Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence
|
|
|
- Harold Ross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence Bowon Lee Department of Electronic Engineering Inha University Incheon, South Korea NVIDIA Deep Learning Day Seoul, South Korea October 31, 2017 Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
2 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array 3 Sound Source Localization 4 Human Hearing 5 Blind Source Separation 6 Concluding Remarks Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
3 Telephone (1876) Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
4 Home Assistants (Current) Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
5 AVICAR Project at UIUC ( ) AVICAR Video Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
6 ConnectUs Project at HP Labs ( ) ConnectUs Video Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
7 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array 3 Sound Source Localization 4 Human Hearing 5 Blind Source Separation 6 Concluding Remarks Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
8 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
9 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
10 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
11 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
12 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
13 Audio Communication Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
14 Signal Processing for Audio Communication Output signal of the capture engine ŷ n (t) = M {f mn y m }(t) m=1 }{{} microphone array processing Topics of Acoustic Signal Processing Beamforming Blind Source Separation Sound Source Localization Multichannel Echo Cancellation + L {q ln x l }(t) l=1 } {{ } echo cancellation Dereverberation, Noise Suppression, Speaker Diarization Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
15 Signal Processing for Audio Communication Output signal of the capture engine ŷ n (t) = M {f mn y m }(t) m=1 }{{} microphone array processing Topics of Acoustic Signal Processing Beamforming Blind Source Separation Sound Source Localization Multichannel Echo Cancellation + L {q ln x l }(t) l=1 } {{ } echo cancellation Dereverberation, Noise Suppression, Speaker Diarization Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
16 Signal Processing for Audio Communication Output signal of the capture engine ŷ n (t) = M {f mn y m }(t) m=1 }{{} microphone array processing Topics of Acoustic Signal Processing Beamforming Blind Source Separation Sound Source Localization Multichannel Echo Cancellation + L {q ln x l }(t) l=1 } {{ } echo cancellation Dereverberation, Noise Suppression, Speaker Diarization Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
17 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array 3 Sound Source Localization 4 Human Hearing 5 Blind Source Separation 6 Concluding Remarks Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
18 Sound Sources in an Acoustic Scene Sound source of interest Noise source Object Microphones M-1 Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
19 Time-Delay Estimation Example: Signals at two microphones Amplitude Samples Mic 1 Mic 2 Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
20 Signal Model: Two Microphones Signals in the discrete time domain { x1 [n] = s[n]+v 1 [n] x 2 [n] = s[n ]+v 2 [n] x 1 [n], x 2 [n]: Captured signal at each microphone s[n]: Source signal = f s τ: Time difference of arrival (TDOA) in samples v 1 [n], v 2 [n]: Noise and reverberation at each microphone Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
21 Signal Model: Two Microphones Signals in the discrete time domain { x1 [n] = s[n]+v 1 [n] x 2 [n] = s[n ]+v 2 [n] x 1 [n], x 2 [n]: Captured signal at each microphone s[n]: Source signal = f s τ: Time difference of arrival (TDOA) in samples v 1 [n], v 2 [n]: Noise and reverberation at each microphone Time-Delay Estimation A problem to find given x 1 [n] and x 2 [n] Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
22 Generalized Cross Correlation Method for TDE Signals in the frequency domain { X1 (ω) = S(ω)+V 1 (ω) X 2 (ω) = S(ω)e jω + V 2 (ω) Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
23 Generalized Cross Correlation Method for TDE Signals in the frequency domain { X1 (ω) = S(ω)+V 1 (ω) X 2 (ω) = S(ω)e jω + V 2 (ω) Generalized Cross Correlation (GCC) Method ˆ = arg max ψ(ω)x 1 (ω)x2 (ω)ejω dω ω Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
24 Generalized Cross Correlation Method for TDE Signals in the frequency domain { X1 (ω) = S(ω)+V 1 (ω) X 2 (ω) = S(ω)e jω + V 2 (ω) Generalized Cross Correlation (GCC) Method ˆ = arg max ψ(ω)x 1 (ω)x2 (ω)ejω dω ω Phase Transform (PHAT) ψ PHAT (ω) = 1/ X 1 (ω)x2 (ω) X 1 (ω)x2 ˆ = arg max (ω) X 1 (ω)x2 dω (ω) ejω ω Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
