Correlation of umbilical cord blood volume with CD34+ cells concentration
|
|
|
- Gervase Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IJBTI 2011 ;1 : Chandra et al. 1 2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Correlation of umbilical cord blood volume with CD34+ cells concentration Tulika Chandra, Sheeba Afreen, Ashutosh Kumar, Uma Singh ABSTRACT Aims: Umbilical cord blood (UCB) has been recently considered as an alternative source of hematopoitic progenitor cells for clinical application. The parameters commonly used to evaluate a UCB unit and predict transplant outcomes have been total nucleated cell count (TNCs), CD34+ cells concentration and total volume of cord blood collected. The volume of cord blood collection is also important for the high yield of CD34+ cells concentration and TNCs. The aim of the study was to find the correlation of umbilical cord blood volume with cord blood derived CD34+ cells concentration. Methods: Umbilical cord blood was collected from normal vaginal and cesarean deliveries. Total volume of cord blood collection was noted. It was immediately processed and assessed for Tulika Chandra 1, Sheeba Afreen 1,2, Ashutosh Kumar 2, Uma Singh 3 Affiliations: 1 Department of Transfusion Medicine and Blood Bank, Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University (Earlier King Georg s Medical University), Lucknow Uttar Pradesh, India; 2 Professor, Department of Pathology, Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University (Earlier King Georg s Medical University), Lucknow Uttar Pradesh, India; 3 Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University (Earlier King Georg s Medical University), Lucknow Uttar Pradesh, India. Corresponding Author: Dr. Tulika Chandra, Assistant Professor, Department of Transfusion Medicine and Blood Bank, Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India; Ph: ; tulikachandra@rediffmail.com Received: 27 April 2011 Accepted: 09 August 2011 Published: 31 October 2011 total nucleated cells count and CD34+ cells concentration. Assessment of maternal and neonatal parameters such as mode of delivery, baby s birth weight and sex, cord blood volume and CD34+ cells concentration was made. Results: Total volume of cord blood and CD34+ cells concentration positively correlated with cesarean delivery and higher birth weight of the baby (p<0.01). We also found that, CD34+ cells concentration was higher in greater volume of collected cord blood. Conclusions: Our study concludes that higher volume of cord blood should be preferred for processing and stem cell infusion. Keywords: CD34+ cells, TNC, Cord blood volume, Stem cells Chandra T, Afreen S, Kumar A, Singh U. Correlation of umbilical cord blood volume with CD34+ cells concentration. International Journal of Blood Transfusion and Immunohematology 2011;1: Article ID: IJBTITC2011. doi: /ijbti OA 3 INTRODUCTION Umbilical cord blood (UCB) contains hematopoitic stem/progenitor cells that have proven useful clinically to reconstitute the hematopoitic system in children and adults. This source of stem cells has been successfully used to replace bone marrow transplantation. Cord blood has several advantages over adult hematopoitic stem cell sources. These include ease and safety of
2 IJBTI 2011 ;1 : Chandra et al. 1 3 procurement, rapid availability, no donor attrition, decreased viral transmission, unlimited supply, increased ethnic representation, abundance of hematopoitic progenitor cells, enhanced in vitro proliferative and self renewal capacity, immaturity of T cell mediated immunity, reduced graft versus host disease (GVHD) and diminished need of HLA matching [1 3]. Hence, for the first time in 1988, cord blood (CB) was used as an alternative source of HSCT in a child with Fanconi anemia [4] which had several benefits such as ability to tolerate HLA mismatched transplants [5, 6], a lower risk of acute and chronic GVHD [7, 8] and lower risk of blood transmitted infectious diseases. It has been shown that cord blood contains sufficient progenitor cells to provide durable engraftment. As a response to the initial encouraging clinical results of cord blood transplants, several cord blood banks have been established worldwide [9]. Cord blood processing and cryopreservation is a very costly procedure. Cord blood units (CBU) require expensive storage in nitrogen tanks, but only a small percentage of them are used for transplantation. The parameters commonly used to evaluate a UCB unit and predict transplant outcomes have been total nucleated cell count (TNCs), CD34+ cells concentration and total volume of cord blood collected. The volume of cord blood collection is crucial for the yield of high number of TNC and CD34+ cells when the collection is performed for banking and transplantation reasons. High cord blood nucleated and CD34+ cell counts as well as the number of haematopoitic progenitor cells (Colony forming cells) in the transplant are associated with good transplantation results [10]. In clinical application, the number of mononuclear cells and CD34+ cells infused have proved to be the major prognostic factor for faster engraftment and prolonged survival. The aim of the present study is to find the correlation between umbilical cord blood volume and cord blood derived CD34+ cells concentration. This would help in reducing the cost for collection, transfer, storage and analysis of cord blood units (CBUs). MATERIALS AND METHODS Five hundred umbilical cord blood samples were obtained from both vaginal and cesarean deliveries from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CSMMU, Lucknow, India. Informed consent was taken prior to the collection of cord blood. Women with known history of hepatitis, infectious disease, diabetes mellitus, severe hypertension, abortions or bad obstetrics history were excluded from the study. Only healthy pregnant adult woman without any complications were included. Cord blood was collected from 380 (76%) normal vaginal and 120 (24%) cesarean deliveries after the completion of delivery before placenta expulsion. After the delivery of the baby the cord was clamped and a needle was inserted into the umbilical vein above the clamp. The blood was drained via gravity into the sterile collection bag, containing Citrate Phosphate Dextrose Adenine (CPDA) as an anticoagulant. Cord blood donor infants: Birth weight, sex of the baby, mode of delivery and gestational age of the baby were recorded. Infants delivered at term (31 41 wks) were included in our study. After collection, the cord blood was sent in the transport boxes to the Department of Transfusion Medicine, C.S.M.M.U, Lucknow. Cord Blood Processing: Processing was done within 24 hours of cord blood collection. Aliquots of blood were used for routine testing, including cell counts, CD34+ cell concentration, and viability assay. Transmissible disease testing for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV 2), Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg), Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and syphilis were also performed. The processing of samples, which included the determination of cord blood volumes, the determination of initial level of total nucleated cells (TNC) and mononuclear cells (MNC) before centrifugation was done. The UCB product was then mixed with hydroxyethyl starch in a 5:1 ratio and centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 10 min. The WBC rich plasma was expressed in a separate bag and again centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 10 min. The WBC poor plasma was expressed and discarded. The remaining suspension of mononuclear cells was left whose counts were recorded. The UCB mononuclear cells were cryopreserved using the cryoprotectant solution containing 50% DMSO in 5% (wt/vol) Dextran 40 at a final concentration of 10%. Laboratory Assays: The Total nucleated cell count was performed by automated cell counter (Sysmex KX 21, Japan). The viability was tested with Trypan Blue; dye exclusion method. The CD34+ cells were performed by using flow cytometry analysis. Statistics: Data were reported as means ± standard deviation. Descriptive statistics were presented for each maternal and neonatal factor. The Pearson correlation test was used for analysis. The level of statistical significance was set at 0.01 two sided for Pearson correlation (p < 0.01). RESULTS Total 500 UCB samples were analyzed. Amongst them according to their newborn sex distribution, 282 infants (56.4%) were males and 218 (43.6%) were females. The median gestational age was 38 wks (mean 37.57±1.82 wks, range 31 41). The distribution of birth weight was normal (mean 2790±426 gram, range , table 1). The median of mother s age was 28 yrs (mean 28.47±4.26, range years). The mean of the total volume collection and total CD34+ cells concentrations were ml (median 80, range ml) and 0.41±0.42 % (median 0.20, range %) respectively in vaginal delivery. The mean of the total volume collection and CD34+ cells concentration were ±17.80 ml (range ml) and 2.42 ±
