THE INVISIBLE WORLD OF MICROBES
|
|
|
- Moris Lambert Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE INVISIBLE WORLD OF MICROBES Cells are the building blocks of all life. People have cells. So do dogs, cats, spiders, and gnats. So do trees and flowers and tomatoes and blades of grass. All lifeforms all living organisms are made from cells. Each human body has about a 100 trillion cells. That s 100,000,000,000,000 - an almost unimaginable number. And every single cell is active, constantly going through processes that keep the cell (and your body) alive. It s like a small city inside your cells! If you were a micronaut and could enter the world inside a single cell, you would be amazed by everything going on. Cells digest food. Cells carry oxygen to your lungs. Cells fight infection and also heal wounds. The human body has about 200 types of cells. You have red blood cells and brain cells. You even have cells for making tears and cells for making earwax.
2 Humans are multicellular, which means we re made of more than one cell. But LOTS of life-forms have just one cell. You might think having only a single cell would limit your options, but there are hundreds of thousands of different species of singlecelled life-forms. In fact, half of all life on Earth (by weight) is made of single-celled microbes. The simplest life-forms on Earth have just one cell. An example of a one-celled life-form is a bacterium. These species of bacteria all cause diseases in humans. But not all bacteria are harmful some are even helpful.
3 Almost all single-celled organisms are too small to see with the naked eye. But you can see them clearly with microscopes. The earliest forms of life on Earth were simple single-celled organisms. In fact, single-celled organisms were the only forms of life on Earth for over a billion years. There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, like the bacterium pictured here, are simple cells. They don t have a lot of internal parts, just cytoplasm, and DNA floating in the middle with no nucleus. In contrast, eukaryotic cells are complex, with lots of parts and a nucleus that protects the DNA.
4 Today, we can look deep inside of cells using ultra-powerful microscopes. But there was a time when people did not know cells even existed. The first to notice them was a scientist named Robert Hooke in the 1600s. When he looked through his microscope at a piece of cork which is actually part of a tree he saw a network of what looked like tiny rooms. What he saw reminded him of cells the tiny rooms that monks in a monastery live in so that s what he called them. There was no photography when Robert Hooke saw plant cells through his microscope in So he drew pictures of what they looked like. After seeing what Hooke had discovered, another scientist, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, made his own cell discoveries. When he took a sample of plaque from his own mouth and looked at it under one of his microscopes, he observed that there were many very little living animalcules, very prettily a-moving. What he called animalcules were actually bacteria the first anyone had ever seen. The idea that there were beasties living inside our bodies blew people s minds and opened the door to a huge number of scientific discoveries.
5 Want to know something a little creepy and a little amazing? Every human being, in addition to human cells, has trillions of non-human cells. These non-human cells are called your microbiome. Most of the microbes in your microbiome are in your guts, and they help with digesting food and keeping you healthy. You share your body with approximately 100 trillion bacteria! Recently a large group of scientists working on the Human Microbiome Project discovered that it s normal to have about 10,000 different species of microbes in (and on) your body. And these microbes are not just sitting around. These singlecelled microbes do things like make essential vitamins and fight off infections. In people, microbes inside our bodies outnumber our own human cells 10-to-1!
6 The cells of plants, including the ones we eat, have stiff walls around them made of a material called cellulose. People can t digest cellulose, and any cellulose we eat passes out of our bodies in our waste. Cellulose is actually a type of sugar that has energy in it. To digest the cellulose and get its energy, many animals rely on their own unique microbiomes. Lots of plant-eating (and wood-eating) species from cows to koalas to termites have special bacteria in their guts that can break down cellulose. Without these bacteria, these vegetarian creatures would go hungry. All other bears are meat-eaters. But panda bears pretty much eat just one thing: bamboo. How do they survive on that diet? Pandas can extract energy from bamboo thanks to their microbiomes. Scientists have discovered special microbes that can break down cellulose in the pandas guts.
7 It took a long time for scientists to figure out what caused certain diseases and some diseases are still being worked on. In Hooke and Leeuwenhoek s day in the 1600s, a lot of people thought diseases were spread by bad air. What they meant by that was the funky-smelling air near garbage dumps or sewers. When Leeuwenhoek discovered microscopic life, scientists started wondering if microbes (a.k.a. germs) might be invading the body and causing diseases. That might seem obvious today, but it was such a radical notion back then that it took almost 200 years for the idea to be completely proved and accepted. This 19th-century drawing shows death stalking the air as a cholera epidemic breaks out. Cholera is caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. It is not spread to humans through the air, but by drinking water and shellfish that are contaminated by the bacteria.
