Pressure Ulcers ecourse
|
|
|
- Archibald Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors & Implications Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 1 of 38
2 Pressure Ulcers 2.3 Risk Factors & Implications 1. General Risk Factors 1.1 Section Title JILL: Hi, I m Jill along with Mark. Welcome to this final lesson in Module 2 of the Pressure Ulcers course. In this unit we will be covering 3 topics the general risk factors for developing pressure ulcers the risk factors for pressure ulcers in a hospital setting and the implications and consequences that pressure ulcers have on patients and the healthcare system. Are you ready, Mark? MARK: Yes, I am let s go! CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 2 of 38
3 1.2 Populations at Risk JILL: So Mark, what types of individuals do you think are most at risk for developing pressure ulcers? MARK: From what we have learned about the causes of pressure ulcers, I would guess that those with restricted mobility. JILL: Yes, you re right. The patients or residents that are routinely considered at risk for pressure ulcers include the following: patients or residents who are bedridden or use wheelchairs. Other vulnerable individuals include stroke victims patients and residents with diabetes or dementia. Patients who are sedated for any reason and individuals with spinal cord injuries those who cannot feel their legs are both at risk for pressure ulcers. MARK: So these are the types of patients and residents that we need to watch closely for possible pressure ulcer development. JILL: Uh huh let now take a look at some general risk factors. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 3 of 38
4 1.3 General Risk Factors JILL: Here are eleven common risk factors associated with the development of pressure ulcers. MARK: Wow that list is longer than I expected! I imagine that we are going to examine each of these in a bit more detail. JILL: Yes we are Mark. Let s start with immobility. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 4 of 38
5 1.4 Immobility JILL: One of the greatest risks for pressure ulcers is impaired mobility. These patients are unable to adequately adjust their positions frequently enough to relieve pressure. MARK: That certainly makes sense. I can think of several reasons why individuals become immobile. Some examples that come to mind are patients who are: neurologically impaired heavily sedated or anesthetized restrained or demented or recovering from a traumatic injury such as a pelvic or femur fracture. Did I miss any important ones, Jill? JILL: No, I think you got the main reasons for impaired mobility. If immobility is prolonged, muscle and soft tissue atrophy may develop, decreasing the bulk over which bony prominences are supported. This increases the pressure at these sites, and thus increases the risk of pressure ulcers. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 5 of 38
6 1.5 Advanced Age JILL: Mark, what features of old age do you think contribute to pressure ulcer risk? MARK: The first reason is that as you get older, your skin becomes more fragile. You are more susceptible to skin and tissue damage. JILL: Right. Skin become more fragile as epidermal turnover slows, vascularization decreases, and skin layers adhere less securely to one another. Another reason? MARK: I would say that older people have less fat. JILL: Yes, older adults have less lean body mass and less subcutaneous tissue to cushion bony areas. Anything else? MARK: I would think that seniors generally have more health problems that would make them more vulnerable. JILL: Yes, they do. Underlying problems such as poor nutrition and hydration and impaired respiratory and immune systems increase pressure ulcer risks. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 6 of 38
7 1.6 Incontinence JILL: Another risk factor is incontinence. Mark, can you summarize the reasons why incontinence increases the risks for pressure ulcer development? MARK: Sure thing. Incontinence increases a patient s exposure to moisture and over time increases the risk of skin breakdown. Urinary and fecal incontinence can result in excessive moisture and chemical irritation. Fecal incontinence can cause more damage because the pathogens in the stools may result in increased infections. JILL: Yes, moisture is a predisposing factor with regard to the development of pressure ulcers. Moisture alters the resiliency of the epidermis to external forces. Shear and friction are increased in the presence of mild to moderate moisture. However, shear and friction actually decrease when there is a large amount of moisture. MARK: Interesting so that means I should keep my incontinent patients either very dry, and let them get very wet! Just kidding! (chuckles) JILL: Yes, I know you are. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 7 of 38
8 1.7 Infection JILL: Infection is considered a risk factor. Compressed skin has a lower resistance to bacterial infections. Infection may also reduce the pressure needed to cause tissue death. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 8 of 38
9 1.8 Low Blood Pressure JILL: Low blood pressure is another risk factor. MARK: Everyone knows that high blood pressure is bad for you, but I wasn t aware that low blood pressure is also a risk. Why is this? JILL: Low blood pressure can lead to tissue ischemia, particularly in patients with vascular disorders. As tissue perfusion drops, the skin is less tolerant of sustained external blood pressure, increasing the risk of damage from ischemia. MARK: Okay, that makes sense. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 9 of 38
10 1.9 Malnutrition JILL: A strong correlation exists between poor nutrition and the development of pressure ulcers. Why do you think that is Mark? MARK: Proper nutrition will keep your skin and body healthy and thus more resistant to pressure ulcers. JILL: Yes, that is correct. Also the body requires increased protein for healing malnutrition decreases protein levels and albumin. A direct correlation exists between pressure ulcer stage and the degree of hypoalbuminemia. MARK: I guess that makes a strong case to get my patients to eat lots of steak and peas to keep their protein levels up. (laughs). JILL: One study found that patients admitted to hospital with pressure ulcers were below the usual body weight had low pre-albumin levels and were not getting enough nutrition to meet their needs. Certain vitamin deficiencies, particularly vitamins A, C and E may also contribute to pressure ulcer development. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 10 of 38
11 MARK: Interesting information about nutrition and vitamins. What other intrinsic factors are there? JILL: Dehydration is another determining factor in poor nutritional status and susceptibility to pressure ulcers. Water is an essential nutrient and serves as a solvent for minerals, vitamins and amino acids. It also helps maintain normal cell function. In addition, water is critical to the hydration of wound sites and in oxygen perfusion. Adequate hydration is an essential part of wound healing. MARK: I would think that, in a pinch, beer would work just as well to keep the patient hydrated. (laughs). JILL: Yes, Mark, I m sure your patients would appreciate the beer to go along with their steak and peas. (giggles). CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 11 of 38
12 1.10 Devices JILL: Here is one risk factor that we may not pay enough attention to medical equipment! MARK: Are you saying that the devices we use to help patients get better, may actually contribute to development of pressure ulcers? JILL: Yes. As we discussed before, any damage resulting from medical devices should be classified and recorded as a pressure ulcer. Here are some examples. Pressure ulcers occur on patients lips due to pressure from endotracheal tubes ears due to nasal cannula and on thighs because of the hard surfaces of urinary catheters. MARK: Now that I know that, I am going to be extra careful in checking these devices on my patients to make sure that no rubbing is happening. What other factors are there? CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 12 of 38
13 1.11 Friction JILL: Well, remember our discussion about you ironing the bed sheets? Rubbing against sheets, wrinkled bedding or clothing, and poorly adjusted supports such as splints and casts are common causes of pressure ulcers. MARK: Okay, something else to check. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 13 of 38
