Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol. glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide, lactulose. treatment of functional constipation in children
|
|
|
- Amberlynn Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. 2 Resident, Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine And Student Research Committee, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran BACKGROUND: Constipation is one of the common problems in childhood and consists of 3% of referrals to pediatricians and 25% of pediatric gastroenterologists. Aperients are common alternatives for treating chronic constipation. The present study aimed to compare the efficacy of three laxatives [polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide, and lactulose]. METHODS: In this randomized clinical trial, 1 to 6 year old children with functional chronic constipation (the patients had functional chronic constipation based on ROME III criteria) were studied. 75 patients were divided into three 25 member groups through randomization method. The patients of each group received either of the polyethylene glycol, magnesium hydroxide, or lactulose medications in a standard dosage. After a month, the results were assessed and analyzed through statistical tests. RESULTS: Comparing the frequency of increased defecation in patients of the three groups also found no significant difference among them; however, mean increase of defecation frequency was higher in the magnesium hydroxide group. Compared to patients who had more than three times of defecation per week, PEG group was significantly higher than the other two groups (p < 0.05). Comparing the side effects showed that the prevalence of side effects was lower in the polyethylene glycol group than the other two groups. The patients had a significantly higher satisfaction from the taste of polyethylene glycol and lactulose (p < 0.01). CONCLUSIONS: Although the total mean of increase in defecation frequency after the treatment was higher in the magnesium hydroxide group, the indicator of defecation frequency greater than three times per week was higher in the polyethylene glycol group which indicated the success of treatment in this group. In total, comparing the therapeutic results and satisfaction of the patients, it can be concluded that polyethylene glycol can be used as one of the best alternatives to treat constipation. KEYWORDS: Constipation, Polyethylene Glycol, Magnesium Hydroxide and Lactulose, Laxatives BACKGROUND Constipation is one of the common issues among children and also the cause of 3 percent of referrals to pediatricians. [1] The actual incidence of constipation estimated between 1 to 30 percent. [1] The highest prevalence of constipation reported in preschool aged children. [1] According to definition, if the frequency of defecations is less than twice a week or it is done once every three days while painful, it is considered as constipation. [2] Clinical manifestations of constipation include a wide range of items such as irregular bowel movement, small and hard stool, painful stool excretion with large diameter and fecal incontinence (encopresis; volitional or non volitional feces excretion). [3,4] The main causes of constipation in children divided into functional and organic categories. [5] In more than 95 percent of the cases, functional constipation is the cause of constipation in children. [6] According to diagnostic indicators of ROME III which has been defined by multinational working teams to develop diagnostic criteria for functional disorders, [7,8] the prove of functional constipation has been two cases out of 6 descriptive indicators (frequency of defecations, hardness, incontinence or retentive posturing) which should be observed one month in infants or two months in children (Table 1). For treatment of functional chronic constipation; based on the intensity of constipation in growth stage, [9] which usually is a detailed program, use of laxatives, behavioral changes, nutritional modifications and accurate follow up is necessary. [10] The used laxatives are polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide, lactulose and mineral oils. [11] Various studies have been done so far reviewing the efficacy of laxatives to treat functional constipation which mainly have compared the two drugs to each other. [12 15] In this study, we intent to determine Address for correspondence: Hossein Saneian,, Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. saneian@med.mui.ac.ir Received: ; Revised: ; Accepted: March 2012 Special Issue (1) Journal of Research in Medical Sciences S145
