- Conclusion: This study confirmed the very good acceptability and efficacy of Urgotul in the treatment of skin lesions in patients with EB.
|
|
|
- Aileen Stokes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using Urgotul dressing for the management of epidermolysis bullosa skin lesions VOL 14, NO 10, November 2005 Objective: To evaluate the acceptability, tolerance and efficacy of Urgotul wound dressing in the management of epidermolysis bullosa (EB) skin lesions. - Method: This was an open-label uncontrolled clinical trial involving 20 patients (11 adults and nine children) with EB simplex or dystrophic EB. Patients were selected from the register of EB patients at the investigating centre and included if they presented with at least one skin lesion requiring management with a non-adherent wound dressing. Lesions were treated with the study dressing for a maximum of four weeks. All dressing changes, wound parameters, pain and effect on quality of life were recorded. - Results: All patients completed the trial. Nineteen out of 20 wounds healed within 8.7 +/- 8.5 days. Overall, 11 patients (55%) considered that their quality of life had improved following use of the dressing, which was also reported to be pain free and 'very easy' or 'easy' to remove at most dressing changes. Nineteen out of 20 patients stated that they would use the study dressing to manage their lesions in future. - Conclusion: This study confirmed the very good acceptability and efficacy of Urgotul in the treatment of skin lesions in patients with EB. - Declaration of interest: This study was sponsored by Laboratoires Urgo (Dijon, France). Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a heterogeneous group of rare, inherited skin diseases characterised by recurring painful skin lesions, often precipitated by minor trauma resulting in dermo-epidermal separation or split. Treatment for this family of 23 genetic skin disorders is mainly supportive as there is as yet no radical and effective therapy for them.1 Severe forms of EB may involve the eyes, oral mucosa and the oesophagus; some may produce scarring and deformities in the extremities. There are three major forms of EB, depending on the level of cleavage in the skin (Box 1). In patients with EB, wound healing is impaired by multiple factors including: - Foreign bodies such as dressing residue - Bacteria - Nutritional deficiencies - Tissue anoxia - Ageing2 - Glucocorticoids. In addition, pain at dressing removal is a major issue, particularly for children.3,4 To limit any additional risk of trauma, wounds should be covered with a non-adherent dressing, such as petrolatum-impregnated gauze, hydrogel, silicone or an absorbent foam silicone covered with a non-adherent pad and secured with soft, roller gauze bandages (non-adherent and atraumatic upon removal) and elastic tubular dressings.5-7 Clinical trials on Urgotul (Laboratoires Urgo), a lipidocolloid dressing, have demonstrated its acceptability and efficacy in children and adults8 with a wide range of acute wounds (superficial burns, abrasions, traumatic wounds) and chronic wounds (leg ulcers, pressure ulcers, dehisced wounds)9-14 and in a very large observational study.15
2 The characteristics of this dressing (Box 2), specifically pain-free removal, appear to be congruent with the treatment of skin lesions in patients with EB. A clinical trial was therefore conducted to evaluate the acceptability and efficacy of Urgotul (the study dressing) in EB patients who were familiar with the evaluation of topical treatments for their skin lesions. Method Study design This was an open single-centre prospective non- randomised clinical trial conducted on patients with EB. Thirty potential participants were identified from a register of diagnosed cases of EB and were sent a letter inviting them to participate in the study; 20 agreed. The study procedure was outlined to them and written consent obtained. Inclusion criteria - Children aged =12 months or adults - Patients with at least one current skin lesion less than 300cm2 in size that required topical treatment and protection with a simple greasy wound dressing. Exclusion criteria - Known hypersensitivity to carboxymethylcellulose - A clinically infected wound - Squamous cell carcinoma - Current participation in another clinical trial. Study protocol At the inclusion visit the patients' sex, age, EB category, age at disease onset, and main medical and surgical history were recorded. If multiple lesions were present, the one that best met the inclusion criteria was selected as the target lesion and its largest and smallest axes were measured. Lesion history and previous topical treatments given were noted. Lesions were photographed after cleansing with a saline solution. The patient, family or a private nurse performed the dressing changes and wound cleansing. Patients completed a diary after each dressing change in which they recorded: - Method of dressing removal (simple removal, removal after soaking the dressing or after bathing) - Overall ease of removal (very easy/easy/difficult) - Presence of odour (none/mild/severe) - Any wound bleeding (none/mild/severe) - Global evaluation of dressing adherence to the wound bed (none/mild/severe) - Ease of dressing application (very easy, easy, difficult) - Presence of dressing-induced pruritus, exudate leakage or any other local adverse event such as bleeding, overgranulation or infection. Patients were very familiar with these types of wounds, so would be able to recognise if there was a problem in the wound bed. However, they were asked to call the investigating centre or at least visit their GP if a local adverse event occurred during the study. At each dressing change pain was recorded using a study-specific four-item verbal scale: none/mild to moderate/severe/very severe. If pain was present, its intensity was measured using a 100mm visual analogue scale (VAS) in adults and children aged six years or more - a 100mm line with a continuum of 0 (no pain) to 100 (worst imaginable pain). Children under three years had their pain rated by their parents; those aged three to six years used a VAS scale