8 The credit for proving that specific germs cause specific diseases is usually given to the French scientist Louis Pasteur. In the 19 th century, silk (which comes from silkworms) was used for clothing. But the silkworms were suffering from a mysterious disease; they were dying in large numbers and the ones that survived couldn t spin silk thread. The silk producers asked Pasteur to find a solution. When Pasteur studied the silkworms under a microscope, he found two different disease-causing microbes. These germs were passed from silk moths to their eggs, and then from the droppings of silkworms onto leaves that the silkworms ate. Pasteur had identified the specific cause of the disease. He had also identified how it was spread from one silkworm to another. Pasteur and other scientists soon realized that they needed to apply the same methods to discover the causes of human diseases. Within a few decades, the microbes responsible for many deadly diseases had been identified. Scientists began to look for vaccines and cures a process that continues today. In the old days, surgeons didn t wash their hands before performing surgery and as a result about half their patients died of infections. The surgeons were picking up germs from one patient and spreading them to another. When they began cleaning their hands and keeping operating rooms and equipment sterile, death rates decreased.
9 This one-celled microbe is a real pest. Giardia can get into your gut if you drink contaminated water and cause a disease called giardiasis. The major symptom is diarrhea. Ugh. Giardia have four pairs of flagella (the little pink whips), and they use these to move around. Although Leeuwenhoek discovered Giardia under his microscope in the 1600s, it wasn t until about 1910 that scientists realized Giardia caused disease. Today, giardiasis can be treated with antibiotics. One of the most dangerous single-celled organisms in the world is one that causes malaria. Plasmodium falciparum is a protozoan that hitches a ride in the bodies of mosquitoes before getting into its real target: vertebrate animals. When a mosquito infected with the malaria parasite sips the blood of a human, the parasites slip into the human s bloodstream, quickly ride the bloodstream to the human s liver, and infect the liver cells. The parasite multiplies inside each cell until tens of thousands of new parasites burst the cell and move on to invade red blood cells, where they reproduce again. All this wreaks havoc on the human body, resulting in chills and fever and in some cases death. While there are medicines to help cure malaria, scientists are still searching for a vaccine that will prevent Plasmodium from making people sick.
10 Seen through an electron microscope, a malaria microbe invades a red blood cell. In many parts of the world, people sleep with mosquito nets around their beds to protect against mosquito bites and the diseases mosquitoes carry, such as malaria and dengue fever.
11 Tiny and very dangerous, the pill shapes among the yellow-green goo are Yersinia pestis, the bacteria that cause the bubonic plague. Another deadly single-celled organism is the Yersinia pestis. This bacteria caused the Bubonic Plague also called the Black Death that killed over 25 million people during the Middle Ages. The Yersinia pestis bacteria live in the guts of fleas. Rats carried these fleas into the homes of humans, and the plague would be passed along from rat to human through a flea bite. Because people did not know what caused the plague, the disease spread far and wide, resulting in sickness and death all over Europe.
12 Of course, not all microbes cause disease. In fact, plenty of them mind their own business, and others are downright amazing. Extremophiles are single-celled microbes that can live in very weird places places that scientists used to think were impossible for life to survive. They live underneath glaciers, inside rocks, and in the ocean next to boiling-hot deep sea vents. There is more life on Earth, in more places on Earth, than we ever imagined! This hot spring in Yellowstone National Park is full of extremophiles that like living in high temperatures. Two hundred degrees feels just right to them. The orange rings at the edge of the spring are actually mats of single-celled extremophiles. The different shades of orange are different species of extremophiles.
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Before Statement After
 CHAPTER 17 Immunity and Disease LESSON 1 Diseases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
CHAPTER 17 Immunity and Disease LESSON 1 Diseases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Bacteria. Remember they are everywhere! In your food (yogurt), air (germs) on your body (remember our video?)