3 IJBTI 2011 ;1 : Chandra et al. 1 4 Table 1: Characteristics of the study subjects by study site (n=500). Characteristics Mean ± SD or N (%) Newborn gender Male 282 (56.4%) Female 218(43.6%) Gestation Duration (weeks) 37.57± 1.82 Birth weight gram 168 (33.6%) gram 332 (66.4%) Total UCB volume collection Normal Vaginal Delivery 173 Caesarian Delivery % (median: 2.60, range: %) respectively in cesarean delivery (table 2, 3). The mean of the CB volume and CD34+ cells concentration were significantly higher in cesarean delivery than in normal vaginal delivery (p < 0.01). The mean of the CB volume and CD34+ cells concentration were significantly higher in heavier birth weight of the baby than in normal birth weight of the baby (p < 0.01). Baby sex has no effect on total volume of cord blood collection and CD34+ cells concentration. The mean of the total CD34+ cells concentration was 0.42±0.44% (median 0.22, range %) for the group of ml of total volume of cord blood collection. The mean of the total CD34+ cells concentration was 2.41±0.99% (median 2.17, range %) for the group of ml of total volume of cord blood collection (table 2). The CD34+ cells concentration was higher in higher volume of cord blood collection. The CD34+ cells concentration was positively correlated with higher volume of cord blood collection (p<0.01). DISCUSSION Umbilical cord blood has been recently considered as an alternative source of hematopoietic progenitor cells for clinical application [11]. The main difference between cord blood and bone marrow is the smaller number of cells obtained in the cord blood product. As a result, until now, cord blood has been used primarily for children. Some ways to resolve this problem consist of screening and selection of proper cord blood donors before collection, choosing the best methods for collection, increasing the recovery rate of cord blood processing and ex vivo expansion of cord blood [12]. Table 2: Descriptive Statistics of the cord blood derived CD34+ cells concentration in different group (n=500). Characteristics CD34+ cell concentration (%) Mode of delivery Mean ± SD Median Range Normal vaginal ± delivery Caesarian 2.42 ± delivery Birth weight (gram) ± ± Total volume collection (ml) ± ± Table 3: Descriptive Statistics of the total volume of cord blood collection in different group (n=500). Characteristics Mode of delivery Total volume collection (ml) Mean ± SD Median Range Normal vaginal delivery ± Caesarian delivery ± Birth weight (gram) ± ± The expansion of cord blood cells is being studied as a method of increasing the number of progenitor cells, but no conclusive data is available, thus only the improvement of collection and selection of proper cord blood unit represent an effective strategy for improving the efficacy and reducing the costs of this therapy. The success of UCB cells transplantation is largely related to the number of TNC and CD34+ cells. The quality of Cord blood unit depends on its content in total nucleated cells (TNC), colony forming cells (CFC) and CD34+ cells [13]. Furthermore, a number of factors have been described that may influence the total volume collected, quantification of UCB CD34+ cells, and TNC and that may account for the variations in the reported results. Some studies shows that caesarian deliveries provides collection of a higher volume of cord blood than vaginal deliveries. They also stated that higher cord blood volume is correlated with high concentration of
4 IJBTI 2011 ;1 : Chandra et al. 1 5 CD34+ cells [14]. Previous studies reported that the mode of delivery has no impact on CB yield [15]. It has been reported that volume, as expected, is clearly associated with higher cell counts, CFU GM and CD34+ cell counts [16]. In our study, Cord Blood volume was significantly higher in CDs than in VDs (p < 0.01). Similarly, CD34+cell count was also higher in CDs than in VDs (p < 0.01). Other studies reported that there was a positive correlation between volume of collected umbilical cord blood and newborn weight as well as a positive correlation was found between newborn weight with CD34+ cells and total nucleated cell count [17]. In our study, there was a positive correlation between volume of collected UCB and higher birth weight of the baby, (p < 0.01) which can thus result in an increase in the absolute number of CD34+ cells. Other studies showed that no association was detected between baby sex with total volume of cord blood collected. It has been also shows that factor like sex can affect the concentration of CD34+ cells [18]. In our analysis no connection was detected between baby sex with total volume of cord blood collected, CD34+ cell count and Total nucleated count. Some studies shows that, as the volume of collected UCB directly affects the quantity of CD34+ cells per micro liter of blood and possibly the quantity of total nucleated cells. A significant positive correlation was found between the relative number of CD34+/CD117 cells and the volume of UCB, the CD34+ cells. In another study volume, as expected, is clearly associated with higher CD34+ cells counts. Many cord blood banks have set a lower limit of acceptable volume, such as cc without anticoagulant [19]. Cord blood can be collected either before or after the delivery of the placenta; in their programmed cord blood is collected before delivery of the placenta [20]. Early cord blood clamping may increase the volume of collection, but raises ethical concerns, and is generally practiced [21, 22]. In a study, where 1,200 donors were evaluated, it was observed that high volume samples were correlated with high doses of TNCs, CD34+ cells and colony forming units of granulocytes and macrophages (CFU GM) [23]. In our analysis we also find that there was a significant positive correlation between the total volume of cord blood collection with cord blood derived CD34+ cells concentration. CONCLUSION In conclusion, total volume of cord blood and CD34+ cells concentration were positively correlated with cesarean delivery and higher birth weight of the baby. Baby sex have no effect on cord blood volume and CD34+ cells concentration. The volume of collected umbilical cord blood showed positively correlation with CD34+ cells concentration. Author Contributions Tulika Chandra Substantial contributions to Sheeba Afreen Substantial contributions to Ashutosh Kumar Substantial contributions to Uma Singh Substantial contributions to conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and Guarantor The corresponding author is the guarantor of submission. Conflict of Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest Copyright Tulika Chandra et al. 2011; This article is distributed under the terms of Creative Commons attribution 3.0 License which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any means provided the original authors and original publisher are properly credited. (Please see /copyright policy.php for more information.) REFERENCES 1. Cairo MS, Wagner JE. Placental and/or umbilical cord blood: an alternative source of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. Blood 1997;90: Gluckman E. Current status of umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Exp Hematol 2000;28: Wadlow RC, Porter DL. Umbilical cord blood transplantation: where do we stand. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2002;8: Gluckman E, Broxmeyer HE, Auerbach AD, et al. Hematopoitic reconstitution in a patient with Fanconi anemia by means of umbilical cord blood from an HLA identical sibling. N Engl J Med 1989;321: Newberger P, Queseenbery P. Umbilical cord blood as a new and promising source of unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. I curr opin pediat 1996;8:29 32.
