: Abdominal Emergencies
|
|
|
- Evelyn Manning
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTRODUCTION Abdominal complaints are very common in emergency medicine. The specific cause of the abdominal pain can very rarely be determined in the pre-hospital environment, however performing a good patient assessment and gathering a good history can help point to the probable cause. When dealing with abdominal complaints, it is most important that the clinician be able to recognize if a patient is unstable and requires urgent transport to definitive care. SAFETY Vomiting is a common occurrence in patients with abdominal pain. The clinician should wear appropriate personal protective equipment to protect against splashing emesis. ASSESSMENT Most abdominal pain can be categorized into three types tension, inflammatory, or ischemic. Tension pain is caused by distension of a hollow organ such as in the case of a bowel obstruction, constipation, renal colic (in the ureter), or early appendicitis. Fluid accumulation from trauma or other causes can also cause this type of pain. These patients have a hard time finding a position of comfort or sitting still. Inflammatory pain often feels deep and can be generalized if the visceral peritoneum is involved. As the parietal peritoneum becomes inflamed, the pain begins to localize. Patients with inflammatory pain often prefer to lie still and avoid movement. Pancreatitis, late appendicitis, and cholecystitis all cause inflammatory-type pain. It is also important to note that abdominal pain can be referred from another area, such as epigastric pain occurring during a myocardial infarction. The reverse of this is also true, where some abdominal pain can be referred to other areas of the body, such as shoulder pain from diaphragmatic irritation, or back pain with cholecystitis. Determining the specific cause of abdominal pain is very difficult, if not impossible, in the pre-hospital setting. The most important diagnoses to consider first are those which are life-threatening. Acute Life-Threatening Abdominal Emergencies Aortic Aneurysm (ruptured or leaking) In patients presenting with sudden onset of abdominal, flank or back pain, a leaking or ruptured aneurysm cannot be ruled out. Ask about a family or personal history of AAA. Other signs and symptoms can include hypotension, syncope, a pulsatile mass, and sudden onset of severe pain (may be stabbing, ripping, or tearing); often resembles renal colic Ectopic Pregnancy Ectopic pregnancy should be considered in any woman of childbearing age complaining of abdominal or pelvic pain or PV bleeding. Myocardial Infarction Women, older adults and patients with diabetes often present with symptoms other than chest pain, such as abdominal or back pain. A 12-lead ECG must be obtained. Traumatic Rupture of Abdominal Organs (mainly liver or spleen) This patient may have a history of blunt or penetrating trauma (even minor trauma) and may present with hypotension, tachycardia and/or syncope. Ischemic pain is the least common type of pain, but is the most serious. If an organ loses blood flow due to an arterial occlusion, the area will become necrotic very quickly. The pain associated with ischemia is sudden in onset and very intense. Often, the level of pain reported is disproportionate to the assessment findings (e.g. patient will report 10/10 pain but will have a soft, non-tender, non-distended abdomen). Analgesics rarely help this type of pain. Mesenteric artery occlusion or strangulated bowel both cause ischemic-type pain. These patients will want to remain still, much like patients with inflammatory pain. Uncontrolled GI Bleed Caused by peptic ulcer disease, erosive gastritis/esophagitis, or esophageal/gastric varices. These patients may present with hematemesis, melena, hypotension, tachycardia, syncope and an altered level of consciousness. In addition to asking OPQRST and SAMPLE questions, an appropriate history would also include questions regarding symptoms such as fever or chills, nausea, vomiting, and GI or PV bleeding. Changes in appetite, bowel movements, urination, or menses should also be explored. Clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion when onset of
2 pain is sudden. Abdominal emergencies with sudden pain are often more serious as this may signify the rupture of an organ or vascular structure. A general physical exam should identify the location of the pain as well as guarding, bruising, rigidity, or the appearance of a pulsatile mass. Bruising around the navel or the flanks suggest severe bleeding within the abdominal cavity. When assessing the abdomen, look for scars which may suggest previous surgeries. Previous surgery is a risk factor for bowel obstruction. Bowel obstruction must be considered in a patient who is vomiting with no associated diarrhea. It must also be considered in elderly patients with constipation-like symptoms. The abdomen is divided into 4 quadrants (and 9 regions). The location of the pain can help to determine the etiology (See Figure 1). Abdominal pathologies may present atypically, especially in the elderly, and pain can often present in overlapping regions. Figure 1: Differential Diagnosis Based on Classic Region of Pain RUQ Cholecystitis Hepatitis Bile duct pathology Biliary colic Right Flank Renal colic AAA Pyelonephritis RLQ Appendicitis IBD Diverticulitis Ovarian torsion Endometriosis Ectopic pregnancy Inguinal