MALARIOMETRIC SURVEY IN KEOUDOM DISTRICT, LAOS: SENSITIVITY OF PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM TO ANTI MALARIALS AND AUTOMEDICATION WITH CHLOROQUINE
|
|
|
- Nathan Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MALARIOMETRIC SURVEY IN KEOUDOM DISTRICT, LAOS: SENSITIVITY OF PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM TO ANTI MALARIALS AND AUTOMEDICATION WITH CHLOROQUINE Michal Giboda 1, Khomliene Pholsena2, Bouasy Hongvanthong2, Jaroslav Gutvirth 3 and Ivo Rubik4 linstitute of Parasitology, Czechoslovak Academy of Science, CS Ceske Budejovice, Branisovska 31, Czechoslovakia; 2Institute of Malaria and Parasitic Diseases, Ministry of Public Health, Vientiane, Lao People's Democratic Republic; 3Regional Hospital, CS Ceske Budejovice, Czechoslovakia; 4Institute of Tropical Health, Prague, Czechoslovakia. Abstract. A malariometric survey was conducted in the Keoudom District, in the northern part of Vientiane Province, Laos, where an artificial dam-lake on the Nam River is located. The parasite rate of the whole cohort representing 1,105 subjects was 2.44% with the predominance of Plasmodium vivax (70%), while P. Jalciparum represented 30% with the average parasite density index 3. The low spleen rate (2.3%) characterized the study area as a hypoendemic zone. IFAT antibodies were examined in 419 sub jects. The seropositivity of 195 persons < 15 years was 13.7% while in > 15 year old subjects seropositivity was 61.6% with a low GMRT in both groups (140 : 148). Automedication with aminoquinoline was assayed by urinary analysis in 125 outpatients. Of these, 36 (28.8%) were positive, 89 (71.2%) negative. The frequency of positive blood films for P. Jalciparum was higher in subjects with aminoquinoline in the urine (36.1 %) than in those without (IOJ %). Chloroquine sensitivity assay of 15 strains of P. Jalciparum displayed resistance in 39.3%. INTRODUCTION Laos is situated in the monsoon zone, its climate is mostly warm and humid. The coolest month is January, with an average temperature in the south of about 2YC, in the north 1ST. The dry winter season occurs between November and April, the wet season between May and October. Malarial transmission is perennial with its peak between July and August, the warmest months of the year. Plasmodium Jalciparum has been regarded as the dominant species in Laos, with the proportion reaching 75-95% (Pholsena, 1988). However, these data do not appear to be uniform throughout the country over time. Acheson (1970) in screening subjects participating in the construction of a dam on the Nam Ngum River in the Keoudom District, and members of their families, reported that the dominant species of the area was P. vivax (64%). Most of the data on prevalence of malaria in Laos have originated in diagnostic laboratories (passive case detection, PCD). Statistics of the In stitute of Malaria and Parasitic Diseases (lmpd) Vol 23 No 3 September 1992 in Vientiane indicated a slide-positivity rate (SPR) of 13.5% in Luang Prabang, 18% in Vientiane, 21.8% in Savanakhet, 5.6% in Champassak Prov inces (Pholsena, 1988). Our investigation conducted in the Keuodom District in the area of the Nam Ngum dam-lake followed these aims: (I) determination of endemi city of malaria in the area - blood examination for parasitemia, sera for antimalarial antibody; (2) sensitivity testing in vivo of P. Jalciparum to chloro quine and quinine; (3) to establish the extent of automedication with chloroquine which is freely available on the market. MATERIALS AND METHODS Description of the study area The Keoudom District occupies the northern part of Vientiane Province, at about 80 km from the capital, Vientiane. A major part of the District is occupied by lowlands with dispersed forest stands. The District holds the largest body of water in Laos - an artificial dam-lake on the Nam 383
2 SOUTHEAST ASEAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH Ngum River, covering about 420 km 2, its water table being about 200 m above sea level. The dam was constructed between 1968 and At the time of its construction, numerous Japanese, Thai and Lao workers acquired malaria (Ebisawa et ai, 1970). The dam-lake is surrounded by mountains, of which the highest is Phadang, altitude 1,621 m and its banks are lined by small villages. Baseline data for a malariometric survey were obtained from: (a) parasitological examination of blood films of all subjects present at the time in the villages (active case detection, ACD), (b) classification of spleen size according to Hackett's method (WHO, 1963) and (c) determination of antibody against P. Jalciparum antigen by a single cross-sectional survey. Our study was performed in August 1989 at the peak of the wet season, in four selected villages: 1. Khet Song inhabitants, 112 houses, 43% of inhabitants were examined. 2. Donmai -241 inhabitants, 50 houses, 83% of inhabitants were examined. 3. Nanin - situated in a forest-covered plane directly adjoining the Nam Ngum River, 430 inhabitants, 81 houses, 43% inhabitants were examined. 4. Camps of the power plant workers (PPW) and their families living under different hygienic conditions, 39% of the camp population were examined. Parasitological examination A malariological team examined thick and thin blood films of residents of each locality present at that time but a preference was give to the younger age groups. Spleen examination Splenic enlargement was assessed by palpation with the subject in an upright position, in every individual whose blood had been tested. In viyo test for response of P. falciparum to chloroquine and quinine. The test was made with outpatients of IMPD between June and July Chloroquine (25 mg chloroquine baselkg body wt) was administered in a three day course. 384 Quinine at a daily dose of 1.5 g was administered for 7 days. The results of the 10 days follow-up of the parasitemia was taken for the final evaluation of the in vivo test (Myint Lwin et ai, 1985; Giboda and Denis, 1988). Automedication with chloroquine Prior to microscopic examination of the blood, all outpatients of the IMPD were screened for 4 aminoquinoline in the urine using the Dill-Glasko test. If the blood film was positive for P. Jalciparum orland P. Jalciparum gametocytes, the record was made complete by adding the name of the locality in which infection had been contracted. RESULTS In 1988 the population of the Keoudom District numbered 15,970, of which 1,105 subjects (7%) were examined for the presence of plasmodia in the blood. Summarized results are presented in Table 1. The parasite rate of the whole cohort was 2.44%. A low prevalence rate was recorded in age group 0-2, regarded as the best indicator of a recent transmission of malaria. There was a predominance of P. vivax (70%), while P. Jalciparum represented 30%. The average parasite density index of P. Jalciparum was 3 representing asexual parasites in I III of blood. A comparison of data on P. Jalciparum parasitemia in patients examined at the IMPD, Vientiane is presented in Table 2. Parasitemia up to 10,00011l1 of blood occurred in 71.6% of the 67 positive subjects. High parasitemia (> 100,00011l1) was clustered in the age group < 10 years. Using the indirect immunofluorescence test (IFAT), 419 sera were examined for IgG antibody against the antigen of P. Jalciparum. Of these, 195 sera were from patients below the age of 15 years and 224 were from patients above this age (Table 3). In the group < 15 years, 86% of sera were negative, while in the group > 15 years, no antibody was detected in as few as 30% of the subjects examined. Serum negativity was highest in both age groups from the PPW camps. In the remaining three localities, most sera were obtained from subjects older than 15 years. The highest serum positivity was in the locality of Donmai, but the Vol 23 No 3 September 1992