2 Table 1. Indicators of diagnosis the functional constipation in children [8] Rome III criteria for the diagnosis of functional constipation in children Infants and Toddlers At least two of the following present for at least one month Two or fewer defecations per week At least one episode of incontinence after the acquisition of toileting skills History of excessive stool retention History of painful or hard bowel movement Presence of a large faces mass in the rectum History of large-diameter stool which may obstruct the toilet Children with developmental age 4 to 18 years At least two of the following present for at least two months Two or fewer defecations per week At least one episode of fecal incontinence per week History of retentive posturing or excessive volitional stool retention History of painful or hard bowel movement Presence of a large faces mass in the rectum History of large-diameter stool which may obstruct the toilet the advantages and disadvantages of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulose on treatment of functional constipation in children through a comparative review. The results can be used to develop an appropriate protocol for treatment of functional constipation in children. METHODS In this prospective clinical trial, 1 to 6 year old children with functional chronic constipation were studied who referred to Pediatric Clinic of Amin Hospital, Isfahan during a year. The children could be enrolled in the study provided they had pebble like and hard stool or hard bowel movement twice a week or more along with no evidence of any structural, endocrine and metabolic diseases for two months. Moreover, they could be excluded from the study provided that they had any organic suspected symptoms (fever, vomiting, urinary incontinence, diarrhea, growth disorder, anal stenosis, unexplained bleeding with fisher and/or an abnormal point in examination such as abnormal DTR during the treatment), having known cardiac, pulmonary, neurological and renal diseases and anorectal malformation during the treatment, having any disease causes children s treatment course not to be improved, loss of follow up and also changing disease diagnosis and/or treatment withdrawal. The sample size calculated 75 subjects divided in three 25 subject groups by systematic randomization using the randomization software. After obtaining the patients history and full clinical examination (such as rectum examination) by pediatric resident, they entered the study provided not to have suspected symptoms (fever, vomiting, urinary incontinence, diarrhea, growth disorder, anal stenosis, bleeding and etc). Besides, systematic randomized sampling method was used for sample allocation in each of the three groups. It should be noted that ethically none of the patients received placebo. Moreover, in terms of hard fecal impaction, first the fecal impaction evacuated outpatient or admitted with edible paraffin enema and also saline enema (3 nights edible paraffin enema and 3 nights saline enema). The intervention conducted in four stages as the following: 1. Verbal education and pamphlet by pediatric resident 2. Diet (prepared list) 3. Laxatives for a month and disimpaction, if necessary. 4. Patients follow up (a week later and then monthly for 4 6 month The four mentioned staged conduced for all the patients and the difference was only in laxative they received. The first group received lactose (Tolid Daroo, Tehran, Iran) 1 cc/kg/day (augmentable to 3 cc/kg/day and its report, if any). The second group received magnesium hydroxide (Tolid Daroo, Tehran, Iran) 1 cc /kg/day (augmentable to 3 cc/kg/day and its report, if any) and the third group received polyethylene glycol with no electrolyte 40% (School of Pharmacy, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran) 1 cc /kg/day (augmentable to 3 cc/kg/day and its report, if any). Therapeutic result was evaluated as defecation equal or more than 3 times a week without pain and bleeding (smooth, relax and large diameter) in addition with fecal incontinence less than twice a month at the end of one month treatment. The data were analyzed through non parametric tests as chi square, ANOVA, and Mann Whitney pare the efficacy of the three used drugs. Software SPSS version 15 was used for statistical analysis. S146 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences March 2012 Special Issue (1)
3 RESULTS other groups (p = 0.040). Comparing the demographic indicators of the study subjects are illustrated in table 2. As indicated, the study subjects had no difference in terms of age, weight, height and also in terms of constipation onset age, frequency of defecation and duration of constipation. In terms of sex also the number of boys and girls in the three groups showed no significant difference together (p < 0.05). After passing the treatment course, the mean increase of defecation frequency in magnesium hydroxide (4.67 ± 2.29) was significantly lower than PEG (3.56 ± 1.99) and lactulose (3.16 ± 1.72) (P = 0.015); however, comparing the mean increase of defecation frequency among the three groups and according to division showed an increase which significantly there was no difference between the three groups (Table 3) (p = 0.100). However, statistical analysis showed that the number of those had defecation more than three times a week was significantly more in PEG group than two The clinical examination before the study showed that the frequency of fecal impaction in PEG group was 10 subjects (33.3%), in magnesium hydroxide group was 5 subjects (16.7%) and in lactulose group was 8 subjects (26.7%). In this regard, there was no significant difference