A METHOD FOR ESTIMATING THE BACTERIA IN THE CIRCULATING BLOOD IN RABBITS.*
|
|
|
- Isabella Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published Online: 1 September, 1914 Supp Info: Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 15, 2018 A METHOD FOR ESTIMATING THE BACTERIA IN THE CIRCULATING BLOOD IN RABBITS.* BY CARROLL G. BULL, M.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) Not a few of the determinations in experimental bacteriology have to do with the testing of bacteria for their infectious power. The laboratory animals principally employed for this purpose are small, and afford few reliable criteria which can be used to decide the result. The criterion which, because of its very definite character, is usually relied upon is the development of severe illness and the intervention of death; but this criterion cannot take account of degrees of intensity of infection, except as they affect the period of survival of the animal after inoculation, which is manifestly a coarse differential. All who have conducted so called virulence tests with bacteria have felt the need of other means of differentiation than mere survival or death of the inoculated animal. In the course of some experiments on the therapeutics of streptococcal and pneumococcal infections, this need became imperative, so that a means was sought that should yield data capable of comparison at different periods and intervals after inoculation, and which did not rely alone on the ultimate result of recovery or death. The starting point of the quest was the well known phenomenon, first observed by yon Fodor 1 and investigated accurately by Wyssokowitsch, 2 namely, that bacteria injected into the circulation are soon filtered out of the blood and, according to their degree of infectiousness, are destroyed or reappear, multiply, and, when of sufficient power, ultimately cause death. Hence the question which arose was whether the disappearance, reappearance, and multiplication proceed with a degree of regularity and consistency rendering a numerical estimate feasible of the bacteria in the circulating blood. * Received for publication, June 28, yon Fodor, J., Arch. f. Hyg., 1886, iv, I3O. 2 Wyssokowitsch, W., Ztschr. f. Hyg. u. In[ectionskra~kh i
2 238 Bacteria in Circulating Blood. The later studies of WeiP and of Reichstein, 4 which deal with the fate and the estimation of streptococci within the blood stream, offered an encouraging affirmative on this point, so that the next question to arise was whether blood taken repeatedly from superficial vessels sufficed for the purposes of the estimation. EXPERIMENTAL PART. Bacteria and Injections.--The streptococcus used in the following experiments was originally isolated from the throat of a scarlet fever patient. It is a typical hemolytic, Gram-positive, chain-forming streptococcus. It has been repeatedly passed through rabbits and, at the beginning of this work, 0.25 of a cubic centimeter of' a twenty-four-hour bouillon culture 5 per kilo of body-weight killed rabbits within one to five days. The pneumococcus used belongs to :group I according to Neufeld's classification. Its virulence has been maintained by repeated passages through mice and rabbits, o.ooi of a cubic centimeter of a twenty-four-hour bouillon culture per kilo of body-weight kills rabbits within one to three days. In all experiments the bacteria were injected into the ear veins. Taking the Blood,--The uninjected ear was carefully shaved and washed with 95 per cent. alcohol. The marginal vein was pricked and a few drops of blood allowed to flow out before any was taken for the cultures. Then a definite number of drops were caught directly into sterile Petri dishes. A tube of agar, previously melted and cooled to 420 C., was immediately poured into the dishes and the blood and agar were thoroughly mixed. Two or more plates 8 Well, E., Ztschr. ~. Hyg. u. [nfectionskrankh., 1911, Ixviii, Reichstein, S., Centralbl. f. Bakteriol., zte Abt., Orig., 1913, lxxiii, 2o9. 5We have found blood bouillon (3 to 5 drops of sterile defibrinated rabbit blood in a tube of 5 c.c. of beef infusion bouillon) to be an excellent medium for streptococci and pneumococci. The difficulty of " infecting" large quantities of medium with loop inoculations from bouillon to bouillon is eliminated (Gillespie). The bacteria do not lose this virulence as readily in this medium as in ordinary bouillon. Another advantage is that the bacteria live in this medium for long periods of time without being transferred. Streptococci will live for 6 months when the cultures are kept in the dark at low temperature; it is not necessary to seal the tubes in any way. Pneumococci will live for at least 6 weeks. This medium was used throughout the experiments instead of plain bouillon.
3 Carroll G. Bull. 239 were made from each rabbit, the amount of blood varying from one to ten drops, according to the supposed degree of infection. In this way plates were obtained on which the colonies could be easily counted and the various plates compared. The above procedure permits of frequent taking of blood with the least possible disturbance to the rabbit. Contaminations rarely occur if the ear is properly cleansed and a few drops are allow~ed to flow out before taking the blood for the cultures. Blood from the first few drops adheres to the surface of the ear and the following drops run over this without coming in contact with the skin. The accuracy of the method might be objected to, because the measuring of the blood is as inaccurate as the size of one drop of blood may differ from another. If the veins are pricked by a stab with the same sharp-pointed instrument and the surface oi the ear is held in a perpendicular position so as not to allow the blood to collect in large quantities before flowing off, drops of fairly constant size can be obtained and the number of colonies on various plates of the same number of drops is remarkably uniform. The accuracy of the procedure can also be tested by infecting a series of rabbits with the same quantity of a bacterial suspension per kilo of body-weight and taking cultures at stated intervals in a short time after the injections. Experiment I, as given below, was done with this object in view. STREPTOCOCCUS INFECTIONS. Experiment I.--Each of seven rabbits was injected intravenously with 0.25 c.c. of a fresh bouillon culture of streptococci per kilo of body-weight. Cultures were made from the opposite ear 3o minutes and 5~ hours afterwards. In this, as in all other experiments, the number of colonies was calculated on the basis of ten drops of blood, The results are given in table I. TABLE I.. Rabbit. L Rabbit.. 2. Rabbit. :3.. Rabbit. 4.. Rabbit. 5.. Rabbit 6. Rabbit 7- Colonies at 30 min... 14o I45 I35 zoo I3o 13o Ioo Colonies at 5~'~ hrs... / 8 ] 9 ] 20 [ 22 I Io I I~ J IO Many experiments of this character were performed and similar results were always obtained. The first cultures were made after
4 240 Bacteria in Circulating Blood. ample time had elapsed for a thorough and uniform distribution of the bacteria in the blood stream and the number of colonies obtained from the different rabbits shows only slight variations. At the next bleeding, five hours later, the plates were still uniform, although a great reduction in the number of colonies had occurred. These results are probably due to the fact that this initial disappearance of the bacteria from the blood depends largely upon mechanical forces which are about the same in each animal. A biological reaction between the host and the infecting organism had evidently played a very slight r61e up to this time; otherwise, such uniform results could not be expected. Such an experiment also shows that this method of taking blood gives dependable data. In following the progress of the infections further, it was found that they may take one of three courses, mainly depending upon the virulence of the bacteria. A series of experiments was carried out just after the bacteria had been passed through a number of rabbits. The infections ran an acute course, the blood was never free of bacteria, and the autopsies showed no evidence of localization. After two months' cultivation on artificial media, no animal passages being made, the same amount of bacteria caused a chronic infection in a majority of the animals. There were longer or shorter intervals during which the septicemias were slight or entirely absent. After a time the bacteria suddenly reappeared in the blood and the animals died within a few hours to two days. Autopsies showed localized infections, from which the second blood invasion undoubtedly came. When the bacteria were still less virulent, they permanently disappeared from the blood and the animals recovered. Examples of these types of infection are reported in the following tables. Experiment 2.--Each rabbit was given 0.25 c.c. per kilo of body:weight of the ame suspension of streptococci into the ear vein. The blood for the cultures ~vas taken from the opposite ear at the times indicated in the protocols. The number of colonies was estimated on the basis of ten drops of blood. An examination of table II shows that the infections, with the exception of rabbits 2 and 3, ran a remarkably uniform course. From the time of the injections to about five hours afterwards there is a rapid decrease in the number of bacteria. From five to six
5 Carroll G. Bull. 241 ~,-d 8 ~ o ~ & 8 o 8 ~X..~,~ X,.~ X..~ ~X.~X o & g ~, g g & oo ~ oo o o g X..~ "~ ~ '~ ~ '~ ~' "~ -~ '~.~ '~ I ~
