CHALLENGING UTI S: PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT
|
|
|
- Muriel Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHALLENGING UTI S: PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT Wendy L. Wright, MS, RN, APRN, FNP, FAANP Adult/Family Nurse Practitioner Owner Wright & Associates Family Healthcare, Amherst Concord, NH Partner Partners in Healthcare Education, LLC 1 Objectives Upon completion of this lecture, the participant will be able to: Discuss the various pathogens causing complicated UTIs Identify the treatment (pharmacologic and otherwise) algorithms for individuals with complicated UTIs Discuss the impact of antimicrobial resistance on the treatment of complicated UTIs 2 Urinary Tract Infections Most frequently occurring bacterial infection In the US, 8 million visits yearly for UTI s Up to 100,000 hospitalizations Approximately 15% of all antibiotic prescriptions are for UTI s 40% - 50% lifetime prevalence in women Griebling TL. Urinary tract infection in women. In: Litwin MS, Saigal CS, eds. Urologic Diseases in America. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Washington, D.C.: GPO; NIH publication :
2 Urinary Tract Infections: Statistics 25-35% of young, sexually active women will have at least one UTI per year Although environmental factors play a role (I.e. failure to void after intercourse), genetics also plays a role First-degree relatives of women with recurrent infection have an increased frequency of UTI s even when there is no anatomical abnormality Believed to be an alteration in the bacteria aggregation sites in the bladder and urethra Griebling TL. Urinary tract infection in women. In: Litwin MS, Saigal CS, eds. Urologic Diseases in America. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Washington, Wright, D.C.: 2014GPO; NIH publication : Genetic Predisposition Robust fucosyltransferase activity discourages bacterial adherence within the bladder Also, presence of few bacterial adhesion receptor sites is also thought to be protective Women who have a lot of receptor sites or minimal fucosyltransferase activity tend to have more UTI s particularly from E. Coli and have less lactobacilli in the periurethral region again, making a UTI more likely 5 Pathogenesis Urinary tract is normally sterile Intercourse is often responsible; with increased risk in those who void infrequently Bacterial colonization of the perirectal/vaginal area Bacteria are able to ascend through urethra into bladder Asymptomatic bacterial colonization of bladder Increase in infection rates during pregnancy 6 2
3 Urinary Tract Infections Lower: Cystitis Asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB) Upper Pyelonephritis (with or without bacteremia) 7 Two Types Two Additional Classifications Uncomplicated Bladder infection or cystitis Complicated Occurs in individuals with structural abnormalities May be asymptomatic or symptomatic May involve the kidneys 8 Consensus Regarding Definition Unfortunately, no true consensus exists regarding a definition but generally thought to be a UTI which occurs in someone at higher risk for an adverse outcomes 9 3
4 Complicated UTI Definition Infection of the lower or upper urinary tract Presence of a metabolic abnormality, anatomic abnormality, functional abnormality or the presence of a urinary catheter At much greater risk for sepsis or bacteremia overview accessed Complicated UTIs: Predisposing Factors Multiple pregnancies Benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) Prostate cancer Neurogenic bladder Immunocompromised states Underlying diseases Indwelling catheters overview accessed Risk Factors for Complicated UTI Structural abnormalities BPH Renal calculi and obstruction Catheter Stent Neurogenic Bladder Metabolic or Hormonal Influences Diabetes Pregnancy overview accessed
5 Risk Factors Immunodeficiency Transplant recipients Neutropenia HIV disease Recent antibiotic usage Recent surgical procedure Hospitalized patients overview accessed Risk Factors Age and Gender Male gender Pediatric Advanced age Pregnancy 14 Not all are Risk Factors are Created Equal Structural abnormalities Often most difficult to treat Neurogenic bladder, cystocele, rectocele Frequently relapse May require surgical intervention Metabolic and Immune-Modulated Easier to treat Less likely to recur 15 5
6 Symptoms of Complicated UTI Highly variable May vary from fever only to a myriad of symptoms Dysuria Suprapubic pain Urinary frequency and urgency Foul smelling urine Flank pain Fever and chills Rigors Orthostasis 16 Fever Sepsis Falls Additional Signs and Symptoms: Younger and Older Patient Mental status change Increased or new urinary incontinence Hematuria Anorexia Vomiting 17 Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis: Pathogens Gorbach et al, 1999 Guidelines for Infections in Primary Care 18 6
7 Complicated UTI: Pathogens Complicated UTI S epidermidis 15% E coli 32% Pseudomonas 20% Enterococci 22% E coli Proteus Klebsiella Enterococci Pseudomonas Mixed Other S epidermidis overview accessed Pathogens: A Discussion E. Coli: Most common cause of both uncomplicated and complicated UTI s Enterococci: Most common gram positive cause of UTI Often associated with recent antibiotic therapy Consider recent urologic procedure Often cause in the patient with an obstructive pathology accessed Pathogens: A Discussion Staphylococcus saphrophyticus Gram positive organism Second most common cause in sexually active woman Pseudomonas Often seen in the individual with an obstructive pathology accessed
8 cuti Pathogens Proteus and Klebsiella Predispose the patient to stone formation and are more often than not seen in patients with calculi Tend to be polymicrobial in the setting of an indwelling catheter or stent placement Kasper, D.L. (2005). Harrison s Manual of Medicine (16 th ed.). New York, NY.: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 22 Step Approach to Bacteriuria Patient symptomatic NO YES Complicating Factors? NO Recurrent Symptoms? NO YES YES NO Complicated UTI Asymptomatic bacteriuria Recurrent UTI Upper Tract Symptoms? YES Pyelonephritis Uncomplicated cystitis Adapted Wright, from 2014 Orenstein R et. al. Am Fam Phys. 1999:59: cuti: Diagnosis History Symptomatic Asymptomatic Physical Examination Assess for CVA tenderness Consider STI Consider Urologic abnormality 24 8
9 cuti: Diagnosis Urinalysis Macro or microscopic hematuria Alkaline ph Present with urea splitting bacteria (Proteus) > 10 wbc/hpf Positive result on leukocyte dipstick correlates well with > 10 wbc/hpf + Nitrite dipstick for bacteriuria High rate of false negatives WBC Casts suggests upper UTI 25 Important Reminders Odor: Rancid or ammonia odor suggests urea-splitting organism (Proteus) Leukocyte esterase May not be present in a neutropenic patient Nitrites Should be conducted on 1 st morning urine Or no void x 1 hour (takes 1 hour for nitrate to nitrite conversion to occur) May be negative in early infection or gram positive organism 26 ph 5 6: average : acid ph 6.5-8: alkaline ph Important Reminders If alkaline ph: consider urea splitting organism such as Proteus Proteus allows urea to be split into CO2 and ammonia which causes a rise in urine s ph accessed