25 Sound Source Localization With a Microphone Array Multi-microphone extension of the GCC method M M ˆq = arg max ψ(ω)x m (ω)xk (ω)ejω q mk dω, q Q m=1 k=1 ω Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
26 Sound Source Localization With a Microphone Array Multi-microphone extension of the GCC method M M ˆq = arg max ψ(ω)x m (ω)xk (ω)ejω q mk dω, q Q m=1 k=1 ω where q mk = q k q m and Q denotes the search space of all potential source locations. Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
27 Sound Source Localization With a Microphone Array Multi-microphone extension of the GCC method M M ˆq = arg max ψ(ω)x m (ω)xk (ω)ejω q mk dω, q Q m=1 k=1 ω where q mk = q k q m and Q denotes the search space of all potential source locations. With the PHAT weighting, it can be simplified as M X m (ω) q ˆq = arg max q Q ω X m (ω) ejω m m=1 2 dω, Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
28 Steered Response Power With Phase-Transform SRP-PHAT Power Plot Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
29 SRP-PHAT Computation on GPU SingleCPU thread Block Block Block n... Serial scan CPU!based common approach Parallel scan Our GPU!based approach Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
30 Simultaneous Speaker Detection and Localization Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
31 System Setup RGB Camera Microphone Array Camera s Field of View Eight microphones and one RGB camera Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
32 Multimodal Speaker Detection and Localization Use the HMM competition scheme Run it for each one of the detected faces The SRP-PHAT plot has many local maxima for multiple simultaneous speaker cases Mid-Fusion of the parameters before HMM competition 1 Mid-Fusion Algorithm for Speaker Detection and Localization 1 V. P.Minotto, C. R. Jung, and B. Lee, Simultaneous-Speaker Voice Activity Detection and Localization Using Mid-Fusion of SVM and HMMs, IEEE TMM 2014 Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
33 Sound Source Localization Note that: Sound source localization methods work reasonably well For long (200 ms or longer) signals, With relatively low reverberation and background noise, or With the help of multimodal sensor fusion Otherwise, they usually fail. Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
34 Sound Source Localization Note that: Sound source localization methods work reasonably well For long (200 ms or longer) signals, With relatively low reverberation and background noise, or With the help of multimodal sensor fusion Otherwise, they usually fail. It is generally believed that: Humans do much better than any algorithmic methods. Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
35 Sound Source Localization Note that: Sound source localization methods work reasonably well For long (200 ms or longer) signals, With relatively low reverberation and background noise, or With the help of multimodal sensor fusion Otherwise, they usually fail. It is generally believed that: Humans do much better than any algorithmic methods. Cocktail party effect The ultimate goal of acoustic sensing Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
36 Cocktail Party Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
37 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array 3 Sound Source Localization 4 Human Hearing 5 Blind Source Separation 6 Concluding Remarks Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
38 Human Hearing Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
39 Human Ear (source: Theory and Applications of Digital Speech Processing, Rabiner and Schafer, Pearson, 2011) Acoustic wavefront hits the eardrum (outer ear) Movement at the eardrum is transmitted via ossicles (middle ear) Stapes is attached to the oval window of the cochlea (inner ear) Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
40 Sound Representation in the Auditory System (source: Theory and Applications of Digital Speech Processing, Rabiner and Schafer, Pearson, 2011) Cochlear processing Vibration at the oval window is converted to fluid motion in the cochlea Fluid motion causes mechanical vibration on the basilar membrane Mechanical vibration causes action potential in the inner hair cell These action potentials trigger neural firings to be aggregated in the central auditory system Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
41 Auditory System: A Neural Network (source: Theory and Applications of Digital Speech Processing, Rabiner and Schafer, Pearson, 2011) Auditory System The auditory cortex serves as the central processing unit It creates multiple representations of the neural firings Then the human brain perceives the sound Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
42 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Acoustic Sensing With a Microphone Array 3 Sound Source Localization 4 Human Hearing 5 Blind Source Separation 6 Concluding Remarks Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