 Bacteria Remember they are everywhere! In your food (yogurt), air (germs) on your body (remember our video?) Anton van Leeuwenhoek found them by accident. Remember him? Bacteria are prokaryotes. The genetic
Bacteria Remember they are everywhere! In your food (yogurt), air (germs) on your body (remember our video?) Anton van Leeuwenhoek found them by accident. Remember him? Bacteria are prokaryotes. The genetic
Infectious Disease. Unit 6 Lesson 1
 Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease
 Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
What are Germs? Click on the germ to find out more.
 Click here to start What are Germs? Germs are tiny organisms that cause disease. Germs can make you ill if they get into your stomach or your lungs. You need a microscope to see germs. Germs are carried
Click here to start What are Germs? Germs are tiny organisms that cause disease. Germs can make you ill if they get into your stomach or your lungs. You need a microscope to see germs. Germs are carried
Lesson Objectives. Core Content Objectives. Language Arts Objectives
 Dr. Wellbody s Heroes 7 Lesson Objectives Core Content Objectives Students will: Explain that germs can cause disease in the body Explain the importance of vaccination in preventing disease Identify Edward
Dr. Wellbody s Heroes 7 Lesson Objectives Core Content Objectives Students will: Explain that germs can cause disease in the body Explain the importance of vaccination in preventing disease Identify Edward
LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK. How can we prove infection causes disease?
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Correlation a connection between two factors. Causation when a change in one factor results in a change in another. Vector an organism that transmits a pathogen from reservoir to host.
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Correlation a connection between two factors. Causation when a change in one factor results in a change in another. Vector an organism that transmits a pathogen from reservoir to host.
Chapter 1. The Science of Biology. h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology Section 1: What is Science? The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology Section 1: What is Science? The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural
MICROORGANISM NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS
 MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
Tetanus - Aids - Tuberculosis - Diphtheria - Rabies - Cancer - Poliomyelitis
 Plagues Old and New N 1 During the course of history, populations all over the world have been struck down by contagious diseases. There was a time when town and countryside lived in fear of catching the
Plagues Old and New N 1 During the course of history, populations all over the world have been struck down by contagious diseases. There was a time when town and countryside lived in fear of catching the
Section One: Background Material
 Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
Biology. Slide 1 of 30. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Unit B: Cells and Systems
 Unit B: Cells and Systems 1 S C I E N C E 8 Scientific investigation leads to new knowledge about body systems and new medical applications. 2 S E C T I O N 4. 0 1 Developing a Theory for Disease 3 T O
Unit B: Cells and Systems 1 S C I E N C E 8 Scientific investigation leads to new knowledge about body systems and new medical applications. 2 S E C T I O N 4. 0 1 Developing a Theory for Disease 3 T O
Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Community Interactions
 Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Community Interactions Name: In lab this week we will work on developing an understanding of community interactions. Prior to lab answer the following questions to
Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Community Interactions Name: In lab this week we will work on developing an understanding of community interactions. Prior to lab answer the following questions to
Where are we heading?
 Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Key Stage 2 Science PSHE English Estimated Teaching Time
 Key Stage 2 Science Working Scientifically Animals Including Humans (Upper KS2 only) PSHE Core Theme 1: Health and Wellbeing English Reading and Comprehension Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes The Spread
Key Stage 2 Science Working Scientifically Animals Including Humans (Upper KS2 only) PSHE Core Theme 1: Health and Wellbeing English Reading and Comprehension Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes The Spread
McGraw-Hill Open Court Grade 4
 Unit 3/Week 1 Title: Medicine: Past and Present Suggested Time:5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.4.1, RI.4.2, RI.4.3, RI.4.5; RF.4.3, RF.4.4; W.4.1, W.4.2, W.4.4, W.4.9; Sl.4.1;
Unit 3/Week 1 Title: Medicine: Past and Present Suggested Time:5 days (45 minutes per day) Common Core ELA Standards: RI.4.1, RI.4.2, RI.4.3, RI.4.5; RF.4.3, RF.4.4; W.4.1, W.4.2, W.4.4, W.4.9; Sl.4.1;
Disease Prevention and Public Health. SPC2P Biology
 Disease Prevention and Public Health SPC2P Biology What is disease and should we be concerned about its prevention? A Brief History The black death (bubonic plague) killed between 30% and 60% of the entire
Disease Prevention and Public Health SPC2P Biology What is disease and should we be concerned about its prevention? A Brief History The black death (bubonic plague) killed between 30% and 60% of the entire
Grade 6 Standard 5 Unit Test Microorganisms. 1. Which of the following correctly describes the size of fungi compared to the size of bacteria?