5 IJBTI 2011 ;1 : Chandra et al Rubinstein P, Carrier C, Scaradavou A et al. Outcomes among 562 recipients of placental blood transplants from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med 1998;339: Cohen S, Dominguez E, Lowd ell M, Madrigal J. The immunological properties of cord blood overview of current research presented at 2nd Euro cord workshop. Bone marrow transplant 1998;22(suppl 1): Varadi G, Elchalal U, Brautbar C, Nagler A. Human umbilical cord blood for hematopoietic progenitor cells transplantation. J Leuk Lymphoma 1995;20: Sirchia G, Rebulla P, Leachy L. Implementation of a quality system (iso 9000 series) for placental blood bnking. J Hematother 1998;7: Gluckman E, Rocha V, Boyer Chammard A, Locatelli F, Arcese W, Pasquini R. Outcome of cord blood transplantation from related and unrelated donors. N Engl J Med 1997;337: Thompson C. umbilical cords. turning garbage into clinical gold. Science 1995;268: Mohyeddin Bonab M, Goliaei Z, Alimoghaddam K, Ghavamzadeh. Evaluation of the Affect of Maternal and Neonatal Factors on Cord Blood Parameters. Heamatology, Oncology & BMT Research center 2004;1(1): Wagner JE, Kurtzberg J. Cord blood stem cells. CurrOpin Hematol 1997;4: Yamada T, Okamoto Y, Kasamatsu H, Horie Y, Yamashita N, Matsumoto K. Factors affecting the volume of umbilical cord blood collections. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2000;79: Lim FT, van Winsen L, Willemze R, Kanhai HH, Falkenburg JH. Influence of delivery on numbers of leukocytes, leukocyte subpopulations, and hematopoietic progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Blood Cells 1994;20: Ballen KK, Wilson M, Wuu J et al. Bigger is better maternal and neonatal predictors of hematopoietic potential of umbilical cord blood units. Bone marrow transplant 2001;27(1): Raquel Canabarro, Heloísa Sporleder, Thaís Gomes, Geancarlo Zanatta, Letícia Scribe, Fernando Freitas, Jorge Neumann, and Patricia Pranke. Immunophenotypic evaluation, and physiological and laboratory correlations of hematopoietic stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Biocell 2007;31(3): Nakagawa R, Watanabe T, Kawano Y, Kanai S, Suzuka H, Kaneko M, et al.. Analysis of maternal and neonatal factors that influence the nucleated and CD34+ cell yield for cord blood banking. Transfusion 2004;44: Kogler G, Callejas J, Hakenberg P et al. Hematopoietic transplant potential of unrelated cord blood: critical issues. J Hematother 1996; Wall DA, Noffsinger JM, Mueckl KA et al. Feasibility of an obstetrician based cord cell transplant. J Maternal Fetal Med 1997;6: Bertolini F, Lazzari L, Corsini C et al. Cord blood banking for stem cell transplant. Inter J Artificial Org 1993;16: Sugarman J, Reisner EG, Kurtzberg J. Ethical aspects of banking placental blood for transplantation. JAMA 1995;274: Bradley MB, Cairo MS Cord Blood Immunology and Stem Cell Transplantation. Hum Immunol 2005;66:
Study for the improvement of umbilical cord blood sampling using a new trial apparatus
 bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jog.12179 J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 40, No. 2: 405 409, February 2014 Study for the improvement of umbilical cord blood sampling using a new trial apparatus Naoki Masaoka
bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jog.12179 J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 40, No. 2: 405 409, February 2014 Study for the improvement of umbilical cord blood sampling using a new trial apparatus Naoki Masaoka
Research Article Mean Platelet Volume Reflect Hematopoietic Potency and Correlated Blood Group O in Cord Blood from Healthy Newborn
 BioMed Volume 2013, Article ID 754169, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/754169 Research Article Mean Platelet Volume Reflect Hematopoietic Potency and Correlated Blood Group O in Cord Blood from
BioMed Volume 2013, Article ID 754169, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/754169 Research Article Mean Platelet Volume Reflect Hematopoietic Potency and Correlated Blood Group O in Cord Blood from
Analysis of the Viability of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells. Sachdeva N
 Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES
 CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
Cord Blood Bankers are. Angie Yost, MT(ASCP) CM 2016 ASCLS-MO CLMA Spring Meeting
 Cord Blood Bankers are Angie Yost, MT(ASCP) CM 2016 ASCLS-MO CLMA Spring Meeting Objectives Cord blood 101 Manufacturing and cryopreservation Characterization testing Why Do We Need Cord Blood? Each year,
Cord Blood Bankers are Angie Yost, MT(ASCP) CM 2016 ASCLS-MO CLMA Spring Meeting Objectives Cord blood 101 Manufacturing and cryopreservation Characterization testing Why Do We Need Cord Blood? Each year,
The number of nucleated cells reflects the hematopoietic content of umbilical cord blood for transplantation
 Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 24, 965 970 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt The number of nucleated cells reflects the hematopoietic
Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 24, 965 970 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt The number of nucleated cells reflects the hematopoietic
Placental and Umbilical Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells
 Placental and Umbilical Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells Policy Number: 7.01.50 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2001 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Placental and Umbilical Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells Policy Number: 7.01.50 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2001 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking and Transplantation
 Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking and Transplantation JOHN W. ADAMSON New York Blood Center, New York, New York, USA Key Words. Cord blood Stem cells Cord blood banking Cord blood transplantation. Cord blood.stern
Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking and Transplantation JOHN W. ADAMSON New York Blood Center, New York, New York, USA Key Words. Cord blood Stem cells Cord blood banking Cord blood transplantation. Cord blood.stern
Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate
 3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
Medical Policy. MP Placental and Umbilical Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells
 Medical Policy MP 7.01.50 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 7.01.50 Last Review: 01/30/2018 Effective Date: 01/30/2018 Section: Surgery Related Policies 8.01.20 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Non- Hodgkin Lymphomas
Medical Policy MP 7.01.50 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 7.01.50 Last Review: 01/30/2018 Effective Date: 01/30/2018 Section: Surgery Related Policies 8.01.20 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Non- Hodgkin Lymphomas
CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION STUDY CBU EXCLUSION AND QUARANTINE RELEASE FORM
 (Any answer of Yes indicates exclusion) 1. Informed Consent and Maternal/Infant Demographics a. Lack of confirmation of signed and witnessed informed consent 1 Yes 2 No Is the following information missing
(Any answer of Yes indicates exclusion) 1. Informed Consent and Maternal/Infant Demographics a. Lack of confirmation of signed and witnessed informed consent 1 Yes 2 No Is the following information missing
Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE
 BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease
 Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease Rhiannon is now cured of sickle cell disease after BMT. Blood and marrow transplant (BMT) is a proven cure for sickle cell disease. This handbook
Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease Rhiannon is now cured of sickle cell disease after BMT. Blood and marrow transplant (BMT) is a proven cure for sickle cell disease. This handbook
Cord Blood Transplant. E. Gluckman Eurocord ESH-EBMT training course Vienna 2014
 Cord Blood Transplant E. Gluckman Eurocord ESH-EBMT training course Vienna 2014 Background Since 1988, umbilical cord blood (CB) has been successfully used to treat children and adults needing stem cell
Cord Blood Transplant E. Gluckman Eurocord ESH-EBMT training course Vienna 2014 Background Since 1988, umbilical cord blood (CB) has been successfully used to treat children and adults needing stem cell
About OMICS Group Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
OneMatch Stem Cell and Marrow Network. Training Guide
 OneMatch Stem Cell and Marrow Network Training Guide What is OneMatch all about? OneMatch is a Canadian Program that matches and coordinates the collection of stem cells from potential donors to help save
OneMatch Stem Cell and Marrow Network Training Guide What is OneMatch all about? OneMatch is a Canadian Program that matches and coordinates the collection of stem cells from potential donors to help save
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Transplantation
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Potency & Release Testing for unrelated donor cord blood units
 Potency & Release Testing for unrelated donor cord blood units Joanne Kurtzberg, MD Robertson Cell and Translational Therapy Program Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Carolinas Cord Blood Bank
Potency & Release Testing for unrelated donor cord blood units Joanne Kurtzberg, MD Robertson Cell and Translational Therapy Program Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Carolinas Cord Blood Bank
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
 Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Paola Di Ciaccio Vanja Nikolac
 Paola Di Ciaccio Vanja Nikolac ITALYintheHSCfield:HOWISTHISRULED? Directive 2004/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31March2004 on setting standards of quality and safety for the donation,
Paola Di Ciaccio Vanja Nikolac ITALYintheHSCfield:HOWISTHISRULED? Directive 2004/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31March2004 on setting standards of quality and safety for the donation,
IN UTERO HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION IN CANINES: THE GESTATIONAL WINDOW OF OPPORTUNITY TO MAXIMIZE ENGRAFTMENT
 IN UTERO HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION IN CANINES: THE GESTATIONAL WINDOW OF OPPORTUNITY TO MAXIMIZE ENGRAFTMENT Karin J. Blakemore, M.D. Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine The Bone Marrow Transplant
IN UTERO HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION IN CANINES: THE GESTATIONAL WINDOW OF OPPORTUNITY TO MAXIMIZE ENGRAFTMENT Karin J. Blakemore, M.D. Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine The Bone Marrow Transplant
Transfusion Medicine (Comprehensive, Limited) J, J1
 www.cap.org Transfusion Medicine Analytes/procedures in bold type are regulated for proficiency testing by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Transfusion Medicine (Comprehensive, Limited)
www.cap.org Transfusion Medicine Analytes/procedures in bold type are regulated for proficiency testing by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Transfusion Medicine (Comprehensive, Limited)
What the Transfusion Scientist should know about Stem Cells. Dr Claire Wiggins BBTS September 2017
 What the Transfusion Scientist should know about Stem Cells Dr Claire Wiggins BBTS September 2017 What is a stem cell? Undifferentiated cell Can divide and self renew for long periods Differentiate into
What the Transfusion Scientist should know about Stem Cells Dr Claire Wiggins BBTS September 2017 What is a stem cell? Undifferentiated cell Can divide and self renew for long periods Differentiate into
Hematopoiesis i starts from. HPC differentiates t to sequentially more mature. HPC circulate in very low
 Upstate Cord Blood Bank Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Hematopoiesis i starts from self renewing HPC HPC differentiates t to sequentially more mature blood cells HPC circulate in very low numbers in adults
Upstate Cord Blood Bank Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Hematopoiesis i starts from self renewing HPC HPC differentiates t to sequentially more mature blood cells HPC circulate in very low numbers in adults
REVIEW ARTICLE. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? ASBMT BB&MT. Raymond C. Wadlow, David L. Porter
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 8:637-647 (2002) 2002 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation ASBMT REVIEW ARTICLE Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? Raymond
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 8:637-647 (2002) 2002 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation ASBMT REVIEW ARTICLE Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? Raymond
GVHD. URD unrelated donor
 1 GVHD T-B GVHD 1 RDrelated donor URDunrelated donor 2. Julie M. Vose and Steven Z. Pavletic. Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. In Goldman: Cecil Medicine, 23 rd ed.; chapter 184 (Saunders, An
1 GVHD T-B GVHD 1 RDrelated donor URDunrelated donor 2. Julie M. Vose and Steven Z. Pavletic. Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. In Goldman: Cecil Medicine, 23 rd ed.; chapter 184 (Saunders, An
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Fanconi Anemia
 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Fanconi Anemia John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program University of Minnesota Cell Therapy for Pediatric Diseases NHLBI PACT Workshop 14 15
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Fanconi Anemia John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program University of Minnesota Cell Therapy for Pediatric Diseases NHLBI PACT Workshop 14 15
