Expert consensus on a new enzyme alginogel
|
|
|
- Griffin Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Product REVIEW KEY WORDS Enzyme alginogel Antimicrobial Debridement Moist wound healing It is widely appreciated that cellular and molecular imbalances in the wound bed can often delay healing HILDE BEELE Professor, Wound Clinic and Dept. of Dermatology, Ghent University Hospital, Gent, Belgium CORRADO DURANTE Senior Surgeon, Wound Care Unit, Emergency Department, Army Military Hospital, Rome, Italy JEAN-CHARLES KERIHUEL Medical Director Vertical, Paris, France JAN RICE Co-ordinator in Wound Education, World of Wounds, La Trobe University, Alfred Health Clinical School, Melbourne, Australia Expert consensus on a new enzyme alginogel Flaminal (Flen Pharma) products are alginate gels containing a novel antimicrobial enzyme system. They are designed to promote wound healing and to restore bacterial balance and their use on a wide range of wound types is supported by scientific and clinical evidence (De la Brassinne et al, 2006; Vandenbulcke et al, 2006; De Smet et al, 2009; Durante, 2012). Extensive clinical usage and trialling in Europe and Australasia have provided an evidence base and a list of clinicians with an understanding of the clinical performance of Flaminal products. This expert panel reported that Flaminal products should be classified as enzyme alginogels and identified four key functions continuous wound debridement; antimicrobial activity; maintenance of a moist wound healing environment; and protection of wound edges and epithelial cells. These enzyme alginogels are compatible with the TIME framework, as demonstrated in the case histories. For example, like honey they are one of the few materials said to have a number of modes of action (White, 2005), however, unlike honey they do not sting when applied to wounds (Ingle et al, 2006). Furthermore, Flaminal s triple mode of action avoids the need for multiple products, for example, it has the capability to absorb excess exudate whilst remaining in a gelled state, promote debridement and control bioburden. ARMAND RONDAS Elderly care physician, De Zorggroep, Venlo, The Netherlands; School for Public Health and Primary Care (CAPHRI), Maastricht University, The Netherlands JAN STRYJA Vascular Surgeon, Hospital Podlesi, Trinec, Czech Republic RICHARD WHITE Professor of Tissue Viability, University of Worcester, Worcester, UK 64 Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 1 It is widely appreciated that cellular and molecular imbalances in the wound bed can often delay healing (Eming et al, 2007). Models such as the TIME framework Tissue management, Inflammation and infection control, Moisture balance, Epithelial (edge) advancement offer a logical and systematic approach to wound bed assessment (Falanga, 2004; Dowsett and Ayello, 2004). Table 1 summarises the disturbances in wound bed remodelling associated with each stage of the TIME framework and the relevant treatment approaches. However, the clinical reality is that clinicians often have to deal with several aspects of the TIME framework at the same time, which requires ongoing assessment and realignments in treatment, often using multiple products. Flaminal Flaminal Hydro and Flaminal Forte (Flen Pharma) are the first items to
2 Product REVIEW become available in a new class of wound care products the enzyme alginogels. They comprise hydrated alginate polymers in a polyethyleneglycol (PEG) matrix embedded with a patented antimicrobial enzymatic complex (GLG glucose oxidase combined with lactoperoxidase, stabilised by guaiacol [De la Brassinne, 2006; White, 2006]). These naturally occurring enzymes are found in saliva and milk, and as such are important in the innate immune system. They have excellent biocompatibility with very limited, if any, likelihood of allergy (in the six-year life of the product, there has been one suspected allergic contact dermatitis and one irritant reaction). Working in conjunction, these two enzymes, lactoperoxidase and glucose oxidase, form free radicals via hydrogen peroxide, which destroys the cell walls of adsorbed bacteria in a manner similar to our innate white cell defences (White, 2006). As this is a selective process, only the absorbed bacteria are destroyed and not the essential regenerating cells of the healing wound. Evidence Recent in vitro preclinical studies have demonstrated that low concentrations of this GLG-enzyme system kill antibioticresistant bacterial strains without being cytotoxic to fibroblasts and keratinocytes (Vandebulcke et al, 2006; De Smet et al, 2009). Its mode of action is summarised in Figure 1. The published clinical data includes studies on both acute and chronic wounds, for example, a 70-patient Table 1 Summary of the TIME. model of wound care and the appropriate treatment approaches for each stage TIME component Wound bed disturbance Approach TIME Tissue Barrier to further healing Removal of (debridement) via: - Sharp debridement (surgical/bedside) - Wet-to-dry dressings - Hydrogels - Enzymes - Biosurgery - Negative pressure treatment. References Bishop SM, Walker M, Rogers AA, Chen WY (2003) Importance of moisture balance at the wound-dressing interface. J Wound Care 12(4): De la Brassinne M, Thirion L, Horvat LI (2006) A novel method of comparing the healing properties of two hydrogels in chronic leg ulcers. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 20(2): de Smet K, van den Plas D, Lens D, Sollie P (2009) Pre-clinical evaluation of a new antimicrobial enzyme for the control of wound bioburden. Wounds 21(3): Dowsett C, Ayello E (2004) TIME principles of chronic wound bed preparation and treatment. Br J Nurs (Tissue Viability Supplement) 135: S16 23 Durante C (2012) An open label non-comparative case series on the efficacy of an enzyme alginogel. J Wound Care 21(1): 22 8 TIME TIME Inflammation and infection Imbalance between microorganisms and host resistance, leading to delayed healing Moisture imbalance Increased exudate resulting in increasingly wet wound and border maceration Control of infectious agents: - Topical antibacterial treatment - Wet dressings with topical antiseptics - Iodophors - Tea tree oil-based products - Polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) - Silver dressings - Sugar and honey. Need for absorption of excessive fluid: - Alginates - Foam dressings - Hydrofibers - Super-absorbent filler dressings. TIME Non-migrating wound edge Need to protect wound borders Surgical reconstruction Biologic wound dressings Skin-replacing biologic dressings 66 Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 1