 Grade 6 Standard 5 Unit Test Microorganisms 1. Which of the following correctly describes the size of fungi compared to the size of bacteria? A. Fungi are larger. B. Bacteria are larger. C. They are about
Grade 6 Standard 5 Unit Test Microorganisms 1. Which of the following correctly describes the size of fungi compared to the size of bacteria? A. Fungi are larger. B. Bacteria are larger. C. They are about
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System
 Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
THINKING SCRIPTS RESEARCH GROUPS LOUIS PASTEUR STEVE WILLIAMS CLASSROOM SCRIPT. Name: Character: School:
 THINKING SCRIPTS RESEARCH GROUPS LOUIS BY STEVE WILLIAMS CLASSROOM SCRIPT Name: Character: School: RESEARCH GROUPS LOUIS CAST OF SIX READERS ENQUIRERS READER 1: READER 2: READER 3: READER4: SCIENTISTS
THINKING SCRIPTS RESEARCH GROUPS LOUIS BY STEVE WILLIAMS CLASSROOM SCRIPT Name: Character: School: RESEARCH GROUPS LOUIS CAST OF SIX READERS ENQUIRERS READER 1: READER 2: READER 3: READER4: SCIENTISTS
Why was there so much change in this period?
 Why was there so much change in this period? Germ Theory: Summary? 1) 1861: Germ Theory Bacteria in the air turned things bad (working to find why beer was going sour). Pasteur wondered if this could make
Why was there so much change in this period? Germ Theory: Summary? 1) 1861: Germ Theory Bacteria in the air turned things bad (working to find why beer was going sour). Pasteur wondered if this could make
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part 1 Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1) An infection disease is caused by. a)
Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part 1 Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1) An infection disease is caused by. a)
SEPUP ITEM BANK. Item Banks TR-253. Multiple choice. Circle the best answer.
 Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
World Health Day Vector-borne Disease Fact Files
 World Health Day Vector-borne Disease Fact Files Contents Malaria Junior 1 Senior...2 Dengue Fever Junior 3 Senior.. 4 Chikungunya Junior....5 Senior. 6 Lyme disease Junior 7 Senior 8 Junior Disease Fact
World Health Day Vector-borne Disease Fact Files Contents Malaria Junior 1 Senior...2 Dengue Fever Junior 3 Senior.. 4 Chikungunya Junior....5 Senior. 6 Lyme disease Junior 7 Senior 8 Junior Disease Fact
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Community mobilization in major emergencies
 COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Community mobilization in major emergencies Response: What do you see in these pictures? Disasters that can affect a community such as earthquakes or floods. What are some other
COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Community mobilization in major emergencies Response: What do you see in these pictures? Disasters that can affect a community such as earthquakes or floods. What are some other
Issue 05 This article is about: Career Guidance Interesting Science Real Life Application Real Time News about Science. Tapeworms
 Issue 05 This article is about: Career Guidance Interesting Science Real Life Application Real Time News about Science Tapeworms Ever heard someone say, "He's so skinny he must have a tapeworm"? Tapeworms
Issue 05 This article is about: Career Guidance Interesting Science Real Life Application Real Time News about Science Tapeworms Ever heard someone say, "He's so skinny he must have a tapeworm"? Tapeworms
LESSON -9 GERMS AND DISEASES
 LESSON -9 GERMS AND DISEASES WEB CHART MICROBES VIRUS BACTERIA FUNGUS PROTOZA MEASLES TYPHOID RINGWORM MALARIA DEFINE:- 1. MICROBES- Those organisms which are very small and can only be seen through microscope
LESSON -9 GERMS AND DISEASES WEB CHART MICROBES VIRUS BACTERIA FUNGUS PROTOZA MEASLES TYPHOID RINGWORM MALARIA DEFINE:- 1. MICROBES- Those organisms which are very small and can only be seen through microscope
Food Safety Summary for Food for Learning. Prepared by: Joanna Mestre, BScHE Health Promoter, Environmental Health
 Food Safety Summary for Food for Learning Prepared by: Joanna Mestre, BScHE Health Promoter, Environmental Health Introduction Food safety is about preventing food borne illness. Some people are more vulnerable
Food Safety Summary for Food for Learning Prepared by: Joanna Mestre, BScHE Health Promoter, Environmental Health Introduction Food safety is about preventing food borne illness. Some people are more vulnerable
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
What is HIV? Shoba s story. What is HIV?