14 1.12 Medications JILL: In addition to the increased risk of pressure ulcers caused by medical devices, we have the same problem with some medications. MARK: I don t see how taking medications can possibly cause pressure ulcers. JILL: Well, Mark, some medications can contribute to breakages in skin integrity. Tranquillizers, sedatives and opiates decrease sensory perception and mobility. Steroids can disrupt the normal healing process due to their anti-inflammatory properties, and decrease the general health of tissues. MARK: Okay, I see what you mean. What s left? I suppose next you will be telling me whether I am happy or sad increases my risk for pressure ulcers? (sarcastically) CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 14 of 38
15 1.13 Mental Health JILL: In a way, you are right... it does! Mental health conditions, especially severe depression, can contribute to an increased risk of pressure ulcers. Depressed patients often neglect their personal hygiene, making their skin more vulnerable to injury and infection. Depressed individuals are also less likely to get up and move around. And as we know, restricted mobility is a significant risk factor. Emotional stress has been associated with the formation of pressure ulcers. One of the most common stressors is hospitalization. Up to 75% of elderly patients experience a decrease in functional ability from hospital admission to discharge. MARK: Oh great in addition to all my other nursing duties, now I have to keep my patients happy too? JILL: Yes, Mark it all part of being an exceptional nurse! (Laughs) CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 15 of 38
16 1.14 Smoking JILL: And the last factor found to contribute to pressure ulcers is cigarette smoking. Heavy smokers have a higher incidence of pressure ulcers, and also appear to have higher recurrence rates. MARK: Another good reason to stop smoking! CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 16 of 38
17 1.15 Summary JILL: We have now discussed the 11 known risk factors that contribute to the development of pressure ulcers. To see how many you remembered type the factors into the box on this slide. When you are finished, click on the DONE button to see how you did. After you have reviewed the answers, click on the NEXT button to continue this lesson. Mark you can do it too. MARK: Okay! CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 17 of 38
18 2. Hospital Risk Factors 2.1 Section Title JILL: Over the next few slides we are going to take a look at the risk factors in specific hospital environments. These include the operating room, intensive care, pediatrics and the emergency department. MARK: Gee, it never occurred to me that hospitals add to the risks of developing pressure ulcers. JILL: Yes they do. Accurate and current statistics are difficult to come by. However, the prevalence of pressure ulcers ranges from 10% to 23% in hospitalized patients in western societies. The proportion of newly hospitalized patients developing pressure ulcers ranges between 7% and 38%. 1 Estimates suggest that 50% of the most dangerous hospital acquired pressure ulcers are preventable. 2 Finally one study found that the incidence of pressure ulcers in surgical patients can be as high as 45%. 3 MARK: Gee those numbers are much higher than we what would like to see. [Reference: 1 Schoonhoven; 2 Virgo; 3 Pressure Ulcer Toolkit, p. 10 ] CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 18 of 38
19 2.2 Surgery JILL: Yes they are! Let s start by looking at the risks for pressure ulcers associated with surgery. Lack of mobility is a particular problem for patients recovering from the effects of surgery. Impaired mobility is present in individuals who have been sedated or anesthetized have undergone spinal surgery or may be recovering from a traumatic injury. All of these patients lose the ability to independently change position in bed. MARK: What about the anesthesia? I m sure that increases the risk. JILL: Anesthesia blocks a patient s sensitivity to pain and pressure, causing tissue damage vulnerability. Anesthesia agents can result in some degree of vasodilation that is reflected in lowering of blood pressure and a decrease in tissue perfusion. Finally the compound effect of anesthesia and the cold operating room table causes decreased perfusion. JILL: Another factor is the intensity and duration of pressure. Low-intensity pressure over a long period of time can cause tissue damage, just as high-intensity pressure can cause tissue damage in a short period. Most tissue can withstand excessive pressure only for short periods. It has CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 19 of 38
20 been found that even the healthiest patient is at risk for tissue damage if a surgical procedure is more than 4 hours. JILL: And not surprisingly, increased age increases the risks of pressure ulcers during and after surgery. We have already talked about why older people have skin that is more vulnerable to pressure, shear and friction. MARK: Wow, those are a bunch of risks! I can now see why extra care and attention needs to be paid to patients who may have had surgery. JILL: Wait, we re not finished yet there are a few more risk factors. MARK: Really? What are they? CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 20 of 38
21 2.3 Surgery 2 JILL: Peripheral vascular disease has an impact on pressure ulcer development for patients undergoing surgery. The blood supply in the legs becomes restricted due to the buildup of fatty substances in the arteries of the legs. MARK: And thus with a reduced blood supply to the lower parts of the body, this increases the risk of pressure ulcers developing there. JILL: Right. Another factor that affects risk is the type of surgical procedure. Patients that have heart, vein, trauma injury, transplant, or bariatric surgery, or procedures that involve at-risk positioning such as sitting are considered a high risk. MARK: What about medications do they contribute to risks for developing pressure ulcers? CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 21 of 38
22 JILL: Unfortunately yes they do. Some medications contribute to breakage of skin integrity. Opiates can decrease sensory perception and mobility. Medications given to reverse hypotension can increase oxygenation, particularly in older adults. Hypnotics and sedatives can contribute to a decrease in blood pressure, causing peripheral hypo-perfusion. JILL: Finally, patients being treated for other health conditions may be at greater risk. For example, diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular and peripheral deficiencies, diabetes and neurological or respiratory diseases, also affect tissue perfusion. MARK: which contributes to the development of pressure ulcers. That is some list of risks! Hopefully this is a good reminder to nurses caring for post-operative patients that they need to be extra vigilant and careful. JILL: Good point Mark. Surgery patients are already in enough pain and distress. The last thing they need is to develop pressure ulcers. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 22 of 38
23 2.4 Intensive Care JILL: Patients admitted to an intensive care unit are among the main groups at high risk for pressure ulcer development. MARK: I can understand why. These patients are often immobile for long periods of time. And because they are in intensive care, they obviously have more serious illnesses. JILL: The most common sites for pressure ulcers in intensive care units are the sacrum and heels. This is because most intensive care patients are bedridden. MARK: So that takes care of the intensive care unit. What was next oh yes pediatrics. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 23 of 38
24 2.5 Pediatrics JILL: Yes, on to pediatrics. Acutely ill and immobilized neonates and children are particularly at risk for the development of pressure ulcers. The most common body sites include the ear, sacrum, occipital area and scapula. Infants and children are susceptible to pressure ulcers in areas different from those of adults. Knowledge of the more common pressure ulcer sites in children is important in preventive measures. MARK: Good to know. What are the other risks to hospitalized children? JILL: The length of time of endotracheal tube placement is related to the development of pressure ulcers. Intubation is designed to protect the child s airway but often requires restricting movement and immobilizing the child s head. The use of sedation and paralyzing agents also plays a role in reducing spontaneous body movements. MARK: I see anemia is on the list. What role does anemia play? JILL: Anemia has emerged as a highly significant factor in pressure ulcer development in children. However, the reasons for this are still unclear. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 24 of 38