6 242 Bacteria in Circulating Blood. hours afterwards the bacteria begin to increase in number and septicemia becomes heavier and heavier until t.he death of the animal. The rabbits died in from one and a half to three days. Rabbits 2 and 3, especially 3, showed some variations from this rapid, progressive course. Rabbit 3 lived six days and its blood cultures give a possible explanation for this. At seventy-two hours the blood had reached so great a septicemic state that the animal should have succumbed on the following day. But the rabbit lived and the blood culture showed a retrogression of the infection for two days. This was followed by another exacerbation which was also overcome and succeeded by another retrogression. The rabbit died on the sixth day with a low culture; but six hours elapsed between the last bleeding and the death of the animal. This gave sufficient time for another ascension, which probably occurred, and as a result of which the rabbit died. Such fluctuations or crises cannot be ascribed to the technique, since they were often observed, and also a temporary reduction in the number of bacteria was always accompanied by a prolongation of the rabbit's life. Infections running such zigzag courses are positive indications that a twosided warfare occurs within the body of the host; the bacteria make advances which are successfully met by the defensive power of the rabbit, but, not being entirely killed out, they make another trial. Such a struggle may be prolonged for several days, and the final results depend upon the relative strengths of the aggressive forces of the invading bacteria and the defensive resources of the infected animal. Experiment 3.--This experiment was carried out two months after experiment I. The same strain of streptococcus was used in this experiment and the same quantities of bouillon culture were injected. This strain had been kept on artificial media continuously and had evidently suffered a loss of virulence. The technique was the same as in experiment I. Two typical rabbits are reported in table III. The courses of the infections reported in table III show that the bacteria had lost in aggressiveness but they still possessed an insusceptibility to the destructive influences of the host and were yet able to carry on a local fight in some more or less inaccessible place. The local lesions probably lowered the vitality of the animals to
7 Carroll G. Bull. 243 o g.r. N ~ ~,~ o~ ~ ~ 0 ~ 0 0 ~ 0 ~ ~o ~
8 244 Bacteria in Circulat4ng Blood. such an extent that the bacteria were able to produce a general infection. Or, on the other hand, the life within the tissues of the host increased the infectivity of the bacteria and they were able to overcome the opposition offered by the rabbit. Experiment 4.--This experiment was made one month after experiment 3. The bacteria had been kept on artificial media during this time. The quantities of culture used and other points of technique were the same as in the preceding experiments. Three rabbits are given in table IV to represent the nature of infections obtained at this time. In experiment 4 the bacteria were almost devoid of infecting power and they behaved very much as saprophytes; they rapidly disappeared from the circulation and were not able to reappear. The rabbits showed no signs of disease and remained in perfect condition. PNEUMOCOCCUS INFECTIONS. A number of experiments were carried out with the pneumococcus similar to those just described with the streptococcus. Depending upon the virulence and the number of bacter{a injected, a pneumococcic infection in the rabbit may take any one of the three courses described in the streptococcic infections. The initial decrease in the number of bacteria in the blood may not be as complete as with the streptococcus, especially if a very large number of bacteria are injected. Pneumococci usually begin to reappear in the blood earlier than streptococci. The infections are more acute and severe. The types of infection are even more defined than with the streptococcus. The acute infections last from two to three days. In from two to three hours the bacteria have largely disappeared from the blood. Cultures taken at five hours usually show an increase in the number of colonies and this reaches a heavy septicemia in from eighteen to twenty-four hours. The animals die within forty-eight to seventy-two hours. Rabbit I in table V is an example of this type of infection. If the bacteria have lost in virulence or if a smaller number is injected, a chronic infection occurs. Rabbit 2 of table V represents this class typically. The bacteria disappear from the blood more rapidly and the reappearance is delayed and the increase is slight and is followed by a second decrease. The rabbits usually have a low septicemia for several days. This is followed by a rise and the animal dies within one to two
9 Carroll G. Bull. 245 ~.~ ~ o ~ ~ e~ N S i~... ~ o ~
10 246 Bacteria in Circulating Blood. days. At autopsy severe local lesions are always found. The localization may be in the pericardium, pleura,, peritoneum, or in the subcutaneous tissues of the abdomen. In one rabbit localization occurred in the kidneys. Any two or more of these places may be involved in the same animal, but many times only one is affected. The bacteria accumulate in great quantities in these localities; when present, septicemia almost invariably precedes death. In the third type the rabbit masters the situation within a few hours; (he bacteria disappear from the blood permanently and the animal continues in perfect condition. Rabbit 3 in table V falls in this class. SUMMARY. When rabbits are injected intravenously with a quantity of virulent streptococci or pneumococci sufficient to cause death within two to four days the septicemia takes a definite course with slight variations. The bacteria rapidly decrease in number from the time of the injection to from two to four hours, at which time the blood is sterile or contains only a few bacteria. Within five to six hours the bacteria reappear in the blood and steadily increase until the death of the animal. If the bacteria are less virulent, the same quantity of culture causes a chroniciltype of infection. The same initial decrease in the number of bacteria occurs. The re~ntrance into the blood is somewhat delayed, the septicemia does not reach the height obtained in the acute cases, and a second fall occurs within the course of a few hours. These rabbits show a low blood invasion or a sterile blood culture for several days. During this time they become emaciated to a marked degree. Then the low septicemia rapidly rises or the rabbit with a sterile culture develops a severe septicemia within a few hours and death takes place from a few hours to two days thereafter. In this type of infection local lesions, pericarditis, pleurisy, peritonitis, etc., are usually found. In the infections which run an acute course no gross lesions are found. If the bacteria are still less virulent they never reenter the blood after the initial disappearance and the rabbits remain in good condition. In order to obtain uniform results, the quantity of bacteria injected must not be so large that the bacterial substances
11 Carroll G. Bull. 247.,.., ~...~ >: ~ ~ o -~,-..1 ~X,.: o ~ ~ ~x~ ~ ~ ~ a ~ o.~ - o'- o h ~o,b,,
12 248 Bacteria in Circulating Blood. carried in are sufficient to cause an intoxication of the animal. If the quantity of bacteria injected is below this point the course of the infection depends largely upon the virulence of the infecting organisms. Yet variations in the natural resistance of individual animals may be sufficient to cause quite marked irregularities in the course of the infection. Pneumococci can be standardized so as to produce a particular type of infection more easily than streptococci. In general infections such as those produced by streptococci and pneumococci the number of the bacteria present in the circulating blood at a given time supplies accurate and delicate information regarding the severity of the disease. When the object is to determine the degree of virulence of bacteria, or of the efficiency of an experimental therapeutic method, the mere physical condition and mere death of the inoculated animals are not sufficient and satisfactory guides to the desired information. The death of the inoculated animal and the recovery of the infecting bacteria at autopsy do not give complete information concerning the intensity and course of the infection occurring during life. A large number of bacteria found in the blood and tissues at autopsy do not necessarily prove the existence of a heavy infection before the onset of the death agony, since it is a well known fact that bacteria multiply with enormous rapidity, once the natural resistance of the animal has been overcome. Therefore, if merely the life and death of the animal and autopsy findings must serve as our only guides, we shall lose much incidental information, perhaps of fundamental value. This may be especially true as regards the search for curative substances. Again, the individual animals of the same species, age, and apparently of identical physical condition react to the aggressive force of the infecting organisms variously. This fact is readily found out by the injection of a series of rabbits with lethal quantities of bacteria per body-weight, and by making tests at various periods before death results, which, in the case of streptococci, ranges from one to six days. Consequently a method which enables the determination of the degree and progress of the infection at any desired period is of obvious advantage.
EXPERIMENTAL PNEUMONIA IN MICE FOLLOWING THE INHALATION OF STREPTOCOCCUS H2EMOLYTICUS AND OF FRIEDLANDER'S BACILLUS.