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility E-mail: js2745@columbia.edu Hematopoietic Stem Cells Sustain hematopoiesis
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility E-mail: js2745@columbia.edu Hematopoietic Stem Cells Sustain hematopoiesis
Stem cell transplantation for haemoglobinopathies. Dr P J Darbyshire Birmingham Childrens Hospital
 Stem cell transplantation for haemoglobinopathies Dr P J Darbyshire Birmingham Childrens Hospital Survival by Cohort of Birth (N=977) 1.00 85-97 80-84 75-79 70-74 0.75 Survival Probability 0.50 0.25 P
Stem cell transplantation for haemoglobinopathies Dr P J Darbyshire Birmingham Childrens Hospital Survival by Cohort of Birth (N=977) 1.00 85-97 80-84 75-79 70-74 0.75 Survival Probability 0.50 0.25 P
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity as a Marker of Quality in Cryopreserved Cord Blood
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 4, 297 306, December 2013 Original Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity as a Marker of Quality in Cryopreserved Cord Blood Hirokazu IKEDA, Daisuke TOYAMA, Ryosuke MATSUNO, Yoko FUJIMOTO
Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 4, 297 306, December 2013 Original Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity as a Marker of Quality in Cryopreserved Cord Blood Hirokazu IKEDA, Daisuke TOYAMA, Ryosuke MATSUNO, Yoko FUJIMOTO
Collection of Cord Blood Stem Cells for Transplantation in Thalassemic Patients
 Collection of Cord Blood Stem Cells for Transplantation in Thalassemic Patients Surapol Issaragrisil," Sanan Visuthisakchai," Yaowalak Tangnaitrisorana," Dasnayanee Chandanayingyong? Vinai Suvatte: Voravarn
Collection of Cord Blood Stem Cells for Transplantation in Thalassemic Patients Surapol Issaragrisil," Sanan Visuthisakchai," Yaowalak Tangnaitrisorana," Dasnayanee Chandanayingyong? Vinai Suvatte: Voravarn
Evaluation of Early Post-transplant Leukocyte Recovery Using the Undiluted Erythrocyte Lysing Technique
 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 32, no. 2, 2002 159 Evaluation of Early Post-transplant Leukocyte Recovery Using the Undiluted Erythrocyte Lysing Technique Myungshin Kim, 1 Ja Young Kim,
Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 32, no. 2, 2002 159 Evaluation of Early Post-transplant Leukocyte Recovery Using the Undiluted Erythrocyte Lysing Technique Myungshin Kim, 1 Ja Young Kim,
Clinical Use of Umbilical Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cells
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:34-41 (2006) 2006 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/06/1201-0107$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.09.006 Clinical Use of Umbilical
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:34-41 (2006) 2006 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/06/1201-0107$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.09.006 Clinical Use of Umbilical
Status of umbilical cord blood transplantation in the year 2001
 428 J Clin Pathol 2001;54:428 434 Status of umbilical cord blood transplantation in the year 2001 JMHows Abstract Umbilical cord blood (UCB) transplantation is limited to small recipients because of the
428 J Clin Pathol 2001;54:428 434 Status of umbilical cord blood transplantation in the year 2001 JMHows Abstract Umbilical cord blood (UCB) transplantation is limited to small recipients because of the
Research Article Decreasing Prevalence of Transfusion Transmitted Infection in Indian Scenario
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 173939, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/173939 Research Article Decreasing Prevalence of Transfusion Transmitted Infection in Indian Scenario Tulika Chandra,
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 173939, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/173939 Research Article Decreasing Prevalence of Transfusion Transmitted Infection in Indian Scenario Tulika Chandra,
Cord Blood Banking. The Birth of a New Field
 FEATURE Karen Titus Cord Blood Banking The Birth of a New Field iven the great availability of cord blood every new birth represents a possible source it's little wonder this blood product has drawn intense
FEATURE Karen Titus Cord Blood Banking The Birth of a New Field iven the great availability of cord blood every new birth represents a possible source it's little wonder this blood product has drawn intense
Applications of Cord Blood Stem Cells
 Applications of Cord Blood Stem Cells over 360 families have used their banked cord blood in transplant or regenerative medicine research. 1 88 ViaCord has released over 360 units for transplant or infusion
Applications of Cord Blood Stem Cells over 360 families have used their banked cord blood in transplant or regenerative medicine research. 1 88 ViaCord has released over 360 units for transplant or infusion
Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO
 Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Topics and Controversies in Newborn Stem Cell Medicine
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Give Birth to Hope: An Unique Approach to Public Cord Blood Donation
 Give Birth to Hope: An Unique Approach to Public Cord Blood Donation The Public Health Nursing and Professional Development Unit, North Carolina Division of Public Health, is approved as a provider of
Give Birth to Hope: An Unique Approach to Public Cord Blood Donation The Public Health Nursing and Professional Development Unit, North Carolina Division of Public Health, is approved as a provider of
Leukine. Leukine (sargramostim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
A Review of Procedures Involved in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Banking and Transplantation
 REVIEW ARTICLE IJBC 2014; 7(1): Downloaded from ijbc.ir at 18:16 +0330 on Sunday January 13th 2019 A Review of Procedures Involved in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Banking and Transplantation Nikougoftar
REVIEW ARTICLE IJBC 2014; 7(1): Downloaded from ijbc.ir at 18:16 +0330 on Sunday January 13th 2019 A Review of Procedures Involved in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Banking and Transplantation Nikougoftar
Madrid Cord Blood Bank, b Department of Hematology, c Department of Immunology, Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain
 Original Article A Modified Cord Blood Collection Method Achieves Sufficient Cell Levels for Transplantation in Most Adult Patients Rafael Bornstein, a,b Ana I. Flores, a M. Angeles Montalbán, b Manuel
Original Article A Modified Cord Blood Collection Method Achieves Sufficient Cell Levels for Transplantation in Most Adult Patients Rafael Bornstein, a,b Ana I. Flores, a M. Angeles Montalbán, b Manuel
Blood Transfusion. What is blood transfusion? What are blood banks? When is a blood transfusion needed? Who can donate blood?