10 cuti: Diagnosis Urine culture and sensitivity required Pregnancy test May need additional imaging 28 Additional Diagnostic Options Ultrasound of kidney Polycystic kidneys Atrophic kidney CT scan or IVP if kidney stones suspected Ultrasound of bladder Assess for post-void residual VCUG Assess for vesicoureteral reflux accessed Voiding Cystourethrogram accessed
11 Treatment of Complicated UTIs Decision for treatment should be based upon local resistance patterns, patient population, duration of therapy, cost and side effects Resistance patterns vary depending upon geographic locations Highest resistance patterns: West Coast 31 Gram Negative Surveillance: TRUST II ( ): % susceptible Bacteria LVX CIP AMP CRO CAZ IPM PTZ GEN SXT E Coli Proteus Klebsiella Pseudom S marcesc Citrobacter E. Cloacae LVX = levofloxacin; CIP=ciprofloxacin; AMP = ampicillin; CRO=ceftriaxone; CAZ=ceftazidime; IMP=imipenem; PTZ=piperacillin-taxo; GEN=gentamicin SXT=TMP/SMX 32 Susceptibility of Key Uropathogens Uropathogen Antimicrobial Susceptibility In vitro activity does not necessarily imply a correlation with clinical effectiveness TSN Database-USA. MRL Pharmaceutical Services
12 Complicated UTI: Antimicrobial Choices Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) Fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin) Aminoglycosides (gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin) Third-generation cephalosporins (ceftriaxone) 34 Mild Moderate cuti Guidelines pertain if patient is not residing in long-term care facility or recently received fluoroquinolones Levofloxacin 250 mg mg orally once daily Ciprofloxacin 250 mg mg two times daily or 1000 mg XR once daily 35 Dosage Adjustment Must make sure to account for CrCl in older population May need to reduce dosage based upon level of kidney disease 36 12
13 Culture and Sensitivity Once C&S has returned, may narrow spectrum of antibiotic Consider blood cultures Consider CBC Consider hospitalization, based upon presentation 37 Guidelines for Treatment Severely ill, recent FQ or long-term care facility resident Imipenem Piperacillin-tazobactam Tobramycin or Gentamycin 38 Nosocomial UTI s Up to 40 45% of nosocomial infections are UTI s Usually the result of instrumentation or indwelling catheter 3 10% risk of infection for every day the catheter remains in place Kasper, D.L. (2005). Harrison s Manual of Medicine (16 th ed.). New York, NY.: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc
14 Symptoms: Nosocomial Infections Most frequently will see upper urinary tract symptoms Flank pain, fever, chills, rigors, leukocytosis Lower tract symptoms are often not present Dysuria Kasper, D.L. (2005). Harrison s Manual of Medicine (16 th ed.). New York, NY.: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 40 Treatment If possible, remove catheter Consider condom catheter in men Antimicrobial therapies (dosages for elderly lower) AMP+gentamycin PIP-TZ IMP Ciprofloxacin or Levofloxacin IV Length of treatment days Switch to oral antimicrobial when clinically stable 41 Recurrent UTIs Definition 3 or more episodes per year or 2 or more in 6 months Young woman Treatment Eradicate infection TMP SMX single strength 1 daily x 3 6 months Additional option TMP-SMX DS two tabs at onset of symptoms or TMP- SMX DS 1 post-coital Nitrofurantoin 50 mg at bedtime or post-coital Cephalexin 250 mg at bedtime or post-coital 42 14
15 Pyelonephritis Infection of the upper urinary tract, involving renal parenchyma and renal pelvis Potentially organ and life-threatening infection which results in kidney scarring and may lead to significant renal damage Kidney failure Abscess formation (nephric and perinephric) Sepsis Multiorgan failure 43 Pyelonephritis Annual rates: cases per 10,000 females 3-4 cases per 10,000 males 250,000 cases per year 200,000 require hospitalization 44 Pathogens Most common pathogen continues to be E. Coli Cause of > 90% of pyelonephritis cases Suspect and target E. Coli in the individual with no stones/calculi and mild illness 45 15
16 Other Pathogens Klebsiella pneumoniae Proteus mirabilis Enterococci Staphylococcus aureus Psuedomonas aeruginosa Enterobacter species 46 Symptoms of Pyelonephritis Not always straightforward High variability May be associated with fever, flank pain Dysuria, urinary urgency and frequency Nausea, vomiting, bacteremia Symptoms often begin and advance rapidly 47 Diagnosis made: Pyelonephritis History and physical examination Urine microscopy Culture and sensitivity Blood cultures are now recommended before antibiotic initiation 48 16
17 Pyelonephritis Treatment Options For patient s deemed suitable for outpatient treatment: Obtain urinalysis Obtain blood cultures Antimicrobial therapies Fluoroquinolone (preferred agent) Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (alternative) 49 Mild / Moderate Pyelonephritis Fluoroquinolone x 7-14 days Ciprofloxacin 500 mg 1 po two times daily or ciprofloxacin ER 1000 mg 1 po daily Ofloxacin 400 mg 1 po two times daily Levofloxacin 250 mg once daily Other secondary options TMP/ SMX DS 1 po bid x days AM-CL: 875/125 mg po every 12 hours Consider calculi if the individual relapses after treatment 50 Importance of Rapid Assessment and Treatment During an acute pyelonephritis, there is a significant and rapid reduction in the perfusion of the kidney Subsequent renal tubular dysfunction and scarring is possible if not treated aggressively and rapidly Always suspect pyelonephritis in any patient with UTI symptoms 51 17
18 Caution Children should undergo comprehensive workup after first episode of pyelonephritis as there is frequently an anatomic abnormality Usually, vesicoureteral reflux Renal scarring can be detected in 6 15% of children after a febrile UTI 52 Pathogens E. Coli (>90%) Enterococci Klebsiella Proteus Severe Pyelonephritis IV antibiotic is recommended (total treatment: 14 days) Hospitalization with blood cultures and septic work-up is essential 53 Antimicrobial Treatment: Severe Pyelonephritis Third generation cephalosporins Cefotaxime 1 gram IV every 12 hours; 2 grams IV for lifethreatening cases Ceftriaxone 1 2 grams IV every 24 hours Use 2 grams in individual < 65 years of age Second generation fluoroquinolones Ciprofloxacin 400 mg IV every 12 hours Levofloxacin 250 mg every 24 hours Ampicillin + gentamicin 54 18
19 Severe Pyelonephritis Treatment Step down to oral therapy hours after patient becomes afebrile If no improvement in 72 hours, obtain CT of kidneys Imaging is indicated earlier in the patient with suggestions of obstruction or lifethreatening illness (i.e. abscess) 55 Acute Pyelonephritis and Diabetes Perinephric abscess formation can occur Papillary necrosis is a more common consequence of AP in patients with diabetes Infection of the renal pyramids Acute renal failure with oliguria or anuria can occur Unfortunately, patients with diabetes are more prone to asymptomatic bacteriuria and pyelonephritis Kasper, D.L. (2005). Harrison s Manual of Medicine (16 th ed.). New York, NY.: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 56 Male UTIs UTI s in men < 50 years of age are rare Consideration for the presence of STI s or prostatic abnormality Obtain pretreatment urinalysis, culture and sensitivity. May need GC and chlamydia cultures depending upon risk factors. In general, treatment should be continued for a minimum of days 57 19