 EXPERIMENTAL PNEUMONIA IN MICE FOLLOWING THE INHALATION OF STREPTOCOCCUS H2EMOLYTICUS AND OF FRIEDLANDER'S BACILLUS. BY ERNEST G. STILLMAN, M.D., AND ARNOLD BRANCH, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller
EXPERIMENTAL PNEUMONIA IN MICE FOLLOWING THE INHALATION OF STREPTOCOCCUS H2EMOLYTICUS AND OF FRIEDLANDER'S BACILLUS. BY ERNEST G. STILLMAN, M.D., AND ARNOLD BRANCH, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller
IMMUNITY FACTORS IN PNEUMOCOCCUS INFECTION IN THE DOG.
 Published Online: 1 July, 1916 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.24.1.7 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 21, 2018 IMMUNITY FACTORS IN PNEUMOCOCCUS INFECTION IN THE DOG. BY CARROLL G. BULL,
Published Online: 1 July, 1916 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.24.1.7 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 21, 2018 IMMUNITY FACTORS IN PNEUMOCOCCUS INFECTION IN THE DOG. BY CARROLL G. BULL,
ACTIVE AND PASSIVE IMMUNITY TO PNEUMOCOCCUS INFECTION INDUCED IN RABBITS BY IMMUNI- ZATION WITH R PNEUMOCOCCI.
 ACTIVE AND PAIVE IMMUNITY TO PNEUMOCOCCU INFECTION INDUCED IN RABBIT BY IMMUNI- ZATION WITH R PNEUMOCOCCI. BY WILLIAM. TILLETT, M.D. Frora the Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.)
ACTIVE AND PAIVE IMMUNITY TO PNEUMOCOCCU INFECTION INDUCED IN RABBIT BY IMMUNI- ZATION WITH R PNEUMOCOCCI. BY WILLIAM. TILLETT, M.D. Frora the Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.)
STUDIES ON THE BIOLOGY OF STREPTOCOCCUS.
 Published Online: August, 94 Supp Info: http://doi.org/.84/jem.4..53 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 4, 8 STUDIES ON THE BIOLOGY OF STREPTOCOCCUS. III. AGGLUTINATION AND ABSORPTION OF AGCLUTININ
Published Online: August, 94 Supp Info: http://doi.org/.84/jem.4..53 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 4, 8 STUDIES ON THE BIOLOGY OF STREPTOCOCCUS. III. AGGLUTINATION AND ABSORPTION OF AGCLUTININ
THE AGGLUTINABILITY OF BLOOD AND AGAR STRAINS OF TYPHOID BACILLI.
 THE AGGLUTINABILITY OF BLOOD AND AGAR STRAINS OF TYPHOID BACILLI. BY CARROLL G. BULL, M.D., AND IDA W. PRITCHETT. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for
THE AGGLUTINABILITY OF BLOOD AND AGAR STRAINS OF TYPHOID BACILLI. BY CARROLL G. BULL, M.D., AND IDA W. PRITCHETT. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for
(From the Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute far Medical Research) (Received for publication, May 13, 1936)
 Published Online: 1 October, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.64.4.553 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 30, 2018 A SKIN TEST FOR DETECTING GROUP C HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCAL INFECTION
Published Online: 1 October, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.64.4.553 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 30, 2018 A SKIN TEST FOR DETECTING GROUP C HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCAL INFECTION
Morphology, Cultural Properties, and Virulence of the Strain of Leptospira Isolated in Merida.
 Published Online: 1 November, 1920 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.32.5.627 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 17, 2018 IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES WITH A STRAIN OF LEPTO- SPIRA ISOLATED FROM~
Published Online: 1 November, 1920 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.32.5.627 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 17, 2018 IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES WITH A STRAIN OF LEPTO- SPIRA ISOLATED FROM~
BACTERIA. media for bacteria highly desirable. Douglas and Gordon in England, and more recently Meyer in this country, have proposed
 YEAST AUTOLYSATE AS A CULTURE MEDIUM FOR BACTERIA I. J. KLIGLER From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research Received for publication November 23, 1918 The necessity for conserving
YEAST AUTOLYSATE AS A CULTURE MEDIUM FOR BACTERIA I. J. KLIGLER From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research Received for publication November 23, 1918 The necessity for conserving
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS OF THE RABBIT.
 Published Online: 1 February, 1925 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.41.2.275 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 3, 2018 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS OF THE RABBIT. VI.
Published Online: 1 February, 1925 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.41.2.275 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 3, 2018 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS OF THE RABBIT. VI.
RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
THE RESPIRATION MECHANISM OF PNEUMOCOCCUS. III*
 THE RESPIRATION MECHANISM OF PNEUMOCOCCUS. III* BY M. G. SEVAG A~rD LORE MAIWEG (From the Robert Koch Institute, Berlin, Germany) (Received for publication, April 11, 1934) In two previous communications
THE RESPIRATION MECHANISM OF PNEUMOCOCCUS. III* BY M. G. SEVAG A~rD LORE MAIWEG (From the Robert Koch Institute, Berlin, Germany) (Received for publication, April 11, 1934) In two previous communications
(From the Division of Radiology, Department of Medicine of the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York)
 Published Online: 1 February, 1940 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.71.2.169 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 7, 2019 THE THERMAL INACTIVATION TIME AT 41.5 C. OF THREE STRAINS OF HERPES
Published Online: 1 February, 1940 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.71.2.169 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 7, 2019 THE THERMAL INACTIVATION TIME AT 41.5 C. OF THREE STRAINS OF HERPES
A Change in the Contagious Character of a Strain of Swine Influenza
 SWINE INFLUENZA V. STUDIES ON CONTAGION BY RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Received for publication,
SWINE INFLUENZA V. STUDIES ON CONTAGION BY RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Received for publication,
REACTIONS OF RABBITS TO INTRACUTANEOUS INJEC- TIONS OF PNEUMOCOCCI AND THEIR PRODUCTS
 REACTIONS OF RABBITS TO INTRACUTANEOUS INJEC- TIONS OF PNEUMOCOCCI AND THEIR PRODUCTS V. THE DEVELOPMENT OF EYE REACTIVITY TO DERIVATIVES OF PNEUMOCOCCI BY LOUIS A. JULIANELLE, PH.D. (From the Hospital
REACTIONS OF RABBITS TO INTRACUTANEOUS INJEC- TIONS OF PNEUMOCOCCI AND THEIR PRODUCTS V. THE DEVELOPMENT OF EYE REACTIVITY TO DERIVATIVES OF PNEUMOCOCCI BY LOUIS A. JULIANELLE, PH.D. (From the Hospital
THE OXYGEN CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN RABBITS INFECTED WITH PNEUMOCOCCUS.* BY FRANCIS W. PEABODY, M.D.
 THE OXYGEN CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN RABBITS INFECTED WITH PNEUMOCOCCUS.* BY FRANCIS W. PEABODY, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) It has been shown by
THE OXYGEN CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN RABBITS INFECTED WITH PNEUMOCOCCUS.* BY FRANCIS W. PEABODY, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) It has been shown by
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A RABBIT RESPIRATORY INFECTION. V. EXPERIMENTAL SNUFFLES.
 THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A RABBIT RESPIRATORY INFECTION. V. EXPERIMENTAL SNUFFLES. BY LESLIE T. WEBSTER, M. D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication,
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A RABBIT RESPIRATORY INFECTION. V. EXPERIMENTAL SNUFFLES. BY LESLIE T. WEBSTER, M. D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication,
value as a medium for the in vivo cultivation of different
 THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VIRUS OF EQUINE ENCEPH- ALOMYELITIS ON THE CHORIOALLANTOIC MEMBRANE OF THE DEVELOPING CHICK' ELIZABETH HIGBIE AND BEATRICE HOWITT George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California,
THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VIRUS OF EQUINE ENCEPH- ALOMYELITIS ON THE CHORIOALLANTOIC MEMBRANE OF THE DEVELOPING CHICK' ELIZABETH HIGBIE AND BEATRICE HOWITT George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California,
NON-LACTOSE FERMENTING BACTERIA FROM. While B. coli is generally accepted as a satisfactory index of
 NON-LACTOSE FERMENTING BACTERIA FROM POLLUTED WELLS AND SUB-SOIL' I. J. KLIGLER From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York Received for publication February 1, 1918
NON-LACTOSE FERMENTING BACTERIA FROM POLLUTED WELLS AND SUB-SOIL' I. J. KLIGLER From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York Received for publication February 1, 1918
ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.*
 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
(From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New Jersey)
 THE YIELD OF RABIES VIRUS IN THE CHICK EMBRYO BY BJORN SIGURDSSON, M.D.* (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New Jersey) (Received
THE YIELD OF RABIES VIRUS IN THE CHICK EMBRYO BY BJORN SIGURDSSON, M.D.* (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New Jersey) (Received
THE EFFECT OF NUTRITIONAL DISTURBANCES ON THE SUSCEPTIBILITY OF MICE TO STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS*
 Published Online: 1 January, 1956 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.13.1.19 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on May 14, 218 THE EFFECT OF NUTRITIONAL DISTURBANCES ON THE SUSCEPTIBILITY OF MICE TO STAPHYLOCOCCAL
Published Online: 1 January, 1956 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.13.1.19 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on May 14, 218 THE EFFECT OF NUTRITIONAL DISTURBANCES ON THE SUSCEPTIBILITY OF MICE TO STAPHYLOCOCCAL
THE INFECTION OF MICE WITH SWINE INFLUENZA VIRUS
 Published Online: 1 October, 1935 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.62.4.561 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 19, 2018 THE INFECTION OF MICE WITH SWINE INFLUENZA VIRUS BY RICHARD E. SHOPE,
Published Online: 1 October, 1935 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.62.4.561 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 19, 2018 THE INFECTION OF MICE WITH SWINE INFLUENZA VIRUS BY RICHARD E. SHOPE,
resulting from evaporation of the spray droplets and containing viable bacteria have measurable settling velocities. Under our
 STUDIES ON MICROORGANISMS IN SIMULATED ROOM ENVIRONMENTS II. THE SURVIVAL RATES OF STREPTOCOCCI IN THE DARK' LEON BUCHBINDER AND EARLE B. PHELPS DeLamar Institute of Public Health, College of Physicians
STUDIES ON MICROORGANISMS IN SIMULATED ROOM ENVIRONMENTS II. THE SURVIVAL RATES OF STREPTOCOCCI IN THE DARK' LEON BUCHBINDER AND EARLE B. PHELPS DeLamar Institute of Public Health, College of Physicians
THE OCCURRENCE OF CARRIERS OF DISEASE-PRO- DUCING TYPES OF PNEUMOCOCCUS.
 Published Online: 1 July, 1915 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.22.1.105 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 21, 2018 THE OCCURRENCE OF CARRIERS OF DISEASE-PRO- DUCING TYPES OF PNEUMOCOCCUS.
Published Online: 1 July, 1915 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.22.1.105 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 21, 2018 THE OCCURRENCE OF CARRIERS OF DISEASE-PRO- DUCING TYPES OF PNEUMOCOCCUS.
IMMUNITY STUDIES OF ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER. I. USEFULNESS OF IMMUNE SERUM IN SUPPRESSING AN IMPENDING INFECTION. BY HIDEYO NOGUCHI, M.D.
 IMMUNITY STUDIES OF ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER. I. USEFULNESS OF IMMUNE SERUM IN SUPPRESSING AN IMPENDING INFECTION. BY HIDEYO NOGUCHI, M.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical
IMMUNITY STUDIES OF ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER. I. USEFULNESS OF IMMUNE SERUM IN SUPPRESSING AN IMPENDING INFECTION. BY HIDEYO NOGUCHI, M.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical
THE EFFECTS OF ACIDITY UPON THE GROWTH OF PNEUMOCOCCUS IN CULTURE MEDIA CONTAINING PROTEINS
 THE EFFECTS OF ACIDITY UPON THE GROWTH OF PNEUMOCOCCUS IN CULTURE MEDIA CONTAINING PROTEINS BY WILLIAM H. KELLEY, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine of the Duke University School of Medicine, Durham,
THE EFFECTS OF ACIDITY UPON THE GROWTH OF PNEUMOCOCCUS IN CULTURE MEDIA CONTAINING PROTEINS BY WILLIAM H. KELLEY, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine of the Duke University School of Medicine, Durham,
COAGULATION TIME OF THE BLOOD IN LOBAR PNEUMONIA.*
 COAGULATION TIME OF THE BLOOD IN LOBAR PNEUMONIA.* BY A. R. DOCHEZ, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Observation of the variation in time within which
COAGULATION TIME OF THE BLOOD IN LOBAR PNEUMONIA.* BY A. R. DOCHEZ, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Observation of the variation in time within which
(From the Thorndike Memorial Laboratory, Boston City Hospital, and the Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston)
 STREPTOCOCCI IN INFECTIOUS (ATROPHIC) ARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATIC FEVER BY ROBERT N. NYE, M.D., AND EDGAR A. WAXELBAUM, M.D. (From the Thorndike Memorial Laboratory, Boston City Hospital, and the Department
STREPTOCOCCI IN INFECTIOUS (ATROPHIC) ARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATIC FEVER BY ROBERT N. NYE, M.D., AND EDGAR A. WAXELBAUM, M.D. (From the Thorndike Memorial Laboratory, Boston City Hospital, and the Department
AN OUTBREAK OF MOUSE TYPHOID AND ITS ATTEMPTED CONTROL BY VACCINATION. (Received for publication, Jammry 28, 1922.)
 AN OUTBREAK OF MOUSE TYPHOID AND ITS ATTEMPTED CONTROL BY VACCINATION. BY CLARA J. LYNCH, PH.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication, Jammry
AN OUTBREAK OF MOUSE TYPHOID AND ITS ATTEMPTED CONTROL BY VACCINATION. BY CLARA J. LYNCH, PH.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication, Jammry
THE PASSAGE OF TYPE III RABBIT VIRULENT PNEUMOCOCCI FROM THE VASCULAR SYSTEM INTO JOINTS AND CERTAIN OTHER BODY CAVITIES*t
 Published Online: 1 September, 1939 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.70.3.293 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 26, 2018 THE PASSAGE OF TYPE III RABBIT VIRULENT PNEUMOCOCCI FROM THE VASCULAR
Published Online: 1 September, 1939 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.70.3.293 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 26, 2018 THE PASSAGE OF TYPE III RABBIT VIRULENT PNEUMOCOCCI FROM THE VASCULAR
bacteriology to an analysis of changes occurring in the sea. The FATE OF FRESH WATER BACTERIA IN T
 FATE OF FRESH WATER BACTERIA IN T SEA VICTOR BURKE AD LENNA A. BAIRD Bacteriological Laboratories, State College of Washington, Pullman, Washington Received for publication October 30, 1930 Fresh water
FATE OF FRESH WATER BACTERIA IN T SEA VICTOR BURKE AD LENNA A. BAIRD Bacteriological Laboratories, State College of Washington, Pullman, Washington Received for publication October 30, 1930 Fresh water
THE QUANTITATIVE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN IMMUNE SERUM AND INFECTIVE DOSE OF PARASITES AS DEMONSTRATED BY THE PROTECTION TEST IN MONKEY MALARIA
 THE QUANTITATIVE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN IMMUNE SERUM AND INFECTIVE DOSE OF PARASITES AS DEMONSTRATED BY THE PROTECTION TEST IN MONKEY MALARIA BY LOWELL T. COGGESHALL, M.D., AND MONROE D. EATON, M.D. (From
THE QUANTITATIVE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN IMMUNE SERUM AND INFECTIVE DOSE OF PARASITES AS DEMONSTRATED BY THE PROTECTION TEST IN MONKEY MALARIA BY LOWELL T. COGGESHALL, M.D., AND MONROE D. EATON, M.D. (From
(From the Department of ~Iicrobiology, New York University College of Medicine, New York)
 TRANSFORMATION REACTIONS WITH TWO NON-ALLELIC R MUTANTS OF THE SAME STRAIN OF PNEUMOCOCCUS TYPE VIII BY COLIN M. MACLEOD, M.D., AND MARJORIE R. KRAUSS (From the Department of ~Iicrobiology, New York University
TRANSFORMATION REACTIONS WITH TWO NON-ALLELIC R MUTANTS OF THE SAME STRAIN OF PNEUMOCOCCUS TYPE VIII BY COLIN M. MACLEOD, M.D., AND MARJORIE R. KRAUSS (From the Department of ~Iicrobiology, New York University
THE EXCRETION OF BORIC ACID FROM THE HUMAN BODY.
