. Chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy: an update on research and treatment. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22: Fahlstrom M, Jonsson P, Lorentzon R, et al. Chronic Achilles pain treated with eccentric calf-muslce training. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003;11: Pettrone FA, McCall BR. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy without local anesthesia for chronic lateral epicondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87: Rompe JD, Schoellner C, Nafe B. Evaluation of low-energy extracorporeal shock-wave application for treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A: Spacca G, Necozione S, Cacchio A. Radial shock wave therapy for lateral epicondylitis: a prospective randomised controlled single-blind study. Eura Medicophys. 2005;41: Abt T, Hopfenmuller W, Mellerowicz H. [Shock wave therapy for recalcitrant plantar fasciitis with heel spur: a prospective randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2002; 140: Kudo P, Dainty K, Clarfield M, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial evaluating the treatment of plantar fasciitis with an extracoporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) device: a North American confirmatory study. J Orthop Res. 2006;24: Malay DS, Pressman MM, Assili A, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy versus placebo for the treatment of chronic proximal plantar fasciitis: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, doubleblinded, multicenter intervention trial. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2006;45: Theodore GH, Buch M, Amendola A, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2004;25: Wang CJ, Chen HS, Huang TW. Shockwave therapy for patients with plantar fasciitis: a one-year follow-up study. Foot Ankle Int. 2002;23: Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, et al. Long-term results of extracorporeal shockwave treatment for plantar fasciitis. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34: Buchbinder R, Ptasznik R, Gordon J, et al. Ultrasound-guided extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2002;288: Haake M, Konig IR, Decker T, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a randomized multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A: Speed CA, Nichols D, Richards C, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for lateral epicondylitis a doule blind randomised trial. J Orthop Res. 2002;20: Hammer DS, Rupp S, Kreutz A, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) in patients with chronic proximal plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2002;23: Speed CA, Nichols D, Wies J, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis. A double blind randomised controlled trial. J Orthop Res. 2003;21: Fredberg U, Stengaard-Pedersen K. Chronic tendinopathy tissue pathology, pain mechanisms, and etiology with a special focus on inflammation. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008;18: Kvist H, Kvist M. The operative treatment of chronic calcaneal paratenonitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980;62: Paavola M, Kannus P, Jarvinen TA, et al. Treatment of disorders. Is there a role for corticosteroid injection? Foot Ankle Clin. 2002;7: Shrier I, Matheson GO, Kohl HW 3rd. Achilles itis: are corticosteroid injections useful or harmful? Clin J Sport Med. 1996;6: Bjur D, Alfredson H, Forsgren S. The innervation pattern of the human Achilles : studies of the normal and tendinosis with markers for general and sensory innervation. Cell Tissue Res. 2005;320: Forsgren S, Danielson P, Alfredson H. Vascular NK-1 receptor occurrence in normal and chronic painful Achilles and patellar s: studies on chemically unfixed as well as fixed specimens. Regul Pept. 2005;126: Lind B, Ohberg L, Alfredson H. Sclerosing polidocanol injections in midportion Achilles tendinosis: remaining good clinical results and decreased thickness at 2-year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14: Capasso G, Testa V, Maffulli N. Aprotinin, corticosteroids, and normosaline in the management of patellar tendinopathy in athletes: a prosepctive randomised study. Sports Exer Inj. 1997;3: Dietrich W, Spath P, Zuhlsdorf M, et al. Anaphylactic reactions of aprotinin reexposure in cardiac surgery: relation to antiaprotinin immunoglobulin G and E antibodies. Anesthesiology. 2001;95: Kuninaka T, Senga Y, Senga H, et al. Nature of enhanced mitochondrial oxidative metabolism by a calf blood extract. J Cell Physiol. 1991;146: Niinikoski J, Renvall S. Effect of a deproteinized blood extract on experimental granulation tissue. Acta Chir Scand. 1979;145: Obermaier-Kusser B, Muhlbacher C, Mushack J, et al. Further evidence for a two-step model of glucose-transport regulation. Inositol phosphateoligosaccharides regulate glucose-carrier activity. Biochem J. 1989;261: Murrell GA, Szabo C, Hannafin JA, et al. Modulation of healing by nitric oxide. Inflamm Res. 1997;46: Schaffer MR, Efron PA, Thornton FJ, et al. Nitric oxide, an autocrine regulator of wound fibroblast synthetic function. J Immunol. 1997;158: q 2009 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Pain Enduring Eccentric Exercise for the Treatment of Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy
 Pain Enduring Eccentric Exercise for the Treatment of Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Claire Dixon Laureen Holloway Janice Meier Nick Lo Teresa Lee Supervisors: W Darlene Reid Ph.D. & Sunita Mathur Ph.D.