43 Spectrogram Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
44 Spectrogram Time-Frequency representation of audio Can be treated as a 2D image Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
45 Semantic Segmentation: Fully Convolutional Network Semantic segmentation: Pixel-wise image segmentation Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
46 Blind Source Separation: Fully Convolutaional Network Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
47 Blind Source Separation: Some Results The FCN created the binary mask from a mixture signal Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
48 Summary Acoustic Sensing Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
49 Summary Acoustic Sensing + Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
50 Summary Acoustic Sensing + Artificial Intelligence Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
51 Conclusion Past Current Future Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
52 Questions? Bowon Lee, Inha University Acoustic Sensing With Artificial Intelligence NVIDIA Deep Learning Day / 36
Sound Waves. Sensation and Perception. Sound Waves. Sound Waves. Sound Waves
 Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
Binaural Hearing for Robots Introduction to Robot Hearing
 Binaural Hearing for Robots Introduction to Robot Hearing 1Radu Horaud Binaural Hearing for Robots 1. Introduction to Robot Hearing 2. Methodological Foundations 3. Sound-Source Localization 4. Machine
Binaural Hearing for Robots Introduction to Robot Hearing 1Radu Horaud Binaural Hearing for Robots 1. Introduction to Robot Hearing 2. Methodological Foundations 3. Sound-Source Localization 4. Machine
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
! Can hear whistle? ! Where are we on course map? ! What we did in lab last week. ! Psychoacoustics
 2/14/18 Can hear whistle? Lecture 5 Psychoacoustics Based on slides 2009--2018 DeHon, Koditschek Additional Material 2014 Farmer 1 2 There are sounds we cannot hear Depends on frequency Where are we on
2/14/18 Can hear whistle? Lecture 5 Psychoacoustics Based on slides 2009--2018 DeHon, Koditschek Additional Material 2014 Farmer 1 2 There are sounds we cannot hear Depends on frequency Where are we on
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
A Consumer-friendly Recap of the HLAA 2018 Research Symposium: Listening in Noise Webinar
 A Consumer-friendly Recap of the HLAA 2018 Research Symposium: Listening in Noise Webinar Perry C. Hanavan, AuD Augustana University Sioux Falls, SD August 15, 2018 Listening in Noise Cocktail Party Problem
A Consumer-friendly Recap of the HLAA 2018 Research Symposium: Listening in Noise Webinar Perry C. Hanavan, AuD Augustana University Sioux Falls, SD August 15, 2018 Listening in Noise Cocktail Party Problem
PSY 214 Lecture # (11/9/2011) (Sound, Auditory & Speech Perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
Challenges in microphone array processing for hearing aids. Volkmar Hamacher Siemens Audiological Engineering Group Erlangen, Germany
 Challenges in microphone array processing for hearing aids Volkmar Hamacher Siemens Audiological Engineering Group Erlangen, Germany SIEMENS Audiological Engineering Group R&D Signal Processing and Audiology
Challenges in microphone array processing for hearing aids Volkmar Hamacher Siemens Audiological Engineering Group Erlangen, Germany SIEMENS Audiological Engineering Group R&D Signal Processing and Audiology
What you re in for. Who are cochlear implants for? The bottom line. Speech processing schemes for
 What you re in for Speech processing schemes for cochlear implants Stuart Rosen Professor of Speech and Hearing Science Speech, Hearing and Phonetic Sciences Division of Psychology & Language Sciences
What you re in for Speech processing schemes for cochlear implants Stuart Rosen Professor of Speech and Hearing Science Speech, Hearing and Phonetic Sciences Division of Psychology & Language Sciences
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING
 COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
Computational Perception /785. Auditory Scene Analysis
 Computational Perception 15-485/785 Auditory Scene Analysis A framework for auditory scene analysis Auditory scene analysis involves low and high level cues Low level acoustic cues are often result in
Computational Perception 15-485/785 Auditory Scene Analysis A framework for auditory scene analysis Auditory scene analysis involves low and high level cues Low level acoustic cues are often result in
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Human Acoustic Processing
 Human Acoustic Processing Sound and Light The Ear Cochlea Auditory Pathway Speech Spectrogram Vocal Cords Formant Frequencies Time Warping Hidden Markov Models Signal, Time and Brain Process of temporal
