Index. 2-(a-Hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole (HBB),143 Hypotonicity,
|
|
|
- Candice McKinney
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Index N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,240 Actinomycin D, 39, 86, 116, 314 Adsorption of bacteriophage, on F pili, 36 of picornavirus, 119 of reovirus, Alfalfa mosaic virus, 66, 78, 90 top a, 73, 88 Alphavirus, 172 Arbovirus, see Togavirus Assembly of bacteriophage, models, 38 of plant virus, Bacillus stearothermophilus ribosome, II Bacillus subtilis ribosome, 26 Bacteria metabolism and bacteriophage infection, Bacteriophage RNA-containing, see RNA bacteriophage f2, 4-6, 9, 14, 19, 20 fr, 19 GA,19 MS2, 5, 12-16, 18, 19 M12,4 Q{j,4-9, 12-16, 19,20,29-31,34,81 3R,19 R17, 4-9,12-19 Barley stripe mosaic virus, 64, 78 Binding site, ribosomal, Bluetongue virus, 243, 248, , 263, Bovine enterovirus, 120, 124 Broadbean mottle virus, Bromalein, 176 Brome mosaic virus, 63, 72, 73, 78, 81-83,86-88,90-93 Bromovirus, 66 Budding of togavirus, 191, Capsid, empty, 142 Cardiovirus, 109, 120 Carlavirus, 64 Carnation latent virus, 64 Cauliflower mosaic virus, 63, 66 Cell culture of plant tissue, 62 Chikungunya virus, 173, 181 Chloramphenicol, 86 p-chloromercuribenzoate, 240 Cholesterol, viral, 187, 188 Chrysanthemum stunt disease, 71 Cistron of coat protein, of maturation protein, of polymerase protein, II, Citrus exocortis disease, 71 viroid,63 Coat protein, 12 cistron, properties, repression, repressor role, synthesis, initiation of, 25 Comovirus, 65
2 336 Index Complementation, 33-35, ,305 Cordycepin, 144 Cowpea mosaic virus, 65, 78, 85, 86, 90, 91 Cross reaction, 282 of unfolded protein, 9 Cucumber mosaic virus, 81 Cycloheximide, 143,314 Cytopathology, Cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (CPV), , ,254,256, 258, , , ,318 Dengue virus, 173, 175, 181 Deoxyribonucleic acid, see DNA Detergent, 177 2,6-Diaminopurine, 145 Diphtheria toxin, 144 Dithiothreitol, 176 DNA cellular, viral, , D-particle of orbivirus, 247, 249, Eastern equine encephalitis virus, 173 Eclipse of bacteriophage, 37 Encephalomyocarditis virus, 120, 133 Enterovirus, 109 Ethidium bromide, 145,314 Exocytosis, 193 Fatty acids, viral, Fiji disease virus, 238, 243, 251, 255, 319 Flavovirus, 172,B-Fluorophenylalanine (FPA), Fluorouracil,40, 145 Foot-and-mouth disease virus, 123, 150,B-Galactosidase, 41 Gliotoxin, 145,B-Glucosidase, 240 Glycoprotein, viral, , Guanidine, Growth curve, viral, , Hemagglutination, Herpes simplex virus, 122 Hybridization, RNA-RNA, (a-Hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole (HBB),143 Hypotonicity, Infection of plant tissue by viruses, by abrasion, 70 early events, efficiency, 70 Interference, 122, Interferon, induced by double-stranded RNA, 122 Japanese encephalitis virus, 173, 176, 186, 214,218 Kunjin virus, 173 Lettuce necrotic yellow virus, Lipase, 176 Lipids viral, L-particle of orbivirus, 247, 249, of RNA bacteriophage, 3 Maize rough dwarf virus, 238, 243, ,265,319 Maturation protein cistron, properties, Mengovirus, 124 N-Methyl-isatin-,B-4':4 ' dibutylthiosemicarbazone, 145 Morphogenesis, Murray Valley encephalitis virus, 181 Nepovirus, 65 Nucleocapsid, 183, Nucleotide sequence, 154 rate of addition, Oat sterile dwarf virus, 238 Oligonucleotide, , Orbivirus, , 236, 241, 247, ,256,263 D-particle, 247, 249, L-particle, 247, 249, polypeptide, replication, RNA, 258, 263
3 Index 337 Orbivirus (cont.) transcriptase, 277 Orthoreovirus, see Reovirus Pactamycin, 127, 144 Pangola stunt virus, 238 Particle, defective-interfering, 153, Pea enation mosaic virus, 66, 91 Penetration of bacteriophage, of picornavirus, 120 Periodate, 240 PFU, see Plaque-forming unit Phenethyl alcohol, 144 Phospholipase, 176 Phospholipids, viral, , 199 Picornavirus adsorption, 119 capsid, empty, 113 cardiovirus, 109 and cells, , chemistry, complementation, defective-interfering particle, 153 discoveries, RNA polymerase, 110 replicative form of RNA, 111 translation of polycistronic gene product, 111. elution, 120 enterovirus, 109 environmental factors, genetics, history, homology in nucleotide sequence, 154 hybridization of RNA-RNA, 154 hypotonicity, infection, early events, infectivity of RNA, inhibition of DNA synthesis, of protein of host cell, of RNA synthesis, interference, maturation, 