Pain Enduring Eccentric Exercise for the Treatment of Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Claire Dixon Laureen Holloway Janice Meier Nick Lo Teresa Lee Supervisors: W Darlene Reid Ph.D. & Sunita Mathur Ph.D.
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature
 Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Plantar fasciitis: p. 1/6
 Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Dr Hamish Osborne. Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin
 Dr Hamish Osborne Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin New Approaches to Handling Tendinopathies By Hamish Osborne Definition Tendinopathy Absence of tightly packed collagen bundles Large amount
Dr Hamish Osborne Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin New Approaches to Handling Tendinopathies By Hamish Osborne Definition Tendinopathy Absence of tightly packed collagen bundles Large amount
Eccentric Loading, Shock-Wave Treatment, or a Wait-and-See Policy for Tendinopathy of the Main Body of Tendo Achillis
 Eccentric Loading, Shock-Wave Treatment, or a Wait-and-See Policy for Tendinopathy of the Main Body of Tendo Achillis A Randomized Controlled Trial Jan D. Rompe,* MD, Bernhard Nafe, MD, John P. Furia,
Eccentric Loading, Shock-Wave Treatment, or a Wait-and-See Policy for Tendinopathy of the Main Body of Tendo Achillis A Randomized Controlled Trial Jan D. Rompe,* MD, Bernhard Nafe, MD, John P. Furia,
SPORTS MEDICINE. Abstract In a previous uncontrolled pilot study we demonstrated very good clinical results with eccentric
 Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (2001) 9 :42 47 SPORTS MEDICINE DOI 10.1007/s001670000148 N. Mafi R. Lorentzon H. Alfredson Superior short-term results with eccentric calf muscle training compared
Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (2001) 9 :42 47 SPORTS MEDICINE DOI 10.1007/s001670000148 N. Mafi R. Lorentzon H. Alfredson Superior short-term results with eccentric calf muscle training compared
Confusion. Confusion. Confusion. Confusion Confusio Confusio. n Confusion Confusion. Confusion. Confusion. Confusion. Confusion.
 Centre for Sports and Exercise Medicine Patellar Tendinopathy Conservative and surgical managment Nicola Maffulli Centre Lead and Professor Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon Centre for Sport and
Centre for Sports and Exercise Medicine Patellar Tendinopathy Conservative and surgical managment Nicola Maffulli Centre Lead and Professor Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon Centre for Sport and
UEL. Sport Rehabilitation: Injury to Optimal Performance PTM 0114
 UEL Sport Rehabilitation: Injury to Optimal Performance PTM 0114 The role of eccentric training in the management of Achilles Tendinopathy Analysing and discussing Herrington L. and McCulloch R. (2007)
UEL Sport Rehabilitation: Injury to Optimal Performance PTM 0114 The role of eccentric training in the management of Achilles Tendinopathy Analysing and discussing Herrington L. and McCulloch R. (2007)
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
 A STUDY TO COMPARE THE EFFICACY OF ULTRASOUND WITH ECCENTRIC EXERCISES AND ULTRASOUND WITH CONCENTRIC EXERCISES ON TENDO ACHILLES TENDINITIS IN ATHELETES Ravish V. N 1, R. Raja 2, S. R. Sarala 3, Pavan
A STUDY TO COMPARE THE EFFICACY OF ULTRASOUND WITH ECCENTRIC EXERCISES AND ULTRASOUND WITH CONCENTRIC EXERCISES ON TENDO ACHILLES TENDINITIS IN ATHELETES Ravish V. N 1, R. Raja 2, S. R. Sarala 3, Pavan
Why research on tendon?