hernia Epigastric Pancreatitis GERD MI Peptic ulcer Umbilical Pancreatitis Peptic ulcer Early appendicitis Umbilical hernia IBD Suprapubic PID Endometriosis UTI IBD Diverticulitis Urinary retention LUQ Gastritis Splenic rupture Pancreatitis Left Flank Renal colic AAA Pyelonephritis LLQ Diverticulitis Ovarian torsion Endometriosis Ectopic pregnancy Inguinal hernia ischemic bowel, IBD, gastroenteritis, bowel obstruction, early appendicitis, and pancreatitis. Not all abdominal emergencies present with pain, such as with some GI bleeds. Upper GI bleeding can present with hematemesis (bright red or coffeeground colour) and/or melena (black/tarry stool). Lower GI bleeding typically presents with hematochezia (maroon blood mixed in the stool), or bright-red blood per rectum. All patients with abdominal pain should have a 12- lead ECG obtained and continuous cardiac monitoring. MANAGEMENT If the patient is suspected of having a lifethreatening abdominal emergency, prepare for rapid transport. Dimenhydrinate should be administered if the patient has nausea or vomiting. Analgesia should be considered to reduce pain. Analgesia does not obscure subsequent assessment and diagnostic testing in the emergency department. The patient should not be given anything by mouth, unless the cause is determined to be an MI and the administration of ASA and/or other anti-platelet is required. Dehydration and hypotension can be treated with IV fluids. The majority of patients with acute abdominal pain or gastrointestinal bleeding require lab tests, imaging, and possibly surgery. Management in the pre-hospital setting is for the most part supportive, and the clinician should ensure a thorough history is obtained. Pediatric Abdominal Emergencies The signs and symptoms of abdominal emergencies in pediatric patients will differ depending on their age. In general, signs and symptoms of abdominal emergencies in pediatric patients include: Some conditions may cause diffuse or poorly localized abdominal pain, such as peritonitis, Vomiting Pain Diarrhea
3 Constipation Bleeding Jaundice Abdominal masses Abdominal emergencies may present as irritability, lethargy, or restlessness. It is important to note the patient s behaviour prior to and during assessment. In many cases, the abdominal pain may be from an extraabdominal origin such as pneumonia. Ask the child or parents/guardians if there has been any vomiting or diarrhea and check for or ask about any discolouration or blood in either. A thorough history should also include asking about fever, bowel habits, weight changes and feeding habits. Allow the pediatric patient to remain in the parent/guardian s lap or arms during assessment in order to help establish rapport. The likely etiology of abdominal complaints differs with age. Some of the more serious causes of abdominal emergencies in children include: Infants/neonates Incarcerated hernia Peptic ulcer disease Pyelonephritis Ovarian/testicular torsion Nausea/vomiting/diarrhea and/or abdominal pain in the pediatric population may represent an acute surgical emergency. All pediatric patients with signs or symptoms of abdominal emergencies should be transported to the hospital for further assessment and tests. Key Points - Abdominal Emergencies Be careful not to prematurely rule-out lifethreatening causes Adequately manage pain Consider ACS differential Acquire 12 Lead ECG Necrotizing enterocolitis (premature neonate) Intussusception Incarcerated hernia Volvulus Pyloric stenosis Malrotation of the intestine GERD 2-5 years old Appendicitis Intussusception Volvulus Diabetic ketoacidosis Incarcerated hernia Metabolic acidosis Pneumonia 6 years and older Appendicitis Bowel obstruction Abdominal pain in the geriatric population is a high risk presentation TRANSFER OF CARE Provide all relevant details to the receiving facility: history of present illness, pertinent history, vital signs, treatment rendered and the patient s response to treatment. CHARTING In addition to the mandatory fields it is important to document the following in the epcr text fields: Location and description of pain Any treatment given and response to treatment All 12-leads ECGs should be attached to the PCR. KNOWLEDGE GAPS There is research still to be done to determine the most effective anti-nausea/anti-emetic drug to use in the pre-hospital setting. Any interest in research regarding respiratory distress can be directed to EHS via the following link:
4 EDUCATION Clinicians should maintain knowledge of the various potentially life-threatening causes of abdominal emergencies. The optimal management of these emergencies is under continual review for ongoing continual medical education. Any recommendations for content delivery can be directed to the EHS Quality and Learning Department. QUALITY IMPROVEMENT Recent evidence shows that abdominal pain is undertreated; providing analgesia is appropriate. It is important for the paramedic to record the overall management in the epcr. This will require completion of the various fields in the epcr, including an appropriate text description in the comment section. Only by appropriate, accurate and complete charting can we build the case for new techniques and strategies. REFERENCES cols/toc.cfm Ma, O.J., Cline, D.M., Tintinalli, J.E., Kelen, G.D., & Stapczynski, J.S. (Eds.). (2004). Emergency Medicine Manual (6 th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw- Hill.