between the three groups before the study (P = 0.334). However, after the study, the frequency of this case among the PEG group was zero, in magnesium hydroxide group was 1 subjects (3.3%) and in lactulose group also was 5 subjects (16.7%) which statistically showed a significant reduction in first (p = 0.023) and second group (p = 0.027) and also no significant reduction was seen in the lactulose group (p = 0.123). The reported side effects after drug consumption are shown in table 4. The statistical studies showed that incidence of abdominal pain in PEG significantly was lower than other groups (p = 0.001). Furthermore, the incidence of bloat in PEG and magnesium hydroxide groups was significantly lower than lactulose group (p < 0.001). Table 2. Comparing the demographic characteristics and disease of the study subjects Variables Polyethylene glycol Magnesium hydroxide Lactulose P-value Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Age (years) Weight (kg) Height (cm) Constipation onset age (months) Frequency of defecation(/week) Duration of suffering (months) Table 3. Comparing the increase of defecation frequency among the three groups in terms of division GROUPS TIME Less than 3 times a week 3-5 times a week 6-8 times a week More than 8 times a week Number (%) Number (%) Number (%) Number (%) Polyethylene glycol 4 (13) 12 (40) 13 (44) 1 (3.3) Magnesium hydroxide 3 (10) 4 (13) 16 (54) 7 (23) Lactulose 6 (20) 12 (40) 10 (33) 2 (7) P = Table 4. Comparing the prevalence of pharmacological side effects in the studied groups Side effects Polyethylene glycol Magnesium hydroxide Lactulose P-value Number Number Percentage Number Percentage Abdominal pain 2 (7) Nausea and vomiting 0 (o) Bloat 2 (7) < Diarrhea 0 (0) Irritation around stomach 1 (3) The results presented as number (%). March 2012 Special Issue (1) Journal of Research in Medical Sciences S147
4 Furthermore, magnesium hydroxide significantly caused more diarrhea than other two drugs (p = 0.024). The satisfaction rate of children from taste of drugs in lactulose (76.7%) and PEG (73.3%) significantly was higher than magnesium hydroxide (40.00%) (p = 0.005). However, in terms of parents satisfaction rate from the therapeutic results, successful and partly successful comments in PEG (90%) and magnesium hydroxide (97%) groups significantly was higher than lactulose group (83%) (p = 0.48). Four subjects in PEG (13.3%) and 5 subjects in magnesium hydroxide group (16.7%) and also 10 subjects in lactulose group (23.3%) were forced to change the drug. Although this amount was less in PEG group than other groups, there was no significant difference between the three groups (p = 0.129). DISCUSSION The present study conducted aiming to compare the efficacy of three polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulose drugs to treat functional constipation in children; and the results showed that although every three drugs increased defecation frequency in patients, these findings have been confirmed in other previous studies. [12 15] Crude comparison of mean increase in defecation frequency between the three groups indicated a significant reduction in magnesium hydroxide than other two groups. However, with separating the number of defecation and comparison based on frequency of the study subjects in each category indicated that there was no significant difference among the three groups in this regard. Nevertheless, other aspects for selecting an appropriate medication to treat chronic constipation in children also should be taken into account. Because studies have shown that one of the major causes of failure in constipation treatment is early drug withdrawal or lack of appropriate cooperation by patients. [13 15] Therefore, evaluating the pharmacological side effects is necessary to increase therapeutic efficacy and patients satisfaction. In the present study, the studied side effects of PEG generally were lower than other two drugs. And reduction of abdominal pain and bloat significantly was better by this drug than those other two. This finding was in accordance with other previous studies. [13 15] Among the three studied drugs, magnesium hydroxide significantly caused more diarrhea among the consumers; probably that is why mean defecation frequency in magnesium hydroxide users was higher than two other drugs. The point that the diarrhea frequency was higher in these patients devalued the higher level of defecation frequency. Preanal, abdominal pain during defecation, bleeding during defecation and anus pain during defecation among the three groups had no difference after therapeutic measures and every three drugs similarly (statistically) reduced bleeding, abdominal pain and rectal pain (all the patients had defecation pain at the beginning of the study). In this study, according to the standard criteria and previous studies, the determinant indicator of treatment success was considered three times or more defecation per week along with at least one soiling in two weeks. The results showed that the patients who had more than three defecations per week, it was more in PEG group than two other groups. Therefore, although