 To be or not to be Active with Painful Tendinopathy? Practical Clinical Applications Based on Current Research Using the Achilles Tendon as a Model Why research on tendon? Karin Grävare Silbernagel, PhD,
To be or not to be Active with Painful Tendinopathy? Practical Clinical Applications Based on Current Research Using the Achilles Tendon as a Model Why research on tendon? Karin Grävare Silbernagel, PhD,
AETIOLOGY TENDINOPATHY RESEARCH UPDATE - NOVEMBER Contents
 TENDINOPATHY RESEARCH UPDATE - NOVEMBER 2012 Contents AETIOLOGY... 1 A lower limb assessment tool for athletes at risk of developing patellar tendinopathy.... 1 Triceps surae activation is altered in male
TENDINOPATHY RESEARCH UPDATE - NOVEMBER 2012 Contents AETIOLOGY... 1 A lower limb assessment tool for athletes at risk of developing patellar tendinopathy.... 1 Triceps surae activation is altered in male
NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION
 NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION ACHILLES (Homer 800BC) When Achilles mother Thetis made her son invulnerable by submerging him in the Styx, the river
NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION ACHILLES (Homer 800BC) When Achilles mother Thetis made her son invulnerable by submerging him in the Styx, the river
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Min Wei, PhD* Yujie Liu, MD* Zhongli Li, PhD* Zhigang Wang, PhD*
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Clinical Efficacy Among - Assisted Radio-Frequency Ablation, Extracorporeal Shockwaves, and s in Treatment of Insertional Achilles Tendinosis Min Wei, PhD* Yujie Liu, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Clinical Efficacy Among - Assisted Radio-Frequency Ablation, Extracorporeal Shockwaves, and s in Treatment of Insertional Achilles Tendinosis Min Wei, PhD* Yujie Liu, MD*
A 5-year follow-up study of Alfredson s heel-drop exercise programme in chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy
 1 Sports Medicine Department, The Hague Medical Centre, Leidschendam, The Netherlands 2 Department of Orthopaedics, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, The Netherlands 3 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
1 Sports Medicine Department, The Hague Medical Centre, Leidschendam, The Netherlands 2 Department of Orthopaedics, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, The Netherlands 3 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
Achilles Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions
 APPENDIX D Achilles Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to summarize common medical and surgical interventions which may be considered for the management of
APPENDIX D Achilles Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to summarize common medical and surgical interventions which may be considered for the management of
Dr abedi yekta. Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences
 Dr abedi yekta Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences Pain in midportion of Achilles tendon. Morning stiffness Tendinitis
Dr abedi yekta Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences Pain in midportion of Achilles tendon. Morning stiffness Tendinitis
In an adult population are eccentric exercises effective in reducing pain and improving function in Achilles tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line
 Specific Question: In an adult population are eccentric exercises effective in reducing pain and improving function in Achilles tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate quality evidence for
Specific Question: In an adult population are eccentric exercises effective in reducing pain and improving function in Achilles tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate quality evidence for
Novel Physical Therapy Protocol Results in Increased Compressive Strain and Improved Outcomes in Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
 Novel Physical Therapy Protocol Results in Increased Compressive Strain and Improved Outcomes in Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Meghan Kelly MD PhD, Mary A Bucklin, Ruth Chimenti PhD, Rachel E Olsen,
Novel Physical Therapy Protocol Results in Increased Compressive Strain and Improved Outcomes in Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Meghan Kelly MD PhD, Mary A Bucklin, Ruth Chimenti PhD, Rachel E Olsen,
Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs)
 Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
The American Journal of Sports Medicine
 The American Journal of Sports Medicine http://ajs.sagepub.com/ Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Wolf Petersen, Robert Welp and Dieter Rosenbaum Am J Sports Med 2007 35: 1659 originally published online June
The American Journal of Sports Medicine http://ajs.sagepub.com/ Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Wolf Petersen, Robert Welp and Dieter Rosenbaum Am J Sports Med 2007 35: 1659 originally published online June
It is time to abandon the myth that eccentric
 VOLUME 12.1, 2016 D.O.I: http: doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2016.0097 Stasinopoulos Dimitrios (PhD) 1, Peter Malliaras 2 It is time to abandon the myth that eccentric training is best practice. 1 Vice-Chairperson
VOLUME 12.1, 2016 D.O.I: http: doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2016.0097 Stasinopoulos Dimitrios (PhD) 1, Peter Malliaras 2 It is time to abandon the myth that eccentric training is best practice. 1 Vice-Chairperson
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy
 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
3.3.1 Introduction. Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz
 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy 55 Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy Effectiveness and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disorders of the tendons: A systematic review
3.3 Shock Wave Therapy 55 Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy Effectiveness and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disorders of the tendons: A systematic review
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [Brunel University] On: 12 December 2008 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 773509782] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and
This article was downloaded by: [Brunel University] On: 12 December 2008 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 773509782] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and
INSIGHTS INTO ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
 C H A P T E R 1 4 INSIGHTS INTO ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY Steven R. Carter, DPM TERMINOLOGY The terminology used to describe Achilles tendon pathology can be misleading and sometimes confusing. Often we use
C H A P T E R 1 4 INSIGHTS INTO ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY Steven R. Carter, DPM TERMINOLOGY The terminology used to describe Achilles tendon pathology can be misleading and sometimes confusing. Often we use
Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions
 APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete
 Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete John P. Negrine F.R.A.C.S. Foot and Ankle Surgeon Orthosports Sydney The Bad news Maximum heart rate decreases VO2 Max decreases Runners when compared
Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete John P. Negrine F.R.A.C.S. Foot and Ankle Surgeon Orthosports Sydney The Bad news Maximum heart rate decreases VO2 Max decreases Runners when compared
Achilles and Patellar Tendinopathy Loading Programmes
 Sports Med (2013) 43:267 286 DOI 10.1007/s40279-013-0019-z SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Achilles and Patellar Tendinopathy Loading Programmes A Systematic Review Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Identifying Potential
Sports Med (2013) 43:267 286 DOI 10.1007/s40279-013-0019-z SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Achilles and Patellar Tendinopathy Loading Programmes A Systematic Review Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Identifying Potential
The etiology, pathogenesis and natural course of
 J SPORTS MED PHYS FITNESS 2009;49:171-6 Aim. The etiology, pathogenesis and natural course of Achilles tendinopathy are not yet completely known. Various forms of therapies, either conservative or surgical,
J SPORTS MED PHYS FITNESS 2009;49:171-6 Aim. The etiology, pathogenesis and natural course of Achilles tendinopathy are not yet completely known. Various forms of therapies, either conservative or surgical,
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS
 BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE
 SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety
SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety
Tendon Structure s Lack of Relation to Clinical Outcome After Eccentric Exercises in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 34-43 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Tendon Structure s Lack of Relation to Clinical Outcome After Eccentric Exercises in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 34-43 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Tendon Structure s Lack of Relation to Clinical Outcome After Eccentric Exercises in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis. American University of Beirut Medical Center
 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery
 AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
Physical therapies for Achilles tendinopathy: systematic review and meta-analysis
 Physical therapies for Achilles tendinopathy: systematic review and meta-analysis Author Sussmilch-Leitch, Samuel, Collins, Natalie, Bialocerkowski, Andrea, Warden, Stuart, Crossley, Kay Published 2012
Physical therapies for Achilles tendinopathy: systematic review and meta-analysis Author Sussmilch-Leitch, Samuel, Collins, Natalie, Bialocerkowski, Andrea, Warden, Stuart, Crossley, Kay Published 2012
ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
 www.drgavinshang.co.za ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY Review Article: The Specialist Forum, Sept 2013 The Medical Chronicle, Sept 2013 Dr. Gavin Shang Sports Physician MBBCH (WITS) MPHIL SPORTS MED (UCT/SSISA)
www.drgavinshang.co.za ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY Review Article: The Specialist Forum, Sept 2013 The Medical Chronicle, Sept 2013 Dr. Gavin Shang Sports Physician MBBCH (WITS) MPHIL SPORTS MED (UCT/SSISA)
The role of eccentric exercise in sport injuries rehabilitation
 British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published April 15, 2014 British Medical Bulletin, 2014, 1 29 doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldu006 The role of eccentric exercise in sport injuries rehabilitation Antonio Frizziero,
British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published April 15, 2014 British Medical Bulletin, 2014, 1 29 doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldu006 The role of eccentric exercise in sport injuries rehabilitation Antonio Frizziero,
shaving to treat patellar tendinopathy/jumper s knee? A randomised controlled study
 1 Capio Artro Clinic, Stockholm Sports Trauma Research Centre, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden 2 Sports Medicine Unit, Department of Surgical and Perioperative Science, University of Umeå, Umeå,
1 Capio Artro Clinic, Stockholm Sports Trauma Research Centre, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden 2 Sports Medicine Unit, Department of Surgical and Perioperative Science, University of Umeå, Umeå,
Chronic Plantar Fasciitis Treated with Two Sessions of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2010 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0391 Chronic Plantar Fasciitis Treated with Two Sessions of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2010 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0391 Chronic Plantar Fasciitis Treated with Two Sessions of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Protocols for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction & Achilles Tendinosis. Tara Bries, PT
 Protocols for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction & Achilles Tendinosis Tara Bries, PT Non-Operative Protocol for Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction Based on research by Alvarez et al. (2006) entitled
Protocols for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction & Achilles Tendinosis Tara Bries, PT Non-Operative Protocol for Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction Based on research by Alvarez et al. (2006) entitled
C hronic tendinopathies are common in both recreational
 217 REVIEW The evolution of eccentric training as treatment for patellar tendinopathy (jumper s knee): a critical review of exercise programmes Håvard Visnes, Roald Bahr... Br J Sports Med 2007;41:217
217 REVIEW The evolution of eccentric training as treatment for patellar tendinopathy (jumper s knee): a critical review of exercise programmes Håvard Visnes, Roald Bahr... Br J Sports Med 2007;41:217
Principles of Treatment. Case Studies. Principles of Treatment. Clinical Perspectives for the GP
 Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
Index. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 137 141 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendinopathy, 19 43. See also Achilles classification of, 20 differential diagnosis
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 137 141 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendinopathy, 19 43. See also Achilles classification of, 20 differential diagnosis
Conservative management of mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy: a mixed methods study, integrating systematic review and clinical reasoning
 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 Conservative management of mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy: a mixed methods study, integrating systematic review and clinical reasoning Victoria Rowe 1, Stephanie Hemmings
1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 Conservative management of mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy: a mixed methods study, integrating systematic review and clinical reasoning Victoria Rowe 1, Stephanie Hemmings
EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D.