3 In one case study Flaminal products were used, and two months of daily treatment the wound reduced by 1cm 2 comparative study on partial-thickness hand burns (Kyriopoulos et al, 2010), patients with venous leg ulcers (Lacarrubba et al, 2005; De la Brassinne et al, 2006); and, an in vivo/in vitro antimicrobial study on various chronic wounds with supporting cytotoxicity in vitro (Vandenbulcke et al, 2006). In a retrospective study on two groups of 30 patients with burns, Hoeksema et al (2011) reviewed 10 years of clinical experience with Flaminal. After stratifying burns treated with either Flaminal or with silver sulfadiazine 1% cream according to depth, both superficial (p=0.013) and deep partialthickness wounds (p=0.04) healed faster with Flaminal treatment without the requirement for ancillary wound treatments. Recently, Durante (2012 ) published a report of 23 patients treated with Flaminal for up to 60 days. In this study a mix of acute and chronic wounds were treated with Flaminal to control exudate and bioburden as part of the standard care protocol. Dressings were changed every 1 4 days according to the manufacturer s instructions and/ or clinical need. For wounds exhibiting moderate-to-high exudate levels, foams were used; for low-to-medium exuding wounds, dry dressings were used. Wound volume and surface area were measured at the start of the study and routinely wards the mean volume on inclusion was 2.8 ± 5.6cm 3 and the mean area 2.6 ± 3.8cm 2.Wound pain, surface area and volume, exudate levels, and wound tissues were assessed regularly until healing, or until 60 days had elapsed. Results showed that in all wounds there was a significant decrease in dimensions (p 0.001). This included chronic wounds refractory to treatment with other modalities (treatment of over Figure 2: Full-thickness burn to the foot. Figure 3: Healing extent of burn three weeks treatment with Flaminal. Creates a moist environment in dry wounds, absorbs exudate to promote autolytic debridement + Forms moist gels in the presence of fluids such as wound exudate Hydrogel Alginate Enzyme complex + Enzyme alginogels Flaminal Hydro (3% alginate) for low-to-moderate exuding wounds Flaminal Forte (5.5% alginate) for moderate-toheavily exuding wounds Protects against microbial colonisation and combats infection Figure 1: The components and mechanism of action of Flaminal (White, 2006). References Eming SA, Krieg T, Davidson JM (2007) Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol 127(3): European Community (2011) European Standards: Medical Devices. Test Methods for Primary Wound Dressings. Part 1: Aspects of Absorbency. Available at: enterprise/policies/european-standards/harmonised-standards/medical-devices (accessed 2 March, 2011) Falanga V (2004) Wound bed preparation: science applied to practice. In: European Wound Management Association (EWMA). Position Document. Wound Bed Preparation in Practice. MEP Ltd, London. Available at: woundbedpreparation.com/pdfs/english.pdf (accessed 2 March, 2012) Gelfand JM, Hoffstad O, Margolis DJ (2002) Surrogate endpoints for the treatment of venous leg ulcers. J Invest Dermatol 119(6): Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 1 67
4 Product Clinical REVIEW Figure 4: Full-thickness burn to the patient s knee treatment. Figure 5: The wound two weeks of daily dressings. Figure 6: The wound three weeks of daily dressings. Figure 7: The wound at 13 weeks. 12 weeks duration). In each group of patients wound pain (as assessed using a visual analogue scale [VAS]) decreased over time. The expert panel The expert panel used their clinical experience of Flaminal products, in conjunction with the published evidence, to consider where enzyme alginogels might be positioned according the to the T, I and M elements of the TIME framework ( E components involve biological dressings or surgery and are not appropriate). The panellists brought the following case evidence to the discussion. Case study evidence Australian experience A 91-year-old female patient presented with a three-week-old full-thickness burn to the foot (Figure 2). She received daily Flaminal therapy following her request to continue with her daily commitments prior to a femoropopliteal bypass and a skin graft. The extent of healing three weeks of daily dressing changes is shown in Figure 3. Further evidence is presented via the experience of an 88-year-old female patient with dementia who presented with a full-thickness burn to the knee (Figures 4 7). The use of Flaminal not only avoided the need for hospitalisation, with the associated risk of pressure ulceration, but also facilitated rapid healing, as demonstrated in Figure 7. The efficacy of Flaminal in older patients with burns, a group with high comorbidity rates who are often malnourished, is clear it helps to manage fluid levels and bioburden as well as aiding debridement. Furthermore, the author s experience has shown that when patients who have experienced pain with a cadexomer iodine try Flaminal, they are more than satisfied with both the comfort and efficacy of the product. Flaminal helps to manage fluid levels and bioburden as well as aiding debridement Dutch experience A patient who had undergone bowel resection and colostomy with unsuccessful abdominal reconstruction presented with recurrent parastomal hernia, which was exuding, infected and measured 25cm 2 (Figure 8). An alginate dressing (Kalostat, ConvaTec) and a Hydrofiber (Aquacel, ConvaTec), as well as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), were tried over a period of 8 9 months, without effect. Flaminal products were then used, and two months of daily treatment the wound reduced by 1cm 2 (Figure 9). The patient has since chosen to continue with Flaminal Hydro. In another case, a 92-year-old female patient with venous leg ulcers of over 45 years duration commenced Flaminal Forte therapy at the end of April Previous treatments included a variety of hydrogels with compression therapy (Actico, Activa). After three weeks, the wound tissue appeared healthier even without sharp debridement, although there was no change in size (Figures 10 11). These results suggest that Flaminal may have promoted tissue formation. After continued use of Flaminal three times a week for six months, the wound reduced in size from 12cm 2 to 8.9cm 2 (Figure 12). Czech experience A 60-year-old man presenting with an infected venous leg ulcer of three months duration was treated with Flaminal. The wound exhibited necrotic margins and high exudate levels with an expanding area of wound pain. Swab tests were positive for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. This man was previously under the care of a GP who had opted for local antibiotic ointments and compression bandages. The new strategy involved daily dressing changes (with effective compression), using Flaminal without the concurrent administration of oral antibiotics. Figures demonstrate therapeutic antimicrobial activity through 68 Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 1