total mean increase in defecation frequency after the treatment was higher in magnesium hydroxide, the indicator of defecation frequency more than three times per week which indicates treatment success was reported higher in PEG group. The study of Vo Voskuijl et al also indicated the 2 fold treatment success of PEG than lactulose. [14] However, parents of patients were significantly more satisfied from therapeutic results of PEG and magnesium hydroxide than lactulose which this finding confirmed the above mentioned points. After the treatment course, due to treatment failure or not achieving to the therapeutic goals, some of patients forced to change their drug or increase other drugs. Although the difference between the three groups statistically was not significant, the amount of drug change was lower in PEG than other two drugs. In this study, the prevalence of fecal impaction in rectum was similar among the three groups before the treatment. After the treatment, although the prevalence of fecal impaction in rectum reduced in every three groups, the amount was significantly lower in PEG and magnesium hydroxide groups than lactulose. The study of Dupont et al indicated that lower fecal impaction in rectum was along with consumption of PEG rather than lactulose. [13] S148 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences March 2012 Special Issue (1)
5 The acceptance rate of children and their satisfaction from drug s taste in PEG and lactulose significantly was higher than magnesium hydroxide. In the study of Loening Baucke and Pashankar the acceptance rate of PEG also reported higher than magnesium hydroxide. [15] CONCLUSIONS Generally, comparing the therapeutic results, side effects and satisfactory rate of patients in this study showed that due to lack of serious side effects, PEG (polyethylene glycol) can be used as the first pharmacological alternative to treat functional constipation in children. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This paper is derived from a specialty thesis No in Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. REFERENCES 1. Borowitz SM, Cox DJ, Kovatchev B, Ritterband LM, Sheen J, Sutphen J. Treatment of childhood constipation by primary care physicians: efficacy and predictors of outcome. Pediatrics 2005; 115(4): Di LC. Pediatric anorectal disorders. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2001; 30(1): , ix. 3. Dupont C, Leluyer B, Amar F, Kalach N, Benhamou PH, Mouterde O, et al. A dose determination study of polyethylene glycol 4000 in constipated children: factors influencing the maintenance dose. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006; 42(2): Hyman PE, Milla PJ, Benninga MA, Davidson GP, Fleisher DF, Taminiau J. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: neonate/toddler. Gastroenterology 2006; 130(5): Loening-Baucke V. Chronic constipation in children. Gastroenterology 1993; 105(5): Loening-Baucke V, Pashankar DS. A randomized, prospective, comparison study of polyethylene glycol 3350 without electrolytes and milk of magnesia for children with constipation and fecal incontinence. Pediatrics 2006; 118(2): Orchard JL, Lawson R. Severe colitis induced by soap enemas. South Med J 1986; 79(11): Rasquin A, Di LC, Forbes D, Guiraldes E, Hyams JS, Staiano A, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: child/adolescent. Gastroenterology 2006; 130(5): Richard E, Behrman MD. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 16th ed. philadelphia: Saunders; Rubin GP. Childhood constipation. Am Fam Physician 2003; 67(5): Schonwald A, Rappaport L. Consultation with the specialist: encopresis: assessment and management. Pediatr Rev 2004; 25(8): Thompson WG, Longstreth GF, Drossman DA, Heaton KW, Irvine EJ, Muller-Lissner SA. Functional bowel disorders and functional abdominal pain. Gut 1999; 45 Suppl 2: II43-II van den Berg MM, Benninga MA, Di LC. Epidemiology of childhood constipation: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101(10): Voskuijl W, de LF, Verwijs W, Hogeman P, Heijmans J, Makel W, et al. PEG 3350 (Transipeg) versus lactulose in the treatment of childhood functional constipation: a double blind, randomised, controlled, multicentre trial. Gut 2004; 53(11): Loening-Baucke V, Pashankar DS. A randomized, prospective, comparison study of polyethylene glycol 3350 without electrolytes and milk of magnesia for children with constipation and fecal incontinence. Pediatrics 2006; 118(2): How to cite this article: Saneian H, Mostofizadeh N. Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulose in treatment of functional constipation in children. J Res Med Sci 2012; 17(Special 1): S145-S149. Source of Support: Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Conflict of Interest: None declared. March 2012 Special Issue (1) Journal of Research in Medical Sciences S149
Constipation in childhood is characterized by a low defecation frequency in combination with either involuntary loss of
 USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
The involuntary loss of feces in the underwear after. Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence.