3 with faces. After a maximum of four weeks of treatment, patients were seen at the investigating centre at Saint Louis Hospital. The investigators documented the wound status, photographs and any local or systemic adverse events that had occurred, based on the patients' or parents' diary. This information was recorded during the study period only, so no pre-study scores are available. At week 4, patients were asked a series of questions relating to quality-of-life parameters using a study-specific quality-of-life tool (Box 3); parents of the youngest children in the study based their answers on their experience of managing these recurrent wounds. Again, no pre-study comparative data were recorded. Development of this tool was based on the authors' own experience. Patients were also asked about their general experience of using the study dressing. Statistical methods The descriptive statistical analysis was performed on an intention-to-treat basis for both the principal (acceptability of the dressing and its effect on quality of life) and secondary outcome measures (healing time and tolerance). It considered all patients included in the trial. Ethics The Versailles Ethics Committee (France) approved the study protocol and patient information sheet, and the study was conducted in compliance with good clinical practice. Written informed consent was obtained from the adult patients, or from both parents before their children were enrolled. Results Patients' characteristics Over a five-month period, 20 patients (11 adults and nine children) were included. Their main baseline characteristics are given in Table 1. Disease onset occurred within the first year of life in 18/20 patients (90%) and at three and eight years in the remaining two. Thirteen patients (65%) had dystrophic EB (DEB), with three to six clinical manifestations of the disease (perioral lesions, oesophageal lesions, anal lesions, extremity deformities, ocular lesions and delayed development). The target lesion had been present for between one and 45 days (mean: 8.8 +/ days). The mean largest and smallest axes were 3.9 +/- 2.2cm and 2.5 +/- 1.4cm respectively. In 10 patients a previous dressing had been used on the target lesion (simple gauze in five cases and a petrolatum gauze or non-adherent dressing in the remaining five). These lesions were mainly located on the lower limbs (55%) or on the hands (15%); other locations were the upper limb, chest, foot or neck. In the remaining 10 patients, the target lesions were new, so no dressing or only gauze had been used on them. No patients were lost to follow-up and none interrupted treatment with the study dressing before the fourth week for any reason other than healing. Primary outcomes: acceptability of the dressing and quality of life Overall, 11 patients (55%; seven adults and four children) considered that their quality of life had improved with the use of Urgotul dressing. - Dressing application - This was regarded by patients as easy or very easy in 94.5% of the dressing changes - Dressing-change time - Seven patients (35%; three adults, four children) considered that this took less time than with their previous dressing; nine (45%; five adults and four children) thought it took a similar amount of time; four (20%; three adults and one child) thought it took more time. - Dressing removal - This was regarded as 'easy' or 'very easy' in 98% of changes and as 'difficult' only once in one patient and twice in another. Dry dressing removal was performed in 87.2% of the recorded changes; 12.7% were soaked with saline - Odour - A mild transitory odour was noticed during 19 changes in five patients
4 - Bleeding and adherence - Mild bleeding was reported in 18 changes in five patients and strong adherence of the study dressing to the wound was reported twice in only one patient - Adverse events - Two patients (one adult and one child) reported pruritus once between two dressing changes. One patient reported exudate leakage during four inter-dressing changes. - Pain - A total of 152 dressing changes were documented in the patient diaries. In 87% of cases, analgesia was not required before dressing changes. The remaining 13% only required paracetamol. Ninety-one per cent of the dressing changes were reported to be pain free; of the remainder, 9% were rated as mild to moderate. In adults, only one patient reported pain at dressing changes (mild to moderate pain in four consecutive dressing changes); the mean VAS score was 5mm. In children, pain was rated as severe at only one dressing change in one patient and as mild to moderate at eight changes (only two were given a premedication) in three patients. The highest VAS score recorded in the paediatric population was 24mm. Fifteen subjects (75%; six adults and nine children) stated that dressing changes were less painful with the study dressing than with their usual wound dressing. Characteristics of the dressing changes are given in Table 2. Secondary outcomes: healing time and tolerance - Healing time - Healing was obtained within 8.7 +/- 8.5 days on average (range: 1-36 days). At the final visit 19/20 wounds had healed; the exception was in a 14-year-old girl with DEB whose lesion, which had been present for 1.5 months before inclusion, was considered by the investigator to be stagnating, despite the clear reduction in wound size (50%). This result is similar to her previous experiences with dressings and was thought to be due to the nature of her disease, hallopausiemens EB, the most serious form of DEB. Ten of the 20 patients considered that healing times were shorter with the study dressing. Two thought they were longer than achieved with their previous dressing. The remaining eight patients thought they were the same. - Comfort - Fifteen patients considered the study dressing more comfortable than their usual dressing. Before dressing changes, most adults and all children felt less apprehensive about the procedure than they had with their usual dressing. Nineteen out of 20 patients (95%) said they would use the study dressing again if necessary. The study dressing was never considered as troublesome as their usual dressing in terms of daily activities by either the adults or children. Discussion This open-label uncontrolled clinical trial was conducted in an EB referral centre in France, and involved 20 adults and children already known to the medical investigator. All these patients (or the children's parents) were familiar with the local care of their EB skin lesions. As these recurrent skins lesions heal spontaneously, the main objective was to evaluate the acceptability of the study dressing in this frail population, particularly in terms of pain at dressing change and effect on quality of life. Most patients had participated in previous dressing studies and were familiar with the procedures and how to complete the report files. While this trial was not controlled and the sample was relatively small, the clinical relevance of the observations obtained can be viewed with confidence, given the very low prevalence of this genetic disease in France ( patients). No active drug is yet available for the topical treatment of EB skin lesions,16 and while tissue- engineered skin has appeared to give encouraging results in terms of healing rates and absence of adverse effects,1,17 it is not routinely used. Patients with EB therefore require a non-adherent dressing to avoid trauma and bleeding on removal. In this study, the acceptability and efficacy of the study dressing were considered very good. No patients were withdrawn from the study and none discontinued its use. Application was regarded as easy or very easy by both adult patients and parents. Patients were instructed to report pain during each dressing change, and various tools were used, depending on the patient's age, to evaluate the pain level. This was regarded as important as pain is often one of the most disturbing factors during dressing change.3 Unexpectedly, pain did not appear to be a problem in this sample,