 THE EXCRETION OF BORIC ACID FROM THE HUMAN BODY. BY HARVEY W. WILEY, M.D. (From the Bureau of Chemistry, Washington, D. C.) (Received for publication, December 15, 1906.) In the studies which I have inaugurated
THE EXCRETION OF BORIC ACID FROM THE HUMAN BODY. BY HARVEY W. WILEY, M.D. (From the Bureau of Chemistry, Washington, D. C.) (Received for publication, December 15, 1906.) In the studies which I have inaugurated
OBSERVATIONS ON THE PHAGOCYTOSIS OF THE PNEUMO- COCCUS BY HUMAN WHOLE BLOOD
 Published Online: 1 May, 193 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.51.5.675 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 2, 218 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PHAGOCYTOSIS OF THE PNEUMO- COCCUS BY HUMAN WHOLE BLOOD
Published Online: 1 May, 193 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.51.5.675 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 2, 218 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PHAGOCYTOSIS OF THE PNEUMO- COCCUS BY HUMAN WHOLE BLOOD
THE PRESENCE IN THE BONE-MARROW OF ENZYMES RESEMBLING THOSE OF LEUCOCYTES.
 Published Online: 25 November, 1905 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.7.6.759 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 15, 2018 THE PRESENCE IN THE BONE-MARROW OF ENZYMES RESEMBLING THOSE OF LEUCOCYTES.
Published Online: 25 November, 1905 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.7.6.759 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 15, 2018 THE PRESENCE IN THE BONE-MARROW OF ENZYMES RESEMBLING THOSE OF LEUCOCYTES.
ESCHERICHIA COLI-MUTABILE1. antiseptics employed "activated" the lactase which was present, "activate" the lactase.
 ON THE "ACTIVATION" OF THE LACTASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI-MUTABILE1 CHARLES J. DEERE Department of Chemistry, University of Tennessee School of Biological Sciences, Memphis Received for publication August
ON THE "ACTIVATION" OF THE LACTASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI-MUTABILE1 CHARLES J. DEERE Department of Chemistry, University of Tennessee School of Biological Sciences, Memphis Received for publication August
A SIMPLE METHOD OF REMOVING LEUCOCYTES FROM BLOOD. by virtue of their fluid content, but also by conferring on the patient's blood
 METHOD OF REMOVING LEUCOCYTES FROM BLOOD. 281 the salt content falls below or rises above these limits the leucocytes do not emigrate and do not phagocyte or destroy bacteria. It has been shown also that
METHOD OF REMOVING LEUCOCYTES FROM BLOOD. 281 the salt content falls below or rises above these limits the leucocytes do not emigrate and do not phagocyte or destroy bacteria. It has been shown also that
Host Parasite Relationship. Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU
 Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
METHODS OF CONTROLLING BLACKLEG.
 METHODS OF CONTROLLING BLACKLEG. L. W. Goss. (Reprint from Director's Report, 1915-'16.) The veterinary department of the Kansas State Agricultural College began a series of experiments in 1912 to increase
METHODS OF CONTROLLING BLACKLEG. L. W. Goss. (Reprint from Director's Report, 1915-'16.) The veterinary department of the Kansas State Agricultural College began a series of experiments in 1912 to increase
Studies on the Seif-Disinfecting
 Studies on the Seif-Disinfecting Power of the Skin* JOHN F. NORTON, PH. D., F. A. P. H. A., AND MARGUERITE F. NOVY Department of Health, Detroit, Mich. A RNOLD and his coworkers' have reported experiments
Studies on the Seif-Disinfecting Power of the Skin* JOHN F. NORTON, PH. D., F. A. P. H. A., AND MARGUERITE F. NOVY Department of Health, Detroit, Mich. A RNOLD and his coworkers' have reported experiments
PATCHING AND SECTION OF THE PULMONARY ORIFICE OF THE HEART.*
 Published Online: 1 July, 1914 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20.1.3 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 24, 2018 PATCHING AND SECTION OF THE PULMONARY ORIFICE OF THE HEART.* BY THEODORE
Published Online: 1 July, 1914 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20.1.3 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 24, 2018 PATCHING AND SECTION OF THE PULMONARY ORIFICE OF THE HEART.* BY THEODORE
Routine Use of a Modified Eijkman
 Routine Use of a Modified Eijkman Medium in the Examination of Oysters, Crabmeat, and Other Substances C. A. PERRY, Sc.D., F.A.P.H.A., AND A. A. HAJNA Bureau of Bacteriology, Maryland State Department
Routine Use of a Modified Eijkman Medium in the Examination of Oysters, Crabmeat, and Other Substances C. A. PERRY, Sc.D., F.A.P.H.A., AND A. A. HAJNA Bureau of Bacteriology, Maryland State Department
EXPERIMENTAL EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE CONCEPTION OF ADAPTATION ENERGY
 EXPERIMENTAL EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE CONCEPTION OF ADAPTATION ENERGY HANS SELYE Fro,m the Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada Received for publication May
EXPERIMENTAL EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE CONCEPTION OF ADAPTATION ENERGY HANS SELYE Fro,m the Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada Received for publication May
(14, 15, 16) with serum-leucocyte mixtures. The methods. (1) and his followers used the slide cell technique devised by him and
 THE PNEUMOCOCCIDAL POWER OF WHOLE BLOOD I. DESCRIPTION OF METHOD. RESULTS IN INDIVIDUALS WITH No HISTORY OF LOBAR PNEUMONIA' By W. D. SUTLIFF AND D. R. RHOADES (From the Secand (Cornell) Medical Division
THE PNEUMOCOCCIDAL POWER OF WHOLE BLOOD I. DESCRIPTION OF METHOD. RESULTS IN INDIVIDUALS WITH No HISTORY OF LOBAR PNEUMONIA' By W. D. SUTLIFF AND D. R. RHOADES (From the Secand (Cornell) Medical Division
FATIGUE STUDIED IN REACTION TIME EXPERIMENTS. By. furnish results of a general kind, and does not enable one to arrive at a
 FATIGUE STUDIED IN REACTION TIME EXPERIMENTS. By T. H. MILROY. (From the Physiology Laboratory, Queen's University, Belfast.) (Received for publication 5th April 1909.) MANY methods have been employed
FATIGUE STUDIED IN REACTION TIME EXPERIMENTS. By T. H. MILROY. (From the Physiology Laboratory, Queen's University, Belfast.) (Received for publication 5th April 1909.) MANY methods have been employed
by some of the laboratories from which they were obtained. been taken up in the order of their importance as nearly as
 THE INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS CHEMICAL AND PHYS- ICAL AGENCIES UPON BACILLUS BOTULINUS AND ITS SPORES I. RESISTANCE TO SALT ZAE NORTHRUP WYANT AND RUTH NORMINGTON From the Bacteriological Laboratory of the
THE INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS CHEMICAL AND PHYS- ICAL AGENCIES UPON BACILLUS BOTULINUS AND ITS SPORES I. RESISTANCE TO SALT ZAE NORTHRUP WYANT AND RUTH NORMINGTON From the Bacteriological Laboratory of the
(From the Department of Medicine, the Peiping Union Medical College, Peiping, China)
 Published Online: 1 April, 1934 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.59.4.491 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 9, 2018 VIABLE LEISHMANIA DONOVANI IN NASAL AND ORAL SECRETIONS OF PATIENTS WITH
Published Online: 1 April, 1934 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.59.4.491 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 9, 2018 VIABLE LEISHMANIA DONOVANI IN NASAL AND ORAL SECRETIONS OF PATIENTS WITH
CULTIVATION OF VACCINE VIRUS
 Published Online: 1 October, 1930 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.52.4.465 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 27, 2018 CULTIVATION OF VACCINE VIRUS BY C. P. LI, M.D., Am) T. M. RIVERS, M.D.
Published Online: 1 October, 1930 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.52.4.465 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 27, 2018 CULTIVATION OF VACCINE VIRUS BY C. P. LI, M.D., Am) T. M. RIVERS, M.D.