5 PEP 3x3 TABLES for ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES Throughout the EHS Guidelines, you will see notations after clinical interventions (e.g.: PEP 2 neutral). PEP stands for: the Canadian Prehospital Evidence-based Protocols Project. The number indicates the Strength of cumulative evidence for the intervention: 1 = strong evidence exists, usually from randomized controlled trials; 2 = fair evidence exists, usually from non-randomized studies with a comparison group; and 3 = weak evidence exists, usually from studies without a comparison group, or from simulation or animal studies. Green = the evidence is supportive for the use of the intervention; Yellow = the evidence is neutral; Red = the evidence opposes use of the intervention; White = there is no evidence available for the intervention, or located evidence is currently under review. PEP Recommendations for Abdominal Emergencies Interventions, as of 2013/03/14. PEP is continuously updated. See: for latest recommendations, and for individual appraised articles. The coloured word indicates the direction of the evidence for the intervention: publication. However, the EHS guidance is advisory and has been developed to assist healthcare professionals, together with patients, to make decisions about the management of the patient s health, including treatments. It is intended to support the decision making process and is not a substitute for sound clinical judgment. Guidelines cannot always contain all the information necessary for determining appropriate care and cannot address all individual situations; therefore individuals using these guidelines must ensure they have the appropriate
6 Program Document Number Management System PDN: Title: EENT & Dental Emergencies Type: CPG Effective Date: April 3, 2013 Approval Date: March Review Date: April Replaces: Signature of Program Director Signature of Program Document Coordinator PDN: Title: Type: Field Guide Effective Date: February Approval Date: February Review Date: April 1, 2013 Replaces: Signature of Program Director Signature of program Document Coordinator
Chapter 24 - Abdominal_Emergencies
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 24.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 13, 15, 18, 20 22 24.2 Describe the location, structure, and function of the organs in the abdominal
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 24.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 13, 15, 18, 20 22 24.2 Describe the location, structure, and function of the organs in the abdominal
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/12/2012. Chapter 29. Nontraumatic Abdominal Injuries
 Chapter 29 Nontraumatic Abdominal Injuries Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with nontraumatic abdominal pain Learning Objectives
Chapter 29 Nontraumatic Abdominal Injuries Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with nontraumatic abdominal pain Learning Objectives
Causes of abdominal pain Doctors in the ED spend lots of time and money diagnosing abdominal pain. They still often do not know the exact cause
 1 2 3 What's Going On in There? EMS and Abdominal Pain Kevin McFarlane BSN,RN,CEN,CPEN,EMT Southwest Emergency Education and Consulting What is going on in there Acute Abdomen Sudden onset of pain within
1 2 3 What's Going On in There? EMS and Abdominal Pain Kevin McFarlane BSN,RN,CEN,CPEN,EMT Southwest Emergency Education and Consulting What is going on in there Acute Abdomen Sudden onset of pain within
Gastrointestinal & Genitourinary Emergencies. Lesson Goal. Learning Objectives 9/10/2012
 Gastrointestinal & Genitourinary Emergencies Lesson Goal Recognize, assess & provide care to patients with abdominal cavity injuries Learning Objectives Discuss different causes of nontraumatic abdominal
Gastrointestinal & Genitourinary Emergencies Lesson Goal Recognize, assess & provide care to patients with abdominal cavity injuries Learning Objectives Discuss different causes of nontraumatic abdominal
Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
Abdominal Pain. Luke Donnelly, MD Emergency Medicine
 Abdominal Pain Luke Donnelly, MD Emergency Medicine Objectives Approach to abdominal pain Evaluation Critical diagnoses and treatments Abdominal Pain Most Common ER Complaint Broad Differential Can often
Abdominal Pain Luke Donnelly, MD Emergency Medicine Objectives Approach to abdominal pain Evaluation Critical diagnoses and treatments Abdominal Pain Most Common ER Complaint Broad Differential Can often
: Undifferentiated Patient
 INTRODUCTION Though many patients in the pre-hospital setting have specific complaints such as my belly hurts or I m having chest pain, there are numerous situations in which the patient complains of symptoms
INTRODUCTION Though many patients in the pre-hospital setting have specific complaints such as my belly hurts or I m having chest pain, there are numerous situations in which the patient complains of symptoms
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC
 Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
SEPSIS SYNDROME
 INTRODUCTION Sepsis has been defined as a life threatening condition that arises when the body s response to an infection injures its own tissues and organs. Sepsis may lead to shock, multiple organ failure
INTRODUCTION Sepsis has been defined as a life threatening condition that arises when the body s response to an infection injures its own tissues and organs. Sepsis may lead to shock, multiple organ failure
Abdo Pain rules & regulations. Mark Hartnell 2010
 Abdo Pain rules & regulations Mark Hartnell 2010 Aims Simple rules which might help in patients with abdominal pain Talk about some myths and realities Discuss some practical how to s in day to day treatment
Abdo Pain rules & regulations Mark Hartnell 2010 Aims Simple rules which might help in patients with abdominal pain Talk about some myths and realities Discuss some practical how to s in day to day treatment
ACUTE ABDOMEN. Dr. M Asadi. Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS. Assistant Professor of General Surgery
 ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
Chapter 18 - Gastrointestinal & Urologic Emergencies
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 18 Gastrointestinal and Urologic National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 4) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 18 Gastrointestinal and Urologic National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 4) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation
VOMITING. Tan Lay Zye
 VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
SAEMS ABDOMINAL PAIN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module
 SAEMS ABDOMINAL PAIN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module Dawn Daniels Tucson Medical Center January 2016 PURPOSE This SAEMS Standing Order Training Module has been developed to serve as a template for
SAEMS ABDOMINAL PAIN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module Dawn Daniels Tucson Medical Center January 2016 PURPOSE This SAEMS Standing Order Training Module has been developed to serve as a template for
Abdominal & scrotal pain
 Abdominal & scrotal pain Junior Teach Emergency Department 1 Created by SR Bruijns 03/11/2010 Objectives Understanding of, and emergency management of Acute abdominal pain Undifferentiated abdominal pain
Abdominal & scrotal pain Junior Teach Emergency Department 1 Created by SR Bruijns 03/11/2010 Objectives Understanding of, and emergency management of Acute abdominal pain Undifferentiated abdominal pain
USMLE and COMLEX II. CE / CK Review. General Surgery. 1. Northwestern Medical Review
 USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
Left abdominal pain with back pain
 Search Search Left abdominal pain with back pain Lower left abdominal pain and lower back pain in women - Possible causes of chronic but worsening lower left abdominal pain with simultaneous low back pain?