5 which probably accounts for the high level of satisfaction with the study dressing - 19 out of 20 patients confirmed they will treat new skin lesions with it. However, one of the most important nursing considerations is to educate individuals and their families about proper wound care, products and different dressing techniques18 and to promote the development of new modern dressings adapted to these EB skin lesions. References 1 Fivenson, D.P., Scherschun, L., Choucair, M. et al. Graftskin therapy in epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermato 2003; 48: 6, Uitto, J., Richard, G. Progress in epidermolysis bullosa: genetic classification and clinical implications. Am J Med Genet 2004; 131C: 1, Weiner, M.S. Pain management in epidermolysis bullosa: an intractable problem. Ostomy Wound Manage 2004; 50: 8, Fine, J.D., Johnson, L.B., Weiner, M., Suchindran, C. Assessment of mobility, activities and pain in different subtypes of epidermolysis bullosa. Clin Exp Dermatol 2004; 29: 2, Schober-Flores, C., Epidermolysis bullosa: the challenges of wound care. Dermatol Nurs 2003; 15: 2, , Gannon, B.A., Epidermolysis bullosa: pathophysiology and nursing care. Neonatal Netw 2004; 23: 6, Trent, J.T., Kirsner, R.S. Epidermolysis bullosa: identification and treatment. Adv Skin Wound Care 2003;16: 6, Letouze, A., Voinchet, V., Hoecht, B. et al. Using a new lipidocolloid dressing in paediatric wounds: results of French and German clinical studies. J Wound Care 2004; 13: 6, Benbow, M., Urgotul: alternative to conventional non-adherence dressings. Br J Nurs 2002; 11: 2, Meaume, S., Senet, P., Dumas, R. et al. Urgotul: a novel non-adherent lipidocolloid dressing. Br J Nurs 2002; 11: 16 Suppl, S42-S43, S46-S Benbow, M., Iosson, G. A clinical evaluation of Urgotul to treat acute and chronic wounds. Br J Nurs, 2004;13: 2, Smith, J., Hill, J., Barrett, S. et al. Evaluation of Urgotol plus K-Four compression for venous leg ulcers. Br J Nurs 2004;13: (6 Suppl), S20-S Meaume, S., Ourabah, Z., Cartier, H. et al. Evaluation of a lipidocolloid wound dressing in the local management of leg ulcers. J Wound Care Burton F. An evaluation of non-adherent wound-contact layers for acute traumatic and surgical wounds. J Wound Care, 2004; 13: 9, Meaume, S., Teot, L., Lazareth, I. et al. The importance of pain reduction through dressing selection in routine wound management: the MAPP study. J Wound Care 2004; 13: 10, Fine, J.D., Johnson, L. Evaluation of the efficacy of topical bufexamac in epidermolysis bullosa simplex: a double-blind placebo-controlled crossover trial. Arch Dermatol 1988; 124: 11, Falabella, A.F.,Valencia, I.C., Eaglstein, W.H., Schanchner, L.A. Tissue-engineered skin (Apligraf) in the healing of patients with epidermolysis bullosa wounds. Arch Dermato 2000; 136: 10, Schober-Flores, C. Epidermolysis bullosa: the challenges of wound care. Dermato Nurs 2003; 15: 2, , Hovnanian, A., Duquesnoy, P., Amselem, S. et al. Exclusion of linkage between the collagenase gene and generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa phenotype. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: 5,
6 20 Hovnanian, A., Duquesnoy, P., Blanchet-Bardon, C. et al. Genetic linkage of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa to the type VII collagen gene. J Clin Invest 1992; 90: 3, Pai, S., Marinkovich, M.P. Epidermolysis bullosa: new and emerging trends. Am J Clin Dermatol 2002; 3: 6, Authors C. Blanchet-Bardon, MD, Dermatologist, Department of Dermatology, Saint Louis Hospital, Paris, France; S. Bohbot, MD, Medical Director, Laboratoires Urgo, Chenove, France. claudine.blanchet-bardon@sls.aphop-paris.fr Copyright 2004 Emap Healthcare, part of Emap Communications. All Rights Reserved. Your use of this material is governed by copyright laws, your subscriber agreement and the terms of use for the Journal of Wound Care Web site
7
8
9
10
11
Use of topical negative pressure with a lipidocolloid dressing: results of a clinical evaluation
 Use of topical negative pressure with a lipidocolloid dressing: results of a clinical evaluation Téot L, Lambert L, Ourabah Z, Bey E, Steenman C, Wierzbiecka E, Malikov S, Charles JP, Vives F, Bohbot S
Use of topical negative pressure with a lipidocolloid dressing: results of a clinical evaluation Téot L, Lambert L, Ourabah Z, Bey E, Steenman C, Wierzbiecka E, Malikov S, Charles JP, Vives F, Bohbot S
Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.]
![Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.] Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.]](/thumbs/83/87846749.jpg) University of Groningen Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa Gostynski, Antoni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa Gostynski, Antoni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Compression bandaging remains the basis of venous
 CLINICAL EVALUATION Evaluation of Urgotul plus K-Four compression for venous leg ulcers J Smith, J Hill, S Barrett, W Hayes, P Kirby, S Walsh, E Gittins, F Whitehurst, R Cooper Compression bandaging remains
CLINICAL EVALUATION Evaluation of Urgotul plus K-Four compression for venous leg ulcers J Smith, J Hill, S Barrett, W Hayes, P Kirby, S Walsh, E Gittins, F Whitehurst, R Cooper Compression bandaging remains
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017
 Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Exudate in the early stages of wound healing
 Products & technology Wound management with the Biatain Silicone foam dressing: A multicentre product evaluation Authors: Hugues Cartier, Simon Barrett, Karen Campbell, Jan Forster, Mike Schmalzbauer,
Products & technology Wound management with the Biatain Silicone foam dressing: A multicentre product evaluation Authors: Hugues Cartier, Simon Barrett, Karen Campbell, Jan Forster, Mike Schmalzbauer,
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017
 Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment
 Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Foam dressings have frequently
 The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
An observational evaluation of a new foam adhesive dressing
 An observational evaluation of a new foam adhesive dressing Elizabeth Merlin-Manton, Michelle Greenwood and Adele Linthwaite An observational evaluation of a new foam adhesive dressing Elizabeth Merlin-Manton,
An observational evaluation of a new foam adhesive dressing Elizabeth Merlin-Manton, Michelle Greenwood and Adele Linthwaite An observational evaluation of a new foam adhesive dressing Elizabeth Merlin-Manton,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE Debrisoft for the debridement of acute and chronic wounds 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The Debrisoft
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE Debrisoft for the debridement of acute and chronic wounds 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The Debrisoft
The primary function of low-adherence wound contact
 S35 Product focus S35 A multicentre clinical evaluation of silicone wound contact layer in daily practice Abstract Objective To evaluate clinically the performance of, a silicone-based primary contact
S35 Product focus S35 A multicentre clinical evaluation of silicone wound contact layer in daily practice Abstract Objective To evaluate clinically the performance of, a silicone-based primary contact
Galen ( A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing
 Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed. Closing wounds. Together.
 Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Mild Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Denyer EB CNS DebRA UK 2009
 Mild Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa J. Denyer EB CNS DebRA UK 2009 What is Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB)? EB is a group of inherited disorders in which the skin blisters extremely easily. There are 3 main
Mild Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa J. Denyer EB CNS DebRA UK 2009 What is Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB)? EB is a group of inherited disorders in which the skin blisters extremely easily. There are 3 main
HOW TO APPLY EFFECTIVE MULTILAYER COMPRESSION BANDAGING
 HOW TO APPLY EFFECTIVE MULTILAYER COMPRESSION BANDAGING Alison Hopkins is Clinical Nurse Specialist, East London Wound Healing Centre, Tower Hamlets Primary Care Trust Compression therapy is essential
HOW TO APPLY EFFECTIVE MULTILAYER COMPRESSION BANDAGING Alison Hopkins is Clinical Nurse Specialist, East London Wound Healing Centre, Tower Hamlets Primary Care Trust Compression therapy is essential
Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL. of the infection risk in chronic wound
 Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL of the infection risk in chronic wound Introduction The impact of infection on patients is well
Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL of the infection risk in chronic wound Introduction The impact of infection on patients is well
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation
 Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
DRESSING SELECTION. Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate
 DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds
 Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
REPORT OF EXPERIENCES:
 REPORT OF EXPERIENCES: Non Adherent Dressings in Fragile Skin Conditions: The Use of Soft Silicone Coated Polyurethane Foam Dressing (Mepilex ) in Hereditary and Acquired Bullous Skin Diseases. Hauke Schumann
REPORT OF EXPERIENCES: Non Adherent Dressings in Fragile Skin Conditions: The Use of Soft Silicone Coated Polyurethane Foam Dressing (Mepilex ) in Hereditary and Acquired Bullous Skin Diseases. Hauke Schumann
HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management
 Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology
 The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology The first step in healing a chronic wound is to detoxify it by removing slough, necrotic tissue, exudate and bacteria, while keeping
The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology The first step in healing a chronic wound is to detoxify it by removing slough, necrotic tissue, exudate and bacteria, while keeping
Medical technology guidance
 NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Medical technology guidance The Debrisoft monofilament debridement pad for use in acute or chronic wounds
NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Medical technology guidance The Debrisoft monofilament debridement pad for use in acute or chronic wounds
Advazorb. Hydrophilic foam dressing range
 Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Fibroblast proliferation plays a vital role in helping. Assessing an adherent silicone foam dressing: a clinical evaluation across five NHS trusts
 Assessing an adherent silicone foam dressing: a clinical evaluation across five NHS trusts Abstract The wound contact layer of UrgoTul Absorb Border (Urgo Medical) foam dressing contains a Technology Lipido
Assessing an adherent silicone foam dressing: a clinical evaluation across five NHS trusts Abstract The wound contact layer of UrgoTul Absorb Border (Urgo Medical) foam dressing contains a Technology Lipido
Wounds UK. Wound management using a superabsorbent foam dressing: outcomes of a post-ce-mark primary care clinical evaluation ON THE NET
 September 2015 Volume 11 Issue 3 Wounds UK The quarterly journal exploring standards of care, new areas of expertise and research developments Wound management using a superabsorbent foam dressing: outcomes
September 2015 Volume 11 Issue 3 Wounds UK The quarterly journal exploring standards of care, new areas of expertise and research developments Wound management using a superabsorbent foam dressing: outcomes
West Gloucestershire Primary Care Trust Community Nursing Service. Leg Ulcer Audit. Gloucestershire Primary & Community Care Audit Group
 West Gloucestershire Primary Care Trust Community Nursing Service Leg Ulcer Audit 2006 Gloucestershire Primary & Community Care Audit Group Contents Page number Background 3 Audit Aims 4 Methodology 4
West Gloucestershire Primary Care Trust Community Nursing Service Leg Ulcer Audit 2006 Gloucestershire Primary & Community Care Audit Group Contents Page number Background 3 Audit Aims 4 Methodology 4
Leg ulceration is a common problem, with an
 Clinical evaluation of a dressing with poly absorbent fibres and a silver matrix for managing chronic wounds at risk of infection: a non comparative trial Objective: To assess the efficacy, safety and
Clinical evaluation of a dressing with poly absorbent fibres and a silver matrix for managing chronic wounds at risk of infection: a non comparative trial Objective: To assess the efficacy, safety and
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
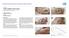 CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Anseong Factory : 70-17, Wonam-ro, Wongok-myeon, Anseong-si, Gyeonggi-do , REPUBLIC OF KOREA
 Care for tomorrow The Solution for Management HQ & Factory : 7, Hyeongjero4Beon-gil, Namsa-myeon, Cheoin-gu, Yong-in-si, Gyeonggi-do 449-884, REPUBLIC OF KOREA TEL: +8-3-33-33 / FAX: +8-3-33-34 Anseong
Care for tomorrow The Solution for Management HQ & Factory : 7, Hyeongjero4Beon-gil, Namsa-myeon, Cheoin-gu, Yong-in-si, Gyeonggi-do 449-884, REPUBLIC OF KOREA TEL: +8-3-33-33 / FAX: +8-3-33-34 Anseong
Understanding our report and advice: Antimicrobial wound dressings (AWDs) for chronic wounds
 Understanding our report and advice: Antimicrobial wound dressings (AWDs) for chronic wounds Health technology assessment report 13 December 2015 Healthcare Improvement Scotland 2015 Published December
Understanding our report and advice: Antimicrobial wound dressings (AWDs) for chronic wounds Health technology assessment report 13 December 2015 Healthcare Improvement Scotland 2015 Published December
Adjunctive Therapies: The Use of Skin Substitutes and Growth Factors in Venous Leg Ulceration (VLU)
 Adjunctive Therapies: The Use of Skin Substitutes and Growth Factors in Venous Leg Ulceration (VLU) Sami Khan, MD FACS Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery SUNY-Stony
Adjunctive Therapies: The Use of Skin Substitutes and Growth Factors in Venous Leg Ulceration (VLU) Sami Khan, MD FACS Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery SUNY-Stony
PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE
 Number 5 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE METEOR CRATER, ARIZONA, USA LEG ULCERS Ulcer Full thickness loss of epidermis and some dermis, which will heal with scarring
Number 5 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE METEOR CRATER, ARIZONA, USA LEG ULCERS Ulcer Full thickness loss of epidermis and some dermis, which will heal with scarring
Wound Healing Community Outreach Service
 Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Wound Management Education Plan January 2011 December 2011 Author: Michelle Gibb Nurse Practitioner Wound Management Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Institute
Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Wound Management Education Plan January 2011 December 2011 Author: Michelle Gibb Nurse Practitioner Wound Management Wound Healing Community Outreach Service Institute
Cost and dressing evaluation of hydrofiber and alginate dressings in the management of community-based patients with chronic leg ulceration
 Cost and dressing evaluation of hydrofiber and alginate dressings in the management of community-based patients with chronic leg ulceration Harding K G, Price P, Robinson B, Thomas S, Hofman D Record Status
Cost and dressing evaluation of hydrofiber and alginate dressings in the management of community-based patients with chronic leg ulceration Harding K G, Price P, Robinson B, Thomas S, Hofman D Record Status
Four Layer Versus Actico Cohesive Short Stretch Bandage Background
 Four Layer Versus Actico Cohesive Short Stretch Bandage Background Cochrane Systematic Review 6/2/01 "Five small studies found no difference in healing between multi-layer high compression (4-layer bandage
Four Layer Versus Actico Cohesive Short Stretch Bandage Background Cochrane Systematic Review 6/2/01 "Five small studies found no difference in healing between multi-layer high compression (4-layer bandage
Data extraction. Specific interventions included in the review Dressings and topical agents in relation to wound healing.
 Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson E A, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D Authors' objectives
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson E A, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D Authors' objectives
SDMA Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
The fber dressing you would design
 The fber dressing you would design Easier removal1 Superior fuid retention2 WITH HYDROLOCK TECHNOLOGY We discovered that fber dressings could perform even better Here at Mölnlycke Health Care, we have
The fber dressing you would design Easier removal1 Superior fuid retention2 WITH HYDROLOCK TECHNOLOGY We discovered that fber dressings could perform even better Here at Mölnlycke Health Care, we have
Franck David 1 Jean-Louis Wurtz 2 Nicolas Breton 3 Olivier Bisch 4 Philippe Gazeu 5 Jean-Charles Kerihuel 6 Odile Guibon 7
 Received: 27 July 2017 Revised: 6 October 2017 Accepted: 11 October 2017 DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12853 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial comparing the performance of a soft silicone-coated
Received: 27 July 2017 Revised: 6 October 2017 Accepted: 11 October 2017 DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12853 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial comparing the performance of a soft silicone-coated
Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected dressings enhance the body s ability to heal the wound. Progression Towards Healing
 Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types. Summary
 Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
o Venous edema o Stasis ulcers o Varicose veins (not including spider veins) o Lipodermatosclerosis
 Wound Care Equipment and Supply Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid July 1, 2018 Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2018, wound care equipment and supply benefits will change for Texas
Wound Care Equipment and Supply Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid July 1, 2018 Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2018, wound care equipment and supply benefits will change for Texas
Application Guide for Full-Thickness Wounds
 Application Guide for Full-Thickness Wounds PriMatrix Dermal Repair Scaffold PriMatrix Ag Antimicrobial Dermal Repair Scaffold Application Guide for Full Thickness Wounds PriMatrix is a unique dermal repair
Application Guide for Full-Thickness Wounds PriMatrix Dermal Repair Scaffold PriMatrix Ag Antimicrobial Dermal Repair Scaffold Application Guide for Full Thickness Wounds PriMatrix is a unique dermal repair
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. A guide to help minimise pain, trauma and stress
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers A guide to help minimise pain, trauma and stress From day one, Safetac was about less pain to patients. It s an easy story it does not stick to the wound, so it does not damage or
Diabetic Foot Ulcers A guide to help minimise pain, trauma and stress From day one, Safetac was about less pain to patients. It s an easy story it does not stick to the wound, so it does not damage or
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing
 Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
Venous Leg Ulcers. Care for Patients in All Settings
 Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
The skin consists of the epidermis, dermis. The challenge of skin tears and lacerations in an emergency environment
 The challenge of skin tears and lacerations in an emergency environment KEY WORDS Atraumatic Non-adhesive silicone foam Patient satisfaction Skin tear Acute traumatic skin injuries are increasing in both
The challenge of skin tears and lacerations in an emergency environment KEY WORDS Atraumatic Non-adhesive silicone foam Patient satisfaction Skin tear Acute traumatic skin injuries are increasing in both
ALLEVYN Life Advanced Foam Wound Dressings
 ALLEVYN Life Advanced Foam Wound Dressings ALLEVYN Life Dressings have a multi-layered design incorporating hydrocellular foam, a hyper-absorber lock away core and a masking layer that has been designed
ALLEVYN Life Advanced Foam Wound Dressings ALLEVYN Life Dressings have a multi-layered design incorporating hydrocellular foam, a hyper-absorber lock away core and a masking layer that has been designed
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: localised and generalised types
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: localised and generalised types This leaflet explains about the localised and generalised
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: localised and generalised types This leaflet explains about the localised and generalised
INTEGRATED THERAPEUTIC SOLUTIONS TO MANAGE AND PREVENT DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS
 INTEGRATED THERAPEUTIC SOLUTIONS TO MANAGE AND PREVENT DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS UE REMOVE EXU D R IA ER T C D TISS UIL EB ATE AN DB A REMOVE REBUILD REDUCE Cutimed Siltec Sorbact featuring DACC Technology
INTEGRATED THERAPEUTIC SOLUTIONS TO MANAGE AND PREVENT DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS UE REMOVE EXU D R IA ER T C D TISS UIL EB ATE AN DB A REMOVE REBUILD REDUCE Cutimed Siltec Sorbact featuring DACC Technology
INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS
 WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
Introducing Mepilex Transfer Ag It all adds up to undisturbed healing. Antimicrobial wound contact layer with Safetac technology
 Introducing Mepilex Transfer Ag It all adds up to undisturbed healing Antimicrobial wound contact layer with Safetac technology Mepilex Transfer Ag Help the body heal The importance of less pain The body
Introducing Mepilex Transfer Ag It all adds up to undisturbed healing Antimicrobial wound contact layer with Safetac technology Mepilex Transfer Ag Help the body heal The importance of less pain The body
We look forward to serving you.
 ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers
 A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
A multinational survey of the assessment of pain when removing dressings. Richard White
 A multinational survey of the assessment of pain when removing dressings Richard White Abstract Background: Skin damage caused by repeated application and removal of adhesive dressings can result in trauma
A multinational survey of the assessment of pain when removing dressings Richard White Abstract Background: Skin damage caused by repeated application and removal of adhesive dressings can result in trauma
Evaluation of the Use of a Silver Collagen Amorphous Gel in the Healing of Post Surgical and Dehisced Lesions
 Evaluation of the Use of a Silver Collagen Amorphous Gel in the Healing of Post Surgical and Dehisced Lesions Presented by: Kathryn Khandaker, RN, BSN, CWCN and Deanna Sue Kohl, RN, BSN, CWOCN, CFCN Introduction:
Evaluation of the Use of a Silver Collagen Amorphous Gel in the Healing of Post Surgical and Dehisced Lesions Presented by: Kathryn Khandaker, RN, BSN, CWCN and Deanna Sue Kohl, RN, BSN, CWOCN, CFCN Introduction:
CASE STUDIES SERIES 2017
 INTERNATIONAL CASE STUDIES Case studies evaluation: BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing in moderate to highly exuding wounds CASE STUDIES SERIES 2017 PUBLISHED BY: Wounds International 1.01 Cargo Works 1 2
INTERNATIONAL CASE STUDIES Case studies evaluation: BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing in moderate to highly exuding wounds CASE STUDIES SERIES 2017 PUBLISHED BY: Wounds International 1.01 Cargo Works 1 2
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
Many patients with chronic wounds. Case reports. The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series
 Case reports The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series Author: Liezl Naude Many patients with chronic wounds will develop infection (Landis et al, 2007; Sibbald
Case reports The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series Author: Liezl Naude Many patients with chronic wounds will develop infection (Landis et al, 2007; Sibbald
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment. Michelle Greenwood. Lorraine Grothier. Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust
 Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE LEG ULCERS. Ulcer Full thickness loss of epidermis and some dermis, which will heal with scarring.
 Number 5 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE METEOR CRATER, ARIZONA, USA LEG ULCERS UPDATED PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE SEPTEMBER 2013 Ulcer Full thickness loss of
Number 5 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE METEOR CRATER, ARIZONA, USA LEG ULCERS UPDATED PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE SEPTEMBER 2013 Ulcer Full thickness loss of
Novel Approaches for Accelerating Wound Healing Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Accelerating Wound Healing Telemedicine
 Novel Approaches for Accelerating Wound Healing Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Accelerating Wound Healing Telemedicine Dr. Julian Vitse, Montellier University Hospital, France Negative Pressure Wound
Novel Approaches for Accelerating Wound Healing Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Accelerating Wound Healing Telemedicine Dr. Julian Vitse, Montellier University Hospital, France Negative Pressure Wound
Managing Wounds. Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse
 Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
Do all foam dressings have the same efficacy in the treatment of chronic wounds? Janice Bianchi, David Gray, John Timmons, Sylvie Meaume
 Do all foam dressings have the same efficacy in the treatment of chronic wounds? The challenge of chronic wounds remains significant both in terms of clinical management, impact on patients and cost to
Do all foam dressings have the same efficacy in the treatment of chronic wounds? The challenge of chronic wounds remains significant both in terms of clinical management, impact on patients and cost to
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Documentation Tips Job Aid
 Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
Making the Most of your Dressing Products Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE
 Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE
 WHEN CHILDHOOD HURTS: EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC LYNN CLARK, RN, MS, CPNP-PC, AP-PMN CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC NOTHING TO DISCLOSE
WHEN CHILDHOOD HURTS: EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC LYNN CLARK, RN, MS, CPNP-PC, AP-PMN CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE JENNY STYERS, RN-BC, MSN, CPNP-AC/PC NOTHING TO DISCLOSE
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR
 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
Traditional Silicone Technology
 Innovative Non-Silicone Low Trauma Adhesives versus Traditional Silicone Technology A Review and Comparison Alan Neil Medical Industry Consultant Advanced Wound Care Lohmann Corporation 2016 Chronic wound
Innovative Non-Silicone Low Trauma Adhesives versus Traditional Silicone Technology A Review and Comparison Alan Neil Medical Industry Consultant Advanced Wound Care Lohmann Corporation 2016 Chronic wound
An investigation of Cutimed Sorbact as an antimicrobial alternative in wound management
 An investigation of Cutimed Sorbact as an antimicrobial alternative in wound management G Kammerlander, E Locher, A Suess-Burghart, B von Hallern, P Wipplinger Abstract Background: Antimicrobial dressings
An investigation of Cutimed Sorbact as an antimicrobial alternative in wound management G Kammerlander, E Locher, A Suess-Burghart, B von Hallern, P Wipplinger Abstract Background: Antimicrobial dressings