25 MARK: I see that nutrition is on this list as well. Same effects as for adults? JILL: Yes. An estimated 15% to 20% of patients admitted to the pediatric intensive unit are malnourished. Nutritional factors, such as impaired intake, low birth weight, low body weight, unintentional weight loss and dehydration may all contribute to the development of pressure ulcers. Malnutrition may cause systemic and immunologic effects. These may further compromise this pediatric population if the effects limit their tissue tolerance to pressure, frictional forces and shear. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 25 of 38
26 2.6 Pediatrics 2 MARK: So medical devices can cause tissue damage in children as well as adults? JILL: Yes. Early staff identification of medical equipment or usage problems can help prevent skin injuries. Daily checks and care of the skin under continuous monitoring devices will prevent the development of pressure ulcers. JILL: Another risk factor with the pediatric population is limited sensory perception. The decreased ability for patients to perceive or to respond to pressure discomfort means they are unable to change position. Infants may not be able to respond to perception of pressure because of immaturity or level of health. MARK: Tissue tolerance is this the same as we discussed before? JILL: Yes it is. Tissue tolerance is the second major determinant of pressure ulcer development. Tissue tolerance in pediatrics involves three extrinsic factors. One exposure to moisture such as perspiration, urine, feces, drainage from fistulas, and wounds. Two Exposure to friction such as casts or orthopedic devices; and three exposure to shear. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 26 of 38
27 MARK: Chronic illness or conditions such as cerebral palsy, place the pediatric population at a high risk for developing pressure ulcers. These patients need special attention if medical equipment is used to stabilize them. JILL: Good point Mark. Just to add that for patients with spina bifida, ill-fitting braces may irritate the skin. Because these patients lack feeling in certain parts of their body, they may not realize that wounds are developing. With these patients, devices such as prosthetics, wheelchairs and casts may also cause pressure ulcers. MARK: So, now we go on to the emergency department. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 27 of 38
28 2.7 Emergency JILL: Yes Mark. What do you think are the risk factors in the emergency unit? MARK: One is that it is not uncommon for patients to spend hours, or even days, in emergency. These patients are often laying on hard support surfaces which can create pressure areas. Depending on the severity of their illness, they may not be able to adjust their position to relieve the pressure. The only other risk I can think of is that there may be tissue damage resulting from the transport to the hospital. JILL: Yes, you have covered the main risk factors for pressure ulcers in emergency. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 28 of 38
29 2.8 Summary JILL: That brings us to the end of this section on pressure ulcer risk factors in the hospital. Care to summarize Mark? MARK: Sure thing. We started with surgery the risks for pressure ulcer development include immobility anesthesia pressure peripheral vascular disease type of surgery medications and comorbidities. Next we went to intensive care. The risk factors there are immobility for extended periods of time these patients have serious health issues and the most common pressure ulcer sites are the sacrum and heels. With the pediatric population we learned that sites for pressure ulcers often differ compared to adults length of intubation is a risk factor as are anemia and poor nutrition. Other risk factors for development of pressure ulcers among children are medical devices limited sensory perception tissue tolerance and chronic illness such as cerebral palsy. Finally, we looked at the risks in the emergency ward. These include tissue damage due to transport to the hospital as well as laying on hard surfaces for long periods of time. JILL: Good job, Mark. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 29 of 38
30 3. Implications 3.1 Section Title JILL: We are now at the last section of this unit the implications and consequences of pressure ulcers. We are NOT going to overwhelm you with statistics to prove pressure ulcers are bad! Those of us caring for patients and residents already know that we need to do more to prevent pressure ulcers. We are only going to give a broad overview of the magnitude and implications of the problem. MARK: Oh good I hate statistics! They make my head spin. (laughs) CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 30 of 38
31 3.2 Implications JILL: So Mark we have already taken a look at some the implications and consequences of pressure ulcers in our Introduction to this course. Why don t you briefly review these implications for us? Feel free to elaborate on any of these points. MARK: Sure thing Jill! The most obvious consequence is that pressure ulcers are a source of pain and discomfort to patients and residents. This is particularly true of category 3 and 4 pressure ulcers. The second point is that pressure ulcers can lead to fatal complications. If the wound becomes infected, it can lead to a serious septic infection, making it difficult for patients to recover. Other common implications include acute bone infection, skin infections, joint infection and acute kidney failure. Fortunately, if pressure ulcers are detected early, they are treatable. When a pressure ulcer develops, it adds to the burden of pre-existing illness or condition for the patient or resident. This means that when pressure ulcers develop while in hospital for treatment of other diseases, length of hospital stay and costs increase. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 31 of 38
32 Speaking of costs, treating and healing pressure ulcers is extremely costly for health care organizations. One estimate 5 I saw places the overall annual cost in the United States at between $5 billion and $8.5 billion, with the cost of health care-acquired pressure ulcers running between $2.2 billion and $3.6 billion. That is B for billion! These expenses include additional nursing time, physician visits, prolonged stay in acute care or long term care, diagnostic and operative procedures, wound care products and equipment, and increased need for rehabilitation services. Jill, these are only the costs for one country America. So imagine the costs associated with pressure ulcers worldwide! JILL: Yes, they are huge! MARK: The final major consequence we want to mention is increased legal liabilities. Because pressure ulcers are preventable and avoidable, the development of them in patients under care may be considered negligence. As a result, more and more successful lawsuits are being filed by the patients and families against the health care organization and care givers involved. JILL: Lawsuits are very stressful, time-consuming, costly and can be career killers. It is best to try and avoid them. Thanks for doing that Mark. MARK: Happy to oblige! [Ref: JCR p. 41] CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 32 of 38
33 3.3 Some Numbers JILL: Now for some general statistics. However, I want to remind everyone that statistics can vary significantly due to country, year data was collected, and differences in what is being measured! Having said that, pressure ulcers are the second leading cause of iatrogenic cause of death in the United States, second only to adverse drug events. Approximately 60,000 U.S. patients are estimated to die each year from complications related to health care-acquired pressure ulcers. An estimated 1.3 to 3 million patients in the United States have pressure ulcers, with the highest incidences occurring among older patients, particularly those who are hospitalized or in long term care organizations. MARK: Again, this is one country. But these numbers show that pressure ulcers are a significant problem that needs to be addressed. JILL: Here is one set of statistics about prevalence rates for different types of care organizations in acute care 10 to 18 percent in long term care 2 to 28 percent and in home care the CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 33 of 38
34 rates range from 0 to 29%. Obviously, these rates will vary depending on the risk factors associated with the individual and the institution. MARK: I would think when planning and implementing pressure ulcer prevention programs, it is probably more important to focus on the risk factors for each individual rather than the type of institution. JILL: Yes, I agree. Pressure ulcers are found in all types of health care organizations and institutions. [Ref: JCR 37] CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 34 of 38