 1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
Achilles tendon injury
 Achilles tendon injury Achilles tendinopathy is highly prevalent in athletes who participate in running-based sports but can also occur in racket sports and in sedentary people. Research suggests there
Achilles tendon injury Achilles tendinopathy is highly prevalent in athletes who participate in running-based sports but can also occur in racket sports and in sedentary people. Research suggests there
AbsolutePT s Tendinitis Approach. By Chad Reilly, President of Absolute Physical Therapy.
 AbsolutePT s Tendinitis Approach. By Chad Reilly, President of Absolute Physical Therapy. Tendinitis, tendinosis, tendinopathy; the name is currently in transition due to the fact that there are no outward
AbsolutePT s Tendinitis Approach. By Chad Reilly, President of Absolute Physical Therapy. Tendinitis, tendinosis, tendinopathy; the name is currently in transition due to the fact that there are no outward
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 01 Page January 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Management of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis using Hyperosmolar Dextrose Injection Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Management of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis using Hyperosmolar Dextrose Injection Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the VISA-A questionnaire for Chilean Spanish-speaking patients
 Keller et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:177 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0882-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the VISA-A questionnaire
Keller et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:177 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0882-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the VISA-A questionnaire
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY (mid-substance): Summary of the Evidence for Physical Therapy Interventions
 ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY (mid-substance): Summary of the Evidence for Physical Therapy Interventions PURPOSE, SCOPE & DISCLAIMER: The purpose of this document is to provide physical therapists with a summary
ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY (mid-substance): Summary of the Evidence for Physical Therapy Interventions PURPOSE, SCOPE & DISCLAIMER: The purpose of this document is to provide physical therapists with a summary
The treatment of patellar tendinopathy
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s10195-012-0220-0 REVIEW ARTICLE The treatment of patellar tendinopathy E. C. Rodriguez-Merchan Received: 4 January 2012 / Accepted: 25 November 2012 /
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s10195-012-0220-0 REVIEW ARTICLE The treatment of patellar tendinopathy E. C. Rodriguez-Merchan Received: 4 January 2012 / Accepted: 25 November 2012 /
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIITIS
 ZAGAZIG UNIVERSITY MEDICAL JOURNAL EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIITIS By Magdy Husseiny Ahmad Mansour Rheumatology &Rehabilitation Department Faculty of Medicine-Zagazig
ZAGAZIG UNIVERSITY MEDICAL JOURNAL EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIITIS By Magdy Husseiny Ahmad Mansour Rheumatology &Rehabilitation Department Faculty of Medicine-Zagazig
J umper s knee (chronic patellar tendinosis) is a troublesome
 423 ORIGINAL ARTICLE and pain in jumper s knee: a prospective clinical and sonographic study in elite junior volleyball players K Gisslén, H Alfredson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
423 ORIGINAL ARTICLE and pain in jumper s knee: a prospective clinical and sonographic study in elite junior volleyball players K Gisslén, H Alfredson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
The mechanism for efficacy of eccentric loading in Achilles tendon injury; an in vivo study in humans
 The mechanism for efficacy of eccentric loading in Achilles tendon injury; an in vivo study in humans Author Rees, J., Lichtwark, Glen, Wolman, R., Wilson, A. Published 2008 Journal Title Rheumatology
The mechanism for efficacy of eccentric loading in Achilles tendon injury; an in vivo study in humans Author Rees, J., Lichtwark, Glen, Wolman, R., Wilson, A. Published 2008 Journal Title Rheumatology
TOPAZ TM What you should know
 TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy
 Acta Orthopaedica 28; 79 (2): 249 256 249 Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy A double-blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy Sten Rasmussen, Marianne Christensen, Iben Mathiesen,
Acta Orthopaedica 28; 79 (2): 249 256 249 Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy A double-blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy Sten Rasmussen, Marianne Christensen, Iben Mathiesen,
Achilles Tendinopathy (Mid-portion)