Search Search Left abdominal pain with back pain Lower left abdominal pain and lower back pain in women - Possible causes of chronic but worsening lower left abdominal pain with simultaneous low back pain?
: STROKE. other pertinent information such as recent trauma, illicit drug use, pertinent medical history or use of oral contraceptives.
 INTRODUCTION A cerebral vascular accident (CVA) or stroke is a lack of blood supply to the brain as a result of either ischemia or hemorrhage. 80% of CVAs are a result of ischemia (embolic or thrombotic)
INTRODUCTION A cerebral vascular accident (CVA) or stroke is a lack of blood supply to the brain as a result of either ischemia or hemorrhage. 80% of CVAs are a result of ischemia (embolic or thrombotic)
9/10/2012. Chapter 44. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont d) Bleeding
 Chapter 44 Bleeding 1 Learning Objectives Describe the etiology, history, and physical findings of external bleeding Predict hemorrhage on the basis of the patient s mechanism of injury Distinguish between
Chapter 44 Bleeding 1 Learning Objectives Describe the etiology, history, and physical findings of external bleeding Predict hemorrhage on the basis of the patient s mechanism of injury Distinguish between
GENI Program: GI and Abdominal Chief Complaints. Kim Macfarlane Clinical Nurse Specialist, Critical Care February 2008
 GENI Program: GI and Abdominal Chief Complaints Kim Macfarlane Clinical Nurse Specialist, Critical Care February 2008 Dehydration Common acute and chronic problem Recognition is critically important to
GENI Program: GI and Abdominal Chief Complaints Kim Macfarlane Clinical Nurse Specialist, Critical Care February 2008 Dehydration Common acute and chronic problem Recognition is critically important to
An Approach to Abdominal Pain
 An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research 11/16/2017. Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument 11/16/2017
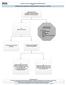 Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
SAEMS ABDOMINAL PAIN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module
 SAEMS ABDOMINAL PAIN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module Mary Ann Matter University Medical Center January 27, 2009 PURPOSE This SAEMS Standing Order Training Module has been developed to serve as a template
SAEMS ABDOMINAL PAIN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module Mary Ann Matter University Medical Center January 27, 2009 PURPOSE This SAEMS Standing Order Training Module has been developed to serve as a template
Surgical Education Series
 Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
Student Notes Chapter 16: Gastrointestinal and Urologic Emergencies 1. Chapter 16. Gastrointestinal and Urologic Emergencies
 Student Notes Chapter 16: Gastrointestinal and Urologic Emergencies 1 Chapter 16 Gastrointestinal and Urologic Emergencies Unit Summary Students who complete this chapter presentation and the related course
Student Notes Chapter 16: Gastrointestinal and Urologic Emergencies 1 Chapter 16 Gastrointestinal and Urologic Emergencies Unit Summary Students who complete this chapter presentation and the related course
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery
 12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
General Surgery Service
 General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
The Acute Abdomen New Mexico Nurse Practitioner Council Annual Conference, 2012
 The Acute Abdomen New Mexico Nurse Practitioner Council Annual Conference, 2012 Darra D. Kingsley, MD Associate Professor, Surgery, University of New Mexico School of Medicine Associate Chief of Staff,
The Acute Abdomen New Mexico Nurse Practitioner Council Annual Conference, 2012 Darra D. Kingsley, MD Associate Professor, Surgery, University of New Mexico School of Medicine Associate Chief of Staff,
- GI and GU are the main sources of AP, but AP can come from extra- and intraabdominal
 Abdominal Pain Karima Sajadi Based on Chapter 27 in Rosen s Emergency Medicine Common CC in ED, but presents lot of challenges for the pts and docs (pts have hard time conveying the nature and quality
Abdominal Pain Karima Sajadi Based on Chapter 27 in Rosen s Emergency Medicine Common CC in ED, but presents lot of challenges for the pts and docs (pts have hard time conveying the nature and quality
Genitourinary. Abdomen JENNIFER NOCE CCEMTP/FP-C/CCP-C