35 3.4 More Numbers JILL: And here are few more statistics. The predominant ages of patients and residents developing pressure ulcers are between 71 and 80 years. Pressure ulcer prevalence in long term care organizations is estimated to be from 11 to 30 percent. Children also develop pressure ulcers, primarily in the occipital region in infants and toddlers, and on the sacrum in the young child. It is estimated that pressure ulcers in pediatric intensive care units are as high as 27% and 20% in neonatal intensive care units. MARK: Those numbers are in the ranges that we mentioned before. JILL: There is no ONE correct number. All we are trying to do is provide a general sense of the prevalence of pressure ulcers. [Ref: JCR p. 38] CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 35 of 38
36 3.5 Wound Implications JILL: Finally, here are just a few numbers about the wound implications of pressure ulcers. Pressure ulcers are listed as the direct cause of death in 7 to 8 percent of all patients with paraplegia. Evaluation of large groups of patients has shown that one third of hospitalized patients with pressure ulcers die during hospitalization. More than half the patients who develop pressure ulcers in the acute setting will die over a 12 month period. We are NOT saying that pressure ulcers were the primary cause of death. However pressure ulcers were contributing factors in some instances. MARK: Any more statistics? JILL: No, Mark I think that these are enough to make our point. For those who want more statistics and research data, we have provided a very good resource on the next slide. MARK: I am now convinced more than ever that we need to do a much better job in assessing, preventing and treating pressure ulcers. What I really, really, really want to learn now is what do I as a nurse have to do to make a difference? JILL: That Mark is what you will learn in the remaining modules! This is Jill along with Mark saying thanks for being with us for this module. We will see you again soon. CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 36 of 38
37 3.6 Resources [No narration] CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 37 of 38
38 3.7 The End [No narration] CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.3: Risk Factors and Implications Page 38 of 38
Pressure Ulcers ecourse
 Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup Module 2 Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup Module
Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup Module 2 Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup Module
Pressure Ulcers ecourse
 Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup All Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup All Page
Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup All Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Knowledge Checkup All Page
Pressure Ulcers ecourse
 Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.1: Definition and Causes Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcer ecourse Module 2.1: Definition
Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 2.1: Definition and Causes Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcer ecourse Module 2.1: Definition
Pressure Ulcers ecourse
 Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 4.1: Prevention of Pressure Ulcers Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module
Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 4.1: Prevention of Pressure Ulcers Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module
CARE OF THE NEONATE: ITS ALL ABOUT THE SKIN. Katherine Kunkel, MSN, RNC-NIC, WCC
 CARE OF THE NEONATE: ITS ALL ABOUT THE SKIN Katherine Kunkel, MSN, RNC-NIC, WCC Learning Objectives Recognize what are risk factors for the neonate within the intensive care unit. Understand the physiology
CARE OF THE NEONATE: ITS ALL ABOUT THE SKIN Katherine Kunkel, MSN, RNC-NIC, WCC Learning Objectives Recognize what are risk factors for the neonate within the intensive care unit. Understand the physiology
Pressure Ulcers ecourse
 Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 5.5: Nutrition Guidelines Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 5.5: Nutrition
Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 5.5: Nutrition Guidelines Handout College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta (Canada) CLPNA.com and StudywithCLPNA.com CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse Module 5.5: Nutrition
CARING FOR THE CLIENT ON COMPLETE BEDREST
 CARING FOR THE CLIENT ON COMPLETE BEDREST INTRODUCTION The human body is designed to move. And just as the human body thrives on movement, it suffers when for one reason or another there is enforced immobility.
CARING FOR THE CLIENT ON COMPLETE BEDREST INTRODUCTION The human body is designed to move. And just as the human body thrives on movement, it suffers when for one reason or another there is enforced immobility.
Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet
 Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future Introduction This leaflet is about pressure ulcers and includes information about what they are what can cause them and how they
Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future Introduction This leaflet is about pressure ulcers and includes information about what they are what can cause them and how they
Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet
 Further information about the content, reference sources or production of this leaflet can be obtained from the Patient Information Centre. Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet This information
Further information about the content, reference sources or production of this leaflet can be obtained from the Patient Information Centre. Pressure Ulcers Patient Information Leaflet This information
Protect Your Skin. It s one of the most important things you can do!
 Protect Your Skin It s one of the most important things you can do! What is the skin? It s the largest organ in the body It protects you from the outside world It houses your sensory nerve endings It senses
Protect Your Skin It s one of the most important things you can do! What is the skin? It s the largest organ in the body It protects you from the outside world It houses your sensory nerve endings It senses
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores
 Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores
 Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
Skin matters Preventing Pressure Ulcers: a Guide for Patients and Carers
 Skin matters Preventing Pressure Ulcers: a Guide for Patients and Carers We recommend that you follow the advice within this leaflet and provided by your healthcare provider. However if anything changes
Skin matters Preventing Pressure Ulcers: a Guide for Patients and Carers We recommend that you follow the advice within this leaflet and provided by your healthcare provider. However if anything changes
CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse: Module 4 Quiz II page 1
 CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse: Module 4 Quiz II 1. When are good times to do a skin inspection of a patient or resident? a. Bathing b. Meal times c. Dressing d. Assisting e. Sleeping 2. For patients who
CLPNA Pressure Ulcers ecourse: Module 4 Quiz II 1. When are good times to do a skin inspection of a patient or resident? a. Bathing b. Meal times c. Dressing d. Assisting e. Sleeping 2. For patients who
Minneapolis VA Health Care System. Pressure Ulcers. Let Us Work Together to Protect Your Skin and Prevent Pressure Ulcers
 Minneapolis VA Health Care System Pressure Ulcers Let Us Work Together to Protect Your Skin and Prevent Pressure Ulcers What Are Pressure Ulcers? Pressure ulcers are also called pressure sores or bed sores.
Minneapolis VA Health Care System Pressure Ulcers Let Us Work Together to Protect Your Skin and Prevent Pressure Ulcers What Are Pressure Ulcers? Pressure ulcers are also called pressure sores or bed sores.
Pressure ulcer recognition and prevention. Mark Collier Tissue Viability Nurse Consultant United Lincoln Hospitals NHS Trust
 Pressure ulcer recognition and prevention Mark Collier Tissue Viability Nurse Consultant United Lincoln Hospitals NHS Trust PRESSURE ULCER RECOGNITION AND PREVENTION.. United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS
Pressure ulcer recognition and prevention Mark Collier Tissue Viability Nurse Consultant United Lincoln Hospitals NHS Trust PRESSURE ULCER RECOGNITION AND PREVENTION.. United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS
DOCTOR: The last time I saw you and your 6-year old son Julio was about 2 months ago?