Human Acoustic Processing Sound and Light The Ear Cochlea Auditory Pathway Speech Spectrogram Vocal Cords Formant Frequencies Time Warping Hidden Markov Models Signal, Time and Brain Process of temporal
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Senses Other Than Vision. Hearing (Audition) Transmission of Vibrations
 Senses Other Than Vision Hearing The Kinesthetic Senses Touch The Chemical Senses Hearing (Audition) Sound begins as pressure waves in a medium (usually air). The frequency of the pressure waves corresponds
Senses Other Than Vision Hearing The Kinesthetic Senses Touch The Chemical Senses Hearing (Audition) Sound begins as pressure waves in a medium (usually air). The frequency of the pressure waves corresponds
Measurements that simulate human hearing psychoacoustics in ITU-T P.863
 Wireless Measurements that simulate human hearing psychoacoustics in ITU-T P.863 Jürgen Fälchle stock.adobe.com Even though telephony now utilizes only a small part of network resources, it remains a core
Wireless Measurements that simulate human hearing psychoacoustics in ITU-T P.863 Jürgen Fälchle stock.adobe.com Even though telephony now utilizes only a small part of network resources, it remains a core
PSY 214 Lecture 16 (11/09/2011) (Sound, auditory system & pitch perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, auditory system, & pitch perception Chapter 11, pages 268-288 Corrections: None needed Announcements: At the beginning of class, we went over some demos from the virtual
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, auditory system, & pitch perception Chapter 11, pages 268-288 Corrections: None needed Announcements: At the beginning of class, we went over some demos from the virtual
Discrete Signal Processing
 1 Discrete Signal Processing C.M. Liu Perceptual Lab, College of Computer Science National Chiao-Tung University http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~cmliu/courses/dsp/ ( Office: EC538 (03)5731877 cmliu@cs.nctu.edu.tw
1 Discrete Signal Processing C.M. Liu Perceptual Lab, College of Computer Science National Chiao-Tung University http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~cmliu/courses/dsp/ ( Office: EC538 (03)5731877 cmliu@cs.nctu.edu.tw
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Binaural processing of complex stimuli
 Binaural processing of complex stimuli Outline for today Binaural detection experiments and models Speech as an important waveform Experiments on understanding speech in complex environments (Cocktail
Binaural processing of complex stimuli Outline for today Binaural detection experiments and models Speech as an important waveform Experiments on understanding speech in complex environments (Cocktail
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
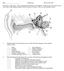 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
Chapter 3. Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics
 Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
SOLUTIONS Homework #3. Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03
 SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
Implementation of Spectral Maxima Sound processing for cochlear. implants by using Bark scale Frequency band partition
 Implementation of Spectral Maxima Sound processing for cochlear implants by using Bark scale Frequency band partition Han xianhua 1 Nie Kaibao 1 1 Department of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong
Implementation of Spectral Maxima Sound processing for cochlear implants by using Bark scale Frequency band partition Han xianhua 1 Nie Kaibao 1 1 Department of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
 Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Hearing Lectures. Acoustics of Speech and Hearing. Auditory Lighthouse. Facts about Timbre. Analysis of Complex Sounds
 Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
Lecture 3: Perception
 ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves
 The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
The Ear. The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
 The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS
 CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
An Auditory-Model-Based Electrical Stimulation Strategy Incorporating Tonal Information for Cochlear Implant
 Annual Progress Report An Auditory-Model-Based Electrical Stimulation Strategy Incorporating Tonal Information for Cochlear Implant Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Engineering Mar.7, 26 Types of Hearing
Annual Progress Report An Auditory-Model-Based Electrical Stimulation Strategy Incorporating Tonal Information for Cochlear Implant Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Engineering Mar.7, 26 Types of Hearing
The speed at which it travels is a function of the density of the conducting medium.