 Genitourinary Abdomen JENNIFER NOCE CCEMTP/FP-C/CCP-C Objectives To student will be able to identify solid and hollow organs of the abdominal cavity The student will be able to identify the importance
Genitourinary Abdomen JENNIFER NOCE CCEMTP/FP-C/CCP-C Objectives To student will be able to identify solid and hollow organs of the abdominal cavity The student will be able to identify the importance
Hernia Advisory Panel. Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson. Funding
 Acute Abdomen Andreas M Kluftinger MD FRCSC Kelowna General Hospital Disclosure Hernia Advisory Panel Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson Funding nil, zilch, zippo, nada, zero Objectives Understand the Pathophysiology
Acute Abdomen Andreas M Kluftinger MD FRCSC Kelowna General Hospital Disclosure Hernia Advisory Panel Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson Funding nil, zilch, zippo, nada, zero Objectives Understand the Pathophysiology
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, abdominal considerations in, 183 184 antiemetics in, 182 auscultation in, 170 C-reactive protein in, 174 175 character
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, abdominal considerations in, 183 184 antiemetics in, 182 auscultation in, 170 C-reactive protein in, 174 175 character
ABy Susan Simmons Holcomb, ARNP-BC, PhD
 cute bdomen: ABy Susan Simmons Holcomb, ARNP-BC, PhD So many things some life-threatening can cause abdominal pain. Here s how to capture the clues quickly and accurately. Determining the cause of abdominal
cute bdomen: ABy Susan Simmons Holcomb, ARNP-BC, PhD So many things some life-threatening can cause abdominal pain. Here s how to capture the clues quickly and accurately. Determining the cause of abdominal
Problem. A 34-year. year-old woman admitted for control of diabetes develops acute abdominal pain that increases in severity over several hours.
 Immediate Questions Problem. A 34-year year-old woman admitted for control of diabetes develops acute abdominal pain that increases in severity over several hours. A. What are the patient's vital signs?
Immediate Questions Problem. A 34-year year-old woman admitted for control of diabetes develops acute abdominal pain that increases in severity over several hours. A. What are the patient's vital signs?
TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 8 Episodes
 TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 8 Episodes Acute Seizure, Syncope, Acute Gastroenteritis, Pediatric Pneumonia, Bronchiolitis, Colposcopy, Hysterectomy,
TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 8 Episodes Acute Seizure, Syncope, Acute Gastroenteritis, Pediatric Pneumonia, Bronchiolitis, Colposcopy, Hysterectomy,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
9/21/15. Joshua Pruitt, MD, FAAEM Medical Director, LifeGuard Air Ambulance Iowa PA Society Fall CME Conference September 29, 2015
 Unless they prove otherwise. ~Every ED attending ever Joshua Pruitt, MD, FAAEM Medical Director, LifeGuard Air Ambulance Iowa PA Society Fall CME Conference September 29, 2015 AAA with rupture Mesenteric
Unless they prove otherwise. ~Every ED attending ever Joshua Pruitt, MD, FAAEM Medical Director, LifeGuard Air Ambulance Iowa PA Society Fall CME Conference September 29, 2015 AAA with rupture Mesenteric
Measuring What Students Know: Writing Effective MCQ Questions
 Measuring What Students Know: Writing Effective MCQ Questions 1 What Can Student Assessments Do? Communicate important content and skills Provide basis for grading, passing, graduation Identify students
Measuring What Students Know: Writing Effective MCQ Questions 1 What Can Student Assessments Do? Communicate important content and skills Provide basis for grading, passing, graduation Identify students
Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen
 Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Medical PCCN. AACN Progressive Critical Care Nursing.
 Medical PCCN AACN Progressive Critical Care Nursing http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pccn Question: 83 What would be identified on the arterial blood gas results as a reflection of acute respiratory
Medical PCCN AACN Progressive Critical Care Nursing http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pccn Question: 83 What would be identified on the arterial blood gas results as a reflection of acute respiratory
Differentiate IgE-mediated food allergy from non-ige mediated food allergy. List the foods and formulas most commonly associated with food allergy.