3 MALARIOMETRIC SURVEY IN LAOS Table I Malariometric survey in Keoudom District, Vientiane Province, Laos. Total 1,105 examined subjects= 7.03% of the district population. Plasmodium Class of spleen enlargement Age Blood film Blood film Parasite species after Hackett groups examined positive rate Pf Fg Pv months months 44 I I 42 I 2-4 years years I years > 15 years Total 1, % 0.18% 1.71% Spleen rate = 2.3% Average enlarged spleen=j.5 + Pf= P. Jalciparum asexual forms, Fg = gametocytes of P. Jalciparum, Pv = P. vivax + + Average parasite density index = 3. Ratio of P. Jalciparum (70 : 30) Table 2 Para site count per mm} of blood by age group in 67 cases diagnosed at the Institute of Malaria and Parasitic Diseases, Vientiane, May - June Age group No. of 1,001-10,000-20,000-30,001-50,001 (years) infections ~ 1,000 9,999 19,999 30,000 50, ,000 > loo,qoo »00 232, , ;000 1,778, pOO ,615 > 50 Total % 56.7% 80.6% 83.6% 89.5% 100% + cumulative% Vol 23 No 3 September '
4 SOUTHEAST ASEAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH Table 3 IFA T antibodies against P. Jalciparum antigen in the sera of 419 inhabitants of 4 villages in Keoudom District, Vientiane Province, August Locality Age Reciprocal titers number of sera with final dilution (%). Serology Total negative ,024 2,048 4,096 8,192 positive GMRT+ < 15 years n= 189 (91.9) (6.7) (2.2) (9.0) 44 PPW Camps> 15 years n= 117 (50.4) (19.6) (1.7) (18.8) (4.3) (4.3) (0.8) (49.6) 88 < 15 years n=o 0 Keth Song > 15 years n=45 (42.4) (15.5) (4.4) (20.0) (8.9) (2.2) (2.2) (2.2) (2.2) (57.8) 133 < 15 years 0 2 n=2 (100) 125 Donmai > 15 years I 0 24 n=27 (11.1) (14.8) (7.4) (37.0) (7.4) (3.7) (14.8) (3.7) (88.9) 173 < 15 years I I 2 3 n=4 (25.0) (25.0) (50.0) (75.0) 3,235 Nanin > 15 years n=35 5 (14.3) I (2.8) (25.7) (11.4) (20.0) (11.4) (11.4) 0 I (2.8) 30 (85.7) 400 < 15 years I 2 I n= 195 (86.3) (6.3) (1.0) (2.0) (1.0) (1.0) (2.0) (13.7) Total > 15 years I 138 n=224 (38.9) (15.6) (2.7) (22.3) (6.7) (6.2) (4.5) (2.2) (0.9) (0.45) (61.1) from positive cases only Table 4 Parasitemia and IFAT antibodies in four localities tested. August Parasitemia IFA T antibodies Locality Blood films Parasite Plasmodium No. Positive for GMRT examined rate species tested antibodies < 15 yr > 15 yr < 15 yr> 15 yr Pf Pv < 15 yr > 15 yr < 15 yr > 15 yr < 15 yr > 15 yr PPW Camps (1.4) (3.4) (9.0) (49.6) Keth Song (2.2) (1.3) (57.8) Donmai (1.9) (2.1) (100) (88.9) Nanin , (3.1) (7.1) (75.0) (85.7) 386 Vol 23 No 3 September 1992
5 MALARIOMETRIC SURVEY IN LAOS Table 5 Presence of aminoquinolines in urine samples of 125 examined at the Institute of Malaria and Parasitic Diseases, Vientiane, June - July Dill - Glazko positive n= % Dill - Glazko negative n= % Positive for Pf % 9/10.1% Positive for Fg only 3 o Average parasitedensity index Table 6 Data on sensitivity of P. Jalciparum to chloroquine reported by different authors. Tested RI RII RIll Authors strains n= % 14.6% 4.6% Al Tawil (1977) n= % 26.3% 2.8% Pholsena (1988) n= % 13.3'Y(, 13.3% Giboda et al (1988) antibody level (GMRT) was highest in the locality of Nanin, corresponding to the highest prevalence of malaria (Table 4). GMRT for outpatients of the IMPD was 368, GMRT of hospitalized malaria patients was 1,893. Results of automedication with 4-aminoquino line obtained from outpatients of the IMPD are shown in Table 5. Using the Dill-Glasko test, we examined 125 patients. Of these, 36 (28.8'Yo) were positive, 89 (71.2%) negative. The frequency of positive blood films for P. Jalciparum was higher in subjects with 4-aminoquinoline in the urine than in those without it (36.1 ;;, : 10.1%). The parasite density index was identical in both groups (6.4 : 6.3). In addition, urine examinations of 40 other subjects from the Keoudom District were all negative. Sensitivity of P. Jalciparum to chloroquine was tested in 33 subjects, but the tests could be completed in only 15 of these. Six showed resistance, 2 each at RI, RII and RIll levels. DISCUSSION The prevalence of malaria was surprisingly low in our study groups. In July 1969, infection with malaria was found in 21.5% of subjects working on the dam-lake and in 24.7% of subjects inhabit ing the village of Thinkeo in the neighboljrhood of the dam-lake; the rate of infection was reduced by 1.6% and 7.2% respectively after one year of antimalarial control measures. P. vivax was predominant in both localities, 60"10 P. vivax; 40% P. Jalciparum (Acheson, 1970). However, in countries of Southeast Asia in which P. Jalciparum is regarded as the predominant species (Kondrashin, 1986) the ratio may be reversed in favor of P. vivax. During an ACD survey in Cambodia, provinces Takeo and Kompong Som, infection with P. vivax was predominant (80%) in 360 subjects from areas with a low prevalence of malaria (1-2%) (unpublished data). A similar distribution was reported from the Lower Mekong Basin in Vietnam among 95,979 persons screened. (Anonymous, 1971). A longitudinal serological survey of populations in endemic areas is needed to obtain information on how much a given pupulation is exposed to malaria infection. Our single cross-section survey gives only a window at one point in time. The results achieved showed that antibody levels in the inhabitants were directly proportional to the malaria endemicity in area. The low seropositivity Vol 23 No 3 September
6 SOUTHEAST ASEAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH in the age group < 15 years (Table 3) as well as low parasitemia in age group 0-2 years (Table I) suggested that both the intensity of transmission and the exposure must have been low. Serological surveillance is valid in this area where the parasite rate dropped below a value of 1-2% and P. vivax prevails (Wernsdorfer, 1979). To assess the trend of the malaria situation in Keoudom District further serological study is needed, particularly in the lower age groups. Automedication with antimalarials is common in endemic areas where the population is familiar with malaria symptoms (Facer et ai, 1990). Automedication may have a negative impact on the spread of resistant strains of P. Jalciparum. In respect to this statement it is interesting that P. Jalciparum gametocytes were present only in the blood of Dill-Glasko positive persons. Ebisawa et al (1970) were the first to point out a reduced sensitivity chloroquine in strains of P. Jalciparum from Laos. The first reliable report was made by AI Tawil (1977) who