5 Figure 8: Recurrent parastomal hernia treatment. Figure 9: The same wound following two months of treatment with Flaminal. bioburden reduction. The Flaminal also managed the associated exudate and was easy to use. Of clinical significance was the finding that one week the wound was granulating and clear of slough. After one month, swab tests for infection were negative, wound pain and exudate were reduced and healing was evident. While antimicrobial activity is generally not the primary objective of clinical observations/consultations (this is reserved instead for research studies), experience in over 20 cases has so far revealed that Flaminal can have a positive effect on infected ulcers. Italian experience This was a single-centre, open-label case series investigating the efficacy of Flaminal in 23 patients with acute and chronic wounds of diverse aetiology (Table 2). Flaminal was applied in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions and wounds were covered Figure 10: A venous leg ulcer Flaminal treatment. Figure 13: Venous leg ulcer in a 60-year-old man. Figure 14: The same wound area shown one week s treatment. Figure 11: The same wound three weeks of Flaminal treatment. Figure 15: The wound one month s treatment. Figure 16: The wound five months treatment. Figure 12: After six months, the wound had reduced in size from 12cm 2 to 8.9cm Wounds UK UK 2012, 2012, Vol Vol 8, No 12, 1 No 69 12
6 Product REVIEW KEY POINTS???????.????????. cm 2 /cm 3 4,5 4 3,5 3 2,5 2 1,5 1 0, Surface Volume 60 Figure 17: Mean (+SEM) change in wound size and volume over time. References Hoeksema H, Vermeulen B, Verbelen J, et al (2011) Flaminal Forte: an enzyme alginogel: 10 years experience in burn care. Presentation at the European Burns Association Meeting. September 14 17, The Hague, Netherlands Ingle R, Levin J, Polinder K (2006) Wound healing with honey a randomised controlled trial. S Afr Med J 96(9): Kantor J, Margolis DJ (2000) Expected healing rates for chronic wounds. Wounds 12(6): Kyriopoulos E, Van den Plas D, Papadopoulos O (2010) The use of a new wound alginogel for the treatment of partial-thickness hand burns. Wounds 22(6): Lacarrubba E, Patania I, Micale G (2005). Open label evaluation of an alginate hydrogel in the treatment of leg ulcers. Ital J Dermatol Venereol 140(1): 83 8 with secondary dressings. A scheduled treatment protocol was applied and patients were assessed at 14, 30 and 60 days. As shown in Figure 17, this treatment facilitated a clear reduction in wound size and volume over time. It is also noteworthy that in four of the pressure ulcer cases, healing was evident just six days of treatment. Further analysis of healing progression is shown in Figure 18, which illustrates a quantitative overview of the presence of,, and for each wound type prior to treatment (week 0) and two, four and eight weeks. The wounds began responding within two weeks of treatment, with higher proportions of, and visible, as well as a lack of. Figure 19 summarises how pain levels (visual analogue scale [VAS] evaluation) fluctuated, and dressing change at the associated time points, suggesting a trend for a dampening of patient perceived pain over time this effect may have contributed to the improved healing seen over time (Figure 17), or could have resulted from the healing and reduction in size. These quantifiable outcomes are supplemented by feedback from the care givers: Flaminal is very easy to use and provides the option to incorporate a second dressing of choice [the study incorporated non-adherent dressings and gauze but foams were most often used] its presence beneath other dressings has not presented any issues. It demonstrates very good efficacy in wounds with predominant Grampositive organisms and compliance with Flaminal schedules has also been Table 2 Patient demographics in a single-centre, single-arm, open-label case series investigating the efficacy of enzyme alginogels. Frequency (%) Acute (n) Chronic (n) Median duration (range), days Pressure ulcer 9 (39.1) (128 7,128) Diabetic ulcer 7 (30.4) (22 1,593) Traumatic wound 3 (13.0) (0 397) Arterial ulcer 1 (4.3) 0 1 1,195 Other 3 (13.0) (0 731) Total 23 (100) 70 Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 1
7 Product REVIEW Percentage of wound area Week 0 Week 2 Week 4 Week 8 Pressure ulcers (n=9) Diabetic ulcers (n=7) Traumatic wounds(n=3) Arterial ulcer (n=1) Other (n=3) Figure 18: The proportion of wound area covered by,, and the study for each wound type. References Vandenbulcke K, L-I Laenen Horvat, de Mil M, et al (2006) Evaluation of the antibacterial action and toxicity of two new hydrogels: a pilot study. Lower Extrem Wounds 5(2): White RJ (2005) Natural approaches to wound management: a focus on honey and honeybased dressings. Wounds UK 1(3 Suppl): S1 60 White R (2006) Flaminal: a novel approach to wound bioburden control. Wounds UK 2(3): 64 9 Van Den Plas D, De Smet K, Sollie P (2006) Improved Antimicrobial Peroxidase Compositions. Available at: patentscope/search/en/wo (accessed 2 March, 2012) 72 Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 1 noted one year in some cases (Durante, 2012). Classification and reimbursement a French perspective The French perspective focused on the current reimbursement structure in France. Two classes of hydrogels are recognised at present physical and chemical and Flaminal falls into the later. Alginates are also a recognised category in the reimbursement of dressings in France they vary according to carbohydrate structure in terms of fluid uptake. The enzyme alginogel classification suggested for Flaminal currently does not fit any existing French category. The requirement to demonstrate reference to a traditional product has already been fulfilled, in as far as Flaminal has been compared with Intrasite Gel (Smith & Nephew) (De la Brassinne et al, 2006), which was found to be effective at reducing wound volume and surface area at seven days. However, larger well-designed randomised clinical trials are needed with outcome measures including healing rates and wound area regression four or more weeks of treatment (Kantor and Margolis, 2000; Gelfand et al, 2002). Modes of action Based on its composition and modes of action, Flaminal is positioned as an enzyme alginogel. Enzyme alginogels should be positioned thus in clinical application: Exudate management: there is a standard British Pharmacopaeia test, which has been accepted as a European Standard (European Community, 2011). Multiple samples of Flaminal Forte and Hydro have been subjected to this test in isolation and found to absorb 31.7% and 16.3% of their weight respectively. According to the Standard, this puts them in classes 4 and 2 Bioburden management Autolytic debridement. The concentration of alginate was selected carefully so that light to moderate exudate was managed by Flaminal Hydro and heavier levels by the Forte product bioburden management is facilitated via the neutrophil-like peroxidase contained in the gel (Van Den Plas et al, 2006). Autolytic debridement could be demonstrated by the effective moisture balance achieved, which is vital to promote optimum healing (Bishop et al, 2003). There was a consensus among the panel brought together for this document that there was limited evidence of autolytic debridement published in clinical reports, despite the positive results achieved without the need for sharp surgical debridement, and that further investigation is needed in this area.