 Gastroenterology Description: The resident will be exposed to various clinical symptoms and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract which are commonly seen by the gastroenterologist. The resident will be
Gastroenterology Description: The resident will be exposed to various clinical symptoms and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract which are commonly seen by the gastroenterologist. The resident will be
BIOE221. Session 6. Abdominal Examination. Bioscience Department. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 BIOE221 Session 6 Abdominal Examination Bioscience Department Examination of the Abdomen Session objectives Understand the organs / structures that are present in the abdominal cavity Understand the importance
BIOE221 Session 6 Abdominal Examination Bioscience Department Examination of the Abdomen Session objectives Understand the organs / structures that are present in the abdominal cavity Understand the importance
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION. RNs WITH ADDITIONAL AUTHORIZED PRACTICE CLINICAL DECISION TOOL AUGUST 2017
 DEFINITION Cholelithiasis Presence of gall stones in the biliary tract. Biliary Colic Right upper quadrant pain due to obstruction of a bile duct by a gallstone. Cholecystitis Inflammation of the gallbladder
DEFINITION Cholelithiasis Presence of gall stones in the biliary tract. Biliary Colic Right upper quadrant pain due to obstruction of a bile duct by a gallstone. Cholecystitis Inflammation of the gallbladder
DOMINATE THE CLERKSHIP REVIEW PACKET. What are the electrolyte compositions of NS, LR, Plasmalyte A? Na Cl K HCO3 Ca Mg ph NS LR Plasmalyte A
 DOMINATE THE CLERKSHIP REVIEW PACKET POST OP CARE Fluids What percent of total body water does each compartment (extracellular, intracellular, interstitial, intravascular) make up? What are the electrolyte
DOMINATE THE CLERKSHIP REVIEW PACKET POST OP CARE Fluids What percent of total body water does each compartment (extracellular, intracellular, interstitial, intravascular) make up? What are the electrolyte
From Inflammation to Ischemia May apply to all luminal structures Obstruction Small or large bowel Appendix Gall bladder Ureter Hydrostatic Pressure:
 The Acute Abdomen Surgical Issues for the Family Practitioner Rochelle A. Dicker, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Anesthesia UC San Francisco Visceral Pain Vague Deep Associated with nausea/vomiting
The Acute Abdomen Surgical Issues for the Family Practitioner Rochelle A. Dicker, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Anesthesia UC San Francisco Visceral Pain Vague Deep Associated with nausea/vomiting
Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
Block 5 VIRGINIA CAMPUS Gastrointestinal and Renal Systems 2018
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
Block 5 VIRGINIA CAMPUS Gastrointestinal and Renal Systems 2018
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
Chapter 26. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont d) 9/10/2012. Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 26 Gastrointestinal Disorders 1 Learning Objectives Describe the incidence, morbidity, and mortality rates of GI emergencies Identify risk factors predisposing to GI emergencies Discuss the anatomy,
Chapter 26 Gastrointestinal Disorders 1 Learning Objectives Describe the incidence, morbidity, and mortality rates of GI emergencies Identify risk factors predisposing to GI emergencies Discuss the anatomy,
CLASS 1. PATHOLOGY 3. PATHOLOGY 5. PATHOLOGY 7. PATHOLOGY 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 16 Tuesday, July 17 Wednesday, July 18 Thursday, July 19 Friday, July 20 1. PATHOLOGY 3. PATHOLOGY 5. PATHOLOGY 7. PATHOLOGY 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO SDL: Diseases of the Oral
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 16 Tuesday, July 17 Wednesday, July 18 Thursday, July 19 Friday, July 20 1. PATHOLOGY 3. PATHOLOGY 5. PATHOLOGY 7. PATHOLOGY 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO SDL: Diseases of the Oral
Department of Pediatrics, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2013.16.4.219 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2013 December 16(4):219-224 Review Article PGHN Acute Abdominal Pain in Children Joon Sung
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2013.16.4.219 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2013 December 16(4):219-224 Review Article PGHN Acute Abdominal Pain in Children Joon Sung
Abdominal Assessment
 Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Review. 1. Peritonitis would MOST likely result following injury to the: A. liver. B. spleen. C. kidney. D. stomach.
 Chapter 28 Review Review 1. Peritonitis would MOST likely result following injury to the: A. liver. B. spleen. C. kidney. D. stomach. Review Answer: D Rationale: In general, solid organs bleed when injured
Chapter 28 Review Review 1. Peritonitis would MOST likely result following injury to the: A. liver. B. spleen. C. kidney. D. stomach. Review Answer: D Rationale: In general, solid organs bleed when injured
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries. Chapter 28
 Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL
 .. ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL THE ABDOMEN SECTION EIGHT Version 1.1 2010 Update PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL OJECTIVES: THE ABDOMEN The objectives indicate what you should know,
.. ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL THE ABDOMEN SECTION EIGHT Version 1.1 2010 Update PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL OJECTIVES: THE ABDOMEN The objectives indicate what you should know,
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Gastroenterology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Gastroenterology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the general pediatrician in the assessment and management of patients with
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Gastroenterology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the general pediatrician in the assessment and management of patients with
General'Surgery'Service'
 General'Surgery'Service' Patient Care Goals and Objectives 1)! Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric 2)! Interpret the results of clinical evaluations (history, physical examination) performed on patients being