 DOCTOR: The last time I saw you and your 6-year old son Julio was about 2 months ago? MOTHER: Um, ya, I think that was our first time here. DOCTOR: Do you remember if you got an Asthma Action Plan? MOTHER:
DOCTOR: The last time I saw you and your 6-year old son Julio was about 2 months ago? MOTHER: Um, ya, I think that was our first time here. DOCTOR: Do you remember if you got an Asthma Action Plan? MOTHER:
Preventing Pressure Ulcers
 Patient information Preventing Pressure Ulcers i Important information and care guide for patients at risk of pressure ulcers. Reproduced with kind permission from Healthcare Improvement Scotland Golden
Patient information Preventing Pressure Ulcers i Important information and care guide for patients at risk of pressure ulcers. Reproduced with kind permission from Healthcare Improvement Scotland Golden
Objectives are included in the participant handout and include the detail for the last objective: Describe a pressure ulcer prevention program for a
 1 Objectives are included in the participant handout and include the detail for the last objective: Describe a pressure ulcer prevention program for a nursing home, including: Education of residents, staff
1 Objectives are included in the participant handout and include the detail for the last objective: Describe a pressure ulcer prevention program for a nursing home, including: Education of residents, staff
Spinal Cord Injury Info Sheet An information series produced by the Spinal Cord Program at GF Strong Rehab Centre.
 Spinal Cord Injury Info Sheet An information series produced by the Spinal Cord Program at GF Strong Rehab Centre. What does skin do? 1. It protects you. 2. It provides sensory information. 3. It helps
Spinal Cord Injury Info Sheet An information series produced by the Spinal Cord Program at GF Strong Rehab Centre. What does skin do? 1. It protects you. 2. It provides sensory information. 3. It helps
Preventing pressure ulcers
 Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Preventing pressure ulcers Patient information guide for adults at risk of pressure ulcers Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141
Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Preventing pressure ulcers Patient information guide for adults at risk of pressure ulcers Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141
Pressure Injury Assessment Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated October 31,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
H2O to Go! Hydration. It s easier than you think to get dehydrated. No water, no go...
 H2O to Go! Hydration You ve probably heard those narrators on the National Geographic specials say things like, Water gives life, or, Without water there could be no life. They may be overly dramatic,
H2O to Go! Hydration You ve probably heard those narrators on the National Geographic specials say things like, Water gives life, or, Without water there could be no life. They may be overly dramatic,
Stroke. Objectives: After you take this class, you will be able to:
 Stroke Objectives: After you take this class, you will be able to: 1. Describe the signs of a stroke and how a stroke happens. 2. Discuss stroke risk factors. 3. Detail the care and rehabilitation of a
Stroke Objectives: After you take this class, you will be able to: 1. Describe the signs of a stroke and how a stroke happens. 2. Discuss stroke risk factors. 3. Detail the care and rehabilitation of a
Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development
 Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Pressure ulcers can develop in a relatively short time, therefore it is important to prevent them or notice and recognise early signs of damage.
 Preventing Pressure Damage A Guide for Patients and Carers What is pressure damage? A pressure ulcer, (previously often referred to as a bed sore or pressure sore ) is a localised area of damage to the
Preventing Pressure Damage A Guide for Patients and Carers What is pressure damage? A pressure ulcer, (previously often referred to as a bed sore or pressure sore ) is a localised area of damage to the
Preventing Pressure Ulcers
 Patient information Preventing Pressure Ulcers i Important information and care guide for patients at risk of pressure ulcers. Reproduced with kind permission from Healthcare Improvement Scotland Golden
Patient information Preventing Pressure Ulcers i Important information and care guide for patients at risk of pressure ulcers. Reproduced with kind permission from Healthcare Improvement Scotland Golden
How to prevent pressure ulcers
 How to prevent pressure ulcers Information for patients Find out more at 01522 511566 StBarnabasHospice.co.uk @StBarnabasLinc StBarnabasLinc Prevention is better than cure You have been given this information
How to prevent pressure ulcers Information for patients Find out more at 01522 511566 StBarnabasHospice.co.uk @StBarnabasLinc StBarnabasLinc Prevention is better than cure You have been given this information
Promoting Skin Integrity in End of Life Care. Part 1. Tracey McKenzie Head of Tissue Viability Services TSDFT
 Promoting Skin Integrity in End of Life Care Part 1 Tracey McKenzie Head of Tissue Viability Services TSDFT To Understand the Extrinsic Factors of Pressure Ulcer (PU) development To understand the Intrinsic
Promoting Skin Integrity in End of Life Care Part 1 Tracey McKenzie Head of Tissue Viability Services TSDFT To Understand the Extrinsic Factors of Pressure Ulcer (PU) development To understand the Intrinsic
Preparing for Approaching Death
 Preparing for Approaching Death Old Colony Hospice created this guide for our hospice family and caregivers by revising and adapting the following journal article: Hospice Techniques: Preparing for the
Preparing for Approaching Death Old Colony Hospice created this guide for our hospice family and caregivers by revising and adapting the following journal article: Hospice Techniques: Preparing for the
Prepared and Presented by: Ms. Sohad Noorsaeed, RN. MSN
 Prepared and Presented by: Ms. Sohad Noorsaeed, RN. MSN Learning Outcomes Upon the completion of Skin integrity lecture, the learners will be able to: 1. Describe factors affecting skin integrity. 2. Identify
Prepared and Presented by: Ms. Sohad Noorsaeed, RN. MSN Learning Outcomes Upon the completion of Skin integrity lecture, the learners will be able to: 1. Describe factors affecting skin integrity. 2. Identify
Information for Patients/Relatives/Carers on how to prevent pressure ulcers ( bedsores ) Tissue Viability Chief Nurse
 Information for Patients/Relatives/Carers on how to prevent pressure ulcers ( bedsores ) Tissue Viability Chief Nurse This leaflet has been designed to give you important information and to answer some
Information for Patients/Relatives/Carers on how to prevent pressure ulcers ( bedsores ) Tissue Viability Chief Nurse This leaflet has been designed to give you important information and to answer some
Prevention and management of pressure ulcers
 The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust Prevention and management of pressure ulcers Nursing A guide for patients and carers Contents What is a pressure ulcer?... 1 Who gets pressure ulcers?...
The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust Prevention and management of pressure ulcers Nursing A guide for patients and carers Contents What is a pressure ulcer?... 1 Who gets pressure ulcers?...
Pressure Ulcers in the Developmentally Disabled Arizona Department of Economic Security Division of Developmental Disabilities
 Pressure Ulcers in the Developmentally Disabled Arizona Department of Economic Security Division of Developmental Disabilities Compiled by Nancy Braden MD, Medical Director, Mercy Care Plan 1 PRESSURE
Pressure Ulcers in the Developmentally Disabled Arizona Department of Economic Security Division of Developmental Disabilities Compiled by Nancy Braden MD, Medical Director, Mercy Care Plan 1 PRESSURE
Mom! You re drinking a lot lately. Are you all right? I think so. But, you re right. I seem to be thirsty all the time. And, I m tired a lot too.