 1 What is HIV? Shoba s story What is HIV? The immune system HIV inside a cell Medicines against HIV The future Answering Shoba s questions Shoba s story Shoba is a fifteen-year-old student in Pakistan.
1 What is HIV? Shoba s story What is HIV? The immune system HIV inside a cell Medicines against HIV The future Answering Shoba s questions Shoba s story Shoba is a fifteen-year-old student in Pakistan.
Cell Basics. Basic Unit of Life. Prokaryotic. Eukaryotic. Plant Cell. Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Bacteria. Very Complex.
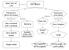 Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
2011 Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. All rights reserved.
 2011 Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. All rights reserved. Traveling Viruses Part I Purpose To generate a discussion of how diseases can be transmitted. Materials For each student: Disposable
2011 Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. All rights reserved. Traveling Viruses Part I Purpose To generate a discussion of how diseases can be transmitted. Materials For each student: Disposable
Biology. Magic Doctor. Magic Doctor. Topic Two: Immunity. 1) The first line of defense in our immune system is composed of what?
 Biology Topic Two: Immunity Magic Doctor 1) The first line of defense in our immune system is composed of what? Skin, nose, eye lashes, eyelids. 2) White blood cells and red blood cells are produced in
Biology Topic Two: Immunity Magic Doctor 1) The first line of defense in our immune system is composed of what? Skin, nose, eye lashes, eyelids. 2) White blood cells and red blood cells are produced in
Unit 13.2: Viruses. Vocabulary capsid latency vaccine virion
 Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
You ve spent your whole life with those miniature minions hiding inside you. Isn t it time you got to know them?
 Non-fiction: Uninvited Guests Uninvited Guests By Kirsten Weir Meet the parasites, microbes, and creepy-crawlies in (and on) you. You re Never Alone. Sleeping in your bedroom. Taking a shower. No matter
Non-fiction: Uninvited Guests Uninvited Guests By Kirsten Weir Meet the parasites, microbes, and creepy-crawlies in (and on) you. You re Never Alone. Sleeping in your bedroom. Taking a shower. No matter
Microbiology. Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites
 Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
4. Which sentence is a
 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness?
 3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L AA
 OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
Knowledge is power: 815 Second Avenue New York, NY Toll Free HEAL
 Knowledge is power: The Truth About Malaria 815 Second Avenue New York, NY 10017 Toll Free 855.312.HEAL www.inspirationfund.org Chapter One: What is malaria?...3 Chapter Two: Where can malaria be found?...6
Knowledge is power: The Truth About Malaria 815 Second Avenue New York, NY 10017 Toll Free 855.312.HEAL www.inspirationfund.org Chapter One: What is malaria?...3 Chapter Two: Where can malaria be found?...6
The invisible world of germs and cells
 DG3 DISCUSSION GUIDE 1 What is the smallest living thing that you can see with your naked eyes? DG1 OBJECTIVE: To introduce the of living microorganisms. 1. Ask: What is the smallest living thing that
DG3 DISCUSSION GUIDE 1 What is the smallest living thing that you can see with your naked eyes? DG1 OBJECTIVE: To introduce the of living microorganisms. 1. Ask: What is the smallest living thing that
MicroLife Review Sheet
 Name: KEY Due Date: MicroLife Review Sheet Directions: Complete the review sheet to help study for the unit test. This is only a guide of what will be on the test. Be sure to use this, notes, lab booklet,
Name: KEY Due Date: MicroLife Review Sheet Directions: Complete the review sheet to help study for the unit test. This is only a guide of what will be on the test. Be sure to use this, notes, lab booklet,
OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA
 OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA SC.6.L.14.5 AA Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, reproductive,
OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA SC.6.L.14.5 AA Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, reproductive,
Bacteria: More Than Pathogens By Trudy M. Wassenaar
 Misunderstood bacteria Bacteria are usually associated with dirt, disease, and death. Bacteria suffer from negative public relations. You probably associate bacteria with the three D's: dirt, disease and
Misunderstood bacteria Bacteria are usually associated with dirt, disease, and death. Bacteria suffer from negative public relations. You probably associate bacteria with the three D's: dirt, disease and
bacteria review 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
The Cell and Its Chemical Compounds
 Cell Theory Cell - The basic unit of structure and function in living things. All of an organism s process or functions are carried out in the cell. Robert Hooke - One of the first people to observe cells
Cell Theory Cell - The basic unit of structure and function in living things. All of an organism s process or functions are carried out in the cell. Robert Hooke - One of the first people to observe cells
Communicable and Noncommunicable. Diseases
 Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
Mouth Health. Quiz. To protect your toothbrush from harmful germs, you should: Leave it out in the open air. Store it in a closed container
 Mouth Health Quiz Add up your points at the end to see how mouth health smart you are! If you answer a question correctly, you get 2 points. If you answer it incorrectly, you get one point. To protect
Mouth Health Quiz Add up your points at the end to see how mouth health smart you are! If you answer a question correctly, you get 2 points. If you answer it incorrectly, you get one point. To protect
Chapter 10. Objectives. Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious diseases. Describe how the human body fights diseases.
 Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Objectives Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious diseases. Describe how the human body fights diseases. Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Disease What
Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Objectives Describe the difference between infectious and noninfectious diseases. Describe how the human body fights diseases. Lesson 1 Disease and Your Body Disease What
Food Safety: Basic Overview of Safely Handling Food
 Food Safety: Basic Overview of Safely Handling Food Food Safety Training The Nevada County Environmental Health Department requires that one person be in the food booth at any given time with a working
Food Safety: Basic Overview of Safely Handling Food Food Safety Training The Nevada County Environmental Health Department requires that one person be in the food booth at any given time with a working
Chapter 8 Review. 4. Scientists do not consider viruses as true living organisms because they
 Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level
 Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? cell unicellular multicellular DISCOVERY OF CELLS Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek THE CELL THEORY
 NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? A cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. Living things can be either unicellular (made up entirely of only one cell) or
NOTES CELL UNIT WHAT IS A CELL? A cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. Living things can be either unicellular (made up entirely of only one cell) or
PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether each of the following statements are true or false.
 MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III. Reading Assignment. Unit Lesson. UNIT III STUDY GUIDE Essential Parts: Cells
 UNIT III STUDY GUIDE Essential Parts: Cells Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Evaluate concepts and theories of basic biological sciences
UNIT III STUDY GUIDE Essential Parts: Cells Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Evaluate concepts and theories of basic biological sciences
Elkins School District
 Elkins School District Alternate Method of Instruction (AMI) AMI Day # 2 School Name Teacher Name Subject / Course Name Assignment Description Elkins High School Ms. Ramsey Environmental Science ONLINE:
Elkins School District Alternate Method of Instruction (AMI) AMI Day # 2 School Name Teacher Name Subject / Course Name Assignment Description Elkins High School Ms. Ramsey Environmental Science ONLINE:
A History of Microbiology
 A History of Microbiology Miasmatic Theory The Miasmatic Theory postulates that disease is caused by "bad air" or "mal aria", known as miasmatic odors. It was thought that these miasmatic odors arose from
A History of Microbiology Miasmatic Theory The Miasmatic Theory postulates that disease is caused by "bad air" or "mal aria", known as miasmatic odors. It was thought that these miasmatic odors arose from
Introduction Evolution of Metabolism
 2 Introduction Evolution of Metabolism Activity for Our Cells, Our Selves Movie Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including
2 Introduction Evolution of Metabolism Activity for Our Cells, Our Selves Movie Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Abstract. Introduction
 DECEMBER FEBRUARY 2017 2018 What How can causes we keep lizards kids brains from dying to from change diarrhea? size? Authors: Authors: Susan Crow, Meghan Pawlowski, Manyowa Meki, Patricia Lara LaDage,
DECEMBER FEBRUARY 2017 2018 What How can causes we keep lizards kids brains from dying to from change diarrhea? size? Authors: Authors: Susan Crow, Meghan Pawlowski, Manyowa Meki, Patricia Lara LaDage,
University of Georgia Cooperative Extension Bulletin 693. Food, Hands and Bacteria
 Reviewed by William C. Hurst and A. Estes Reynolds, Extension Food Scientists Originally prepared by George A. Schuler and James A. Christian, retired Extension Food Scientists University of Georgia Cooperative
Reviewed by William C. Hurst and A. Estes Reynolds, Extension Food Scientists Originally prepared by George A. Schuler and James A. Christian, retired Extension Food Scientists University of Georgia Cooperative
Chapter 13. Preventing Infectious Diseases. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
Context: Malaria, a disease spread by mosquitoes, kills more than two million people every year.