8 Pressure ulcers (n=9) Diabetic ulcers (n=7) Traumatic wounds(n=3) Additionally, as clinicians frequently have to deal with multiple aspects of the TIME framework simultaneously, having a product with a triple mode of action could be cost-effective. Other benefits include its ease of use, particularly in small and hard-to-reach wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers. Arterial ulcer (n=1) Other (n=3) Week 0 Week 2 Week 4 Week 8 Figure 19: Evolution of pain, as measured by VAS pain score,, and application of the enzyme alginogel (adapted from Durante, 2012). a greater influence on dressing selection. Flaminal, with its triple mode of action (Figure 1), is unique and so should not be regarded as either hydrogel, alginate or antimicrobial, but rather as a synthesis of the three. Similarly, its unique enzyme component affords an antimicrobial function with negligible risk of selecting for resistance. KEY POINTS Flaminal gel is designed for the management of exuding acute and chronic wounds and bioburden control A panel of international experts has recommended that it be designated an Enzyme alginogel to reflect its composition A The panel has also reviewed all available evidence and has prioritised the use of Flaminal gels to four key functions: - continuous wound debridement - antimicrobial activity - maintenance of a moist wound healing environment - protection of wound edges and epithelial cells. Compared with alternative dressings, such as aliginates in sheet form, Flaminal is highly conformable Compared with alternative dressings, such as aliginates in sheet form, Flaminal is highly conformable. Furthermore, its antimicrobial effect is not accompanied by any cytotoxicity (contrary to experience with other antimicrobials, such as silver). As the antimicrobial effect is not that of a typical topical antibiotic, resistance is highly unlikely. The panel stated that further analysis of the effect of Flaminal on wound bacterial colonisation and the formation of biofilms would be appropriate. Conclusion While the composition of a dressing is important for classification, its mechanism of action should possibly be The general consensus of this meeting of wound care clinicians is that there is a place for this new class of dressing in care frameworks, but that it also presents a need for the following: Larger scale randomised clinical trials to demonstrate efficacy of the main performance characteristics listed above Performance versus current comparative competitors (some are listed in Table 1 for the T, I and M aspects of the TIME framework); In vivo proof of the unique antimicrobial action of the enzyme component. While the clinical evidence to date is definitely promising, these further studies are needed to confirm that Flaminal can avoid the unnecessary requirement for multiple products, presenting a real cost saving and supporting applications for reimbursement from healthcare authorities worldwide. Acknowledgement Richard White is a consultant to Flen Pharma. Wuk Wounds UK 2012, Vol 8, No 1 73
Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types. Summary
 Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Wound Management. E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP
 Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment. Michelle Greenwood. Lorraine Grothier. Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust
 Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Galen ( A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing
 Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
DRESSING SELECTION. Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate
 DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
Making the Most of your Dressing Products Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE
 Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
Disclosures for Tarik Alam. Wound Bed Preparation. Wound Prognosis. Session Objectives. Debridement 4/26/2015
 Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
Mean percent reduction in ulcer area from baseline at six weeks 62 % SANTYL Ointment + supportive care* + sharp debridement 1 (P<0.
 Evaluating two common adjuncts to sharp debridement in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers Mean percent reduction in ulcer area from baseline at six weeks 62 % 40 % SANTYL Ointment + supportive care*
Evaluating two common adjuncts to sharp debridement in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers Mean percent reduction in ulcer area from baseline at six weeks 62 % 40 % SANTYL Ointment + supportive care*
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment
 Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Prontosan. Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing
 Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds
 Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey
 Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
RN Cathy Hammond. Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch
 RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected dressings enhance the body s ability to heal the wound. Progression Towards Healing
 Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
This article is based on a symposium held
 Advances in wound cleansing: an integrated approach LIZ OVENS Independent Tissue Viability Specialist Nurse SALLY IRVING Independent Tissue Viability Nurse Consultant This article is based on a symposium
Advances in wound cleansing: an integrated approach LIZ OVENS Independent Tissue Viability Specialist Nurse SALLY IRVING Independent Tissue Viability Nurse Consultant This article is based on a symposium
We look forward to serving you.
 ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT
 TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management
 Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
Wound Dressing. Choosing the Right Dressing
 Wound Dressing Choosing the Right Dressing Benefits of using the correct Drsg Helps create the optimal wound environment Increases healing rates Reduces pain Decreases infection rates Cost effective Care
Wound Dressing Choosing the Right Dressing Benefits of using the correct Drsg Helps create the optimal wound environment Increases healing rates Reduces pain Decreases infection rates Cost effective Care
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development
 Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017
 Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED
 10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS
 WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
The Risk. Background / Bias. Integrating Wound Care into a Limb Preservation Initiative 4/24/2009
 Stimulating Wound Granulation: Advances in NPWT and other Measures (Wound Bed Preparation) Charles Andersen MD, FACS, FAPWCA Clinical Prof of Surgery UW, USUHS Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation
Stimulating Wound Granulation: Advances in NPWT and other Measures (Wound Bed Preparation) Charles Andersen MD, FACS, FAPWCA Clinical Prof of Surgery UW, USUHS Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation
Advazorb. Hydrophilic foam dressing range
 Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Multi-Center Clinical Results with PluroGel PSSD in Chronic Wounds
 Multi-Center Clinical Results with PluroGel PSSD in Chronic Wounds Presented at a Satellite Symposium during the European Wound Management Association (EWMA) 2012 24 May 2012 Vienna, Austria Multi-Center
Multi-Center Clinical Results with PluroGel PSSD in Chronic Wounds Presented at a Satellite Symposium during the European Wound Management Association (EWMA) 2012 24 May 2012 Vienna, Austria Multi-Center
Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge. Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN
 Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN Projects and Posters These resources were developed by creative VA nurses who had no special
Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN Projects and Posters These resources were developed by creative VA nurses who had no special
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017
 Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Acute and Chronic WOUND ASSESSMENT. Wound Assessment OBJECTIVES ITEMS TO CONSIDER
 WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
Fundamentals Of Wound Management. Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse
 Fundamentals Of Wound Management Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse Wound Management What are we trying to achieve? Maintaining a controlled set of local conditions that is able to sustain the
Fundamentals Of Wound Management Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse Wound Management What are we trying to achieve? Maintaining a controlled set of local conditions that is able to sustain the
An investigation of Cutimed Sorbact as an antimicrobial alternative in wound management
 An investigation of Cutimed Sorbact as an antimicrobial alternative in wound management G Kammerlander, E Locher, A Suess-Burghart, B von Hallern, P Wipplinger Abstract Background: Antimicrobial dressings
An investigation of Cutimed Sorbact as an antimicrobial alternative in wound management G Kammerlander, E Locher, A Suess-Burghart, B von Hallern, P Wipplinger Abstract Background: Antimicrobial dressings
Foam dressings have frequently
 The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell
 Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell Objectives Identify the stages of pressure ulcer according to the depth of tissue destruction. Discuss the differences
Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell Objectives Identify the stages of pressure ulcer according to the depth of tissue destruction. Discuss the differences
Exudate in the early stages of wound healing
 Products & technology Wound management with the Biatain Silicone foam dressing: A multicentre product evaluation Authors: Hugues Cartier, Simon Barrett, Karen Campbell, Jan Forster, Mike Schmalzbauer,
Products & technology Wound management with the Biatain Silicone foam dressing: A multicentre product evaluation Authors: Hugues Cartier, Simon Barrett, Karen Campbell, Jan Forster, Mike Schmalzbauer,
THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed. Closing wounds. Together.
 Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing
 Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
What did we find living under some silver dressings? * NEW in vitro Evidence. Not all silver dressings are created equal. *As demonstrated in vitro
 NEW in vitro Evidence What did we find living under some silver dressings? * Not all silver dressings are created equal.. Micro-contouring, bacteria killing* 1,2 *As demonstrated in vitro Dressing technology
NEW in vitro Evidence What did we find living under some silver dressings? * Not all silver dressings are created equal.. Micro-contouring, bacteria killing* 1,2 *As demonstrated in vitro Dressing technology
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers
 A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
BIOSORB GELLING FIBRE DRESSING. Key facts: In vitro evidence
 BIOSORB GELLING FIBRE DRESSING Key facts: In vitro evidence BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing WHAT IS IT? BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing is a soft, conformable non-woven dressing made from sodium carboxymethyl
BIOSORB GELLING FIBRE DRESSING Key facts: In vitro evidence BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing WHAT IS IT? BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing is a soft, conformable non-woven dressing made from sodium carboxymethyl
Surgical site infections have been
 For patients undergoing complex abdominal or bowel surgery, the risk of infection and the resultant dehiscence if an infection occurs can pose a great challenge LINDSEY BULLOUGH Tissue Viability Nurse,
For patients undergoing complex abdominal or bowel surgery, the risk of infection and the resultant dehiscence if an infection occurs can pose a great challenge LINDSEY BULLOUGH Tissue Viability Nurse,
Basic Dressing Categories
 Category of Dressing Examples Advantages/Indications Disadvantages/Contraindications Hydrofiber Aquacel AG - ConvaTec Aquacel - Convatec Excellent for absorbing excess exudate These dressings form a gel
Category of Dressing Examples Advantages/Indications Disadvantages/Contraindications Hydrofiber Aquacel AG - ConvaTec Aquacel - Convatec Excellent for absorbing excess exudate These dressings form a gel
GP Practice Woundcare Formulary
 Agreed jointly by Ipswich and East Suffolk and West Suffolk Clinical Commissioning Groups GP Practice Woundcare Formulary Version 28 October 2017 Formulary items should be prescribed wherever possible.
Agreed jointly by Ipswich and East Suffolk and West Suffolk Clinical Commissioning Groups GP Practice Woundcare Formulary Version 28 October 2017 Formulary items should be prescribed wherever possible.