determined in vivo chloroquine sensitivity of 48 strains of P. Jalciparum from the surroundings of Vientiane using a 7 days follow-up observation period. Data on chloroquine sensitivity of 202 strains of P. Jalciparum were collected in IMPD between 1980 and 1986 (Pholsena, 1988). A comparison of earlier tests with recent ones indicated the relative number of resistant strains did not increase over more than 13 years except for a slight shift to category R III (Table 6). Because Vientiane Province was the site of origin of most of the tested strains in the three studies, the results gave a picture of dynamicslstability of resistance. The apparently constant level of resistance as well as degree of resistance in the zone of Vientiane Province is somewhat surprising but RIll degree of resistance is relatively rarely seen while RI and RII responses seem to remain more prevalent even in the oldest know foci (Wernsdorfer, 1981). The in vitro testing of sensitivity is necessary to determine the proportion of resistant/sensitive clones within P. Jalciparum strains circulated in the areas. So far quinine-resistant strains have not beeri reported from Laos, but we observed a reduced sensitivity to this drug evidencing itself in a prolonged disappearance of asexual parasites from the blood. REFERENCES Acheson MA. Report on a visit to Laos. Assignment Report, Mekong Committee, Anonymous. Malaria in the Lower Mekong Basin. UN Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East. Mekong Committee, Sixteenth Advisory Board Meeting, Sept Al Tawil N. Response offalciparum malaria to a standard regimen of chloroquine in Vientiane, Lao People's Democratic Republic. J Trap Med Hyg 1977; 81 : Ebisawa I, Muto T, Kameo S, Mitsni G. Response of Laotian malaria strains to chemotherapy. Jpn Exp Med 1970; 40 : Facer C, Lockyer M, Mitchell G, Pudney M, Walliker D. BSP Malaria meeting, February 1990; Parasitol Today 6 : Giboda M, Denis MB. Response of Kampuchean strain of Plasmodium Jalcjparum to antimalarials: in vivo assessment of quinine and quinine plus tetracycline; multiple drug resistance in vitro. J Trap Med Hyg 1988; 91 : Kondrashin AV. Malaria in Southeast Asia. Southeast Asian J Trap Med Public Health 1986; 17 : Lwin M, Htut A, Myint O. The in vivo and in vitro sensitivity of Plasmodium Jalcjparum to quinine. Southeast Asian J Trap Med Public Health 1985; 16 : Pholsena K. Contribution 11 la lutte anti-paludique en Republique Democratique Populaire Lao (Apercu historique caracteristiques epidemiologiques reponses aux mesures anti-paludiques). Institut de Malariologie et des Maladies Parasitaires, Ministere de la Sante Publique, Vientiane, PhD Thesis. Wernsdorfer WH. Serological methods as epidemiological tools in situations of disappearing malaria. In: Immunodiagnostic techniques in malaria, Transactions of the Third Meeting of the Scientific Working Group on the Immunology in Malaria. Panama, June UNDPlWORLD BANK/WHO, 1979: Wernsdorfer WH, ed. Drug-resistant Malaria. The Report of a Meeting held in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, August UNDP/WORLD BANK/ WHO. 1981: WHO. Terminology of Malaria and of Malaria Eradication. Geneva: WHO. Monogr Ser 1963; Vol 23 No 3 September 1992
ENDEMIC MALARIA IN FOUR VILLAGES IN ATTAPEU PROVINCE, LAO PDR
 ENDEMIC MALARIA IN FOUR VILLAGES IN ATTAPEU PROVINCE, LAO PDR R Phetsouvanh 1, I Vythilingam 2, B Sivadong 1, S Lokman Hakim 2, ST Chan 2 and S Phompida 1 1 Center for Malaria, Parasitology and Entomology,
ENDEMIC MALARIA IN FOUR VILLAGES IN ATTAPEU PROVINCE, LAO PDR R Phetsouvanh 1, I Vythilingam 2, B Sivadong 1, S Lokman Hakim 2, ST Chan 2 and S Phompida 1 1 Center for Malaria, Parasitology and Entomology,
SPECIAL REPORT* SEROEPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MALARIA IN DIFFERENT ENDEMIC AREAS OF INDONESIA
 SPECIAL REPORT* SEROEPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MALARIA IN DIFFERENT ENDEMIC AREAS OF INDONESIA Inge Sutanto, Wita Pribadi, Rusli Muljono, Lisawati Susanto, Rawina Sutjahjono, Hehdry Astuti and Rochida
SPECIAL REPORT* SEROEPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MALARIA IN DIFFERENT ENDEMIC AREAS OF INDONESIA Inge Sutanto, Wita Pribadi, Rusli Muljono, Lisawati Susanto, Rawina Sutjahjono, Hehdry Astuti and Rochida
DOUBLE BLIND RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL OF TWO DIFFERENT REGIMENS OF ORAL ARTESUNATE IN FALCIPARUM MALARIA
 DOUBLE BLIND RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL OF TWO DIFFERENT REGIMENS OF ORAL ARTESUNATE IN FALCIPARUM MALARIA Danai Bunnag, Chaisin Viravan, Sornchai Looareesuwan, Juntra Karbwang and T-ranakchit Harinasuta
DOUBLE BLIND RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL OF TWO DIFFERENT REGIMENS OF ORAL ARTESUNATE IN FALCIPARUM MALARIA Danai Bunnag, Chaisin Viravan, Sornchai Looareesuwan, Juntra Karbwang and T-ranakchit Harinasuta
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran
 Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran Aliehsan Heidari, Manizheh Nourian, Hossein Keshavarz Associate Prof. Dept.
Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran Aliehsan Heidari, Manizheh Nourian, Hossein Keshavarz Associate Prof. Dept.
APPENDIX 1 DATA COLLECTION AND DISSEMINATION STEPS
 APPENDIX 1 DATA COLLECTION AND DISSEMINATION STEPS 97 Country/ area APPENDIX 2a DRUG REGIMENS SEA REGION, 2001 (dosage for adults) : P. falciparum Lab confirmed Treatment failure Severe malaria Pregnancy
APPENDIX 1 DATA COLLECTION AND DISSEMINATION STEPS 97 Country/ area APPENDIX 2a DRUG REGIMENS SEA REGION, 2001 (dosage for adults) : P. falciparum Lab confirmed Treatment failure Severe malaria Pregnancy
REVIEW THE CHALLENGES OF MALARIA ELIMINATION IN YUNNAN PROVINCE, PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
 Malaria elimination in Yunnan, PR China REVIEW THE CHALLENGES OF MALARIA ELIMINATION IN YUNNAN PROVINCE, PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA Jianwei Xu and Hui Liu Yunnan Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Puer,
Malaria elimination in Yunnan, PR China REVIEW THE CHALLENGES OF MALARIA ELIMINATION IN YUNNAN PROVINCE, PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA Jianwei Xu and Hui Liu Yunnan Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Puer,
Anti-Malaria Chemotherapy
 Anti-Malaria Chemotherapy Causal Prophylaxis prevent infection (ie, liver stage) Suppressive Prophylaxis prevent clinical disease (ie, blood stages) Treatment Therapy (or clinical cure) relieve symptoms
Anti-Malaria Chemotherapy Causal Prophylaxis prevent infection (ie, liver stage) Suppressive Prophylaxis prevent clinical disease (ie, blood stages) Treatment Therapy (or clinical cure) relieve symptoms
Antimalarial drug resistance
 Antimalarial drug resistance Md Mushfiqur Rahman*, Leonard Ortega**, R M Rastogi* and Krongthong Thimasarn* Abstract Antimalarial drug resistance is of great concern in the WHO South-East Asia (SEA) Region.
Antimalarial drug resistance Md Mushfiqur Rahman*, Leonard Ortega**, R M Rastogi* and Krongthong Thimasarn* Abstract Antimalarial drug resistance is of great concern in the WHO South-East Asia (SEA) Region.