1/5. Introduction. Primary endpoint Time to reach readiness for closure by surgical intervention or left for closure by secondary intention
 1/5 Introduction Materials and methods Animal studies show that intermittent NPWT has potential to increase the rate of granulation tissue formation compared with adjustable intermittent (AI) NPWT 1 However,
1/5 Introduction Materials and methods Animal studies show that intermittent NPWT has potential to increase the rate of granulation tissue formation compared with adjustable intermittent (AI) NPWT 1 However,
Level 2 Leg Ulcer Management Service. Service Level Agreement Background. Contents:
 Level 2 Leg Ulcer Management Service Service Level Agreement 2016-2019 Contents: 1. Background to Leg Ulcer Management Service 2. Service Details 3. Accreditation 4. Service Standards 5. Finance Details
Level 2 Leg Ulcer Management Service Service Level Agreement 2016-2019 Contents: 1. Background to Leg Ulcer Management Service 2. Service Details 3. Accreditation 4. Service Standards 5. Finance Details
The Georgetown Team Approach to Diabetic Limb Salvage: 2013
 The Georgetown Team Approach to Diabetic Limb Salvage: 2013 John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Disclosures: None Need
The Georgetown Team Approach to Diabetic Limb Salvage: 2013 John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Disclosures: None Need
Integra. PriMatrix Dermal Repair Scaffold PATIENT INFORMATION. Questions? Contact us: Clinician: Phone #: In case of emergency, dial 9-1-1
 Integra PriMatrix Dermal Repair Scaffold PATIENT INFORMATION Questions? Contact us: Clinician: Phone #: In case of emergency, dial 9-1-1 Your Path to Recovery Your health care provider has chosen to use
Integra PriMatrix Dermal Repair Scaffold PATIENT INFORMATION Questions? Contact us: Clinician: Phone #: In case of emergency, dial 9-1-1 Your Path to Recovery Your health care provider has chosen to use
John Timmons, David Gray, Fiona Russell
 Silflex soft silicone wound contact dressing It is hard to believe that it has taken so long for the message to get through, that dressings and dressing removal should not cause additional pain or trauma
Silflex soft silicone wound contact dressing It is hard to believe that it has taken so long for the message to get through, that dressings and dressing removal should not cause additional pain or trauma
Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice
 Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice Wound management Conclusion In an observational study of 86
Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice Wound management Conclusion In an observational study of 86
Open Wound( 개방창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이있는경우 ex)abrasion, Burn,Laceration 등 Closed Wound( 폐쇄창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이없는내부조직의손상 ex)closed Fracture, Ligament tear 등
 신체조직의연속성이파괴된상태 Open Wound( 개방창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이있는경우 ex)abrasion, Burn,Laceration 등 Closed Wound( 폐쇄창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이없는내부조직의손상 ex)closed Fracture, Ligament tear 등 Partial Thickness Skin Injury - dermis 의일부만손상을입은경우
신체조직의연속성이파괴된상태 Open Wound( 개방창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이있는경우 ex)abrasion, Burn,Laceration 등 Closed Wound( 폐쇄창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이없는내부조직의손상 ex)closed Fracture, Ligament tear 등 Partial Thickness Skin Injury - dermis 의일부만손상을입은경우
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Silver Dressings. Sajida Khatri PrescQIPP Primary Care Lead.
 Silver Dressings Sajida Khatri PrescQIPP Primary Care Lead www.prescqipp.info Available at: www.prescqipp.info/silverdressings 2 Introduction PrescQIPP Silver dressings bulletin published in March 2014
Silver Dressings Sajida Khatri PrescQIPP Primary Care Lead www.prescqipp.info Available at: www.prescqipp.info/silverdressings 2 Introduction PrescQIPP Silver dressings bulletin published in March 2014
Ray Norris, Rachel Henchy
 Use of low frequency ultrasound therapy in the treatment of recalcitrant leg ulcers: case series This series of case reports looks at the efficacy of low frequency ultrasound using the MIST Therapy System
Use of low frequency ultrasound therapy in the treatment of recalcitrant leg ulcers: case series This series of case reports looks at the efficacy of low frequency ultrasound using the MIST Therapy System
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
4-layer compression bandaging system (includes microbe binding wound contact layer) Latex-free, 4-layer compression bandaging system
 JOBST Comprifore JOBST Comprifore at a glance: provides effective levels of sustained graduated compression provides built in safety and ease of application Insures compliance and maximum healing for cost
JOBST Comprifore JOBST Comprifore at a glance: provides effective levels of sustained graduated compression provides built in safety and ease of application Insures compliance and maximum healing for cost
2008 American Medical Association and National Committee for Quality Assurance. All Rights Reserved. CPT Copyright 2007 American Medical Association
 Chronic Wound Care ASPS #1: Use of wound surface culture technique in patients with chronic skin ulcers (overuse measure) This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance Measure
Chronic Wound Care ASPS #1: Use of wound surface culture technique in patients with chronic skin ulcers (overuse measure) This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance Measure
GP Practice Woundcare Formulary
 Agreed jointly by Ipswich and East Suffolk and West Suffolk Clinical Commissioning Groups GP Practice Woundcare Formulary Version 28 October 2017 Formulary items should be prescribed wherever possible.
Agreed jointly by Ipswich and East Suffolk and West Suffolk Clinical Commissioning Groups GP Practice Woundcare Formulary Version 28 October 2017 Formulary items should be prescribed wherever possible.
