Maria Polaczuk Occupational Therapist Wellington Regional Pain Management Service Graded Motor Imagery
|
|
|
- Rudolph Spencer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Maria Polaczuk Occupational Therapist Wellington Regional Pain Management Service 2014 Graded Motor Imagery
2 Introduction Whenever we get a referral for a patient with a unilateral or neuropathic pain condition, one of the first tools we reach for in our pain therapy tool kit is Graded Motor Imagery therapy. Graded Motor Imagery combines several (evidence based) therapies, which target the synapses in the brain and provides a top down therapy that can alter the sensitive networks of the neuromatrix in the brain and brain stem.
3 Theory behind it... The Gate Control Theory of Pain ( Melzack and Wall 1965 ) introduced the Central Nervous System Mechanisms as an essential component of the pain process. However the pain experience phantom pain after limb or organ amputation and the pain experienced by persons with paraplegia, and neuropathic pain could not be explained by the Gate Control Theory. The Neuromatrix concept was suggested and identified that brain mechanisms may underlie some kinds of chronic pain.
4 Phantom Limb Pain When a limb is amputated the proprioceptive and visual inputs for that limb are removed, but the nerves are still in tact Approximately % of amputees are affected by phantom pain Even though there is no limb the representation of the limb is still held on the somatosensory cortex.
5 A Brain Neurone
6 Phantom Pain FMRI Studies by Herta Flor et al ( 1995 ) 2006 proved that there was neuronal activation in the somatosensory cortex area representing the amputated limb during the patients experience of phantom pain. The intensity of phantom limb pain is correlated with the extent of cortical reorganization in the somatosensory cortex and motor cortex.
7 FMRI proof that cortical reorganisation occurs during PLP ( Herta Flor et al Phantom Limb Pain as a perceptual correlate of massive cortical reorganisation of the somatosensory cortex in upper extremity amputees nature 357 ( 1995 ) ) FMRI Proof PLP is from the Brain Amputee with PL Amputee, no PL Control
8 HOW DID GMI COME ABOUT? GMI is an eclectic therapy designed in 2004 by Dr G Lorimer Moseley and David Butler. It s conception responded to the plethora of studies that were coming out regarding the relationship between the plasticity of the brain and chronic pain states and the process of central sensitisation. More importantly it responded to the Neuromatrix paradigm of Pain initiated by the late Patrick Wall and Ronald Melzack. David Butler says that GMI has been designed to activate the somatosensory and motor cortices which desmudges the brain and facilitates cortical reorganisation.
9 GMI is a sequential therapy... 1.Laterality reconstruction attempts to restore the accuracy and speed of identifying the left and right sides of the body.( Recognising left and right ) 2. Motor Imagery is the Mental representations of postures, movement and activities without any body movement. ( Imagining Action) aimed at activating the premotor cortex. 3. Mirror Therapy is the use of a Mirror to present the reverse image of a limb to the brain tricking the brain.
10 1. GMI Laterality Training Implicit Motor Imagery Loss of laterality is known to occur in patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, and Phantom Limb Pain ( Schwoebel et al 2002, Nico et al 2002, Moseley 2004 ) The Patient is taught to safely recognise right and left in images of feet / hands / shoulders / neck / back with different postures. The goal of this therapy is to stimulate the somatosensory cortex on the contra lateral side of the affected limb. The brain is plastic and changeable if given the right stimulus for long enough, it is possible to reconstruct the brain s feature of laterality
11 1. Laterality discrimination, recognition, and restoration Programme licence was purchased on an 2 monthly basis at The Patient is given a Token and Key to the recognise website and is expected to practice laterality exercises every waking hour or as many as possible, for hands, feet, neck and shoulder and backs. Both patient and therapist access the website to monitor progress and results of the hand laterality exercises, which shows timing and pain levels. Normal accuracy is considered at 92.5% with an average time of 2.4 seconds for hands and 1.6 seconds for neck and shoulders.
12 LEFT OR RIGHT?
13 2. From Laterality to Motor Imagery The progression from laterality to motor imagery came about because studies showed that Limb Laterality recognition activates pre motor ( association ) cortices not the primary motor cortex. Motor Imagery is the mental rehearsal of postures or an action without the actual movement imagining the body part in a certain position Functional Neuro imaging studies by ( Grezes and Decety 2001 ) show that motor imagery and action are mediated by the same neuronal circuits.