 What is blood transfusion? A blood transfusion is a safe, common procedure in which blood is given through an intravenous (IV) line in one of the blood vessels. A blood transfusion usually takes two to
What is blood transfusion? A blood transfusion is a safe, common procedure in which blood is given through an intravenous (IV) line in one of the blood vessels. A blood transfusion usually takes two to
Protocol Number: 10-CBA National Clinical Trial (NCT) Identified Number: NCT
 A multicenter access and distribution protocol for unlicensed cryopreserved cord blood units (CBUs) for transplantation in pediatric and adult patients with hematologic malignancies and other indications
A multicenter access and distribution protocol for unlicensed cryopreserved cord blood units (CBUs) for transplantation in pediatric and adult patients with hematologic malignancies and other indications
2/26/2016. Types of Stem Cells: Agenda. Objectives
 PAMET, March 5, 2016 Umbilical Cord Blood for Public Banking and Research Regenerative Medicine: Curing disease by repairing or replacing organs and systems through cellular and tissue engineering Bladder
PAMET, March 5, 2016 Umbilical Cord Blood for Public Banking and Research Regenerative Medicine: Curing disease by repairing or replacing organs and systems through cellular and tissue engineering Bladder
The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness.
 The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness. Robert Liwski, MD, PhD, FRCPC Medical Director HLA Typing Laboratory Department of Pathology Dalhousie
The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness. Robert Liwski, MD, PhD, FRCPC Medical Director HLA Typing Laboratory Department of Pathology Dalhousie
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Preventing CMV Transmission through Leukodepletion
 Preventing CMV Transmission through Leukodepletion Possibility & Facts Prof.S.B.Rajadhyaksha, MD,DTM,PGDMLS Head, Dept. of Transfusion Medicine Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai 1 Donor Leukocytes Linked
Preventing CMV Transmission through Leukodepletion Possibility & Facts Prof.S.B.Rajadhyaksha, MD,DTM,PGDMLS Head, Dept. of Transfusion Medicine Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai 1 Donor Leukocytes Linked
Implementation of the Stem Cell Therapeutic and Research Act of 2005
 Implementation of the Stem Cell Therapeutic and Research Act of 2005 The 6 th Annual Somatic Cell Therapy Symposium Bethesda, MD September 26, 2006 James F. Burdick, M.D. U.S. Department of Health and
Implementation of the Stem Cell Therapeutic and Research Act of 2005 The 6 th Annual Somatic Cell Therapy Symposium Bethesda, MD September 26, 2006 James F. Burdick, M.D. U.S. Department of Health and
What are stem cells? A stem cell can differentiate into any one of 220 different specialised cells in the body STEM CELLS
 What are stem cells? Stem cells are often called MASTER CELLS, and form the foundation for your entire body as building blocks for the blood, immune system, tissue and organs. They can REPLICATE or REGENERATE
What are stem cells? Stem cells are often called MASTER CELLS, and form the foundation for your entire body as building blocks for the blood, immune system, tissue and organs. They can REPLICATE or REGENERATE
The future of HSCT. John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD
 The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
SECOND ANNUAL INTERNATIONAL UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD SYMPOSIUM
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:728-739 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1010-0009$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2004.06.010 SECOND ANNUAL INTERNATIONAL
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:728-739 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1010-0009$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2004.06.010 SECOND ANNUAL INTERNATIONAL
Evaluation of Volume and Total Nucleated Cell Count as Cord Blood Selection Parameters A Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve Modeling Approach
 Hematopathology / Umbilical Cord Blood Selection Evaluation of Volume and Total Nucleated Cell Count as Cord Blood Selection Parameters A Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve Modeling Approach José
Hematopathology / Umbilical Cord Blood Selection Evaluation of Volume and Total Nucleated Cell Count as Cord Blood Selection Parameters A Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve Modeling Approach José
PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases
 PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Viruses in July (ViJ), 2004 Overview Epidemiology Perinatal transmission
PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Viruses in July (ViJ), 2004 Overview Epidemiology Perinatal transmission
Blood Product Modifications: Leukofiltration, Irradiation and Washing
 1. Leukocyte Reduction Definitions and Standards: o Process also known as leukoreduction, or leukofiltration o Applicable AABB Standards, 25th ed. Leukocyte-reduced RBCs At least 85% of original RBCs
1. Leukocyte Reduction Definitions and Standards: o Process also known as leukoreduction, or leukofiltration o Applicable AABB Standards, 25th ed. Leukocyte-reduced RBCs At least 85% of original RBCs
Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Faculty Disclosures Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Nothing to disclose Jeanne McCarthy-Kaiser, PharmD, BCOP Clinical Pharmacist, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant/Long- Term Follow-Up
Faculty Disclosures Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Nothing to disclose Jeanne McCarthy-Kaiser, PharmD, BCOP Clinical Pharmacist, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant/Long- Term Follow-Up
Transplantation - Challenges for the future. Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust
 Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
& 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved /07 $
 () 9, & Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 8-9/ $. www.nature.com/bmt ORIGINAL ARTICLE The impact of post-thaw colony-forming units-granulocyte/macrophage on engraftment following unrelated cord
() 9, & Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 8-9/ $. www.nature.com/bmt ORIGINAL ARTICLE The impact of post-thaw colony-forming units-granulocyte/macrophage on engraftment following unrelated cord
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS
 DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
The National Marrow Donor Program. Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Simon Bostic, URD Transplant Recipient
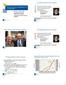 1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy
 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
D7.1 Report summarising results of survey of EU countries to identify volumes and trends in relation to the import and export of stem cells
 Disclaimer: The content of this Deliverable represents the views of the author only and is his/her sole responsibility; it cannot be considered to reflect the views of the European Commission and/or the