Interesting Case Series. Skin Grafting in Pyoderma Gangrenosum
 Interesting Case Series Skin Grafting in Pyoderma Gangrenosum Marco Romanelli, MD, PhD, Agata Janowska, MD, Teresa Oranges, MD, and Valentina Dini, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology, University of Pisa,
Interesting Case Series Skin Grafting in Pyoderma Gangrenosum Marco Romanelli, MD, PhD, Agata Janowska, MD, Teresa Oranges, MD, and Valentina Dini, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology, University of Pisa,
A New Approach To Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using Keratin Gel Technology
 A New Approach To Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using Keratin Gel Technology Farheen Walid, BA, Shrunjay R. Patel, BSc, Stephanie Wu, DPM, MS Center for Lower Extremity Ambulatory Research (CLEAR), Scholl College
A New Approach To Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using Keratin Gel Technology Farheen Walid, BA, Shrunjay R. Patel, BSc, Stephanie Wu, DPM, MS Center for Lower Extremity Ambulatory Research (CLEAR), Scholl College
Reality TV Managing patients in the real world. Wounds UK Harrogate 2009
 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Wounds UK Harrogate 2009 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Brenda M King Nurse Consultant Tissue Viability Sheffield PCT Harrogate 2009 Familiar
Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Wounds UK Harrogate 2009 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Brenda M King Nurse Consultant Tissue Viability Sheffield PCT Harrogate 2009 Familiar
Cuticell Contact. Silicone Wound Contact Layer. Highly Flexible Atraumatic Single-sided adherence
 Cuticell Contact Silicone Wound Contact Layer Highly Flexible Atraumatic Single-sided adherence Cuticell Contact impressively wound calming Cuticell Contact is a silicone wound contact layer that has a
Cuticell Contact Silicone Wound Contact Layer Highly Flexible Atraumatic Single-sided adherence Cuticell Contact impressively wound calming Cuticell Contact is a silicone wound contact layer that has a
Acute and Chronic WOUND ASSESSMENT. Wound Assessment OBJECTIVES ITEMS TO CONSIDER
 WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
The clinical performance of PermaFoam cavity in the management of chronic wounds: a prospective, non-randomized clinical observation study
 The clinical performance of PermaFoam cavity in the management of chronic wounds: a prospective, non-randomized clinical observation study Woundmanagement Summary In the treatment of patients with chronic
The clinical performance of PermaFoam cavity in the management of chronic wounds: a prospective, non-randomized clinical observation study Woundmanagement Summary In the treatment of patients with chronic
Chapter 28. Wound Care. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 28 Wound Care Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 28.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe skin tears, circulatory ulcers, and diabetic
Chapter 28 Wound Care Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 28.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe skin tears, circulatory ulcers, and diabetic
Promoting best practice in leg ulcer management
 Promoting best practice in leg ulcer management Sylvie Hampton MA BSc (Hons) DpSN RGN Independent Tissue Viability Consultant Nurse Leg Ulcers - What are the causes? Chronic leg ulcers are defined as those
Promoting best practice in leg ulcer management Sylvie Hampton MA BSc (Hons) DpSN RGN Independent Tissue Viability Consultant Nurse Leg Ulcers - What are the causes? Chronic leg ulcers are defined as those
Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants-
 Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants- Wound Cleansing,Types & Presentation Elizabeth DeFeo, RN, WCC, OMS, CWOCN Wound, Ostomy, & Continence Specialist ldefeo@cornerstonevna.org Outline/Agenda At completion
Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants- Wound Cleansing,Types & Presentation Elizabeth DeFeo, RN, WCC, OMS, CWOCN Wound, Ostomy, & Continence Specialist ldefeo@cornerstonevna.org Outline/Agenda At completion
Excision of Morton s Neuroma
 Excision of Morton s Neuroma Day Surgery Unit Patient information leaflet This leaflet outlines the risks, general advice and information about foot surgery called an excision of a Morton s Neuroma. If
Excision of Morton s Neuroma Day Surgery Unit Patient information leaflet This leaflet outlines the risks, general advice and information about foot surgery called an excision of a Morton s Neuroma. If
DEBRIDEMENT. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
Static Magnet device, 4UlcerCare, prevents Leg Ulcer Recurrence: Potential Cost Savings in leg ulcer management
 Static Magnet device, 4UlcerCare, prevents Leg Ulcer Recurrence: Potential Cost Savings in leg ulcer management Abstract Nyjon K. Eccles MRCP PhD The Chiron Clinic, 104 Harley St, London W1G 7JD info@chironclinic.com
Static Magnet device, 4UlcerCare, prevents Leg Ulcer Recurrence: Potential Cost Savings in leg ulcer management Abstract Nyjon K. Eccles MRCP PhD The Chiron Clinic, 104 Harley St, London W1G 7JD info@chironclinic.com
Post-surgical wound management of pilonidal cysts by using a haemoglobin spray
 Post-surgical wound management of pilonidal cysts by using a haemoglobin spray Nesat Mustafi 1 & Peter Engels 2 1 Wound center, Nordwest Hospital, Frankfurt, Germany, 2 Bergisch Gladbach, Germany Objective:
Post-surgical wound management of pilonidal cysts by using a haemoglobin spray Nesat Mustafi 1 & Peter Engels 2 1 Wound center, Nordwest Hospital, Frankfurt, Germany, 2 Bergisch Gladbach, Germany Objective:
Management of diabetic foot ulcers with a TLC-NOSF wound dressing
 Management of diabetic foot ulcers with a TLC-NOSF wound dressing l Objective: To evaluate the efficacy, tolerance and acceptability of UrgoStart Contact (Laboratoires Urgo), a new wound dressing impregnated
Management of diabetic foot ulcers with a TLC-NOSF wound dressing l Objective: To evaluate the efficacy, tolerance and acceptability of UrgoStart Contact (Laboratoires Urgo), a new wound dressing impregnated