14 2. Graded Motor Imagery The Patient is shown pictures from the recognise website, magazines, you tube clips, movies, sitting in café s etc. They are asked to imagine adopting the posture on the screen with their own arm, leg, neck and shoulders, or back and then returning their body part to where it was. They are asked to imagine a pain free smooth action. Viewing static snapshots that imply human action activate the human motor system. ( Urgesi, Moro et al 2006 ) Grasping at tools : Corticospinal excitability reflects observed had movements ( a study reported in the Cerebral Cortex )
15 The result of conscious access to neurosignatures representing intention, preparation carrying out and eventual movement has been used in sports in healthy people. (Dickstein and Deutsch 2007 ) 2. Motor Imagery.
16
17 3. GMI - Mirror Therapy - Vilayanur Ramachandran is a neuroscientist who is known for the invention of the mirror box and MVF ( Mirror Visual Feedback )in the 1990 s. MVF has since been proven an effective therapy for those with phantom pain, and many other unilateral pain conditions. FMRI studies have since verified that the brain represents the actual perception not the physical stimulus.
18 3 GMI Mirror Therapy instructions This is a simple self administered therapy, 25 minutes per day, relaxed environment, 8 weeks before re-evaluating it s use, can do booster sessions if pain returns, might need support, must look in the mirror for the duration of the treatment, take off jewellery or identifying features, can do gentle movements with foot or arm.
19 3 GMI Mirror Therapy Performing various actions whilst observing the reflected image of the intact limb (live example ) Activities are graded to sequentially unsmudge the brain Graded via speed of performance, number of repetitions Patients can massage their limb to enhance the activity in the visual cortex particularly the dorsal visual stream where kinaesthetic and visual inputs converge ( Macaluso et al 2000 ) Vision dominates over proprioception ( Pascale Touzalin, Chretien et al 2010 ) No significant correlation between amount of time since amputation and benefit of treatment
20 The Phantom of the Mirror A Case Study Mrs S with Lamb chop 4 days post amputation! The illusion of the phantom is played out in the mirror! Mrs S is now 2 years post amputation, she practices the Mirror Visual Feedback Technique every night just before going to sleep. She has had no phantom pain since 6 days post amputation, and she is back working fulltime.
21 Mirror Therapy The invasion of areas neighbouring the representation of the amputated limb into the cortical representation zone is related to pain intensity Pain Relief induced by Mirror Therapy is accompanied by a reversion of cortical organization. Reduction of this shift is correlated to the reduction in pain experienced.
22 Mirror therapy FMRI imaging before and after 4 weeks Mirror training and practice resulted in mirrored hand movements caused significant bilateral activation in SMC before and after treatments as well as the insular cortex and the inferior parietal cortex. However distortions of the phantom might complicate the integration of visual and proprioceptive inputs into a coherent percept and reduce the effects of mirror therapy
23 Telescoping Phantom In the case of the telescoping phantom limb Mirror Therapy was unable to reduce the activity in the Inferior Parietal Cortex The perceived intensity of telescoping was negatively correlated with the treatment effect Without telescoping reported 50% decrease in PLP with telescoping 1% success ( Herta Flor et al 2013)
24
25 Virtual Reality Treatment - Advantages High Adaptability image can be processed in several ways before presenting it on head mounted display If amputee experiences phantom as shrunken or telescoping can If CRPS may have swollen limbs or perceive them as larger than they are MT may fail to achieve spatial congruence between mirrored image of intact limb and the percept of the amputated limb
26 New findings about Mirror Therapy and Virtual Reality The concept of body matrix ( Moseley) proposes that activity in specific cortical regions is related to the ability to subjectively incorporate a limb not belonging to one s body. The feeling of observing one s own hand, or body part is necessary for treatment benefit.