20 Epididymitis Symptoms Dysuria Fever Painful swelling of epididymis and scrotum Often unilateral pain and discomfort Most common pathogens Men < 35 years N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis Men > 35 years or MSM (insertive partner) E. Coli 58 Differential Diagnosis Testicular torsion must be considered Time is very important in the individual with torsion Loss of cremasteric reflex No fever Doppler flow study/us of testicle Stat urology consult 59 Treatment Options Men < 35 years of age Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM as a single dose plus Doxycycline 100 mg BID X 10 days Scrotal elevation Bedrest Analgesics 60 20
21 Treatment Options Men > 35 years of age ciprofloxacin 500 mg QD days or levofloxacin 750 mg QD X days or IV ampicillin with sulbactam or IV 3 rd generation cephalosporin 61 Acute Prostatitis Symptoms Fever, chills, dysuria Tender, boggy prostate Malaise, myalgias and flu-like symptoms Most common in men > 50 years of age or those with indwelling catheter Kasper, D.L. (2005). Harrison s Manual of Medicine (16 th ed.). New York, NY.: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 62 Pathogens: Acute Prostatitis Men < 35 years of age N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis Men > 35 years of age E. Coli 63 21
22 Treatment: Acute Prostatitis Men < 35 years of age Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM as a single dose plus Doxycycline 100 mg BID X 10 days Avoid fluoroquinolones due to increased antimicrobial resistance 64 Treatment Options Men > 35 years of age Ciprofloxacin 500 mg QD days or Levofloxacin 750 mg QD X days or TMP-SMX 1 DS tablet po bid x days 65 Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis Uncommon condition More common in middle aged-older men Most common symptoms: Relapsing UTIs but without symptoms in between episodes Urinary symptoms are often vague Often has history of an acute prostatitis Prostate often feels normal Lacks acuity of acute prostatitis Kasper, D.L. (2005). Harrison s Manual of Medicine (16 th ed.). New York, NY.: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc
23 Chronic Prostatitis Pathogens E. Coli (80%) Enterococci (15%) P. aeruginosa Treatment options Ciprofloxacin 500 mg bid x 4 weeks Levofloxacin 750 mg daily x 4 weeks TMP SMX DS 1 po bid x 1 3 months If no improvement, consider prostatic calculi Relapsing symptoms are common 67 Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Does not need to be treated routinely Exceptions to this rule may be: Pregnant women Children Patient s who are s/p renal transplant Neutropenic patients 68 Pregnant Women Screen for UTI and asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women Treatment is usually for 7 days Amoxicillin, nitrofurantoin, TMP-SMX, cephalosporin (2 nd or 3 rd generation) Once positive, recommended to screen monthly through pregnancy 69 23
24 Increased water Frequent voiding Prevention Consider topical estrogen Cranberry tablets Prevent constipation Pre and post-coital voiding Surgical correction of predisposing factors Urodynamic physical therapy accessed Thank You! I Would Be Happy to Entertain any Comments or Questions 71 Wendy L. Wright, APRN WendyARNP@aol.com
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys.
 UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
Urinary tract infection. Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine
 Urinary tract infection Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine Objectives To differentiate between types of urinary tract infections To recognize the epidemiology of UTI in
Urinary tract infection Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine Objectives To differentiate between types of urinary tract infections To recognize the epidemiology of UTI in
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms that may indicate presence of UTI (both complicated and uncomplicated) List common causative organisms and risk factors for UTIs
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms that may indicate presence of UTI (both complicated and uncomplicated) List common causative organisms and risk factors for UTIs
UTI IN ELDERLY. Zeinab Naderpour
 UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Michelle Eslami, M.D., FACP Professor of Medicine Division of Geriatrics David Geffen SOM at UCLA Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) One of most common infections in outpatient and
Urinary Tract Infections Michelle Eslami, M.D., FACP Professor of Medicine Division of Geriatrics David Geffen SOM at UCLA Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) One of most common infections in outpatient and
Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK
 Urinary Tract Infections Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK 07 08 2009. Getting Clear on the Terminology UTI Cystitis Urosepsis Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Asymptomatic UTI Pyuria Symptomatic UTI Pylonephritis
Urinary Tract Infections Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK 07 08 2009. Getting Clear on the Terminology UTI Cystitis Urosepsis Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Asymptomatic UTI Pyuria Symptomatic UTI Pylonephritis
EMPIRICAL TREATMENT OF SELECT INFECTIONS ADULT GUIDELINES. Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection
 URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN LONG TERM CARE. Tuesday, 8 November, 11
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN LONG TERM CARE OBJECTIVES UNDERSTAND THE SCALE OF DISEASE IN LTC SETTINGS DEVELOP AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE DIFFERENT PRESENTATIONS OF UTIs IN THIS SETTING AND WORKUP BECOME AWARE
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN LONG TERM CARE OBJECTIVES UNDERSTAND THE SCALE OF DISEASE IN LTC SETTINGS DEVELOP AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE DIFFERENT PRESENTATIONS OF UTIs IN THIS SETTING AND WORKUP BECOME AWARE
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring
 Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
11/15/2010. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria UTI. Symptomatic UTI. Asymptomatic UTI. Cystitis. Pylonephritis. Pyuria. Urosepsis
 Urinary Tract Infections Renal vein Inferior vena cava Urinary bladder Urethra Renal artery Kidney Aorta Ureter Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. 06 08 2010. (a) Sherwood Fig. 12-6a, p.530 An introduction
Urinary Tract Infections Renal vein Inferior vena cava Urinary bladder Urethra Renal artery Kidney Aorta Ureter Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. 06 08 2010. (a) Sherwood Fig. 12-6a, p.530 An introduction
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
Anatomy kidney ureters bladder urethra upper lower
 Urinary tract Anatomy The urinary tract consists of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urinary tract infections can be either: upper or lower based primarily on the anatomic location of the infection.
Urinary tract Anatomy The urinary tract consists of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urinary tract infections can be either: upper or lower based primarily on the anatomic location of the infection.