 Mom! You re drinking a lot lately. Are you all right? I think so. But, you re right. I seem to be thirsty all the time. And, I m tired a lot too. Maybe you should see the doctor? n c Alicia went to the
Mom! You re drinking a lot lately. Are you all right? I think so. But, you re right. I seem to be thirsty all the time. And, I m tired a lot too. Maybe you should see the doctor? n c Alicia went to the
WHY THE HEEL? Sharon Lucich, PT, CWS. By the end of this session, the learner will be able to:
 WHY THE HEEL? Sharon Lucich, PT, CWS Objectives By the end of this session, the learner will be able to: 1. Describe the unique anatomical features that contribute to the development of heel pressure ulcers
WHY THE HEEL? Sharon Lucich, PT, CWS Objectives By the end of this session, the learner will be able to: 1. Describe the unique anatomical features that contribute to the development of heel pressure ulcers
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED
 WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
Enhanced Recovery Programme Liver surgery
 Enhanced Recovery Programme Liver surgery General Surgery Patient information leaflet Introduction When you are admitted to hospital for your surgery you will be taking part in an enhanced recovery programme.
Enhanced Recovery Programme Liver surgery General Surgery Patient information leaflet Introduction When you are admitted to hospital for your surgery you will be taking part in an enhanced recovery programme.
What to expect following spinal cord injury. Information for patients Therapy Services
 What to expect following spinal cord injury Information for patients Therapy Services Introduction This leaflet aims to explain what spinal cord injury is and what to expect over the next few months. What
What to expect following spinal cord injury Information for patients Therapy Services Introduction This leaflet aims to explain what spinal cord injury is and what to expect over the next few months. What
Bed Sores No More! Pressure Injuries Risk Factors and Updated Staging Methodology. Nicolle Samuels, MSPT, CLT-LANA, CWS, CKTP
 Bed Sores No More! Pressure Injuries Risk Factors and Updated Staging Methodology Nicolle Samuels, MSPT, CLT-LANA, CWS, CKTP Objectives Understand updated definitions as well as staging and classification
Bed Sores No More! Pressure Injuries Risk Factors and Updated Staging Methodology Nicolle Samuels, MSPT, CLT-LANA, CWS, CKTP Objectives Understand updated definitions as well as staging and classification
Why Is Mommy Like She Is?
 Why Is Mommy Like She Is? A Book For Kids About PTSD Deployment Edition Patience H. C. Mason Patience Press High Springs, Florida PP Patience Press 2010 by Patience Mason All rights reserved. No part of
Why Is Mommy Like She Is? A Book For Kids About PTSD Deployment Edition Patience H. C. Mason Patience Press High Springs, Florida PP Patience Press 2010 by Patience Mason All rights reserved. No part of
information The Enhanced Recovery Programme for Total Hip Replacement (1 of 6) What will happen before I come into hospital?
 information If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk. You are entitled
information If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk. You are entitled
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) What is Addiction?
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) What is Addiction? https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents What is Addiction? Do You or a Loved One Have a Drug Abuse Problem? Signs of Drug Abuse and Addiction
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) What is Addiction? https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents What is Addiction? Do You or a Loved One Have a Drug Abuse Problem? Signs of Drug Abuse and Addiction
Interacting with people
 Learning Guide Interacting with people 28518 Interact with people to provide support in a health or wellbeing setting Level 2 5 credits Name: Workplace: Issue 1.0 Copyright 2017 Careerforce All rights
Learning Guide Interacting with people 28518 Interact with people to provide support in a health or wellbeing setting Level 2 5 credits Name: Workplace: Issue 1.0 Copyright 2017 Careerforce All rights
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS
 SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
Patient and Family Education. Bladder Exstrophy. What is bladder exstrophy? How common is bladder exstrophy? What causes bladder exstrophy?
 Patient and Family Education Bladder Exstrophy What is bladder exstrophy? Bladder exstrophy (x-tro-fee) is a bladder that is not formed right. The bladder and genitals are split in half, turned inside
Patient and Family Education Bladder Exstrophy What is bladder exstrophy? Bladder exstrophy (x-tro-fee) is a bladder that is not formed right. The bladder and genitals are split in half, turned inside
ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM
 ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM PURPOSE To introduce the program, tell the participants what to expect, and set an overall positive tone for the series. AGENDA Item Time 0.1 Acknowledgement
ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM PURPOSE To introduce the program, tell the participants what to expect, and set an overall positive tone for the series. AGENDA Item Time 0.1 Acknowledgement
Preventing delirium while in hospital Tips for family, whānau, and friends who are supporting an older person
 Preventing delirium while in hospital Tips for family, whānau, and friends who are supporting an older person This brochure shares some simple ways you can help our care staff to prevent delirium, recognize
Preventing delirium while in hospital Tips for family, whānau, and friends who are supporting an older person This brochure shares some simple ways you can help our care staff to prevent delirium, recognize
Update on Pressure Ulcers: Utilizing an Interdisciplinary Approach to Pressure Ulcer Prevention. Charlene A. Demers GNP-BC, CWOCN
 Update on Pressure Ulcers: Utilizing an Interdisciplinary Approach to Pressure Ulcer Prevention Charlene A. Demers GNP-BC, CWOCN Scope of the Issue Cost $9 billion to $11 billion $20,000-$150,000 per ulcer
Update on Pressure Ulcers: Utilizing an Interdisciplinary Approach to Pressure Ulcer Prevention Charlene A. Demers GNP-BC, CWOCN Scope of the Issue Cost $9 billion to $11 billion $20,000-$150,000 per ulcer
Preventing CLABSI & CAUTI Preventive Measures for Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infection & Catheter Associated UTI
 Preventing CLABSI & CAUTI Preventive Measures for Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infection & Catheter Associated UTI Kaiser Permanente For Internal use only Objectives By the end of this lesson, you
Preventing CLABSI & CAUTI Preventive Measures for Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infection & Catheter Associated UTI Kaiser Permanente For Internal use only Objectives By the end of this lesson, you
THE POTENTIAL IMPACT OF VITALSTIM THERAPY ON HEALTHCARE COSTS: A White PaperVitalStim Therapy has significant
 Dysphagia THE POTENTIAL IMPACT OF VITALSTIM THERAPY ON HEALTHCARE COSTS: A White PaperVitalStim Therapy has significant Contents potential to dramatically impact the health care costs arising from oropharyngeal
Dysphagia THE POTENTIAL IMPACT OF VITALSTIM THERAPY ON HEALTHCARE COSTS: A White PaperVitalStim Therapy has significant Contents potential to dramatically impact the health care costs arising from oropharyngeal
Section 4 Decision-making
 Decision-making : Decision-making Summary Conversations about treatments Participants were asked to describe the conversation that they had with the clinician about treatment at diagnosis. The most common
Decision-making : Decision-making Summary Conversations about treatments Participants were asked to describe the conversation that they had with the clinician about treatment at diagnosis. The most common
Sores That Will Not Heal
 Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Active Living with Arthritis Podcast #9 Being a Caregiver: Caring for Someone and Managing Your Arthritis
 Active Living with Arthritis Podcast #9 Being a Caregiver: Caring for Someone and Managing Your Arthritis Karen: Welcome to another Active Living with Arthritis podcast, presented by ENACT center at Boston
Active Living with Arthritis Podcast #9 Being a Caregiver: Caring for Someone and Managing Your Arthritis Karen: Welcome to another Active Living with Arthritis podcast, presented by ENACT center at Boston
Prevention and management of Pressure ulcers
 Prevention and management of Pressure ulcers A guide for patients, carers and relatives What is a pressure ulcer? Pressure ulcers are an injury to the skin and/or underlying tissues. They are also known
Prevention and management of Pressure ulcers A guide for patients, carers and relatives What is a pressure ulcer? Pressure ulcers are an injury to the skin and/or underlying tissues. They are also known
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
In the Ageing Well Survey, 2007, skin care issues were among the top three health priorities identified by respondents.