 Lesson Title: Malaria Grade: 6 Subject: Social Studies URL: www.gng.org/pulse/malaria_2a.doc Lesson Description: This lesson explores the malaria virus through the story of Kofi, a five year old boy whose
Lesson Title: Malaria Grade: 6 Subject: Social Studies URL: www.gng.org/pulse/malaria_2a.doc Lesson Description: This lesson explores the malaria virus through the story of Kofi, a five year old boy whose
The School of "Self-Applied" 1 Prevention. Clean Water
 Clean Water I have written about clean water since the beginning of my journey into selfhealth. People in general want to take water for granite and believe it is free or in recent history, they consume
Clean Water I have written about clean water since the beginning of my journey into selfhealth. People in general want to take water for granite and believe it is free or in recent history, they consume
What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390
 386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
INFECTION CONTROL: MRSA AND OTHER RESISTANT GERMS
 INFECTION CONTROL: MRSA AND OTHER RESISTANT GERMS Objectives: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1. Discuss the difference between bacteria and viruses. 2. Explain why some antibiotics no longer
INFECTION CONTROL: MRSA AND OTHER RESISTANT GERMS Objectives: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1. Discuss the difference between bacteria and viruses. 2. Explain why some antibiotics no longer
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Malaria prevention and control
 COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Malaria prevention and control Point to first picture: What do you see in this picture? 1. A small child who looks very sick. The child is sweating and shaking. There are mosquitoes
COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Malaria prevention and control Point to first picture: What do you see in this picture? 1. A small child who looks very sick. The child is sweating and shaking. There are mosquitoes
Protect the quality and safety of your food
 Protect the quality and safety of your food Description of tool This tool provides useful information about protecting the quality and safety of food. School teachers can use this information while teaching
Protect the quality and safety of your food Description of tool This tool provides useful information about protecting the quality and safety of food. School teachers can use this information while teaching
WATER AND HEALTH (Water Induced Diseases)
 WATER AND HEALTH (Water Induced Diseases) Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 In human body, water is of utmost physiological importance and
WATER AND HEALTH (Water Induced Diseases) Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 In human body, water is of utmost physiological importance and
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes
 Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
year 7 REVISION Spring Assessment - Biology
 year 7 REVISION Spring Assessment - Biology year 7 REVISION Microscope and Cells THE MICROSCOPE Used to view things too small for the naked eye. Consists of lenses of different magnification to make things
year 7 REVISION Spring Assessment - Biology year 7 REVISION Microscope and Cells THE MICROSCOPE Used to view things too small for the naked eye. Consists of lenses of different magnification to make things
Pathogens and disease
 Pathogens and disease Task 1: Have a go at completing the exam questions for 35 minutes. Task 2: Review the mark scheme and touch up on the areas we need to work on. Pathogens and disease Pathogens: Microorganisms
Pathogens and disease Task 1: Have a go at completing the exam questions for 35 minutes. Task 2: Review the mark scheme and touch up on the areas we need to work on. Pathogens and disease Pathogens: Microorganisms
Bacteriology Virology Mycology Parasitology Immunology Pathology Epidemiology. Microbe alternate terms Germs, microorganisms, pathogens, agents, bugs
 1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
Human Body Systems - Parasites
 Human Body Systems - Parasites Grade Range: Middle School Key Terms Lesson Time: 40 minutes Materials and Resources Circulatory system Digestive system Immune system Malaria Nervous system Parasite Plasmodium
Human Body Systems - Parasites Grade Range: Middle School Key Terms Lesson Time: 40 minutes Materials and Resources Circulatory system Digestive system Immune system Malaria Nervous system Parasite Plasmodium
2013 Disease Detectives
 2013 Disease Detectives Since the catastrophic earthquake that hit Haiti in January of 2010, there have been an alarming number of cases of Cholera, spread by the Vibrio cholera bacterium, reported within