Disclaimer: The content of this Deliverable represents the views of the author only and is his/her sole responsibility; it cannot be considered to reflect the views of the European Commission and/or the
D7.1 Report summarising results of survey of EU countries to identify volumes and trends in relation to the import and export of stem cells
 Disclaimer: The content of this Deliverable represents the views of the author only and is his/her sole responsibility; it cannot be considered to reflect the views of the European Commission and/or the
Disclaimer: The content of this Deliverable represents the views of the author only and is his/her sole responsibility; it cannot be considered to reflect the views of the European Commission and/or the
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017
 Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Disclosures. Committee on Blood and Blood Products) Co-investigator CBS Small Project. in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
 Neonatal Transfusion: Irradiation and CMV 6 th Annual Blood Matters Conference November 6 th, 2015 Disclosures Member of NAC (National Advisory Committee on Blood and Blood Products) Co-investigator CBS
Neonatal Transfusion: Irradiation and CMV 6 th Annual Blood Matters Conference November 6 th, 2015 Disclosures Member of NAC (National Advisory Committee on Blood and Blood Products) Co-investigator CBS
HEMATOPOIETIC ENGRAFTMENT IN ADULT RECIPIENTS OF UMBILICAL-CORD BLOOD FROM UNRELATED DONORS
 HEMATOPOIETIC ENGRAFTMENT IN ADULT RECIPIENTS OF UMBILICAL-CORD BLOOD FROM UNRELATED DONORS HEMATOPOIETIC ENGRAFTMENT AND SURVIVAL IN ADULT RECIPIENTS OF UMBILICAL-CORD BLOOD FROM UNRELATED DONORS MARY
HEMATOPOIETIC ENGRAFTMENT IN ADULT RECIPIENTS OF UMBILICAL-CORD BLOOD FROM UNRELATED DONORS HEMATOPOIETIC ENGRAFTMENT AND SURVIVAL IN ADULT RECIPIENTS OF UMBILICAL-CORD BLOOD FROM UNRELATED DONORS MARY
Leukine. Leukine (sargramostim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.85.08 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Leukine Description Leukine
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.85.08 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Leukine Description Leukine
Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women. Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School
 Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School Obstetric Complications and HIV Obstetric complications are not increased in
Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School Obstetric Complications and HIV Obstetric complications are not increased in
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014
 Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
The Hep B Moms Program: A Primary Care Model for Management of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy
 The Hep B Moms Program: A Primary Care Model for Management of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy Janice Lyu, MS Senior Hepatitis B Program Associate Charles B. Wang Community Health Center (CBWCHC) Charles B Wang
The Hep B Moms Program: A Primary Care Model for Management of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy Janice Lyu, MS Senior Hepatitis B Program Associate Charles B. Wang Community Health Center (CBWCHC) Charles B Wang
Graft source and Stem cell collection SULADA PUKIAT, MD
 + Graft source and Stem cell collection SULADA PUKIAT, MD + Hematopoietic stem cells Hematopoietic stem cells are CD34 + /CD45 dim /SSC low /FSClow to intermediate Neutrophils Bone NK cells T cells Basophils
+ Graft source and Stem cell collection SULADA PUKIAT, MD + Hematopoietic stem cells Hematopoietic stem cells are CD34 + /CD45 dim /SSC low /FSClow to intermediate Neutrophils Bone NK cells T cells Basophils
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
 Exercise 8 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Objectives 1. State the purpose for performing the DAT. 2. State what a positive DAT indicates. 3. List the reagents which are used for performing the DAT. 4.
Exercise 8 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Objectives 1. State the purpose for performing the DAT. 2. State what a positive DAT indicates. 3. List the reagents which are used for performing the DAT. 4.
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28461 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Brink, Marloes Hendrika ten Title: Individualized therapeutics in allogeneic stem
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28461 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Brink, Marloes Hendrika ten Title: Individualized therapeutics in allogeneic stem
Density Separation of Umbilical Cord Blood and Recovery of Hemopoietic Progenitor Cells: Implications for Cord Blood Banking
 Density Separation of Umbilical Cord Blood and Recovery of Hemopoietic Progenitor Cells: Implications for Cord Blood Banking Camillo Almici, Carinelo Carlo-Stella, Lina Mangoni, Daniela Garau, Luca Cottafavi,
Density Separation of Umbilical Cord Blood and Recovery of Hemopoietic Progenitor Cells: Implications for Cord Blood Banking Camillo Almici, Carinelo Carlo-Stella, Lina Mangoni, Daniela Garau, Luca Cottafavi,
NiCord Single Unit Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Results of Phase I/II Trials
 NiCord Single Unit Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Results of Phase I/II Trials Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute Adult Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
NiCord Single Unit Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Results of Phase I/II Trials Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute Adult Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
Specific Requirements
 Specific Requirements AIMS Specific requirements your patients have for transfusion and how this is managed Classify which patients require: Irradiated components CMV negative components Washed components
Specific Requirements AIMS Specific requirements your patients have for transfusion and how this is managed Classify which patients require: Irradiated components CMV negative components Washed components
Tunisian recommendations on ART : process and results
 Second Arab Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases May 24-26, 2012. Tunisian recommendations on ART : process and results M. BEN MAMOU UNAIDS Email: BenmamouM@unaids.org M. CHAKROUN
Second Arab Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases May 24-26, 2012. Tunisian recommendations on ART : process and results M. BEN MAMOU UNAIDS Email: BenmamouM@unaids.org M. CHAKROUN
Valencia, 05/04/ #EBMT16
 Transplantation of Ex vivo Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood (NiCord ) Results in Decreased Infection Burden and Hospital Length of Stay in the First 100 Days Sarah Anand, Samantha Thomas, Terry Hyslop, Kelly
Transplantation of Ex vivo Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood (NiCord ) Results in Decreased Infection Burden and Hospital Length of Stay in the First 100 Days Sarah Anand, Samantha Thomas, Terry Hyslop, Kelly
Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV: Our Experience in South India
 pg 62-66 Original Article Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV: Our Experience in South India Karthekeyani Vijaya 1, Alexander Glory 2, Solomon Eileen 3, Rao Sarita 4, Rao P.S.S.Sunder 5 1