Ph.D. Thesis: Protective immune response in P.falciparum malaria 2011 CHAPTER I: Introduction. S.D. Lourembam 16
 CHAPTER I: Introduction S.D. Lourembam 16 1. INTRODUCTION Malaria remains a major global health problem with 300 to 500 million clinical infections and more than a million deaths reported each year. In
CHAPTER I: Introduction S.D. Lourembam 16 1. INTRODUCTION Malaria remains a major global health problem with 300 to 500 million clinical infections and more than a million deaths reported each year. In
DECLINING MEFLOQUINE SENSITIVITY OF PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM ALONG THE THAI-MYANMAR BORDER
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH DECLINING MEFLOQUINE SENSITIVITY OF PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM ALONG THE THAI-MYANMAR BORDER Chaiporn Rojanawatsirivet 1, Kanungnit Congpuong 1, Saowanit Vijaykadga
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH DECLINING MEFLOQUINE SENSITIVITY OF PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM ALONG THE THAI-MYANMAR BORDER Chaiporn Rojanawatsirivet 1, Kanungnit Congpuong 1, Saowanit Vijaykadga
College of Alternative Medicine, Ghana Abstract
 Assessment of Efficacy of Homoeopathic Remedies for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Malaria ( A Case Study in Effiduase, Sekyere East District of Ashanti Region Ghana) Article by Eric Gyamfi 1, John Awuni
Assessment of Efficacy of Homoeopathic Remedies for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Malaria ( A Case Study in Effiduase, Sekyere East District of Ashanti Region Ghana) Article by Eric Gyamfi 1, John Awuni
CLINICAL TRIALS OF MEFLOQUINE WITH TETRACYCLINE
 CLINICAL TRIALS OF MEFLOQUINE WITH TETRACYCLINE Danai Bunnag, Juntra Karbwang, Chaisin Viravan, Sunee Chitamas and Tranakchit Harinasuta Department of Clinical Tropical Medicine and Hospital for Tropical
CLINICAL TRIALS OF MEFLOQUINE WITH TETRACYCLINE Danai Bunnag, Juntra Karbwang, Chaisin Viravan, Sunee Chitamas and Tranakchit Harinasuta Department of Clinical Tropical Medicine and Hospital for Tropical
Malaria Risk Areas in Thailand Border
 Malaria Risk Areas in Thailand Border Natthawut Kaewpitoon PhD*, **, Ryan A Loyd MD***, Soraya J Kaewpitoon MD**, ***, Ratana Rujirakul MEd** * Faculty of Public Health, Vongchavalitkul University, Nakhon
Malaria Risk Areas in Thailand Border Natthawut Kaewpitoon PhD*, **, Ryan A Loyd MD***, Soraya J Kaewpitoon MD**, ***, Ratana Rujirakul MEd** * Faculty of Public Health, Vongchavalitkul University, Nakhon
GREATER MEKONG SUB-REGION ELIMINATION OF MALARIA (GEMS) PRIVATE SECTOR MALARIA SURVEILLANCE
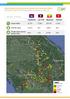 GREATER MEKONG SUB-REGION ELIMINATION OF MALARIA (GEMS) PRIVATE SECTOR MALARIA SURVEILLANCE JANUARY JUNE 218 Cambodia Lao PDR Myanmar Vietnam Cases tested 51,71 17,162 291,317 4,334 Positive cases 6,43
GREATER MEKONG SUB-REGION ELIMINATION OF MALARIA (GEMS) PRIVATE SECTOR MALARIA SURVEILLANCE JANUARY JUNE 218 Cambodia Lao PDR Myanmar Vietnam Cases tested 51,71 17,162 291,317 4,334 Positive cases 6,43
MALARIA INFECTION AMONG THE MIGRANT POPULATION ALONG THE THAI-MYANMAR BORDER AREA
 MALARIA INFECTION AMONG THE MIGRANT POPULATION ALONG THE THAI-MYANMAR BORDER AREA Wisit Chaveepojnkamjorn and Natchaporn Pichainarong Department of Epidemiology, Faculty of Public Health, Mahidol University,
MALARIA INFECTION AMONG THE MIGRANT POPULATION ALONG THE THAI-MYANMAR BORDER AREA Wisit Chaveepojnkamjorn and Natchaporn Pichainarong Department of Epidemiology, Faculty of Public Health, Mahidol University,
HALOFANTRINE HYDROCHLORIDE - EFFICACY AND SAFETY IN CHILDREN WITH ACUTE MALARIA
 HALOFANTRINE HYDROCHLORIDE - EFFICACY AND SAFETY IN CHILDREN WITH ACUTE MALARIA Pages with reference to book, From 8 To 10 Mushtaq A. Khan, Gui Nayyer Rehman, S.A. Qazi ( Children Hospital, Pakistan Institute
HALOFANTRINE HYDROCHLORIDE - EFFICACY AND SAFETY IN CHILDREN WITH ACUTE MALARIA Pages with reference to book, From 8 To 10 Mushtaq A. Khan, Gui Nayyer Rehman, S.A. Qazi ( Children Hospital, Pakistan Institute
Spatial distribution of malaria in Peninsular Malaysia from 2000 to 2009
 Alias et al. Parasites & Vectors 2014, 7:186 RESEARCH Spatial distribution of malaria in Peninsular Malaysia from 2000 to 2009 Open Access Haridah Alias 1*, Johari Surin 1, Rohela Mahmud 1, Aziz Shafie
Alias et al. Parasites & Vectors 2014, 7:186 RESEARCH Spatial distribution of malaria in Peninsular Malaysia from 2000 to 2009 Open Access Haridah Alias 1*, Johari Surin 1, Rohela Mahmud 1, Aziz Shafie
MONITORING THE THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY OF ANTIMALARIALS AGAINST UNCOMPLICATED FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH MONITORING THE THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY OF ANTIMALARIALS AGAINST UNCOMPLICATED FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND C Rojanawatsirivej 1, S Vijaykadga 1, I Amklad 1, P Wilairatna
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH MONITORING THE THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY OF ANTIMALARIALS AGAINST UNCOMPLICATED FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND C Rojanawatsirivej 1, S Vijaykadga 1, I Amklad 1, P Wilairatna
Managing malaria. Scenarios. Scenario 1: Border provinces, Cambodia. Key facts. Your target region: Cambodia /Thailand border
 Managing malaria Scenario 1: Border provinces, Cambodia You have been made responsible for three border provinces in Cambodia; Koh Kong Province, Perah Vihear Province and Sampovloun operational district.
Managing malaria Scenario 1: Border provinces, Cambodia You have been made responsible for three border provinces in Cambodia; Koh Kong Province, Perah Vihear Province and Sampovloun operational district.
How to design intranational deferral Malaria in Greece
 How to design intranational deferral Malaria in Greece Constantina Politis Coordinating Haemovigilance Centre (SKAE) Hellenic Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (KEELPNO) Malaria - Key Facts Malaria
How to design intranational deferral Malaria in Greece Constantina Politis Coordinating Haemovigilance Centre (SKAE) Hellenic Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (KEELPNO) Malaria - Key Facts Malaria
USE OF ROUTINELY COLLECTED PAST SURVEILLANCE DATA IN IDENTIFYING AND MAPPING HIGH-RISK AREAS IN A MALARIA ENDEMIC AREA OF SRI LANKA
 USE OF ROUTINELY COLLECTED PAST SURVEILLANCE DATA IN IDENTIFYING AND MAPPING HIGH-RISK AREAS IN A MALARIA ENDEMIC AREA OF SRI LANKA AR Wickremasinghe 1, DM Gunawardena 2 and STC Mahawithanage 3 1 Department
USE OF ROUTINELY COLLECTED PAST SURVEILLANCE DATA IN IDENTIFYING AND MAPPING HIGH-RISK AREAS IN A MALARIA ENDEMIC AREA OF SRI LANKA AR Wickremasinghe 1, DM Gunawardena 2 and STC Mahawithanage 3 1 Department
Interpretation of the World Malaria Report Country Profile
 Interpretation of the World Malaria Report Country Profile Acknowledgements This presentation was developed to help explain the components of the World Malaria Report Country Profile. The 2017 World Malaria
Interpretation of the World Malaria Report Country Profile Acknowledgements This presentation was developed to help explain the components of the World Malaria Report Country Profile. The 2017 World Malaria
Modeling of re-emerging Plasmodium vivax in the Northern Area of the Republic ofkorea Based on a Mathematical Model
 Journal of the Faculty of Environmental Science and Technology, Okayama University Vol.ll, No.I, pp.1-7, March 26 Modeling of re-emerging Plasmodium vivax in the Northern Area of the Republic ofkorea Based
Journal of the Faculty of Environmental Science and Technology, Okayama University Vol.ll, No.I, pp.1-7, March 26 Modeling of re-emerging Plasmodium vivax in the Northern Area of the Republic ofkorea Based
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF IMPORTED MALARIA CASES IN JORDAN BETWEEN 2000 AND 2005
 EPIDEMIOLOGY OF IMPORTED MALARIA CASES IN JORDAN BETWEEN 2000 AND 2005 Suleiman Meneizel MD*, Katiba Rabadi MD**, Hayel Muhareb, MD^, Ghassan Kawar MD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To determine some epidemiological
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF IMPORTED MALARIA CASES IN JORDAN BETWEEN 2000 AND 2005 Suleiman Meneizel MD*, Katiba Rabadi MD**, Hayel Muhareb, MD^, Ghassan Kawar MD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To determine some epidemiological
Malaria elimination in Jiangsu China