CASE STUDIES SERIES 2017
 INTERNATIONAL CASE STUDIES Case studies evaluation: BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing in moderate to highly exuding wounds CASE STUDIES SERIES 2017 PUBLISHED BY: Wounds International 1.01 Cargo Works 1 2
INTERNATIONAL CASE STUDIES Case studies evaluation: BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing in moderate to highly exuding wounds CASE STUDIES SERIES 2017 PUBLISHED BY: Wounds International 1.01 Cargo Works 1 2
Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL. of the infection risk in chronic wound
 Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL of the infection risk in chronic wound Introduction The impact of infection on patients is well
Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL of the infection risk in chronic wound Introduction The impact of infection on patients is well
The Management of Lower Limb Oedema. Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE 2018
 The Management of Lower Limb Oedema Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE 2018 Causes of oedema Venous stasis Lymphoedema Heart Failure Dependency Liver and kidney failure Medications Cellulitis Low protein Under
The Management of Lower Limb Oedema Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE 2018 Causes of oedema Venous stasis Lymphoedema Heart Failure Dependency Liver and kidney failure Medications Cellulitis Low protein Under
o Venous edema o Stasis ulcers o Varicose veins (not including spider veins) o Lipodermatosclerosis
 Wound Care Equipment and Supply Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid July 1, 2018 Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2018, wound care equipment and supply benefits will change for Texas
Wound Care Equipment and Supply Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid July 1, 2018 Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2018, wound care equipment and supply benefits will change for Texas
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED
 WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
SDMA Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
Wound Management in the Elderly
 Wound Management in the Elderly Stephanie Yates, MSN, ANP, ANP-BC, CWOCN Nurse Practitioner/CNS Duke University Medical Center Durham, NC stephanie.yates@duke.edu Skin Condition Key quality indicator To
Wound Management in the Elderly Stephanie Yates, MSN, ANP, ANP-BC, CWOCN Nurse Practitioner/CNS Duke University Medical Center Durham, NC stephanie.yates@duke.edu Skin Condition Key quality indicator To
Wound Healing: General Principles. Mansour Dib MD
 Wound Healing: General Principles Mansour Dib MD Normal Wound Healing Chronic Wounds: Stuck Where does it get stuck? Mostly Proliferation Sometimes Remodeling Why? Systemic factors Local factors How do
Wound Healing: General Principles Mansour Dib MD Normal Wound Healing Chronic Wounds: Stuck Where does it get stuck? Mostly Proliferation Sometimes Remodeling Why? Systemic factors Local factors How do
Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice
 Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice Wound management Conclusion In an observational study of 86
Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice Wound management Conclusion In an observational study of 86
I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use!
 I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use! Introduction: Originating from battlefield medicine much of what we use today is an evolution of material science combined with our understanding
I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use! Introduction: Originating from battlefield medicine much of what we use today is an evolution of material science combined with our understanding
easy made Cutimed Sorbact
 PRODUCTS FOR PRACTICE Cutimed Sorbact made easy Volume 3 Issue 2 May 2012 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction Bacterial colonisation and infection may contribute to delayed healing and present a major
PRODUCTS FOR PRACTICE Cutimed Sorbact made easy Volume 3 Issue 2 May 2012 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction Bacterial colonisation and infection may contribute to delayed healing and present a major
Wound management accounts for
 An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
Wound management accounts for
 An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection. KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection. KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
NPUAP Mission. Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wound Dressings for the Management of Pressure Injuries. npuap.org
 Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wound Dressings for the Management of Pressure Injuries Margaret Goldberg, MSN, RN, CWOCN June 29, 2016 NPUAP Mission The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) serves
Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wound Dressings for the Management of Pressure Injuries Margaret Goldberg, MSN, RN, CWOCN June 29, 2016 NPUAP Mission The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) serves
The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology
 The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology The first step in healing a chronic wound is to detoxify it by removing slough, necrotic tissue, exudate and bacteria, while keeping
The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology The first step in healing a chronic wound is to detoxify it by removing slough, necrotic tissue, exudate and bacteria, while keeping
Currently, the NHS is facing the challenge of
 Evaluation of a superabsorbent dressing in a primary care organization Jackie Stephen-Haynes and Claire Stephens Jackie Stephen-Haynes is Professor and Nurse Consultant, Practice Development Unit, Birmingham
Evaluation of a superabsorbent dressing in a primary care organization Jackie Stephen-Haynes and Claire Stephens Jackie Stephen-Haynes is Professor and Nurse Consultant, Practice Development Unit, Birmingham
Cost and dressing evaluation of hydrofiber and alginate dressings in the management of community-based patients with chronic leg ulceration
 Cost and dressing evaluation of hydrofiber and alginate dressings in the management of community-based patients with chronic leg ulceration Harding K G, Price P, Robinson B, Thomas S, Hofman D Record Status
Cost and dressing evaluation of hydrofiber and alginate dressings in the management of community-based patients with chronic leg ulceration Harding K G, Price P, Robinson B, Thomas S, Hofman D Record Status
ULCERS 1/12/ million diabetics in the US (2012) Reamputation Rate 26.7% at 1 year 48.3% at 3 years 60.7% at 5 years
 Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
The Proven Multifunctional Dressing
 The Proven Multifunctional Dressing belongs to an innovative class of multifunctional wound care dressings. dressings effectively cleanse, fill, absorb and moisten wounds throughout the healing continuum.
The Proven Multifunctional Dressing belongs to an innovative class of multifunctional wound care dressings. dressings effectively cleanse, fill, absorb and moisten wounds throughout the healing continuum.