27 ILLUSIONS CAN HELP PATIENTS MANAGE THEIR PAIN.
28
29 References: Flor Herta et al., An augmented reality home-training system based on the mirror training and imagery approach Published online : 13 December 2013 Internet - Ted Talks Ramachandran s lectures on illusion Ramachandran V.S. and Altschuler Eric, The use of visual feedback, in particular MVF, in restoring brain function. BRAIN 2009: D.Butler and Moseley L, EXPLAIN PAIN Noigroup Publications, Adelaide, Australia, 2003 Moseley G.L Parsons T.J (2008) Visual distortions of limb modulates the pain and swelling evoked by movement. Current Biology,18(22),R1047-R1048. doi: /j.cub
Stanmore Therapy Service Approach to Management of Phantom Pain in the Post-operative Phase
 Stanmore Therapy Service Approach to Management of Phantom Pain in the Post-operative Phase Jennifer Fulton Physiotherapy Clinical Specialist in Amputee Rehabilitation PHANTOM LIMB PHENOMENON Truly it
Stanmore Therapy Service Approach to Management of Phantom Pain in the Post-operative Phase Jennifer Fulton Physiotherapy Clinical Specialist in Amputee Rehabilitation PHANTOM LIMB PHENOMENON Truly it
BodyinMind.org. CRPS symposium June 2011
 BodyinMind.org CRPS symposium June 2011 Acute injury rehabilitation Chronic pain management Acute injury CRPS Chronic pain Injury 6 weeks 3 months Convention Acute injury rehabilitation Chronic pain management
BodyinMind.org CRPS symposium June 2011 Acute injury rehabilitation Chronic pain management Acute injury CRPS Chronic pain Injury 6 weeks 3 months Convention Acute injury rehabilitation Chronic pain management
Title Managing pain by visually distorting the size of a painful body parts. Is there any therapeutic value?
 Title Managing pain by visually distorting the size of a painful body parts. Is there any therapeutic value? Authors Priscilla G. Wittkopf 1, 2 Mark I. Johnson 1, 2 1 Centre for Pain Research, Faculty
Title Managing pain by visually distorting the size of a painful body parts. Is there any therapeutic value? Authors Priscilla G. Wittkopf 1, 2 Mark I. Johnson 1, 2 1 Centre for Pain Research, Faculty
 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Right hemisphere. Left hemisphere. Demonstration: Contralateral processing. Motor functions on left side of body Perceives left side of space
 Week 6 Lab: Hemispheric Functions - Contralateral processing Back to Index Right hemisphere Motor functions on left side of body Perceives left side of space Left hemisphere Motor functions on right side
Week 6 Lab: Hemispheric Functions - Contralateral processing Back to Index Right hemisphere Motor functions on left side of body Perceives left side of space Left hemisphere Motor functions on right side
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses
 Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
NEUROPLASTICITY. Implications for rehabilitation. Genevieve Kennedy
 NEUROPLASTICITY Implications for rehabilitation Genevieve Kennedy Outline What is neuroplasticity? Evidence Impact on stroke recovery and rehabilitation Human brain Human brain is the most complex and
NEUROPLASTICITY Implications for rehabilitation Genevieve Kennedy Outline What is neuroplasticity? Evidence Impact on stroke recovery and rehabilitation Human brain Human brain is the most complex and
Phantom limb pain. Advice for amputee patients
 Phantom limb pain Advice for amputee patients The purpose of this information leaflet is to increase your understanding of phantom pain. All pain sufferers benefit from knowing more and understanding the
Phantom limb pain Advice for amputee patients The purpose of this information leaflet is to increase your understanding of phantom pain. All pain sufferers benefit from knowing more and understanding the
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 34. Touch receptors
 Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 34 Why can t you tickle yourself? Touch receptors Last time we talked about the mechanoreceptors involved touch perception It is important to remember that touch is a
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 34 Why can t you tickle yourself? Touch receptors Last time we talked about the mechanoreceptors involved touch perception It is important to remember that touch is a
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 34 Why can t you tickle yourself? Touch receptors Last time we talked about the mechanoreceptors involved touch perception It is important to remember that touch is a
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 34 Why can t you tickle yourself? Touch receptors Last time we talked about the mechanoreceptors involved touch perception It is important to remember that touch is a
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception. Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital.
 Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch!
 Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
Cortical Map Plasticity. Gerald Finnerty Dept Basic and Clinical Neuroscience
 Cortical Map Plasticity Gerald Finnerty Dept Basic and Clinical Neuroscience Learning Objectives Be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics of a cortical map 2. Appreciate that the term plasticity is
Cortical Map Plasticity Gerald Finnerty Dept Basic and Clinical Neuroscience Learning Objectives Be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics of a cortical map 2. Appreciate that the term plasticity is
Duplex Theory of Texture Perception
 Duplex Theory of Texture Perception Katz (1925) proposed that perception of texture depends on two cues: Spatial cues are determined by the size, shape, and distribution of surface elements Temporal cues
Duplex Theory of Texture Perception Katz (1925) proposed that perception of texture depends on two cues: Spatial cues are determined by the size, shape, and distribution of surface elements Temporal cues
Mirror neurons. Romana Umrianova
 Mirror neurons Romana Umrianova The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations Giacomo Rizzolatti and Corrado Sinigaglia Mechanism that unifies action
Mirror neurons Romana Umrianova The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations Giacomo Rizzolatti and Corrado Sinigaglia Mechanism that unifies action
Applications of Graded Motor Imagery in a Patient with Chronic Upper Extremity Pain. Following Multiple Thoracic Outlet Surgeries: A Case Report
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Applications of Graded Motor Imagery in a Patient with Chronic Upper Extremity Pain Following Multiple Thoracic Outlet Surgeries: A Case Report 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Applications of Graded Motor Imagery in a Patient with Chronic Upper Extremity Pain Following Multiple Thoracic Outlet Surgeries: A Case Report 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
Rehabilitative Qigong & Tai Chi Fundamentals. The Science of Vision and Mental Imagery
 Rehabilitative Qigong & Tai Chi Fundamentals The Science of Vision and Mental Imagery!" Introduction! Body, Breath, Vision Focus! We think in images! Body and brain can t tell the difference between what
Rehabilitative Qigong & Tai Chi Fundamentals The Science of Vision and Mental Imagery!" Introduction! Body, Breath, Vision Focus! We think in images! Body and brain can t tell the difference between what
There is evidence showing mirror therapy to reduce phantom limb pain in adult clients with lower limb amputations
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics 2009 There is evidence showing mirror therapy to reduce phantom limb pain in adult clients with lower limb amputations
Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics 2009 There is evidence showing mirror therapy to reduce phantom limb pain in adult clients with lower limb amputations
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT
 PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? brain. deprived of sight?
 How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense
 The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
Overview of Questions
 Overview of Questions What are the sensors in the skin, what do they respond to and how is this transmitted to the brain? How does the brain represent touch information? What is the system for sensing
Overview of Questions What are the sensors in the skin, what do they respond to and how is this transmitted to the brain? How does the brain represent touch information? What is the system for sensing
Mirror Therapy for the Lower-Extremities Post- Stroke
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository March 2015 Mirror Therapy for the Lower-Extremities Post- Stroke Lucas David Crosby The University of Western Ontario
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository March 2015 Mirror Therapy for the Lower-Extremities Post- Stroke Lucas David Crosby The University of Western Ontario
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions.
 Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
I can t find it! Distorted body image and tactile dysfunction in patients with chronic back pain
 Pain 140 (2008) 239 243 Clinical note I can t find it! Distorted body image and tactile dysfunction in patients with chronic back pain G. Lorimer Moseley * Department of Physiology, Anatomy & Genetics,
Pain 140 (2008) 239 243 Clinical note I can t find it! Distorted body image and tactile dysfunction in patients with chronic back pain G. Lorimer Moseley * Department of Physiology, Anatomy & Genetics,
PSYC 223 BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY
 PSYC 223 BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY Session 5 ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM PART II Lecturer: Dr. Adote Anum, Dept. of Psychology Contact Information: aanum@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
PSYC 223 BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY Session 5 ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM PART II Lecturer: Dr. Adote Anum, Dept. of Psychology Contact Information: aanum@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
Saebo Mirror Box Product Manual
 Saebo Mirror Box Product Manual No Plateau In Sight Introduction Saebo is pleased to introduce a simple and effective therapy tool used to treat motor dysfunction. Saebo s Mirror Box Therapy, a treatment