 Malaria elimination in Jiangsu China Prof. Gao Qi Jiangsu Institute of Parasitic Diseases, P.R. China APMEN VI Annual Business and Technical meeting Manila, The Philippines March 11-13, 2014 Geographical
Malaria elimination in Jiangsu China Prof. Gao Qi Jiangsu Institute of Parasitic Diseases, P.R. China APMEN VI Annual Business and Technical meeting Manila, The Philippines March 11-13, 2014 Geographical
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centers: Indication: Treatment: Objective: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The structure of the repetitive region of the. P. vivax CS protein appears to be more complex, with
 Antibody responses to Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax sporozoites in areas with stable and unstable malaria G. Del Giudice,l P.-H. Lambert,1 K. Mendis,2 A. Pessi,3 & M. Tanner4 Availability of synthetic
Antibody responses to Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax sporozoites in areas with stable and unstable malaria G. Del Giudice,l P.-H. Lambert,1 K. Mendis,2 A. Pessi,3 & M. Tanner4 Availability of synthetic
Sensitivity and Specificity of Rapid Diagnostic Test with Microscopic Gold Standard to Identify Plasmodium Species
 International Journal of Public Health Science (IJPHS) Vol.5, No.4, December2016, pp. 354~358 ISSN: 2252-8806 354 Sensitivity and Specificity of Rapid Diagnostic Test with Microscopic Gold Standard to
International Journal of Public Health Science (IJPHS) Vol.5, No.4, December2016, pp. 354~358 ISSN: 2252-8806 354 Sensitivity and Specificity of Rapid Diagnostic Test with Microscopic Gold Standard to
Malaria Situation and Plan for Elimination in China
 Malaria Situation and Plan for Elimination in China Dr. Guan Yayi National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, China CDC Current Situation Contents Vivax malaria in China The Support from Global Fund Malaria
Malaria Situation and Plan for Elimination in China Dr. Guan Yayi National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, China CDC Current Situation Contents Vivax malaria in China The Support from Global Fund Malaria
Plasmodium Vivax Malaria Transmission in a Network of Villages
 World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 44 28 Vivax Malaria Transmission in a Network of Villages P. Pongsumpun, and I. M. Tang Abstract Malaria is a serious, acute and chronic relapsing infection
World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 44 28 Vivax Malaria Transmission in a Network of Villages P. Pongsumpun, and I. M. Tang Abstract Malaria is a serious, acute and chronic relapsing infection
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article. DOI: /sjams India
 DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.6.22 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(6B):1981-198 5 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.6.22 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(6B):1981-198 5 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
Emergence of chikungunya in Moonlapamok and Khong Districts, Champassak Province, the Lao People s Democratic Republic, May to September 2012
 Outbreak Investigation Report Emergence of chikungunya in Moonlapamok and Khong Districts, Champassak Province, the Lao People s Democratic Republic, May to September 2012 Chanthavy Soulaphy, a Phouthone
Outbreak Investigation Report Emergence of chikungunya in Moonlapamok and Khong Districts, Champassak Province, the Lao People s Democratic Republic, May to September 2012 Chanthavy Soulaphy, a Phouthone
Ten year trend analysis of malaria prevalence in Kola Diba, North Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia
 Alemu et al. Parasites & Vectors 2012, 5:173 RESEARCH Open Access Ten year trend analysis of malaria prevalence in Kola Diba, North Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia Abebe Alemu *, Dagnachew Muluye, Mikrie Mihret,
Alemu et al. Parasites & Vectors 2012, 5:173 RESEARCH Open Access Ten year trend analysis of malaria prevalence in Kola Diba, North Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia Abebe Alemu *, Dagnachew Muluye, Mikrie Mihret,
Evaluation of Malaria Surveillance System in Hooghly district of West Bengal - India
 Original Research Article Evaluation of Malaria Surveillance System in Hooghly district of West Bengal - India Dan Amitabha 1,*, Kunal Kanti De 2, Pasi A R 3, Jalaluddeen M 4, Roy Bibhash 5 1 Airport Health
Original Research Article Evaluation of Malaria Surveillance System in Hooghly district of West Bengal - India Dan Amitabha 1,*, Kunal Kanti De 2, Pasi A R 3, Jalaluddeen M 4, Roy Bibhash 5 1 Airport Health
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 60(2), 1999, pp Copyright 1999 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 60(2), 1999, pp. 238 243 Copyright 1999 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, COMPARATIVE TRIAL OF A NEW ORAL COMBINATION OF ARTEMETHER
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 60(2), 1999, pp. 238 243 Copyright 1999 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND, COMPARATIVE TRIAL OF A NEW ORAL COMBINATION OF ARTEMETHER
MALARIA P. FALCIPARUM / P. VIVAX
 MALARIA P. FALCIPARUM / P. VIVAX 1. EXPLANATION OF THE TEST: Malaria is a serious, sometimes fatal, parasitic disease characterized by fever, chills, and anemia and is caused by a parasite that is transmitted
MALARIA P. FALCIPARUM / P. VIVAX 1. EXPLANATION OF THE TEST: Malaria is a serious, sometimes fatal, parasitic disease characterized by fever, chills, and anemia and is caused by a parasite that is transmitted
Directorate of National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme
 NATIONAL DRUG POLICY ON MALARIA (2008) Directorate of National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (Directorate General of Health Services) Ministry of Health and Family Welfare 22-Shamnath Marg,, Delhi-110054..
NATIONAL DRUG POLICY ON MALARIA (2008) Directorate of National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (Directorate General of Health Services) Ministry of Health and Family Welfare 22-Shamnath Marg,, Delhi-110054..
RECRUDESCENCE, POOR RESPONSE OR RESISTANCE TO QUININE OF FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND
 RECRUDESCENCE, POOR RESPONSE OR RESISTANCE TO QUININE OF FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND NIBHA JAROONVESAMA, TRANAKCHIT HAR1NASUTA*' and LAVAN MUANGMANEE Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and
RECRUDESCENCE, POOR RESPONSE OR RESISTANCE TO QUININE OF FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND NIBHA JAROONVESAMA, TRANAKCHIT HAR1NASUTA*' and LAVAN MUANGMANEE Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and
INTRODUCTION PATIENTS, MATERIALS, AND METHODS
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 66(5), 2002, pp. 492 502 Copyright 2002 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene A RETROSPECTIVE EXAMINATION OF SPOROZOITE-INDUCED AND TROPHOZOITE-INDUCED INFECTIONS
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 66(5), 2002, pp. 492 502 Copyright 2002 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene A RETROSPECTIVE EXAMINATION OF SPOROZOITE-INDUCED AND TROPHOZOITE-INDUCED INFECTIONS
Malaria Outbreak in District Korea, Chhattisgarh
 Malaria Outbreak in District Korea, Chhattisgarh A.K. Mishra, S.K. Chand Abstract Malaria is a major public health problem in India. Recently malaria, particularly that caused by Plasmodium falciparum
Malaria Outbreak in District Korea, Chhattisgarh A.K. Mishra, S.K. Chand Abstract Malaria is a major public health problem in India. Recently malaria, particularly that caused by Plasmodium falciparum
A Simple Dose Regimen of Artesunate and Amodiaquine Based on Arm Span- or Age Range for Childhood Falciparum Malaria: A Preliminary Evaluation
 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL PEDIATRICS, VOL. 58, NO. 4, 2012 A Simple Dose Regimen of Artesunate and Amodiaquine Based on Arm Span- or Age Range for Childhood Falciparum Malaria: A Preliminary Evaluation by Akintunde
JOURNAL OF TROPICAL PEDIATRICS, VOL. 58, NO. 4, 2012 A Simple Dose Regimen of Artesunate and Amodiaquine Based on Arm Span- or Age Range for Childhood Falciparum Malaria: A Preliminary Evaluation by Akintunde
RELAPSEIREINFECTION PATTERNS OF PLASMODIUM VIVAX INFECTION: A FOUR YEAR STUDY
 RELAPSEIREINFECTION PATTERNS OF PLASMODIUM VIVAX INFECTION: A FOUR YEAR STUDY RN Prasad', KJ Virk' and VP Sharma 2 'Malaria Research Centre, Field Station Khirni Bagh, Sadar Bazar, 'Shahjahanpur 242001