 Sound is a compression wave which (unlike light) must have a medium to conduct it. If the medium is uniform in density, the sound will spread at as a uniform ring of circles (actually spheres). The speed
Sound is a compression wave which (unlike light) must have a medium to conduct it. If the medium is uniform in density, the sound will spread at as a uniform ring of circles (actually spheres). The speed
J Jeffress model, 3, 66ff
 Index A Absolute pitch, 102 Afferent projections, inferior colliculus, 131 132 Amplitude modulation, coincidence detector, 152ff inferior colliculus, 152ff inhibition models, 156ff models, 152ff Anatomy,
Index A Absolute pitch, 102 Afferent projections, inferior colliculus, 131 132 Amplitude modulation, coincidence detector, 152ff inferior colliculus, 152ff inhibition models, 156ff models, 152ff Anatomy,
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Hearing. By Jack & Tori
 Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
Bioscience in the 21st century
 Bioscience in the 21st century Lecture 2: Innovations and Challenges Dr. Michael Burger Outline: Review of last lecture Organization of the nervous system (in brief) The mapping concept Bionic implants
Bioscience in the 21st century Lecture 2: Innovations and Challenges Dr. Michael Burger Outline: Review of last lecture Organization of the nervous system (in brief) The mapping concept Bionic implants
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT. Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction
 SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
Running head: HEARING-AIDS INDUCE PLASTICITY IN THE AUDITORY SYSTEM 1
 Running head: HEARING-AIDS INDUCE PLASTICITY IN THE AUDITORY SYSTEM 1 Hearing-aids Induce Plasticity in the Auditory System: Perspectives From Three Research Designs and Personal Speculations About the
Running head: HEARING-AIDS INDUCE PLASTICITY IN THE AUDITORY SYSTEM 1 Hearing-aids Induce Plasticity in the Auditory System: Perspectives From Three Research Designs and Personal Speculations About the
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics
 9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
Systems for Improvement of the Communication in Passenger Compartments
 Systems for Improvement of the Communication in Passenger Compartments Tim Haulick/ Gerhard Schmidt thaulick@harmanbecker.com ETSI Workshop on Speech and Noise in Wideband Communication 22nd and 23rd May
Systems for Improvement of the Communication in Passenger Compartments Tim Haulick/ Gerhard Schmidt thaulick@harmanbecker.com ETSI Workshop on Speech and Noise in Wideband Communication 22nd and 23rd May
Can You Hear Me Now?
 An Introduction to the Mathematics of Hearing Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington April 26, 2007 Some Questions How does hearing work? What are the important structures and mechanisms
An Introduction to the Mathematics of Hearing Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington April 26, 2007 Some Questions How does hearing work? What are the important structures and mechanisms
An Auditory System Modeling in Sound Source Localization
 An Auditory System Modeling in Sound Source Localization Yul Young Park The University of Texas at Austin EE381K Multidimensional Signal Processing May 18, 2005 Abstract Sound localization of the auditory
An Auditory System Modeling in Sound Source Localization Yul Young Park The University of Texas at Austin EE381K Multidimensional Signal Processing May 18, 2005 Abstract Sound localization of the auditory
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 30. Organ of Corti
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 30 Waves, waves, waves. Organ of Corti Tectorial membrane Sits on top Inner hair cells Outer hair cells The microphone for the brain 1 Hearing Perceptually,
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 30 Waves, waves, waves. Organ of Corti Tectorial membrane Sits on top Inner hair cells Outer hair cells The microphone for the brain 1 Hearing Perceptually,
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
EMANATIONS FROM RESIDUUM OSCILLATIONS IN HUMAN AUDITORY SYSTEM
 EMANATIONS FROM RESIDUUM OSCILLATIONS IN HUMAN AUDITORY SYSTEM V.S. Balaji, N.R.Raajan, S. Rakesh Kumar, Har Narayan Upadhyay School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, SASTRA University Thanjavur,