118 membrane, role of, morphogenesis, multiplication inhibited, Picornavirus (cont.) mutant, 147 agents, 148 temperature-sensitive, particle, defective-interfering (01), 153 penetration, 120 recombination, genetic, reproduction, rescue phenomenon, 151 rhinovirus, 109 sedimentation coefficient, 113 specificity, 121 structure, synthesis of protein, of viral RNA, terminology, 109 Pilus, 36 Plant reoviruses, see Reoviruses Plant RNA viruses, Plaque-forming unit (PFU), 115, Polarity of translation, Poliovirus interference, 122 length of RNA, 114 purified, 114 RNA, length of, 114 type I, L Sc 2ab, 149 Polymerase, see RNA polymerase Polyribosome, Potato spindle tuber disease, 71 viroid,63 Potato virus X, 64 Potato virus Y, 64 Potato yellow dwarf virus, 63, 64 Potexvirus, 64 Potyvirus, 64 Procapsid, see Capsid, empty Proflavine, 145 Protein, viral, , kinetics, polypeptide, , 185,213 synthesis, translation, in vitro, Protomer, immature, 142 Puromycin, 143, 144,206,314 Pyronine, 145 Raspberry ringspot virus, 91
4 338 Index Reoviridae capsid polypeptides, capsomers, classification, cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus, 234 orbivirus, 233 orthoreovirus, 233 core polypeptides, discovery of double-stranded RNA, 231 morphogenesis, morphology, nature of virion, 235 nucleotide addition, rate of, occurrence, properties, 243 reproduction, RNA, nature of, spikes, , 252 stability against physical agents, 256 transcriptase, , 285, 287 transcription, Reovirus, , , 256, ,274,278, adsorption, capsid polypeptides, cell, DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, complementation, 305 DNA synthesis by cell, enumeration of particles, formation of RNA, genome of ten segments, 305 growth cycle, one-step, hemagglutination, inhibitors, interferon, messenger RNA, ten species of, 297 transcription, translation, morphology, mutant of Fields and Joklik, of genome segment deletion, 311 of Ikegami and Gomatos, 310 temperature-sensitive, oligonucleotides, , particle enumeration, of plants, 234, , , ,274,278, Reovirus (cont.) plaque formation, protein synthesis of cell, purification, replication, RNA, formation, messenger, transcriptase, transcription of mrna, in vitro, in vivo, translation of mrna, in vitro, in vivo, uncoating, uptake, Replicase, see RNA polymerase Replication of viral nucleic acid, 71-86, Replication complex, 116, 119, 132 Replicative form (RF), see RNA replicative form Replicative intermediate (RI), Repression, 16 Reproduction of picornavirus, of reoviridae, of RNA bacteriophage, I-59 of RNA plant virus, of togavirus, Rescue phenomenon, 151 RF, see RNA replicative form Rhinovirus, 109 RI, see Replicative intermediate ~ j b o n u c4, l 180 e a s e, Ribosome of Bacillus stearothermophilus, II, 26 of Bacillus subtilis, 26 binding site, of Escherichia coli, 26 specificity, 26 Rice dwarf virus, 238, 243, 251, 255, 258, 265,319 Rifampicin, 38 RNA bacteriophage adsorption, assembly, coat protein, 19 complementary strand, 33-35
5 Index 339 RNA bacteriophage (cont.) discovery, I eclipse, 37 genes, 2 genome structure primary, 25 secondary, 25 and host metabolism, L-particle, 3 minus strand, 8 nascent RNA, particles, 2-3 penetration, plus strand, 8 properties, 2-20 release from cell, 38 replication, in vitro, 29 in vivo, replicative form, 28, replicative intermediate, 28, reproduction, I-59 strand, complementary, minus, 8 plus, 8 structure, primary, 4-5 secondary, 18 tertiary, 18 synthesis, and host metabolism, ' -terminus, ' -terminus, 5-7 translation, RNA ligase, 140 RNA, messenger, , RNA plant viruses, see individual viruses assembly, classification, genome of virus, host-virus system, infection, early events, properties, replication of viral nucleic acid, mechanism, site of, in vitro, in vivo, replicate form (RF), replicate intermediate (RI), 78 RNA plant viruses (cont.) reproduction, RNA, low molecular weight (LMC), RNA properties, translation of viral nucleic acid, control mechanism, in infected tissues, transmission, types, virus-host system, RNA polymerase, RNA-dependent, 4, 20,23,29,81-84, , , ,285,287 cistron, 11,15,16 host cell factors, inhibition, 123 of orbivirus, 277 protein, 13,20 Q(3, 29-31, 34, 81 repression, 16 translation, 27 RNA replicative form (RF), 77-78, III, RNA replicative intermediate (RI), 28, 201 RNA, viral, interjacent, , 208, 209 messenger, synthesis, replication mechanism, time course, 131 Satellite tobacco necrosis virus, 65, 72, 74 Satellite tobacco ringspot virus, 65, 72 Scrapie, 63 Semliki forest virus, 173, 181, 188, 192, 193,196,198 Sindbis virus, 173, 174, , 192, 196, 197,211 Sparsomycin, 144 Spikes, , 252 st. Louis encephalitis virus, 173, 181, Thiouracil,95 Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), 61, 64, 72, 77,79,80-88,93 Tobacco necrosis virus, 87 Tobacco rattle virus, 64, 72, 89, 95 RNA, long, 75