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
1/5. Introduction. Primary endpoint Time to reach readiness for closure by surgical intervention or left for closure by secondary intention
 1/5 Introduction Materials and methods Animal studies show that intermittent NPWT has potential to increase the rate of granulation tissue formation compared with adjustable intermittent (AI) NPWT 1 However,
1/5 Introduction Materials and methods Animal studies show that intermittent NPWT has potential to increase the rate of granulation tissue formation compared with adjustable intermittent (AI) NPWT 1 However,
Palliative Care. EPUAP/NPUAP Publish New Pressure Ulcer Guidelines for. Treatment. Improving Quality of Care Based on CMS Guidelines 39
 Treatment EPUAP/NPUAP Publish New Pressure Ulcer Guidelines for Palliative Care Dealing with the end of a loved one s life is difficult enough, but when wound and skin care issues are involved, the decisions
Treatment EPUAP/NPUAP Publish New Pressure Ulcer Guidelines for Palliative Care Dealing with the end of a loved one s life is difficult enough, but when wound and skin care issues are involved, the decisions
DEBRIDEMENT. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
NovoSorb BTM. A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold. Regenerating tissue. Changing lives.
 NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
Managing Wounds. Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse
 Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
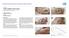 CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
Open Wound( 개방창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이있는경우 ex)abrasion, Burn,Laceration 등 Closed Wound( 폐쇄창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이없는내부조직의손상 ex)closed Fracture, Ligament tear 등
 신체조직의연속성이파괴된상태 Open Wound( 개방창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이있는경우 ex)abrasion, Burn,Laceration 등 Closed Wound( 폐쇄창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이없는내부조직의손상 ex)closed Fracture, Ligament tear 등 Partial Thickness Skin Injury - dermis 의일부만손상을입은경우
신체조직의연속성이파괴된상태 Open Wound( 개방창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이있는경우 ex)abrasion, Burn,Laceration 등 Closed Wound( 폐쇄창상 ) 피부나점막의손상이없는내부조직의손상 ex)closed Fracture, Ligament tear 등 Partial Thickness Skin Injury - dermis 의일부만손상을입은경우
The compatibility of INTRASITE Gel and ACTICOAT : An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment. *smith&nephew
 The compatibility of INTRASITE Gel and ACTICOAT : An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment *smith&nephew An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment of the compatibility of ACTICOAT and ACTICOAT 7 with INTRASITE Gel
The compatibility of INTRASITE Gel and ACTICOAT : An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment *smith&nephew An In-Vivo and In-Vitro assessment of the compatibility of ACTICOAT and ACTICOAT 7 with INTRASITE Gel
Abilar Questions and Answers
 Abilar Questions and Answers Question Answer Product Information What is Abilar Resin Salve? What are the main properties of Abilar? How is Resin different from colophony (rosin)? Abilar Resin Salve is
Abilar Questions and Answers Question Answer Product Information What is Abilar Resin Salve? What are the main properties of Abilar? How is Resin different from colophony (rosin)? Abilar Resin Salve is
Simple, gentle and affordable. *smith&nephew V1STA Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
 Simple, gentle and affordable *smith&nephew V1STA Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Smith & Nephew s extensive presence and portfolio means that for every wound, at every stage, there is an appropriate solution.
Simple, gentle and affordable *smith&nephew V1STA Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Smith & Nephew s extensive presence and portfolio means that for every wound, at every stage, there is an appropriate solution.
3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing. Matrix. Your questions answered
 3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing Matrix Your questions answered 3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing Frequently Asked Questions What is Tegaderm Matrix? Matrix is a wound dressing impregnated with polyhydrated
3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing Matrix Your questions answered 3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing Frequently Asked Questions What is Tegaderm Matrix? Matrix is a wound dressing impregnated with polyhydrated
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice.
 Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Wound bed preparation: TIME in practice
 Wound bed preparation: TIME in practice Wound bed preparation is now a well established concept and the TIME framework has been developed as a practical tool to assist practitioners when assessing and
Wound bed preparation: TIME in practice Wound bed preparation is now a well established concept and the TIME framework has been developed as a practical tool to assist practitioners when assessing and
Interesting Case Series. Skin Grafting in Pyoderma Gangrenosum
 Interesting Case Series Skin Grafting in Pyoderma Gangrenosum Marco Romanelli, MD, PhD, Agata Janowska, MD, Teresa Oranges, MD, and Valentina Dini, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology, University of Pisa,
Interesting Case Series Skin Grafting in Pyoderma Gangrenosum Marco Romanelli, MD, PhD, Agata Janowska, MD, Teresa Oranges, MD, and Valentina Dini, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology, University of Pisa,
3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing. Conquer Non-healing. Wounds
 Conquer Non-healing Wounds Chronic wounds Chronic wounds have been defined as those that fail to progress through a normal, orderly and timely sequence of repair. Or, wounds that pass through the repair
Conquer Non-healing Wounds Chronic wounds Chronic wounds have been defined as those that fail to progress through a normal, orderly and timely sequence of repair. Or, wounds that pass through the repair
Dress for Success. Dot Weir, RN, CWON, CWS Catholic Health Advanced Wound Healing Centers Buffalo, New York
 Dress for Success Dot Weir, RN, CWON, CWS Catholic Health Advanced Wound Healing Centers Buffalo, New York The Ideal Dressing Manages exudate appropriately: Does not desiccate or macerate Allows for gaseous
Dress for Success Dot Weir, RN, CWON, CWS Catholic Health Advanced Wound Healing Centers Buffalo, New York The Ideal Dressing Manages exudate appropriately: Does not desiccate or macerate Allows for gaseous
UNIQUE SURGICAL DRESSING. StopBac. bac GRADE MEDICAL.