EMANATIONS FROM RESIDUUM OSCILLATIONS IN HUMAN AUDITORY SYSTEM V.S. Balaji, N.R.Raajan, S. Rakesh Kumar, Har Narayan Upadhyay School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, SASTRA University Thanjavur,
Multimedia Systems 2011/2012
 Multimedia Systems 2011/2012 Perception Prof. Dr. Paul Müller University of Kaiserslautern Department of Computer Science Integrated Communication Systems ICSY http://www.icsy.de Outline Multimedia and
Multimedia Systems 2011/2012 Perception Prof. Dr. Paul Müller University of Kaiserslautern Department of Computer Science Integrated Communication Systems ICSY http://www.icsy.de Outline Multimedia and
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
THE MECHANICS OF HEARING
 CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
Hearing. and other senses
 Hearing and other senses Sound Sound: sensed variations in air pressure Frequency: number of peaks that pass a point per second (Hz) Pitch 2 Some Sound and Hearing Links Useful (and moderately entertaining)
Hearing and other senses Sound Sound: sensed variations in air pressure Frequency: number of peaks that pass a point per second (Hz) Pitch 2 Some Sound and Hearing Links Useful (and moderately entertaining)
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing
 SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits
 TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits Biomedical Engineering Kit: Artificial Sensory Artificial Hearing Activity TEAK Bioengineering Artificial
TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits Biomedical Engineering Kit: Artificial Sensory Artificial Hearing Activity TEAK Bioengineering Artificial
SENSATION & PERCEPTION
 SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
Sonic Spotlight. Binaural Coordination: Making the Connection
 Binaural Coordination: Making the Connection 1 Sonic Spotlight Binaural Coordination: Making the Connection Binaural Coordination is the global term that refers to the management of wireless technology
Binaural Coordination: Making the Connection 1 Sonic Spotlight Binaural Coordination: Making the Connection Binaural Coordination is the global term that refers to the management of wireless technology
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio
 Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio Applications: audio players (e.g. MP3), DVD-audio, digital audio broadcast, music synthesizer, digital amplifier and equalizer, 3D sound synthesis 1 Properties
Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio Applications: audio players (e.g. MP3), DVD-audio, digital audio broadcast, music synthesizer, digital amplifier and equalizer, 3D sound synthesis 1 Properties
(Thomas Lenarz) Ok, thank you, thank you very much for inviting me to be here and speak to you, on cochlear implant technology.
 (Thomas Lenarz) Ok, thank you, thank you very much for inviting me to be here and speak to you, on cochlear implant technology. I want to briefly mention what hearing loss is. And what a cochlear implant
(Thomas Lenarz) Ok, thank you, thank you very much for inviting me to be here and speak to you, on cochlear implant technology. I want to briefly mention what hearing loss is. And what a cochlear implant
Robust Neural Encoding of Speech in Human Auditory Cortex
 Robust Neural Encoding of Speech in Human Auditory Cortex Nai Ding, Jonathan Z. Simon Electrical Engineering / Biology University of Maryland, College Park Auditory Processing in Natural Scenes How is
Robust Neural Encoding of Speech in Human Auditory Cortex Nai Ding, Jonathan Z. Simon Electrical Engineering / Biology University of Maryland, College Park Auditory Processing in Natural Scenes How is
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, Auditory system. http:
 Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
HCS 7367 Speech Perception
 Long-term spectrum of speech HCS 7367 Speech Perception Connected speech Absolute threshold Males Dr. Peter Assmann Fall 212 Females Long-term spectrum of speech Vowels Males Females 2) Absolute threshold
Long-term spectrum of speech HCS 7367 Speech Perception Connected speech Absolute threshold Males Dr. Peter Assmann Fall 212 Females Long-term spectrum of speech Vowels Males Females 2) Absolute threshold
how we hear. Better understanding of hearing loss The diagram above illustrates the steps involved.