RELAPSEIREINFECTION PATTERNS OF PLASMODIUM VIVAX INFECTION: A FOUR YEAR STUDY RN Prasad', KJ Virk' and VP Sharma 2 'Malaria Research Centre, Field Station Khirni Bagh, Sadar Bazar, 'Shahjahanpur 242001
 Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
TECHNICAL REPORT SECOND SLIDE PANEL EXTERNAL QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAM FOR MALARIA MICROSCOPY DIAGNOSIS
 TECHNICAL REPORT SECOND SLIDE PANEL 2012-2013 EXTERNAL QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAM FOR MALARIA MICROSCOPY DIAGNOSIS REGIONAL MALARIA PROGRAM NEGLECTED, TROPICAL AND VECTOR-BORNE DISEASES COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
TECHNICAL REPORT SECOND SLIDE PANEL 2012-2013 EXTERNAL QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAM FOR MALARIA MICROSCOPY DIAGNOSIS REGIONAL MALARIA PROGRAM NEGLECTED, TROPICAL AND VECTOR-BORNE DISEASES COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
Southeast Asia and China FMD Campaign
 Southeast Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila SEACFMD Regional Coordinator OIE Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign FMD Status Risk factors The new SEACFMD Roadmap
Southeast Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila SEACFMD Regional Coordinator OIE Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign FMD Status Risk factors The new SEACFMD Roadmap
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 CHAPTER VIII SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Malaria is considered as the most widely occurring disease affecting humans of the world which gets spread by the bite of female Anopheles mosquito. It is so severe
CHAPTER VIII SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Malaria is considered as the most widely occurring disease affecting humans of the world which gets spread by the bite of female Anopheles mosquito. It is so severe
Road map for malaria control (and elimination): public health priorities
 Road map for malaria control (and elimination): public health priorities Anne E McCarthy, MD, FRCPC, DTM&H Director Tropical Medicine and International Health Clinic Ottawa Hospital Professor of Medicine
Road map for malaria control (and elimination): public health priorities Anne E McCarthy, MD, FRCPC, DTM&H Director Tropical Medicine and International Health Clinic Ottawa Hospital Professor of Medicine
Combination Anti-malarial Therapy and WHO Recommendations
 Prakaykaew Charunwatthana 2, and Sasithon Pukrittayakamee 1,2 1 Associate Fellow of the Royal Institute, Academy of Science 2 Department of Clinical Tropical Medicine, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol
Prakaykaew Charunwatthana 2, and Sasithon Pukrittayakamee 1,2 1 Associate Fellow of the Royal Institute, Academy of Science 2 Department of Clinical Tropical Medicine, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol
Update on autochthonous Plasmodium vivax malaria in Greece
 RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Update on autochthonous Plasmodium vivax malaria in Greece 11 October 2011 Main conclusions and recommendations Greece has reported thirty-six cases of Plasmodium vivax infection
RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Update on autochthonous Plasmodium vivax malaria in Greece 11 October 2011 Main conclusions and recommendations Greece has reported thirty-six cases of Plasmodium vivax infection
University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Bikaner), V.P.O. Bajor, Dist. Sikar, Rajasthan, India
 REVIEW ARTICLE www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Malaria, A Widely Prevalent Mosquito-Borne Infection in Humans and Recommended Herbal Therapy Subha Ganguly 1*, Satarupa Roy 2 1 Associate Department of Veterinary
REVIEW ARTICLE www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Malaria, A Widely Prevalent Mosquito-Borne Infection in Humans and Recommended Herbal Therapy Subha Ganguly 1*, Satarupa Roy 2 1 Associate Department of Veterinary
Risk of malaria in Travelers
 Malaria Prevention & Chemoprophylaxis Risk of malaria in Travelers Watcharapong Piyaphanee MD, Board Int Med, CTH, Dip Trav Med, MFTM RCPS (Glasgow) Travel Medicine Research Unit Faculty of Tropical Medicine,
Malaria Prevention & Chemoprophylaxis Risk of malaria in Travelers Watcharapong Piyaphanee MD, Board Int Med, CTH, Dip Trav Med, MFTM RCPS (Glasgow) Travel Medicine Research Unit Faculty of Tropical Medicine,
Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Malaysia; 2
 SEROPREVALENCE OF RICKETSIAL ANTIBODIES AMONG URBAN MALAYSIANS ANTIBODY PREVALENCE OF ORIENTIA TSUTSUGAMUSHI, RICKETTSIA TYPHI AND TT118 SPOTTED FEVER GROUP RICKETTSIAE AMONG MALAYSIAN BLOOD DONORS AND
SEROPREVALENCE OF RICKETSIAL ANTIBODIES AMONG URBAN MALAYSIANS ANTIBODY PREVALENCE OF ORIENTIA TSUTSUGAMUSHI, RICKETTSIA TYPHI AND TT118 SPOTTED FEVER GROUP RICKETTSIAE AMONG MALAYSIAN BLOOD DONORS AND
40% (90% (500 BC)
 MALARIA causative agent = Plasmodium species 40% of world s population lives in endemic areas 3-500 million clinical cases per year 1.5-2.7 million deaths (90% Africa) known since antiquity early medical
MALARIA causative agent = Plasmodium species 40% of world s population lives in endemic areas 3-500 million clinical cases per year 1.5-2.7 million deaths (90% Africa) known since antiquity early medical
Against intervention No recommendation Strong Conditional Conditional Strong. For intervention. High Moderate Low Very low
 Draft recommendation: Consider using MDA as an additional tool for the elimination of malaria in low prevalence island or nonisland settings where the risk of imported malaria is low Balance of desirable
Draft recommendation: Consider using MDA as an additional tool for the elimination of malaria in low prevalence island or nonisland settings where the risk of imported malaria is low Balance of desirable
HUMASIS MALARIA ANTIGEN TEST HIGH SENSITIVE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF MALARIA INFECTION
 HUMASIS MALARIA ANTIGEN TEST HIGH SENSITIVE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF MALARIA INFECTION References 1) World Malaria Report 2010, WHO 2) Rapid diagnostic tests for malaria parasites, Clin. Microbiol. Rev.
HUMASIS MALARIA ANTIGEN TEST HIGH SENSITIVE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF MALARIA INFECTION References 1) World Malaria Report 2010, WHO 2) Rapid diagnostic tests for malaria parasites, Clin. Microbiol. Rev.
14th Stakeholders Meeting
 14th Stakeholders Meeting Steady progress towards malaria elimination: Interventions for today and tomorrow Denpasar, Bali 11 12 October 2017 Dr. Iriani Samad : INDONESIA S PROGRESS IN MALARIA ELIMINATION
14th Stakeholders Meeting Steady progress towards malaria elimination: Interventions for today and tomorrow Denpasar, Bali 11 12 October 2017 Dr. Iriani Samad : INDONESIA S PROGRESS IN MALARIA ELIMINATION
In several African countries in sub-saharan Africa, malaria is the leading cause of death in children under five.
 TECHNICAL SEMINAR - MALARIA SLIDE 1 Technical Seminar - Malaria Malaria is an extremely important cause of mortality in different parts of world. In this technical seminar, I ll discuss the rationale for
TECHNICAL SEMINAR - MALARIA SLIDE 1 Technical Seminar - Malaria Malaria is an extremely important cause of mortality in different parts of world. In this technical seminar, I ll discuss the rationale for
Malaria. Population at Risk. Infectious Disease epidemiology BMTRY 713 (Lecture 23) Epidemiology of Malaria. April 6, Selassie AW (DPHS) 1
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Progress on the Containment of Artemisinin Tolerant Malaria Parasites in South-East Asia (ARCE) Initiative
 Progress on the Containment of Artemisinin Tolerant Malaria Parasites in South-East Asia (ARCE) Initiative I. Background For many years, the border area between Cambodia and Thailand has been the source
Progress on the Containment of Artemisinin Tolerant Malaria Parasites in South-East Asia (ARCE) Initiative I. Background For many years, the border area between Cambodia and Thailand has been the source
38 Current Concepts in
 38 Current Concepts in Management of Falciparum Malaria Abstract: Artemisinin based Combination Therapy (ACT) is the preferred agent to treat drug resistance uncomplicated Plasmodium Falciparum (PF) Malaria.
38 Current Concepts in Management of Falciparum Malaria Abstract: Artemisinin based Combination Therapy (ACT) is the preferred agent to treat drug resistance uncomplicated Plasmodium Falciparum (PF) Malaria.