6 340 Index Tobacco rattle virus (cant.) satellite, 73 short, 74 Tobacco ringspot virus, 65, 72, 78, 81 Tobacco streak virus, 91; see also Satellite tobacco viruses Tobravirus, see Tobacco rattle virus Togavirus budding, 191, carbohydrates, 184 cholesterol, 187, 188 composition, chemical, by electron microscopy, 173, 174 cytopathology, density, 174 effect of enzyme on, 176 exocytosis, 193 fatty acids, genetics, glycoprotein, , glycosylation, 212 group A, 173 group B, 173 growth curve, infection of cell, lipids, messenger RNA, viral, morphogenesis, mutant, temperature-sensitive, 197 nucleocapsid, 183, particle, defective-interfering, phospholipids, , 199 polymerase, viral RNA, polypeptide, 185,213 properties, , 183 protein, viral, , purification, replication, reproduction, Togavirus (cant.) RNA, viral, , messenger, transcription, sedimentation coefficient, 177 ~ r u c t u r ~ symmetry, 177 terminology, , 183 transcription, of viral RNA, Tomato bushy stunt virus, 65 Tomato spotted wilt virus, 63, 66 Tombusvirus, 65 Transcriptase, see RNA polymerase Transcription, , Translation, control, 27 of mrna, polarity, of protein, regulation, 20-22, 25 of viral nucleic acid, in vitro, 24 Transmission of plant viruses, Trypsin, 176 Turnip yellow mosaic virus, 65, 77, 79, 81-83,86,94,95 Tymovirus, 65 Uncoating, Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, 173 Vesicular stomatitis virus, 122 Viroid, 63, 72 RNA, Virus, see individual viruses Western equine encephalitis virus, 173, 181 Wound tumor virus (WTV), 63, 65, ,243, , ,256,258,264,265,319
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES
 STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
Viruses defined acellular organisms genomes nucleic acid replicate inside host cells host metabolic machinery ribosomes
 The Viruses Viruses Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid, obligately replicate inside host cells using host metabolic machinery and ribosomes to form a pool
The Viruses Viruses Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid, obligately replicate inside host cells using host metabolic machinery and ribosomes to form a pool
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Introduction to viruses. BIO 370 Ramos
 Introduction to viruses BIO 370 Ramos 1 2 General Structure of Viruses Size range most
Introduction to viruses BIO 370 Ramos 1 2 General Structure of Viruses Size range most
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Chapter 13. Viruses, Viroides and Prions
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroides and Prions 1 A GLIMPSE OF HISTORY Tobacco mosaic disease (1890s) D. M. Iwanowsky, Martinus Beijerinck determined caused by filterable virus too small to be seen with light
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroides and Prions 1 A GLIMPSE OF HISTORY Tobacco mosaic disease (1890s) D. M. Iwanowsky, Martinus Beijerinck determined caused by filterable virus too small to be seen with light
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2. Bacteriophages. 3. Animal Viruses. 4. Viroids & Prions
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Multiplication of RNA Plant Viruses. C.L. Mandahar
 Multiplication of RNA Plant Viruses C.L. Mandahar MULTIPLICATION OF RNA PLANT VIRUSES Multiplication of RNA Plant Viruses by C. L. MANDAHAR Botany Department, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India A C.I.P.
Multiplication of RNA Plant Viruses C.L. Mandahar MULTIPLICATION OF RNA PLANT VIRUSES Multiplication of RNA Plant Viruses by C. L. MANDAHAR Botany Department, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India A C.I.P.
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. What exactly is a Virus? 11/7/ Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2.