Saebo Mirror Box Product Manual No Plateau In Sight Introduction Saebo is pleased to introduce a simple and effective therapy tool used to treat motor dysfunction. Saebo s Mirror Box Therapy, a treatment
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
ARTICLE IN PRESS. G. Lorimer Moseley* School of Physiotherapy, The University of Sydney, P.O. Box 170, East St, Lidcombe, Sydney, NSW 1825, Australia
 Pain xx (2005) 1 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/pain Is successful rehabilitation of complex regional pain syndrome due to sustained attention to the affected limb? A randomised clinical trial G. Lorimer Moseley*
Pain xx (2005) 1 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/pain Is successful rehabilitation of complex regional pain syndrome due to sustained attention to the affected limb? A randomised clinical trial G. Lorimer Moseley*
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Neural codes PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 12. COC illusion
 Neural codes PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 12 Is 100 billion neurons enough? COC illusion The COC illusion looks like real squares because the neural responses are similar True squares COC squares Ganglion
Neural codes PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 12 Is 100 billion neurons enough? COC illusion The COC illusion looks like real squares because the neural responses are similar True squares COC squares Ganglion
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13
 Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Single cell tuning curves vs population response. Encoding: Summary. Overview of the visual cortex. Overview of the visual cortex
 Encoding: Summary Spikes are the important signals in the brain. What is still debated is the code: number of spikes, exact spike timing, temporal relationship between neurons activities? Single cell tuning
Encoding: Summary Spikes are the important signals in the brain. What is still debated is the code: number of spikes, exact spike timing, temporal relationship between neurons activities? Single cell tuning
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
The Three Pearls DOSE FUNCTION MOTIVATION
 The Three Pearls DOSE FUNCTION MOTIVATION Barriers to Evidence-Based Neurorehabilitation No placebo pill for training therapy Blinded studies often impossible Outcome measures for movement, language, and
The Three Pearls DOSE FUNCTION MOTIVATION Barriers to Evidence-Based Neurorehabilitation No placebo pill for training therapy Blinded studies often impossible Outcome measures for movement, language, and
Graded Motor Imagery. The Science, Theory and Prac6ce. Tim Cocks and Robyn Cook
 Graded Motor Imagery The Science, Theory and Prac6ce Tim Cocks and Robyn Cook Acknowledgements The brains, the inspira6on, the champions of GMI David Butler at noi group noigroup.com Lorimer Moseley at
Graded Motor Imagery The Science, Theory and Prac6ce Tim Cocks and Robyn Cook Acknowledgements The brains, the inspira6on, the champions of GMI David Butler at noi group noigroup.com Lorimer Moseley at
The Motor Systems. What s the motor system? Plan
 The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
Dr. Mark Ashton Smith, Department of Psychology, Bilkent University
 UMAN CONSCIOUSNESS some leads based on findings in neuropsychology Dr. Mark Ashton Smith, Department of Psychology, Bilkent University nattentional Blindness Simons and Levin, 1998 Not Detected Detected
UMAN CONSCIOUSNESS some leads based on findings in neuropsychology Dr. Mark Ashton Smith, Department of Psychology, Bilkent University nattentional Blindness Simons and Levin, 1998 Not Detected Detected
Why is neuroplasticity needed? Session 301: Rerouting Neural Pathways: Advancing Pediatric Function Through Neuroplasticity Karen Pryor PhD, PT, DPT
 To comply with professional boards/associations standards: I declare that I (or my family) do not have a financial relationship in any amount, occurring in the last 12 months with a commercial interest
To comply with professional boards/associations standards: I declare that I (or my family) do not have a financial relationship in any amount, occurring in the last 12 months with a commercial interest
What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain is always subjective
 Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
A controlled pilot study of the utility of mirror visual feedback in the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome (type 1)
 Rheumatology 2003;42:97 101 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg041, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org A controlled pilot study of the utility of mirror visual feedback in the treatment of complex
Rheumatology 2003;42:97 101 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg041, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org A controlled pilot study of the utility of mirror visual feedback in the treatment of complex
Observational Learning Based on Models of Overlapping Pathways
 Observational Learning Based on Models of Overlapping Pathways Emmanouil Hourdakis and Panos Trahanias Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas (FORTH) Science and Technology
Observational Learning Based on Models of Overlapping Pathways Emmanouil Hourdakis and Panos Trahanias Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas (FORTH) Science and Technology