Diagnosis and Management of UTI s in Care Home Settings. To Dip or Not to Dip?
 Diagnosis and Management of UTI s in Care Home Settings To Dip or Not to Dip? 1 Key Summary Points: Treat the patient NOT the urine In people 65 years, asymptomatic bacteriuria is common. Treating does
Diagnosis and Management of UTI s in Care Home Settings To Dip or Not to Dip? 1 Key Summary Points: Treat the patient NOT the urine In people 65 years, asymptomatic bacteriuria is common. Treating does
It is an infection affecting any of the following parts like kidney,ureter,bladder or urethra
 UTI Dr jayaprakash.k.p,asst prof,ich,govt.medical college,kottayam What is UTI? It is an infection affecting any of the following parts like kidney,ureter,bladder or urethra What is prevalence of UTI?
UTI Dr jayaprakash.k.p,asst prof,ich,govt.medical college,kottayam What is UTI? It is an infection affecting any of the following parts like kidney,ureter,bladder or urethra What is prevalence of UTI?
Urinary Tract Infections KIDNEY INFECTIONS. Dr. AMMAR FADIL
 Urinary Tract Infections KIDNEY INFECTIONS Dr. AMMAR FADIL General principles Urinary tract infections (UTIs) is inflammatory response of the urothelium to bacterial invasion. are common affect men and
Urinary Tract Infections KIDNEY INFECTIONS Dr. AMMAR FADIL General principles Urinary tract infections (UTIs) is inflammatory response of the urothelium to bacterial invasion. are common affect men and
Treatment Regimens for Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections. Characteristic Pathogen. E. coli, S.saprophyticus P.mirabilis, K.
 HEALTHSPAN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12, 4-14 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next Review:
HEALTHSPAN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12, 4-14 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next Review:
MICHIGAN MEDICINE GUIDELINES FOR TREATMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN ADULTS
 When to Order a Urine Culture: Asymptomatic bacteriuria is often treated unnecessarily, and accounts for a substantial burden of unnecessary antimicrobial use. National guidelines recommend against testing
When to Order a Urine Culture: Asymptomatic bacteriuria is often treated unnecessarily, and accounts for a substantial burden of unnecessary antimicrobial use. National guidelines recommend against testing
TMP/SMZ DS Ciprofloxacin Norfloxacin Ofloxacin Cefadroxil * 30 Amoxicilin 86* 19 25
 Evidence-Based Evaluation and Treatment of UTI UTI Prevalence Leslee L. Subak, MD Associate Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology & Biostatistics University of California, San Francisco 50%
Evidence-Based Evaluation and Treatment of UTI UTI Prevalence Leslee L. Subak, MD Associate Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology & Biostatistics University of California, San Francisco 50%
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela
 Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Antibiotic Guidelines for URINARY TRACT/ UROLOGY infections
 Antibiotic Guidelines f URINARY TRACT/ UROLOGY infections CLINICAL CONDITION USEFUL INFORMATION RECOMMENDATIONS ALTERNATIVE (suitable in serious penicillin allergy) Asymptomatic Bacteriuria (in the absence
Antibiotic Guidelines f URINARY TRACT/ UROLOGY infections CLINICAL CONDITION USEFUL INFORMATION RECOMMENDATIONS ALTERNATIVE (suitable in serious penicillin allergy) Asymptomatic Bacteriuria (in the absence
Pediatric urinary tract infection. Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013
 Pediatric urinary tract infection Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013 objectives EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSATIVE PATHOGENS PATHOGENESIS CATEGORIES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN pediatrics
Pediatric urinary tract infection Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013 objectives EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSATIVE PATHOGENS PATHOGENESIS CATEGORIES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN pediatrics
SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Definition inflammatory
URINARY TRACT INFECTION SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Definition inflammatory
Urinary Tract Infections in Hospitalized Patients
 Urinary Tract Infections in Hospitalized Patients Puerto Rico Chapter Annual Meeting Daniel C. DeSimone, MD March 9, 2019 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures for speaker: Date of presentation: 3/9/2019 No relevant
Urinary Tract Infections in Hospitalized Patients Puerto Rico Chapter Annual Meeting Daniel C. DeSimone, MD March 9, 2019 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures for speaker: Date of presentation: 3/9/2019 No relevant
Urinary Tract Infections: From Simple to Complex. Adriane N Irwin, MS, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Assistant Professor Ambulatory Care October 25, 2014
 Urinary Tract Infections: From Simple to Complex Adriane N Irwin, MS, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Assistant Professor Ambulatory Care October 25, 2014 Learning Objectives Develop empiric antimicrobial treatment
Urinary Tract Infections: From Simple to Complex Adriane N Irwin, MS, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Assistant Professor Ambulatory Care October 25, 2014 Learning Objectives Develop empiric antimicrobial treatment
Urinary Tract Infections. Keri A. Mattes, Pharm.D., BCPS September 15, 2003
 Urinary Tract Infections Keri A. Mattes, Pharm.D., BCPS September 15, 2003 Urinary Tract Infections 7 million episodes of acute cystitis and 250,000 episodes of pyelonephritis annually in the U.S. Epidemiology
Urinary Tract Infections Keri A. Mattes, Pharm.D., BCPS September 15, 2003 Urinary Tract Infections 7 million episodes of acute cystitis and 250,000 episodes of pyelonephritis annually in the U.S. Epidemiology
RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS: WHAT AN INTERNIST
 RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS: WHAT AN INTERNIST MUST KNOW PROF. MD. ENAMUL KARIM Professor of Medicine Green Life Medical College INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the commonest
RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS: WHAT AN INTERNIST MUST KNOW PROF. MD. ENAMUL KARIM Professor of Medicine Green Life Medical College INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the commonest
Pyelonephritis. I m not telling you it s going to be easy. I m telling you it s going to be worth it.
 Please check the editing file to see if there are any changes Pyelonephritis Important! Doctor s Notes Only found in females slides Only found in males slides Extra Notes I m not telling you it s going
Please check the editing file to see if there are any changes Pyelonephritis Important! Doctor s Notes Only found in females slides Only found in males slides Extra Notes I m not telling you it s going
OCTOBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS. Presence of bacteria in the urine with no symptoms or clinical signs.
 OCTOBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended for primary care health professionnals. It is provided for information purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
OCTOBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended for primary care health professionnals. It is provided for information purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE)
 KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next
No Need to Agonize! Tips for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Complicated UTIs
 ASCENSION TEXAS No Need to Agonize! Tips for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Complicated UTIs Austin Area Society of Health-System Pharmacists April 26, 2018 Amy Carr, PharmD PGY-2 Infectious Diseases Pharmacy
ASCENSION TEXAS No Need to Agonize! Tips for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Complicated UTIs Austin Area Society of Health-System Pharmacists April 26, 2018 Amy Carr, PharmD PGY-2 Infectious Diseases Pharmacy
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Robinson, J, et al. and the Canadian Pediatric Society. Urinary tract infection in infants and children: Diagnosis and management. Pediatr Child Health 2014;
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Robinson, J, et al. and the Canadian Pediatric Society. Urinary tract infection in infants and children: Diagnosis and management. Pediatr Child Health 2014;
Microbiology. Hani Masaadeh. Hadeel Al-Momani
 Microbiology UTI 1 Hani Masaadeh Hadeel Al-Momani 1 Page #1 Date :27/4/2016 Lecture#1 Micro Lecture#21 UGS Subject : UTI *Urinary tract is normally sterile due to the fact that bacteria moving upwards
Microbiology UTI 1 Hani Masaadeh Hadeel Al-Momani 1 Page #1 Date :27/4/2016 Lecture#1 Micro Lecture#21 UGS Subject : UTI *Urinary tract is normally sterile due to the fact that bacteria moving upwards
When should UTIs be treated in the Elderly? Shelby L. Wentworth, MS4 University of Florida College of Medicine 29 AUG 2018
 When should UTIs be treated in the Elderly? Shelby L. Wentworth, MS4 University of Florida College of Medicine 29 AUG 2018 UTIs in Patients >/ 65 yo - Most common infectious illness [1]. - Urinary tract
When should UTIs be treated in the Elderly? Shelby L. Wentworth, MS4 University of Florida College of Medicine 29 AUG 2018 UTIs in Patients >/ 65 yo - Most common infectious illness [1]. - Urinary tract
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
Urinary tract infections Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Urinary tract infections Dr. Hala Al Daghistani UTIs are considered to be one of the most common bacterial infections. Diagnosis depends on the symptoms, urinalysis, and urine culture. UTIs occur more
Urinary tract infections Dr. Hala Al Daghistani UTIs are considered to be one of the most common bacterial infections. Diagnosis depends on the symptoms, urinalysis, and urine culture. UTIs occur more
GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS M. Grabe (chairman), M.C. Bishop, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, B. Lobel, K.G. Naber, J. Palou, P. Tenke Introduction
GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS M. Grabe (chairman), M.C. Bishop, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, B. Lobel, K.G. Naber, J. Palou, P. Tenke Introduction
Bacterial Infections of the Urinary System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m64804 1 Bacterial Infections of the Urinary System * Douglas Risser This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Learning
OpenStax-CNX module: m64804 1 Bacterial Infections of the Urinary System * Douglas Risser This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Learning
Urology and Urinary Tract Infections in Adults
 Urology and Urinary Tract Infections in Adults Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version
Urology and Urinary Tract Infections in Adults Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version
Investigators Meeting
 Outcomes of Urinary Tract Infection Management by Pharmacists (R x OUTMAP) Investigators Meeting June 11, 2017 Overview 1. Introductions and Opening Remarks 2. Epidemiology and Definitions 3. UTI Assessment
Outcomes of Urinary Tract Infection Management by Pharmacists (R x OUTMAP) Investigators Meeting June 11, 2017 Overview 1. Introductions and Opening Remarks 2. Epidemiology and Definitions 3. UTI Assessment
Review of Urinary Tract Infection
 Review of Urinary Tract Infection Anthony P. Buonanno, Jr., MD Lehigh Area Medical Associates, Allentown, Pennsylvania Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine, Penn State University, Hershey,
Review of Urinary Tract Infection Anthony P. Buonanno, Jr., MD Lehigh Area Medical Associates, Allentown, Pennsylvania Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine, Penn State University, Hershey,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Dr Caroline CHARLIER-WOERTHER Université Paris Descartes Paris, France Definitions Clinical presentation by type Complications Spectrum of pathogens Pathophysiology Management
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Dr Caroline CHARLIER-WOERTHER Université Paris Descartes Paris, France Definitions Clinical presentation by type Complications Spectrum of pathogens Pathophysiology Management
UTI. Monica Tegeler, MD
 4 UTI Monica Tegeler, MD 2 Diagnosis Stone criteria >100,000 colonies of bacteria growing in urine with no more than 2 species of microorganisms Dysuria OR Fever AND 1 of following: Frequency Urgency Suprapubic
4 UTI Monica Tegeler, MD 2 Diagnosis Stone criteria >100,000 colonies of bacteria growing in urine with no more than 2 species of microorganisms Dysuria OR Fever AND 1 of following: Frequency Urgency Suprapubic
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I
 Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Bugs in Urology Infections of the lower urinary tract. Mr Chandran Tanabalan, MRCS MSc Urology SpR Homerton University Hospital
 Bugs in Urology Infections of the lower urinary tract Mr Chandran Tanabalan, MRCS MSc Urology SpR Homerton University Hospital Outline UTIs Recurrent cystitis/ UTIs Catheter Associated UTIs (CAUTIs) Epididymitis/
Bugs in Urology Infections of the lower urinary tract Mr Chandran Tanabalan, MRCS MSc Urology SpR Homerton University Hospital Outline UTIs Recurrent cystitis/ UTIs Catheter Associated UTIs (CAUTIs) Epididymitis/
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
Urinary Tract Infections: From Pyelonephritis to Asymptomatic Bacteriuria. Leslee L. Subak, MD
 Urinary Tract Infections: From Pyelonephritis to Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology & Urology University of California, San Francisco UTI Prevalence
Urinary Tract Infections: From Pyelonephritis to Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology & Urology University of California, San Francisco UTI Prevalence
UTI: A practical approach. Justin Seroy, DO Infectious Disease Attending BUMC-P
 UTI: A practical approach Justin Seroy, DO Infectious Disease Attending BUMC-P UTI Pathophysiology Uropathogens colonize urethra, vagina or perineal area -> Enter lower urinary tract ->bladder ->kidney
UTI: A practical approach Justin Seroy, DO Infectious Disease Attending BUMC-P UTI Pathophysiology Uropathogens colonize urethra, vagina or perineal area -> Enter lower urinary tract ->bladder ->kidney
Evidence Based Management of Urinary Tract Infections
 Evidence Based Management of Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common bacterial infection in humans. They account for more than 8.6 million physician visits (84% by women)
Evidence Based Management of Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common bacterial infection in humans. They account for more than 8.6 million physician visits (84% by women)
Managing Urinary Tract Infections in the Nursing Home: Myths, Mysteries and Realities
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Geriatrics and Gerontology Volume 1 Number 2 Managing Urinary Tract Infections in the Nursing Home: Myths, Mysteries and Realities H Kamel Citation H Kamel. Managing Urinary
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Geriatrics and Gerontology Volume 1 Number 2 Managing Urinary Tract Infections in the Nursing Home: Myths, Mysteries and Realities H Kamel Citation H Kamel. Managing Urinary
None. Appropriate collection minimizes contamination Sample should be delivered to the laboratory in a timely fashion to limit bacterial growth
 None Christopher J. Graber, MD MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine, UCLA Infectious Diseases Section VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System November 19, 2011 Clin Infect Dis 2005;40:643-54 Clin
None Christopher J. Graber, MD MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine, UCLA Infectious Diseases Section VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System November 19, 2011 Clin Infect Dis 2005;40:643-54 Clin
ASPIRES Urinary Tract Infection Algorithm
 ASPIRES Urinary Tract Infection Algorithm Dr. Jennifer Grant Dr. Tim Lau Donna Leung February 2013 VCH Antimicrobial Stewardship 1 Programme: Innovation, Research, Education & Safety KEY PRINCIPLES 1.