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Reoviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
Size nm m m
 1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University Modified by Ossi Turunen, Aalto University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids,
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University Modified by Ossi Turunen, Aalto University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids,
Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions SLOs What are the Characteristics
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions SLOs What are the Characteristics
Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses. Virus Characteristics. Viral Host Range
 Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses Topics Characteristics Structure/Classification Multiplication Cultivation and replication Non-viral infectious agents Treatment 1 Virus Characteristics obligate intracellular
Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses Topics Characteristics Structure/Classification Multiplication Cultivation and replication Non-viral infectious agents Treatment 1 Virus Characteristics obligate intracellular
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Virology. What is a virus? How do viruses differ from cellular microorganisms?
 Virology What is a virus? How do viruses differ from cellular microorganisms? 1. Acellular o consist of a particle consisting of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat. o In extracellular form a virus
Virology What is a virus? How do viruses differ from cellular microorganisms? 1. Acellular o consist of a particle consisting of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat. o In extracellular form a virus
VIRUSES. 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart.
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR VIRUSES 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart. Viral Part Description of Part 2. Some viruses have an envelope
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR VIRUSES 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart. Viral Part Description of Part 2. Some viruses have an envelope
Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions General Characteristics of Viruses Obligatory intracellular parasites
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions General Characteristics of Viruses Obligatory intracellular parasites
Virus Basics. General Characteristics of Viruses. Chapter 13 & 14. Non-living entities. Can infect organisms of every domain
 Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-forms Commonly referred to by organism they infect
Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-forms Commonly referred to by organism they infect
The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents. Acellular Agents
 viruses protein and nucleic acid viroids RNA virusoids RNA prions proteins The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents Acellular Agents Viruses major cause of
viruses protein and nucleic acid viroids RNA virusoids RNA prions proteins The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents Acellular Agents Viruses major cause of
Virus Basics. General Characteristics of Viruses 5/9/2011. General Characteristics of Viruses. Chapter 13 & 14. Non-living entities
 Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-formsf Commonly referred to by organism they infect
Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-formsf Commonly referred to by organism they infect
History of Virology. Russian Bacteriologist Dimitri Iwanowski TMD tobacco mosaic disease TMV isolated and purified
 Viruses & Prions Viruses Virus miniscule, acellular, infectious agent having one or several pieces of either DNA or RNA No cytoplasmic membrane, cytosol, organelles Cannot carry out any metabolic pathway
Viruses & Prions Viruses Virus miniscule, acellular, infectious agent having one or several pieces of either DNA or RNA No cytoplasmic membrane, cytosol, organelles Cannot carry out any metabolic pathway
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Viral reproductive cycle
 Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses
 Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses 7:1 Viral Structure and Classification VIRUS: a biological particle composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protein coat CAPSID: protein coat surrounding a
Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses 7:1 Viral Structure and Classification VIRUS: a biological particle composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protein coat CAPSID: protein coat surrounding a
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
19 Viruses BIOLOGY. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Structural Features and Characteristics
 9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
Introductory Virology. Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS
 Introductory Virology Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS Lecture outline Definition of viruses and general characteristics Structure of virus (virion) Chemical composition of viruses Virus morphology
Introductory Virology Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS Lecture outline Definition of viruses and general characteristics Structure of virus (virion) Chemical composition of viruses Virus morphology
General Virology I. Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department
 General Virology I Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department ١ General Virology I Lecture Outline Introduction istory Definition
General Virology I Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department ١ General Virology I Lecture Outline Introduction istory Definition
NOMENCLATURE & CLASSIFICATION OF PLANT VIRUSES. P.N. Sharma Department of Plant Pathology, CSK HPKV, Palampur (H.P.)
 NOMENCLATURE & CLASSIFICATION OF PLANT VIRUSES P.N. Sharma Department of Plant Pathology, CSK HPKV, Palampur (H.P.) What is the purpose of classification? To make structural arrangement comprehension for
NOMENCLATURE & CLASSIFICATION OF PLANT VIRUSES P.N. Sharma Department of Plant Pathology, CSK HPKV, Palampur (H.P.) What is the purpose of classification? To make structural arrangement comprehension for
Viruses. An Illustrated Guide to Viral Life Cycles to Accompany Lecture. By Noel Ways
 Viruses An Illustrated Guide to Viral Life Cycles to Accompany Lecture By Noel Ways Viral Life Cycle Step #1, Adhesion: During adhesion, specific receptors for specific molecules on potential host cell
Viruses An Illustrated Guide to Viral Life Cycles to Accompany Lecture By Noel Ways Viral Life Cycle Step #1, Adhesion: During adhesion, specific receptors for specific molecules on potential host cell
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION
 VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
5/6/17. Diseases. Disease. Pathogens. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Pathogens are disease-causing organisms
 5/6/17 Disease Diseases I. II. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Biol 105 Chapter 13a Pathogens Pathogens are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic.