Nana Isberg Nielsen Master Thesis, INTRODUCTION MIRROR VISUAL FEEDBACK: BACKGROUND, THEORY, USE AND FURTHER DIRECTIONS 12
 Table of Consents Nana Isberg Nielsen Master Thesis, 2011 1.0 INTRODUCTION 5 1.1 PROBLEM DEFINITION 7 1.2 SELECTION 7 1.3 DISPOSITION 7 1.4 DEFINITIONS 8 1.4.1 MIRROR VISUAL FEEDBACK 8 1.4.2 COMPLEX AND
Table of Consents Nana Isberg Nielsen Master Thesis, 2011 1.0 INTRODUCTION 5 1.1 PROBLEM DEFINITION 7 1.2 SELECTION 7 1.3 DISPOSITION 7 1.4 DEFINITIONS 8 1.4.1 MIRROR VISUAL FEEDBACK 8 1.4.2 COMPLEX AND
doi: /brain/awr077 Brain 2011: 134;
 doi:10.1093/brain/awr077 Brain 2011: 134; 1373 1386 1373 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Mental practice with motor imagery in stroke recovery: randomized controlled trial of efficacy Magdalena Ietswaart,
doi:10.1093/brain/awr077 Brain 2011: 134; 1373 1386 1373 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Mental practice with motor imagery in stroke recovery: randomized controlled trial of efficacy Magdalena Ietswaart,
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Anosognosia for Hemiplegia
 Anosognosia for Hemiplegia Anosognosia Denial of illness (paralysis, also blindness) Limb doesn t move, but no expression of frustration Confabulation: arm belongs to someone else Rationalization: didn
Anosognosia for Hemiplegia Anosognosia Denial of illness (paralysis, also blindness) Limb doesn t move, but no expression of frustration Confabulation: arm belongs to someone else Rationalization: didn
Pain Care Doesn t Have to Be Torture
 Pain Care Doesn t Have to Be Torture How explaining pain to your patient can change the conversation and promote alliance and self-efficacy efficacy PRESENTED BY NORA STERN, PT, MSPT PROVIDENCE ST. JOSEPH
Pain Care Doesn t Have to Be Torture How explaining pain to your patient can change the conversation and promote alliance and self-efficacy efficacy PRESENTED BY NORA STERN, PT, MSPT PROVIDENCE ST. JOSEPH
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
Sensory Processing Disorder
 Disorder 101 Ingrid M. Kanics Kanics Inclusive Design Services, LLC imkanics@mindspring.com Sensory Integration Sensory Regulation Disorder Background: A. Jean Ayres, Occupational Therapist Neuroscience
Disorder 101 Ingrid M. Kanics Kanics Inclusive Design Services, LLC imkanics@mindspring.com Sensory Integration Sensory Regulation Disorder Background: A. Jean Ayres, Occupational Therapist Neuroscience
Degree of freedom problem
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019
 PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019 NEUROPATHIC PAIN PAIN ARISING AS DIRECT CONSEQUENCE OF A LESION OR DISEASE AFFECTING THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM AFFECTS 3-8% OF POPULATION
PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019 NEUROPATHIC PAIN PAIN ARISING AS DIRECT CONSEQUENCE OF A LESION OR DISEASE AFFECTING THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM AFFECTS 3-8% OF POPULATION
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement. Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement. Neural control of movement
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
LEAH KRUBITZER RESEARCH GROUP LAB PUBLICATIONS WHAT WE DO LINKS CONTACTS
 LEAH KRUBITZER RESEARCH GROUP LAB PUBLICATIONS WHAT WE DO LINKS CONTACTS WHAT WE DO Present studies and future directions Our laboratory is currently involved in two major areas of research. The first
LEAH KRUBITZER RESEARCH GROUP LAB PUBLICATIONS WHAT WE DO LINKS CONTACTS WHAT WE DO Present studies and future directions Our laboratory is currently involved in two major areas of research. The first
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Prepared by Holly Fales, OTS, Rachel Frandrup, OTS, Jaye Jennings, OTS, & Kelsey Kittler, OTS (12/10/2015). Available at
 1 There is moderate evidence that mirror therapy is as effective as alternative interventions in reducing phantom limb pain in adults with unilateral amputations. Prepared by: Holly Fales, OTS (fales.holl@uwlax.edu);
1 There is moderate evidence that mirror therapy is as effective as alternative interventions in reducing phantom limb pain in adults with unilateral amputations. Prepared by: Holly Fales, OTS (fales.holl@uwlax.edu);
Movement management of low back pain Dr Neil Langridge DClinP MSc MMACP MCSP
 Movement management of low back pain Dr Neil Langridge DClinP MSc MMACP MCSP What underlies LBP? MRI Disc degeneration = 91% Loss of disc height = 51% Disc bulges = 64% Disc protrusion = 32% Annular tear
Movement management of low back pain Dr Neil Langridge DClinP MSc MMACP MCSP What underlies LBP? MRI Disc degeneration = 91% Loss of disc height = 51% Disc bulges = 64% Disc protrusion = 32% Annular tear
Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools
 Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools Anatomical Orientation Clinical Orientation Atlas Fig. 6-24 The Reality of the Clinical Environment Atlas Fig. 6-24A One Cardinal Plane to Learn AND Understand
Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools Anatomical Orientation Clinical Orientation Atlas Fig. 6-24 The Reality of the Clinical Environment Atlas Fig. 6-24A One Cardinal Plane to Learn AND Understand
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Vision II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology?
 ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
Effect and mechanism of mirror therapy on rehabilitation of lower limb motor function in patients with stroke hemiplegia.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (22): 10165-10170 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect and mechanism of mirror on rehabilitation of lower limb motor function in patients with stroke hemiplegia. Haiyan
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (22): 10165-10170 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect and mechanism of mirror on rehabilitation of lower limb motor function in patients with stroke hemiplegia. Haiyan
[RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction
![[RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction [RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction](/thumbs/79/79754305.jpg) [RG online edits added 6-23-04; updated 6-30-04] Unit 3: The Nervous System Introduction Everything you do, everything you feel, every thought that you have, every sensation that you experience, involves
[RG online edits added 6-23-04; updated 6-30-04] Unit 3: The Nervous System Introduction Everything you do, everything you feel, every thought that you have, every sensation that you experience, involves
An Overview of BMIs. Luca Rossini. Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications
 An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [JHU John Hopkins University] On: 15 October 2009 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 906385011] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in
This article was downloaded by: [JHU John Hopkins University] On: 15 October 2009 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 906385011] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in
1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements?
 Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
Pain. Pain. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Psyc 2906: Sensation--Introduction 9/27/2006
 Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Mechanosensation. Central Representation of Touch. Wilder Penfield. Somatotopic Organization
 Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
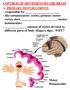 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Selective bias in temporal bisection task by number exposition
 Selective bias in temporal bisection task by number exposition Carmelo M. Vicario¹ ¹ Dipartimento di Psicologia, Università Roma la Sapienza, via dei Marsi 78, Roma, Italy Key words: number- time- spatial
Selective bias in temporal bisection task by number exposition Carmelo M. Vicario¹ ¹ Dipartimento di Psicologia, Università Roma la Sapienza, via dei Marsi 78, Roma, Italy Key words: number- time- spatial
Benjamin Blankertz Guido Dornhege Matthias Krauledat Klaus-Robert Müller Gabriel Curio
 Benjamin Blankertz Guido Dornhege Matthias Krauledat Klaus-Robert Müller Gabriel Curio During resting wakefulness distinct idle rhythms located over various brain areas: around 10 Hz (alpha range) over
Benjamin Blankertz Guido Dornhege Matthias Krauledat Klaus-Robert Müller Gabriel Curio During resting wakefulness distinct idle rhythms located over various brain areas: around 10 Hz (alpha range) over
Understanding Chronic Pain: An Educational Session on Chronic Pain
 Understanding Chronic Pain: An Educational Session on Chronic Pain Matilda Nowakowski, Ph.D., C.Psych. Linette Savage Chronic Pain Clinic, St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Objectives To better understand
Understanding Chronic Pain: An Educational Session on Chronic Pain Matilda Nowakowski, Ph.D., C.Psych. Linette Savage Chronic Pain Clinic, St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Objectives To better understand
Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control
 Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control How Your Brain Works - Week 10 Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net The Story So Far In the first few lectures we introduced you to some
Making Things Happen: Simple Motor Control How Your Brain Works - Week 10 Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net The Story So Far In the first few lectures we introduced you to some
A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to
 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Neuroscience Tutorial
 Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
MASSAGE FEEL THE DIFFERENCE REMEDIAL, SPORTS, RELAXATION, INJURY PROFESSIONAL CHINESE MASSAGE
 MASSAGE PROFESSIONAL CHINESE MASSAGE FEEL THE DIFFERENCE REMEDIAL, SPORTS, RELAXATION, INJURY ZHONG S UNIQUE MASSAGE EXPERIENCE Dr Jason Zhong Dr Jason Zhong is a western-trained medical doctor and anaesthetist
MASSAGE PROFESSIONAL CHINESE MASSAGE FEEL THE DIFFERENCE REMEDIAL, SPORTS, RELAXATION, INJURY ZHONG S UNIQUE MASSAGE EXPERIENCE Dr Jason Zhong Dr Jason Zhong is a western-trained medical doctor and anaesthetist
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization
 LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization THE VISUAL SYSTEM Higher Visual Processing Martin Paré Assistant Professor Physiology & Psychology Most of the cortex that covers the cerebral hemispheres is
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization THE VISUAL SYSTEM Higher Visual Processing Martin Paré Assistant Professor Physiology & Psychology Most of the cortex that covers the cerebral hemispheres is
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
the true value of Rebound Therapy lies in the fact that part of what occurs is not on earth Eddy Anderson Rebound Therapy
 the true value of Rebound Therapy lies in the fact that part of what occurs is not on earth Eddy Anderson Rebound Therapy 2 What is Rebound Therapy? The phrase Rebound Therapy was coined by the founder,
the true value of Rebound Therapy lies in the fact that part of what occurs is not on earth Eddy Anderson Rebound Therapy 2 What is Rebound Therapy? The phrase Rebound Therapy was coined by the founder,
Prof Wayne Derman MBChB,BSc (Med)(Hons) PhD, FFIMS. Pain Management in the Elite Athlete: The 2017 IOC Consensus Statement
 Prof Wayne Derman MBChB,BSc (Med)(Hons) PhD, FFIMS Pain Management in the Elite Athlete: The 2017 IOC Consensus Statement 2 as 20 Experts published and leaders in their respective field 12 month lead in
Prof Wayne Derman MBChB,BSc (Med)(Hons) PhD, FFIMS Pain Management in the Elite Athlete: The 2017 IOC Consensus Statement 2 as 20 Experts published and leaders in their respective field 12 month lead in
Joel F. Lehrer, MD, FACS
 Joel F. Lehrer, MD, FACS I will provide some background information, some clinical experiences with patients with vestibular disorders and cite some research and literature to accomplish my aim. This is
Joel F. Lehrer, MD, FACS I will provide some background information, some clinical experiences with patients with vestibular disorders and cite some research and literature to accomplish my aim. This is
Introduction to the Special Issue on Multimodality of Early Sensory Processing: Early Visual Maps Flexibly Encode Multimodal Space
 BRILL Multisensory Research 28 (2015) 249 252 brill.com/msr Introduction to the Special Issue on Multimodality of Early Sensory Processing: Early Visual Maps Flexibly Encode Multimodal Space Roberto Arrighi1,
BRILL Multisensory Research 28 (2015) 249 252 brill.com/msr Introduction to the Special Issue on Multimodality of Early Sensory Processing: Early Visual Maps Flexibly Encode Multimodal Space Roberto Arrighi1,
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
SENSORY PLASTICITY. Sensory Plasticity
 801 Sensory Plasticity SENSORY PLASTICITY You may have the idea that the visual, auditory and somatosensory systems are static pathways (i.e., the neural wiring is in place and simply does its job). To
801 Sensory Plasticity SENSORY PLASTICITY You may have the idea that the visual, auditory and somatosensory systems are static pathways (i.e., the neural wiring is in place and simply does its job). To
THE IMPORTANCE OF COORDINATIVE ABILITIES IN ACHIEVING ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE
 THE IMPORTANCE OF COORDINATIVE ABILITIES IN ACHIEVING ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE Lecturer PhD Neluţa Smîdu E-mail: nelysmadu@yahoo.com D.E.F.S. A.S.E. Bucharest Abstract During the training process, the development
THE IMPORTANCE OF COORDINATIVE ABILITIES IN ACHIEVING ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE Lecturer PhD Neluţa Smîdu E-mail: nelysmadu@yahoo.com D.E.F.S. A.S.E. Bucharest Abstract During the training process, the development
General Bookthoughts:
 The Emerging Mind Category: Brain Science Vilayanur Ramachandran (VR) This Bookthought is by Thoughtpiece.com, editor RM, done in 2009 based on the paperback published 2003 General Bookthoughts: These
The Emerging Mind Category: Brain Science Vilayanur Ramachandran (VR) This Bookthought is by Thoughtpiece.com, editor RM, done in 2009 based on the paperback published 2003 General Bookthoughts: These
Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions. Visual awareness
 Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions Visual awareness Phylosphy of mind Art AI Normal and abnormal states Coma Drugs Hypnosis Religion Cosciousness 2 Unconscious processes Normal and abnormal contents
Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions Visual awareness Phylosphy of mind Art AI Normal and abnormal states Coma Drugs Hypnosis Religion Cosciousness 2 Unconscious processes Normal and abnormal contents
An Alternative to Traditional Mirror Therapy. Illusory Touch Can Reduce Phantom Pain When Illusory Movement Does Not
 CASE REPORT Illusory Touch Can Reduce Phantom Pain When Illusory Does Not Laura Schmalzl, PhD,* Christina Ragno, MSc,w and H. Henrik Ehrsson, MD, PhD* Objectives: There is evidence that amputation leads
CASE REPORT Illusory Touch Can Reduce Phantom Pain When Illusory Does Not Laura Schmalzl, PhD,* Christina Ragno, MSc,w and H. Henrik Ehrsson, MD, PhD* Objectives: There is evidence that amputation leads