THE USE OF YELLOW FEVER VIRUS MODIFIED BY IN VITRO CULTIVATION FOR HUMAN IMMUNIZATION
 THE USE OF YELLOW FEVER VIRUS MODIFIED BY IN VITRO CULTIVATION FOR HUMAN IMMUNIZATION BY MAX THEILER, M.R.C.S., L.R.C.P., ANn HUGH H. SMITH, M.D. (From the Laboratories of the International Health Division,
THE USE OF YELLOW FEVER VIRUS MODIFIED BY IN VITRO CULTIVATION FOR HUMAN IMMUNIZATION BY MAX THEILER, M.R.C.S., L.R.C.P., ANn HUGH H. SMITH, M.D. (From the Laboratories of the International Health Division,
THE EFFECT OF TESTICULAR EXTRACTS ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM
 55 THE EFFECT OF TESTICULAR EXTRACTS ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM BY L. MIRVISH AND L. P. BOSMAN. (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Cape Town.) {Received 12th February 1929.) IT has long been
55 THE EFFECT OF TESTICULAR EXTRACTS ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM BY L. MIRVISH AND L. P. BOSMAN. (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Cape Town.) {Received 12th February 1929.) IT has long been
A Change in the Type of Lesion Produced by the Fibroma Virus
 A CHANGE IN RABBIT FIBROMA VIRUS SUGGESTING MUTATION II. BEHAVIOR 0]~ THE VARIANT VIRUS IN COTTONTAIL RABBITS BY RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller
A CHANGE IN RABBIT FIBROMA VIRUS SUGGESTING MUTATION II. BEHAVIOR 0]~ THE VARIANT VIRUS IN COTTONTAIL RABBITS BY RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller
Consequently, the authors decided to investigate the various A STUDY OF METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF
 A STUDY OF METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS IN BACTERIAL CULTURES COLORIMETRIC METHODS DOROTHEA KLEMME AND CHARLES F. POE Division of Sanitary Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, University
A STUDY OF METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS IN BACTERIAL CULTURES COLORIMETRIC METHODS DOROTHEA KLEMME AND CHARLES F. POE Division of Sanitary Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, University
GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which
 ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
differing from the Neisser-Wechsberg leucocidin, which does not affect human CLASSIFICATION OF 110 STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
 CLASSIFICATION OF 110 STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS Lederle Laboratories, Inc., Pearl River, New York Received for publication April 24, 1942 A collection of strains of Staphylococcus aureus was studied
CLASSIFICATION OF 110 STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS Lederle Laboratories, Inc., Pearl River, New York Received for publication April 24, 1942 A collection of strains of Staphylococcus aureus was studied
EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS
 EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS INTRACELLULAR GROWTH OF Salmonella enteritidis INGESTED IN MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES OF MICE, AND CELLULAR BASIS OF IMMUNITY SUSUMU MITSUHASHI, ICHIEI SATO, AND TOKUMITSU TANAKA
EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS INTRACELLULAR GROWTH OF Salmonella enteritidis INGESTED IN MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES OF MICE, AND CELLULAR BASIS OF IMMUNITY SUSUMU MITSUHASHI, ICHIEI SATO, AND TOKUMITSU TANAKA
ON THE MECHANISM OF CARCINOGENESIS BY CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS
 ON THE MECHANISM OF CARCINOGENESIS BY CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS IZRAEL RIEGER (From the Research Institute of the Royal Cancer H osjjital (Free), London, S. W. 3) INTRODUCTION The object of the experiments described
ON THE MECHANISM OF CARCINOGENESIS BY CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS IZRAEL RIEGER (From the Research Institute of the Royal Cancer H osjjital (Free), London, S. W. 3) INTRODUCTION The object of the experiments described
A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
Streptococcus thermophilus which grows actively at temperatures
 STREPTOCOCCI WHICH GROW AT HIGH TEMPERATURES Department of Dairy Industry, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York Received for publication, "April 16, 1931 INTRODUCTION Although streptococci have been exhaustively
STREPTOCOCCI WHICH GROW AT HIGH TEMPERATURES Department of Dairy Industry, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York Received for publication, "April 16, 1931 INTRODUCTION Although streptococci have been exhaustively
THE NORMAL LIMITS OF VARIATION OF THE METHY- LENE-BLUE REDUCTION TEST '
 THE NORMAL LIMITS OF VARIATION OF THE METHY- LENE-BLUE REDUCTION TEST ' By A. C. FAY Dairy Bacteriologist^ Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station INTRODUCTION The methylene-blue reduction or reducíase
THE NORMAL LIMITS OF VARIATION OF THE METHY- LENE-BLUE REDUCTION TEST ' By A. C. FAY Dairy Bacteriologist^ Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station INTRODUCTION The methylene-blue reduction or reducíase
The Bacteriological Examination of Exudate
 STUDIES ON AN UNCOMPLICATED CORYZA OF THE DOMESTIC FOWL VI. COCCOBACILLI]~OI~_M BODIES IN BIRDS INFECTED WITH THE CORYZA OF SLOW ONSET BY JOHN B. NELSON, PH.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant
STUDIES ON AN UNCOMPLICATED CORYZA OF THE DOMESTIC FOWL VI. COCCOBACILLI]~OI~_M BODIES IN BIRDS INFECTED WITH THE CORYZA OF SLOW ONSET BY JOHN B. NELSON, PH.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant
SOME OBSERVATIONS UPON SODIUM ALGINATE. By 0. M. SOLANDT. From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.
 582.6 SOME OBSERVATIONS UPON SODIUM ALGINATE. By 0. M. SOLANDT. From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge. (Received for publication 13th December 1940.) ALGINIC acid was discovered by Stanford in 1883
582.6 SOME OBSERVATIONS UPON SODIUM ALGINATE. By 0. M. SOLANDT. From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge. (Received for publication 13th December 1940.) ALGINIC acid was discovered by Stanford in 1883
plant inoculations, to fulfil Koch's postulates, are
 THE VALUE OF SEROLOGICAL TESTS FOR THE IDEN- TIFICATION OF PSEUDOMONAS MALVACEARUM Wellcome Tropical Research Laboratories, Khartoum Received for publication April 15, 1931 The chief objects of the present
THE VALUE OF SEROLOGICAL TESTS FOR THE IDEN- TIFICATION OF PSEUDOMONAS MALVACEARUM Wellcome Tropical Research Laboratories, Khartoum Received for publication April 15, 1931 The chief objects of the present
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES. Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to:
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
Immune System. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Immune System Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the bacteria is the cause of pneumonia? a. staphylococci c. Treponema
Class: Date: Immune System Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the bacteria is the cause of pneumonia? a. staphylococci c. Treponema
Identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae in
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 173-177 Copyright 01975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Application of Counterimmunoelectrophoresis in the Identification
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 173-177 Copyright 01975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Application of Counterimmunoelectrophoresis in the Identification
nitrogen-containiing groups gives increased solubility, but the
 THE BACTERIOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME NEW WATER SOLUBLE ORGANO-MERCURY COMPOUNDS, JOHN H. WALDO, H. A. SHONLE AND H. M. POWELL Lilly Research Laboratories, Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana
THE BACTERIOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME NEW WATER SOLUBLE ORGANO-MERCURY COMPOUNDS, JOHN H. WALDO, H. A. SHONLE AND H. M. POWELL Lilly Research Laboratories, Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana
Organisms used. The routine test organism was a putrefactive anaerobe, Company, and Bacilus stearothermophilus, strain NCA 1518.