5/6/17 Disease Diseases I. II. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Biol 105 Chapter 13a Pathogens Pathogens are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic.
How could the small size of viruses have helped researchers detect viruses before the invention of the electron microscope? 13-1
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 5 6 Chapter 3 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions General Characteristics of Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses Obligatory intracellular parasites Contain DNA or RNA Contain a protein
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 5 6 Chapter 3 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions General Characteristics of Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses Obligatory intracellular parasites Contain DNA or RNA Contain a protein
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses
 Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
VIRUS VIROID PRION. Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, Mahidolwittayanusorn School
 VIRUS VIROID PRION Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, Mahidolwittayanusorn School What is virus? Living? Need food? Reproduction? Cell? Cytoplasm? Cell membrane? Metabolism? Size? Component? Adenovirus
VIRUS VIROID PRION Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, Mahidolwittayanusorn School What is virus? Living? Need food? Reproduction? Cell? Cytoplasm? Cell membrane? Metabolism? Size? Component? Adenovirus
Viruses. Properties. Some viruses contain other ingredients (e.g., lipids, carbohydrates), but these are derived from their host cells.
 Viruses Properties They are obligate intracellular parasites. Probably there are no cells in nature that escape infection by one or more kinds of viruses. (Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.)
Viruses Properties They are obligate intracellular parasites. Probably there are no cells in nature that escape infection by one or more kinds of viruses. (Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.)
the world and viruses
 More than 5,450 viruses belonging to more than 2,000 species, 287 genera, 73 families and 3 orders are recognized in the 8th ICTVreport report. the world and viruses 1 1889 H2N2 Emerging viruses in the
More than 5,450 viruses belonging to more than 2,000 species, 287 genera, 73 families and 3 orders are recognized in the 8th ICTVreport report. the world and viruses 1 1889 H2N2 Emerging viruses in the
AP Biology Reading Guide. Concept 19.1 A virus consists of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 19: Viruses Overview Experimental work with viruses has provided important evidence that genes are made of nucleic acids. Viruses were also important in working out
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 19: Viruses Overview Experimental work with viruses has provided important evidence that genes are made of nucleic acids. Viruses were also important in working out
Virus and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation - 1
 Virus and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation - 1 We have discussed the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA duplication and in transcription and protein synthesis. We now turn to how cells regulate
Virus and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation - 1 We have discussed the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA duplication and in transcription and protein synthesis. We now turn to how cells regulate
2) What is the difference between a non-enveloped virion and an enveloped virion? (4 pts)
 Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
8/13/2009. Diseases. Disease. Pathogens. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. Bacteria Shapes. Domain Bacteria Characteristics
 Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus?
 Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus? A virus is an invective agent consisting of a nucleic acid in a protein coat, able to multiply only within the living cells of a host. A bacteriophage ( bacteria
Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus? A virus is an invective agent consisting of a nucleic acid in a protein coat, able to multiply only within the living cells of a host. A bacteriophage ( bacteria
III. What are the requirements for taking and passing this course?
 1 Molecular Virology Lecture # 1: Course Introduction I. Instructor and Background Dr. Richard Kuhn rjkuhn@bragg.bio.purdue.edu B-129 Lilly Hall 494-1164 Office Hours - Wednesday 10:30-11:30 II. Objective:
1 Molecular Virology Lecture # 1: Course Introduction I. Instructor and Background Dr. Richard Kuhn rjkuhn@bragg.bio.purdue.edu B-129 Lilly Hall 494-1164 Office Hours - Wednesday 10:30-11:30 II. Objective:
Picornaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
MINUTES OF THE THIRD MEETING OF ICTV held in MADRID, 12 and 16 September 1975
 MINUTES OF THE THIRD MEETING OF ICTV held in MADRID, 12 and 16 September 1975 3/1 Members present 12 September - 32 16 September - 34 3/2. Elections. Prof. R.E.F. MATTHEWS was elected president (unanimously)
MINUTES OF THE THIRD MEETING OF ICTV held in MADRID, 12 and 16 September 1975 3/1 Members present 12 September - 32 16 September - 34 3/2. Elections. Prof. R.E.F. MATTHEWS was elected president (unanimously)
Chair of Medical Biology, Microbiology, Virology, and Immunology STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND PHYSIOLOGY OF VIRUSES
 Chair of Medical Biology, Microbiology, Virology, and Immunology STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND PHYSIOLOGY OF VIRUSES Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites, which by definition contain either
Chair of Medical Biology, Microbiology, Virology, and Immunology STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND PHYSIOLOGY OF VIRUSES Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites, which by definition contain either
Viruses Tomasz Kordula, Ph.D.