ASPIRES Urinary Tract Infection Algorithm Dr. Jennifer Grant Dr. Tim Lau Donna Leung February 2013 VCH Antimicrobial Stewardship 1 Programme: Innovation, Research, Education & Safety KEY PRINCIPLES 1.
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Dr Mere Kende MBBS, MMed (Path), MAACB, MACRRM, MACTM Lecturer, SMHS, Taurama campus, UPNG Urinary Tract Infections Definitions (Terms) Microbiology and epidemiology Pathogenesis
Urinary Tract Infections Dr Mere Kende MBBS, MMed (Path), MAACB, MACRRM, MACTM Lecturer, SMHS, Taurama campus, UPNG Urinary Tract Infections Definitions (Terms) Microbiology and epidemiology Pathogenesis
6/4/2018. Conflicts Disclosure. Objectives. Introduction. Classifications of UTI. Host Defenses. Management of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
 Conflicts Disclosure Presenter has no conflicts of interest to disclose Management of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections COLIN M. GOUDELOCKE, M.D. JUNE 14, 2018 Objectives Attendees will review the identification
Conflicts Disclosure Presenter has no conflicts of interest to disclose Management of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections COLIN M. GOUDELOCKE, M.D. JUNE 14, 2018 Objectives Attendees will review the identification
Urinary Tract Infections Fall 2003
 Urinary Tract Infections Fall 2003 Keri A. Mattes, Pharm.D., BCPS kmattes@stlcop.edu Therapeutics III Required Reading Mullenix TA, Prince RA. Unrinary Tract Infections and Prostatitis. In: DiPiro JT,
Urinary Tract Infections Fall 2003 Keri A. Mattes, Pharm.D., BCPS kmattes@stlcop.edu Therapeutics III Required Reading Mullenix TA, Prince RA. Unrinary Tract Infections and Prostatitis. In: DiPiro JT,
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acinetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant, 497 498 Adolescents, urinary tract infections in, 520 521 Aminoglycosides, for UTIs and
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acinetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant, 497 498 Adolescents, urinary tract infections in, 520 521 Aminoglycosides, for UTIs and
Nicolette Janzen, MD Texas Children's Hospital
 Which UTIs Need a VCUG? Applying AAP Guidelines Nicolette Janzen, MD Texas Children's Hospital Goals 1 2 3 4 5 Review the guidelines Present clinical scenarios Discuss VCUG and nuclear cystogram Discuss
Which UTIs Need a VCUG? Applying AAP Guidelines Nicolette Janzen, MD Texas Children's Hospital Goals 1 2 3 4 5 Review the guidelines Present clinical scenarios Discuss VCUG and nuclear cystogram Discuss
Which is urinary tract infection (UTI) How is urinary tract infection. Clinical features of UTI in the elderly. Preventive measures in the elderly
 O Which is urinary tract infection (UTI) How is urinary tract infection How is the diagnosis of UTI in the elderly Clinical features of UTI in the elderly Therapeutic considerations in the elderly Preventive
O Which is urinary tract infection (UTI) How is urinary tract infection How is the diagnosis of UTI in the elderly Clinical features of UTI in the elderly Therapeutic considerations in the elderly Preventive
Children s Services Medical Guideline
 See also: NICE Guidelines These local guidelines are in conjunction with NICE UTI Algorithms Renal scarring and subsequent nephropathy are important causes of later hypertension and renal failure. Early
See also: NICE Guidelines These local guidelines are in conjunction with NICE UTI Algorithms Renal scarring and subsequent nephropathy are important causes of later hypertension and renal failure. Early
An update on the management of urinary tract infection. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 3, p
 Title An update on the management of urinary tract infection Author(s) Chan, TM Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 3, p. 137-141 Issued Date 1997 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/45038 Rights
Title An update on the management of urinary tract infection Author(s) Chan, TM Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 3, p. 137-141 Issued Date 1997 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/45038 Rights
UTI Update: Have We Been Led Astray? Disclosure. Objectives
 UTI Update: Have We Been Led Astray? KAAP Sept 28, 2012 Robert Wittler, MD 1 Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a financial relationship or interest with any entity related
UTI Update: Have We Been Led Astray? KAAP Sept 28, 2012 Robert Wittler, MD 1 Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a financial relationship or interest with any entity related
Antibiotic Protocols for Paediatrics Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Antibiotic Protocols for Paediatrics Steve Biko Academic Hospital Respiratory tract infections in children Uncomplicated URTI A child with a cold should not receive an antibiotic Paracetamol (15 mg/kg/dose
Antibiotic Protocols for Paediatrics Steve Biko Academic Hospital Respiratory tract infections in children Uncomplicated URTI A child with a cold should not receive an antibiotic Paracetamol (15 mg/kg/dose
Urogenital Tract / 3 rd year Urinary Tract Infections. Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi MD, PhD Associate Prof. of Medical Microbiology
 Urogenital Tract / 3 rd year Urinary Tract Infections Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi MD, PhD Associate Prof. of Medical Microbiology Urinary Tract Infections ILOs 1. Define UTI 2. Classification 3. List the common
Urogenital Tract / 3 rd year Urinary Tract Infections Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi MD, PhD Associate Prof. of Medical Microbiology Urinary Tract Infections ILOs 1. Define UTI 2. Classification 3. List the common
UTIs in children ( with controversies ) By Dr. Lindokuhle Mahlase
 UTIs in children ( with controversies ) By Dr. Lindokuhle Mahlase Epidemiology By age 7 years, 8 % of girls and 2 % of boys will have had a UTI. Most infections occur in the first 2 years of life ; boys
UTIs in children ( with controversies ) By Dr. Lindokuhle Mahlase Epidemiology By age 7 years, 8 % of girls and 2 % of boys will have had a UTI. Most infections occur in the first 2 years of life ; boys
MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS KEYWORDS: Urinary tract infection (UTI); cystitis; pyelonephritis; uropathogens; antibiotics LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will
MODULE 2: ADULT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS KEYWORDS: Urinary tract infection (UTI); cystitis; pyelonephritis; uropathogens; antibiotics LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will
1/21/2016. Overview. Significance
 Asymptomatic Bacteriuria: Myths, Magic and Management Christopher Ohl MD Professor of Medicine, Section on Infectious Diseases Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston Salem, NC Slide credits to Katie Wallace,
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria: Myths, Magic and Management Christopher Ohl MD Professor of Medicine, Section on Infectious Diseases Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston Salem, NC Slide credits to Katie Wallace,
Guidelines for the management of urinary tract infections in children 0-17 years
 Guidelines for the management of urinary tract infections in children 0-17 years Guideline to be used where appropriate in conjunction with the Ashford and St Peter s sepsis guideline (Dr Ruth Mew 2016)
Guidelines for the management of urinary tract infections in children 0-17 years Guideline to be used where appropriate in conjunction with the Ashford and St Peter s sepsis guideline (Dr Ruth Mew 2016)
GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS
 16 GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS K.G. Naber (chairman), B. Bergman, M.C. Bishop, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, B. Lobel, F. Jimenez-Cruz, F.P. Selvaggi
16 GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS K.G. Naber (chairman), B. Bergman, M.C. Bishop, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, B. Lobel, F. Jimenez-Cruz, F.P. Selvaggi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERNS IN GRAM NEGATIVE URINARY ISOLATES TO CIPROFLOXACIN, CO-TRIMOXAZOLE AND NITROFURANTOIN
 SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERNS IN GRAM NEGATIVE URINARY ISOLATES TO CIPROFLOXACIN, CO-TRIMOXAZOLE AND NITROFURANTOIN Anoop Sinha 1, Benny P V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Anoop Sinha, Benny PV. Susceptibility
SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERNS IN GRAM NEGATIVE URINARY ISOLATES TO CIPROFLOXACIN, CO-TRIMOXAZOLE AND NITROFURANTOIN Anoop Sinha 1, Benny P V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Anoop Sinha, Benny PV. Susceptibility
PYELONEPHRITIS. Wendy Glaberson 11/8/13
 PYELONEPHRITIS Wendy Glaberson 11/8/13 A 19mo infant girl was seen in the ED 3 days ago and diagnosed with a UTI. She was afebrile at the time and discharged on broad spectrum antibiotics. The child returns
PYELONEPHRITIS Wendy Glaberson 11/8/13 A 19mo infant girl was seen in the ED 3 days ago and diagnosed with a UTI. She was afebrile at the time and discharged on broad spectrum antibiotics. The child returns
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia
 Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection
 Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection C. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asyntomatic Bacteriuria in Adults (2005) Pyuria accompanying asymptomatic
Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection C. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asyntomatic Bacteriuria in Adults (2005) Pyuria accompanying asymptomatic
Definition/Epidemiology Approach to premenopausal and postmenopausal women A couple tricky cases DISCLOSURES. No financial relationships to disclose.
 DISCLOSURES RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS No financial relationships to disclose. Anna C. Kirby, MD, MAS Acting Assistant Professor University of Washington Division of Urogynecology Department of
DISCLOSURES RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS No financial relationships to disclose. Anna C. Kirby, MD, MAS Acting Assistant Professor University of Washington Division of Urogynecology Department of
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Device-associated Events Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: The urinary tract is the most common site of healthcare-associated infection, accounting for more than 30% of
Device-associated Events Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: The urinary tract is the most common site of healthcare-associated infection, accounting for more than 30% of
Urinary Tract Infection
 67 Urinary Tract Infection Dr Kawa Ahmad PhD Pharmaceutics 1 Introduction The term urinary tract infection (UTI) usually refers to the presence of organisms in the urinary tract together with symptoms,
67 Urinary Tract Infection Dr Kawa Ahmad PhD Pharmaceutics 1 Introduction The term urinary tract infection (UTI) usually refers to the presence of organisms in the urinary tract together with symptoms,
Customary urine test is the dip stick and the mid-stream culture of voided urine. Up to 77% of cystitis cases are cultured
 9 million visits/year! Customary urine test is the dip stick and the mid-stream culture of voided urine. Up to 77% of cystitis cases are cultured Interpretation of the culture result has been controversial-
9 million visits/year! Customary urine test is the dip stick and the mid-stream culture of voided urine. Up to 77% of cystitis cases are cultured Interpretation of the culture result has been controversial-
EAU GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 EAU GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2018) G. Bonkat (Co-chair), R. Pickard (Co-chair), R. Bartoletti, T. Cai, F. Bruyere, S.E. Geerlings, B. Köves, F. Wagenlehner Guidelines
EAU GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2018) G. Bonkat (Co-chair), R. Pickard (Co-chair), R. Bartoletti, T. Cai, F. Bruyere, S.E. Geerlings, B. Köves, F. Wagenlehner Guidelines
Urine bench. Urine test for: SARAH Sugar
 Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: The urinary tract is the most common site of healthcare-associated infection, accounting for more than 30% of infections reported by acute
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: The urinary tract is the most common site of healthcare-associated infection, accounting for more than 30% of infections reported by acute
Key Definitions. Downloaded from
 Key Definitions In order to make sure that every member of the team is clear about the definitions that will be used, we have provided a list of key terms in the next few pages along with commonly used
Key Definitions In order to make sure that every member of the team is clear about the definitions that will be used, we have provided a list of key terms in the next few pages along with commonly used
Urinary tract infection ประส ทธ อ พาพรรณ สาขาว ชาโรคต ดเช อ ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยศ รนคร นทรว โรฒ
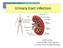 Urinary tract infection ประส ทธ อ พาพรรณ สาขาว ชาโรคต ดเช อ ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยศ รนคร นทรว โรฒ Introduction Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are extremely common. Most frequent in
Urinary tract infection ประส ทธ อ พาพรรณ สาขาว ชาโรคต ดเช อ ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยศ รนคร นทรว โรฒ Introduction Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are extremely common. Most frequent in
Educational Module for Nursing Assistants in Long-term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
 Educational Module for Nursing Assistants in Long-term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Minnesota Department of Health Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention,
Educational Module for Nursing Assistants in Long-term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Minnesota Department of Health Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention,
Update in diagnosis and management of UTIs
 Update in diagnosis and management of UTIs I have no disclosures Brian S. Schwartz, MD UCSF, Division of Infectious Diseases Lecture outline Challenges in cystitis Complicated UTI/pyelonephritis Asymptomatic
Update in diagnosis and management of UTIs I have no disclosures Brian S. Schwartz, MD UCSF, Division of Infectious Diseases Lecture outline Challenges in cystitis Complicated UTI/pyelonephritis Asymptomatic
DOWNLOAD OR READ : URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 urinary tract infections in children urinary tract infections in pdf urinary tract infections in children MID 11
DOWNLOAD OR READ : URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 urinary tract infections in children urinary tract infections in pdf urinary tract infections in children MID 11
Drugs for UTIs and STDs. Dr.Vishaal Bhat Associate Professor MMMC Manipal
 Drugs for UTIs and STDs Dr.Vishaal Bhat Associate Professor MMMC Manipal Classification of UTI s Clinical: Asymptomatic (98%) Symptomatic (1-2%) Anatomical: Lower tract dis: asymptomatic bacteriuria and
Drugs for UTIs and STDs Dr.Vishaal Bhat Associate Professor MMMC Manipal Classification of UTI s Clinical: Asymptomatic (98%) Symptomatic (1-2%) Anatomical: Lower tract dis: asymptomatic bacteriuria and
Still Feelin the Burn? You Might Have a Urinary Tract Infection
 Still Feelin the Burn? You Might Have a Urinary Tract Infection Jason Alegro, Pharm.D. BCPS Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences, Roosevelt University Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacy Specialist,
Still Feelin the Burn? You Might Have a Urinary Tract Infection Jason Alegro, Pharm.D. BCPS Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences, Roosevelt University Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacy Specialist,
GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS
 24 GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS K. Naber (chairman), B. Bergman, M. Bishop, T. Bjerklund- Johansen, H. Botto, B. Lobel, F. Jimenez-Cruz, F. Selvaggi Eur Urol
24 GUIDELINES ON THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY AND MALE GENITAL TRACT INFECTIONS K. Naber (chairman), B. Bergman, M. Bishop, T. Bjerklund- Johansen, H. Botto, B. Lobel, F. Jimenez-Cruz, F. Selvaggi Eur Urol
Clinical guideline Published: 22 August 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg54
 Urinary tract infection in under 16s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 22 August 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg54 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Urinary tract infection in under 16s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 22 August 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg54 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Still Feelin the Burn? You Might Have a Urinary Tract Infection
 Still Feelin the Burn? You Might Have a Urinary Tract Infection Jason Alegro, Pharm.D. BCPS Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences, Roosevelt University Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacy Specialist,
Still Feelin the Burn? You Might Have a Urinary Tract Infection Jason Alegro, Pharm.D. BCPS Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences, Roosevelt University Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacy Specialist,
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE PATTERN OF PATHOGENS IN PEDIATRIC URINARY TRACT INFECTION
 CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE PATTERN OF PATHOGENS IN PEDIATRIC URINARY TRACT INFECTION Yupaporn Amornchaicharoensuk Faculty of Medicine, Navamindradhiraj University, Bangkok, Thailand
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE PATTERN OF PATHOGENS IN PEDIATRIC URINARY TRACT INFECTION Yupaporn Amornchaicharoensuk Faculty of Medicine, Navamindradhiraj University, Bangkok, Thailand
P. Brandstrom has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve.
 P. Brandstrom has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Prophylaxis or not? Per Brandström Queen Silvia Children s Hospital Gothenburg
P. Brandstrom has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Prophylaxis or not? Per Brandström Queen Silvia Children s Hospital Gothenburg
INFECTION SURVEILLANCE
 INFECTION SURVEILLANCE IN LONG-TERM CARE 5 TH ANNUAL WYOMING INFECTION PREVENTION CONFERENCE, 2015 Russ Forney, PhD, MT(ASCP), Mountain-Pacific Quality Health THE PROBLEM Long-Term Care Acute Care Time
INFECTION SURVEILLANCE IN LONG-TERM CARE 5 TH ANNUAL WYOMING INFECTION PREVENTION CONFERENCE, 2015 Russ Forney, PhD, MT(ASCP), Mountain-Pacific Quality Health THE PROBLEM Long-Term Care Acute Care Time
Paediatrica Indonesiana. Urine dipstick test for diagnosing urinary tract infection
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Urine dipstick test for diagnosing urinary tract infection Syarifah Julinawati, Oke Rina, Rosmayanti, Rafita Ramayati, Rusdidjas Abstract
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Urine dipstick test for diagnosing urinary tract infection Syarifah Julinawati, Oke Rina, Rosmayanti, Rafita Ramayati, Rusdidjas Abstract
H(a)ematuria. FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute
 H(a)ematuria FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute From Philadelphia to Bristol, England Southmead Hospital, 1916 Southmead Hospital, 2013 Southmead Hospital, 2014 H(a)ematuria Blood
H(a)ematuria FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute From Philadelphia to Bristol, England Southmead Hospital, 1916 Southmead Hospital, 2013 Southmead Hospital, 2014 H(a)ematuria Blood
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
Plazomicin for complicated urinary tract infection
 October 2016 Horizon Scanning Research & Intelligence Centre Plazomicin for complicated urinary tract infection NIHR HSRIC ID: 9787 Lay summary Serious infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria are becoming
October 2016 Horizon Scanning Research & Intelligence Centre Plazomicin for complicated urinary tract infection NIHR HSRIC ID: 9787 Lay summary Serious infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria are becoming
Outpatient treatment in women with acute pyelonephritis after visiting emergency department
 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:369-373 Outpatient treatment in women with acute pyelonephritis after visiting emergency department Hee Kyoung Choi 1,*, Jin-Won Chung 2, Won Sup Oh 3,
LETTER TO THE EDITOR Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:369-373 Outpatient treatment in women with acute pyelonephritis after visiting emergency department Hee Kyoung Choi 1,*, Jin-Won Chung 2, Won Sup Oh 3,
Webposting Clinical Trial Results Synopsis
 Study Summary This summary information is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This summary information is not intended to replace
Study Summary This summary information is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This summary information is not intended to replace
An interview with Professor George A. Richard, MD, Department of Pediatrics, Nephrology Division, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA
 An interview with Professor George A. Richard, MD, Department of Pediatrics, Nephrology Division, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are so prevalent that at some
An interview with Professor George A. Richard, MD, Department of Pediatrics, Nephrology Division, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are so prevalent that at some
Prescribing Guidelines for Urinary Tract Infections
 Prescribing Guidelines for Urinary Tract Infections Urinary Tract Infections in Children Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common infections of childhood that may affect any part of the urinary tract,
Prescribing Guidelines for Urinary Tract Infections Urinary Tract Infections in Children Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common infections of childhood that may affect any part of the urinary tract,