 THE EFFECT OF OXIDATIVE RANCIDITY IN UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS ON THE GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES NORMAN G. ROTH2 AND H. 0. HALVORSON Department of Bacteriology, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois
THE EFFECT OF OXIDATIVE RANCIDITY IN UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS ON THE GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES NORMAN G. ROTH2 AND H. 0. HALVORSON Department of Bacteriology, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois
IMMUNITY OF MICE FOLLOWING SUBCUTANEOUS VACCINATION WITH ST. LOUIS ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS
 IMMUNITY OF MICE FOLLOWING SUBCUTANEOUS VACCINATION WITH ST. LOUIS ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS BY LESLIE T. WEBSTER, M.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Researck) (Received for
IMMUNITY OF MICE FOLLOWING SUBCUTANEOUS VACCINATION WITH ST. LOUIS ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS BY LESLIE T. WEBSTER, M.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Researck) (Received for
PHENANTHRIDINE COMPOUNDS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (195), 5, 398. THE CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC ACTION OF PHENANTHRIDINE COMPOUNDS PART IV ACTIVITY IN VITRO BY J. A. LOCK From the Wellcome Laboratories of Tropical Medicine, N.W.1 183, Euston
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (195), 5, 398. THE CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC ACTION OF PHENANTHRIDINE COMPOUNDS PART IV ACTIVITY IN VITRO BY J. A. LOCK From the Wellcome Laboratories of Tropical Medicine, N.W.1 183, Euston
EFFECT OF THE AMINO ACIDS AND DIALYZABLE CONSTITUENTS OF EMBRYONIC TISSUE JUICE ON THE GROWTH OF FIBROBLASTS.
 Published Online: 1 September, 1926 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.44.3.397 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on May 11, 2018 EFFECT OF THE AMINO ACIDS AND DIALYZABLE CONSTITUENTS OF EMBRYONIC TISSUE
Published Online: 1 September, 1926 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.44.3.397 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on May 11, 2018 EFFECT OF THE AMINO ACIDS AND DIALYZABLE CONSTITUENTS OF EMBRYONIC TISSUE
Increased Microbiological Challenge Test with Bunsen Burner Inside the Cabinet
 Increased Microbiological Challenge Test with Bunsen Burner Inside the Cabinet Introduction Bunsen Burner is the most frequently used apparatus in the laboratory as a source of heat. Typically used inside
Increased Microbiological Challenge Test with Bunsen Burner Inside the Cabinet Introduction Bunsen Burner is the most frequently used apparatus in the laboratory as a source of heat. Typically used inside
CONTENT OF ICE CREAM MIX' A. C. FAY AND N. E. OLSON Kansas State Agricultural College. Received for publication, April 15, 1927 INTRODUCTION
 THE EFFECT OF GELATIN ON THE BACTERIAL CONTENT OF ICE CREAM MIX' A. C. FAY AND N. E. OLSON Kansas State Agricultural College Received for publication, April 15, 197 INTRODUCTION During the past few years
THE EFFECT OF GELATIN ON THE BACTERIAL CONTENT OF ICE CREAM MIX' A. C. FAY AND N. E. OLSON Kansas State Agricultural College Received for publication, April 15, 197 INTRODUCTION During the past few years
Fig. 1. Clinical condition. before operation.
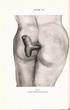 PLATE IX. Fig. 1. Clinical condition before operation. A CASE OF RECTAL PROLAPSE. BY D. Robertson, M.B., Ch.B. (Edin.), AND D. G. C. Tasker, M.S. (Lond.), F.R.C.S. (Eng.). On many occasions in the practice
PLATE IX. Fig. 1. Clinical condition before operation. A CASE OF RECTAL PROLAPSE. BY D. Robertson, M.B., Ch.B. (Edin.), AND D. G. C. Tasker, M.S. (Lond.), F.R.C.S. (Eng.). On many occasions in the practice
THE RELATION OF NATURAL HUMORAL ANTIPNEUMO- COCCAL IMMUNITY TO THE INCEPTION OF LOBAR PNEUMONIA
 Published Online: 1 September, 1930 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.52.3.421 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 5, 2018 THE RELATION OF NATURAL HUMORAL ANTIPNEUMO- COCCAL IMMUNITY TO THE
Published Online: 1 September, 1930 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.52.3.421 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 5, 2018 THE RELATION OF NATURAL HUMORAL ANTIPNEUMO- COCCAL IMMUNITY TO THE
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF JAUNDICE
 CHARLES L. HARTSOCK, M.D. The yellow or greenish yellow staining of the blood plasma and body tissues, to which the clinical term jaundice has been applied, is due to an excessive amount of one of the
CHARLES L. HARTSOCK, M.D. The yellow or greenish yellow staining of the blood plasma and body tissues, to which the clinical term jaundice has been applied, is due to an excessive amount of one of the
AMYL-META-CRESOL. THE DISINFECTANT AND ANTISEPTIC PROPERTIES OF. administer large doses daily without toxic symptoms.
 DISINFECTANT PROPERTIES OF AMYL-META-CRESOL. 331 SUMMARY. 1. The toxicity of amyl-meta-cresol and hexyl resorcinol has been determined on rats and mice. Both compounds are relatively non-toxic, the cresol
DISINFECTANT PROPERTIES OF AMYL-META-CRESOL. 331 SUMMARY. 1. The toxicity of amyl-meta-cresol and hexyl resorcinol has been determined on rats and mice. Both compounds are relatively non-toxic, the cresol
STUDIES IN BLOOD DIASTASE. FACTORS WHICH CAUSE. The effects of the following procedures on the blood diastase have
 STUDIES IN BLOOD DIASTASE. FACTORS WHICH CAUSE VARIATIONS IN THE AMOUNT OF DIASTASE IN THE BLOOD. By CHARLES REID and B. NARAYANA. From the Department of Physiology, Prince of Wales Medical College, Patna.
STUDIES IN BLOOD DIASTASE. FACTORS WHICH CAUSE VARIATIONS IN THE AMOUNT OF DIASTASE IN THE BLOOD. By CHARLES REID and B. NARAYANA. From the Department of Physiology, Prince of Wales Medical College, Patna.
CURVE OF SUGAR EXCRETION IN SEVERE DIABETES.
 CURVE OF SUGAR EXCRETION IN SEVERE DIABETES. BY HANNAH FELSHER. (From the Otho S. A. Sprague Memorial Institute Laboratory oj Clinical Research, Rush Medical College, Chicago.) (Received for publication,
CURVE OF SUGAR EXCRETION IN SEVERE DIABETES. BY HANNAH FELSHER. (From the Otho S. A. Sprague Memorial Institute Laboratory oj Clinical Research, Rush Medical College, Chicago.) (Received for publication,
BISMUTH, WITH REFERENCE TO ITS
 VI NOTES ON THE PHARMACOLOGY OF BISMUTH, WITH REFERENCE TO ITS EMPLOYMENT IN THE THERAPY OF SYPHILIS By SVEND LOMHOLT, O.B.E., M.D. (From the Finsen Light Institute, Copenhagen. DR. A. REYN, Director.)
VI NOTES ON THE PHARMACOLOGY OF BISMUTH, WITH REFERENCE TO ITS EMPLOYMENT IN THE THERAPY OF SYPHILIS By SVEND LOMHOLT, O.B.E., M.D. (From the Finsen Light Institute, Copenhagen. DR. A. REYN, Director.)
ethylene glycol. The latter was regarded as the more suitable solvent, by Smith and Clark (1937) one of the important differential points
 STUDIES OF THE COMMON AEROBIC SPORE-FORMING BACILLI, I. STAINING FOR FAT WITH SUDAN BLACK B-SAFRANIN KENNETH L. BURDON,2 Consultant, JULIA C. STOKES, Junior Bacteriologist, AND CECIL E. KIMBROUGH, Assistant
STUDIES OF THE COMMON AEROBIC SPORE-FORMING BACILLI, I. STAINING FOR FAT WITH SUDAN BLACK B-SAFRANIN KENNETH L. BURDON,2 Consultant, JULIA C. STOKES, Junior Bacteriologist, AND CECIL E. KIMBROUGH, Assistant
SACCHARIDES IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM DOSAGE
 THE USE OF THE SKIN TEST WITH THE TYPE SPECIFIC POLY- SACCHARIDES IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM DOSAGE IN PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA By COLIN M. MAcLEOD, CHARLES L. HOAGLAND, AND PAUL B. BEESON (From the Hospital
THE USE OF THE SKIN TEST WITH THE TYPE SPECIFIC POLY- SACCHARIDES IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM DOSAGE IN PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA By COLIN M. MAcLEOD, CHARLES L. HOAGLAND, AND PAUL B. BEESON (From the Hospital
THE BACTERICIDAL PROPERTIES OF ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATED LIPIDS OF THE SKIN
 THE BACTERICIDAL PROPERTIES OF ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATED LIPIDS OF THE SKIN BY FRANKLIN A. STEVENS, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine, College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, and the
THE BACTERICIDAL PROPERTIES OF ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATED LIPIDS OF THE SKIN BY FRANKLIN A. STEVENS, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine, College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, and the
BY LESLIE T. WEBSTER, M.D.