General'Surgery'Service' Patient Care Goals and Objectives 1)! Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric 2)! Interpret the results of clinical evaluations (history, physical examination) performed on patients being
Abdominal pain in children. University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn Faculty of Medical Sciences Department od Clinical Pediatrics
 Abdominal pain in children University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn Faculty of Medical Sciences Department od Clinical Pediatrics Abdominal pain in childhoodgeneral informations One of the most frequent
Abdominal pain in children University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn Faculty of Medical Sciences Department od Clinical Pediatrics Abdominal pain in childhoodgeneral informations One of the most frequent
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very common problem in emergency medicine. Between
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very common problem in emergency medicine. Between
Chapter 22. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/18/2012. Chest and Abdominal Emergencies
 Chapter 22 and Abdominal Emergencies Learning Objectives Discuss emergency medical care considerations for patient with penetrating chest injury Differentiate care of an open wound to the chest from an
Chapter 22 and Abdominal Emergencies Learning Objectives Discuss emergency medical care considerations for patient with penetrating chest injury Differentiate care of an open wound to the chest from an
By Junaid Asghar M Med, FAFP Consultant Adult Emergency Medicine. King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre- Riyadh- KSA
 By Junaid Asghar M Med, FAFP Consultant Adult Emergency Medicine King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre- Riyadh- KSA Case No 1 A VIP patient brings his 21 years son in EM with the complaints
By Junaid Asghar M Med, FAFP Consultant Adult Emergency Medicine King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre- Riyadh- KSA Case No 1 A VIP patient brings his 21 years son in EM with the complaints
Always keep it in the differential
 Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Skin Susceptible to injury; longer time Senses of the senses Respiratory system Decreased ability to exchange
 1 Geriatric Review 2 Geriatrics Geriatric patients are individuals older than years of age. In 2000, the geriatric population was almost 35 million. By 2020, the geriatric population is projected to be
1 Geriatric Review 2 Geriatrics Geriatric patients are individuals older than years of age. In 2000, the geriatric population was almost 35 million. By 2020, the geriatric population is projected to be
Acute Abdominal Emergencies
 CHAPTER 18 Acute Abdominal Emergencies Abdominal Anatomy & Physiology Abdominal A & P Abdominal A & P Most organs contained in the peritoneum Visceral Peritoneum Covers organs Parietal Peritoneum Attached
CHAPTER 18 Acute Abdominal Emergencies Abdominal Anatomy & Physiology Abdominal A & P Abdominal A & P Most organs contained in the peritoneum Visceral Peritoneum Covers organs Parietal Peritoneum Attached
European Board Examination in Emergency Medicine. Example MCQs.
 European Board Examination in Emergency Medicine Example MCQs. The Part A of the EBEEM consists of 120 multiple choice questions (MCQ) which cover the European Curriculum for Emergency Medicine. The following
European Board Examination in Emergency Medicine Example MCQs. The Part A of the EBEEM consists of 120 multiple choice questions (MCQ) which cover the European Curriculum for Emergency Medicine. The following
LOKUN! I got stomach ache!
 LOKUN! I got stomach ache! Mr L is a 67year old Chinese gentleman who is a non smoker, social drinker. He has a medical history significant for Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Chronic
LOKUN! I got stomach ache! Mr L is a 67year old Chinese gentleman who is a non smoker, social drinker. He has a medical history significant for Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Chronic
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings
 August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
Abdominal pain. Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Pediatric Lecturer Jazan Faculty of Medicine
 Abdominal pain Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Pediatric Lecturer Jazan Faculty of Medicine Objectives Understand the principal causes of acute abdominal pain in children. Describe the characteristics of visceral
Abdominal pain Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Pediatric Lecturer Jazan Faculty of Medicine Objectives Understand the principal causes of acute abdominal pain in children. Describe the characteristics of visceral
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum. Elective Student S. C.
 Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases. Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT)
 Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
APR-DRG Description Ave Charge
 Abdominal Pain 16,500.25 2.8 6,000.09 Acute & Subacute Endocarditis 15,339.30 3.0 5,113.10 Acute Myocardial Infarction 17,687.46 2.6 6,802.87 Alcohol Abuse & Dependence 19,126.64 4.2 4,553.96 Alcoholic
Abdominal Pain 16,500.25 2.8 6,000.09 Acute & Subacute Endocarditis 15,339.30 3.0 5,113.10 Acute Myocardial Infarction 17,687.46 2.6 6,802.87 Alcohol Abuse & Dependence 19,126.64 4.2 4,553.96 Alcoholic
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING
 GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
Abdominal pain with back pain
 Abdominal pain with back pain The Borg System is 100 % Abdominal pain with back pain Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Abdominal pain with back pain The Borg System is 100 % Abdominal pain with back pain Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Diffuse abdominal pain in all quadrants
 Diffuse abdominal pain in all quadrants University of São Paulo, School of Medicine, Clinicas Hospital, São Paulo, SP, Brazil. Right iliac region pain is caused by sigmoid colon, left urinary tract or
Diffuse abdominal pain in all quadrants University of São Paulo, School of Medicine, Clinicas Hospital, São Paulo, SP, Brazil. Right iliac region pain is caused by sigmoid colon, left urinary tract or
Pelvic Pain. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