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
Constipation in children
 Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka
 Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS
 BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014
 Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Constipation in children usually is functional (ie, constipation
 Efficacy and Complications of Polyethylene Glycols for Treatment of Constipation in Children A Meta-Analysis Si-Le Chen, MD, Shi-Rong Cai, MD, PhD, Liang Deng, MD, Xin-Hua Zhang, MD, PhD, Te-Dong Luo,
Efficacy and Complications of Polyethylene Glycols for Treatment of Constipation in Children A Meta-Analysis Si-Le Chen, MD, Shi-Rong Cai, MD, PhD, Liang Deng, MD, Xin-Hua Zhang, MD, PhD, Te-Dong Luo,
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
 Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
Paediatric constipation
 EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS constipation Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Best practice Paediatric constipation Diagnosis and treatment Dr Tim De Maayer Paediatric Gastroenterologist
EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS constipation Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Best practice Paediatric constipation Diagnosis and treatment Dr Tim De Maayer Paediatric Gastroenterologist
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT
 Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone. Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club
 Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Constipation in Children. Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG*
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
Managing functional constipation in children
 PRACTICE POINT Managing functional constipation in children A Rowan-Legg; Canadian Paediatric Society Community Paediatrics Committee Paediatr Child Health 2011;16(10):661-5 Posted: Dec 1 2011 Reaffirmed:
PRACTICE POINT Managing functional constipation in children A Rowan-Legg; Canadian Paediatric Society Community Paediatrics Committee Paediatr Child Health 2011;16(10):661-5 Posted: Dec 1 2011 Reaffirmed:
Managing Defecation Disorders in Children
 A SUPPLEMENT TO Internal Medicine News Managing Defecation Disorders in Children Perspectives on Constipation and Encopresis: Current Issues and New Findings Infant Dyschezia and Functional Constipation
A SUPPLEMENT TO Internal Medicine News Managing Defecation Disorders in Children Perspectives on Constipation and Encopresis: Current Issues and New Findings Infant Dyschezia and Functional Constipation
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation in childhood
 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin
 Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Chronic constipation, often accompanied by encopresis. Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty. Patients and Methods
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
IPS Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki. Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.
 Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.H Dubai 22-24 Feb. 2018 Objectives: Why constipation?!!! Is it a burden
Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.H Dubai 22-24 Feb. 2018 Objectives: Why constipation?!!! Is it a burden
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
Chronic Childhood Constipation Is Associated with Impaired Quality of Life: A Case-Controlled Study
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 41:56 60 Ó July 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Chronic Childhood Constipation Is Associated with Impaired Quality of Life: A Case-Controlled
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 41:56 60 Ó July 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Chronic Childhood Constipation Is Associated with Impaired Quality of Life: A Case-Controlled
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report
 Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Gordon, Morris, Macdonald, John, Parker, Claire, Akobeng, Anthony and Thomas, Adrian
 Article Osmotic and stimulant laxatives for the management of childhood constipation Gordon, Morris, Macdonald, John, Parker, Claire, Akobeng, Anthony and Thomas, Adrian Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/15372/
Article Osmotic and stimulant laxatives for the management of childhood constipation Gordon, Morris, Macdonald, John, Parker, Claire, Akobeng, Anthony and Thomas, Adrian Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/15372/
Human Anatomy rectum
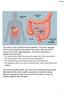 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
Current Treatment of Childhood Constipation
 Ann Nestlé [Engl] 2007;65:73 79 DOI: 10.1159/000101716 O livia Liem a, b Carlo Di Lorenzo b Jan A.J.M. Taminiau a Hayat M. Mousa b Marc A. Benninga a a Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition,
Ann Nestlé [Engl] 2007;65:73 79 DOI: 10.1159/000101716 O livia Liem a, b Carlo Di Lorenzo b Jan A.J.M. Taminiau a Hayat M. Mousa b Marc A. Benninga a a Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition,
Constipation is a common disorder in children,
 The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence
 The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up
 1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
The Effect of Adding Synbiotics to Polyethylene Glycol in Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 5357-5367) The Effect of Adding Synbiotics to Polyethylene Glycol in Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study M Mahdavi 1, *MR
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 5357-5367) The Effect of Adding Synbiotics to Polyethylene Glycol in Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study M Mahdavi 1, *MR
Why does my stomach hurt? Exploring irritable bowel syndrome
 Why does my stomach hurt? Exploring irritable bowel syndrome By Flavio M. Habal, MD, PhD, FRCPC Case In this article: 1. What is IBS? A 45-year-old female is referred to your office with recurrent 2. How
Why does my stomach hurt? Exploring irritable bowel syndrome By Flavio M. Habal, MD, PhD, FRCPC Case In this article: 1. What is IBS? A 45-year-old female is referred to your office with recurrent 2. How
C onstipation is a common problem in children, accounting
 723 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of constipation: clinical factors and colonic transit time F de Lorijn, M P van Wijk, J B Reitsma, R van Ginkel, J A J M Taminiau, M A Benninga... See end of article for
723 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of constipation: clinical factors and colonic transit time F de Lorijn, M P van Wijk, J B Reitsma, R van Ginkel, J A J M Taminiau, M A Benninga... See end of article for
TREATMENT SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION
 SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Management of childhood constipation
 J Pediatr Rev. 2013;1(1)45-51 Management of childhood constipation Hassan Karami 1 Leila Shokohi 2* 1 Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Faculty of Medicine, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences,Sari,
J Pediatr Rev. 2013;1(1)45-51 Management of childhood constipation Hassan Karami 1 Leila Shokohi 2* 1 Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Faculty of Medicine, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences,Sari,
Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS OVERVIEW
 Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS A major medical conditions that commonly is seen among persons with IDD and may lead to serious complications is constipation.
Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS A major medical conditions that commonly is seen among persons with IDD and may lead to serious complications is constipation.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Constipation. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Constipation. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
Protectives and Adsorbents. Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry
 Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
CENTENE PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS DRUG REVIEW 3Q17 July August
 BRAND NAME Symproic GENERIC NAME Naldemedine MANUFACTURER Shionogi Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL March 23, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE Anticipated to launch mid-summer 2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug
BRAND NAME Symproic GENERIC NAME Naldemedine MANUFACTURER Shionogi Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL March 23, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE Anticipated to launch mid-summer 2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System. Antidiarrheal and Laxatives
 Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antidiarrheal and Laxatives Diarrhea Abnormal frequent passage of loose stools or Abnormal passage of stools with increased frequency, fluidity, and weight,
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antidiarrheal and Laxatives Diarrhea Abnormal frequent passage of loose stools or Abnormal passage of stools with increased frequency, fluidity, and weight,
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination
 Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
I n order to give the best care to patients and families,
 642 ARCHIMEDES Towards evidence based medicine for paediatricians Edited by Bob Phillips... I n order to give the best care to patients and families, paediatricians need to integrate the highest quality
642 ARCHIMEDES Towards evidence based medicine for paediatricians Edited by Bob Phillips... I n order to give the best care to patients and families, paediatricians need to integrate the highest quality
Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Constipation is a common and distressing pediatric problem, with a prevalence ranging from 7% to 30% in both western
 Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Paola Coccorullo, MD, Caterina Strisciuglio, MD, Massimo Martinelli,
Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Paola Coccorullo, MD, Caterina Strisciuglio, MD, Massimo Martinelli,
Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
Colon Transit Time Test in Korean Children with Chronic Functional Constipation
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.1.38 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2016 March 19(1):38-43 Original Article PGHN Colon Transit Time Test in Korean Children
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.1.38 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2016 March 19(1):38-43 Original Article PGHN Colon Transit Time Test in Korean Children
Comparison of strategies and goals for treatment of chronic constipation among gastroenterologists and general practitioners
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (18) 31, 1-6 Comparison of strategies and goals for treatment of chronic constipation among gastroenterologists and general practitioners Dan Carter a,c, Eytan
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (18) 31, 1-6 Comparison of strategies and goals for treatment of chronic constipation among gastroenterologists and general practitioners Dan Carter a,c, Eytan
There are clues to help to decide if the bellyache is a medical problem:
 Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Nursing Principles & Skills II. Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction
 Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
SYMPROIC (naldemedine tosylate) oral capsule
 SYMPROIC (naldemedine tosylate) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
SYMPROIC (naldemedine tosylate) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation
 Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly
 Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
RECOMMENDATIONS PII: S
 RECOMMENDATIONS : Consensus Practice Guidelines of Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and Pediatric Gastroenterology Chapter of Indian Academy of Pediatrics SURENDER
RECOMMENDATIONS : Consensus Practice Guidelines of Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and Pediatric Gastroenterology Chapter of Indian Academy of Pediatrics SURENDER
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management
 UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
Go Back All Documents Expand Sections Collapse Sections Comment
 1 of 10 01/06/2014 09:10 AM Go Back All Documents Expand Sections Collapse Sections Comment Valid only on date printed: 2014-01-06 09:09. Discard immediately after use! Clinical Practice Guideline Issuing
1 of 10 01/06/2014 09:10 AM Go Back All Documents Expand Sections Collapse Sections Comment Valid only on date printed: 2014-01-06 09:09. Discard immediately after use! Clinical Practice Guideline Issuing
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH
 Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH
 Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Gastrointestinal Society 2016 SURVEY RESULTS
 Gastrointestinal Society 2016 SURVEY RESULTS Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) The GI (Gastrointestinal) Society represents Canadians living with gastrointestinal diseases and disorders including those who
Gastrointestinal Society 2016 SURVEY RESULTS Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) The GI (Gastrointestinal) Society represents Canadians living with gastrointestinal diseases and disorders including those who
Opioid-Induced Constipation
 Objectives Opioid-Induced Constipation Brianna Jansma, PharmD Alex Smith, PharmD Megan Robinson, PharmD Summarize epidemiology of opioid-induced constipation (OIC) Understand opiates effects on the gastrointestinal
Objectives Opioid-Induced Constipation Brianna Jansma, PharmD Alex Smith, PharmD Megan Robinson, PharmD Summarize epidemiology of opioid-induced constipation (OIC) Understand opiates effects on the gastrointestinal
daily; available as 10- mg g PO
 Overview of the PRN: The Pain and Palliative Care PRN of ACCP is an organization of pharmacy practitioners, clinical scientists, pharmacy educators, and others. Its mission is to advance pain and palliative
Overview of the PRN: The Pain and Palliative Care PRN of ACCP is an organization of pharmacy practitioners, clinical scientists, pharmacy educators, and others. Its mission is to advance pain and palliative
Approaching Childhood Constipation Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology. Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Epidemiology.