 Viruses Tomasz Kordula, Ph.D. Resources: Alberts et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell, pp. 295, 1330, 1431 1433; Lehninger CD Movie A0002201. Learning Objectives: 1. Understand parasitic life cycle of
Viruses Tomasz Kordula, Ph.D. Resources: Alberts et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell, pp. 295, 1330, 1431 1433; Lehninger CD Movie A0002201. Learning Objectives: 1. Understand parasitic life cycle of
19/06/2013. Viruses are not organisms (do not belong to any kingdom). Viruses are not made of cells, have no cytoplasm, and no membranes.
 VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
Overview of virus life cycle
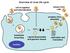 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
11/15/2011. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Viral Genomes. Structural Features and Characteristics
 Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
Structure & Function of Viruses
 Structure & Function of Viruses Discovery of Viruses Louis Pasteur- looks for a causative agent for rabies, says too small, can not find it 1892 Dimitry Ivanosky- studies tobacco disease, can not find
Structure & Function of Viruses Discovery of Viruses Louis Pasteur- looks for a causative agent for rabies, says too small, can not find it 1892 Dimitry Ivanosky- studies tobacco disease, can not find
Virus Infections and Hosts
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44597 1 Virus Infections and Hosts OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44597 1 Virus Infections and Hosts OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Chapter 25. 바이러스 (The Viruses)
 Chapter 25 바이러스 (The Viruses) Generalized Structure of Viruses 2 2 Virus Classification Classification based on numerous characteristics Nucleic acid type Presence or absence of envelope Capsid symmetry
Chapter 25 바이러스 (The Viruses) Generalized Structure of Viruses 2 2 Virus Classification Classification based on numerous characteristics Nucleic acid type Presence or absence of envelope Capsid symmetry
ICTVdB Virus Descriptions
 [Home] [Index of Viruses ] [Descriptions] [ Character List ] [ Picture Gallery ] [ Interactive Key ] [ Data Entry] [ 2002 ICTV] ICTVdB Virus Descriptions Descriptions are generated automatically from the
[Home] [Index of Viruses ] [Descriptions] [ Character List ] [ Picture Gallery ] [ Interactive Key ] [ Data Entry] [ 2002 ICTV] ICTVdB Virus Descriptions Descriptions are generated automatically from the
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
Basic Properties of Viruses and Virus Cell Interaction
 WBV5 6/27/03 10:28 PM Page 49 Basic Properties of Viruses and Virus Cell Interaction II PART VIRUS STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION CLASSIFICATION SCHEMES THE BEGINNING AND END OF THE VIRUS REPLICATION CYCLE
WBV5 6/27/03 10:28 PM Page 49 Basic Properties of Viruses and Virus Cell Interaction II PART VIRUS STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION CLASSIFICATION SCHEMES THE BEGINNING AND END OF THE VIRUS REPLICATION CYCLE
Bacteriophage Reproduction
 Bacteriophage Reproduction Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles The following information is taken from: http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/index.html#charvir Bacteriophage Structure More complex
Bacteriophage Reproduction Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles The following information is taken from: http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/index.html#charvir Bacteriophage Structure More complex
I. Bacteria II. Viruses including HIV. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. 5. Cell wall present in many species. 6. Reproduction by binary fission
 Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including are disease-causing organisms Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including are disease-causing organisms Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Virology Introduction. Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment.
 DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
Genomes and Genetics
 Genomes and Genetics Lecture 3 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016...everywhere an interplay between nucleic acids and proteins; a spinning wheel in which the thread makes the spindle and the spindle
Genomes and Genetics Lecture 3 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016...everywhere an interplay between nucleic acids and proteins; a spinning wheel in which the thread makes the spindle and the spindle
Translation. Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation of eukaryotic translation involves many initiation factors
 Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Proposed EPPO validation of plant viral diagnostics using next generation sequencing
 Proposed EPPO validation of plant viral diagnostics using next generation sequencing Ian Adams, Ummey Hany, Rachel Glover, Erin Lewis, Neil Boonham, Adrian Fox Adoption of Next Generation Sequencing for
Proposed EPPO validation of plant viral diagnostics using next generation sequencing Ian Adams, Ummey Hany, Rachel Glover, Erin Lewis, Neil Boonham, Adrian Fox Adoption of Next Generation Sequencing for
Nucleic acid: singled stranded, double stranded, RNA, or DNA, linear or circular. Capsid: protein coat that is most of the mass of the virus.
 Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses 1. Depending on view may be regarded as exceptionally complex aggregates of nonliving chemicals or as exceptionally simple living microbes. 2. Contain a single
Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses 1. Depending on view may be regarded as exceptionally complex aggregates of nonliving chemicals or as exceptionally simple living microbes. 2. Contain a single
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Viruses. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Viruses CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin
Viruses CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin
LEC 2, Medical biology, Theory, prepared by Dr. AYAT ALI
 General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
Structural biology of viruses
 Structural biology of viruses Biophysical Chemistry 1, Fall 2010 Coat proteins DNA/RNA packaging Reading assignment: Chap. 15 Virus particles self-assemble from coat monomers Virus Structure and Function
Structural biology of viruses Biophysical Chemistry 1, Fall 2010 Coat proteins DNA/RNA packaging Reading assignment: Chap. 15 Virus particles self-assemble from coat monomers Virus Structure and Function
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
numbe r Done by Corrected by Doctor
 numbe r 5 Done by Mustafa Khader Corrected by Mahdi Sharawi Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh Viral Replication Mechanisms: (Protein Synthesis) 1. Monocistronic Method: All human cells practice the monocistronic
numbe r 5 Done by Mustafa Khader Corrected by Mahdi Sharawi Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh Viral Replication Mechanisms: (Protein Synthesis) 1. Monocistronic Method: All human cells practice the monocistronic
One of the classifications was if the virus is enveloped or naked.
 Last time we gave an introduction about viruses, we talked about; definition of viruses, characters of viruses, structures of viruses and classification of viruses. One of the classifications was if the
Last time we gave an introduction about viruses, we talked about; definition of viruses, characters of viruses, structures of viruses and classification of viruses. One of the classifications was if the
AP Biology. Viral diseases Polio. Chapter 18. Smallpox. Influenza: 1918 epidemic. Emerging viruses. A sense of size
 Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Multiplication. Bernard Roizman. General Concepts
 Multiplication Bernard Roizman General Concepts The pathologic effects of viral diseases result from (a) toxic effect of viral genes products on the metabolism of infected cells, (b) reactions of the host
Multiplication Bernard Roizman General Concepts The pathologic effects of viral diseases result from (a) toxic effect of viral genes products on the metabolism of infected cells, (b) reactions of the host
Virology. *Viruses can be only observed by electron microscope never by light microscope. The size of the virus: nm in diameter.
 Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability
 Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions CHAPTER SUMMARY Viruses, viroids, and prions are acellular (noncellular) disease-causing agents that lack cell structure and cannot metabolize,
Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions CHAPTER SUMMARY Viruses, viroids, and prions are acellular (noncellular) disease-causing agents that lack cell structure and cannot metabolize,
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Viruses. Picture from:
 Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
Aseptic meningitis: inflammation of meninges with sterile CSF (without any causative organisms which can be grown on culture media).
 You have to refer to the slides, since I have included the extra information only. Slide #1: Both illnesses aseptic meningitis and encephalitis can be caused by the same viruses; that viruses which cause
You have to refer to the slides, since I have included the extra information only. Slide #1: Both illnesses aseptic meningitis and encephalitis can be caused by the same viruses; that viruses which cause
Name Class Date. Infection in which a virus inserts its nucleic acid into the DNA of the host cell and is duplicated with the cell s DNA
 Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
Subject Index. Budding of frog virus 3, study by immunological and cytochemical methods in electron microscopy 305
 Subject Index Adenovirus, simian adenovirus 7 infectious DNA-protein complex 54 Adenovirus type 12, transformation characteristics of temperature-sensitive mutants Antibody - hepatitis B subtypes in chimpanzees
Subject Index Adenovirus, simian adenovirus 7 infectious DNA-protein complex 54 Adenovirus type 12, transformation characteristics of temperature-sensitive mutants Antibody - hepatitis B subtypes in chimpanzees
Dr. Gary Mumaugh. Viruses
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Viruses Viruses in History In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch found evidence that the cause of foot-and-mouth disease in livestock was an infectious particle smaller than any
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Viruses Viruses in History In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch found evidence that the cause of foot-and-mouth disease in livestock was an infectious particle smaller than any
D. J. Dargan,* C. B. Gait and J. H. Subak-Sharpe
 Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 407-411. Printed in Great Britain 407 The effect of cicloxolone sodium on the replication in cultured cells of adenovirus type 5, reovirus type 3, poliovirus type
Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 407-411. Printed in Great Britain 407 The effect of cicloxolone sodium on the replication in cultured cells of adenovirus type 5, reovirus type 3, poliovirus type
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh
 number 3 Done by Mahdi Sharawi Corrected by Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh *Note: Please go back to the slides to view the information that the doctor didn t mention. Prions Definition: Prions are rather ill-defined
number 3 Done by Mahdi Sharawi Corrected by Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh *Note: Please go back to the slides to view the information that the doctor didn t mention. Prions Definition: Prions are rather ill-defined
Medical Virology. Herpesviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, and Retro virus. - Herpesviruses Structure & Composition: Herpesviruses
 Medical Virology Lecture 2 Asst. Prof. Dr. Dalya Basil Herpesviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, and Retro virus - Herpesviruses Structure & Composition: Herpesviruses Enveloped DNA viruses. All herpesviruses have
Medical Virology Lecture 2 Asst. Prof. Dr. Dalya Basil Herpesviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, and Retro virus - Herpesviruses Structure & Composition: Herpesviruses Enveloped DNA viruses. All herpesviruses have
VIROLOGY PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS WILEY. John B. Carter and Venetia A. Saunders
 VIROLOGY PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS John B. Carter and Venetia A. Saunders WILEY -urief Contents Preface to Second Edition xix Preface to First Edition xxi Abbreviations Used in This Book xxiii Greek
VIROLOGY PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS John B. Carter and Venetia A. Saunders WILEY -urief Contents Preface to Second Edition xix Preface to First Edition xxi Abbreviations Used in This Book xxiii Greek
Viruses. Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus
 Viruses Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus What is a virus? A virus is a microscopic, infectious agent that may infect any type of living cell. Viruses must infect living cells in order to make more
Viruses Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus What is a virus? A virus is a microscopic, infectious agent that may infect any type of living cell. Viruses must infect living cells in order to make more
19 2 Viruses Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 What Is a Virus? What Is a Virus? Viruses are particles of nucleic acid, protein, and in some cases, lipids. Viruses can reproduce only by infecting living cells. 2 of 34 What Is a Virus? Viruses
1 of 34 What Is a Virus? What Is a Virus? Viruses are particles of nucleic acid, protein, and in some cases, lipids. Viruses can reproduce only by infecting living cells. 2 of 34 What Is a Virus? Viruses
Viruses and Prions (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Viruses and Prions (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Viruses and Prions (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Chapter 6 An Introduction to Viruses
 Chapter 6 An Introduction to Viruses Introduction All life-forms can be infected by viruses. Some viruses generate serious epidemics, from dengue fever to influenza to AIDS. Others fill essential niches
Chapter 6 An Introduction to Viruses Introduction All life-forms can be infected by viruses. Some viruses generate serious epidemics, from dengue fever to influenza to AIDS. Others fill essential niches
ACQUIRED IMMUNODEFICIENCY SYNDROME AND ITS OCULAR COMPLICATIONS
 ACQUIRED IMMUNODEFICIENCY SYNDROME AND ITS OCULAR COMPLICATIONS Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS ) is an infectious disease caused by a retrovirus, the human immunodeficiency virus(hiv). AIDS is
ACQUIRED IMMUNODEFICIENCY SYNDROME AND ITS OCULAR COMPLICATIONS Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS ) is an infectious disease caused by a retrovirus, the human immunodeficiency virus(hiv). AIDS is
VIRUSES. Biology Applications Control. David R. Harper. Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
 VIRUSES Biology Applications Control David R. Harper GS Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON vii Chapter 1 Virus Structure and 2.2 VIRUS MORPHOLOGY 26 Infection 1 2.3 VIRAL CLASSIFICATION
VIRUSES Biology Applications Control David R. Harper GS Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON vii Chapter 1 Virus Structure and 2.2 VIRUS MORPHOLOGY 26 Infection 1 2.3 VIRAL CLASSIFICATION
RNA Recombination in Animal and Plant Viruses
 MCROBOLOGCAL REVEWS, Mar. 1992, p. 61-79 0146-0749/92/010061-19$02.00/0 Copyright ) 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 56, No. 1 RNA Recombination in Animal and Plant Viruses MCHAEL M. C. LA
MCROBOLOGCAL REVEWS, Mar. 1992, p. 61-79 0146-0749/92/010061-19$02.00/0 Copyright ) 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 56, No. 1 RNA Recombination in Animal and Plant Viruses MCHAEL M. C. LA
1. Virus 2. Capsid 3. Envelope
 VIRUSES BIOLOGY II VOCABULARY- VIRUSES (22 Words) 1. Virus 2. Capsid 3. Envelope 4. Provirus 5. Retrovirus 6. Reverse transcriptase 7. Bacteriophage 8. Lytic Cycle 9. Virulent 10. Lysis 11. Lysogenic Cycle
VIRUSES BIOLOGY II VOCABULARY- VIRUSES (22 Words) 1. Virus 2. Capsid 3. Envelope 4. Provirus 5. Retrovirus 6. Reverse transcriptase 7. Bacteriophage 8. Lytic Cycle 9. Virulent 10. Lysis 11. Lysogenic Cycle
Wednesday, October 19, 16. Viruses
 Viruses Image of an animal cell More realistic size of a virus compared to an animal cell Cells can fulfill all characteristics of life Viruses on their own can be considered lifeless chemicals, unless?
Viruses Image of an animal cell More realistic size of a virus compared to an animal cell Cells can fulfill all characteristics of life Viruses on their own can be considered lifeless chemicals, unless?
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
Some living things are made of ONE cell, and are called. Other organisms are composed of many cells, and are called. (SEE PAGE 6)
 Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