Prevalence of Human Malaria Infection in Lal Qilla Pakistan
 American Journal of Biomedical Sciences ISSN: 1937-9080 nwpii.com/ajbms Prevalence of Human Malaria Infection in Lal Qilla Pakistan Akbar Hussain 1, Tauseef Ahmad *1, Syyed Gauhar Jamal 2, Inamullah 2
American Journal of Biomedical Sciences ISSN: 1937-9080 nwpii.com/ajbms Prevalence of Human Malaria Infection in Lal Qilla Pakistan Akbar Hussain 1, Tauseef Ahmad *1, Syyed Gauhar Jamal 2, Inamullah 2
South East Asia and China FMD Campaign
 South East Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila Regional Coordinator OUTLINE The new SEACFMD FMD Status SEACFMD Activities 2009/2010 SEACFMD Plan 2010/2011 The OIE General Assembly has approved
South East Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila Regional Coordinator OUTLINE The new SEACFMD FMD Status SEACFMD Activities 2009/2010 SEACFMD Plan 2010/2011 The OIE General Assembly has approved
Activities of the OIE Sub-Regional Representation for South-East Asia
 Activities of the OIE Sub-Regional Representation for South-East Asia Ronello C. Abila Sub-Regional Representative Staff of SRR SE Asia Ronello Abila Sub-Regional Representative Dirk Van Aken Deputy Sub-Regional
Activities of the OIE Sub-Regional Representation for South-East Asia Ronello C. Abila Sub-Regional Representative Staff of SRR SE Asia Ronello Abila Sub-Regional Representative Dirk Van Aken Deputy Sub-Regional
Malaria Updates. Fe Esperanza Espino Department of Parasitology Research Institute for Tropical Medicine
 Malaria Updates Fe Esperanza Espino Department of Parasitology Research Institute for Tropical Medicine Outline General epidemiology of malaria in the Philippines P falciparum Updates in treatment Recognizing
Malaria Updates Fe Esperanza Espino Department of Parasitology Research Institute for Tropical Medicine Outline General epidemiology of malaria in the Philippines P falciparum Updates in treatment Recognizing
FMD Control in South East Asia: science based approach to development of roadmaps and PVS Tools to support capacity building.
 FMD Control in South East Asia: science based approach to development of roadmaps and PVS Tools to support capacity building Ronello Abila Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign
FMD Control in South East Asia: science based approach to development of roadmaps and PVS Tools to support capacity building Ronello Abila Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign
Usefulness of Modified Centrifuged Blood Smear in Diagnosis of Malaria
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 3(2016) pp. 764-769 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.503.088
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 3(2016) pp. 764-769 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.503.088
Importance of active case detection in a malaria elimination programme
 Wickremasinghe et al. Malaria Journal 2014, 13:186 RESEARCH Open Access Importance of active case detection in a malaria elimination programme Renu Wickremasinghe 1,3*, Sumadhya Deepika Fernando 2,3, Janani
Wickremasinghe et al. Malaria Journal 2014, 13:186 RESEARCH Open Access Importance of active case detection in a malaria elimination programme Renu Wickremasinghe 1,3*, Sumadhya Deepika Fernando 2,3, Janani
S Krudsood 1, K Chalermrut 2, C Pengruksa 2, S Srivilairit 2, U Silachamroon 3, S Treeprasertsuk 3, S Kano 4, GM Brittenham 5 and S Looareesuwan 3
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL OF TWO-FIXED COMBINATIONS DIHYDROARTEMISININ-NAPTHOQUINE- TRIMETHOPRIM (DNP ) AND ARTEMETHER-LUMEFANTRINE (COARTEM / RIAMET ) IN THE
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL OF TWO-FIXED COMBINATIONS DIHYDROARTEMISININ-NAPTHOQUINE- TRIMETHOPRIM (DNP ) AND ARTEMETHER-LUMEFANTRINE (COARTEM / RIAMET ) IN THE
Copyright by Population Services International and ACTwatch 2016.
 Malaria markets in the Greater Mekong Sub-Region: 2015-2016 1 Copyright by Population Services International and ACTwatch 2016. Suggested Citation: Malaria Markets in the Greater Mekong Sub-Region: 2015-2016.
Malaria markets in the Greater Mekong Sub-Region: 2015-2016 1 Copyright by Population Services International and ACTwatch 2016. Suggested Citation: Malaria Markets in the Greater Mekong Sub-Region: 2015-2016.
Overview of human cases of AI H5N1 since 1997
 Overview of human cases of AI H5N1 since 1997 Dr Sylvie Briand WHO Global Influenza Programme 7 October 2008 1 FAO-OIE- WHO Joint Technical Consultation on AI at the Human-Animal Interface Review of the
Overview of human cases of AI H5N1 since 1997 Dr Sylvie Briand WHO Global Influenza Programme 7 October 2008 1 FAO-OIE- WHO Joint Technical Consultation on AI at the Human-Animal Interface Review of the
Epidemiological trends of malaria in an endemic district Tumkur, Karnataka
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Krishna C et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Jun;4(6):2141-2145 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Krishna C et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Jun;4(6):2141-2145 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
Alberta Health Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines July 2012
 July 2012 Malaria Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition Confirmed Case Laboratory confirmation
July 2012 Malaria Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition Confirmed Case Laboratory confirmation
This Malaria Operational Plan has been approved by the U.S. Global Malaria Coordinator and reflects collaborative discussions with the national
 This Malaria Operational Plan has been approved by the U.S. Global Malaria Coordinator and reflects collaborative discussions with the national malaria control programs and partners in country. The final
This Malaria Operational Plan has been approved by the U.S. Global Malaria Coordinator and reflects collaborative discussions with the national malaria control programs and partners in country. The final
MALARIA SELF-CARE IN NIMBORAN SUBDISTRICT, JAYAPURA DISTRICT, PAPUA PROVINCE, INDONESIA
 Malaria Self-care, Papua Province, Indonesia MALARIA SELF-CARE IN NIMBORAN SUBDISTRICT, JAYAPURA DISTRICT, PAPUA PROVINCE, INDONESIA Betty Roosihermiatie 1, Widjiartini 1, Astridya Paramita 1, Agung Nugroho
Malaria Self-care, Papua Province, Indonesia MALARIA SELF-CARE IN NIMBORAN SUBDISTRICT, JAYAPURA DISTRICT, PAPUA PROVINCE, INDONESIA Betty Roosihermiatie 1, Widjiartini 1, Astridya Paramita 1, Agung Nugroho
Hui Liu 1, Jian-Wei Xu 1*, Qi-Zhang Xu 2 and Yi-Rou Zeng 3
 Liu et al. BMC Public Health (2018) 18:560 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5469-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Retrospective analysis of risk factors of slide positivity among febrile patients in the
Liu et al. BMC Public Health (2018) 18:560 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5469-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Retrospective analysis of risk factors of slide positivity among febrile patients in the
S Pinlaor 1, K Ieamviteevanich 2, P Pinlaor 3, W Maleewong 1 and V Pipitgool 1
 SEROPREVALENCE OF SPECIFIC TOTAL IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Ig), IgG AND IgM ANTIBODIES TO TOXOPLASMA GONDII IN BLOOD DONORS FROM LOEI PROVINCE, NORTHEAST THAILAND S Pinlaor 1, K Ieamviteevanich 2, P Pinlaor 3, W
SEROPREVALENCE OF SPECIFIC TOTAL IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Ig), IgG AND IgM ANTIBODIES TO TOXOPLASMA GONDII IN BLOOD DONORS FROM LOEI PROVINCE, NORTHEAST THAILAND S Pinlaor 1, K Ieamviteevanich 2, P Pinlaor 3, W
MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY
 MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY Calvin L. Wilson MD Clinical Professor of Family Medicine and Public Health University of Colorado Anschutz OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the unique characteristics
MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY Calvin L. Wilson MD Clinical Professor of Family Medicine and Public Health University of Colorado Anschutz OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the unique characteristics
Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance (MBDS) Network
 center for health and aging Health Information Technology and Policy Lab Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance (MBDS) Network MBDS Network Partners, with support from The Rockefeller Foundation Summary After
center for health and aging Health Information Technology and Policy Lab Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance (MBDS) Network MBDS Network Partners, with support from The Rockefeller Foundation Summary After
MESA research grants 2014
 MESA research grants 2014 MESA operational research grant Principal investigator Mopping up and getting to zero: mapping residual malaria transmission for targeted response in urban Lusaka, Zambia. Daniel
MESA research grants 2014 MESA operational research grant Principal investigator Mopping up and getting to zero: mapping residual malaria transmission for targeted response in urban Lusaka, Zambia. Daniel