 How we hear Better understanding of hearing loss begins by understanding how we hear. The diagram above illustrates the steps involved. 1. Sound waves are collected by the outer ear and channeled along
How we hear Better understanding of hearing loss begins by understanding how we hear. The diagram above illustrates the steps involved. 1. Sound waves are collected by the outer ear and channeled along
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment
 INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
Adaptation of Classification Model for Improving Speech Intelligibility in Noise
 1: (Junyoung Jung et al.: Adaptation of Classification Model for Improving Speech Intelligibility in Noise) (Regular Paper) 23 4, 2018 7 (JBE Vol. 23, No. 4, July 2018) https://doi.org/10.5909/jbe.2018.23.4.511
1: (Junyoung Jung et al.: Adaptation of Classification Model for Improving Speech Intelligibility in Noise) (Regular Paper) 23 4, 2018 7 (JBE Vol. 23, No. 4, July 2018) https://doi.org/10.5909/jbe.2018.23.4.511
Single-Channel Sound Source Localization Based on Discrimination of Acoustic Transfer Functions
 3 Single-Channel Sound Source Localization Based on Discrimination of Acoustic Transfer Functions Ryoichi Takashima, Tetsuya Takiguchi and Yasuo Ariki Graduate School of System Informatics, Kobe University,
3 Single-Channel Sound Source Localization Based on Discrimination of Acoustic Transfer Functions Ryoichi Takashima, Tetsuya Takiguchi and Yasuo Ariki Graduate School of System Informatics, Kobe University,
Digital. hearing instruments have burst on the
 Testing Digital and Analog Hearing Instruments: Processing Time Delays and Phase Measurements A look at potential side effects and ways of measuring them by George J. Frye Digital. hearing instruments
Testing Digital and Analog Hearing Instruments: Processing Time Delays and Phase Measurements A look at potential side effects and ways of measuring them by George J. Frye Digital. hearing instruments
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Speaker s Notes: AB is dedicated to helping people with hearing loss hear their best. Partnering with Phonak has allowed AB to offer unique
 1 General Slide 2 Speaker s Notes: AB is dedicated to helping people with hearing loss hear their best. Partnering with Phonak has allowed AB to offer unique technological advances to help people with
1 General Slide 2 Speaker s Notes: AB is dedicated to helping people with hearing loss hear their best. Partnering with Phonak has allowed AB to offer unique technological advances to help people with
Glossary For Parents. Atresia: closure of the ear canal or absence of an ear opening.
 Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
In-Ear Microphone Equalization Exploiting an Active Noise Control. Abstract
 The 21 International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering The Hague, The Netherlands, 21 August 27-3 In-Ear Microphone Equalization Exploiting an Active Noise Control. Nils Westerlund,
The 21 International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering The Hague, The Netherlands, 21 August 27-3 In-Ear Microphone Equalization Exploiting an Active Noise Control. Nils Westerlund,
Speech Generation and Perception
 Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
INTRODUCTION TO HEARING DEVICES
 INTRODUCTION TO HEARING DEVICES Neuchâtel, June 12 th 2014, Louisa Busca Grisoni CONTENTS 1 NORMAL HEARING (NH) AND HEARING LOSS (HL) 2 HEARING DEVICES 3 SIGNAL PROCESSING IN HEARING DEVICES 4 CONCLUSIONS
INTRODUCTION TO HEARING DEVICES Neuchâtel, June 12 th 2014, Louisa Busca Grisoni CONTENTS 1 NORMAL HEARING (NH) AND HEARING LOSS (HL) 2 HEARING DEVICES 3 SIGNAL PROCESSING IN HEARING DEVICES 4 CONCLUSIONS
L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics
 L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics Introduction to Speech Processing Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna CSE@TAMU
L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics Introduction to Speech Processing Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna CSE@TAMU
Outline. The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
 The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
For this lab you will use parts of Exercise #18 in your Wise lab manual. Please be sure to read those sections before coming to lab
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Hearing Loss. How does the hearing sense work? Test your hearing
 Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