 2 Caring For Your Skin Skin The Functions of the Skin Skin acts to protect internal organs from disease, excrete waste products, regulate body temperature and provide sensation through nerve endings. Skin
2 Caring For Your Skin Skin The Functions of the Skin Skin acts to protect internal organs from disease, excrete waste products, regulate body temperature and provide sensation through nerve endings. Skin
Grade 7 Lesson Substance Use and Gambling Information
 Grade 7 Lesson Substance Use and Gambling Information SUMMARY This lesson is one in a series of Grade 7 lessons. If you aren t able to teach all the lessons, try pairing this lesson with the Understanding
Grade 7 Lesson Substance Use and Gambling Information SUMMARY This lesson is one in a series of Grade 7 lessons. If you aren t able to teach all the lessons, try pairing this lesson with the Understanding
Preventing. pressure ulcers. A guide for adults at risk of. pressure ulcers
 Preventing pressure ulcers A guide for adults at risk of pressure ulcers Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications
Preventing pressure ulcers A guide for adults at risk of pressure ulcers Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications
Improving the care of people with dementia in acute general hospital wards
 Improving the care of people with dementia in acute general hospital wards Prof Rowan H. Harwood Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust & University of Nottingham rowan.harwood@nuh.nhs.uk This presentation
Improving the care of people with dementia in acute general hospital wards Prof Rowan H. Harwood Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust & University of Nottingham rowan.harwood@nuh.nhs.uk This presentation
Chapter 36 & 37. Types of wounds. Skin Tear
 Chapter 36 & 37 Wound Care and Pressure Ulcers Types of wounds A wound is a break in the skin d/t trauma, surgical incision, pressure sore, circulatory ulcers Abrasion, Contusion, Incision, Laceration,
Chapter 36 & 37 Wound Care and Pressure Ulcers Types of wounds A wound is a break in the skin d/t trauma, surgical incision, pressure sore, circulatory ulcers Abrasion, Contusion, Incision, Laceration,
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide
 Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
Anxiety- Information and a self-help guide Anxiety Anxiety can be a very normal and healthy response to stressful situations, such as paying bills or sitting an exam. However, it becomes a problem when
Your anaesthetic for heart surgery
 Your anaesthetic for heart surgery Information for patients and carers First Edition 2018 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet gives you information about your anaesthetic for adult heart (cardiac)
Your anaesthetic for heart surgery Information for patients and carers First Edition 2018 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet gives you information about your anaesthetic for adult heart (cardiac)
PRESSURE ULCERS SIMPLIFIED
 10 PRESSURE ULCERS SIMPLIFIED This leaflet is intended to give you information and answers to some question you may have around pressure ulcers PRESSURE ULCERS SIMPLIFIED Pressure ulcer development has
10 PRESSURE ULCERS SIMPLIFIED This leaflet is intended to give you information and answers to some question you may have around pressure ulcers PRESSURE ULCERS SIMPLIFIED Pressure ulcer development has
Community Caregivers. Effects of Immobility, Transfers and Positioning Test
 Community Caregivers Effects of Immobility, Transfers and Positioning Test Name: Date: For each question, choose the best response or responses. 1. The key effect of immobility is: a. Increased incontinence
Community Caregivers Effects of Immobility, Transfers and Positioning Test Name: Date: For each question, choose the best response or responses. 1. The key effect of immobility is: a. Increased incontinence
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip
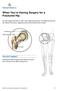 When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
INTERIOR DESIGN: Optimize Your Environment for Healing or Preventing Skin Breakdown. While the idea is not new, the term
 INTERIOR DESIGN: Optimize Your Environment for Healing or Preventing Skin Breakdown By Heather L. Orsted, RN, BN, ET, MSc and Sue Rosenthal, BA, MA INTERIOR DESIGN is a concept that is useful for both
INTERIOR DESIGN: Optimize Your Environment for Healing or Preventing Skin Breakdown By Heather L. Orsted, RN, BN, ET, MSc and Sue Rosenthal, BA, MA INTERIOR DESIGN is a concept that is useful for both
Preventing and managing pressure ulcers
 Preventing and managing pressure ulcers Information for patients, family and carers Nursing and Patient Experience Patient information leaflet What is a Pressure Ulcer? A pressure ulcer is an area of damage
Preventing and managing pressure ulcers Information for patients, family and carers Nursing and Patient Experience Patient information leaflet What is a Pressure Ulcer? A pressure ulcer is an area of damage
Whose Problem Is It? Mental Health & Illness in Long-term Care
 Whose Problem Is It? Mental Health & Illness in Long-term Care Revised by M. Smith (2005) from M. Smith & K.C. Buckwalter (1993), Whose Problem Is It? Mental Health & Illness in Long-term Care, The Geriatric
Whose Problem Is It? Mental Health & Illness in Long-term Care Revised by M. Smith (2005) from M. Smith & K.C. Buckwalter (1993), Whose Problem Is It? Mental Health & Illness in Long-term Care, The Geriatric
What to expect in the last few days of life
 What to expect in the last few days of life Contents Introduction... 3 What are the signs that someone is close to death?... 4 How long does death take?... 6 What can I do to help?... 7 Can friends and
What to expect in the last few days of life Contents Introduction... 3 What are the signs that someone is close to death?... 4 How long does death take?... 6 What can I do to help?... 7 Can friends and
Skin and Temperature Management following Spinal Cord Injury. North West Regional Spinal Injuries Centre Southport & Ormskirk NHS Trust
 Skin and Temperature Management following Spinal Cord Injury Functions of the skin The skin is the largest organ of the integumentary system The skin is the interface with the environment and plays an
Skin and Temperature Management following Spinal Cord Injury Functions of the skin The skin is the largest organ of the integumentary system The skin is the interface with the environment and plays an
Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community
 2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
Sepsis 911 Leader Script
 Sepsis 911 Leader Script SLIDE 1 Sepsis 911 Welcome to Sepsis 9-1-1. My name is. I m speaking to you today about sepsis, something that you may not have heard of before you joined us today. You re not
Sepsis 911 Leader Script SLIDE 1 Sepsis 911 Welcome to Sepsis 9-1-1. My name is. I m speaking to you today about sepsis, something that you may not have heard of before you joined us today. You re not
Spinal injury. Structure of the spine
 Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stage 5 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stage 5 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Take Your Nervous System to the Gym
 Resiliency Building Skills to Practice for Trauma Recovery www.new-synapse.com /aps/wordpress/ Much of trauma healing is helping the nervous system become more resilient. Rather than spend a few hours
Resiliency Building Skills to Practice for Trauma Recovery www.new-synapse.com /aps/wordpress/ Much of trauma healing is helping the nervous system become more resilient. Rather than spend a few hours
Lumbar Epidural Injections. Treatment to Reduce Pain
 Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Northern Ireland Chest Heart & Stroke. What are Chest, Heart and Stroke conditions?