 Published Online: 1 June, 1924 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.39.6.843 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on April 25, 218 THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A RABBIT RESPIRATORY INFETION. II. LINIAL, PATHOLOGIAL,
Published Online: 1 June, 1924 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.39.6.843 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on April 25, 218 THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF A RABBIT RESPIRATORY INFETION. II. LINIAL, PATHOLOGIAL,
I. QUANTITATIVE OBSERVATION OF THE ACTION
 Japan. J. Microb., Vol. 5, No. 4, 1961 UDC: 576. 882. 822. 3. 095. 18 : 547. 295. 6 FUNGICIDAL ACTION OF CAPRYLIC ACID FOR CANDIDA ALBICANS I. QUANTITATIVE OBSERVATION OF THE ACTION TOHRU TSUKAHARA Department
Japan. J. Microb., Vol. 5, No. 4, 1961 UDC: 576. 882. 822. 3. 095. 18 : 547. 295. 6 FUNGICIDAL ACTION OF CAPRYLIC ACID FOR CANDIDA ALBICANS I. QUANTITATIVE OBSERVATION OF THE ACTION TOHRU TSUKAHARA Department
hanging-drop technique. The results are macroscopic. They are Semi-solid media have been employed for many years in the
 THE USE OF SEMI-SOLID AGAR FOR THE DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY' RALPH P. TITTSLER AND LESLIE A. SANDHOLZER Department of Bacteriology, University of Rochester, School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester,
THE USE OF SEMI-SOLID AGAR FOR THE DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY' RALPH P. TITTSLER AND LESLIE A. SANDHOLZER Department of Bacteriology, University of Rochester, School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester,
GONOCOCCAL AND NON-GONOCOC-
 VI THE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS BETWEEN GONOCOCCAL AND NON-GONOCOC- CAL EPIDIDYMITIS By KENNETH M. WALKER, F.R.C.S., Surgeon-in-Charge of Genito- Urinary Departments, Royal Northern Hospital and Miller General
VI THE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS BETWEEN GONOCOCCAL AND NON-GONOCOC- CAL EPIDIDYMITIS By KENNETH M. WALKER, F.R.C.S., Surgeon-in-Charge of Genito- Urinary Departments, Royal Northern Hospital and Miller General
(From the Department of Bacteriology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada)
 Published Online: 1 October, 1932 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.56.4.507 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 13, 2018 A COMPARISON BETWEEN CONVALESCENT SERUM AND NON-CONVALESCENT SERUM
Published Online: 1 October, 1932 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.56.4.507 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 13, 2018 A COMPARISON BETWEEN CONVALESCENT SERUM AND NON-CONVALESCENT SERUM
disease. Seventy-six separate observations have been made on 35
 THE PNEUMOCOCCIDAL POWER OF WHOLE BLOOD II. ESTIATIONS IN LOBAR PNEUMONIA' By W. D. SUTLIFF ANi D. R. RHOADES (From the Second (Corndl) Medical Division and the Patholqgical Department of Belevue Hospital,
THE PNEUMOCOCCIDAL POWER OF WHOLE BLOOD II. ESTIATIONS IN LOBAR PNEUMONIA' By W. D. SUTLIFF ANi D. R. RHOADES (From the Second (Corndl) Medical Division and the Patholqgical Department of Belevue Hospital,
IMMUNIZATION EXPERIMENTS WITH SWINE INFLUENZA VIRUS Bx RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D.
 Published Online: 1 July, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.64.1.47 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on June 27, 2018 IMMUNIZATION EXPERIMENTS WITH SWINE INFLUENZA VIRUS Bx RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D.
Published Online: 1 July, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.64.1.47 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on June 27, 2018 IMMUNIZATION EXPERIMENTS WITH SWINE INFLUENZA VIRUS Bx RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D.
Exercise 15-B PHYSIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA CONTINUED: AMINO ACID DECARBOXYLATION, CITRATE UTILIZATION, COAGULASE & CAMP TESTS
 Exercise 15-B PHYSIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA CONTINUED: AMINO ACID DECARBOXYLATION, CITRATE UTILIZATION, COAGULASE & CAMP TESTS Decarboxylation of Amino Acids and Amine Production The decarboxylation
Exercise 15-B PHYSIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA CONTINUED: AMINO ACID DECARBOXYLATION, CITRATE UTILIZATION, COAGULASE & CAMP TESTS Decarboxylation of Amino Acids and Amine Production The decarboxylation
volume and surface area. Walker and Winslow (1932) reported metabolic rates per cell being observed towards the end of the
 A COMPARISON OF THE METABOLIC ACTIVITIES OF AEROBACTER AEROGENES, EBERTHELLA TYPHI AND ESCHERICHIA COLI C. E. CLIFTON Department of Bacteriology and Experimental Pathology, Stanford University, California
A COMPARISON OF THE METABOLIC ACTIVITIES OF AEROBACTER AEROGENES, EBERTHELLA TYPHI AND ESCHERICHIA COLI C. E. CLIFTON Department of Bacteriology and Experimental Pathology, Stanford University, California
BLOOD DENSITY IN GUINEA PIG ANAPHYLAXIS AND IN HAY FEVER ARTIFICIALLY INDUCED*
 BLOOD DENSITY IN GUINEA PIG ANAPHYLAXIS AND IN HAY FEVER ARTIFICIALLY INDUCED* J. H. BLACK AND HARDY A. KEMP From the Department of Bacteriology and Preventive Medicine, Baylor University School of Medicine,
BLOOD DENSITY IN GUINEA PIG ANAPHYLAXIS AND IN HAY FEVER ARTIFICIALLY INDUCED* J. H. BLACK AND HARDY A. KEMP From the Department of Bacteriology and Preventive Medicine, Baylor University School of Medicine,
THE MULTIPLICATION OF THE VIRUS OF YELLOW FEVER IN AEDES AEGYPTI*
 Published Online: 1 August, 1937 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.66.2.133 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 6, 2018 THE MULTIPLICATION OF THE VIRUS OF YELLOW FEVER IN AEDES AEGYPTI* BY LORING
Published Online: 1 August, 1937 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.66.2.133 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 6, 2018 THE MULTIPLICATION OF THE VIRUS OF YELLOW FEVER IN AEDES AEGYPTI* BY LORING
(From the Laboratories of the International Health Division of The Rockefeller Foundation, New York)
 Published Online: 1 August, 1939 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.70.2.209 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 26, 2018 NEUTRALIZATION OF EPIDEMIC INFLUENZA VIRUS THE LINEAR RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
Published Online: 1 August, 1939 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.70.2.209 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 26, 2018 NEUTRALIZATION OF EPIDEMIC INFLUENZA VIRUS THE LINEAR RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
INTUBATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA.*
 Published Online: 1 July, 1912 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.16.1.17 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 18, 2018 PERMANENT INTUBATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA.* BY ALEXIS CARREL, M.D. (From
Published Online: 1 July, 1912 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.16.1.17 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 18, 2018 PERMANENT INTUBATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA.* BY ALEXIS CARREL, M.D. (From
M6ller, McIntosh and Van Slyke (5) has been employed. The cases. changes in functional activity. Indications suggesting that such changes
 STUDIES OF UREA EXCRETION. VIII. THE EFFECTS ON THE UREA CLEARANCE OF CHANGES IN PROTEIN AND SALT CONTENTS OF THE DIET BY CUTHBERT L. COPE I (From the Hospital of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical
STUDIES OF UREA EXCRETION. VIII. THE EFFECTS ON THE UREA CLEARANCE OF CHANGES IN PROTEIN AND SALT CONTENTS OF THE DIET BY CUTHBERT L. COPE I (From the Hospital of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical
