Memantine Reverses Social Withdrawal Induced by Ketamine in Rats
|
|
|
- Clement Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exp Neurobiol Mar;22(1): pissn eissn Original Article Memantine Reverses Social Withdrawal Induced by Ketamine in Rats Ezequiel Uribe 1,2 *, José Landaeta 1, Richard Wix 1 and Antonio Eblen 1 1 Laboratorio de Neurofisiología, Escuela De Ciencias Biomédicas y Tecnológicas Dr. Guillermo Mujica Sevilla, Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad de Carabobo, Valencia, 2 Hospital Dr. Rafael González Plaza, Departamento de Neuropsiquiatría. INSALUD, Gobernación del Estado Carabobo. Edo. Carabobo 2001, Venezuela The objective of this study was to determine the effect of memantine on schizophrenia-like symptoms in a ketamine-induced social withdrawal model in rats. We examined therapeutic effects of memantine, an NMDA antagonist, and haloperidol, a classic antipsychotic drug, on this behavioral model. Administration of memantine (10 or 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 ) significantly reduced ketamine-induced social withdrawal, and this effect was more effective than that of haloperidol (0.25 mg ㆍ kg -1 ) by restoring the social interaction between rats with no modification in general motor activity. These results suggest that memantine could have a therapeutic potential for schizophrenia. Key words: experimental psychosis, ketamine, NMDA, haloperidol, social interaction test INTRODUCTION Schizophrenia is a polygenic, multi-factorial disease whose etiology remains unknown. The wide range of symptoms and differences in the course and prognosis suggest that schizophrenia arises from the dysfunction of several neurotransmitter systems, generating a wide range of neurophysiological alterations that are not identifiable in all patients. Since its inception, schizophrenia has been managed with dopamine antagonists, which effectively reverses positive symptoms, but does not improve residual symptoms produced for the long term, such as cognitive impairment, social withdrawal, affective dysregulation, and disability [1]. In addition, 10-30% of patients do not improve with dopamine antagonists and become refractory to treatment Received February 8, 2013, Revised March 10, 2013, Accepted March 11, 2013 *To whom correspondence should be addressed. TEL: , FAX: ezequiel.uribe@hotmail.com; jcuriven@hotmail.com [1]. Recently, the glutaminergic system has been suggested to be linked with schizophrenia, after it was shown that N-methyl- D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists such as ketamine, phencyclidine, and MK 801 were beneficial for both positive and negative symptoms of the disease [2]. Yet, the only available treatment for schizophrenia is the drugs that act on the dopaminergic system, and no alternative drugs that act on other neurotransmitter systems are available. Repeated treatment of ketamine in rats generates social withdrawal and aggression, alterations which are reminiscent of the symptoms of schizophrenia in humans [3]. In the present study, we attempted to reproduce a model of psychosis by treatment with ketamine in rats. After establishment of psychosis model, we assessed reversibility of the condition with memantine, a modulator of the NMDA receptor, and compared the effect with that of haloperidol, a potent dopamine antagonist. The degrees of social withdrawal were analyzed in the social interaction test (SIT) and quantified. Copyright Experimental Neurobiology This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Implications for the Treatment of Schizophrenia MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals Male Sprague-Dawley rats (weight, g) were placed in separate cages with food and water provided ad libitum, and room temperature of 22 o C. They were remained in auditory and olfactory contact with the other rats until use. The social interaction test (SIT) The social interaction test (SIT) was performed in an open stainless steel cage ( cm) by following the method of Becker et al. [3]. The floor of the cage was uniformly distributed with rice shells. A digital camera (PCwebCam, Genius TM ) was placed over the cage attached to a laptop to film the behavior of rats at 30 frames/second. Ambient illumination was uniformly distributed at approximately 30 lux with a light-dark scheme of 12 h light/12 h dark. After the third day of habituation in the test room, rats were familiarized with the SIT scene without recording. The laboratory was silent while the tests were performed. On next day, recording was carried out for 7 minutes after placing pairs of rats in the cage. Initial tests were performed in pairs of randomly selected rats without medication. Then, the rats were divided into two groups: one group received 30 mg ㆍ kg -1 ketamine intraperitoneally (i.p), (n=20) for 5 days and the other group (n=20) received 0.9% saline i.p. for 5 days. The SIT was performed with pairs of rats randomly selected from each group. Treatment was suspended for 5 days; at the end of which the SIT was repeated under the same pair conditions. Then, the ketamine group (n=20) was divided into four groups of five rats, each received memantine (10 mg ㆍ kg -1 ), memantine (15 mg ㆍ kg -1 ), haloperidol (0.25 mg ㆍ kg -1 ) or 0.9% NaCl solution, all diluted in 1 ml of 0.9% saline and administered i.p daily for 5 days after which the SIT was conducted again (Fig. 1). Video files taken during each test (7 min test) were analyzed using Tracker V4.05 software by measuring the distance (cm) between the pair of rats and the total distance traveled (cm) for each rat during the test. These determinations were calibrated in two-dimensions (ordinate and abscissa). Distance measurements were taken from image frames with 1 Hz frequency, generating a total of 420 measurements (8,400 measurements/group) for each variable. The speed of each rat during the SIT was calculated from their total traveled distance and time used for it, expressed as cm ㆍ s -1. Distance between rats (DBR) was used as the schizophrenia sign, whereas total traveled distance (TTD) and speed during SIT were used to assess the impact of the drugs on motor activity. Statistical analysis The data were processed using STATISTICA 8 software and parametric descriptive statistics. Pearson s correlations were performed. A p<0.05 was considered significant for all tests. Comparisons of quantitative variables for each treatment group were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that at least two groups were different from each other. Post-hoc t-tests (LSD test) were performed to adjust for the inflated probability of a Type I error. RESULTS Establishment of a rat model of psychosis-like behavior A rat model of psychosis-like behavior was established by repea- Table 1. Distance between rats in the groups immediate after ketamine treatment and 5 days after washout Fig. 1. A (n: 20) B (n: 20), A 1 (n: 5): memantine 10 mg ㆍ kg -1, A 2 (n: 5): memantine 10 mg ㆍ kg -1, A 3 (n: 5): haloperidol 0.25 mg ㆍ kg -1, A 4 : saline. After treatment for 5 days After 5 days of washout Control (n=20) (35.5%) (35.1%) Ketamine (n=20) (38.2%) (39.1%) p Distance between rats was recorded after treatment with ketamine for 5 days and after 5 days of washout. Data were presented as means (% of total distance) in cm. Numbers of animals for each group:
3 Ezequiel Uribe, et al. ted treatment with ketamine as scheduled (Fig. 1). Ketaminewithdrawal significantly reduced social interaction between the rats by increasing the distance between them during the SIT. These changes remained for 5 days of ketamine withdrawal (Table 1). Examination of the effects of memantine and haloperidol Memantine (10 mg ㆍ kg -1 ) reduced the distance between rats (DBR) during the SIT after ketamine withdrawal, and this effect was greater than that shown by the placebo (saline). No significant differences were observed in DBR after administering 10 or 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantine but 10 mg ㆍ kg -1 induced a greater decrease in the DBR than that of haloperidol (Fig. 2). Ketamine also produced a reduction in the distance traveled per second (Fig. 3) compared with that in the control, and this effect persisted after ketamine withdrawal. No significant difference was found between the groups. Memantine induced a greater reduction in distance traveled per second than that in the placebo group, and this effect was more intense for the 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantine than that in the 10 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantine group (Table 2). The reduction in TTD was higher for the memantine groups than that for haloperidol. Data analysis with ANOVA followed by a post hoc test (LSD test) showed no statistical correlation between DBR and rat speed during the SIT (Table 3). DISCUSSION Fig. 2. Distance between rats for treatment groups during the social interaction test. Distance between rats was expressed as means±sd in cm. Treatment groups: (A) rats without pharmacological intervention, (B) 5 days after ketamine withdrawal, (C) 10 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantine after ketamine withdrawal, (D) saline after ketamine withdrawal, (E) 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantine after ketamine withdrawal, (F) 0.25 mg ㆍ kg -1 haloperidol after ketamine withdrawal. The ketamine-induced psychosis model in rats reproduces behavioral symptoms that mimic schizophrenic psychosis in humans [3], as well as the primary pathophysiological changes generated by this disease [4]. When the membrane NMDA receptor is blocked by ketamine in GABAergic interneurons, there is a failure to correctly interpret the degree of excitation of pyramidal neurons; resulting in an excessive glutamate action; thus, inducing an overstimulation of the ventral tegmental area and finally, the classic hyper-dopaminergic state characteristic of schizophrenia [5]. Ketamine has hepatic clearance of 19.1 ml ㆍ min -1 ㆍ kg -1, which ensures the excretion of its eight active metabolites about 24 h after administration [6]. Ketamine, which blocks NMDA, is known to generate long lasting molecular changes in the brain at least 14 days after complete withdrawal [4]. Table 2. Distance between rats and speed measured in groups and/or experimental phases Fig. 3. Average speed for treatment groups during the social interaction test. Average speed was expressed as means±sd in cm ㆍ s -1. Treatment groups: (A) rats without pharmacological intervention, (B) 5 days after ketamine withdrawal, (C) 10 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantine after ketamine withdrawal, (D) placebo after ketamine withdrawal, (E) 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantina after ketamine withdrawal, (F) 0,25 mg ㆍ kg -1 haloperidol after ketamine withdrawal. Drug DBR Speed Controls Ketamine without other drug Memantine 10 mg ㆍ kg -1 Memantine 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 Haloperidol Placebo a,b,c a,b,c Distance between rats (DBR) was presented by means in cm and speed was means in cm ㆍ s -1. The differences between the values of the groups treated with 10 and 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 memantine were not significant. a p< compared with control group; b p< compared with placebo group; c p< compared with haloperidol group. 20
4 Implications for the Treatment of Schizophrenia Table 3. Post hoc analysis of the distance between rats and average speed of rats during the social interaction test (A) (0) 18,493 (1) 19,697 (2) 19,639 (3) 12,394 (4) 17,881 (5) 12,259 (6) 18, (B) (0) 4,5938 (1) 3,6968 (2) 3,5560 (3) 1,8781 (4) 4,0717 (5) 1,2605 (6) 2, Post hoc analysis of the distance between rats (A) and speed (B) using LSD test. (A) Probabilities for post hoc tests error: between MS=102.17, df=28,973. (B) Probabilities for post hoc tests Error: Between MS=16.274, df=28,973. Groups of treatment: (0) Rats without pharmacological intervention, (1) 5 days after ketamine withdrawal, (2) after ketamine withdrawal, (3) memantine 10 mg ㆍ kg -1 after ketamine withdrawal, (4) placebo after ketamine withdrawal, (5) memantina 15 mg ㆍ kg -1 after ketamine withdrawal, (6) Haloperidol 0.25 mg ㆍ kg -1 after ketamine withdrawal. In our study, memantine was administered at 10 mg ㆍ kg -1 after ketamine treatment and memantine treatment resulted in a greater reversal of social isolation than that of the placebo or haloperidol (0.25 mg ㆍ kg -1 ). This antipsychotic action did not show a doseeffect. Memantine induced a reduction in the total traveled distance, and a dose dependent effect at 10 and 15 mg ㆍ kg -1. Thus, the sedative effect of memantine must be considered to explain this observation. Although previous studies described the use of higher doses of memantine [7], all of our rats died in a preliminary study at doses >30 mg ㆍ kg -1. No correlation was observed between the distance traveled per second (speed) and DBR (social isolation), suggesting that the effect of memantine on this ketamine-induced psychotic symptom probably was not due to an action of memantine on rat motility. In addition, regarding that a social withdrawal model induced by ketamine in rats is an approach to behavioral changes of schizophrenia in human, these data suggest that memantine has a therapeutic potential for this disease. The therapeutic effect of memantine in ketamine-induced psychosis model of schizophrenia suggests the importance of glutamatergic dysfunction in schizophrenia. In fact, glutamatergic dysfunction in schizophrenia has been suggested to be one of the neurotransmitter systems involved. Current evidence suggests that the wide variety of clinical conditions among patients with schizophrenia could be caused by different endophenotypes [8], which in turn, induce differences in the response to antipsychotic treatments. For example, 10-30% of patients with schizophrenia become resistant to conventional antipsychotic treatment [1], but respond to clozapine, which is an atypical antipsychotic drug with a high impact on NMDA receptor modulation [9], suggesting that these patients may have a different endophenotype that requires an alternative pharmacological intervention. REFERENCES 1. Lehman AF, Lieberman JA, Dixon LB, McGlashan TH, Miller AL, Perkins DO, Kreyenbuhl J; American Psychiatric Association; Steering Committee on Practice Guidelines (2004) Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia, second edition. Am J Psychiatry 161: Krystal JH, Karper LP, Seibyl JP, Freeman GK, Delaney R, Bremner JD, Heninger GR, Bowers MB Jr, Charney DS (1994) Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans. Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51: Becker A, Grecksch G, Bernstein HG, Höllt V, Bogerts B (1999) Social behaviour in rats lesioned with ibotenic acid in the hippocampus: quantitative and qualitative analysis. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 144:
5 Ezequiel Uribe, et al. 4. Keilhoff G, Becker A, Grecksch G, Wolf G, Bernstein HG (2004) Repeated application of ketamine to rats induces changes in the hippocampal expression of parvalbumin, neuronal nitric oxide synthase and cfos similar to those found in human schizophrenia. Neuroscience 126: Homayoun H, Moghaddam B (2007) NMDA receptor hypofunction produces opposite effects on prefrontal cortex interneurons and pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 27: Evers A, Crowder M. (2011) Generals anesthetics. In: Goodman & Gilman s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 12 edition (Brunton LL, Chabner B, Knollmann BC, eds), pp McGraw-Hill, New York. 7. Creeley C, Wozniak DF, Labruyere J, Taylor GT, Olney JW (2006) Low doses of memantine disrupt memory in adult rats. J Neurosci 26: Gottesman II, Gould TD (2003) The endophenotype concept in psychiatry: etymology and strategic intentions. Am J Psychiatry 160: Olney JW, Farber NB (1994) Efficacy of clozapine compared with other antipsychotics in preventing NMDA-antagonist neurotoxicity. J Clin Psychiatry 55 Suppl B:
Effects of Ketamine on Healthy Participants and Individuals Suffering from Schizophrenia. John Smith. Physiological Foundations of Psychology 71733
 Effects of Ketamine on Healthy Participants and Individuals Suffering from Schizophrenia John Smith Physiological Foundations of Psychology 71733 Long Beach City College, Spring 2002 Abstract The purpose
Effects of Ketamine on Healthy Participants and Individuals Suffering from Schizophrenia John Smith Physiological Foundations of Psychology 71733 Long Beach City College, Spring 2002 Abstract The purpose
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs
 Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders
 The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
Pharmacological Characterization of Locomotor Sensitization Induced by Chronic Phencyclidine Administration
 0022-3565/01/2963-905 913$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 3 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3123/882979
0022-3565/01/2963-905 913$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 3 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3123/882979
SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Atypical (2
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Atypical (2
PERCEPTION: Gain Control & Integration. Mark A. Geyer, Ph.D. Departments of Psychiatry & Neurosciences University of California, San Diego
 PERCEPTION: Gain Control & Integration Mark A. Geyer, Ph.D. Departments of Psychiatry & Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Perception Integration Integration: The processes linking the output
PERCEPTION: Gain Control & Integration Mark A. Geyer, Ph.D. Departments of Psychiatry & Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Perception Integration Integration: The processes linking the output
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal
 ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia
 Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
Outline. Outline. Background Literature and Slides 10/23/2013. The Schizophrenia Research Forum online: Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior
 Background Literature and Slides Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior Roberto Fernández Galán, PhD Assistant Professor of Neurosciences Mt. Sinai Health Care Foundation Scholar Alfred P. Sloan Research
Background Literature and Slides Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior Roberto Fernández Galán, PhD Assistant Professor of Neurosciences Mt. Sinai Health Care Foundation Scholar Alfred P. Sloan Research
Differential modulation of glutamatergic transmission by 3,5-dibromo-Lphenylalanine
 Molecular Pharmacology This article has Fast not been Forward. copyedited Published and formatted. on The February final version 1, may 2005 differ as from doi:10.1124/mol.104.005983 this version. Differential
Molecular Pharmacology This article has Fast not been Forward. copyedited Published and formatted. on The February final version 1, may 2005 differ as from doi:10.1124/mol.104.005983 this version. Differential
Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development. John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University
 Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University Four problems We don t know the disorders sufficiently The biology is complex and heterogeneous We have animal
Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University Four problems We don t know the disorders sufficiently The biology is complex and heterogeneous We have animal
Is the Acute NMDA Receptor Hypofunction a Valid Model of Schizophrenia?
 Schizophrenia Bulletin vol. 38 no. 1 pp. 9 14, 2012 doi:10.1093/schbul/sbr133 Advance Access publication on September 28, 2011 SCHIZOPHRENIA IN TRANSLATION Is the Acute NMDA Receptor Hypofunction a Valid
Schizophrenia Bulletin vol. 38 no. 1 pp. 9 14, 2012 doi:10.1093/schbul/sbr133 Advance Access publication on September 28, 2011 SCHIZOPHRENIA IN TRANSLATION Is the Acute NMDA Receptor Hypofunction a Valid
Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenic twin. Normal twin
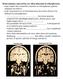 Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Functional neuroimaging in schizophrenia: diagnosis and drug discovery
 Review Functional neuroimaging in schizophrenia: diagnosis and drug discovery Philip McGuire 1, Oliver D Howes 1, James Stone 2 and Paolo Fusar-Poli 1 1 Sections of Neuroimaging, Division of Psychological
Review Functional neuroimaging in schizophrenia: diagnosis and drug discovery Philip McGuire 1, Oliver D Howes 1, James Stone 2 and Paolo Fusar-Poli 1 1 Sections of Neuroimaging, Division of Psychological
!"#$%& ' ( )%& &* "&' SA +& : <+" " = KLMN " < We X 7A4 &* !"# $% & '"' '() *! +,-. &/0 +,-. & 1() &2' *** .
 1386 ( ")/85 $%/!"! "# $%%&' ()!"#$%& ' ( )%& & & < +& 9'=%& + ',-. " /01 23 '4 # "&' 56& 7&4 8 %& 9 ';3.!"#$%&
1386 ( ")/85 $%/!"! "# $%%&' ()!"#$%& ' ( )%& & & < +& 9'=%& + ',-. " /01 23 '4 # "&' 56& 7&4 8 %& 9 ';3.!"#$%&
PRINCIPLES OF NEUROSCIENCE III
 PRINCIPLES OF NEUROSCIENCE III MOLECULAR NEUROPHARMACOLOGY & ITS CLINICAL APPLICATION GMS6023 -- SPRING/2016 2 CREDITS CLASS LOCATION: MBI BUILDING, L1-101 MEETING TIME: MONDAY, WEDNESDAY, FRIDAY (10 AM-12
PRINCIPLES OF NEUROSCIENCE III MOLECULAR NEUROPHARMACOLOGY & ITS CLINICAL APPLICATION GMS6023 -- SPRING/2016 2 CREDITS CLASS LOCATION: MBI BUILDING, L1-101 MEETING TIME: MONDAY, WEDNESDAY, FRIDAY (10 AM-12
There is extensive evidence that a family history of alcoholism
 Article Altered NMDA Glutamate Receptor Antagonist Response in Individuals With a Family Vulnerability to Alcoholism Ismene L. Petrakis, M.D. Diana Limoncelli, B.A. Ralitza Gueorguieva, Ph.D. Peter Jatlow,
Article Altered NMDA Glutamate Receptor Antagonist Response in Individuals With a Family Vulnerability to Alcoholism Ismene L. Petrakis, M.D. Diana Limoncelli, B.A. Ralitza Gueorguieva, Ph.D. Peter Jatlow,
BL-1020: First-in-Class GABA-Enhanced Antipsychotic For Schizophrenia
 BL-1020: First-in-Class GABA-Enhanced Antipsychotic For Schizophrenia December 2012 Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains "forward-looking statements." These statements include words like
BL-1020: First-in-Class GABA-Enhanced Antipsychotic For Schizophrenia December 2012 Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains "forward-looking statements." These statements include words like
Recent Advances in the Antipsychotic Treatment of People with schizophrenia. Robert W. Buchanan, M.D.
 Recent Advances in the Antipsychotic Treatment of People with schizophrenia Robert W. Buchanan, M.D. Antipsychotic medications are the primary class of drugs used in the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia.
Recent Advances in the Antipsychotic Treatment of People with schizophrenia Robert W. Buchanan, M.D. Antipsychotic medications are the primary class of drugs used in the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia.
Neural model of emotional regulation structures - Circuits involving prefrontal cortex and subcortical limbic structures - MDE associated with
 Topics Brain and signalling changes in depression Ketamine activity in refractory depression Mechanism of Action New Data Dose finding Route of Administration Activity in Other Disorders Neural model of
Topics Brain and signalling changes in depression Ketamine activity in refractory depression Mechanism of Action New Data Dose finding Route of Administration Activity in Other Disorders Neural model of
Introduction. J Mwanza 1, R Paul 1, JM Ncheka 1, P Petlovani 1. 1.University of Zambia School of Medicine, Department of Psychiatry
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Appropriateness of antipsychotic drugs prescribed for First episode psychosis by clinicians at Chainama Hills college hospital in Lusaka J Mwanza 1, R Paul 1, JM Ncheka 1, P Petlovani
RESEARCH ARTICLE Appropriateness of antipsychotic drugs prescribed for First episode psychosis by clinicians at Chainama Hills college hospital in Lusaka J Mwanza 1, R Paul 1, JM Ncheka 1, P Petlovani
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity
 Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity : What is Schizophrenia? Literally split mind A mental disorder comprising most major psychotic disorders; characterized
Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity : What is Schizophrenia? Literally split mind A mental disorder comprising most major psychotic disorders; characterized
Office Management of Patients Living With Schizophrenia
 Office Management of Patients Living With Schizophrenia Dr. Richardson O. Tachere, MD; MPH; M.A (Health Mgt.); FRCPC. Psychiatrist, CMHA, Kitchener. A Day in Psychiatry - 2017 Wednesday November 8 th,
Office Management of Patients Living With Schizophrenia Dr. Richardson O. Tachere, MD; MPH; M.A (Health Mgt.); FRCPC. Psychiatrist, CMHA, Kitchener. A Day in Psychiatry - 2017 Wednesday November 8 th,
Sensory Gating Measures. Auditory P50 Response Prepulse Inhibition of Startle (PPI) Bruce Turetsky, M.D. IOM Workshop June 22, 2010
 Sensory Gating Measures Auditory P50 Response Prepulse Inhibition of Startle (PPI) Bruce Turetsky, M.D. IOM Workshop June 22, 2010 Heuristically, sensory gating denotes the ability to filter out irrelevant
Sensory Gating Measures Auditory P50 Response Prepulse Inhibition of Startle (PPI) Bruce Turetsky, M.D. IOM Workshop June 22, 2010 Heuristically, sensory gating denotes the ability to filter out irrelevant
Animal Models of Psychosis: Current State and Future Directions
 Curr Behav Neurosci Rep (2014) 1:100 116 DOI 10.1007/s40473-014-0013-2 PSYCHOSIS (R GUR AND B CLEMENTZ, SECTION EDITORS) Animal Models of Psychosis: Current State and Future Directions Alexandra D. Forrest
Curr Behav Neurosci Rep (2014) 1:100 116 DOI 10.1007/s40473-014-0013-2 PSYCHOSIS (R GUR AND B CLEMENTZ, SECTION EDITORS) Animal Models of Psychosis: Current State and Future Directions Alexandra D. Forrest
CONTROVERSIES AND NEW DIRECTIONS
 BIPOLAR Introduction DISORDER IN CHILDHOOD AND EARLY ADOLESCENCE Introduction MELISSA P. D ELBELLO, DAVID AXELSON, and BARBARA GELLER CONTROVERSIES AND NEW DIRECTIONS Although the existence and diagnostic
BIPOLAR Introduction DISORDER IN CHILDHOOD AND EARLY ADOLESCENCE Introduction MELISSA P. D ELBELLO, DAVID AXELSON, and BARBARA GELLER CONTROVERSIES AND NEW DIRECTIONS Although the existence and diagnostic
Investigating Glutamatergic Mechanism in Attention and Impulse Control Using Rats in a Modified 5-Choice Serial Reaction Time Task
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Investigating Glutamatergic Mechanism in Attention and Impulse Control Using Rats in a Modified 5-Choice Serial Reaction Time Task Abigail Benn*, Emma S. J. Robinson Department of Physiology
RESEARCH ARTICLE Investigating Glutamatergic Mechanism in Attention and Impulse Control Using Rats in a Modified 5-Choice Serial Reaction Time Task Abigail Benn*, Emma S. J. Robinson Department of Physiology
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
Memantine Enhances the Effect of Olanzapine in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Memantine Enhances the Effect of Olanzapine in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Ahmad Fakhri 1, Sirous Pakseresht 1, Mohammad Reza Haghdoost 1, Nasihat
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Memantine Enhances the Effect of Olanzapine in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Ahmad Fakhri 1, Sirous Pakseresht 1, Mohammad Reza Haghdoost 1, Nasihat
CHAPTER 3. Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment
 CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
The effects of environmental enrichment on nicotine sensitization in a rodent model of schizophrenia
 East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Undergraduate Honors Theses 5-2014 The effects of environmental enrichment on nicotine sensitization in a rodent model
East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Undergraduate Honors Theses 5-2014 The effects of environmental enrichment on nicotine sensitization in a rodent model
Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place
 Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place Preference Stephanie Willis, Jonnique Adjmul, Shabaaz Sandhu, Antoniette M. Maldonado-Devincci, Cheryl Kirsten ABSTRACT The present
Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place Preference Stephanie Willis, Jonnique Adjmul, Shabaaz Sandhu, Antoniette M. Maldonado-Devincci, Cheryl Kirsten ABSTRACT The present
Glutamate Overview. How can one neurotransmitter have so many diverse functions?
 tamate Overview How can one neurotransmitter have so many diverse functions? Darryle Schoepp, Ph.D. Senior Vice President and Franchise Head, Neuroscience Control of Excitability via Amino Acid Neurotransmitters
tamate Overview How can one neurotransmitter have so many diverse functions? Darryle Schoepp, Ph.D. Senior Vice President and Franchise Head, Neuroscience Control of Excitability via Amino Acid Neurotransmitters
DOPAMINERGIC AND GLUTAMATERGIC DYSFUNCTIONS IN
 Chapter DOPAMINERGIC AND GLUTAMATERGIC DYSFUNCTIONS IN THE NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Wen-Jun Gao * Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia,
Chapter DOPAMINERGIC AND GLUTAMATERGIC DYSFUNCTIONS IN THE NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Wen-Jun Gao * Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia,
Looking to the Horizon: Novel Agents in Development for the Treatment of Depression
 Handout for the Neuroscience Education Institute (NEI) online activity: Looking to the Horizon: Novel Agents in Development for the Treatment of Depression Learning Objectives Explain the neurobiological
Handout for the Neuroscience Education Institute (NEI) online activity: Looking to the Horizon: Novel Agents in Development for the Treatment of Depression Learning Objectives Explain the neurobiological
Computational Neuropharmacology
 Computational Neuropharmacology Schizophrenia: Symptoms & Pathologies Computational Models of Mental Illness: Neurons, synapses and modulators Example: Working Memory Model Pharmaceutical Industry: Progress
Computational Neuropharmacology Schizophrenia: Symptoms & Pathologies Computational Models of Mental Illness: Neurons, synapses and modulators Example: Working Memory Model Pharmaceutical Industry: Progress
#CHAIR2016. September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL. Sponsored by
 #CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by Bending the Illness Curve: A New Treatment Model for Early Stage Psychoses Jeffrey A. Lieberman, M.D. Columbia University College
#CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by Bending the Illness Curve: A New Treatment Model for Early Stage Psychoses Jeffrey A. Lieberman, M.D. Columbia University College
Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health
 Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Supplementary Methods
 1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
Does nicotine alter what is learned about non-drug incentives?
 East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Undergraduate Honors Theses 5-2014 Does nicotine alter what is learned about non-drug incentives? Tarra L. Baker Follow
East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Undergraduate Honors Theses 5-2014 Does nicotine alter what is learned about non-drug incentives? Tarra L. Baker Follow
Time course of prepulse inhibition disruption induced by dopamine agonists and NMDA antagonists: Effects of drug administration regimen
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, Department of Psychology Psychology, Department of 9-2011 Time course of prepulse inhibition disruption
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, Department of Psychology Psychology, Department of 9-2011 Time course of prepulse inhibition disruption
Effects of acute and repeated systemic administration of ketamine on prefrontal acetylcholine release and sustained attention performance in rats
 Psychopharmacology (2002) 161:168 179 DOI 10.1007/s00213-002-1004-7 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Christopher L. Nelson Joshua A. Burk John P. Bruno Martin Sarter Effects of acute and repeated systemic administration
Psychopharmacology (2002) 161:168 179 DOI 10.1007/s00213-002-1004-7 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Christopher L. Nelson Joshua A. Burk John P. Bruno Martin Sarter Effects of acute and repeated systemic administration
Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder
 Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD January
Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD January
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters. Paul Glue
 Amino Acid Neurotransmitters Paul Glue Objectives Review: Relative abundance of AAs vs monoamines Pharmacology of glutamate, GABA Postulated role of glutamate, GABA dysfunction in neuropsych disorders
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters Paul Glue Objectives Review: Relative abundance of AAs vs monoamines Pharmacology of glutamate, GABA Postulated role of glutamate, GABA dysfunction in neuropsych disorders
The Neurobiology of Mood and Psychotic Disorders
 The Neurobiology of Mood and Psychotic Disorders Daphne J. Holt, MD, PhD Co-Director, Schizophrenia Clinical and Research Program Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor,
The Neurobiology of Mood and Psychotic Disorders Daphne J. Holt, MD, PhD Co-Director, Schizophrenia Clinical and Research Program Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor,
Circuit-based framework for understanding neurotransmitter and risk gene interactions in schizophrenia
 Opinion Circuit-based framework for understanding neurotransmitter and risk gene interactions in schizophrenia John E. Lisman 1, Joseph T. Coyle 2, Robert W. Green 3, Daniel C. Javitt 4, Francine M. Benes
Opinion Circuit-based framework for understanding neurotransmitter and risk gene interactions in schizophrenia John E. Lisman 1, Joseph T. Coyle 2, Robert W. Green 3, Daniel C. Javitt 4, Francine M. Benes
Lauren Harms 1,2,3, Ross Fulham 2,3,4, Juanita Todd 2,3,4, Ulrich Schall 2,3,5, Markku Penttonen 6, Deborah Hodgson 1,2,3, Patricia Michie 2,3,4
 PRIORITY CENTRE FOR TRANSLATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE & MENTAL HEALTH RESEARCH Mismatch Responses To Frequency Deviants In The Surface EEG Of Awake, Freely Moving Rats: A Platform For Examining Pharmacological
PRIORITY CENTRE FOR TRANSLATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE & MENTAL HEALTH RESEARCH Mismatch Responses To Frequency Deviants In The Surface EEG Of Awake, Freely Moving Rats: A Platform For Examining Pharmacological
Risperidone and ritanserin but not haloperidol block effect of dizocilpine on the active allothetic place avoidance task
 Risperidone and ritanserin but not haloperidol block effect of dizocilpine on the active allothetic place avoidance task Vera Bubenikova-Valesova*, Ales Stuchlik, Jan Svoboda, Jan Bures, and Karel Vales
Risperidone and ritanserin but not haloperidol block effect of dizocilpine on the active allothetic place avoidance task Vera Bubenikova-Valesova*, Ales Stuchlik, Jan Svoboda, Jan Bures, and Karel Vales
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
#CHAIR2016. September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL. Sponsored by
 #CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by #CHAIR2016 Ketamine: Promising Path or False Prophecy in the Development of Novel Therapeutics for Mood Disorders Alan F. Schatzberg,
#CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by #CHAIR2016 Ketamine: Promising Path or False Prophecy in the Development of Novel Therapeutics for Mood Disorders Alan F. Schatzberg,
A preliminary naturalistic study of low-dose ketamine for depression and suicide ideation in the emergency department
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (2011), 14, 1127 1131. f CINP 2011 doi:10.1017/s1461145711000629 A preliminary naturalistic study of low-dose ketamine for depression and suicide ideation
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (2011), 14, 1127 1131. f CINP 2011 doi:10.1017/s1461145711000629 A preliminary naturalistic study of low-dose ketamine for depression and suicide ideation
Animal models of schizophrenia. Juan E Belforte
 Animal models of schizophrenia Juan E Belforte Louis Wain, (1860-1939) Schizophrenia overview Major international health problem Worldwide lifetime prevalence ~1% Incidence rate ~2 per 10,000 per year
Animal models of schizophrenia Juan E Belforte Louis Wain, (1860-1939) Schizophrenia overview Major international health problem Worldwide lifetime prevalence ~1% Incidence rate ~2 per 10,000 per year
Animal models of schizophrenia. Juan E Belforte
 Animal models of schizophrenia Juan E Belforte Louis Wain, (1860-1939) Schizophrenia overview Major international health problem Worldwide lifetime prevalence ~1% Incidence rate ~2 per 10,000 per year
Animal models of schizophrenia Juan E Belforte Louis Wain, (1860-1939) Schizophrenia overview Major international health problem Worldwide lifetime prevalence ~1% Incidence rate ~2 per 10,000 per year
ES.S10: Drugs and the Brain Syllabus Spring 2013 Zak Fallows
 ES.S10: Drugs and the Brain Syllabus Spring 2013 Zak Fallows About the Class: One-Sentence Description: This class is a multidisciplinary introduction to pharmacology, neurotransmitters, drug mechanisms,
ES.S10: Drugs and the Brain Syllabus Spring 2013 Zak Fallows About the Class: One-Sentence Description: This class is a multidisciplinary introduction to pharmacology, neurotransmitters, drug mechanisms,
Hippocampal dysregulation of dopamine system function and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia
 Opinion Hippocampal dysregulation of dopamine system function and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia Daniel J. Lodge 1 and Anthony A. Grace 2 1 Department of Pharmacology and Center for Biomedical Neuroscience,
Opinion Hippocampal dysregulation of dopamine system function and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia Daniel J. Lodge 1 and Anthony A. Grace 2 1 Department of Pharmacology and Center for Biomedical Neuroscience,
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder
 Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago, IL 6/8/2016 Disclosure Information My research is
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago, IL 6/8/2016 Disclosure Information My research is
Pharmacological management of behavioural problems in children with acquired brain injury. A/Professor A Vance
 Pharmacological management of behavioural problems in children with acquired brain injury Outline of presentation 1. The key types of acquired brain injury behavioural problems 2. A useful clinical model
Pharmacological management of behavioural problems in children with acquired brain injury Outline of presentation 1. The key types of acquired brain injury behavioural problems 2. A useful clinical model
Received July 30, 1999; revised September 10, 1999; accepted September
 Animal Models of Negative Symptoms: M100907 Antagonizes PCP-Induced Immobility in a Forced Swim Test in Mice Roy Corbett, Ph.D., Lily Zhou, M.D., Stephen M. Sorensen, Ph.D., and Cesare Mondadori, Ph.D.
Animal Models of Negative Symptoms: M100907 Antagonizes PCP-Induced Immobility in a Forced Swim Test in Mice Roy Corbett, Ph.D., Lily Zhou, M.D., Stephen M. Sorensen, Ph.D., and Cesare Mondadori, Ph.D.
Schizophrenia & the Antipsychotics
 splitting of mind (cognition/emotion) from reality 1% of population globally shamans or mentally ill Several subtypes: paranoid / catatonic / disorganized / undifferentiated / residual positive ( exaggerated)
splitting of mind (cognition/emotion) from reality 1% of population globally shamans or mentally ill Several subtypes: paranoid / catatonic / disorganized / undifferentiated / residual positive ( exaggerated)
With growing knowledge of disease
 PHARMACOLOGIC STRATEGIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS Terry E. Goldberg, PhD* ABSTRACT Cognitive dysfunction is considered a major determinant and predictor of long-term disability and has,
PHARMACOLOGIC STRATEGIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS Terry E. Goldberg, PhD* ABSTRACT Cognitive dysfunction is considered a major determinant and predictor of long-term disability and has,
Cognitive Function Test. NOR & spatial NOR task. Introduction. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Estrogen Receptor (ER) in Brain
 Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
This is Your Brain on LSD
 This is Your Brain on LSD Kayla Ortiz Rafael Yitzhakian What is LSD? What is LSD? LSD (acid) Lysergic acid diethylamide Hallucinogenic drug Serotonergic psychedelic Banned in the U.S. in the 60 s Classified
This is Your Brain on LSD Kayla Ortiz Rafael Yitzhakian What is LSD? What is LSD? LSD (acid) Lysergic acid diethylamide Hallucinogenic drug Serotonergic psychedelic Banned in the U.S. in the 60 s Classified
Final Exam PSYC2022. Fall (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication with cannabis.
 Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
CURRICULUM VITAE. Jonathan Dickerson B.S. Biology, Wilmington College.
 CURRICULUM VITAE Jonathan Dickerson Education: 1999-2003 B.S. Biology, Wilmington College. 2004-2010 Ph.D., Neuroscience Graduate Program, University of Cincinnati. Thesis Advisor: Dr. Kim Seroogy 2007
CURRICULUM VITAE Jonathan Dickerson Education: 1999-2003 B.S. Biology, Wilmington College. 2004-2010 Ph.D., Neuroscience Graduate Program, University of Cincinnati. Thesis Advisor: Dr. Kim Seroogy 2007
Piecing the Puzzle Together: Pharmacologic Approaches to Behavioral Management in Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Piecing the Puzzle Together: Pharmacologic Approaches to Behavioral Management in Autism Spectrum Disorder Hannah Sauer, PharmD PGY1 Pediatric Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives
Piecing the Puzzle Together: Pharmacologic Approaches to Behavioral Management in Autism Spectrum Disorder Hannah Sauer, PharmD PGY1 Pediatric Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives
Computational Psychiatry: Tasmia Rahman Tumpa
 Computational Psychiatry: Tasmia Rahman Tumpa Computational Psychiatry: Existing psychiatric diagnostic system and treatments for mental or psychiatric disorder lacks biological foundation [1]. Complexity
Computational Psychiatry: Tasmia Rahman Tumpa Computational Psychiatry: Existing psychiatric diagnostic system and treatments for mental or psychiatric disorder lacks biological foundation [1]. Complexity
Clinical Guidelines for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Schizophrenia
 Clinical Guidelines for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Community Behavioral Health (CBH) is committed to working with our provider partners to continuously improve the quality of behavioral healthcare
Clinical Guidelines for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Community Behavioral Health (CBH) is committed to working with our provider partners to continuously improve the quality of behavioral healthcare
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain -
 - Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
Effects of Olanzapine and Clozapine on Radial Maze Performance in Naive and MK-801-Treated Mice
 Original Article Effects of Olanzapine and Clozapine on Radial Maze Performance in Naive and MK-1-Treated Mice Authors Affiliation O. Mutlu, I. K. Celikyurt, G. Ulak, P. Tanyeri, F. Y. Akar, F. Erden Kocaeli
Original Article Effects of Olanzapine and Clozapine on Radial Maze Performance in Naive and MK-1-Treated Mice Authors Affiliation O. Mutlu, I. K. Celikyurt, G. Ulak, P. Tanyeri, F. Y. Akar, F. Erden Kocaeli
BRAIN PLASTICITY: AGING AND NEUROPSYCHICATRIC DISORDERS:
 1 BRAIN PLASTICITY: AGING AND NEUROPSYCHICATRIC DISORDERS: Brief Scientific Report Francisco Mora Departamento de Fisiologia Facultad de Medicina Universidad Complutense Ciudad Universitaria 28040 Madrid
1 BRAIN PLASTICITY: AGING AND NEUROPSYCHICATRIC DISORDERS: Brief Scientific Report Francisco Mora Departamento de Fisiologia Facultad de Medicina Universidad Complutense Ciudad Universitaria 28040 Madrid
Effects of anesthesia upon 18 F-FDG uptake in rhesus monkey brains
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 5, 373 377, 2005 Effects of anesthesia upon 18 F-FDG uptake in rhesus monkey brains Takashi ITOH,* Shunichi WAKAHARA,** Takayuki NAKANO,** Kazutoshi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 5, 373 377, 2005 Effects of anesthesia upon 18 F-FDG uptake in rhesus monkey brains Takashi ITOH,* Shunichi WAKAHARA,** Takayuki NAKANO,** Kazutoshi
Multiple Limbic Regions Mediate the Disruption of Prepulse Inhibition Produced in Rats by the Noncompetitive NMDA Antagonist Dizocilpine
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 15, 1998, 18(20):8394 8401 Multiple Limbic Regions Mediate the Disruption of Prepulse Inhibition Produced in Rats by the Noncompetitive NMDA Antagonist Dizocilpine
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 15, 1998, 18(20):8394 8401 Multiple Limbic Regions Mediate the Disruption of Prepulse Inhibition Produced in Rats by the Noncompetitive NMDA Antagonist Dizocilpine
22 JWA :00-15:
 22 JWA 2018 2018 7 7 13:00-15:00 1 2 1702004 2018 7 7 Saturday, 7 th July, 2018 12:30-2F 1 13:00-14:00 1 (SL-1) Special Lecture 1 Monoaminergic drugs vs. fast-acting antidepressants: effects on glutamate
22 JWA 2018 2018 7 7 13:00-15:00 1 2 1702004 2018 7 7 Saturday, 7 th July, 2018 12:30-2F 1 13:00-14:00 1 (SL-1) Special Lecture 1 Monoaminergic drugs vs. fast-acting antidepressants: effects on glutamate
AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
^ PRIMER OF DRUG ACTION A comprehensive gyide to the actions, uses, and side effects of psychoactive drugs
 ^ PRIMER OF DRUG ACTION A comprehensive gyide to the actions, uses, and side effects of psychoactive drugs wm, ROBERT M.JULIEN M.D.. PH.D. Claire D. Advokat, Ph.D. Louisiana State University and Joseph
^ PRIMER OF DRUG ACTION A comprehensive gyide to the actions, uses, and side effects of psychoactive drugs wm, ROBERT M.JULIEN M.D.. PH.D. Claire D. Advokat, Ph.D. Louisiana State University and Joseph
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION. Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre
 1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
The official electronic file of this thesis or dissertation is maintained by the University Libraries on behalf of The Graduate School at Stony Brook
 Stony Brook University The official electronic file of this thesis or dissertation is maintained by the University Libraries on behalf of The Graduate School at Stony Brook University. Alll Rigghht tss
Stony Brook University The official electronic file of this thesis or dissertation is maintained by the University Libraries on behalf of The Graduate School at Stony Brook University. Alll Rigghht tss
Drugs 101: Behavioral Pharmacology
 Drugs 101: Behavioral Pharmacology Eb Blakely, Ph.D., BCBA-D Quest, Inc./Florida Institute of Technology Drug Facts Drug effects are dose-dependent Drugs effects are time-dependent Drugs are toxic at high
Drugs 101: Behavioral Pharmacology Eb Blakely, Ph.D., BCBA-D Quest, Inc./Florida Institute of Technology Drug Facts Drug effects are dose-dependent Drugs effects are time-dependent Drugs are toxic at high
Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology
 Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD February 2017 Lundbeck,
Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD February 2017 Lundbeck,
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Panax ginseng Attenuates MK-801-Induced Stereotypy in Mice
 스트레스硏究 : 第 17 卷第 4 號 2009 원저 Panax ginseng Attenuates MK-801-Induced Stereotypy in Mice *Kohwang Medical Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Medicinal Crops Division, Ginseng and Medicinal
스트레스硏究 : 第 17 卷第 4 號 2009 원저 Panax ginseng Attenuates MK-801-Induced Stereotypy in Mice *Kohwang Medical Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Medicinal Crops Division, Ginseng and Medicinal
1 BASIC NEUROSCIENCE. Basic Neuroscience
 1 BASIC NEUROSCIENCE QUESTION ONE An excitatory signal is received at the dendrite of a pyramidal glutamate neuron. When the signal is released from the incoming presynaptic dopaminergic axon, it is received
1 BASIC NEUROSCIENCE QUESTION ONE An excitatory signal is received at the dendrite of a pyramidal glutamate neuron. When the signal is released from the incoming presynaptic dopaminergic axon, it is received
Brian A. Coffman, PhD
 Brian A. Coffman, PhD Research Instructor Department of Psychiatry University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital Pittsburgh, PA Dr. Brian Coffman is a Research Instructor
Brian A. Coffman, PhD Research Instructor Department of Psychiatry University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital Pittsburgh, PA Dr. Brian Coffman is a Research Instructor
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia
 Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
Treatments for schizophrenia: a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs
 FEATURE REVIEW : a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs S Miyamoto 1, GE Duncan 2, CE Marx 3 and JA Lieberman 2 (2005) 10, 79 104 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group
FEATURE REVIEW : a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs S Miyamoto 1, GE Duncan 2, CE Marx 3 and JA Lieberman 2 (2005) 10, 79 104 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group
TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE
 TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE Angel Lago-Rodriguez 1, Binith Cheeran 2 and Miguel Fernández-Del-Olmo 3 1. Prism Lab, Behavioural Brain Sciences, School of
TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE Angel Lago-Rodriguez 1, Binith Cheeran 2 and Miguel Fernández-Del-Olmo 3 1. Prism Lab, Behavioural Brain Sciences, School of
Alcohol: Its effects on the brain and implications for future treatment. Dr Mark Daglish
 Alcohol: Its effects on the brain and implications for future treatment Senior Lecturer in Addiction Psychiatry University of Queensland Dr Mark Daglish Director of Addiction Psychiatry Royal Brisbane
Alcohol: Its effects on the brain and implications for future treatment Senior Lecturer in Addiction Psychiatry University of Queensland Dr Mark Daglish Director of Addiction Psychiatry Royal Brisbane
Schizophrenia and comorbid cannabis use disorders: Brain structure, function and the effect of antipsychotic medications Machielsen, Marise
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Schizophrenia and comorbid cannabis use disorders: Brain structure, function and the effect of antipsychotic medications Machielsen, Marise Link to publication Citation
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Schizophrenia and comorbid cannabis use disorders: Brain structure, function and the effect of antipsychotic medications Machielsen, Marise Link to publication Citation
Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
Neurofunctional Characterization of the At- Risk Mental State for Psychosis. Elizabeth Johnson Sumner. Department of Neurobiology Duke University
 Neurofunctional Characterization of the At- Risk Mental State for Psychosis Elizabeth Johnson Sumner Department of Neurobiology Duke University Date: Approved: R. Alison Adcock, Supervisor Jenni Groh,
Neurofunctional Characterization of the At- Risk Mental State for Psychosis Elizabeth Johnson Sumner Department of Neurobiology Duke University Date: Approved: R. Alison Adcock, Supervisor Jenni Groh,
C O N F I D E N T I A L ASSESSMENT OF XXX EFFECTS ON RECURRENT SEIZURE ACTIVITY IN THE RAT PILOCARPINE MODEL
 C O N F I D E N T I A L ASSESSMENT OF XXX EFFECTS ON RECURRENT SEIZURE ACTIVITY IN THE RAT PILOCARPINE MODEL 6 May 2015 This study was conducted under the terms of a Research Agreement between NeuroDetective
C O N F I D E N T I A L ASSESSMENT OF XXX EFFECTS ON RECURRENT SEIZURE ACTIVITY IN THE RAT PILOCARPINE MODEL 6 May 2015 This study was conducted under the terms of a Research Agreement between NeuroDetective
Investigaciones Biomédicas de Barcelona, CSIC (IDIBAPS), Barcelona, Spain. Running title: Monoamine receptors and antipsychotic action
 Current Pharmaceutical Design UNRAVELING MONOAMINE RECEPTORS INVOLVED IN THE ACTION OF TYPICAL AND ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS ON GLUTAMATERGIC AND SEROTONERGIC TRANSMISSION IN PREFRONTAL CORTEX Xavier López-Gil
Current Pharmaceutical Design UNRAVELING MONOAMINE RECEPTORS INVOLVED IN THE ACTION OF TYPICAL AND ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS ON GLUTAMATERGIC AND SEROTONERGIC TRANSMISSION IN PREFRONTAL CORTEX Xavier López-Gil
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: (Vraylar) Reference Number: CP.PMN.91 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 Line of Business: Commercial, Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy
Clinical Policy: (Vraylar) Reference Number: CP.PMN.91 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 Line of Business: Commercial, Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy
Presented at the American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting May 20 24, 2017 San Diego, CA.
 Original Presentations Key Words: amines, antipsychotic agents, double-blind method, mood disorders, psychopharmacology, psychotic disorders, schizophrenia, tardive dyskinesia, valbenazine Efficacy of
Original Presentations Key Words: amines, antipsychotic agents, double-blind method, mood disorders, psychopharmacology, psychotic disorders, schizophrenia, tardive dyskinesia, valbenazine Efficacy of
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