3/22/2011. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Appendicitis. Lemone and Burke Chapter 26
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, surgery of, abdominal pain and, 163 vascular anatomy of, 253 255 Abdominal aortic aneurysm, 264 266 Abdominal emergencies, vascular,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, surgery of, abdominal pain and, 163 vascular anatomy of, 253 255 Abdominal aortic aneurysm, 264 266 Abdominal emergencies, vascular,
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
OBJECTIVES VISCERAL PAIN RECEPTORS LOCATION & NATURE OF THE PAIN LOCATION OF VISCERAL PAIN RECEPTORS 4/12/2018. Nancy Brown, APRN, CPNP April 18, 2018
 Nancy Brown, APRN, CPNP April 18, 2018 OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the principle causes of acute abdominal pain in children. 2. Make symptom based diagnoses of functional abdominal pain in children. 3. Recognize
Nancy Brown, APRN, CPNP April 18, 2018 OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the principle causes of acute abdominal pain in children. 2. Make symptom based diagnoses of functional abdominal pain in children. 3. Recognize
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses
 Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Evaluation of the adult with abdominal pain in the emergency department
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Evaluation of the adult with abdominal pain in the emergency department Authors: John L Kendall, MD, FACEP, Maria E Moreira, MD Section Editor:
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Evaluation of the adult with abdominal pain in the emergency department Authors: John L Kendall, MD, FACEP, Maria E Moreira, MD Section Editor:
Good morning! July 24, 2014
 Good morning! July 24, 2014 Prep #1 A 2-year-old boy presents to your office with a 2-day history of swelling of the right eye. He has been otherwise well. There are scattered insect bites on his body,
Good morning! July 24, 2014 Prep #1 A 2-year-old boy presents to your office with a 2-day history of swelling of the right eye. He has been otherwise well. There are scattered insect bites on his body,
Abdominal Pain among Older Adults
 Gastrointestinal Disease Abdominal Pain among Older Adults M. Bachir Tazkarji, MD, CCFP, CAQ Geriatric Medicine, Lecturer, Family Medicine Department, University of Toronto; Toronto Rehabilitation Institute,
Gastrointestinal Disease Abdominal Pain among Older Adults M. Bachir Tazkarji, MD, CCFP, CAQ Geriatric Medicine, Lecturer, Family Medicine Department, University of Toronto; Toronto Rehabilitation Institute,
Hypotension / Shock. Adult Medical Section Protocols. Protocol 30
 Hypotension / Shock History Blood loss - vaginal or gastrointestinal bleeding, AAA, ectopic Fluid loss - vomiting, diarrhea, fever nfection Cardiac ischemia (M, CHF) Medications Allergic reaction regnancy
Hypotension / Shock History Blood loss - vaginal or gastrointestinal bleeding, AAA, ectopic Fluid loss - vomiting, diarrhea, fever nfection Cardiac ischemia (M, CHF) Medications Allergic reaction regnancy
Pediatric Surgery MUHC MCH Siste. Objectives of Training
 Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Be Prepared Evacuation or not?
 Be Prepared Evacuation or not? Vu Le Tran, MD Cardiovascular Division Victoria Healthcare Clinic 1 Level of danger Myocardial infarction: USA > 1 million annually, death in one third (50% occurring within
Be Prepared Evacuation or not? Vu Le Tran, MD Cardiovascular Division Victoria Healthcare Clinic 1 Level of danger Myocardial infarction: USA > 1 million annually, death in one third (50% occurring within
ALTERED LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS
 INTRODUCTION An altered level of consciousness (LOC) refers to a change in a patient s state of awareness (ability to relate to self and the environment) and arousal (alertness) ranging from a state of
INTRODUCTION An altered level of consciousness (LOC) refers to a change in a patient s state of awareness (ability to relate to self and the environment) and arousal (alertness) ranging from a state of
Ultrasound Of The Acute Abdomen a survival guide. Alison McGuinness Consultant sonographer Mid Yorks Hospitals NHS Trust
 Ultrasound Of The Acute Abdomen a survival guide Alison McGuinness Consultant sonographer Mid Yorks Hospitals NHS Trust Definition Rapid onset of severe abdominal pain usually requiring admission to hospital
Ultrasound Of The Acute Abdomen a survival guide Alison McGuinness Consultant sonographer Mid Yorks Hospitals NHS Trust Definition Rapid onset of severe abdominal pain usually requiring admission to hospital
Request Card Task ANSWERS
 Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
PEDIATRIC GI EMERGENCIES. AGE-RELATED DIAGNOSIS Early Infancy EXAMINATION TIPS PEDIATRIC ABDOMINAL PAIN. How Common Is It?
 PEDIATRIC ABDOMINAL PAIN How Common Is It? PEDIATRIC GI EMERGENCIES Ghazala Q. Sharieff, MD 5% of unscheduled visits 2% of patients are admitted 1% need operative intervention EXAMINATION TIPS Palpate
PEDIATRIC ABDOMINAL PAIN How Common Is It? PEDIATRIC GI EMERGENCIES Ghazala Q. Sharieff, MD 5% of unscheduled visits 2% of patients are admitted 1% need operative intervention EXAMINATION TIPS Palpate
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION. Vol. 13: Abdomen
 BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 13: Abdomen So tell me a little bit about the abdominal pain that you ve been experiencing. Your learning objectives for mastering the abdomen examination
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 13: Abdomen So tell me a little bit about the abdominal pain that you ve been experiencing. Your learning objectives for mastering the abdomen examination
GI POTPOURRI. What is the best diagnostic test? Presentation #1: Vomiting. I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures GI POTPOURRI Andi Marmor, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics UCSF, San Francisco General Hospital Presentation #1: Vomiting Caraway, a 3 week old boy, is brought to your walk-in clinic
I have no disclosures GI POTPOURRI Andi Marmor, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics UCSF, San Francisco General Hospital Presentation #1: Vomiting Caraway, a 3 week old boy, is brought to your walk-in clinic
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