 Achilles Tendinopathy (Mid-portion) What is Achilles tendinopathy? Achilles tendinopathy or tendinitis is a term that has been used for many years to describe pain, swelling and thickening around the Achilles
Achilles Tendinopathy (Mid-portion) What is Achilles tendinopathy? Achilles tendinopathy or tendinitis is a term that has been used for many years to describe pain, swelling and thickening around the Achilles
Achilles Tendon Anatomy. Achilles Tendon Anatomy. Acute Achilles Rupture. Acute Achilles Rupture 8/19/14. Primary plantarflexor
 Disclosure Conditions of the Achilles Tendon Brian Clowers, M.D. I have no financial relationships that would influence the content of this presentation Oklahoma Sports and Orthopedic Institute September
Disclosure Conditions of the Achilles Tendon Brian Clowers, M.D. I have no financial relationships that would influence the content of this presentation Oklahoma Sports and Orthopedic Institute September
JON KARLSSON, MD, PhD Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg Sweden
 JON KARLSSON, MD, PhD Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg Sweden No company connections to disclose. Editor of KNEE SURGERY SPORTS TRAUMATOLOGY ARTHROSCOPY (KSSTA). WHY DOES IT HAPPEN? The pathological
JON KARLSSON, MD, PhD Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg Sweden No company connections to disclose. Editor of KNEE SURGERY SPORTS TRAUMATOLOGY ARTHROSCOPY (KSSTA). WHY DOES IT HAPPEN? The pathological
Topical glyceryl trinitrate treatment of chronic patellar tendinopathy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
 1 Department of Steunebrink Sportsmedicine, Eelde, The Netherlands 2 Department of Sportsmedicine, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands 3 Department of Sportsmedicine, Medical
1 Department of Steunebrink Sportsmedicine, Eelde, The Netherlands 2 Department of Sportsmedicine, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands 3 Department of Sportsmedicine, Medical
Surgical treatment for midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a systematic review
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-016-4062-9 ANKLE Surgical treatment for midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a systematic review T. P. A. Baltes 1 R. Zwiers 1 J. I. Wiegerinck 1 C. N. van Dijk 1 Received: 24 September
DOI 10.1007/s00167-016-4062-9 ANKLE Surgical treatment for midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a systematic review T. P. A. Baltes 1 R. Zwiers 1 J. I. Wiegerinck 1 C. N. van Dijk 1 Received: 24 September
Intelect Focus Shockwave
 Intelect Focus Shockwave A non-invasive treatment, proven effective for plantar fasciitis Intelect Focus Shockwave - the Technology Greater Power & Depth for Better Treatment In Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Intelect Focus Shockwave A non-invasive treatment, proven effective for plantar fasciitis Intelect Focus Shockwave - the Technology Greater Power & Depth for Better Treatment In Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon
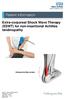 Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6459-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6459-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page
Musculoskeletal health is a necessary component of overall
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE No Effect of Eccentric Training on Jumper s Knee in Volleyball Players During the Competitive Season A Randomized Clinical Trial Håvard Visnes, Stud Med, PT,* Aasne Hoksrud, Stud Med,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE No Effect of Eccentric Training on Jumper s Knee in Volleyball Players During the Competitive Season A Randomized Clinical Trial Håvard Visnes, Stud Med, PT,* Aasne Hoksrud, Stud Med,*
Karthikeyan Rajendran, Sam Thamburaj A and Ilayaraja Alagia Thiruvevenkadam
 2017; 3(9): 446-450 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(9): 446-450 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-07-2017 Accepted: 05-08-2017 Karthikeyan Rajendran Sam
2017; 3(9): 446-450 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(9): 446-450 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-07-2017 Accepted: 05-08-2017 Karthikeyan Rajendran Sam
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR
 SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
Common%Work%Related%Foot% and%ankle%problems
 Common%Work%Related%Foot% and%ankle%problems Dr. George H. Theodore Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Foot and Ankle Consultant Boston Red Sox New England Patriots Boston Bruins Work%Related%Foot%and%Ankle%
Common%Work%Related%Foot% and%ankle%problems Dr. George H. Theodore Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Foot and Ankle Consultant Boston Red Sox New England Patriots Boston Bruins Work%Related%Foot%and%Ankle%
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed.