pg 62-66 Original Article Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV: Our Experience in South India Karthekeyani Vijaya 1, Alexander Glory 2, Solomon Eileen 3, Rao Sarita 4, Rao P.S.S.Sunder 5 1
One-Unit versus Two-Unit Cord-Blood Transplantation for Hematologic Cancers
 The new england journal of medicine Original Article One-Unit versus Two-Unit Cord-Blood Transplantation for Hematologic Cancers John E. Wagner, Jr., M.D., Mary Eapen, M.B., B.S., Shelly Carter, D.Sc.,
The new england journal of medicine Original Article One-Unit versus Two-Unit Cord-Blood Transplantation for Hematologic Cancers John E. Wagner, Jr., M.D., Mary Eapen, M.B., B.S., Shelly Carter, D.Sc.,
WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME. An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency
 WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency WHAT IS WISKOTT ALDRICH SYNDROME? Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (WAS) is a serious medical condition that causes problems both with the immune system
WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency WHAT IS WISKOTT ALDRICH SYNDROME? Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (WAS) is a serious medical condition that causes problems both with the immune system
Gestational Diabetes. Gestational Diabetes:
 Gestational Diabetes Detection and Management Steven Gabbe, MD The Ohio State University Medical Center Gestational Diabetes: Detection and Management Learning Objectives: At the conclusion of this presentation,
Gestational Diabetes Detection and Management Steven Gabbe, MD The Ohio State University Medical Center Gestational Diabetes: Detection and Management Learning Objectives: At the conclusion of this presentation,
journal of medicine The new england Outcomes after Transplantation of Cord Blood or Bone Marrow from Unrelated Donors in Adults with Leukemia abstract
 The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 november 25, 2004 vol. 351 no. 22 Outcomes after Transplantation of Cord Blood or Bone Marrow from Unrelated Donors in Adults with Leukemia Mary
The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 november 25, 2004 vol. 351 no. 22 Outcomes after Transplantation of Cord Blood or Bone Marrow from Unrelated Donors in Adults with Leukemia Mary
Unrelated Donor StemCell Transplantation: The Role of the National Marrow Donor Program
 Unrelated Donor StemCell Transplantation: The Role of the National Marrow Donor Program August 01, 2003 Palliative and Supportive Care [1], Oncology Journal [2] By Chatchada Karanes, MD [3], Dennis Confer,
Unrelated Donor StemCell Transplantation: The Role of the National Marrow Donor Program August 01, 2003 Palliative and Supportive Care [1], Oncology Journal [2] By Chatchada Karanes, MD [3], Dennis Confer,
Hepatitis and pregnancy
 Hepatitis and pregnancy Pierre-Jean Malè MD Training Course in Reproductive Health Research WHO Geneva 2008 26.02.2008 Liver disease and pregnancy: three possible etiologic relationship the patient has
Hepatitis and pregnancy Pierre-Jean Malè MD Training Course in Reproductive Health Research WHO Geneva 2008 26.02.2008 Liver disease and pregnancy: three possible etiologic relationship the patient has
William R Prather. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. (2008) 8(8):
 Technology Evaluation 1. Introduction 2. Umbilical cord blood as a source of hematopoietic stem cells 3. Mesenchymal stromal cells 4. Pluristem Therapeutics, Inc. 5. Expert opinion Placental-derived and
Technology Evaluation 1. Introduction 2. Umbilical cord blood as a source of hematopoietic stem cells 3. Mesenchymal stromal cells 4. Pluristem Therapeutics, Inc. 5. Expert opinion Placental-derived and
General Terms: Appendix B. National Marrow Donor Program and The Medical College of Wisconsin
 Glossary of Terms This appendix is divided into two sections. The first section, General Terms, defines terms used throughout the CIBMTR data collection forms. The second section, FormsNet TM 2 Terms,
Glossary of Terms This appendix is divided into two sections. The first section, General Terms, defines terms used throughout the CIBMTR data collection forms. The second section, FormsNet TM 2 Terms,
Stem Cells Expressing Homing Receptors Could be Expanded From Cryopreserved and Unselected Cord Blood
 J Korean Med Sci 2004; 19: 635-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Stem Cells Expressing Homing Receptors Could be Expanded From Cryopreserved and Unselected Cord Blood We
J Korean Med Sci 2004; 19: 635-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Stem Cells Expressing Homing Receptors Could be Expanded From Cryopreserved and Unselected Cord Blood We
Transfer protocol of human HSC into NOG mice
 Transfer protocol of human HSC into NOG mice Mice: Adult NOG mice are aged 8-12 weeks. Newborn mice are 1 2 days old. 8-12 week old NOG mice irradiated with 2.5 Gy Intravenous transfer of 1-0.5 x 10 5
Transfer protocol of human HSC into NOG mice Mice: Adult NOG mice are aged 8-12 weeks. Newborn mice are 1 2 days old. 8-12 week old NOG mice irradiated with 2.5 Gy Intravenous transfer of 1-0.5 x 10 5
Neutrophil Recovery: The. Posttransplant Recovery. Bus11_1.ppt
 Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
Objectives. Cord Blood is RelaOvely Recent Technology BMT Pharmacists Conference: Debate - Haploidentical vs. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant
 214 BMT Pharmacists Conference: Debate - Haploidentical vs. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant Claudio G Brunstein Associate Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN Objectives Defend
214 BMT Pharmacists Conference: Debate - Haploidentical vs. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant Claudio G Brunstein Associate Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN Objectives Defend
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B
 Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25)
 3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
Course of Maternal Human Immunodeficiency Virus
 Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2:251-254 (1995) (C) 1995 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Effect of Successive Single-Gestation Pregnancies on the Course of Maternal Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease
Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2:251-254 (1995) (C) 1995 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Effect of Successive Single-Gestation Pregnancies on the Course of Maternal Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease
CHAPTER 2 PROTOCOL DESIGN
 CHAPTER 2 PROTOCOL DESIGN CHAPTER 2 PROTOCOL DESIGN 2.1 ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA Participants fulfilling the following criteria will be eligible for enrollment in the protocol: 1. Participant is diagnosed
CHAPTER 2 PROTOCOL DESIGN CHAPTER 2 PROTOCOL DESIGN 2.1 ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA Participants fulfilling the following criteria will be eligible for enrollment in the protocol: 1. Participant is diagnosed
Summary of Key Points. WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017
 Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK. HCT in Children
 Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