 UNIQUE SURGICAL DRESSING Innovative medical wound care devices Patented nanotechnology solution utilizing silver M r. Flaster bac www.stopbac.eu STOPBAC STERILE PRODUCTS STANDARD ADHESIVE DRESSING Suitable
UNIQUE SURGICAL DRESSING Innovative medical wound care devices Patented nanotechnology solution utilizing silver M r. Flaster bac www.stopbac.eu STOPBAC STERILE PRODUCTS STANDARD ADHESIVE DRESSING Suitable
Anseong Factory : 70-17, Wonam-ro, Wongok-myeon, Anseong-si, Gyeonggi-do , REPUBLIC OF KOREA
 Care for tomorrow The Solution for Management HQ & Factory : 7, Hyeongjero4Beon-gil, Namsa-myeon, Cheoin-gu, Yong-in-si, Gyeonggi-do 449-884, REPUBLIC OF KOREA TEL: +8-3-33-33 / FAX: +8-3-33-34 Anseong
Care for tomorrow The Solution for Management HQ & Factory : 7, Hyeongjero4Beon-gil, Namsa-myeon, Cheoin-gu, Yong-in-si, Gyeonggi-do 449-884, REPUBLIC OF KOREA TEL: +8-3-33-33 / FAX: +8-3-33-34 Anseong
CLINICAL EVIDENCE Partial and Deep Partial Burns
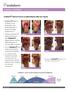 CLINICAL EVIDENCE Partial and Deep Partial Burns Endoform helps to improve re-epithelialization after burn injuries Endoform helps to facilitate tissue granulation and epithelialization in partial and
CLINICAL EVIDENCE Partial and Deep Partial Burns Endoform helps to improve re-epithelialization after burn injuries Endoform helps to facilitate tissue granulation and epithelialization in partial and
Hemostasis Inflammatory Phase Proliferative/rebuilding Phase Maturation Phase
 The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds
 Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds Health Improvement Scotland published their 13th Health Technology Assessment (HTA 13) in December 2015 entitled, Antimicrobial
Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds Health Improvement Scotland published their 13th Health Technology Assessment (HTA 13) in December 2015 entitled, Antimicrobial
BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM. Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS
 BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Contamination Presence of non-replicating microorganisms on the wound surface that evoke no clinical host response - All
BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Contamination Presence of non-replicating microorganisms on the wound surface that evoke no clinical host response - All
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection
 Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Choosing an appropriate dressing for chronic wounds Denise Bell BSc, RGN and Dot Hyam RGN, DipHE
 Choosing an appropriate dressing for chronic wounds Denise Bell BSc, RGN and Dot Hyam RGN, DipHE Chronic wounds are nonhealing with a sometimes complex aetiology, and dressing such wounds can be difficult
Choosing an appropriate dressing for chronic wounds Denise Bell BSc, RGN and Dot Hyam RGN, DipHE Chronic wounds are nonhealing with a sometimes complex aetiology, and dressing such wounds can be difficult
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Wound Care in the Community. Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts
 Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Debridement within the context of the EWMA s debridement guidelines. Emil Schmidt WCNS SDHB - Otago
 Debridement within the context of the EWMA s debridement guidelines Emil Schmidt WCNS SDHB - Otago EWMA Debridement Document Expert consensus document, 2013 Contents Mechanical debridement options Autolytic
Debridement within the context of the EWMA s debridement guidelines Emil Schmidt WCNS SDHB - Otago EWMA Debridement Document Expert consensus document, 2013 Contents Mechanical debridement options Autolytic
Genadyne A4 and foam to treat a postoperative debridment flank abscess
 Genadyne A4 and foam to treat a postoperative debridment flank abscess Michael S. DO, The Wound Healing Center Indianapolis, IN Cynthia Peebles RN D.O.N., Becky Beck RN Heartland at Prestwick NH Avon,
Genadyne A4 and foam to treat a postoperative debridment flank abscess Michael S. DO, The Wound Healing Center Indianapolis, IN Cynthia Peebles RN D.O.N., Becky Beck RN Heartland at Prestwick NH Avon,
Ray Norris, Rachel Henchy
 Use of low frequency ultrasound therapy in the treatment of recalcitrant leg ulcers: case series This series of case reports looks at the efficacy of low frequency ultrasound using the MIST Therapy System
Use of low frequency ultrasound therapy in the treatment of recalcitrant leg ulcers: case series This series of case reports looks at the efficacy of low frequency ultrasound using the MIST Therapy System
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR
 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
Wound Care per HHVNA Wound Product Formulary
 Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
easy made HydroTherapy Wounds uk Hydrotherapy
 Wounds uk VOL 12 ISSUE 4 NOV 2016 Hydrotherapy HydroTherapy made easy Introduction Rapid cleansing, early granulation and sustained epithelialisation are key requirements for the efficient healing of chronic
Wounds uk VOL 12 ISSUE 4 NOV 2016 Hydrotherapy HydroTherapy made easy Introduction Rapid cleansing, early granulation and sustained epithelialisation are key requirements for the efficient healing of chronic
We will dose your Gentamycin. We will dose your Vancomycin
 We will dose your Gentamycin We will dose your Vancomycin We will dose your Heparin We will dose your Warfarin We will do your wound care Animal models show that wounds, including chronic wounds, heal
We will dose your Gentamycin We will dose your Vancomycin We will dose your Heparin We will dose your Warfarin We will do your wound care Animal models show that wounds, including chronic wounds, heal
Workshop on Debridement
 MEDICINSK TEKNIK I SÅRDIAGNOSTIK OCH SÅRBEHANDLING Monday, 20 th of april 2015 Stockholm Sweden Workshop on Debridement Sources for best practice Reference documents available in several languages : WHY
MEDICINSK TEKNIK I SÅRDIAGNOSTIK OCH SÅRBEHANDLING Monday, 20 th of april 2015 Stockholm Sweden Workshop on Debridement Sources for best practice Reference documents available in several languages : WHY
Clinical. Summaries. 3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing. Delayed wound healing: A major clinical problem
 3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing Clinical Summaries Delayed wound healing: A major clinical problem Chronic wounds have been defined as those that fail to progress through a normal, orderly, and timely
3M Tegaderm Matrix Matrix Dressing Clinical Summaries Delayed wound healing: A major clinical problem Chronic wounds have been defined as those that fail to progress through a normal, orderly, and timely