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
STUDY OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA INJECTIONS IN PATIENTS OF TENDINOPATHY IN SOUTH GUJARAT POPULATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE STUDY OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA INJECTIONS IN PATIENTS OF TENDINOPATHY IN SOUTH GUJARAT POPULATION Manish Patel 1, Chintan Sheth 2, Jignesh Patel 1, PrabhavTijoriwala 1 Author s Affiliations:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE STUDY OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA INJECTIONS IN PATIENTS OF TENDINOPATHY IN SOUTH GUJARAT POPULATION Manish Patel 1, Chintan Sheth 2, Jignesh Patel 1, PrabhavTijoriwala 1 Author s Affiliations:
Orthospec. ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy
 Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
Ultrasound Measurement of Cross Sectional Area of the Achilles Tendon in an Asymptomatic Elite Military Population, a Prospective Cohort Study
 Ultrasound Measurement of Cross Sectional Area of the Achilles Tendon in an Asymptomatic Elite Military Population, a Prospective Cohort Study Kevin D. Martin, MAJ, DO; Jeffrey Wake, 2LT, ATC, B.S.; Laura
Ultrasound Measurement of Cross Sectional Area of the Achilles Tendon in an Asymptomatic Elite Military Population, a Prospective Cohort Study Kevin D. Martin, MAJ, DO; Jeffrey Wake, 2LT, ATC, B.S.; Laura
University of Groningen. Patellar tendinopathy van Ark, Mathijs
 University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy van Ark, Mathijs IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy van Ark, Mathijs IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
Citation for published version (APA): Zwerver, J. (2010). Patellar tendinopathy: Prevalence, ESWT treatment and evaluation Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy Zwerver, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy Zwerver, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Achilles Tendon Ruptures Accelerated Functional Rehab vs Immobilization
 Achilles Tendon Ruptures Accelerated Functional Rehab vs Immobilization Michael D. Dujela DPM, FACFAS Fellowship Trained Foot and Ankle Surgeon Washington Orthopaedic Center Director, Foot and Ankle Surgery,
Achilles Tendon Ruptures Accelerated Functional Rehab vs Immobilization Michael D. Dujela DPM, FACFAS Fellowship Trained Foot and Ankle Surgeon Washington Orthopaedic Center Director, Foot and Ankle Surgery,
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy. Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine
 Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
programme in the treatment of rotator cuff tendinopathy A pilot trial to study the effectiveness of an exercise Abstract
 VOLUME 10.2, 2014 A pilot trial to study the effectiveness of an exercise programme in the treatment of rotator cuff tendinopathy D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2014.0079 Stasinopoulos Dimitrios 1, Stasinopoulos
VOLUME 10.2, 2014 A pilot trial to study the effectiveness of an exercise programme in the treatment of rotator cuff tendinopathy D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2014.0079 Stasinopoulos Dimitrios 1, Stasinopoulos
Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort.
 Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort. Poster No.: C-1680 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Morton, T. Parkes, O. Chan,
Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort. Poster No.: C-1680 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Morton, T. Parkes, O. Chan,
Orthotics and Stretching for Heel Pain are BETTER than Injections and Procedures
 Orthotics and Stretching for Heel Pain are BETTER than Injections and Procedures Jacob Wynes DPM, MS, FACFAS Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics University of Maryland School of Medicine Chief
Orthotics and Stretching for Heel Pain are BETTER than Injections and Procedures Jacob Wynes DPM, MS, FACFAS Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics University of Maryland School of Medicine Chief
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016
 Commissioning Policy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible:
Commissioning Policy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible:
Department of Physical Therapy, Sahmyook University, Seoul, Republic of Korea 2
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 136-140 http://www.jssm.org Research article Comparison of pathway and center of gravity of the calcaneus on non-involved and involved sides according
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 136-140 http://www.jssm.org Research article Comparison of pathway and center of gravity of the calcaneus on non-involved and involved sides according
Is Treatment With Topical Glyceryl Trinitrate Effective in Reducing Elbow Pain in Patients With Lateral Epicondylitis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Treatment With Topical Glyceryl Trinitrate
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Treatment With Topical Glyceryl Trinitrate
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain
 Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6460-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page 1 of 6 Plantar fasciitis / heel
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6460-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page 1 of 6 Plantar fasciitis / heel
Make sure you have properly fitting running shoes and break these in gradually. Never wear new running shoes for a race or a long run.
 Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Clinical Study Outcome of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy with and without Haglund s Deformity
 BioMed Research International Volume 216, Article ID 6315846, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/6315846 Clinical Study Outcome of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
BioMed Research International Volume 216, Article ID 6315846, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/6315846 Clinical Study Outcome of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction PREDICTIVE FACTORS FOR FOR RADIAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIOPATHY
 PREDICTIVE FACTORS FOR FOR RADIAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIOPATHY JAVIER CRUPNIK, PT ALDO BUSTOS, MD Introduction Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain.
PREDICTIVE FACTORS FOR FOR RADIAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIOPATHY JAVIER CRUPNIK, PT ALDO BUSTOS, MD Introduction Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain.
Plantar Fasciitis. What is Plantar Fasciitis: Anatomy of the Plantar Fascia: Problems with the Plantar Fascia:
 Plantar Fasciitis What is Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar Fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain in Los Angeles and globally. The Foot and Ankle Institute is a world leader in the research
Plantar Fasciitis What is Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar Fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain in Los Angeles and globally. The Foot and Ankle Institute is a world leader in the research
mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading
 Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy. Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science
 E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
Fluoroscopically Guided Peritendinous Corticosteroid Injection for Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy
 Fluoroscopically Guided Peritendinous Corticosteroid Injection for Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy A Retrospective Review Luke T. Nicholson,* MD, Steven DiSegna,* MD, Joel S. Newman,* MD, and Suzanne L.
Fluoroscopically Guided Peritendinous Corticosteroid Injection for Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy A Retrospective Review Luke T. Nicholson,* MD, Steven DiSegna,* MD, Joel S. Newman,* MD, and Suzanne L.
RPW Shockwave Therapy. Scientific Studies Overview
 RPW Shockwave Therapy Scientific Studies Overview 0 Evidence based indications Myofascial Trigger Points Rotator Cuff & Calcific Tendinitis Spasticity Epicondylitis Hip/Trochanter Pain Cellulitis Hamstring
RPW Shockwave Therapy Scientific Studies Overview 0 Evidence based indications Myofascial Trigger Points Rotator Cuff & Calcific Tendinitis Spasticity Epicondylitis Hip/Trochanter Pain Cellulitis Hamstring
pull your toes and foot toward your head, you will feel this tissue tighten. WHAT CAUSES PLANTAR
 PLANTAR FASCIITIS AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? Plantar fasciitis is pain felt at the bottom of the heel. It is usually felt on the first step out of bed in the morning or when walking again
PLANTAR FASCIITIS AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? Plantar fasciitis is pain felt at the bottom of the heel. It is usually felt on the first step out of bed in the morning or when walking again
Elbow Muscle Power Deficits
 1 Elbow Muscle Power Deficits ICD-9-CM code: 726.32 Lateral epicondylitis ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4300 Lifting, d4452 Reaching, d4401 Grasping Body Structure code: s73012 Muscles
1 Elbow Muscle Power Deficits ICD-9-CM code: 726.32 Lateral epicondylitis ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4300 Lifting, d4452 Reaching, d4401 Grasping Body Structure code: s73012 Muscles
Original article. Introduction. Summary. Methods. 312 Muscles, Ligaments and Tendons Journal 2012; 2 (4):
 Original article Comparison between extracorporeal shockwave therapy, placebo ESWT and endoscopic plantar fasciotomy for the treatment of chronic plantar heel pain in the athlete Amol Saxena 1, Magali
Original article Comparison between extracorporeal shockwave therapy, placebo ESWT and endoscopic plantar fasciotomy for the treatment of chronic plantar heel pain in the athlete Amol Saxena 1, Magali
Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Using a Central Tendon Splitting Approach
 Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Using a Central Tendon Splitting Approach Elizabeth Martin, MD; Ruth Chimenti, DPT; Josh Tome, MS; Andrew Hollenbeck, BS; John Ketz,
Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Using a Central Tendon Splitting Approach Elizabeth Martin, MD; Ruth Chimenti, DPT; Josh Tome, MS; Andrew Hollenbeck, BS; John Ketz,
L J Cannell, J E Taunton, D B Clement, C Smith, K M Khan
 60 The Allan McGavin Sports Medicine Centre and School of Human Kinetics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada L J Cannell J E Taunton D B Clement C Smith K M Khan Correspondence to: Dr Khan
60 The Allan McGavin Sports Medicine Centre and School of Human Kinetics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada L J Cannell J E Taunton D B Clement C Smith K M Khan Correspondence to: Dr Khan