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MALARIA IN AN AREA OF LOW TRANSMISSION IN CENTRAL INDIA
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 75(5), 2006, pp. 812 816 Copyright 2006 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MALARIA IN AN AREA OF LOW TRANSMISSION IN CENTRAL INDIA NEERU SINGH,*
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 75(5), 2006, pp. 812 816 Copyright 2006 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MALARIA IN AN AREA OF LOW TRANSMISSION IN CENTRAL INDIA NEERU SINGH,*
Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR
 J Trop Med Parasitol. 2009;32:23-9. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR Khemphavanh
J Trop Med Parasitol. 2009;32:23-9. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR Khemphavanh
The Relationships between Temperature, Rainfall and the Incidence Rate of Malaria in South East Asia: A Panel Data Analysis
 The Relationships between Temperature, Rainfall and the Incidence Rate of Malaria in South East Asia: A Panel Data Analysis Karnjana Songwathana 1 ABSTRACT The malaria incidence varies greatly in South
The Relationships between Temperature, Rainfall and the Incidence Rate of Malaria in South East Asia: A Panel Data Analysis Karnjana Songwathana 1 ABSTRACT The malaria incidence varies greatly in South
Driving access to medicine
 Driving access to medicine An example from the Novartis Malaria Initiative Hans Rietveld Director, Market Access & Capacity Building Novartis Malaria Initiative Social Forum - Geneva February 20, 2015
Driving access to medicine An example from the Novartis Malaria Initiative Hans Rietveld Director, Market Access & Capacity Building Novartis Malaria Initiative Social Forum - Geneva February 20, 2015
Blood Smears Only 19 May Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 9 May 205 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 9 May 205 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING
 VERSION 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/01/2016 MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING MALARIA MICROSCOPY STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE MM-SOP-09 1. PURPOSE AND SCOPE To describe the procedure for counting malaria parasites on
VERSION 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/01/2016 MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING MALARIA MICROSCOPY STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE MM-SOP-09 1. PURPOSE AND SCOPE To describe the procedure for counting malaria parasites on
Influenza Update N 157
 Influenza Update N 157 13 April 2012 Summary In most areas of the northern hemisphere temperate regions, influenza activity appears to have peaked and is declining. In North America, influenza indicators
Influenza Update N 157 13 April 2012 Summary In most areas of the northern hemisphere temperate regions, influenza activity appears to have peaked and is declining. In North America, influenza indicators
Overview of Malaria Epidemiology in Ethiopia
 Overview of Malaria Epidemiology in Ethiopia Wakgari Deressa, PhD School of Public Health Addis Ababa University Symposium on Neuro-infectious Disease United Nations Conference Center, AA February 28,
Overview of Malaria Epidemiology in Ethiopia Wakgari Deressa, PhD School of Public Health Addis Ababa University Symposium on Neuro-infectious Disease United Nations Conference Center, AA February 28,
Accepted for Publication, Published online February 10, 2014; doi: /ajtmh
 Accepted for Publication, Published online February 10, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.13-0636. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.13-0636 In order to provide our readers with timely
Accepted for Publication, Published online February 10, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.13-0636. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.13-0636 In order to provide our readers with timely
SEACFMD ACTIVITIES FOCUS ON
 SEACFMD ACTIVITIES FOCUS ON 2012-2014 EXPANDED 3RD COORDINATION COMMITTEE MEETING OF OIE/JTF PROJECT ON FMD CONTROL IN ASIA LANZHOU, PR CHINA SEPTEMBER 24, 2014 Dr Karan Kukreja Project Officer OIE Sub-Regional
SEACFMD ACTIVITIES FOCUS ON 2012-2014 EXPANDED 3RD COORDINATION COMMITTEE MEETING OF OIE/JTF PROJECT ON FMD CONTROL IN ASIA LANZHOU, PR CHINA SEPTEMBER 24, 2014 Dr Karan Kukreja Project Officer OIE Sub-Regional
DETERMINING COST-EFFECTIVENESS AND COST COMPONENT OF THREE MALARIA DIAGNOSTIC MODELS BEING USED IN REMOTE NON-MICROSCOPE AREAS
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH DETERMINING COST-EFFECTIVENESS AND COST COMPONENT OF THREE MALARIA DIAGNOSTIC MODELS BEING USED IN REMOTE NON-MICROSCOPE AREAS P Bualombai 1, S Prajakwong 2, N
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH DETERMINING COST-EFFECTIVENESS AND COST COMPONENT OF THREE MALARIA DIAGNOSTIC MODELS BEING USED IN REMOTE NON-MICROSCOPE AREAS P Bualombai 1, S Prajakwong 2, N
FACTS. Approximately 2.48 million malaria cases are reported annually from South Asia. Of Which 75% cases are contributed by India alone.
 MALARIA 2 FACTS Approximately 2.48 million malaria cases are reported annually from South Asia. Of Which 75% cases are contributed by India alone. The magnitude of the problem is further enhanced by P
MALARIA 2 FACTS Approximately 2.48 million malaria cases are reported annually from South Asia. Of Which 75% cases are contributed by India alone. The magnitude of the problem is further enhanced by P
Summary World Malaria Report 2010
 Summary The summarizes information received from 106 malaria-endemic countries and other partners and updates the analyses presented in the 2009 Report. It highlights continued progress made towards meeting
Summary The summarizes information received from 106 malaria-endemic countries and other partners and updates the analyses presented in the 2009 Report. It highlights continued progress made towards meeting
Malaria: Prevention remains our best measure for controlling the disease
 http://www.medicine-on-line.com Malaria: 1/10 Malaria: Prevention remains our best measure for controlling the disease Author: Supervisor: Affiliation: Naomi Cheng Professor Julia Ling The Chinese University
http://www.medicine-on-line.com Malaria: 1/10 Malaria: Prevention remains our best measure for controlling the disease Author: Supervisor: Affiliation: Naomi Cheng Professor Julia Ling The Chinese University
Invest in the future, defeat malaria
 Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Strategy to move from accelerated burden reduction to malaria elimination in the GMS by 2030
 Strategy to move from accelerated burden reduction to malaria elimination in the GMS by 2030 Dr Walter M Kazadi Coordinator Regional Hub Emergency Response to Artemisinin Resistance Regional Hub GMS MMV
Strategy to move from accelerated burden reduction to malaria elimination in the GMS by 2030 Dr Walter M Kazadi Coordinator Regional Hub Emergency Response to Artemisinin Resistance Regional Hub GMS MMV
Malaria. An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture
 Malaria An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture Malaria Malaria is the most important of all tropical parasitic disease,causes death and debility and is endemic throughout the tropics
Malaria An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture Malaria Malaria is the most important of all tropical parasitic disease,causes death and debility and is endemic throughout the tropics
Essential Medicines. WHO
 12 Health Technology and Pharmaceuticals Participants to the Workshop on Pharmaceutical Policies and Access to Good Quality Essential Medicines for Pacific Island Countries observing pharmaceutical services
12 Health Technology and Pharmaceuticals Participants to the Workshop on Pharmaceutical Policies and Access to Good Quality Essential Medicines for Pacific Island Countries observing pharmaceutical services
falciparum malaria in Brazil
 Bulletin ofthe World Health Organization, 63 (3): 603-609 (1985) i World Health Organization 1985 An open, randomized, phase III clinical trial of mefloquine and of quinine plus sulfadoxinepyrimethamine
Bulletin ofthe World Health Organization, 63 (3): 603-609 (1985) i World Health Organization 1985 An open, randomized, phase III clinical trial of mefloquine and of quinine plus sulfadoxinepyrimethamine
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEILLANCE REPORT Malaria in Greece, 2012
 HELLENIC CENTRE FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION MINISTRY OF HEALTH Page 1 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEILLANCE REPORT Malaria in Greece, 2012 Introduction Malaria is a parasitic infection, transmitted through
HELLENIC CENTRE FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION MINISTRY OF HEALTH Page 1 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEILLANCE REPORT Malaria in Greece, 2012 Introduction Malaria is a parasitic infection, transmitted through