 Approaching Childhood Constipation p Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Disclosure Anees Siddiqui, MD, has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Specially for Children Dell
Approaching Childhood Constipation p Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Disclosure Anees Siddiqui, MD, has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Specially for Children Dell
Antidiarrheals Antidiarrheal
 Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Pediatric Gastroenterology Referral Guidelines
 Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
Diagnostic dilemmas and results of treatment for
 36 Department of Paediatrics, Free University Hospital, PO Box 757, 17 MB Amsterdam, The Netherlands CW Keuzenkamp-Jansen CJ Fijnvandraat CMF Kneepkens AC Douwes Correspondence and reprint requests to:
36 Department of Paediatrics, Free University Hospital, PO Box 757, 17 MB Amsterdam, The Netherlands CW Keuzenkamp-Jansen CJ Fijnvandraat CMF Kneepkens AC Douwes Correspondence and reprint requests to:
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST
 COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Associated with
 Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Constipation an Old Friend. Presented by Dr. Keith Harris
 Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Hospital-Level Variation in Practice Patterns and Patient Outcomes for Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Functional Constipation
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Hospital-Level Variation in Practice Patterns and Patient Outcomes for Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Functional Constipation Jamie Librizzi, MD, MSHS, a Samuel Flores, MD, a Keith
RESEARCH ARTICLE Hospital-Level Variation in Practice Patterns and Patient Outcomes for Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Functional Constipation Jamie Librizzi, MD, MSHS, a Samuel Flores, MD, a Keith
Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in childhood constipation: a study using a Delphi technique
 BMJ Paediatrics Open To cite: Kuizenga-Wessel S, Steutel NF, Benninga MA, et al. Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in childhood constipation: a study using a Delphi technique. BMJ Paediatrics
BMJ Paediatrics Open To cite: Kuizenga-Wessel S, Steutel NF, Benninga MA, et al. Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in childhood constipation: a study using a Delphi technique. BMJ Paediatrics
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
What Questions Should You Ask?
 ? Your Doctor Has Ordered a Colonoscopy. What Questions Should You sk? From the merican College of Gastroenterology www.acg.gi.org Normal colon Is the doctor performing your colonoscopy a Gastroenterologist?
? Your Doctor Has Ordered a Colonoscopy. What Questions Should You sk? From the merican College of Gastroenterology www.acg.gi.org Normal colon Is the doctor performing your colonoscopy a Gastroenterologist?
190 Index Case studies, abdominal pain, 2 Crohn s disease, 2 3, cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), 2 fecal incontinence (FI), 2 medical c
 Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Identify electrolytes that should be monitored whenever prolonged or severe diarrhea is present
 Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Surveillance programme
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Surveillance programme Surveillance proposal consultation document Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Surveillance programme Surveillance proposal consultation document Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline
LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP OF HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE: REVIEW OF EARLY AND LATE COMPLICATIONS. S. Agarwala, V. Bhatnagar and D.K. Mitra
 Original Articles LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP OF HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE: REVIEW OF EARLY AND LATE COMPLICATIONS S. Agarwala, V. Bhatnagar and D.K. Mitra From the Department of Pediatric Surgery, All India Institute
Original Articles LONG TERM FOLLOW-UP OF HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE: REVIEW OF EARLY AND LATE COMPLICATIONS S. Agarwala, V. Bhatnagar and D.K. Mitra From the Department of Pediatric Surgery, All India Institute
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation
 Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Flixweed vs. Polyethylene Glycol in the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial
 Iran J Pediatr. 2015 April; 25(2):e425. Published online 2015 April 18. DOI: 10.5812/ijp.425 Research Article Flixweed vs. Polyethylene Glycol in the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized
Iran J Pediatr. 2015 April; 25(2):e425. Published online 2015 April 18. DOI: 10.5812/ijp.425 Research Article Flixweed vs. Polyethylene Glycol in the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized
Vicente Garrigues, Consuelo Gálvez, Vicente Ortiz, Marta Ponce, Pilar Nos, and Julio Ponce
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2004 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 159, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwh072 PRACTICE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2004 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 159, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwh072 PRACTICE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY
SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE Suspension, USP
 SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE Suspension, USP DESCRIPTION Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Suspension, USP can be administered orally or in an enema. It is a cherryflavored suspension containing 15 grams of
SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE Suspension, USP DESCRIPTION Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Suspension, USP can be administered orally or in an enema. It is a cherryflavored suspension containing 15 grams of
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