 Northern Ireland Chest Heart & Stroke What are Chest, Heart and Stroke conditions? Everyone in Northern Ireland knows someone who has suffered from a chest, heart or stroke condition. 40% of adult deaths
Northern Ireland Chest Heart & Stroke What are Chest, Heart and Stroke conditions? Everyone in Northern Ireland knows someone who has suffered from a chest, heart or stroke condition. 40% of adult deaths
Lesson 2: Observation
 Lesson 2: Observation Title Slide Welcome Transcript Hello. My name is Jill Morrow, I am the Medical Director for the Office of Developmental Programs. I will be your narrator for this webcast. Lesson
Lesson 2: Observation Title Slide Welcome Transcript Hello. My name is Jill Morrow, I am the Medical Director for the Office of Developmental Programs. I will be your narrator for this webcast. Lesson
SMS USA PHASE ONE SMS USA BULLETIN BOARD FOCUS GROUP: MODERATOR S GUIDE
 SMS USA PHASE ONE SMS USA BULLETIN BOARD FOCUS GROUP: MODERATOR S GUIDE DAY 1: GENERAL SMOKING QUESTIONS Welcome to our online discussion! My name is Lisa and I will be moderating the session over the
SMS USA PHASE ONE SMS USA BULLETIN BOARD FOCUS GROUP: MODERATOR S GUIDE DAY 1: GENERAL SMOKING QUESTIONS Welcome to our online discussion! My name is Lisa and I will be moderating the session over the
Ginkgo Biloba: How Supportive is the Data?
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/ginkgo-biloba-how-supportive-is-the-data/3203/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/ginkgo-biloba-how-supportive-is-the-data/3203/
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral to Femoral or Iliac to Femoral Crossover Bypass Graft
 Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral to Femoral or Iliac to Femoral Crossover Bypass Graft Why do you need this operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral to Femoral or Iliac to Femoral Crossover Bypass Graft Why do you need this operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer
Death by Bedrest: The Perils of The Hospital
 Death by Bedrest: The Perils of The Hospital Mindy Fain, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Director, Arizona Reynolds Program of Applied Geriatrics Section Head, Geriatrics & Gerontology University of
Death by Bedrest: The Perils of The Hospital Mindy Fain, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Director, Arizona Reynolds Program of Applied Geriatrics Section Head, Geriatrics & Gerontology University of
Femoral shaft fracture surgery (femoral nailing)
 Femoral shaft fracture surgery (femoral nailing) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
Femoral shaft fracture surgery (femoral nailing) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that
The Recovery Journey after a PICU admission
 The Recovery Journey after a PICU admission A guide for families Introduction This booklet has been written for parents and young people who have experienced a Paediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) admission.
The Recovery Journey after a PICU admission A guide for families Introduction This booklet has been written for parents and young people who have experienced a Paediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) admission.
Delirium: Information for Patients and Families
 health information Delirium: Information for Patients and Families 605837 Alberta Health Services, (2016/11) Resources Delirium in the Older Person Family Guide: search delirium at viha.ca Go to myhealth.alberta.ca
health information Delirium: Information for Patients and Families 605837 Alberta Health Services, (2016/11) Resources Delirium in the Older Person Family Guide: search delirium at viha.ca Go to myhealth.alberta.ca
Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Information for Patients having a Breast Reduction Operation
 Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Information for Patients having a Breast Reduction Operation Plastic Surgery Department Leaflet Number 2 Produced: October 2007 Review date: October 2010
Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Information for Patients having a Breast Reduction Operation Plastic Surgery Department Leaflet Number 2 Produced: October 2007 Review date: October 2010
Fluids and Nutrition Standard
 The CARE CERTIFICATE Fluids and Nutrition Standard 1 Learning outcomes 8.1 Understand the principles of hydration, nutrition and food safety 8.2 Support individuals to have access to fluids in accordance
The CARE CERTIFICATE Fluids and Nutrition Standard 1 Learning outcomes 8.1 Understand the principles of hydration, nutrition and food safety 8.2 Support individuals to have access to fluids in accordance
A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco
 Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant
 Page 1 of 5 What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant This information will help you understand the risks, benefits and possible complications involved in a kidney transplant. Please read it carefully.
Page 1 of 5 What You Need to Know about a Kidney Transplant This information will help you understand the risks, benefits and possible complications involved in a kidney transplant. Please read it carefully.
Taking Control of Alcohol Use
 Taking Control of Alcohol Use Session 1: About Alcohol Use. This workbook accompanies the e-course Taking Control of Alcohol Use and is for the exclusive use of clients and customers of Homewood Human
Taking Control of Alcohol Use Session 1: About Alcohol Use. This workbook accompanies the e-course Taking Control of Alcohol Use and is for the exclusive use of clients and customers of Homewood Human
Pearls and Pitfalls of Rapid Sequence Intubation
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/pearls-and-pitfalls-of-rapid-sequenceintubation/3829/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/pearls-and-pitfalls-of-rapid-sequenceintubation/3829/
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE?
 ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS INTRODUCTION Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the nervous system. Multiple sclerosis causes inflammation and damage to the protective coatings in the brain and the nerves.
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS INTRODUCTION Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the nervous system. Multiple sclerosis causes inflammation and damage to the protective coatings in the brain and the nerves.
Letter to the teachers
 Letter to the teachers Hello my name is Sasha Jacombs I m 12 years old and I have had Type 1 Diabetes since I was four years old. Some of the people reading this may not know what that is, so I had better
Letter to the teachers Hello my name is Sasha Jacombs I m 12 years old and I have had Type 1 Diabetes since I was four years old. Some of the people reading this may not know what that is, so I had better
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Heart Valve Replacement
 Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Staying a non-smoker. Booklet 4
 Staying a non-smoker Booklet 4 Congratulations on giving up smoking! Use this booklet to help you stay a non-smoker. Now that you have stopped smoking you will be feeling healthier, and you will be breathing
Staying a non-smoker Booklet 4 Congratulations on giving up smoking! Use this booklet to help you stay a non-smoker. Now that you have stopped smoking you will be feeling healthier, and you will be breathing
Having a nephrostomy tube inserted
 Having a nephrostomy tube inserted Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been advised to have a nephrostomy tube inserted. It includes information
Having a nephrostomy tube inserted Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been advised to have a nephrostomy tube inserted. It includes information