2013 Disease Detectives Since the catastrophic earthquake that hit Haiti in January of 2010, there have been an alarming number of cases of Cholera, spread by the Vibrio cholera bacterium, reported within
Chapter 14. Bugs that Resist Drugs
 Chapter 14 Bugs that Resist Drugs See website Learning Objectives Important Terminology Power point- posted after chapter is completed What happened to Carlos Don, Rebecca Lohsen, Ricky Lannetti? Carlos
Chapter 14 Bugs that Resist Drugs See website Learning Objectives Important Terminology Power point- posted after chapter is completed What happened to Carlos Don, Rebecca Lohsen, Ricky Lannetti? Carlos
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Overview of Cell Structures
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis
 STO-112 Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis Part 1: Diffusion Diffusion is a process by which molecules move into or out of cells. To diffuse into or out of a cell, molecules must pass through the cell
STO-112 Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis Part 1: Diffusion Diffusion is a process by which molecules move into or out of cells. To diffuse into or out of a cell, molecules must pass through the cell
NOTES KEY. Chapter 19 Bacteria (Biotic) and Viruses (Abiotic)
 NOTES KEY Chapter 19 Bacteria (Biotic) and Viruses (Abiotic) BACTERIA - PROKARYOTES Page 471 Definition: Single celled organisms that lack a nucleus, the DNA is free floating in the cytoplasm Classifying
NOTES KEY Chapter 19 Bacteria (Biotic) and Viruses (Abiotic) BACTERIA - PROKARYOTES Page 471 Definition: Single celled organisms that lack a nucleus, the DNA is free floating in the cytoplasm Classifying
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right arrow key or
3. Complete the sentences using: clever, strong, fast, fierce, brave
 1. Circle the right answer. 200 + 00 = 150 + 400 = 220 + 310 = 250 x 4 = six hundred and twenty nine hundred and five eight hundred / nine hundred / seven hundred five hundred and fifty / three hundred
1. Circle the right answer. 200 + 00 = 150 + 400 = 220 + 310 = 250 x 4 = six hundred and twenty nine hundred and five eight hundred / nine hundred / seven hundred five hundred and fifty / three hundred
 The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
The Human Immune System. Video
 The Human Immune System Video What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles A collections of cells, tissues, and organs that
The Human Immune System Video What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles A collections of cells, tissues, and organs that
Introduction to Disease
 Introduction to Disease What is a pathogen? Disease-producing microorganism and toxin VIRUS Viruses exist for one purpose only: to reproduce. To do that, they have to take over the reproductive machinery
Introduction to Disease What is a pathogen? Disease-producing microorganism and toxin VIRUS Viruses exist for one purpose only: to reproduce. To do that, they have to take over the reproductive machinery
How to Take Care of a Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. The care a sick person receives is frequently the most important part of his
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. The care a sick person receives is frequently the most important part of his
CE Unit 7. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Your Body's Defenses
 Your Body's Defenses For follow up on these notes read: Holt: pages 710 720 MSLS: pages 410 420 Blue writing indicates a video is linked to the picture. Click the pictures! Links to Videos are listed on
Your Body's Defenses For follow up on these notes read: Holt: pages 710 720 MSLS: pages 410 420 Blue writing indicates a video is linked to the picture. Click the pictures! Links to Videos are listed on
PLANKTON LAB SEATTLE AQUARIUM OVERVIEW:
 PLANKTON LAB SEATTLE AQUARIUM GRADES: 9 12 DURATION: 30 60 minutes MATERIALS: - Plankton sample - Dissecting microscopes - Petri dishes - Droppers - Plankton ID cards - Student lab worksheets STANDARDS:
PLANKTON LAB SEATTLE AQUARIUM GRADES: 9 12 DURATION: 30 60 minutes MATERIALS: - Plankton sample - Dissecting microscopes - Petri dishes - Droppers - Plankton ID cards - Student lab worksheets STANDARDS:
LESSON 8 GRADES 3 5 TIME: 60 MIN OVERVIEW
 Journal Wonderings ENGAGE & EXPLORE LESSON 8 GRADES 3 5 TIME: 60 MIN OVERVIEW This Journal Wonderings lesson is designed for half of your students to do while the other half are doing the In the Weeds
Journal Wonderings ENGAGE & EXPLORE LESSON 8 GRADES 3 5 TIME: 60 MIN OVERVIEW This Journal Wonderings lesson is designed for half of your students to do while the other half are doing the In the Weeds
